Effect of Virtual Reality on Pain and Anxiety During Epidural Steroid Injection in Patients with Lumbar Radicular Pain: An Open-Label Randomized Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Outcomes
- The primary endpoint was the pain score during the injection, as assessed by a numeric rating scale ranging from 0 to 10 [22].
- Secondary endpoints were anxiety during the injection procedure, as assessed by the STAI, level of satisfaction with the use of the VR headset (measured on a scale from 0 to 10), and safety (occurrence of any one or more adverse events from among the following: discomfort; asthenia; sleepiness; headache; vertigo; difficulty concentrating; nausea; eye fatigue; eye pain; visual fatigue; blurred vision). These adverse events were commonly described in the literature. Furthermore, satisfaction was measured on a scale from 0 to 10 (not satisfied to very satisfied). It was a bespoke measurement.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Role of the Funding Source
3. Results
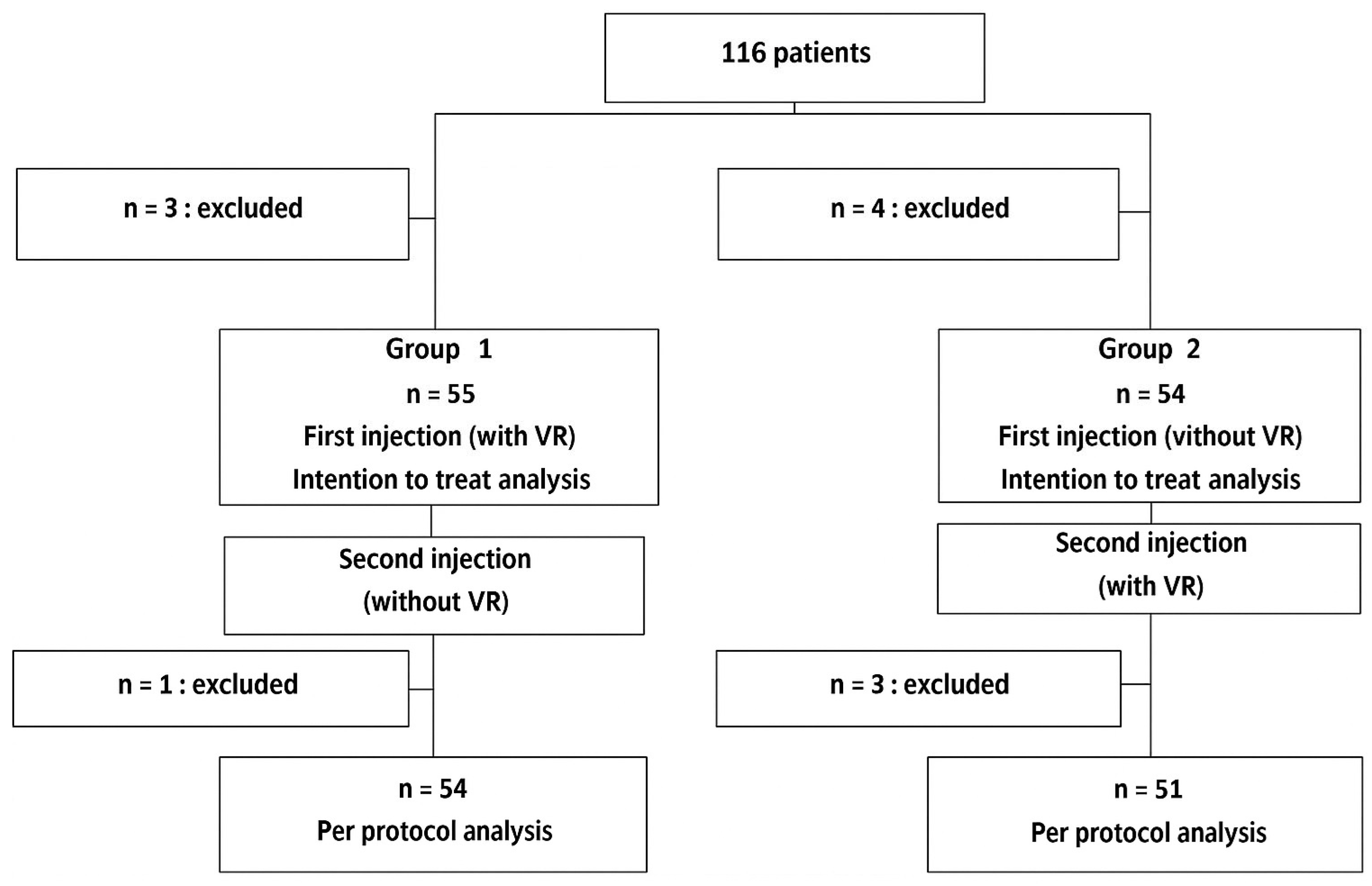
3.1. Population of Study
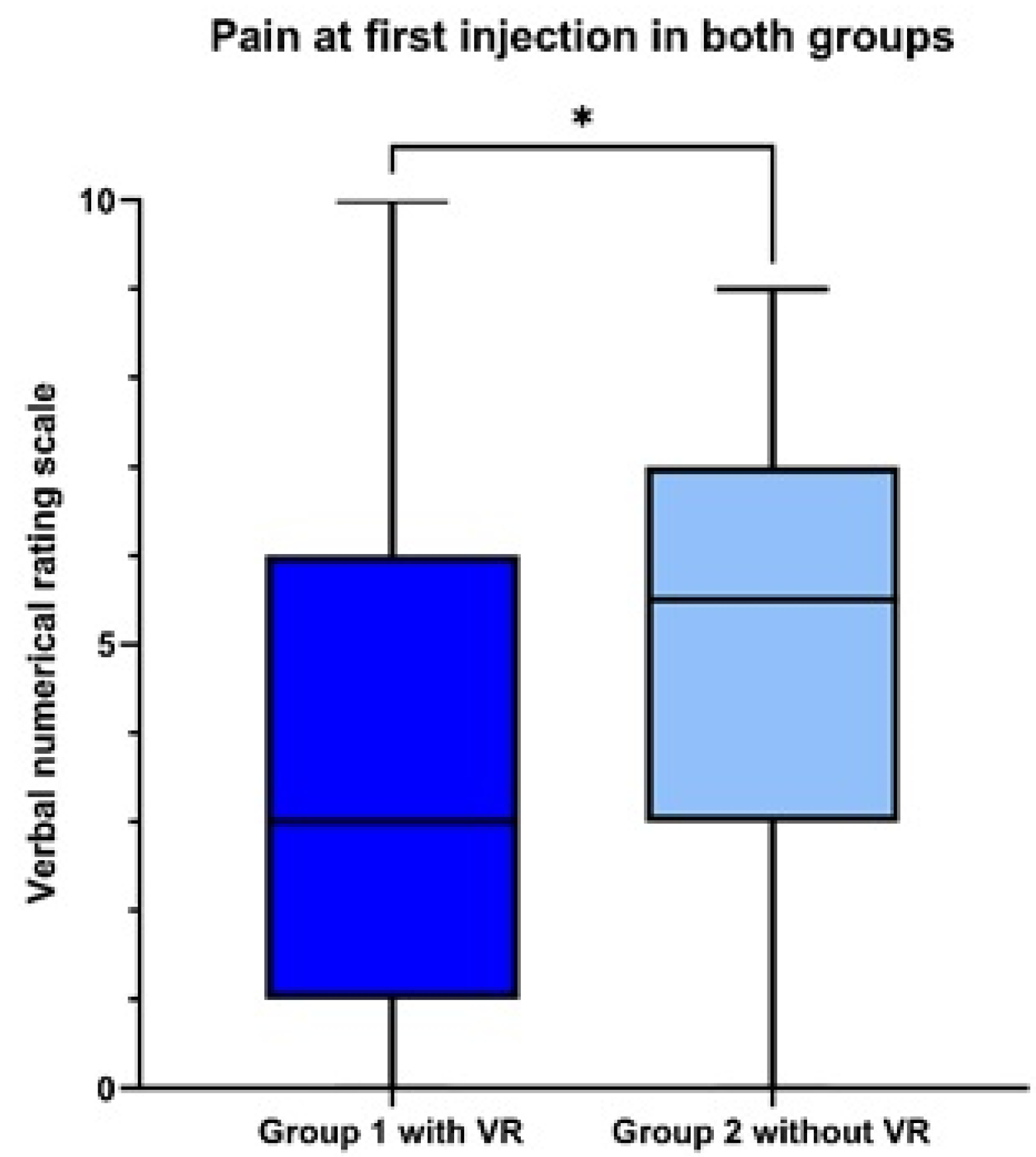
3.2. Primary Outcome
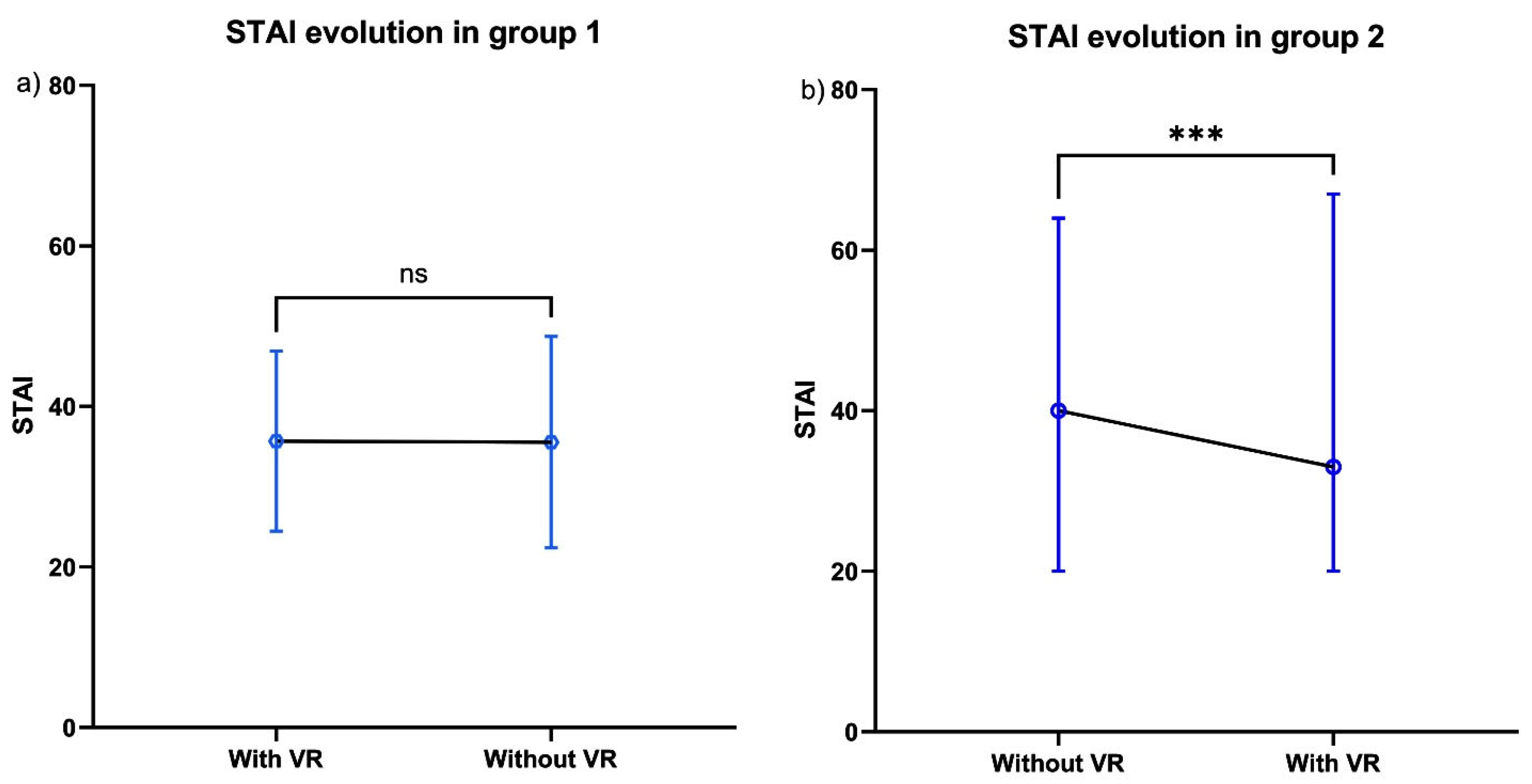
3.3. Secondary Outcome
3.4. Safety
3.5. Satisfaction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VR | Virtual reality |
| STAI | State Trait Anxiety Inventory |
| VNRS | Verbal numeric rating scale |
| MEOPA | Equimolar mixture of oxygen and nitrous oxide |
References
- Kaltenborn, K.-F.; Rienhoff, O. Virtual reality in medicine. Methods Inf. Med. 1993, 32, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, B.; Hoffman, H.G.; Vagnoli, L.; Patterson, D.R.; Alhalabi, W.; Messeri, A.; Grotto, R.L. Virtual Reality Analgesia During Venipuncture in Pediatric Patients With Onco-Hematological Diseases. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, H.G.; Doctor, J.N.; Patterson, D.R.; Carrougher, G.J.; Furness, T.A. Virtual reality as an adjunctive pain control during burn wound care in adolescent patients. Pain 2000, 85, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effectiveness of Virtual Reality in Symptom Management of Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2023, 65, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.S.; Spiegel, B.M.R.; Gregory, K.D. Virtual Reality Reduces Pain in Laboring Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Perinatol. 2021, 38, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verain, J.; Trouillet, C.; Moulin, F.; Christophe, C. Efficacy of virtual reality therapy versus pharmacological sedation for reducing pain and anxiety during coronary catheterisation procedures: A prospective randomised controlled trial. Health Sci. Rep. 2024, 7, e2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilani, M.; Torkaman, G.; Bahrami, F.; Bayat, N. Virtual Reality Exergaming Capability to Change Muscle Strategy During the Limits of Stability Test and Reduce Fear of Falling in Primary Osteoporotic Women. Games Health J. 2023, 12, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özlü, A.; Ünver, G.; Tuna, H.İ.; Menekşeoğlu, A.K. The Effect of a Virtual Reality-Mediated Gamified Rehabilitation Program on Pain, Disability, Function, and Balance in Knee Osteoarthritis: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Study. Games Health J. 2023, 12, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.; Atteya, M.; Kamel, E. Effectiveness of Virtual Reality on Rehabilitation of Chronic Non-specific Low Back Pain Patients. Healthcare 2024, 12, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henríquez-Jurado, J.M.; Osuna-Pérez, M.C.; García-López, H.; Lomas-Vega, R.; López-Ruiz, M.d.C.; Obrero-Gaitán, E.; Cortés-Pérez, I. Virtual reality-based therapy for chronic low back and neck pain: A systematic review with meta-analysis. EFORT Open Rev. 2024, 9, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, M.; Kahveci, A.; Muci, B.; Günendi, Z.; Kaymak Karataş, G. The Effect of Virtual Reality Exercises on Pain, Functionality, Cardiopulmonary Capacity, and Quality of Life in Fibromyalgia Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Study. Games Health J. 2021, 10, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, M.A.; Peng, P.; Hill, D.A. Sciatica: A review of history, epidemiology, pathogenesis, and the role of epidural steroid injection in management. Br. J. Anaesth. 2007, 99, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagala, A.; Gastaldi, R.; Gaudin, P. Infiltrations rachidiennes lombaires. Rev. Rhum. Monogr. 2020, 87, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Bailly, F.; Trouvin, A.-P.; Bercier, S.; Dadoun, S.; Deneuville, J.-P.; Faguer, R.; Fassier, J.-B.; Koleck, M.; Lassalle, L.; Le Vraux, T.; et al. Clinical guidelines and care pathway for management of low back pain with or without radicular pain. Jt. Bone Spine 2021, 88, 105227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafirova, Z.; Sheehan, C.; Hosseinian, L. Update on nitrous oxide and its use in anesthesia practice. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2018, 32, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulkadi, S.; Peters, B.; Vliegen, A.S. Thromboembolic complications of recreational nitrous oxide (ab)use: A systematic review. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2022, 54, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, J.P.; Sharpe, S.; Crowley, K.; Dudley, A.; O’lAoi, R.; Barry, M.; Owens, L.; Doherty, C.P.; Redmond, J.; Yeung, S.-J. Nitrous oxide-induced myeloneuropathy: An emerging public health issue. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 192, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javelot, M.; Chopin, C.; Zarev, A.; Bolko, L.; Hittinger, A.; Coutureau, C.; Duvivier, A.; Salmon, J.H. Intérêt du casque de réalité virtuelle sur la douleur et l’anxiété lors d’une infiltration épidurale par la voie du hiatus sacro-coccygien dans la lomboradicuclalgie. Rev. Du Rhum. 2023, 90 (Suppl. S1), A19–A20. [Google Scholar]
- Javelot, M.; Chopin, C.; Bolko, L.; Hittinger, A.; Coutureau, C.; Duviver, A.; Salmon, J.H. Use of virtual reality headsets to reduce pain and anxiety during epidural infiltration of the sacral hiatus for lumbar radicular pain. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83 (Suppl. S1), 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watters, W.C.; Baisden, J.; Gilbert, T.J.; Kreiner, S.; Resnick, D.K.; Bono, C.M.; Ghiselli, G.; Heggeness, M.H.; Mazanec, D.J.; O’NEill, C.; et al. Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine J. 2008, 8, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreiner, D.S.; Shaffer, W.O.; Baisden, J.L.; Gilbert, T.J.; Summers, J.T.; Toton, J.F.; Hwang, S.W.; Mendel, R.C.; Reitman, C.A. An evidence-based clinical guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis (update). Spine J. 2013, 13, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailly, F.; Fautrel, B.; Gossec, L. Pain assessment in rheumatology—How can we do better? A literature review. Jt. Bone Spine 2016, 83, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Julian, L.J. Measures of anxiety: State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI), Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI), and Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale-Anxiety (HADS-A). Arthritis Care Res. 2011, 63 (Suppl. S11), S467–S472. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Salaffi, F.; Stancati, A.; Silvestri, C.; Ciapetti, A.; Grassi, W. Minimal clinically important changes in chronic musculoskeletal pain intensity measured on a numerical rating scale. Eur. J. Pain 2004, 8, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.; Benveniste, H.; McLellan, A.T. Use and Misuse of Opioids in Chronic Pain. Annu. Rev. Med. 2018, 69, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.P.; Doshi, T.L.; Munjupong, C.S.; Qian, C.; Chalermkitpanit, P.; Pannangpetch, P.; Noragrai, K.; Wang, E.J.; Williams, K.A.; Christo, P.J.; et al. Multicenter, randomized, controlled comparative-effectiveness study comparing virtual reality to sedation and standard local anesthetic for pain and anxiety during epidural steroid injections. Lancet Reg. Health Southeast Asia 2024, 27, 100437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teh, J.J.; Pascoe, D.J.; Hafeji, S.; Parchure, R.; Koczoski, A.; Rimmer, M.P.; Khan, K.S.; Al Wattar, B.H. Efficacy of virtual reality for pain relief in medical procedures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2024, 22, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, H.G.; Richards, T.L.; Van Oostrom, T.; Coda, B.A.; Jensen, M.P.; Blough, D.K.; Sharar, S.R. The analgesic effects of opioids and immersive virtual reality distraction: Evidence from subjective and functional brain imaging assessments. Anesth. Analg. 2007, 105, 1776–178323. [Google Scholar]
- Villemure, C.; Bushnell, C.M. Cognitive modulation of pain: How do attention and emotion influence pain processing? Pain 2002, 95, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bascour-Sandoval, C.; Salgado-Salgado, S.; Gómez-Milán, E.; Fernández-Gómez, J.; Michael, G.; Gálvez-García, G. Pain and Distraction According to Sensory Modalities: Current Findings and Future Directions. Pain Prat. 2019, 19, 686–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.F.; Altman, D.G.; Moher, D.; for the CONSORT Group. CONSORT 2010 Statement: Updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. BMC Med. 2010, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group 1 n = 55 | Group 2 n = 54 | Available Data n = 109 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Females—n (%) | 31 (56.3) | 28 (51.8) | (109) 100% | |
| Age, years—median (Q1–Q3) | 61 (52–69) | 54.5 (44–70) | (109) 100% | |
| Symptom duration, months—median (Q1–Q3) | 6 (3–13) | 6 (2–12) | (109) 100% | |
| Pain at inclusion, by NRS—median (Q1–Q3) | 6 (4–8) | 6 (4–8) | (109) 100% | |
| STAI before the injection—median (Q1–Q3) | 37 (34–49) | 40.5 (34–49) | (106) 97.2% | |
| Employment status n (%) | Unemployed | 9 (16.3) | 8 (14.8) | (109) 100% |
| Retired | 24 (43.6) | 18 (33.3) | ||
| Employed | 22 (40) | 28 (51.8) | ||
| First injection—n (%) | 39 (70.9) | 37 (68.5) | (108) 99% | |
| Practiced sophrology—n (%) | 4 (7.2) | 4 (7.4) | (107) 98% | |
| Practiced hypnosis—n (%) | 4 (7.2) | 4 (7.4) | (107) 98% | |
| Antidepressants—n (%) | 8 (14.5) | 10 (18.5) | (108) 99% | |
| Anxiolytics—n (%) | 7 (12.7) | 7 (12.9) | (107) 98% | |
| VR environment chosen—n (%) | Ocean | 13 (23.6) | 12 (22.2) | 100 (91%) |
| Zen garden | 3 (5.4) | 10 (18.5) | ||
| Snowy mountain | 13 (23.6) | 8 (14.8) | ||
| Sunny mountain | 2 (3.6) | 1 (1.8) | ||
| Beach | 12 (21.8) | 5 (9.2) | ||
| Forest | 12 (21.8) | 9 (16.6) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Javelot, M.; Chopin, C.; Bolko, L.; Hittinger, A.; Geoffroy, M.; Charlot, I.; Adeline, F.; Coutureau, C.; Duvivier, A.; Salmon, J.-H. Effect of Virtual Reality on Pain and Anxiety During Epidural Steroid Injection in Patients with Lumbar Radicular Pain: An Open-Label Randomized Trial. Healthcare 2025, 13, 2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13182376
Javelot M, Chopin C, Bolko L, Hittinger A, Geoffroy M, Charlot I, Adeline F, Coutureau C, Duvivier A, Salmon J-H. Effect of Virtual Reality on Pain and Anxiety During Epidural Steroid Injection in Patients with Lumbar Radicular Pain: An Open-Label Randomized Trial. Healthcare. 2025; 13(18):2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13182376
Chicago/Turabian StyleJavelot, Marine, Clément Chopin, Loïs Bolko, Ambre Hittinger, Marion Geoffroy, Isabelle Charlot, Fanny Adeline, Claire Coutureau, Alice Duvivier, and Jean-Hugues Salmon. 2025. "Effect of Virtual Reality on Pain and Anxiety During Epidural Steroid Injection in Patients with Lumbar Radicular Pain: An Open-Label Randomized Trial" Healthcare 13, no. 18: 2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13182376
APA StyleJavelot, M., Chopin, C., Bolko, L., Hittinger, A., Geoffroy, M., Charlot, I., Adeline, F., Coutureau, C., Duvivier, A., & Salmon, J.-H. (2025). Effect of Virtual Reality on Pain and Anxiety During Epidural Steroid Injection in Patients with Lumbar Radicular Pain: An Open-Label Randomized Trial. Healthcare, 13(18), 2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13182376







