Influence of Positive Ion (Al3+, Sn4+, and Sb5+) Doping on the Basic Resistance and Sensing Performances of ZnO Nanoparticles Based Gas Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis Process
2.2.1. Synthesis of Sn Doped ZnO NPs
2.2.2. Synthesis of Al Doped ZnO NPs and Sb Doped ZnO NPs
2.3. Characterization
2.4. Measurement of Gas Sensors
3. Results
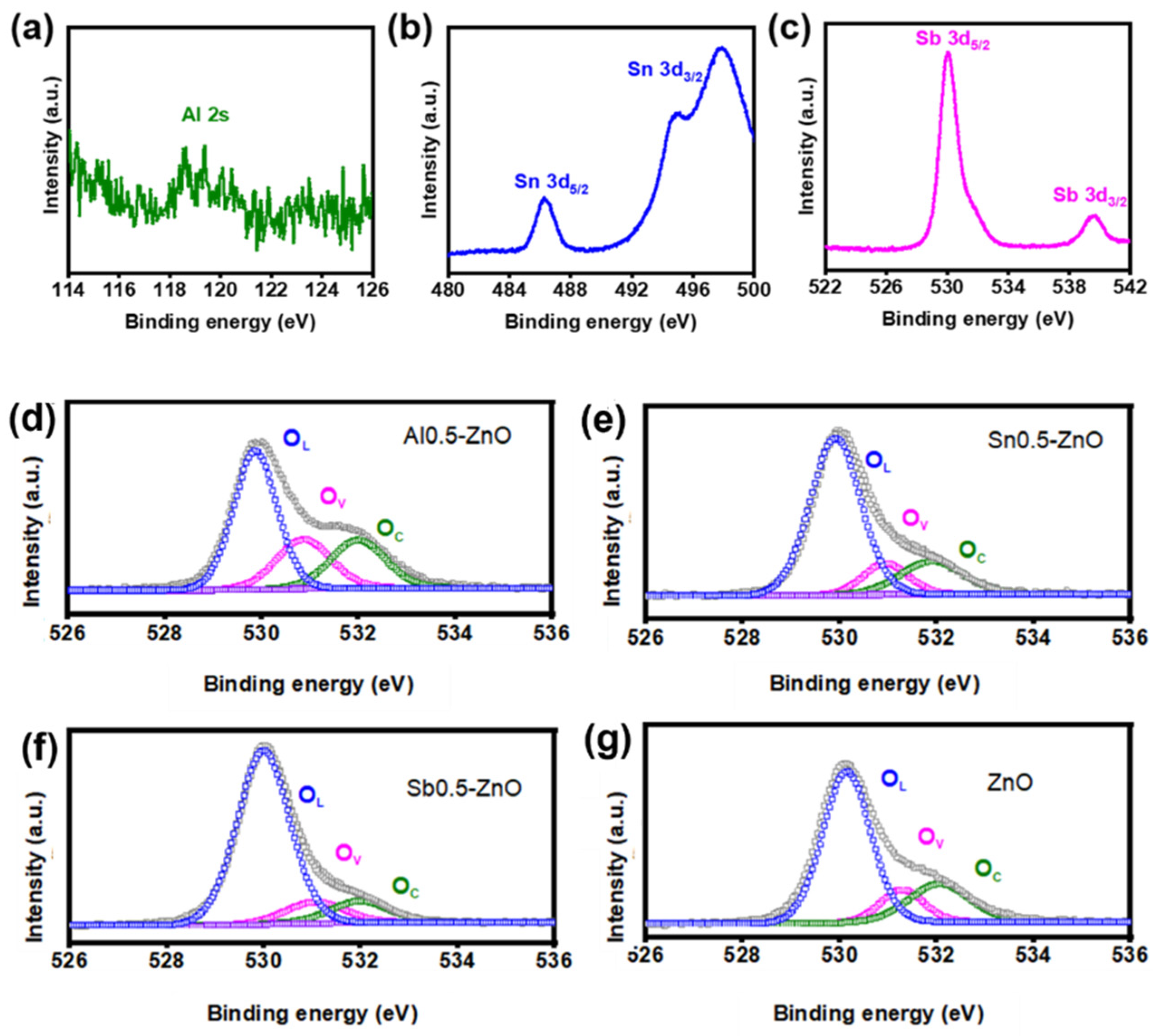
3.1. Material Synthesis and Structural Characterization
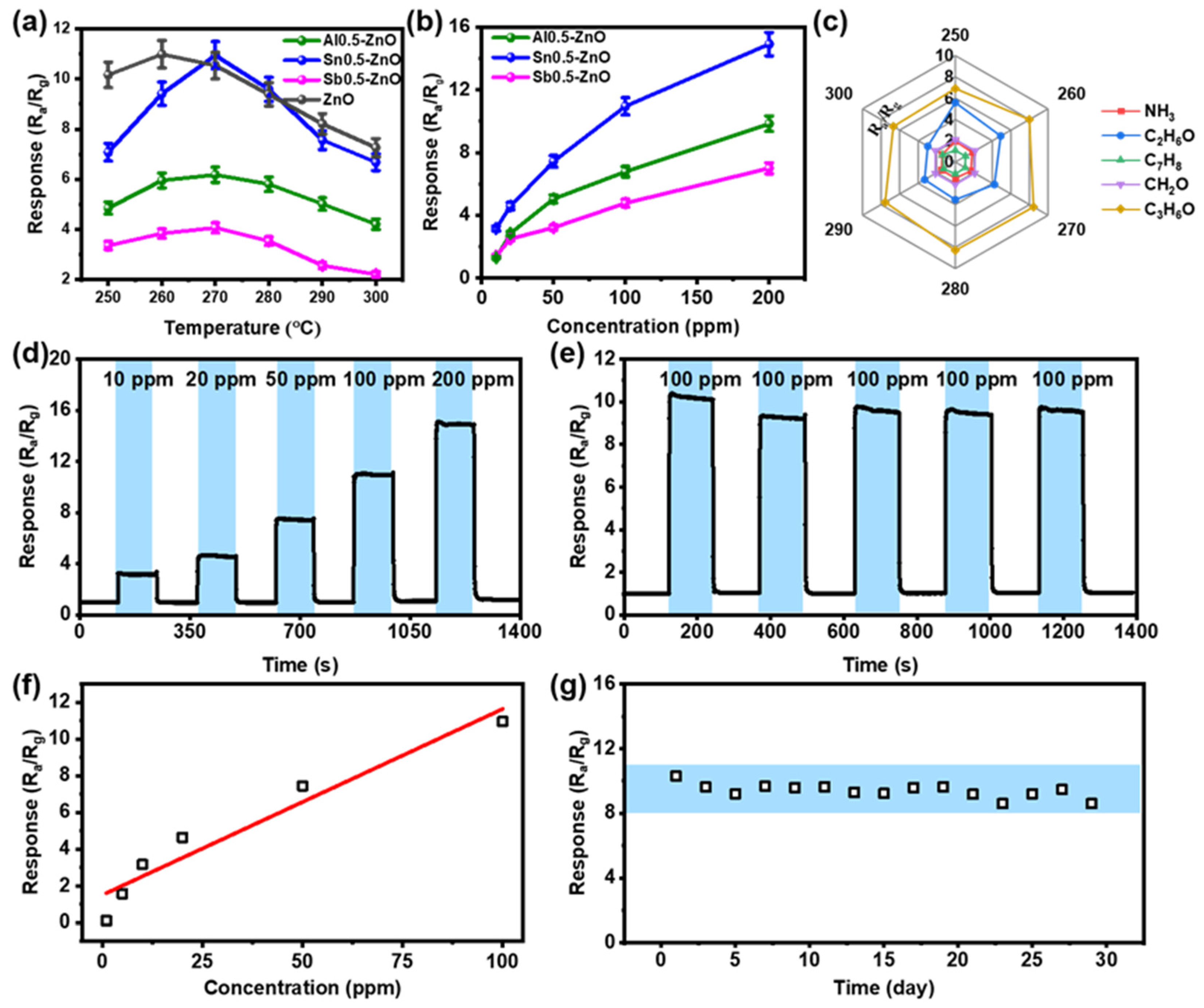
3.2. Measurement of Gas Sensors
3.3. Gas Sensing Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, T.T.; Zhang, T. Recent progress of nanostructured sensing materials from 0D to 3D: Overview of structure–property-application relationship for gas sensors. Small Methods 2021, 5, 2100515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.H.; Ma, T.T.; Pinna, N.; Zhang, J. Two-dimensional nanostructured materials for gas sensing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1702168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghule, B.G.; Shinde, N.M.; Raut, S.D.; Shaikh, S.F.; Al-Enizi, A.M.; Kim, K.H.; Mane, R.S. Porous metal-graphene oxide nanocomposite sensors with high ammonia detectability. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 589, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Guo, Z. Engineering NiO sensitive materials and its ultra-selective detection of benzaldehyde. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 467, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, K.P.; Zhu, L.Y.; Yang, J.H.; Hang, C.Z.; Tao, J.J.; Ma, H.P.; Jiang, A.Q.; Zhang, D.W.; Lu, H.L. Precise preparation of WO3@SnO2 core shell nanosheets for efficient NH3 gas sensing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 568, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.D.; van Dao, D.; Kim, D.S.; Lee, H.J.; Oh, S.Y.; Lee, I.H.; Yu, Y.T. Effect of core and surface area toward hydrogen gas sensing performance using Pd@ZnO core-shell nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 587, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, N.; Cao, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, T. The effect of different crystalline phases of In2O3 on the ozone sensing performance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 418, 126290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.R.; Akbar, S.A.; Morris, P.A. Nanoscale metal oxide-based heterojunctions for gas sensing: A review. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 250–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, W. Fabrication of SnO2-SnO nanocomposites with p-n heterojunctions for the low-temperature sensing of NO2 gas. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 12133–12142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Qiao, G.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Cui, H. Core-double shell ZnO@In2O3@ZnO hollow microspheres for superior ethanol gas sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 341, 130002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Wang, A.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Y. Enhanced acetone sensing properties of Pt@Al-doped ZnO core-shell nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 329, 129153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewale, P.S.; Yu, Y.S.; Kim, J.H.; Bobade, C.R.; Uplane, M.D. H2S gas sensitive Sn-doped ZnO thin films: Synthesis and characterization. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2015, 112, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.L.; Chen, K.C.; Tsai, T.Y.; Hsueh, T.J. Fabrication of gas sensor based on p-type ZnO nanoparticles and n-type ZnO nanowires. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 182, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xian, J.; Wang, W.; Cheng, K.; Zeng, M.; Zhang, A.; Wu, S.; Gao, X.; Lu, X.; Liu, J.M. Ultrafast response and high-sensitivity acetone gas sensor based on porous hollow Ru-doped SnO2 nanotubes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 352, 131061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Yamazaki, T.; Liu, Z.; Meng, D.; Kikuta, T.; Nakatani, N.; Saito, M.; Mori, M. Microstructure and H2 gas sensing properties of undoped and Pd-doped SnO2 nanowires. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 135, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Bulemo, P.M.; Koo, W.T.; Ko, J.; Kim, I.D. Chemiresistive acetylene sensor fabricated from Ga-doped ZnO nanofibers functionalized with Pt catalysts. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 343, 130137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimifard, R.; Golobostanfard, M.R.; Abdizadeh, H. Sol-gel derived Al and Ga co-doped ZnO thin films: An optoelectronic study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 290, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Chai, L.; Wang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Deng, P.; Chen, Y. Evaluating the doping effect of Fe, Ti and Sn on gas sensing property of ZnO. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 147, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.D.; Jin, K.L.; Xu, J.C.; Han, Y.B.; Jin, H.X.; Jin, D.F.; Peng, X.L.; Hong, B.; Li, J.; Yang, Y.T.; et al. High-valence cations-doped mesoporous nickel oxides nanowires: Nanocasting synthesis, microstructures and improved gas-sensing performance. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 296, 126622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Mirzaei, A.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.W.; Hishita, S.; Kim, S.S. Enhancement of gas sensing by implantation of Sb-ions in SnO2 nanowires. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Wu, X.; Zhang, D.; Shen, G.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y. CdO activated Sn-doped ZnO for highly sensitive, selective and stable formaldehyde sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 152, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.T.; Cao, S.; Zhang, R.; Tu, J.; Fei, T.; Zhang, T. Effect of Cation Substitution on the Gas-Sensing Performances of Ternary Spinel MCo2O4 (M = Mn, Ni, and Zn) Multishelled Hollow Twin Spheres. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 28023–28032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, T.T.; Tu, N.H.; Le, H.H.; Ryu, K.Y.; Le, K.B.; Pillai, K.; Yi, J. Improving the ethanol sensing of ZnO nano-particle thin films—The correlation between the grain size and the sensing mechanism. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 152, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupan, C.; Khaledialidusti, R.; Mishra, A.K.; Postica, V.; Terasa, M.I.; Magariu, N.; Pauporté, T.; Viana, B.; Drewes, J.; Vahl, A.; et al. Pd-functionalized ZnO: Eu columnar films for room-temperature hydrogen gas sensing: A combined experimental and computational approach. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 24951–24964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Yi, J. Superior NO2 sensing of MOF-derived indium-doped ZnO porous hollow cages. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 37489–37498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, R.; Güntner, A.T.; Parka, Y.; Rim, H.J.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, W. Sensing of acetone by Al-doped ZnO. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 283, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, M.; Ding, F.; Cao, Y.; Hu, P.; Fan, J.; Lu, C.; Yuan, F.; Shi, C.; Chen, Y. Sn doped ZnO layered porous nanocrystals with hierar chical structures and modified surfaces for gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 201, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Shen, Y.; Maboudian, R.; Carraro, C.; Han, C.; Liu, W.; Wei, D. Facile synthesis of ZnO-SnO2 hetero-structured nanowires for high-performance NO2 sensing application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 333, 129613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Tian, X.; Jiang, X.; Jiang, L.; Hou, P.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Yang, H.; Cao, R.; Xu, X. Facile preparation of hierarchical Sb-doped In2O3 microstructures for acetone detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 270, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ai, P.; Gong, N.; Wu, Y.; Yu, D. Room temperature ppb level H2S detection of a single Sb-doped SnO2 nanoribbon device. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 216, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, D.; Liu, F.; Liu, F.; Liang, X.; Yan, X.; Gao, Y.; Lu, G. The role of Ce doping in enhancing sensing performance of ZnO-based gas sensor by adjusting the proportion of oxygen species. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagedorn, K.; Li, W.; Liang, Q.; Dilger, S.; Noebels, M.; Wagner, M.R.; Reparaz, J.S.; Dollinger, A.; der Günne, J.S.A.; Dekorsy, T.; et al. Catalytically doped semiconductors for chemical gas sensing: Aerogel-like aluminum-containing zinc oxide materials prepared in the gas phase. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 3424–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaparadza, A.; Rananavare, S.B. Room temperature Cl2 sensing using thick nanoporous films of Sb-doped SnO2. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 245501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, L.L.; Yuan, S.; Chen, Z.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Xue, X.Y. Enhanced gas sensing performance of SnO2/α-MoO3 heterostructure nanobelts. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 225502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, T.T.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, T. MOF–derived 1 D A–Fe2O3/NiFe2O4 heterojunction as efficient sensing materials of acetone vapors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 281, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.X.; Tong, R.X.; Yan, Z.; Ji, L.F.; Xu, X.H. d-electron-dependent transparent conducting oxide of V-doped ZnO thin films. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 822, 153706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sensitive Materials | Preparation Method | Original Resistance (MΩ) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ga-doped ZnO nanofibers functionalized with Pt catalysts | Electrospinning | 93.2 | [16] |
| ZnO@In2O3@ZnO hollow microspheres | Oil bath hydrothermal reaction | 120 | [10] |
| Pt@Al-doped ZnO core–shell nanoparticles | Hydrothermal reaction | 17,000 | [11] |
| ZnO nano-particle thin films | Sol-gel | 110 | [23] |
| Positive Ion doped ZnO nanoparticle | Sol-gel | 0.28 | This work |
| Sample | Oxygen Species | Binging Energy (eV) | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al0.5-ZnO | OL | 529.87 | 61.2% |
| OV | 530.87 | 18.4% | |
| OC | 531.99 | 20.4% | |
| Sn0.5-ZnO | OL | 529.90 | 67.5% |
| OV | 530.94 | 10.2% | |
| OC | 531.90 | 22.3% | |
| Sb0.5-ZnO | OL | 529.99 | 78.6% |
| OV | 531.05 | 10.1% | |
| OC | 531.98 | 11.3% | |
| ZnO | OL | 530.13 | 68% |
| OV | 531.23 | 10.2% | |
| OC | 532.08 | 21.1% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Cao, S.; Sui, N.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, T.; He, Y.; Zhang, T. Influence of Positive Ion (Al3+, Sn4+, and Sb5+) Doping on the Basic Resistance and Sensing Performances of ZnO Nanoparticles Based Gas Sensors. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10090364
Zhang P, Cao S, Sui N, Xu Y, Zhou T, He Y, Zhang T. Influence of Positive Ion (Al3+, Sn4+, and Sb5+) Doping on the Basic Resistance and Sensing Performances of ZnO Nanoparticles Based Gas Sensors. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(9):364. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10090364
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Peng, Shuang Cao, Ning Sui, Yifeng Xu, Tingting Zhou, Yuan He, and Tong Zhang. 2022. "Influence of Positive Ion (Al3+, Sn4+, and Sb5+) Doping on the Basic Resistance and Sensing Performances of ZnO Nanoparticles Based Gas Sensors" Chemosensors 10, no. 9: 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10090364
APA StyleZhang, P., Cao, S., Sui, N., Xu, Y., Zhou, T., He, Y., & Zhang, T. (2022). Influence of Positive Ion (Al3+, Sn4+, and Sb5+) Doping on the Basic Resistance and Sensing Performances of ZnO Nanoparticles Based Gas Sensors. Chemosensors, 10(9), 364. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10090364






