A Mixed Statistical and Machine Learning Approach for the Analysis of Multimodal Trail Making Test Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Related Work
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Visual Sequential Search Test
2.2. VSST Experimental Dataset Description
- average gaze position along x axis (pixels);
- average gaze position along y axis (pixels);
- fixation ID (integer) ( = saccade);
- pupil size (left);
- pupil size (right);
- timestamp (every 4 ms);
- stimulus (code of the image shown in the screen).
2.3. ETT Image Dataset
2.4. Statistical and Deep Learning Methods for the VSST Data Analysis
2.4.1. Statistical Methods
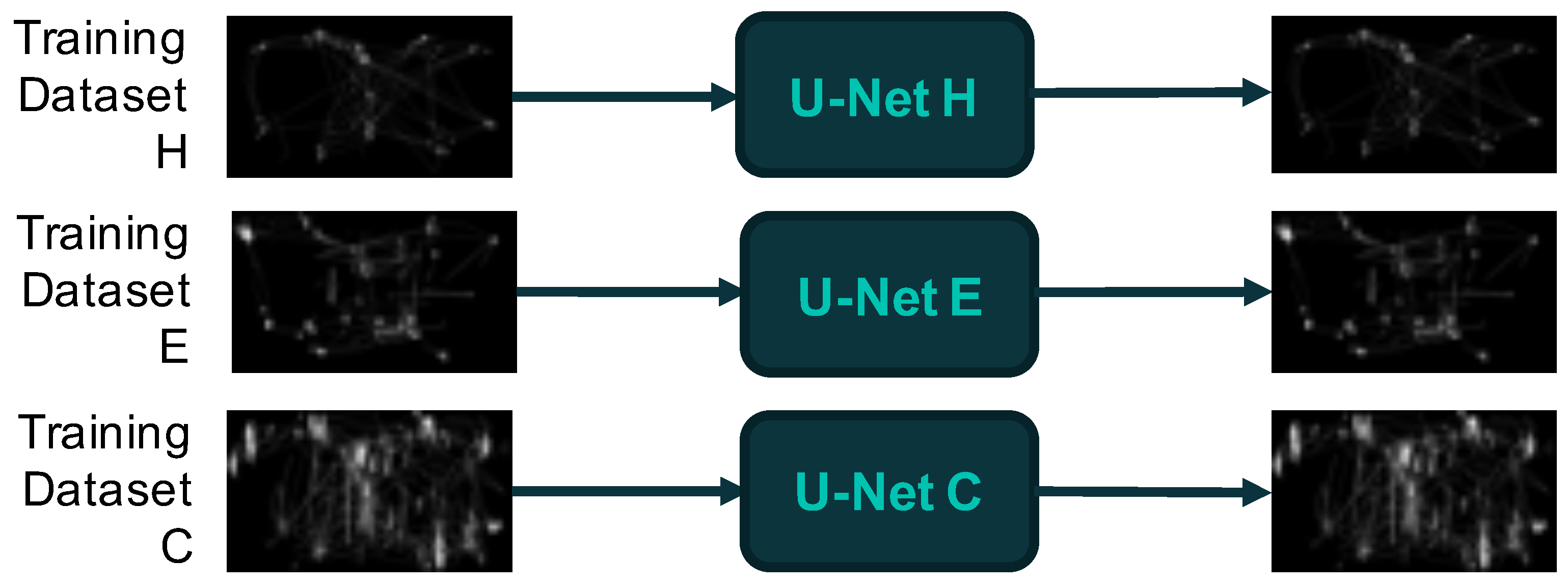
2.4.2. Deep Learning Modelling: Autoencoders and the U-Net Architecture
2.4.3. K-Means Clustering
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Statistical Analysis of Pupil and Blinking Data
3.1.1. Outliers Detection and Kruskall–Wallis Test
3.1.2. Bootstrapping Method
3.2. Mapping Latent Space Representations of ETT Images to Phenotypic Groups
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kredel, R.; Vater, C.; Klostermann, A.; Hossner, E.J. Eye-tracking technology and the dynamics of natural gaze behavior in sports: A systematic review of 40 years of research. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verma, R.; Lalla, R.; Patil, T.B. Is blinking of the eyes affected in extrapyramidal disorders? An interesting observation in a patient with Wilson disease. In Case Reports 2012; BMJ Publishing Group: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Medathati, N.V.K.; Ruta, D.; Hillis, J. Towards inferring cognitive state changes from pupil size variations in real world conditions. In Proceedings of the ACM Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications, New York, NY, USA, 2–5 June 2020; Volume 22, pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zivkovic, M.; Bacanin, N.; Venkatachalam, K.; Nayyar, A.; Djordjevic, A.; Strumberger, I.; Al-Turjman, F. COVID-19 cases prediction by using hybrid machine learning and beetle antennae search approach. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacanin, N.; Stoean, R.; Zivkovic, M.; Petrovic, A.; Rashid, T.A.; Bezdan, T. Performance of a Novel Chaotic Firefly Algorithm with Enhanced Exploration for Tackling Global Optimization Problems: Application for Dropout Regularization. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakar, S.; Ghosh, M.; Bhowmik, S.; Sarkar, R.; Nasipuri, M. A GA based hierarchical feature selection approach for handwritten word recognition. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 2533–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaci, M.; Pancino, N.; Andreini, P.; Bonechi, S.; Bongini, P.; Rossi, A.; Bianchini, M. Deep Learning Techniques for Dragonfly Action Recognition. In Proceedings of the ICPRAM, Valletta, Malta, 22–24 February 2020; pp. 562–569. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; He, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, X. Disease classification based on eye movement features with decision tree and random forest. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Cuentas, N.I.; Roman-Gonzalez, A.; Gilman, R.H.; Barrientos, F.; Ting, J.; Hidalgo, D.; Zimic, M. Developing an eye-tracking algorithm as a potential tool for early diagnosis of autism spectrum disorder in children. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duque, A.; Vázquez, C. Double attention bias for positive and negative emotional faces in clinical depression: Evidence from an eye-tracking study. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 2015, 46, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duque, A.; Vazquez, C. A failure to show the efficacy of a dot-probe attentional training in dysphoria: Evidence from an eye-tracking study. J. Clin. Psychol. 2018, 74, 2145–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellough, J.L.; Beevers, C.G.; Ellis, A.J.; Wells, T.T. Time course of selective attention in clinically depressed young adults: An eye tracking study. Behav. Res. Ther. 2008, 46, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanchez, A.; Vazquez, C.; Marker, C.; LeMoult, J.; Joormann, J. Attentional disengagement predicts stress recovery in depression: An eye-tracking study. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 2013, 122, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hochstadt, J. Set-shifting and the on-line processing of relative clauses in Parkinson’s disease: Results from a novel eye-tracking method. Cortex 2009, 45, 991–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, B.C.; Cazzoli, D.; Pflugshaupt, T.; Bohlhalter, S.; Vanbellingen, T.; Müri, R.M.; Nyffeler, T. Eyetracking during free visual exploration detects neglect more reliably than paper-pencil tests. Cortex 2020, 129, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, S.; Respondek, G.; Stamelou, M.; Dowiasch, S.; Stoll, J.; Bremmer, F.; Einhauser, W. Validation of mobile eye-tracking as novel and efficient means for differentiating progressive supranuclear palsy from Parkinson’s disease. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trepagnier, C. Tracking gaze of patients with visuospatial neglect. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2002, 8, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R. The Feasibility of Using Virtual Reality and Eye Tracking in Research With Older Adults With and Without Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maj, C.; Azevedo, T.; Giansanti, V.; Borisov, O.; Dimitri, G.M.; Spasov, S.; Merelli, I. Integration of machine learning methods to dissect genetically imputed transcriptomic profiles in alzheimer’s disease. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Veneri, G.; Pretegiani, E.; Rosini, F.; Federighi, P.; Federico, A.; Rufa, A. Evaluating the human ongoing visual search performance by eye–tracking application and sequencing tests. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2012, 107, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veneri, G.; Pretegiani, E.; Fargnoli, F.; Rosini, F.; Vinciguerra, C.; Federighi, P.; Federico, A.; Rufa, A. Spatial ranking strategy and enhanced peripheral vision discrimination optimize performance and efficiency of visual sequential search. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 40, 2833–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Inverno, G.A.; Brunetti, S.; Sampoli, M.L.; Mureşanu, D.F.; Rufa, A.; Bianchini, M. VSST analysis: An algorithmic approach. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U–Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2015, 9351, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Bowie, H. Administration and interpretation of the Trail Making Test. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2277–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, L. Best practices in eye tracking research. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2020, 155, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmqvist, K.; Nyström, M.; Andersson, R.; Dewhurst, R.; Jarodzka, H.; Van de Weijer, J. Eye Tracking: A Comprehensive Guide to Methods and Measures; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- The Mathworks, Inc. MATLAB Version 9.10.0.1613233 (R2021a); The Mathworks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargha, A.; Delaney, H.D. The Kruskal-Wallis test and stochastic homogeneity. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 1998, 23, 170–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amidan, B.G.; Ferryman, T.A.; Cooley, S.K. Data outlier detection using the Chebyshev theorem. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 5–12 March 2005; pp. 3814–3819. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchini, M.; Dimitri, G.M.; Maggini, M.; Scarselli, F. Deep neural networks for structured data. In Computational Intelligence for Pattern Recognition; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 29–51. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancino, N.; Rossi, A.; Ciano, G.; Giacomini, G.; Bonechi, S.; Andreini, P.; Bongini, P. Graph Neural Networks for the Prediction of Protein-Protein Interfaces. In Proceedings of the ESANN, Bruges, Belgium, 2–4 October 2020; pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitri, G.M.; Spasov, S.; Duggento, A.; Passamonti, L.; Toschi, N. Unsupervised stratification in neuroimaging through deep latent embeddings IEEE. In Proceedings of the 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC) IEEE, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–24 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- MacQueen, J. Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Berkley, UK, 1 January 1967; Volume 1, pp. 281–297. [Google Scholar]
- Peddireddy, A.; Wang, K.; Svensson, P.; Arendt-Nielsen, L. Blink reflexes in chronic tension–type headache patients and healthy controls. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2009, 120, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unal, Z.; Domac, F.M.; Boylu, E.; Kocer, A.; Tanridag, T.; Us, O. Blink reflex in migraine headache. North. Clin. Istanb. 2016, 3, 289–292. [Google Scholar]









| Blinking Rate | Maximum Pupil Size Variation | Blinking Average Duration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classes | p-Value | H Statistic | p-Value | H Statistic | p-Value | H Statistic |
| H–C | 0.0059 | 7.5880 | 0.0121 | 6.2899 | 0.1079 | 2.5847 |
| H–E | 0.2092 | 1.5771 | 0.6534 | 0.2016 | 0.5289 | 0.3966 |
| E–C | 0.3258 | 0.9654 | 0.0039 | 8.3394 | 0.0058 | 7.6226 |
| Blinking Rate | Maximum Pupil Size Variation | Blinking Average Duration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classes | p-Value | H Statistic | p-Value | H Statistic | p-Value | H Statistic |
| H–C | 0.0027 | 9.0171 | 0.0075 | 7.1445 | 0.0488 | 3.8814 |
| H–E | 0.1877 | 1.7355 | 0.4984 | 0.4584 | 0.5115 | 0.4309 |
| E–C | 0.2390 | 1.3867 | 0.0008 | 11.3152 | 0.0016 | 9.999 |
| Classes | Blinking Rate | Maximum Pupil Size Variation | Blinking Average Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| H–C | 59.11% | 48.06% | 10.99% |
| E–C | 2.05% | 67.92% | 58.42% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pancino, N.; Graziani, C.; Lachi, V.; Sampoli, M.L.; Ștefǎnescu, E.; Bianchini, M.; Dimitri, G.M. A Mixed Statistical and Machine Learning Approach for the Analysis of Multimodal Trail Making Test Data. Mathematics 2021, 9, 3159. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9243159
Pancino N, Graziani C, Lachi V, Sampoli ML, Ștefǎnescu E, Bianchini M, Dimitri GM. A Mixed Statistical and Machine Learning Approach for the Analysis of Multimodal Trail Making Test Data. Mathematics. 2021; 9(24):3159. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9243159
Chicago/Turabian StylePancino, Niccolò, Caterina Graziani, Veronica Lachi, Maria Lucia Sampoli, Emanuel Ștefǎnescu, Monica Bianchini, and Giovanna Maria Dimitri. 2021. "A Mixed Statistical and Machine Learning Approach for the Analysis of Multimodal Trail Making Test Data" Mathematics 9, no. 24: 3159. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9243159
APA StylePancino, N., Graziani, C., Lachi, V., Sampoli, M. L., Ștefǎnescu, E., Bianchini, M., & Dimitri, G. M. (2021). A Mixed Statistical and Machine Learning Approach for the Analysis of Multimodal Trail Making Test Data. Mathematics, 9(24), 3159. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9243159










