Less Time, Same Insight? Evaluating Short Functional Tests as Substitutes for the Six-Minute Walk Test and the Reliability and Validity of the 2MWT, 3MWT, and 1MSTS in Bariatric Surgery Candidates with Obesity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Power Analysis
2.3. Outcome Measures
2.3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
2.3.2. Functional Performance Tests
2.4. Statistical Analysis
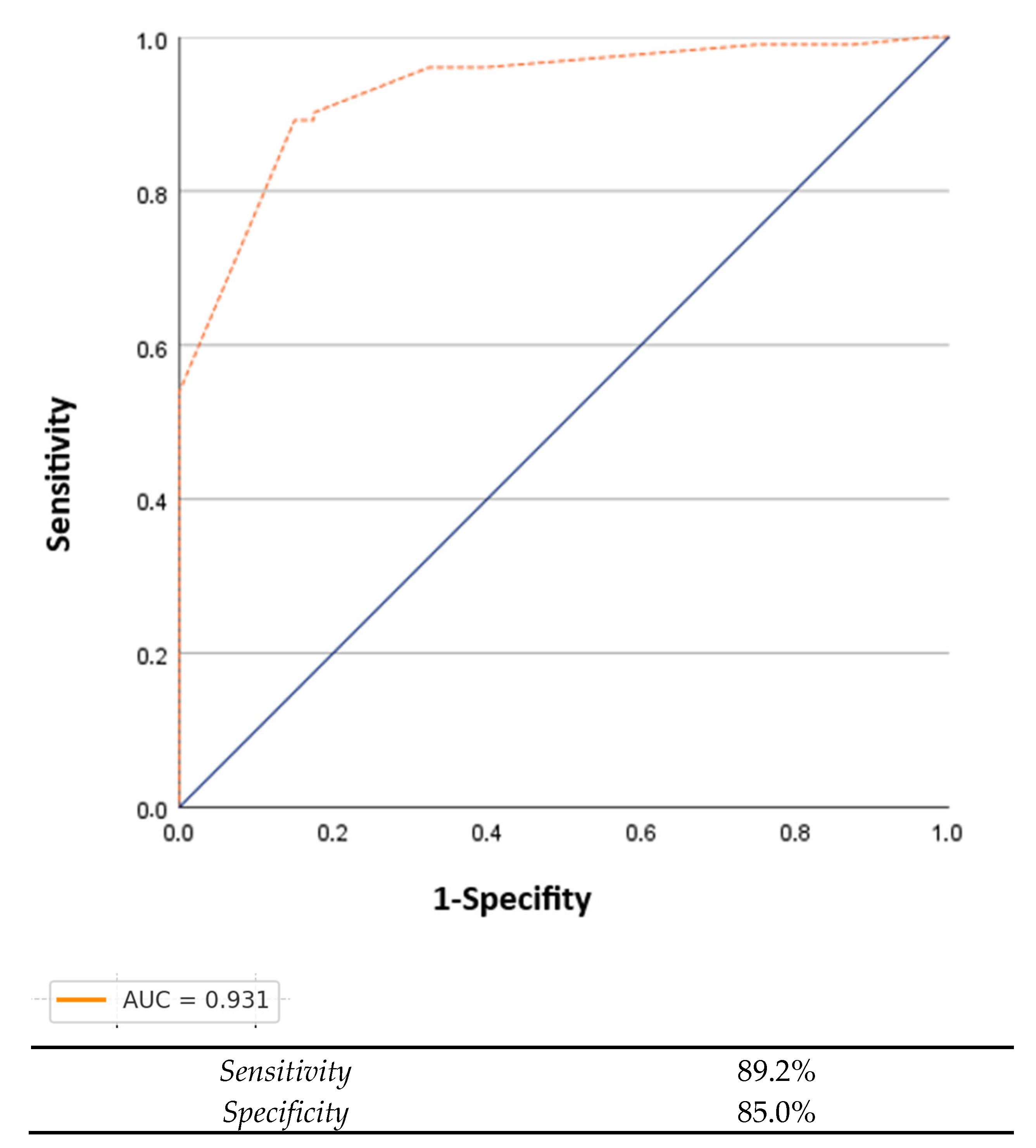
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. Obesity and Overweight. 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 1 July 2025).
- Donini, L.M.; Poggiogalle, E.; Mosca, V.; Pinto, A.; Brunani, A.; Capodaglio, P. Disability affects the 6-minute walking distance in obese subjects (BMI > 40 kg/m2). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pataky, Z.; Armand, S.; Müller-Pinget, S.; Golay, A.; Allet, L. Effects of obesity on functional capacity. Obesity 2014, 22, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourado, V.; Nishiaka, R.; Simões, M.; Lauria, V.; Tanni, S.; Godoy, I.; Gagliardi, A.; Romiti, M.; Arantes, R. Classification of cardiorespiratory fitness using the six-minute walk test in adults: Comparison with cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Pulmonology 2021, 27, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, U.E.; Reynisdottir, S. The six-minute walk test in outpatients with obesity: Reproducibility and known group validity. Physiother. Res. Int. 2008, 13, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beriault, K.; Carpentier, A.; Gagnon, C.; Ménard, J.; Baillargeon, J.-P.; Ardilouze, J.-L.; Langlois, M.-F. Reproducibility of the 6-minute walk test in obese adults. Int. J. Sports Med. 2009, 30, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagat, P. Reference standards for the 6-min walk test in Croatian older adults. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1226585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Penta, M.; Van Chinh, N.; Sauvage, C. Comparison of walking performance with the 6-minute and the 2-minute walk tests in elderly living in the community and in a nursing home. J. Rehabil. Res. Pract. 2025, 6, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel, E.; Unver, B.; Kalkan, S.; Karatosun, V. Reliability and minimal detectable change of the 2-minute walk test and Timed Up and Go test in patients with total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int. 2021, 31, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orange, S.T.; Marshall, P.; Madden, L.A.; Vince, R.V. Can sit-to-stand muscle power explain the ability to perform functional tasks in adults with severe obesity? J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujang, M.A.; Baharum, N. Sample size guideline for correlation analysis. World 2016, 3, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasch-Bernat, M.; Dueñas, L.; Aguilar-Rodríguez, M.; Falla, D.; Schneebeli, A.; Navarro-Bosch, M.; Lluch, E.; Barbero, M. The spatial extent of pain is associated with pain intensity, catastrophizing and some measures of central sensitization in people with frozen shoulder. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, P.L. The six-minute walk test. Respir. Care 2003, 48, 783–785. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iriberri, M.; GáLDIZ, J.B.; Gorostiza, A.; Ansola, P.; Jaca, C. Comparison of the distances covered during 3 and 6 min walking test. Respir. Med. 2002, 96, 812–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Wang, Y.-C.; Gershon, R.C. Two-minute walk test performance by adults 18 to 85 years: Normative values, reliability, and responsiveness. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 96, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, S.A.F.; Faintuch, J.; Fabris, S.M.; Nampo, F.K.; Luz, C.; Fabio, T.L.; Sitta, I.S.; de Batista Fonseca, I.C. Six-minute walk test: Functional capacity of severely obese before and after bariatric surgery. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2009, 5, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orange, S.T.; Metcalfe, J.W.; Liefeith, A.; Jordan, A.R. Validity of various portable devices to measure sit-to-stand velocity and power in older adults. Gait Posture 2020, 76, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Crouch, R. Minimal clinically important difference for change in 6-minute walk test distance of adults with pathology: A systematic review. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2017, 23, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beekman, E.; Mesters, I.; Hendriks, E.J.; Klaassen, M.P.; Gosselink, R.; van Schayck, O.C.; de Bie, R.A. Course length of 30 metres versus 10 metres has a significant influence on six-minute walk distance in patients with COPD: An experimental crossover study. J. Physiother. 2013, 59, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.; Sylvester, K.P.; Newman, J. Shorter walk test durations to detect ambulatory oxygen desaturation in interstitial lung disease: An observational cohort study. ERJ Open Res. 2025, 11, 00891–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, A.E.; Spruit, M.A.; Troosters, T.; Puhan, M.A.; Pepin, V.; Saey, D.; McCormack, M.C.; Carlin, B.W.; Sciurba, F.C.; Pitta, F. An official European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society technical standard: Field walking tests in chronic respiratory disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 1428–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.L.; Pin, T.W. Reliability, validity and minimal detectable change of 2-minute walk test, 6-minute walk test and 10-meter walk test in frail older adults with dementia. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 115, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalzitti, D.A.; Harwood, K.J.; Maring, J.R.; Leach, S.J.; Ruckert, E.A.; Costello, E. Validation of the 2-minute walk test with the 6-minute walk test and other functional measures in persons with multiple sclerosis. Int. J. MS Care 2018, 20, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, D.; Parsons, J.; Hunter, J.P.; Devlin, M.; Walker, J. The 2-minute walk test as a measure of functional improvement in persons with lower limb amputation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2001, 82, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willi, R.; Widmer, M.; Merz, N.; Bastiaenen, C.H.; Zörner, B.; Bolliger, M. Validity and reliability of the 2-minute walk test in individuals with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2023, 61, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W. Comfortable and maximum walking speed of adults aged 20—79 years: Reference values and determinants. Age Ageing 1997, 26, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reychler, G.; Boucard, E.; Peran, L.; Pichon, R.; Le Ber-Moy, C.; Ouksel, H.; Liistro, G.; Chambellan, A.; Beaumont, M. One minute sit-to-stand test is an alternative to 6MWT to measure functional exercise performance in COPD patients. Clin. Respir. J. 2018, 12, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Shigeta, A.; Inagaki, T.; Hayama, N.; Kawame, C.; Naraki, Y.; Naito, A.; Sekine, A.; Suda, R.; Sugiura, T. The utility and safety of one-minute sit-to-stand test in pulmonary hypertension: A prospective study. Respir. Investig. 2025, 63, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, S.; Büsching, G.; Schultz, K.; Lehbert, N.; Jelusic, D.; Keusch, S.; Wittmann, M.; Schuler, M.; Radtke, T.; Frey, M. A multicentre validation of the 1-min sit-to-stand test in patients with COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, R.W.; Crouch, R. 1-minute sit-to-stand test: Systematic review of procedures, performance, and clinimetric properties. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2019, 39, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronberger, C.; Mousavi, R.A.; Öztürk, B.; Willixhofer, R.; Dachs, T.-M.; Rettl, R.; Camuz-Ligios, L.; Rassoulpour, N.; Krall, C.; Litschauer, B. Functional capacity testing in patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH) using the one-minute sit-to-stand test (1-min STST). PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Description * | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 34.94 ± 10.61 | |
| BMI | 45.92 ± 7.09 | |
| Waist-to-Hip Ratio | 0.94 ± 0.08 | |
| Gender | Male | 28 (19.7%) |
| Female | 114 (80.3%) | |
| Smoking | Yes | 49 (34.5%) |
| No | 93 (65.5%) | |
| Six-Minute Walk Test | 412.37 ± 81.11 m | |
| Three-Minute Walk Test | 206.72 ± 30.75 m | |
| Two-Minute Walk Test | 140.27 ± 20.02 m | |
| One-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test | 20.98 ± 4.14 repetitions |
| Test | BMI < 40 r * (p) | BMI 40–50 r * (p) | BMI > 50 r * (p) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Three-Minute Walk Test | 0.718 (0.0004) | 0.765 (<0.001) | 0.930 (<0.001) |
| Two-Minute Walk Test | 0.645 (0.0021) | 0.680 (<0.001) | 0.756 (<0.001) |
| One-Minute Sit-to-Stand Test | 0.172 (0.4697) | 0.320 (0.0021) | 0.339 (0.0576) |
| Test | BMI < 40 R2 (p) * | BMI 40–50 R2 (p) * | BMI > 50 R2 (p) * |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3MWT | 0.515 (p = 0.001) | 0.585 (p = 0.001) | 0.865 (p = 0.001) |
| 2MWT | 0.416 (p = 0.002) | 0.462 (p = 0.001) | 0.572 (p = 0.001) |
| BMI Group | Mean ± SD (3MWT) | ICC * | 95% CI (Lower–Upper) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <40 | 201.45 ± 6.22 m | 0.932 | 0.742–0.977 | <0.001 |
| 40–50 | 211.90 ± 3.21 m | 0.900 | 0.840–0.936 | <0.001 |
| >50 | 209.22 ± 6.58 m | 0.873 | 0.430–0.956 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turan, H.; Yasaci, Z.; Elkan, H. Less Time, Same Insight? Evaluating Short Functional Tests as Substitutes for the Six-Minute Walk Test and the Reliability and Validity of the 2MWT, 3MWT, and 1MSTS in Bariatric Surgery Candidates with Obesity. Healthcare 2025, 13, 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151883
Turan H, Yasaci Z, Elkan H. Less Time, Same Insight? Evaluating Short Functional Tests as Substitutes for the Six-Minute Walk Test and the Reliability and Validity of the 2MWT, 3MWT, and 1MSTS in Bariatric Surgery Candidates with Obesity. Healthcare. 2025; 13(15):1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151883
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuran, Hamdiye, Zeynal Yasaci, and Hasan Elkan. 2025. "Less Time, Same Insight? Evaluating Short Functional Tests as Substitutes for the Six-Minute Walk Test and the Reliability and Validity of the 2MWT, 3MWT, and 1MSTS in Bariatric Surgery Candidates with Obesity" Healthcare 13, no. 15: 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151883
APA StyleTuran, H., Yasaci, Z., & Elkan, H. (2025). Less Time, Same Insight? Evaluating Short Functional Tests as Substitutes for the Six-Minute Walk Test and the Reliability and Validity of the 2MWT, 3MWT, and 1MSTS in Bariatric Surgery Candidates with Obesity. Healthcare, 13(15), 1883. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare13151883


_MD__MPH_PhD.png)



