Sensitive Determination of Moxifloxacin HCl in Pharmaceuticals or Human Plasma Using Luminescence or Eye Vision
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Solutions
2.2. Instruments
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Quantification of Moxi.HCl
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Interaction of Eu (III) with 1,2 Dihydro-2-Oxoquinoloine-4-Carboxylic Acid (DOCA)
3.1.1. UV–Vis Spectroscopy
3.1.2. Luminescence Spectroscopy
3.1.3. The Stoichiometry of Probe
3.2. Moxifloxacin HCl Interaction with the Eu(III)-(DOCA)2 Complex
3.2.1. UV–Vis Absorption Spectroscopy, Luminescence and Investigation of Quenching Mechanism
3.2.2. Binding Constant and Stoichiometry between Moxifloxacin HCl and Eu(III)-(DOCA)2 Complex
3.2.3. Thermodynamic Parameters
3.3. Visible Readout, Calibration Curve, and Limit of Detection for Moxifloxacin HCl
3.4. Interference Study
3.5. Determination of Moxi.HCl in Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guay, D.R. Moxifloxacin in the Treatment of Skin and Skin Structure Infections. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2006, 2, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogarty, C.; Torres, A.; Choudhri, S.; Haverstock, D.; Herrington, J.; Ambler, J. Efficacy of Moxifloxacin for Treatment of Penicillin-, Macrolide- and Multidrug-Resistant Streptococcus Pneumoniae in Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Int. J. Clin. Pr. 2005, 59, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.; Macklin-Doherty, A. The Use of Moxifloxacin for Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Chronic Bronchitis. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2012, 6, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Li, C.; Yu, C.; Xie, H.; Shi, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Lu, L. A Novel Electrospun Membrane Based on Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride/Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Sodium Alginate for Antibacterial Wound Dressings in Practical Application. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The United States Pharmacopoeia. 35, NF 30, vol. 1, United States Pharmacopeial Convention; The United States Pharmacopoeia: Rockville, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Soni, A.K.; Gohel, M.; Thakkar, V.; Baldaniya, L.; Gandhi, T. Simultaneous Determination of Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride and Difluprednate by Ratio Derivative Spectrophotometry. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 387–390. [Google Scholar]
- Attimarad, M.; Al-Dhubiab, B.E.; Alhaider, I.A.; Nair, A.B.; Sree Harsha, N.; Mueen Ahmed, K. Simultaneous Determination of Moxifloxacin and Cefixime by First and Ratio First Derivative Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry. Chem. Cent. J. 2012, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkase, K.N.; Admane, S.S.; Sonkhede, N.G.; Shejwal, S.R. Development and Validation of UV-Spectrophotometric Methods for Determination of Moxifloxacin HCL in Bulk and Pharmaceutical Formulations. Pharma Chem. 2012, 4, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar]
- Attimarad, M.; Chohan, M.S.; Balgoname, A.A. Simultaneous Determination of Moxifloxacin and Flavoxate by RP-HPLC and Ecofriendly Derivative Spectrophotometry Methods in Formulations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1196–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, A.; Chaudhry, A.H.; Ashfaq, K.M.; Malik, T.A. Spectrophotometric Determination of Moxifloxacin HCl in Pure and Blood Sample. Am. J. Pharmtech Res. 2012, 2, 263–270. [Google Scholar]
- Subbaiah, P.R.; Kumudhavalli, M.V.; Saravanan, C.; Kumar, M.; Chandira, R.M. Method Development and Validation for Estimation of Moxifloxacin HCl in Tablet Dosage Form by RP-HPLC Method. Pharm. Anal. Acta 2010, 1, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalariya, P.D.; Namdev, D.; Srinivas, R.; Gananadhamu, S. Application of Experimental Design and Response Surface Technique for Selecting the Optimum RP-HPLC Conditions for the Determination of Moxifloxacin HCl and Ketorolac Tromethamine in Eye Drops. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2014, 21, S373–S382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehata, M.; Fekry, A.M.; Walcarius, A. Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride Electrochemical Detection at Gold Nanoparticles Modified Screen-Printed Electrode. Sensors 2020, 20, 2797–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radi, A.-E.; Wahdan, T.; Anwar, Z.; Mostafa, H. Electrochemical Determination of Gatifloxacin, Moxifloxacin and Sparfloxacin Fluoroquinolonic Antibiotics on Glassy Carbon Electrode in Pharmaceutical Formulations. Drug Test. Anal. 2010, 2, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, H. Spectrofluorimetric, Atomic Absorption Spectrometric and Spectrophotometric Determination of Some Fluoroquinolones. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2005, 2, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghannam, S.M. Atomic Absorption Spectroscopic, Conductometric and Colorimetric Methods for Determination of Some Fluoroquinolone Antibacterials Using Ammonium Reineckate. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2008, 69, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, M.A. New, Simple and Validated Kinetics Spectrophotometric Method for Determination of Moxifloxacine in Its Pharmaceutical Formulations. Arab. J. Chem. 2009, 2, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdellaziz, L.M.; Hosny, M.M. Development and Validation of Spectrophotometric, Atomic Absorption and Kinetic Methods for Determination of Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride. Anal. Chem. Insights 2011, 6, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaple, D.R.; Bhusari, K.P. Spectrophotometric Estimation of Fluroquinolones as Ion-Pairs with Bromocresol Green in Bulk and Pharmaceutical Dosage Form. Asian J. Chem. 2010, 22, 2593–2598. [Google Scholar]
- Ashour, S.; Bayram, R. Development and Validation of Sensitive Kinetic Spectrophotometric Method for the Determination of Moxifloxacin Antibiotic in Pure and Commercial Tablets. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 140, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pekamwar, S.S.; Kalyankar, T.M.; Tambe, B.V.; Wadher, S.J. Validated UV-Visible Spectrophotometric Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Cefixime and Moxifloxacin in Pharmaceutical Dosage Form. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.U.; Suhagia, B.N.; Patel, M.M. Spectrophotometric Methods for Estimation of Moxifloxacin in Pharmaceutical Formulations. Indian Drugs 2005, 42, 112. [Google Scholar]
- Misra, M.; Misra, A.K.; Zope, P.; Panpalia, G.M.; Dorle, A.K. Simple and Validated UV-Spectroscopic Method for Estimation of Moxifloxacin.HCL in Bulk and Formulation. J. Glob. Pharma Technol. 2010, 2, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhumal, D.M.; Shirkhedkar, A.A.; Surana, S.J. Quantitative Determination of Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride in Bulk and Ophthalmic Solution by UV-Spectrophotometry and First Order Derivative Using Area under Curve. Pharm. Lett. 2011, 3, 453–456. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Han, S.J.; Lee, C.; Yoon, J.; Spring, D.R. Development of off–on Fluorescent Probes for Heavy and Transition Metal Ions. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 1679–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, B.; Chen, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, B.; Müllen, K.; Yin, M. Stable Radical Anions Generated from a Porous Perylenediimide Metal-Organic Framework for Boosting near-Infrared Photothermal Conversion. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, T.; Nagano, T. Fluorescent Probes for Sensing and Imaging. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehn, J.-M. Perspectives in Supramolecular Chemistry—From Molecular Recognition towards Molecular Information Processing and Self-Organization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1990, 29, 1304–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.P.; Nolan, C.B.; Stomeo, F. Photochemistry and Photophysics of Coordination Compounds: Lanthanides; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar]
- Lehn, J.-M. Supramolekulare Chemie–Moleküle, Übermoleküle Und Molekulare Funktionseinheiten (Nobel-Vortrag). Angew. Chem. 1988, 100, 91–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, H.A.; Khairy, G.M.; Abd El-Ghany, N.; Ahmed, M.A. A New Luminescent Bio-Probe of Europium(III)-Complex for Sensing Some Biomolecules and CT-DNA. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 374, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzler, D.E.; Chesta, C.; Fernández-Prini, R.; Aramendía, P.F. Dynamic Solvatochromism in Solvent Mixtures. Pure Appl. Chem. 2001, 73, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błasiak, B.; Ritchie, A.W.; Webb, L.J.; Cho, M. Vibrational Solvatochromism of Nitrile Infrared Probes: Beyond the Vibrational Stark Dipole Approach. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 18094–18111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, E.G.; Samuel, A.P.S.; Raymond, K.N. From Antenna to Assay: Lessons Learned in Lanthanide Luminescence. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Q.; Shi, W.; Tao, T.; Fu, Y. Moxifloxacin Detection Based on Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer from Carbon Quantum Dots to Moxifloxacin Using a Ratiometric Fluorescence Probe. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 4226–4232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, R. Lacowicz Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Kluver Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Davydov, N.; Zairov, R.; Mustafina, A.; Syakayev, V.; Tatarinov, D.; Mironov, V.; Eremin, S.; Konovalov, A.; Mustafin, M. Determination of fluoroquinolone antibiotics through the fluorescent response of Eu(III) based nanoparticles fabricated by layer-by-layer technique. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 784, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Liu, J.; He, W.; Hu, Z.; Yao, X.; Chen, X. Probing the Binding of Scutellarin to Human Serum Albumin by Circular Dichroism, Fluorescence Spectroscopy, FTIR, and Molecular Modeling Method. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 1956–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwanathan, K.; Bartlett, M.G.; Stewart, J.T. Determination of moxifloxacin in human plasma by liquid chromatography electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 30, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İnam, R.; Mercan, H.; Yılmaz, E.; Uslu, B. Differential Pulse Polarographic Determination of Moxifloxacin Hydrochloride in Pharmaceuticals and Biological Fluids. Anal. Lett. 2007, 40, 529–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, A.F.; de Souza, M.V.N.; Oliveira, M.A.L. de Validation of a Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Method for the Determination of Ciprofloxacin, Gatifloxacin, Moxifloxacin and Ofloxacin in Pharmaceutical Formulations. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2008, 19, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öbrink-Hansen, K.; Hardlei, T.F.; Brock, B.; Jensen-Fangel, S.; Kragh Thomsen, M.; Petersen, E.; Kreilgaard, M. Moxifloxacin Pharmacokinetic Profile and Efficacy Evaluation in Empiric Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2398–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

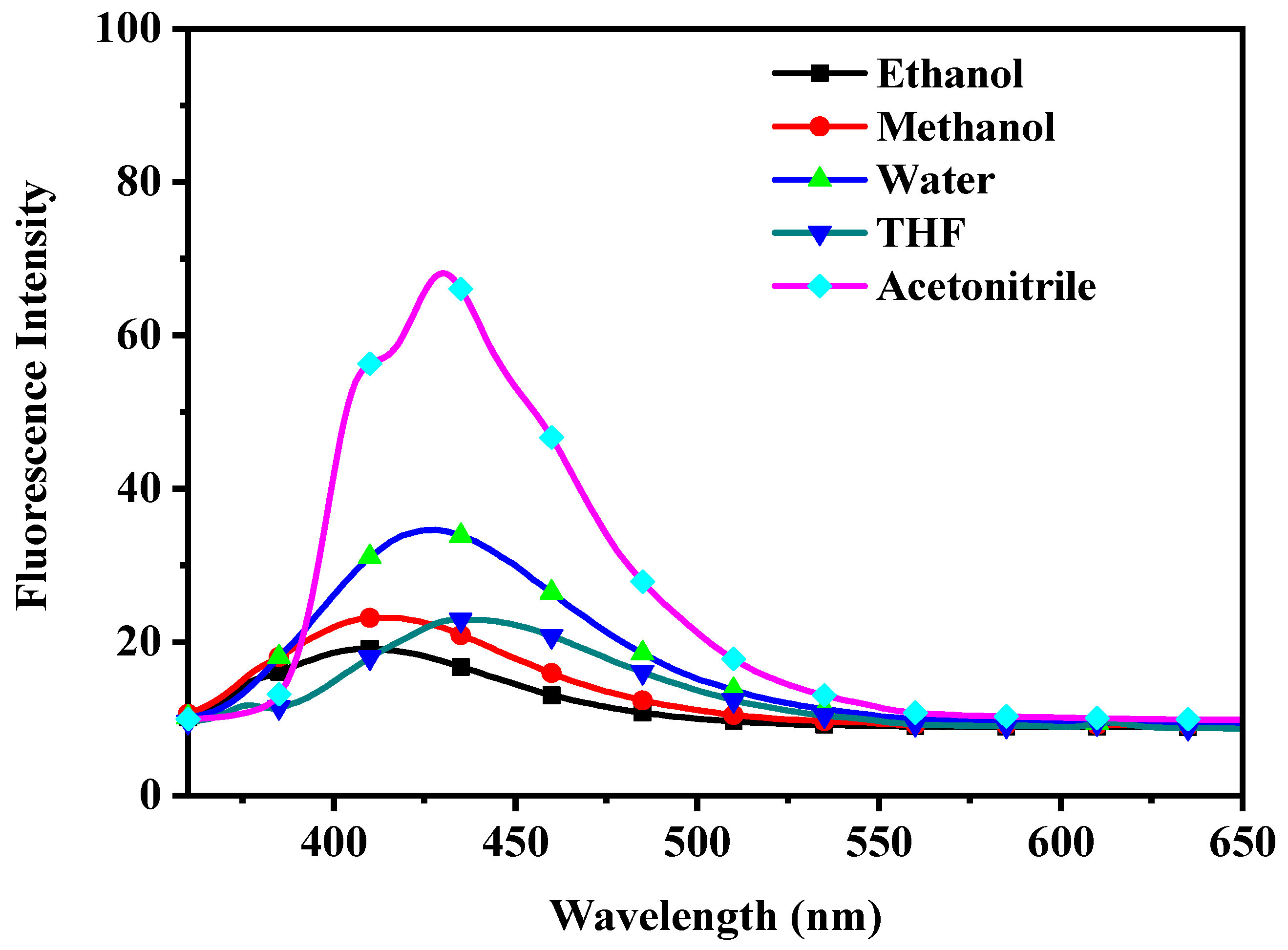
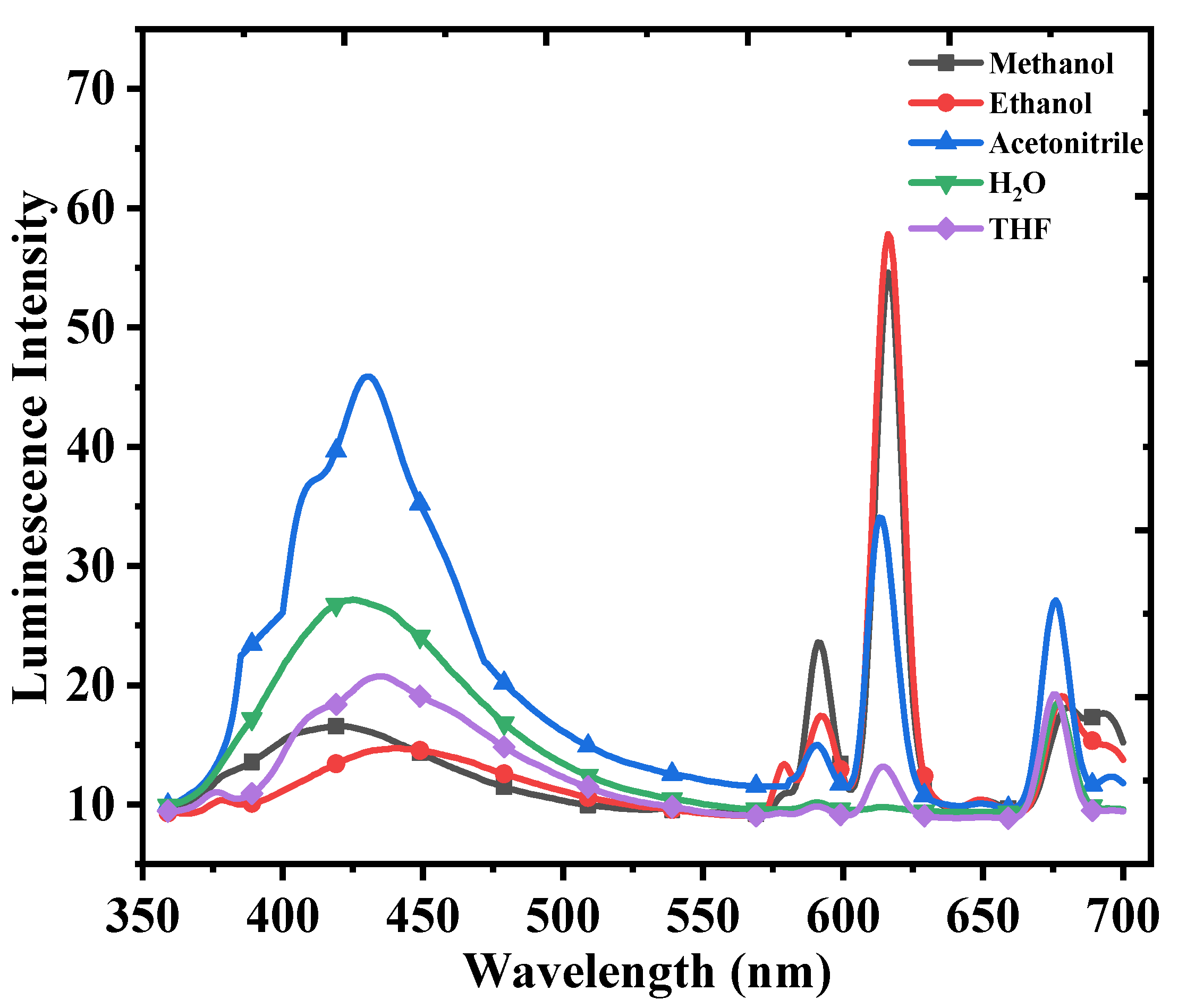



| Temperature (K) | Ksv (104 M−1) | R2 | Ka (104 M−1) | n | R2 | ΔH0 (kJ/mol) | ΔS0 (J/mol K) | ΔG0 (kJ/mol) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 2.53 | 0.9962 | 2.44 | 0.98 | 0.9998 | −6.66 | 61.94 | −25.12 | 0.99828 |
| 303 | 2.40 | 0.9964 | 2.39 | 0.99 | 0.9992 | −25.41 | |||
| 308 | 2.32 | 0.9964 | 2.29 | 1.00 | 0.9994 | −25.74 | |||
| 313 | 2.24 | 0.9963 | 2.21 | 1.00 | 0.9998 | −26.07 | |||
| 318 | 2.12 | 0.9947 | 2.14 | 1.03 | 0.9995 | −26.34 |
| Methods | Linear Range (µg mL−1) | LOD (µg mL−1) | LOQ (µg mL−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RP-HPLC | 5–200 | 0.45 | 1.30 | [9] |
| Differential Pulse Polarography | 22–44 | 0.04 | 0.14 | [40] |
| Electrochemical Detection at Gold Nanoparticles Modified Screen-Printed Electrode | 3.50–210 | 5.08 | 16.91 | [13] |
| Spectrophotometric method | 1–20 | 0.542 | 1.63 | [7] |
| Capillary zone electrophoresis | 25–128 | 0.795 | 2.65 | [41] |
| Solid phase extraction with LC/ESI-MS/MS | 0.001–1 | 0.00005 | 0.001 | [42] |
| Spectrofluorimetry | 0.05–80 | 0.015 | 0.049 | Present method |
| Samples | Dilution Factor | Determined Mean ± SD (µg mL−1) | Added (µg mL−1) | Found (µg mL−1) | Recovery (%) | Total Conc. of Moxi. HCl (µg mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advancrib tablet | 200 | 1.86 ± 0.04 a 2.01 ± 0.03 b | 5 | 7.21 | 107.0 | 372 |
| 10 | 11.53 | 96.7 | ||||
| 20 | 22.12 | 101.3 | ||||
| Vigamox ophthalmic drops | 200 | 1.95 ± 0.15 a 2.12 ± 0.05 b | 5 | 6.58 | 92.6 | 390 |
| 10 | 12.5 | 105.5 | ||||
| 20 | 21.91 | 99.8 | ||||
| Moxavidex tablet | 200 | 2.18 ± 0.26 a 1.94 ± 0.05 b | 5 | 6.98 | 96.0 | 436 |
| 10 | 11.90 | 97.2 | ||||
| 20 | 22.03 | 99.3 | ||||
| Human plasma 1 | 10 | 0.43 ± 0.04 a 0.40 ± 0.01 b | 5 | 4.88 | 89.0 | 4.30 |
| 10 | 10.18 | 97.5 | ||||
| 20 | 22.43 | 101.0 | ||||
| Human plasma 2 | 10 | 0.38 ± 0.02 a 0.41 ± 0.04 b | 5 | 5.06 | 93.6 | 3.80 |
| 10 | 10.86 | 104.8 | ||||
| 20 | 20.45 | 100.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khairy, G.M.; Abd El-Naby, Z.A.; Elgindy, A.M.A.; Duerkop, A.; Abdel Hameed, E.A. Sensitive Determination of Moxifloxacin HCl in Pharmaceuticals or Human Plasma Using Luminescence or Eye Vision. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10100378
Khairy GM, Abd El-Naby ZA, Elgindy AMA, Duerkop A, Abdel Hameed EA. Sensitive Determination of Moxifloxacin HCl in Pharmaceuticals or Human Plasma Using Luminescence or Eye Vision. Chemosensors. 2022; 10(10):378. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10100378
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhairy, Gasser M., Zaitona A. Abd El-Naby, Alaa M. A. Elgindy, Axel Duerkop, and Eman A. Abdel Hameed. 2022. "Sensitive Determination of Moxifloxacin HCl in Pharmaceuticals or Human Plasma Using Luminescence or Eye Vision" Chemosensors 10, no. 10: 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10100378
APA StyleKhairy, G. M., Abd El-Naby, Z. A., Elgindy, A. M. A., Duerkop, A., & Abdel Hameed, E. A. (2022). Sensitive Determination of Moxifloxacin HCl in Pharmaceuticals or Human Plasma Using Luminescence or Eye Vision. Chemosensors, 10(10), 378. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors10100378






