Influence of MHD Hybrid Ferrofluid Flow on Exponentially Stretching/Shrinking Surface with Heat Source/Sink under Stagnation Point Region
Abstract
:1. Introduction
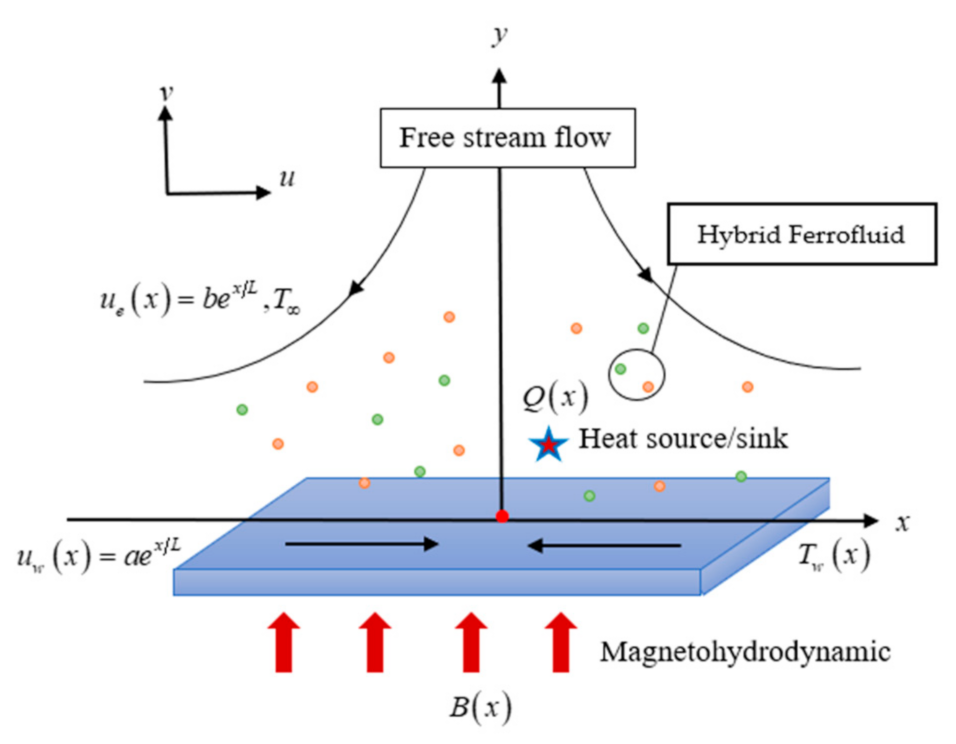
2. Problem Formulation
2.1. Mathematical Framework
2.2. Correlation Used for Hybrid Ferrofluid
2.3. Similarity Solutions
2.4. Physical Quantities
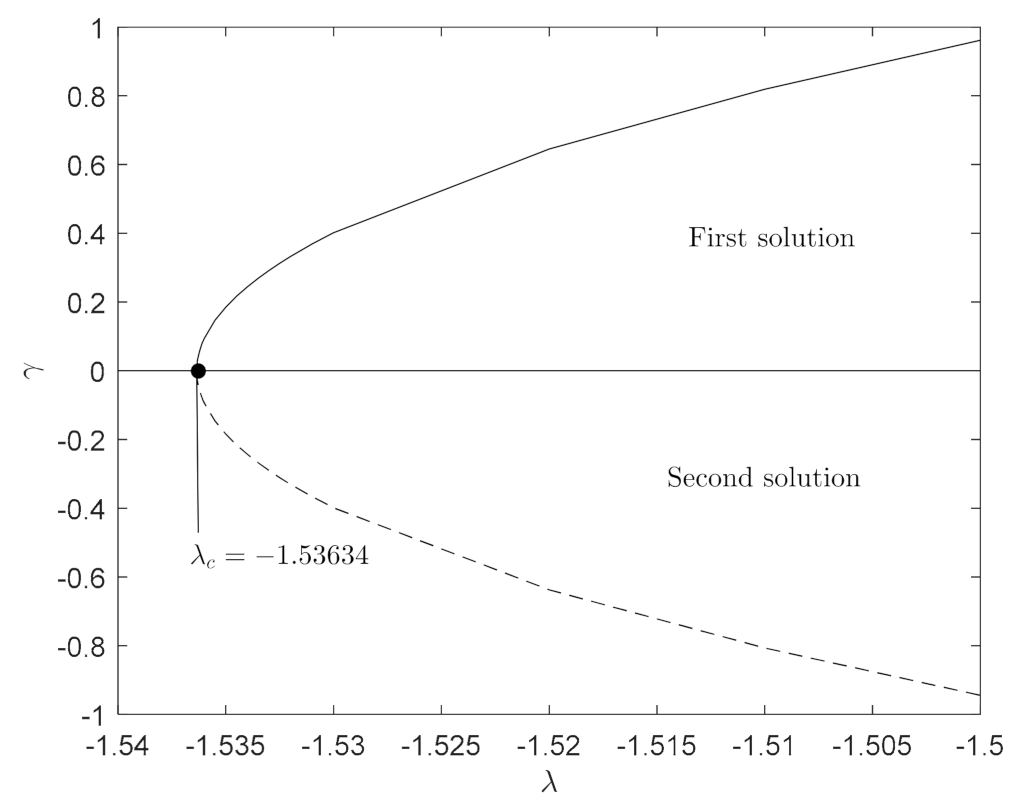
3. Stability Analysis of Solutions
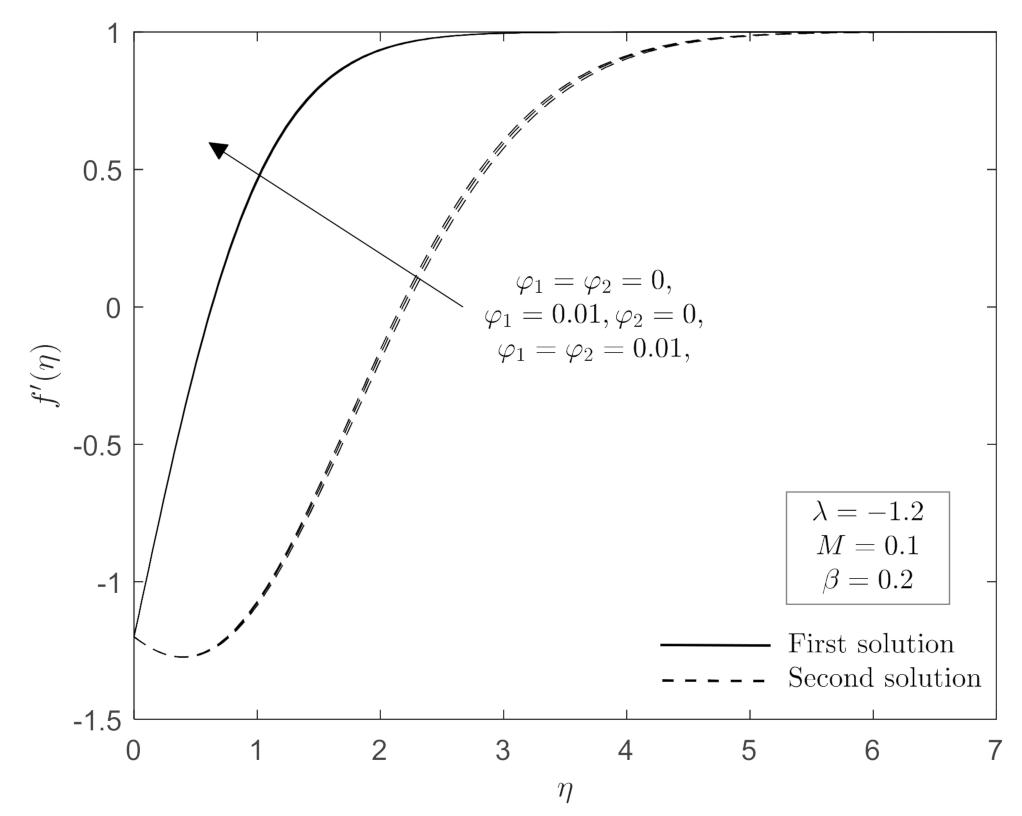
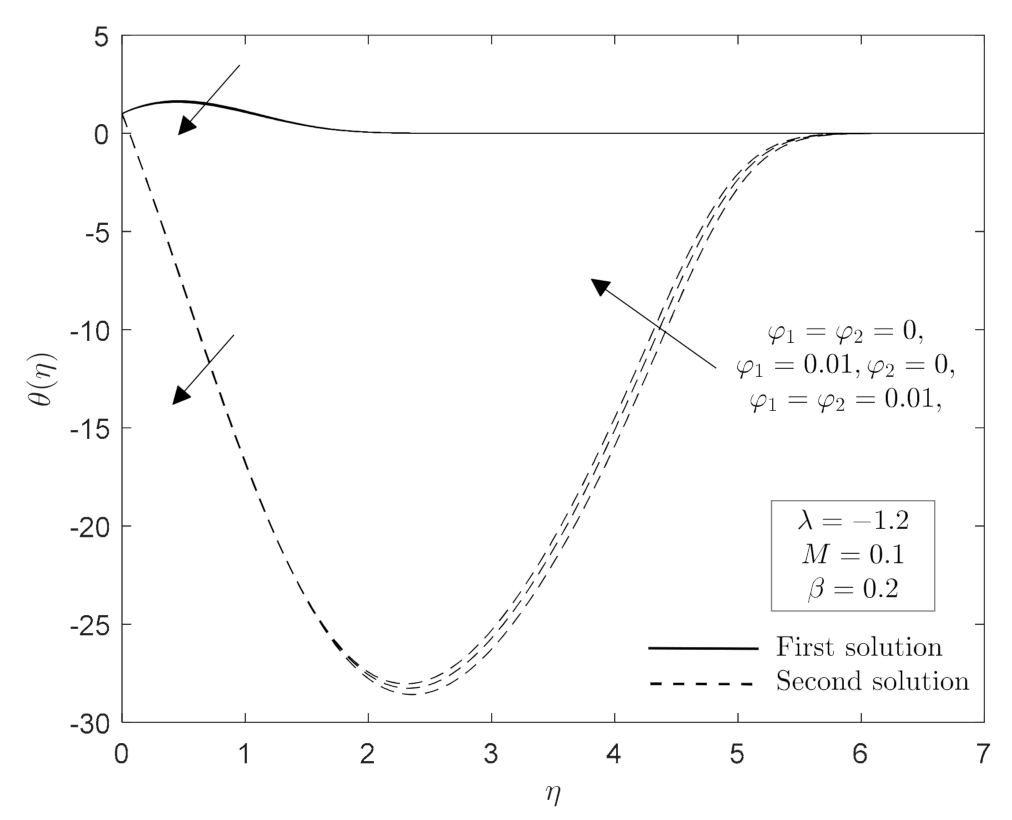
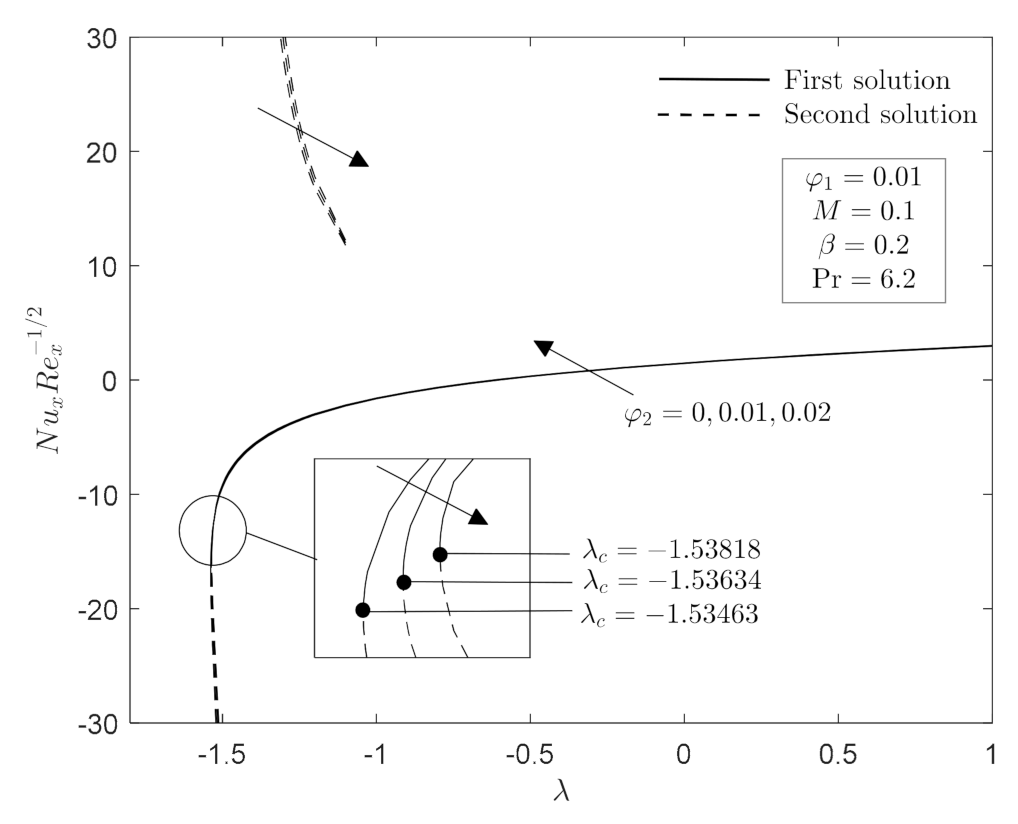
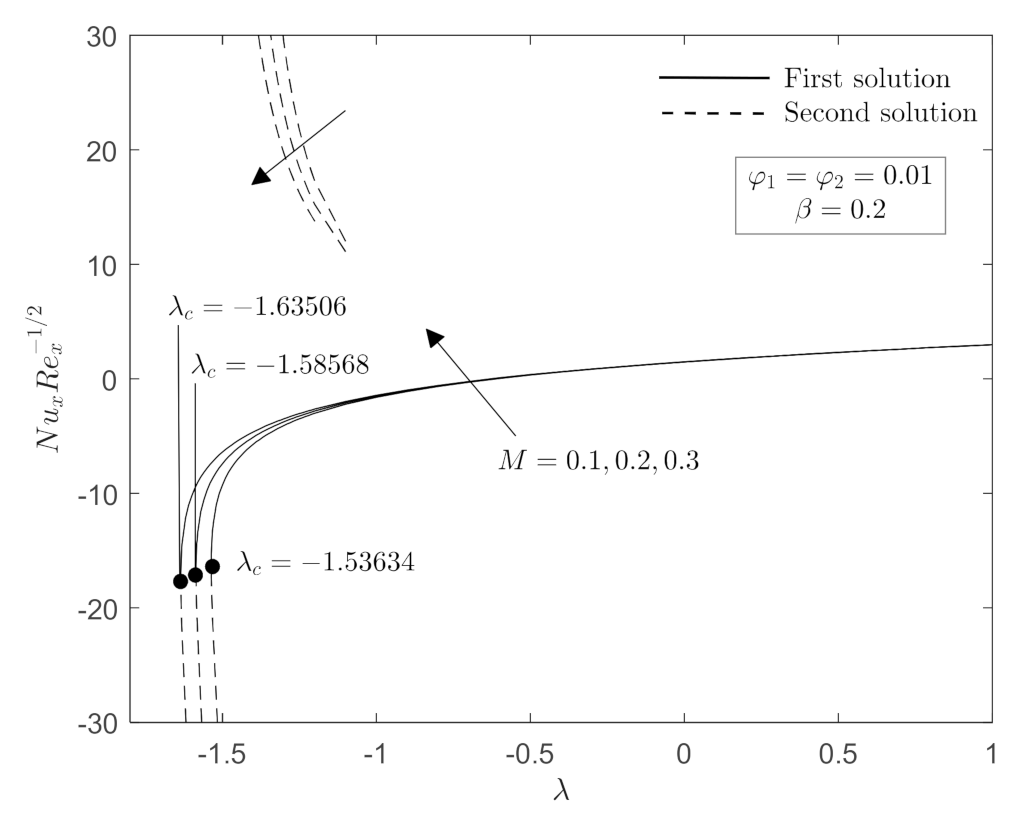
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Validation of Results
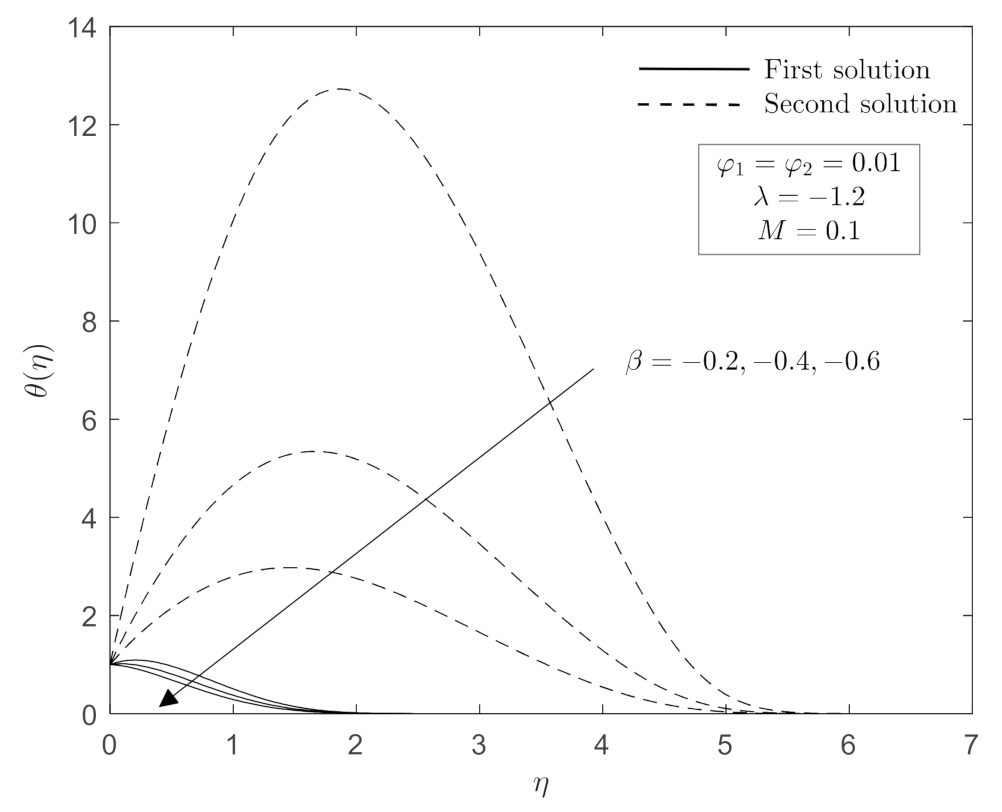
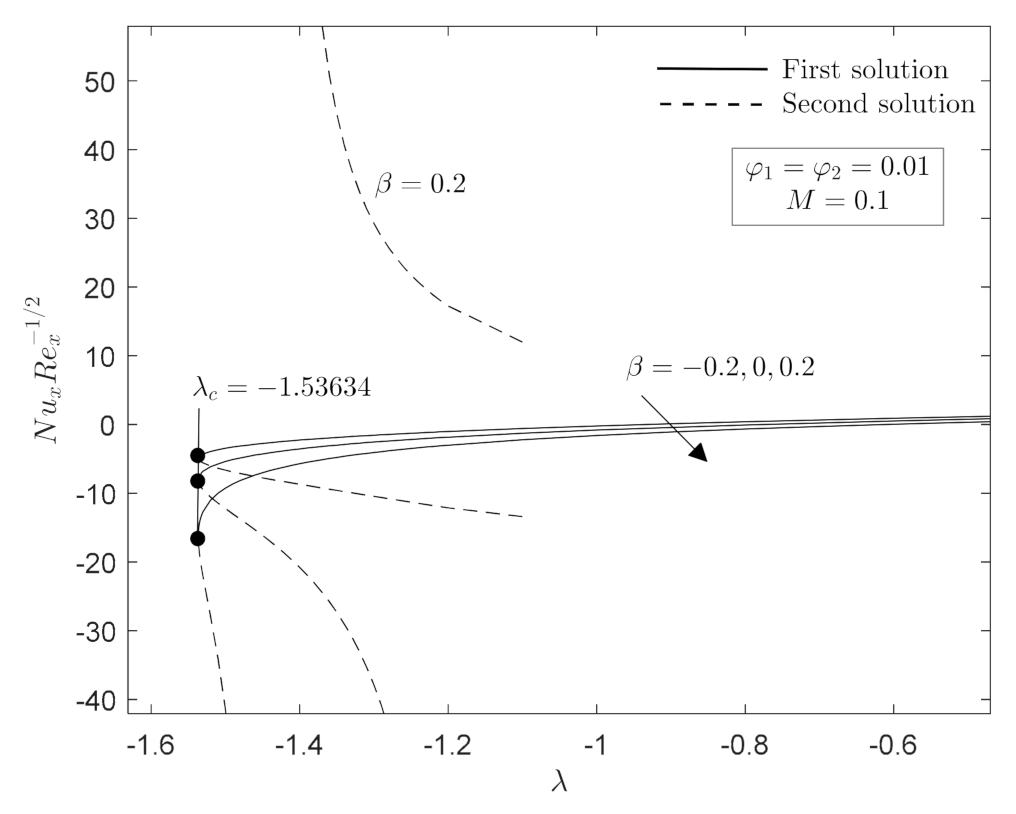
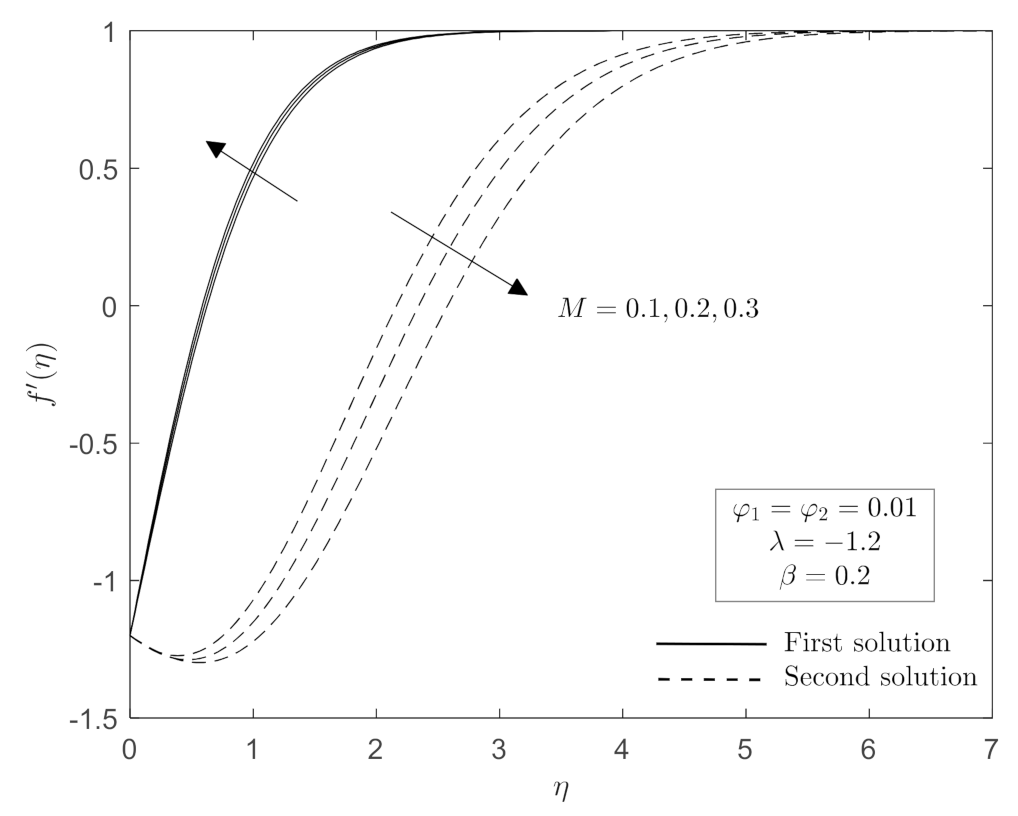
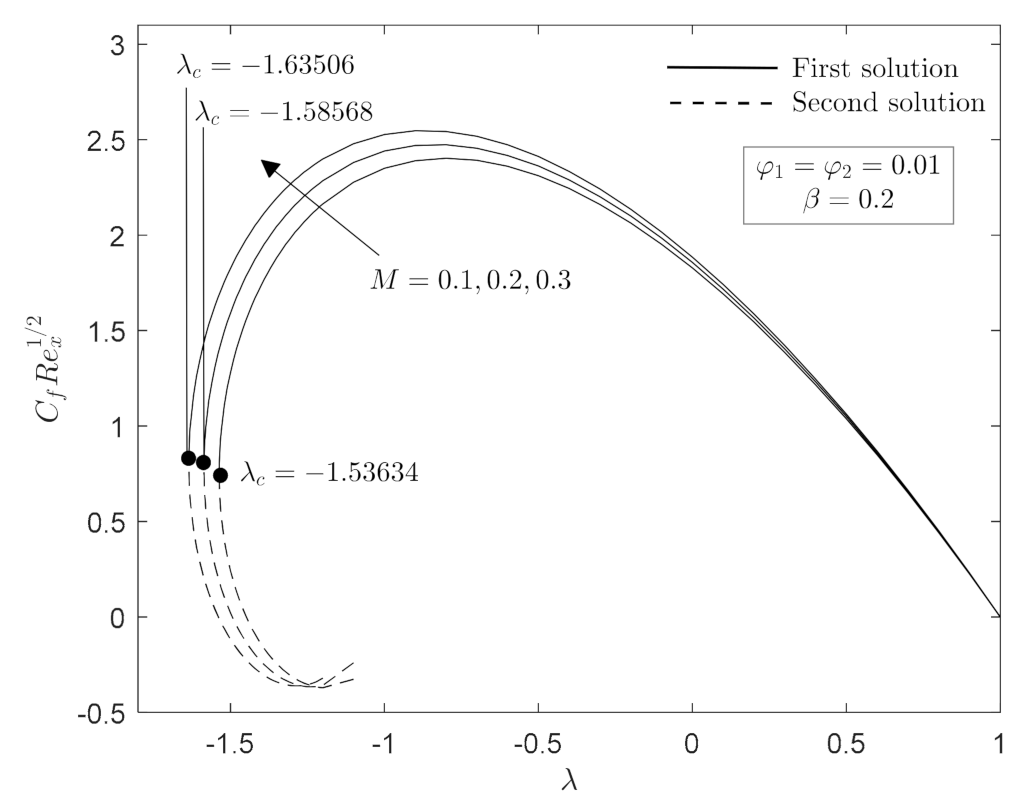
4.2. Interpretation of Results
5. Concluding Remarks
- Non-unique solution (two solutions) occurs for a specific range of shrinking parameter , whereas one solution exists when .
- The range of stretching/shrinking parameter for which the non-unique solutions are in existence increased as magnetic parameter increase, while it decreased with an increase in CoFe2O4 nanoparticle volume fraction.
- The heat transfer and skin friction are escalated for increasing of CoFe2O4 nanoparticle volume fraction and magnetic parameter.
- When the heat source/sink parameter is increased, the surface temperature rises, and the local Nusselt number decreases.
- The first solution is confirmed to be a stable solution from the stability analysis test.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosensweig, R.E. Ferrohydrodynamics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Ruuge, E.K.; Rusetski, A.N. Magnetic fluids as drug carriers: Targeted transport of drugs by a magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1993, 122, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, S.; Peterson, C.; Hoh, C.; Bittner, C. Targeting and retention of magnetic targeted carriers (MTCs) enhancing intra-arterial chemotherapy. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1999, 194, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, C.; Figueiredo Neto, A.M. Ferrofluids: Properties and applications. Braz. J. Phys. 2005, 35, 718–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroze, D.; Siddheshwar, P.G.; Pleiner, H. Chaotic convection in a ferrofluid. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2013, 18, 2436–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Sheikh, M. Numerical study of homogeneous—heterogeneous reactions on stagnation point flow of ferrofluid with non-linear slip condition. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 25, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.S.; Malik, F.; Mustafa, I.; Ghaffari, A.; Riaz, A.; Nisar, K.S. Impact of induced magnetic field on thermal enhancement in gravity driven Fe3O4 ferrofluid flow through vertical non-isothermal surface. Results Phys. 2020, 19, 103472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrez, Z.; El Cafsi, A. Heat exchange enhancement of ferrofluid flow into rectangular channel in the presence of a magnetic field. Appl. Math. Comput. 2021, 391, 125634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabi, B.; Salehi, S. Augmentation of the heat transfer performance of a sinusoidal corrugated enclosure by employing hybrid nanofluid. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2014, 6, 147059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.A.; Devi, S.S.U. Numerical investigation of hydromagnetic hybrid Cu–Al2O3/water nanofluid flow over a permeable stretching sheet with suction. Int. J. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2016, 17, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Venkitaraj, K.P.; Selvakumar, P.; Chandrasekar, M. Synthesis of Al2O3–Cu/water hybrid nanofluids using two step method and its thermo physical properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2011, 388, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhesh, D.; Kalaiselvam, S. Experimental analysis of hybrid nanofluid as a coolant. Procedia Eng. 2014, 97, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esfe, M.H.; Arani, A.A.A.; Rezaie, M.; Yan, W.M.; Karimipour, A. Experimental determination of thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of Ag–MgO/water hybrid nanofluid. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2015, 66, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.M.; Bilal, S.; Hajizadeh, M.R. Hybrid ferrofluid along with MWCNT for augmentation of thermal behavior of fluid during natural convection in a cavity. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2020, 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.A.; Sandeep, N.; Sugunamma, V.; Animasaun, I.L. Effect of irregular heat source/sink on the radiative thin film flow of MHD hybrid ferrofluid. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 2145–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabwey, H.A.; Mahdy, A. Transient flow of micropolar dusty hybrid nanofluid loaded with Fe3O4-Ag nanoparticles through a porous stretching sheet. Results Phys. 2021, 21, 103777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, U.; Liang, H.; Ahmad, H.; Abbas, M.; Iqbal, A.; Hamed, Y.S. Study of (Ag and TiO2)/water nanoparticles shape effect on heat transfer and hybrid nanofluid flow toward stretching shrinking horizontal cylinder. Results Phys. 2021, 21, 103812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, N.S.; Bachok, N.; Arifin, N.M.; Rosali, H. Analysis of Al2O3-Cu nanofluid flow behaviour over a permeable moving wedge with convective surface boundary conditions. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2021, 33, 101370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, T.; Fetecau, C.; Sajid, M. Analytic solution for MHD transient rotating flow of a second-grade fluid in a porous space. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 2008, 9, 1619–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, D. Influence of heat source/sink on MHD flow between vertical alternate conducting walls with Hall effect. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2020, 544, 123562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, K. Effects of heat source/sink on MHD flow and heat transfer over a shrinking sheet with mass suction. Chem. Eng. Res. Bull. 2011, 15, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorla, R.S.R.; Siddiqa, S.; Mansour, M.A.; Rashad, A.M.; Salah, T. Heat source/sink effects on a hybrid nanofluid-filled porous cavity. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 2017, 31, 847–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armaghani, T.; Sadeghi, M.S.; Rashad, A.M.; Mansour, M.A.; Chamkha, A.J.; Dogonchi, A.S.; Nabwey, H.A. MHD mixed convection of localized heat source/sink in an Al2O3-Cu/water hybrid nanofluid in L-shaped cavity. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 2947–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaludin, A.; Naganthran, K.; Nazar, R.; Pop, I. MHD mixed convection stagnation-point flow of Cu-Al2O3/water hybrid nanofluid over a permeable stretching/shrinking surface with heat source/sink. Eur. J. Mech.-B/Fluids 2020, 84, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.N.; Rao, V.S.; Reddy, B.R. Chemical reaction impact on MHD natural convection flow through porous medium past an exponentially stretching sheet in presence of heat source/sink and viscous dissipation. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2021, 25, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y. Stagnation flow towards a shrinking sheet. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2008, 43, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachok, N.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Stagnation-point flow over a stretching/shrinking sheet in a nanofluid. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamal, F.; Zaimi, K.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Stability analysis on the stagnation-point flow and heat transfer over a permeable stretching/shrinking sheet with heat source effect. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2018, 28, 2650–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, N.S.; Bachok, N. Double solutions and stability analysis of micropolar hybrid nanofluid with thermal radiation impact on unsteady stagnation point flow. Mathematics 2021, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, K.; Vajravelu, K. Stagnation-point flow and heat transfer over an exponentially shrinking sheet. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2012, 17, 2728–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachok, N.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Boundary layer stagnation-point flow and heat transfer over an exponentially stretching/shrinking sheet in a nanofluid. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2012, 55, 8122–8128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, N.S.; Bachok, N.; Arifin, N.M.; Rosali, H. Stagnation point flow and heat transfer over an exponentially stretching/shrinking sheet in CNT with homogeneous–heterogeneous reaction: Stability analysis. Symmetry 2019, 11, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lund, L.A.; Omar, Z.; Khan, I.; Baleanu, D.; Nisar, K.S. Dual similarity solutions of MHD stagnation point flow of Casson fluid with effect of thermal radiation and viscous dissipation: Stability analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waini, I.; Ishak, A.; Pop, I. Hybrid nanofluid flow towards a stagnation point on an exponentially stretching/shrinking vertical sheet with buoyancy effects. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2020, 31, 216–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkin, J.H. On dual solutions occurring in mixed convection in a porous medium. J. Eng. Math. 1986, 20, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidman, P.D.; Kubitschek, D.G.; Davis, A.M.J. The effect of transpiration on self-similar boundary layer flow over moving surfaces. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 2006, 44, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.D.; Ingham, D.B.; Pop, I. Mixed convection boundary-layer flow near the stagnation point on a vertical surface in a porous medium: Brinkman model with slip. Transp. Porous Media 2009, 77, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, N.S.; Bachok, N.; Arifin, N.M.; Rosali, H. Numerical solution of stagnation point flow and heat transfer over a nonlinear stretching/shrinking sheet in hybrid nanofluid: Stability analysis. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2020, 76, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, I.; Abbas, Z.; Arif, A.; Javed, T.; Ghaffari, A. Stability analysis for multiple solutions of boundary layer flow towards a shrinking sheet: Analytical solution by using least square method. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2020, 540, 123028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladdin, N.A.L.; Bachok, N.; Anuar, N.S. MHD stagnation point flow in nanofluid over shrinking surface using Buongiorno’s model: A stability analysis. J. Adv. Res. Fluid Mech. Therm. Sci. 2020, 76, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aladdin, N.A.L.; Bachok, N.; Pop, I. Boundary layer flow and heat transfer of Cu-Al2O3/water over a moving horizontal slender needle in presence of hydromagnetic and slip effects. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2021, 123, 105213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shampine, L.F.; Reichelt, M.W. The matlab ode suite. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 1997, 18, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oztop, H.F.; Abu-Nada, E. Numerical study of natural convection in partially heated rectangular enclosures filled with nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikholeslami, M.; Gorji-Bandpy, M.; Ganji, D.D. MHD free convection in an eccentric semi-annulus filled with nanofluid. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2014, 45, 1204–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlili, I.; Mustafa, M.T.; Kumar, K.A.; Sandeep, N. Effect of asymmetrical heat rise/fall on the film flow of magnetohydrodynamic hybrid ferrofluid. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Properties | Hybrid Ferrofluid |
|---|---|
| Density | |
| Thermal conductivity | |
| Heat capacity | |
| Dynamic viscosity | |
| Electrical conductivity |
| Physical Properties | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| water, H2O | 4179 | 997.1 | 0.613 | 0.05 |
| Magnetic nanoparticles | ||||
| Magnetite, Fe3O4 | 670 | 5180 | 9.7 | 0.74 × 106 |
| Cobalt Ferrite, CoFe2O4 | 700 | 4907 | 3.7 | 1.1 × 107 |
| Non-magnetic nanoparticles | ||||
| Copper, Cu | 385 | 8933 | 401 | 5.96 × 107 |
| Titania, TiO2 | 686.2 | 4250 | 8.9538 | 1 × 10−12 |
| Alumina, Al2O3 | 765 | 3970 | 40 | 1 × 10−10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anuar, N.S.; Bachok, N.; Pop, I. Influence of MHD Hybrid Ferrofluid Flow on Exponentially Stretching/Shrinking Surface with Heat Source/Sink under Stagnation Point Region. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222932
Anuar NS, Bachok N, Pop I. Influence of MHD Hybrid Ferrofluid Flow on Exponentially Stretching/Shrinking Surface with Heat Source/Sink under Stagnation Point Region. Mathematics. 2021; 9(22):2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222932
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnuar, Nur Syazana, Norfifah Bachok, and Ioan Pop. 2021. "Influence of MHD Hybrid Ferrofluid Flow on Exponentially Stretching/Shrinking Surface with Heat Source/Sink under Stagnation Point Region" Mathematics 9, no. 22: 2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222932
APA StyleAnuar, N. S., Bachok, N., & Pop, I. (2021). Influence of MHD Hybrid Ferrofluid Flow on Exponentially Stretching/Shrinking Surface with Heat Source/Sink under Stagnation Point Region. Mathematics, 9(22), 2932. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9222932






