Disinfection of Reusable Laryngoscopes: A Survey about the Clinical Practice in Spain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
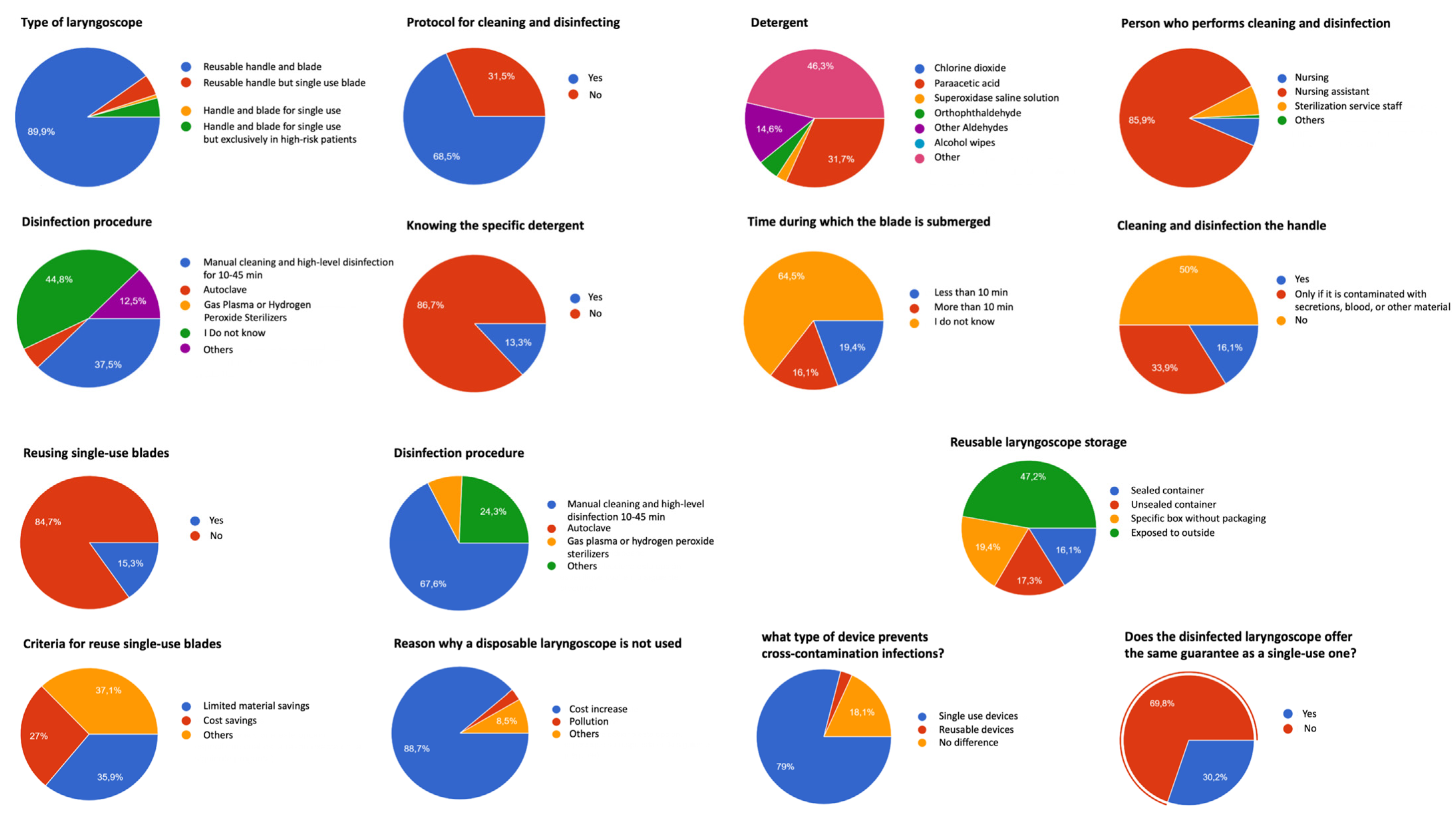
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haque, M.; Sartelli, M.; McKimm, J.; Bin Abu Bakar, M. Health care-associated infections—An overview. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 2321–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maraldi, M.; Lisi, M.; Moretti, G.; Sponchioni, M.; Moscatelli, D. Health care-associated infections: Controlled delivery of cationic antiseptics from polymeric excipients. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 607, 120956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, J.D.; Hopf, H.W. Balancing Infection Control and Environmental Protection as a Matter of Patient Safety: The Case of Laryngoscope Handles. Obstet. Anesth. Dig. 2018, 127, 576–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa, A.N.; Levy, C.; Freitas, M. Laryngoscope blades and handles as sources of cross-infection: An integrative review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2013, 83, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foweraker, J. The laryngoscope as a potential source of cross-infection. J. Hosp. Infect. 1995, 29, 315–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayatollahi, A.A.; Amini, A.; Rahimi, S.; Takrami, S.R.; Darsanaki, R.K.; Nezhad, M.S. Prevalence of gram-negative bacilli isolated from the equipment and surfaces in hospital wards of Golestan province, North of Iran. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 7, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neal, T.; Hughes, C.; Rothburn, M.; Shaw, N. The neonatal laryngoscope as a potential source of cross-infection. J. Hosp. Infect. 1995, 30, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, V.; Ranganathan, P.; Kelkar, R.; Telang, R. Decontamination of laryngoscope blades: Is our practice adequate? J. Postgrad. Med. 2010, 56, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballin, M.S.; McCluskey, A.; Maxwell, S.; Spilsbury, S. Contamination of laryngoscopes. Anaesthesia 1999, 54, 1115–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beamer, J.E.R.; Cox, R.A. MRSA contamination of a laryngoscope blade: A potential vector for cross infection. Anaesthesia 1999, 54, 1010–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, B.; Gorman, L.; Simpson, J.; Curran, E.; McNamee, S.; Lucas, C.; Michie, J.; Platt, D.; Thakker, B. An outbreak of Serratia marcescens in two neonatal intensive care units. J. Hosp. Infect. 2000, 46, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cullen, M.; Trail, A.; Robinson, M.; Keaney, M.; Chadwick, P. Serratia marcescens outbreak in a neonatal intensive care unit prompting review of decontamination of laryngoscopes. J. Hosp. Infect. 2005, 59, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaskar, V.; Dave, N.; Dias, R.; Karnik, P. Disinfection of laryngoscopes: A survey of practice. Indian J. Anaesth. 2017, 61, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morell, R.C.; Ririe, D.; James, R.L.; Crews, D.A.; Huffstetler, K. A Survey of Laryngoscope Contamination at a University and a Community Hospital. Anesthesiology 1994, 80, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.B. Cleaning the laryngoscope blade. Can. J. Anaesth. 1973, 20, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, V.; Thoppil, A.; Young, H.; Sharma, S.; Blunt, M.; Young, P. Chlorhexidine to maintain cleanliness of laryngoscope handles: An audit and laboratory study. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2013, 30, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, R.; Gupta, A.; Gupta, A.; Kumar, M. Laryngoscope decontamination techniques: A survey. J. Anaesthesiol. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 32, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esler, M.D.; Baines, L.C.; Wilkinson, D.J.; Langford, R.M. Decontamination of laryngoscopes: A survey of national practice. Anaesthesia 1999, 54, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucx, M.; Dankert, J.; Beenhakker, M.; Harrison, T. Decontamination of laryngoscopes in The Netherlands. Br. J. Anaesth. 2001, 86, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez-Ríos, M.Á.; Sastre, J.A.; López, T.; Gaszyński, T. Disinfection of Reusable Laryngoscopes: A Survey about the Clinical Practice in Spain. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11081117
Gómez-Ríos MÁ, Sastre JA, López T, Gaszyński T. Disinfection of Reusable Laryngoscopes: A Survey about the Clinical Practice in Spain. Healthcare. 2023; 11(8):1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11081117
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez-Ríos, Manuel Á., José Alfonso Sastre, Teresa López, and Tomasz Gaszyński. 2023. "Disinfection of Reusable Laryngoscopes: A Survey about the Clinical Practice in Spain" Healthcare 11, no. 8: 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11081117
APA StyleGómez-Ríos, M. Á., Sastre, J. A., López, T., & Gaszyński, T. (2023). Disinfection of Reusable Laryngoscopes: A Survey about the Clinical Practice in Spain. Healthcare, 11(8), 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare11081117








