Effects of Shoes That Can Be Tightened Using Wire and Dial on the Dynamic Balance Following Ankle Muscle Fatigue: A Crossover Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
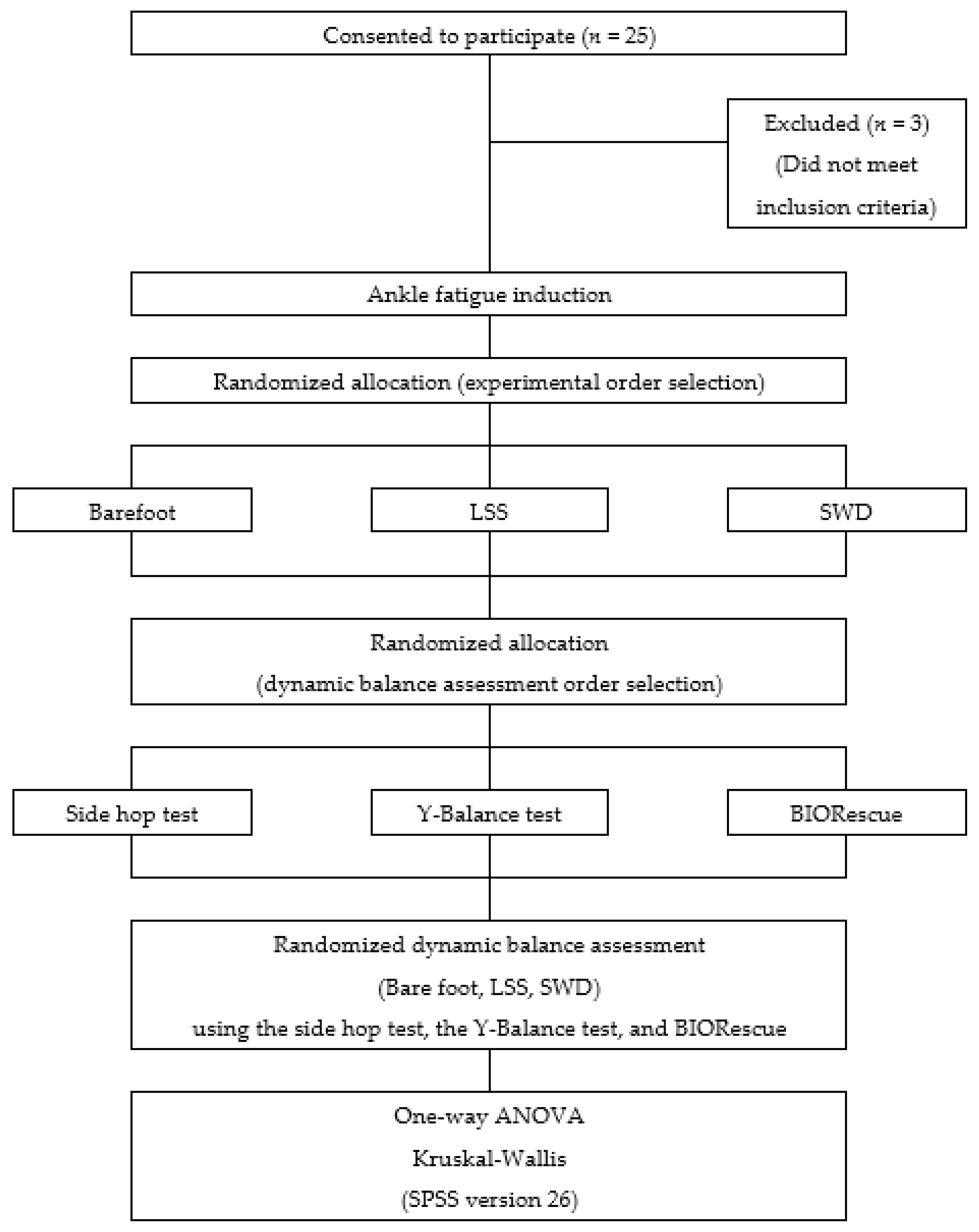
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Shoes
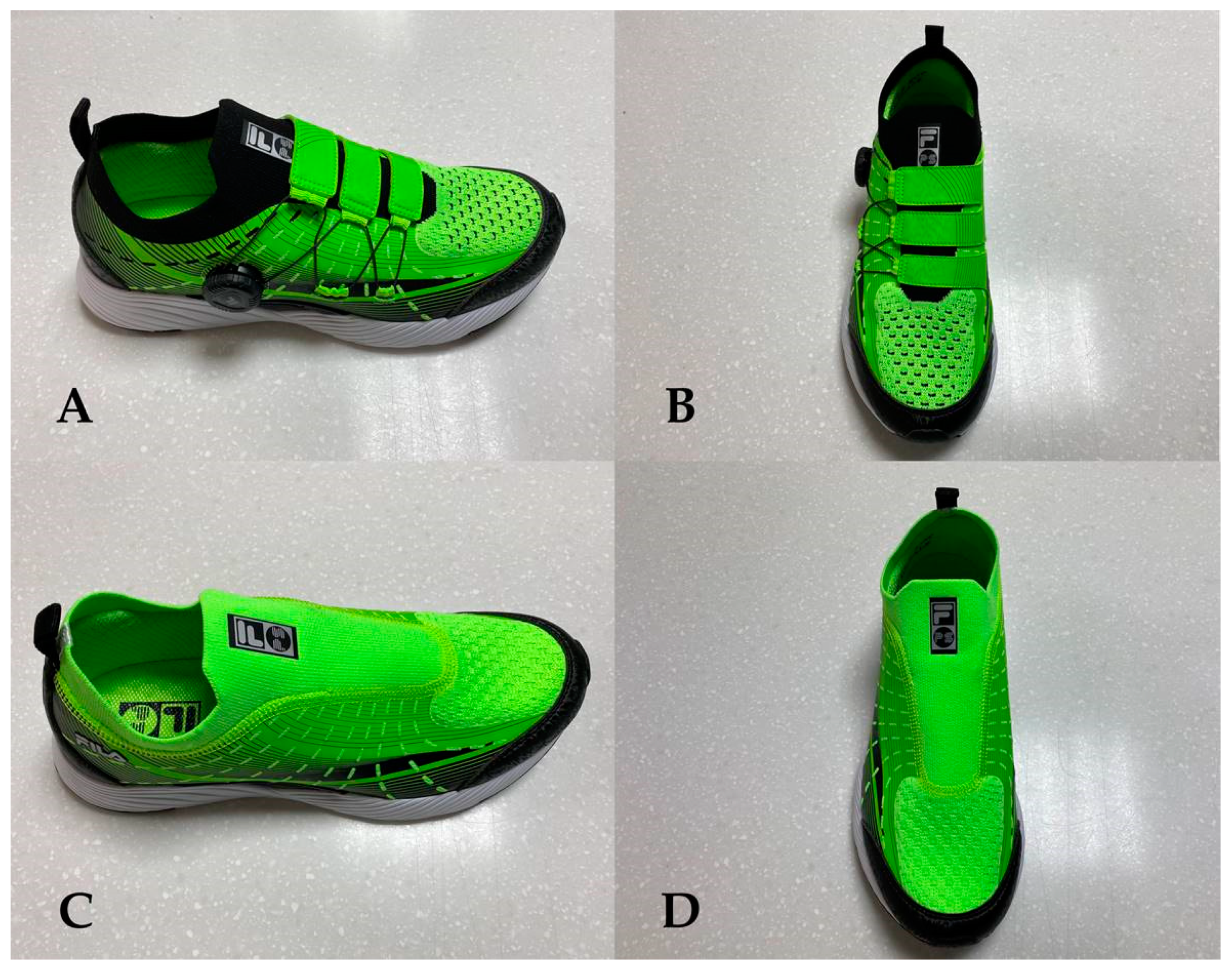
2.3.1. Shoes That Can Be Tightened Using Wire and Dial (SWD)
2.3.2. Lace Shoes of the Slip-on Type (LSS) Based on Elastic Material
2.4. Measurement
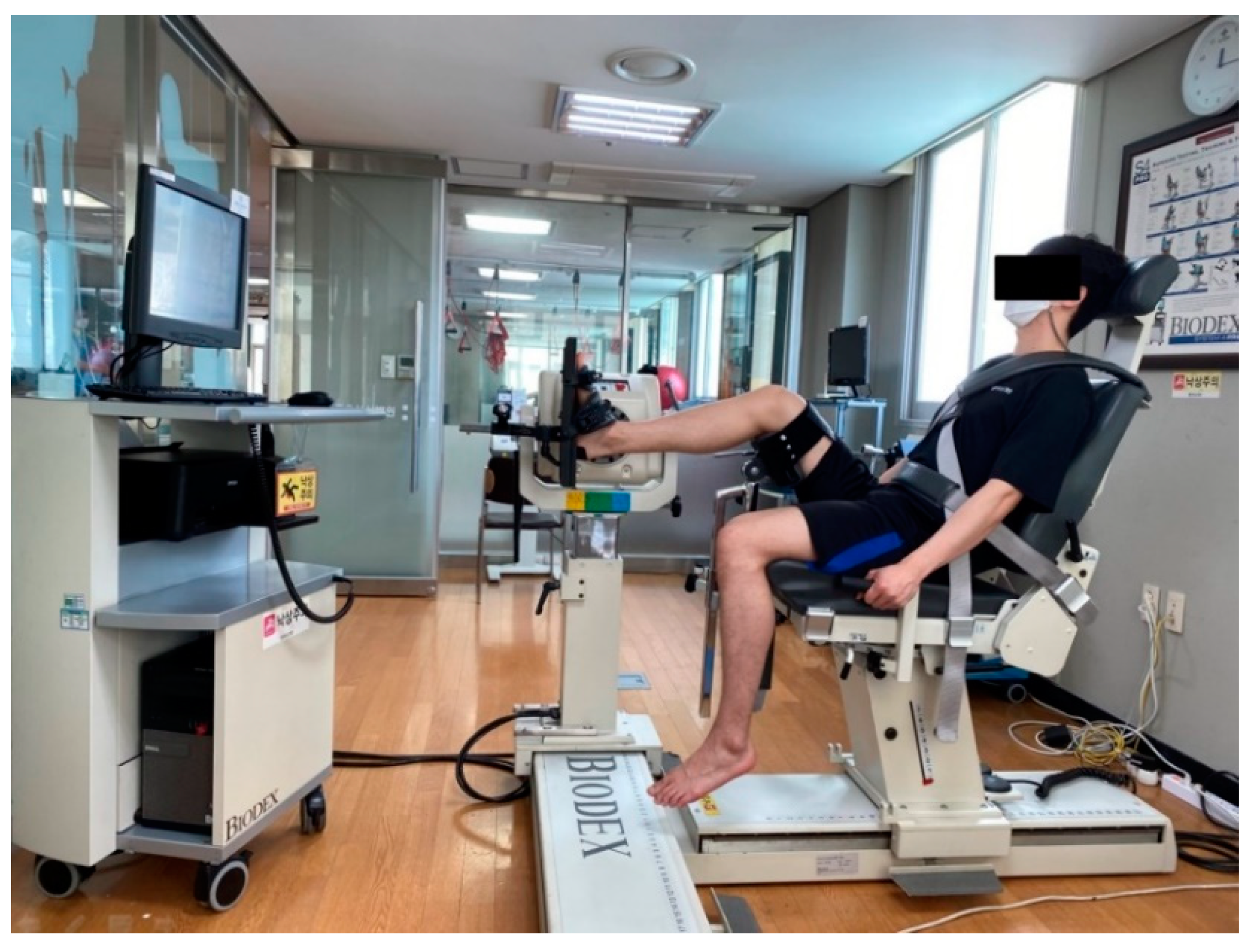
2.4.1. Muscle Fatigue
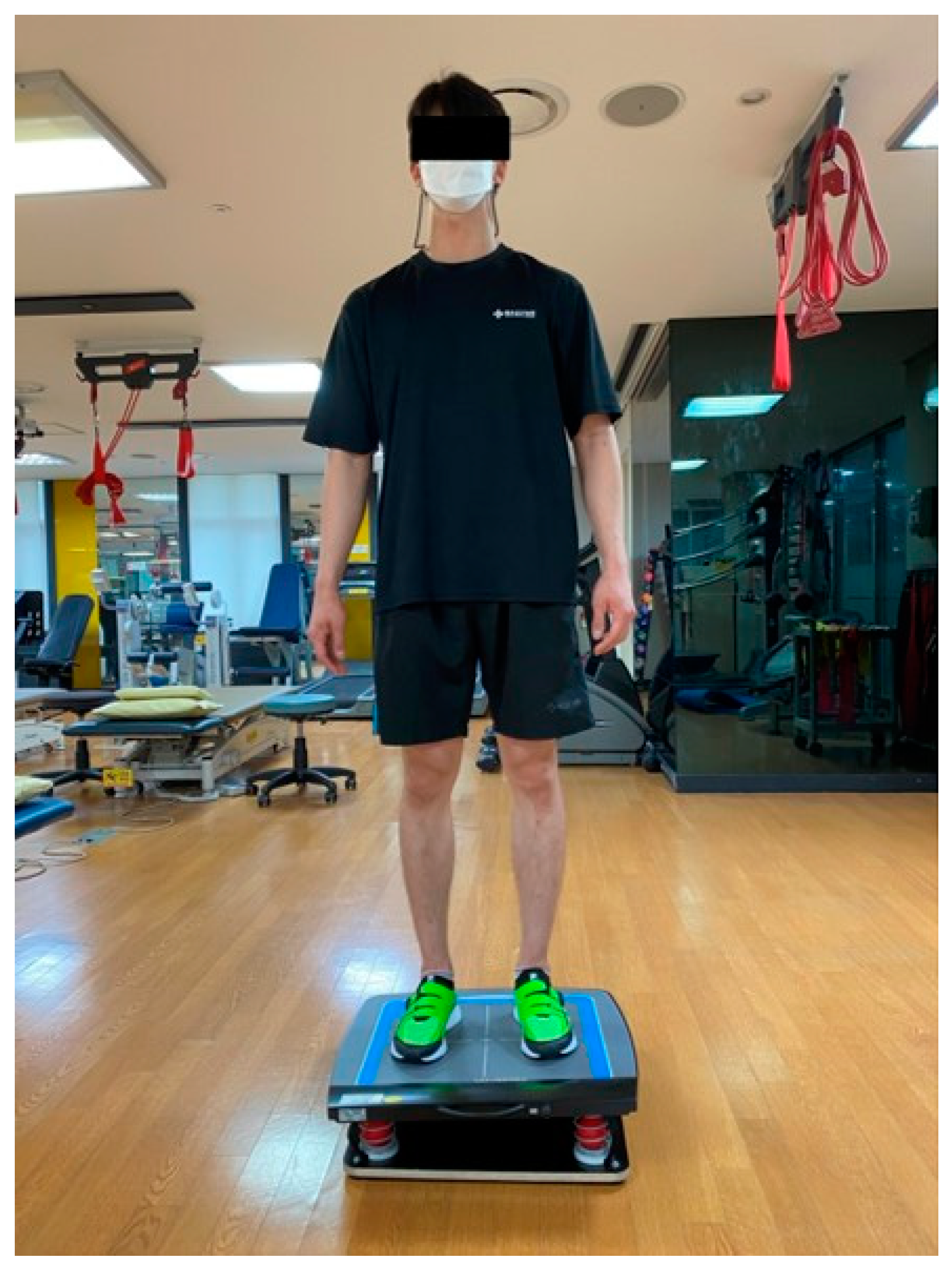
2.4.2. BIORescue
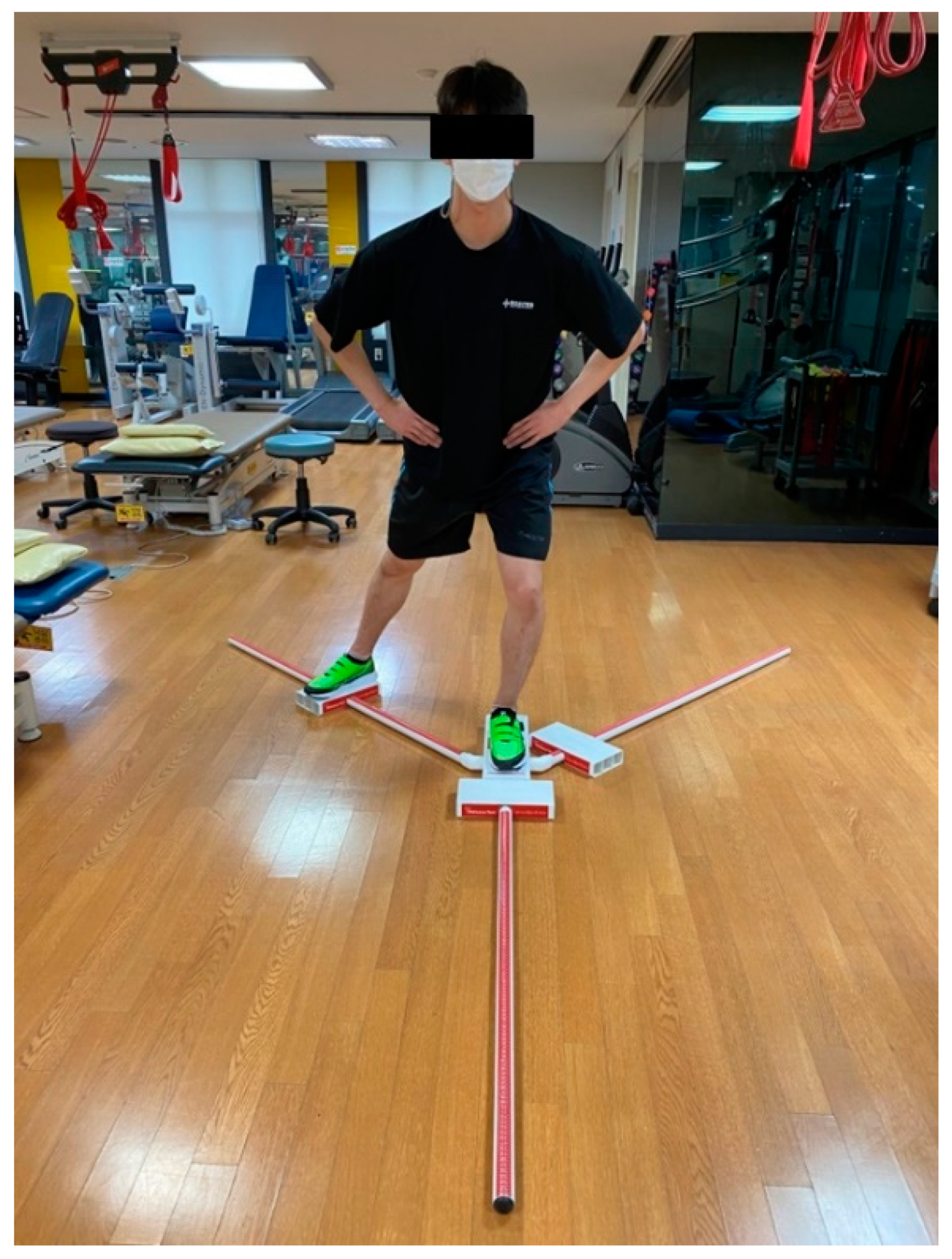
2.4.3. Y-Balance Test
2.4.4. Side-Hop Test
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics
3.2. Dynamic Balance Using Y-Balance
3.3. Dynamic Balance Using Side-Hop Test
3.4. Dynamic Balance Using BIORescue
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fong, D.T.P.; Hong, Y.; Chan, L.K.; Yung, P.S.H.; Chan, K.M. A systematic review on ankle injury and ankle sprain in sports. Sports Med. 2007, 37, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Nomura, T.; Casadio, M.; Morasso, P. Intermittent control with ankle, hip, and mixed strategies during quiet standing: A theoretical proposal based on a double on a double inverted pendulum model. J. Theor. Biol. 2012, 310, 55–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billot, M.; Simoneau, E.M.; Van Hoecke, J.; Martin, A. Age-related relative increases in electromyography activity and torque according to the maximal capacity during upright standing. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 109, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riemann, B.L.; Myers, J.B.; Lephart, S.M. Comparison of the ankle, knee, hip, and trunk corrective action shown during single–leg stance on firm, foam, and multiaxial surfaces. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2003, 84, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, D.S.; Glenn, T.M.; Hutchinson, K.J. Changes in the mean center of balance during balance testing in young adults. Phys. Ther. 1995, 75, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, D.G.; Lamb, G.D.; Westerblad, H. Skeletal muscle fatigue: Cellular mechanisms. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 88, 287–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoka, R.M.; Duchateau, J. Muscle fatigue: What, why and how it influences muscle function. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, N.; Greska, E.; Kollock, R.; Ambegaonkar, J.; Onate, J.A. Changes in lower extremity biomechanics due to a short-term fatigue protocol. J. Athl. Train. 2012, 48, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björklund, M.; Crenshaw, A.G.; Djupsjöbacka, M.; Johansson, H. Position sense acuity is diminished following repetitive low-intensity work to fatigue in a simulated occupational setting. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 81, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.J.; Proske, U. Effect of muscle fatigue on the sense of limb position and movement. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 170, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.C.; McLean, S.G.; Palmieri-Smith, R.M. Quadriceps and hamstring fatigue alters hip and knee mechanics. J. Appl. Biomech. 2010, 26, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo, M.; Aguado, X.; Gonzalez, R.; López, J.L.; Häkkinen, K. Maximal and explosive force production capacity and balance performance in men of different ages. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 1999, 79, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, R.G.T.; Oliveira, L.F.; Nadal, J. Anticipation mechanism in body sway control and effect of muscle fatigue. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2007, 17, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaggie, J.A.; McGregor, S.J. Effects of isokinetic ankle fatigue on the maintenance of balance and postural limits. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2002, 83, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paillard, T. Effects of general and local fatigue on postural control: A review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2012, 36, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gefen, A.; Megido-Ravid, M.; Itzchak, Y.; Arcan, M. Analysis of muscular fatigue and foot stability during high–heeled gait. Gait Posture 2002, 15, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Jiménez, E.M.; Losa-Iglesias, M.E.; Becerro-de-Bengoa-Vallejo, R.; Díaz-Velázquez, J.I.; López-López, D.; Calvo-Lobo, C.; Rodríguez-Sanz, D. Immediate effects of intermittent bilateral ankle plantar flexors static stretching on balance and plantar pressures. J. Manipulative Physiol. Ther. 2020, 43, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Jeon, E.T.; Lee, M.G.; Lee, S.J.; Cho, H.Y. Effects of therapeutic exercise on sea sand on pain, fatigue, and balance in patients with chronic ankle instability: A feasibility study. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2019, 59, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Lee, J.H. Immediate effect of balance taping using kinesiology tape on dynamic and static balance after ankle muscle fatigue. Healthcare 2020, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Díaz, D.; Hita-Contreras, F.; Martínez-Amat, A.; Aibar-Almazán, A.; Kim, K.M. Ankle-joint self-mobilization and crossfit training in patients with chronic ankle instability: A randomized controlled trial. J. Athl. Train. 2020, 55, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, I.R.; Choi, H.S. Immediate effects of ankle-foot orthosis using wire on static balance of patients with stroke with foot drop: A cross-over study. Healthcare 2020, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, H.; Treger, I.; Gruendlinger, L.; Hausdorff, J.M. Neuroprosthesis for footdrop compared with an ankle-foot orthosis: Effects on postural control during walking. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2009, 18, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, D.; Marazzini, F.; Crippa, A.; Cardini, R. Do static or dynamic AFOs improve balance? Clin. Rehabil. 2002, 16, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Routledge: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Feiring, D.C.; Ellenbecker, T.S.; Derscheid, G.L. Test-retest reliability of the biodex isokinetic dynamometer. J. Orhop. Sports Phys. Ther. 1990, 11, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribble, P.A.; Hertel, J. Effect of lower-extremity muscle fatigue on postural control. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2004, 85, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.H.; Cha, Y.J. Effect of gait training with constrained-induced movement therapy (CIMT) on the balance of stroke patients. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Weng, C.; Liu, M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.; He, Y. Effect of whole-body vibration exercise on mobility, balance ability and general health status in frail elderly patients: A pilot randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2014, 28, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geronimi, M. Reproductibilité intra- et intersessions du test des limites de stabilité sur plateforme podobarométrique. Neurophysiol. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 44, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plisky, P.J.; Gorman, P.P.; Butler, R.J.; Kiesel, K.B.; Underwood, F.B.; Elkins, B. The reliability of an instrumented device for measuring components of the star excursion balance test. N. Am. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2009, 4, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herrington, L.; Hatcher, J.; Hatcher, A.; McNicholas, M. A comparison of star excursion balance test reach distances between ACL deficient patients and asymptomatic controls. Knee 2009, 16, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, A.G.; Herrington, L.C. Between-session reliability of the star excursion balance test. Phys. Ther. Sport. 2010, 11, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linek, P.; Sikora, D.; Wolny, T.; Saulicz, E. Reliability and number of trials of Y Balance test in adolescent athletes. Musculoskelet. Sci. Pract. 2017, 31, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caffrey, E.; Docherty, C.L.; Schrader, J.; Klossner, J. The ability of 4 single-limb hopping tests to detect functional performance deficits in individuals with functional ankle instability. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2009, 39, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, K.E.; Kaminski, T.W. Foot characteristics in association with inversion ankle injury. J. Athl. Train. 2007, 42, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Forestier, N.; Teasdale, N.; Nougier, V. Alteration of the position sense at the ankle induced by muscular fatigue in humans. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 43, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuillerme, N.; Boisgontier, M. Muscle fatigue degrades force sense at the ankle joint. Gait Posture 2008, 28, 521–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimmon, Y.; Riemer, R.; Oddsson, L.; Melzer, I. The effect of plantar flexor muscle fatigue on postural control. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2011, 21, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | Mean ± SD or Mode (%) |
|---|---|
| Male | 22 (100) |
| Female | 0 (0) |
| Age (years) | 26.77 ± 3.21 |
| Height (cm) | 176.32 ± 5.21 |
| Weight (kg) | 74.5 ± 9.26 |
| Dominant leg (Right) | 18 (81.81) |
| Dominant leg (Left) | 4 (18.19) |
| Foot size (mm) | 268.64 ± 6.76 |
| Bare Foot | LSS | SWD | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anterior direction (cm) | 61.07 ± 7.56 | 65.29 ± 7.02 | 71.66 ± 8.32 | 0.000 |
| Posteromedial direction (cm) | 93.41 ± 8.39 | 98.18 ± 7.79 | 105.98 ± 9.06 | 0.000 |
| Posterolateral direction (cm) | 101.02 ± 10.13 | 105.39 ± 8.91 | 112.14 ± 9.17 | 0.001 |
| Leg length reach % | 296.32 ± 36.34 | 316.06 ± 29.34 | 340.17 ± 36.82 | 0.000 |
| Bare Foot | LSS | SWD | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Side-hop test(s) | 16.19 ± 4.68 | 13.96 ± 4.29 | 11.57 ± 3.26 | 0.000 |
| Bare Foot | LSS | SWD | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface area ellipse (mm2) | 371.86 ± 199.67 | 212.82 ± 98.74 | 138.68 ± 86.27 | 0.000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, I.-R.; Lee, J.-H. Effects of Shoes That Can Be Tightened Using Wire and Dial on the Dynamic Balance Following Ankle Muscle Fatigue: A Crossover Study. Healthcare 2021, 9, 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9050578
Choi I-R, Lee J-H. Effects of Shoes That Can Be Tightened Using Wire and Dial on the Dynamic Balance Following Ankle Muscle Fatigue: A Crossover Study. Healthcare. 2021; 9(5):578. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9050578
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Im-Rak, and Jung-Hoon Lee. 2021. "Effects of Shoes That Can Be Tightened Using Wire and Dial on the Dynamic Balance Following Ankle Muscle Fatigue: A Crossover Study" Healthcare 9, no. 5: 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9050578
APA StyleChoi, I.-R., & Lee, J.-H. (2021). Effects of Shoes That Can Be Tightened Using Wire and Dial on the Dynamic Balance Following Ankle Muscle Fatigue: A Crossover Study. Healthcare, 9(5), 578. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare9050578







