Simulation and Analysis of Renewable and Nonrenewable Capacity Scenarios under Hybrid Modeling: A Case Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Proposed Methodology of Combined SD/DS Modeling
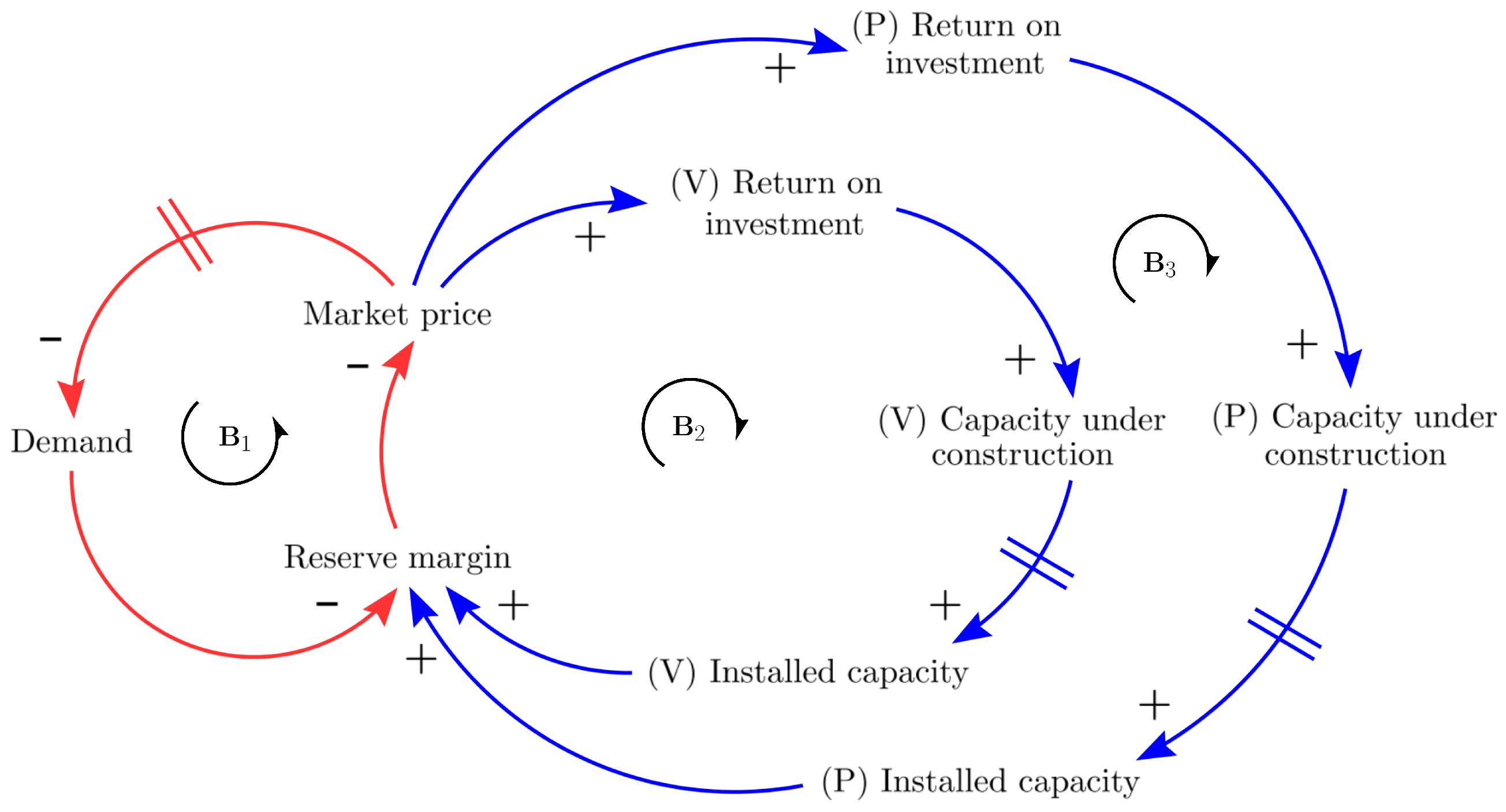
2.1. Dynamic Hypothesis
2.2. Stock-Flow Diagram
2.3. Hydroelectricity Variability Modeling
2.4. Block Diagrams of Simulink
3. Modeling the V/P Scenarios
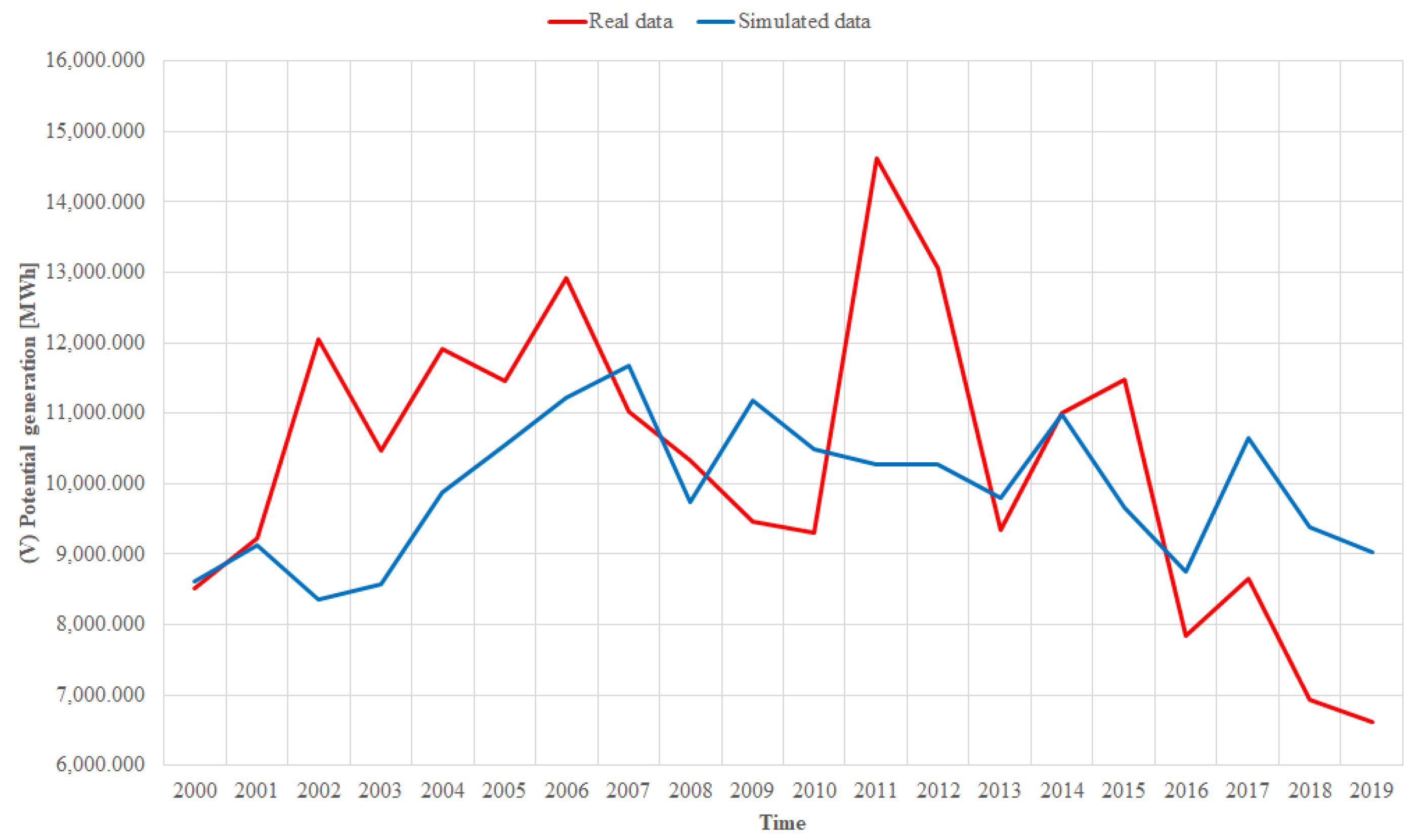
3.1. Model Validation
3.2. Model Assumptions and Limitations
4. Simulation Results: A Bifurcation Perspective
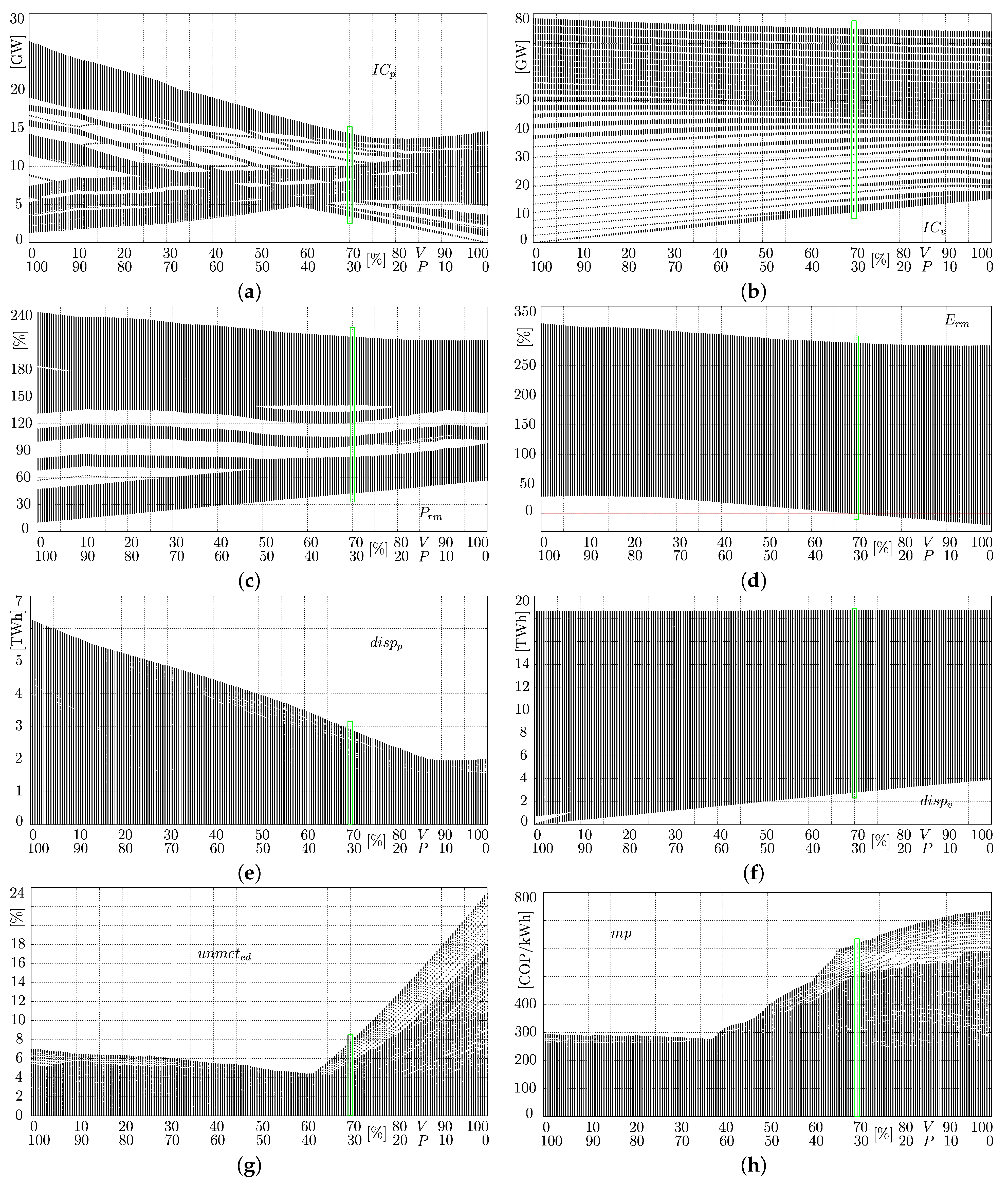
4.1. V/P Installed Capacity Scenarios
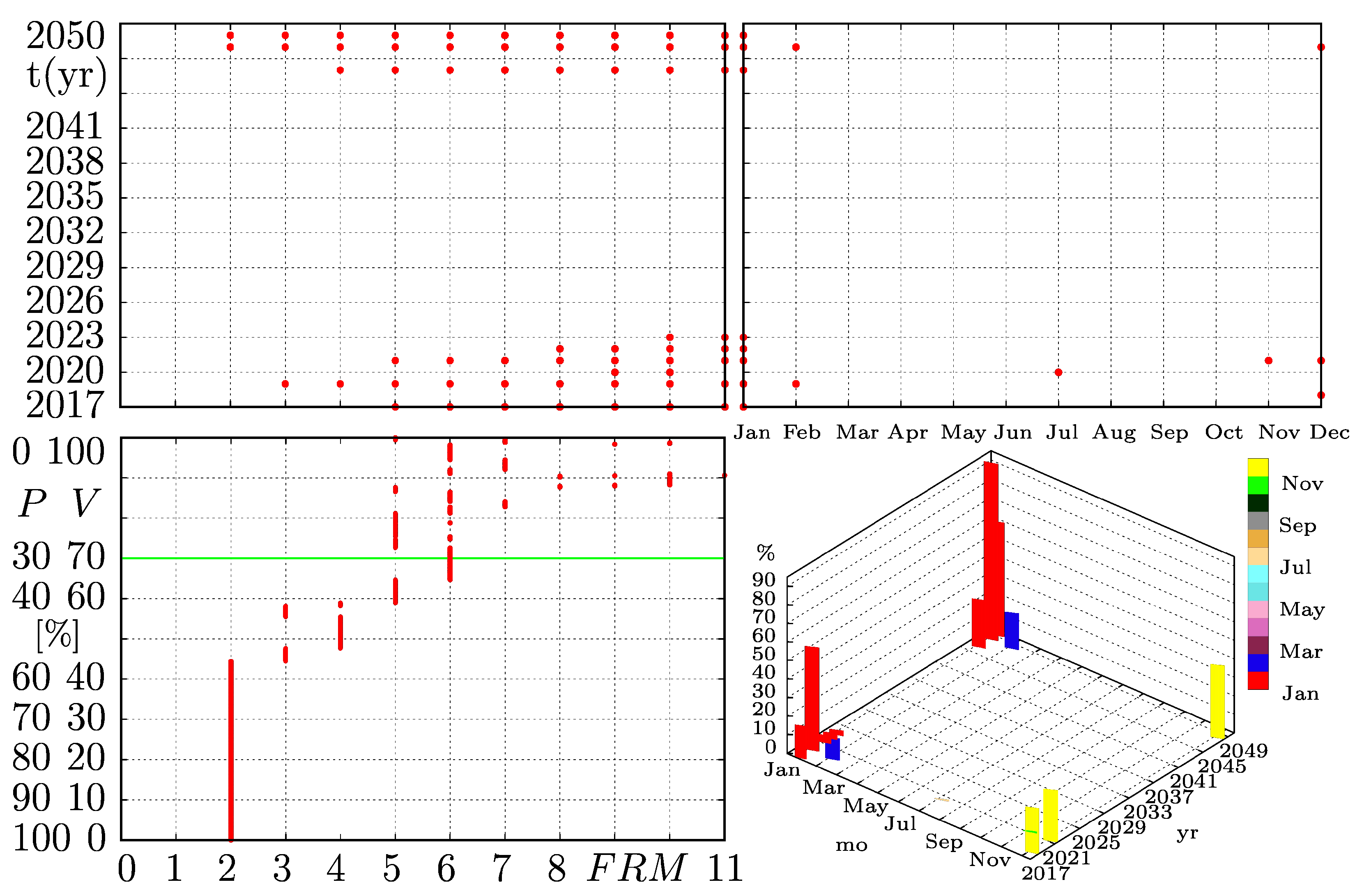
4.2. Confidence Limits and Their Occurrence
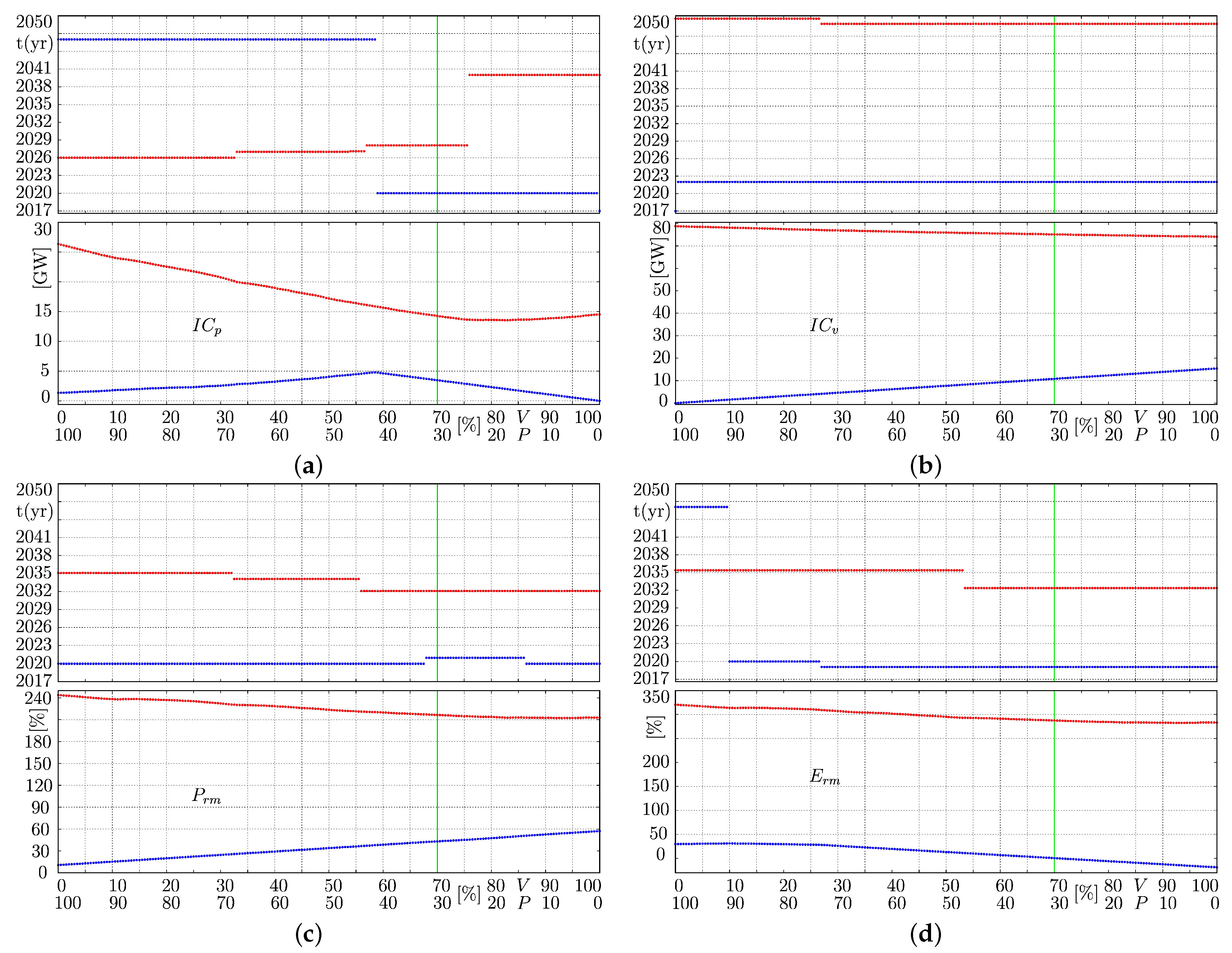
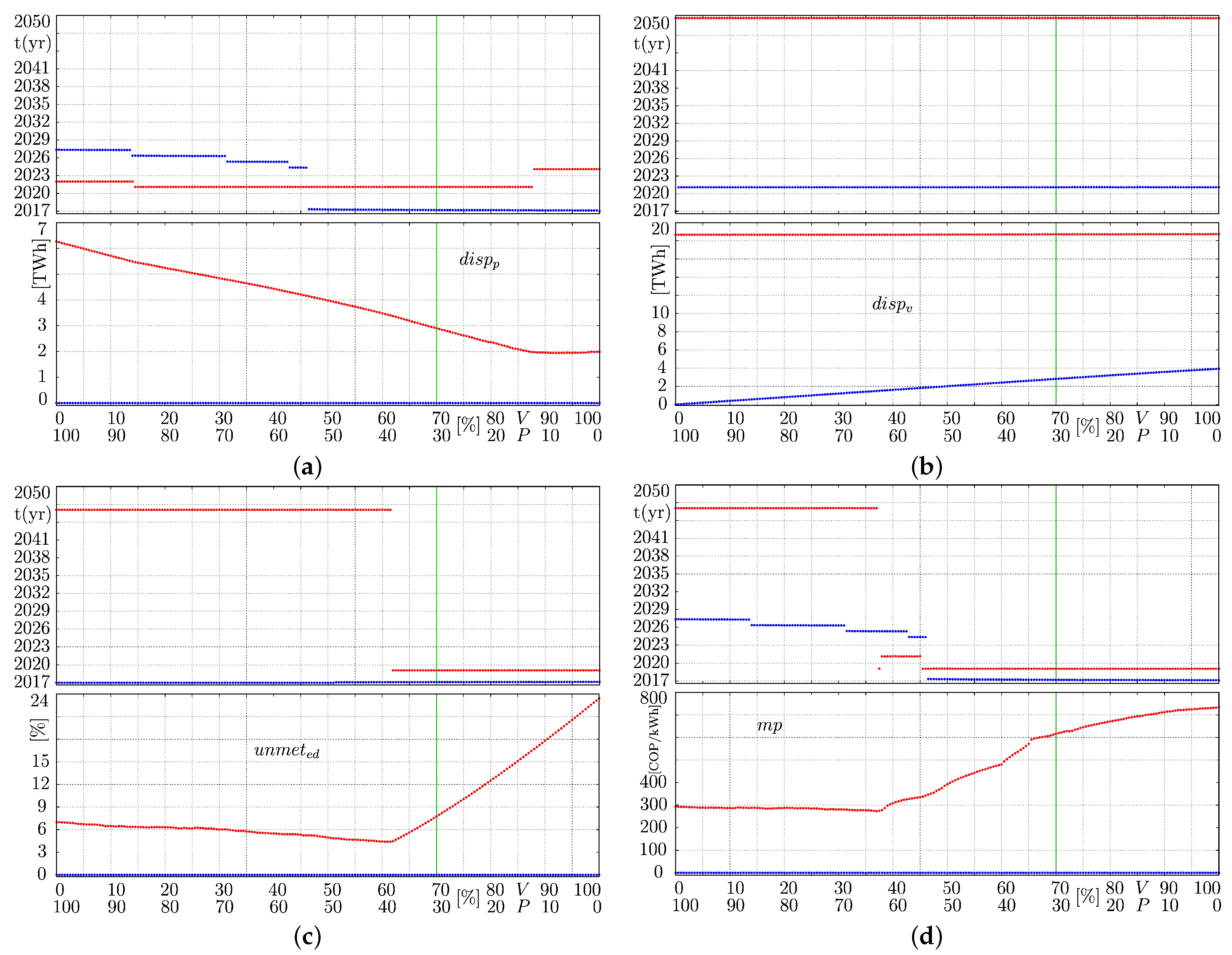
5. Simulation Results: A Control Theory Perspective
5.1. Detailed Rationing Events
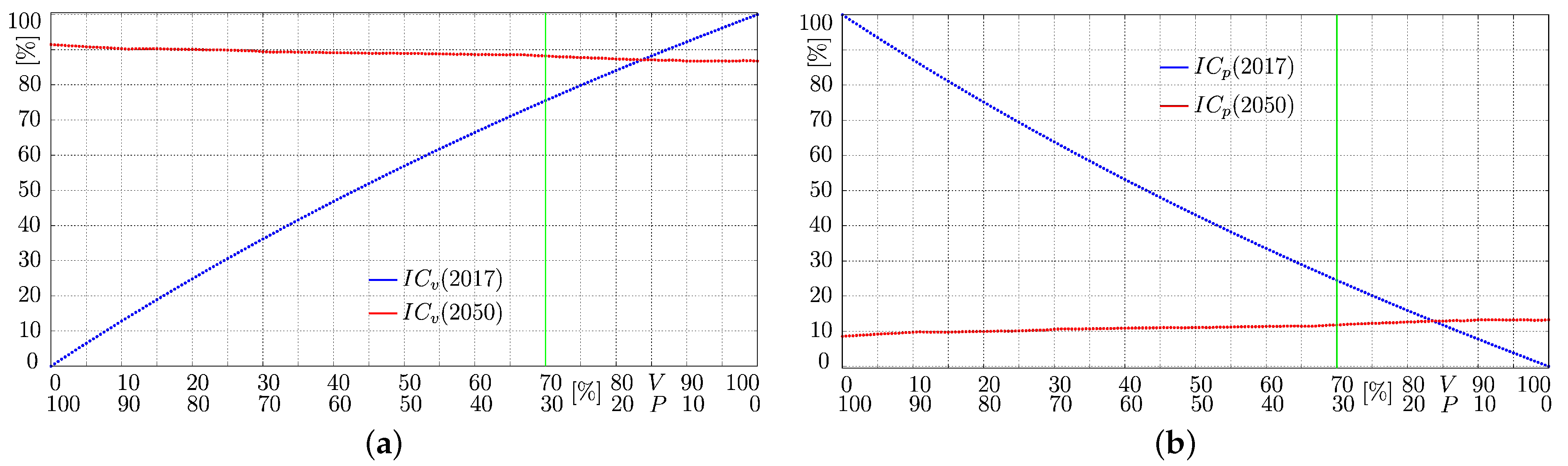
5.2. Leverage Points
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ENSO | El Niño-Southern Oscillation |
| SD | System Dynamics |
| DS | Dynamic Systems |
| FRM | Frequency of rationing months |
| V/P | Variable and permanent generation |
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Simulink Block Diagrams

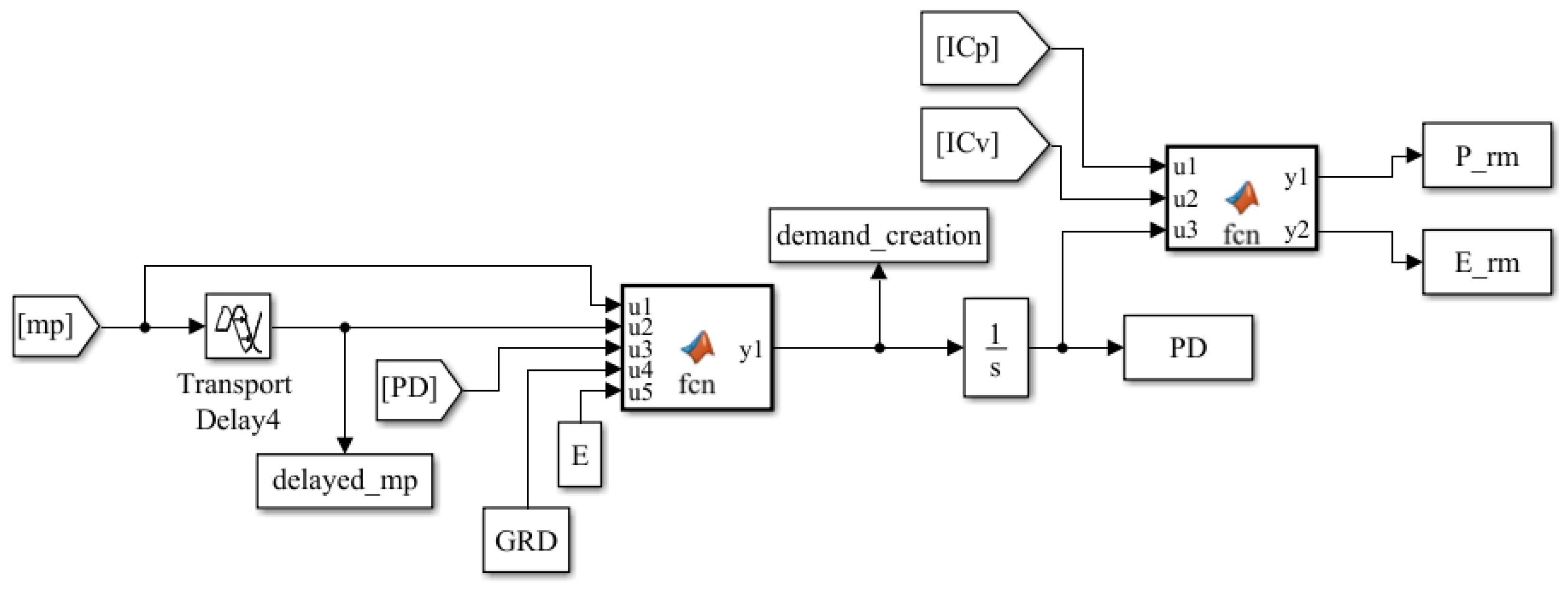
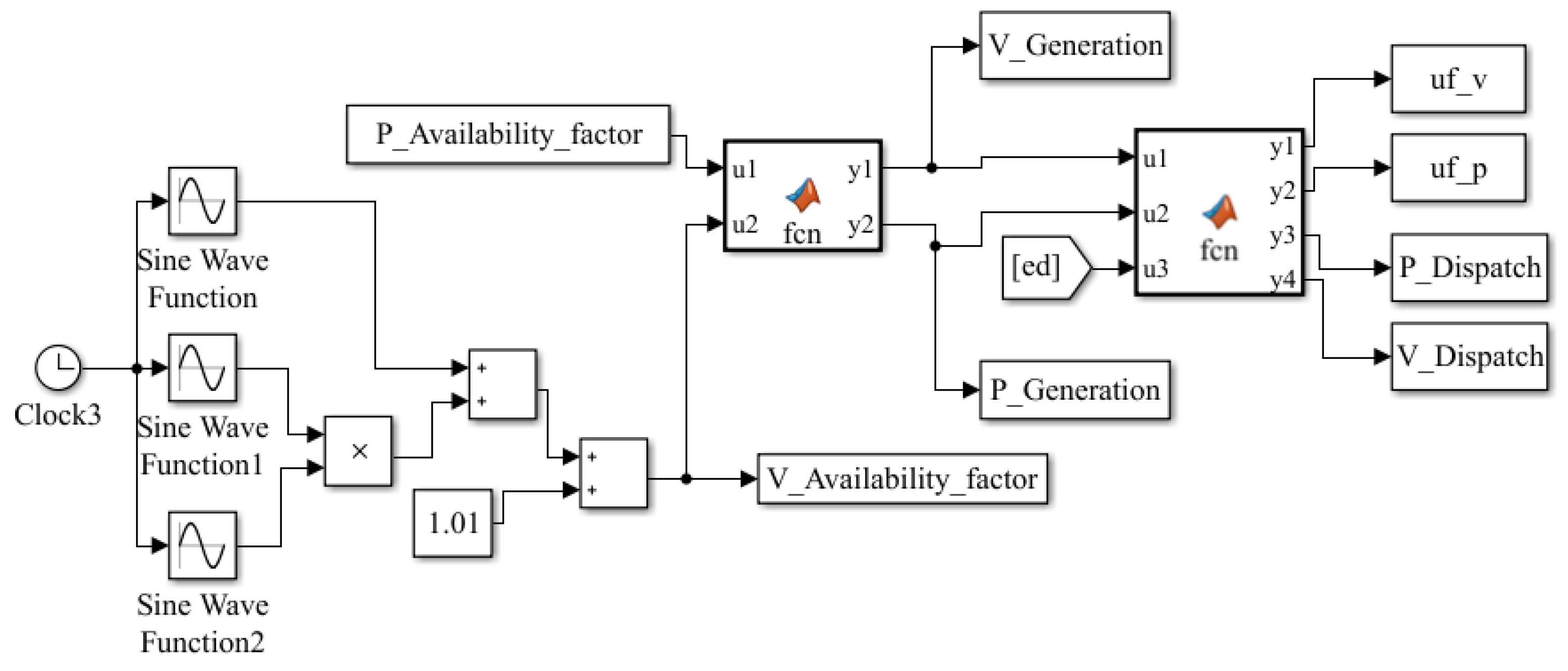
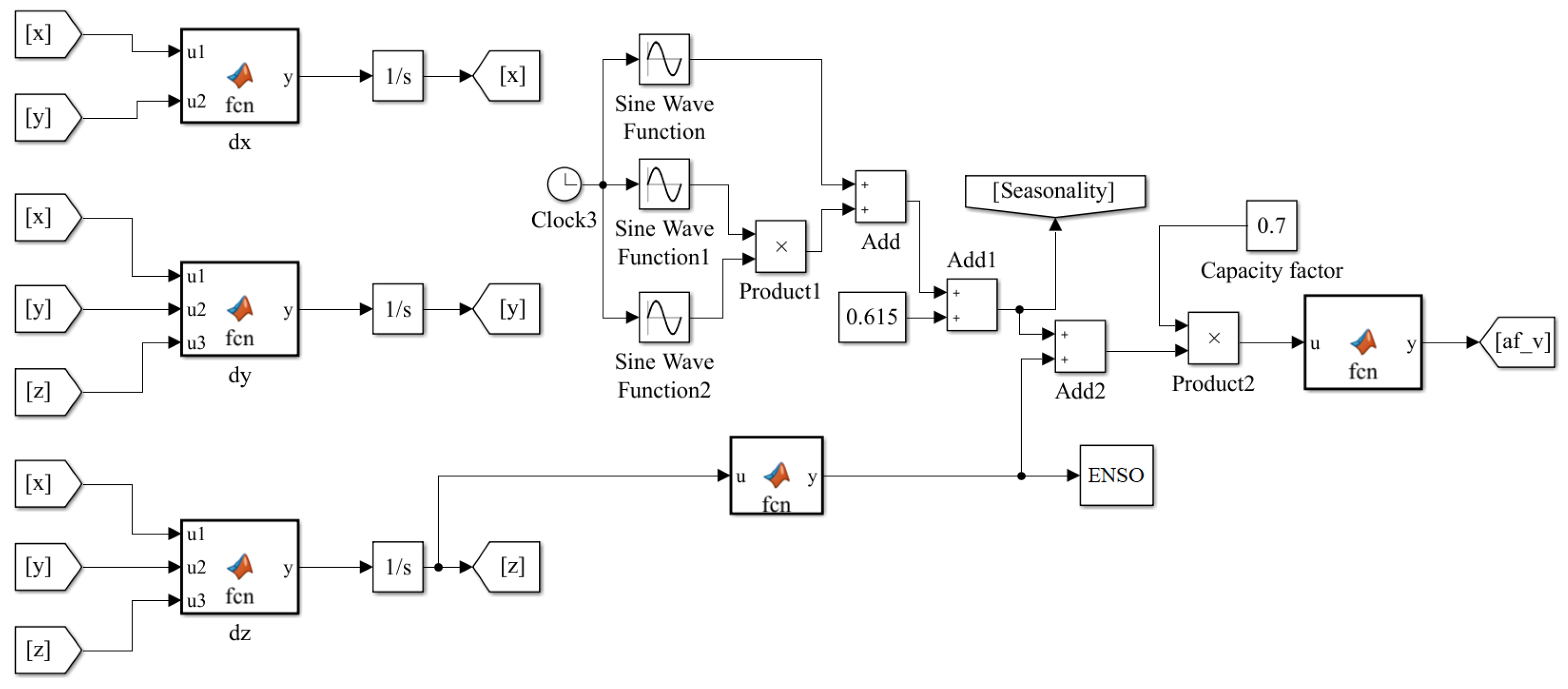
Appendix A.2. System Equations
Appendix A.3. Parameter Values
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Construction time () | 5 yr |
| Lifetime () | 30 yr |
| Growth rate of demand () | 0.039 |
| Variable cost () | 150 COP/kWh |
| Incentives (I) | 0 COP/kWh |
| Variability fixed cost () | 60 COP/kWh |
| 15,521 MW | |
| 9320 MW | |
| 0 MW | |
| Minimum price () | 35 COP/kWh |
| Maximum increase of price () | 350 COP/kWh |
| Elasticity of demand () | −0.3 |
References
- Teufel, F.; Miller, M.; Genoese, M.; Fichtner, W. Review of System Dynamics Models for Electricity Market Simulations; Working Paper Series in Production and Energy; KIT: Karlsruhe Germany, 2013; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Papachristos, G.; Struben, J. System dynamics methodology and research. In Modelling Transitions: Virtues, Vices, Visions of the Future; Routledge: London, UK, 2019; p. 119. [Google Scholar]
- Zapata, S.; Castaneda, M.; Franco, C.J.; Dyner, I. Clean and secure power supply: A system dynamics based appraisal. Energy Policy 2019, 131, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosai, S. Dynamic vulnerability in standalone hybrid renewable energy system. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 180, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asere, L.; Blumberga, A. Government and municipality owned building energy efficiency system dynamics modelling. Energy Procedia 2015, 72, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Xiao, B. Can China achieve its carbon emission peaking? A scenario analysis based on STIRPAT and system dynamics model. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 93, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- York, R.; Bell, S.E. Energy transitions or additions?: Why a transition from fossil fuels requires more than the growth of renewable energy. Energy Res. Soc. Sci. 2019, 51, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, S.; Castaneda, M.; Jimenez, M.; Aristizabal, A.J.; Franco, C.J.; Dyner, I. Long-term effects of 100% renewable generation on the Colombian power market. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2018, 30, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, L.M.; Franco, C.J.; Dyner, I. Assessing emissions-mitigation energy policy under integrated supply and demand analysis: The Colombian case. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112 Pt 5, 3759–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astegiano, P.; Fermi, F.; Martino, A. Investigating the impact of e-bikes on modal share and greenhouse emissions: A system dynamic approach. Transp. Res. Procedia 2019, 37, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Che, Y. Agent and system dynamics-based hybrid modeling and simulation for multilateral bidding in electricity market. Energy 2019, 180, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Tahar, R.M.; Muhammad-Sukki, F.; Munir, A.B.; Rahim, R.A. Application of system dynamics approach in electricity sector modelling: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo, J.D.; Franco, C.J.; Angulo, F. Simulation of demand growth scenarios in the Colombian electricity market: An integration of system dynamics and dynamic systems. Appl. Energy 2018, 216, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo, J.D.; Angulo, F.; Franco, C.J. Analyzing the hydroelectricity variability on power markets from a system dynamics and dynamic systems perspective: Seasonality and ENSO phenomenon. Energies 2020, 13, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aracil, J. Structural stability of low-order system dynamics models. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 1981, 12, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosekilde, E.; Aracil, J.; Allen, P.M. Instabilities and chaos in nonlinear dynamic systems. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1988, 4, 14–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, J.S.; Mosekilde, E.; Sterman, J.D. Hyperchaotic phenomena in dynamic decision making. In Complexity, Chaos, and Biological Evolution; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1991; pp. 397–420. [Google Scholar]
- Sterman, J.D. Deterministic chaos in models of human behavior: Methodological issues and experimental results. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1988, 4, 148–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aracil, J. On the qualitative properties in system dynamics models. Eur. J. Econ. Soc. Syst. 1999, 13, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, J.; Olivar, G.; Franco, C.J.; Dyner, I. Qualitative Analysis of Climate Seasonality Effects in a Model of National Electricity Market. In Analysis, Modelling, Optimization, and Numerical Techniques; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 349–362. [Google Scholar]
- Redondo, J.; Ibarra-Vega, D.; Becerra-Fernandez, M.; Olivar-Tost, G. Making decisions in national energy markets with bifurcation analysis. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1414, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dimitrovski, A.; Ford, A.; Tomsovic, K. An interdisciplinary approach to long-term modelling for power system expansion. Int. J. Crit. Infrastruct. 2006, 3, 235–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heard, B.; Brook, B.; Wigley, T.; Bradshaw, C. Burden of proof: A comprehensive review of the feasibility of 100% renewable-electricity systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 1122–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatzadeh, F.; Mandal, P.; Srivastava, A.K. Demand response for sustainable energy systems: A review, application and implementation strategy. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, Y.A. Elements of Applied Bifurcation Theory; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 112. [Google Scholar]
- Vander Velde, W.E. Multiple-Input Describing Functions and Nonlinear System Design; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Sterman, J.D. Business Dynamics: Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World; Irwin/McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2000; p. 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyner, I. Energy modelling platforms for policy and strategy support. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2000, 51, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- XM. Información Inteligente. 2021. Available online: http://informacioninteligente10.xm.com.co/pages/default.aspx (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- Morcillo, J.D.; Franco, C.J.; Angulo, F. Delays in electricity market models. Energy Strategy Rev. 2017, 16, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, O.; Vaca, P.; Ávila, R. Elasticidades de demanda por electricidad e impactos macroeconómicos del precio de la energía eléctrica en Colombia. Rev. MÉtodos Cuantitativos Para Econ. Empresa 2013, 16, 216–249. [Google Scholar]
- XM. Información Inteligente. 2021. Available online: http://informacioninteligente10.xm.com.co/hidrologia/Paginas/HistoricoHidrologia.aspx (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- Jaramillo, G.P. ¿Atractores extraños (caos) en la hidro-climatología de Colombia? Rev. Acad. Colomb. Cienc 1997, 21, 431–444. [Google Scholar]
- Tziperman, E.; Stone, L.; Cane, M.A.; Jarosh, H. El Niño Chaos: Overlapping of Resonances Between the Seasonal Cycle and the Pacific Ocean-Atmosphere Oscillator. Science 1994, 264, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- XM. Oferta y Generación. Índice Multivariado ENSO. 2021. Available online: http://informesanuales.xm.com.co/2013/SitePages/operacion/2-9-Anex-Indice-multivariado-ENSO.aspx (accessed on 10 January 2021).
- Vallis, G.K. El Niño: A chaotic dynamical system? Science 1986, 232, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhmet, M.; Fen, M.O.; Alejaily, E.M. The Effects of El Niño on the Global Weather and Climate. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.00891. [Google Scholar]
- Slingo, J.; Palmer, T. Uncertainty in weather and climate prediction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2011, 369, 4751–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlas, Y. Formal aspects of model validity and validation in system dynamics. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1996, 12, 183–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qudrat-Ullah, H.; Seong, B.S. How to do structural validity of a system dynamics type simulation model: The case of an energy policy model. Energy Policy 2010, 38, 2216–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPM. Proyecto Hidroeléctrico Ituango. 2019. Available online: https://www.epm.com.co/site/nuestros-proyectos/proyecto-ituango (accessed on 14 February 2021).
- EPM. Especial Contingencia HidroItuango. 2019. Available online: https://www.epm.com.co/site/home/camino-al-barrio/historias-de-barrio/especial-hidroituango-1 (accessed on 14 February 2021).
- XM. XM Presenta Análisis de Posibles Escenarios Para la Atención de la Demanda Eléctrica del País. 2018. Available online: https://www.xm.com.co/Paginas/detalle-noticias.aspx?identificador=1747 (accessed on 10 March 2012).
- ESPXS. Portal BI: Información inteligente. 2020. Available online: http://portalbissrs.xm.com.co/Paginas/Home.aspx (accessed on 5 April 2020).
- Ma, T.; Wang, S. Bifurcation Theory and Applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Kwatny, H.G.; Yu, X.M.; Nwankpa, C. Local bifurcation analysis of power systems using Matlab. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Control Applications, Albany, NY, USA, 28–29 September 1995; pp. 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami, H.; Yoshinaga, T. Codimension Two Bifurcation and its Computational Algorithm. In Bifurcation and Chaos; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 97–132. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, S. MATLAB Programming for Engineers. In Applications of Chaos and Nonlinear Dynamics in Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 3–35. [Google Scholar]
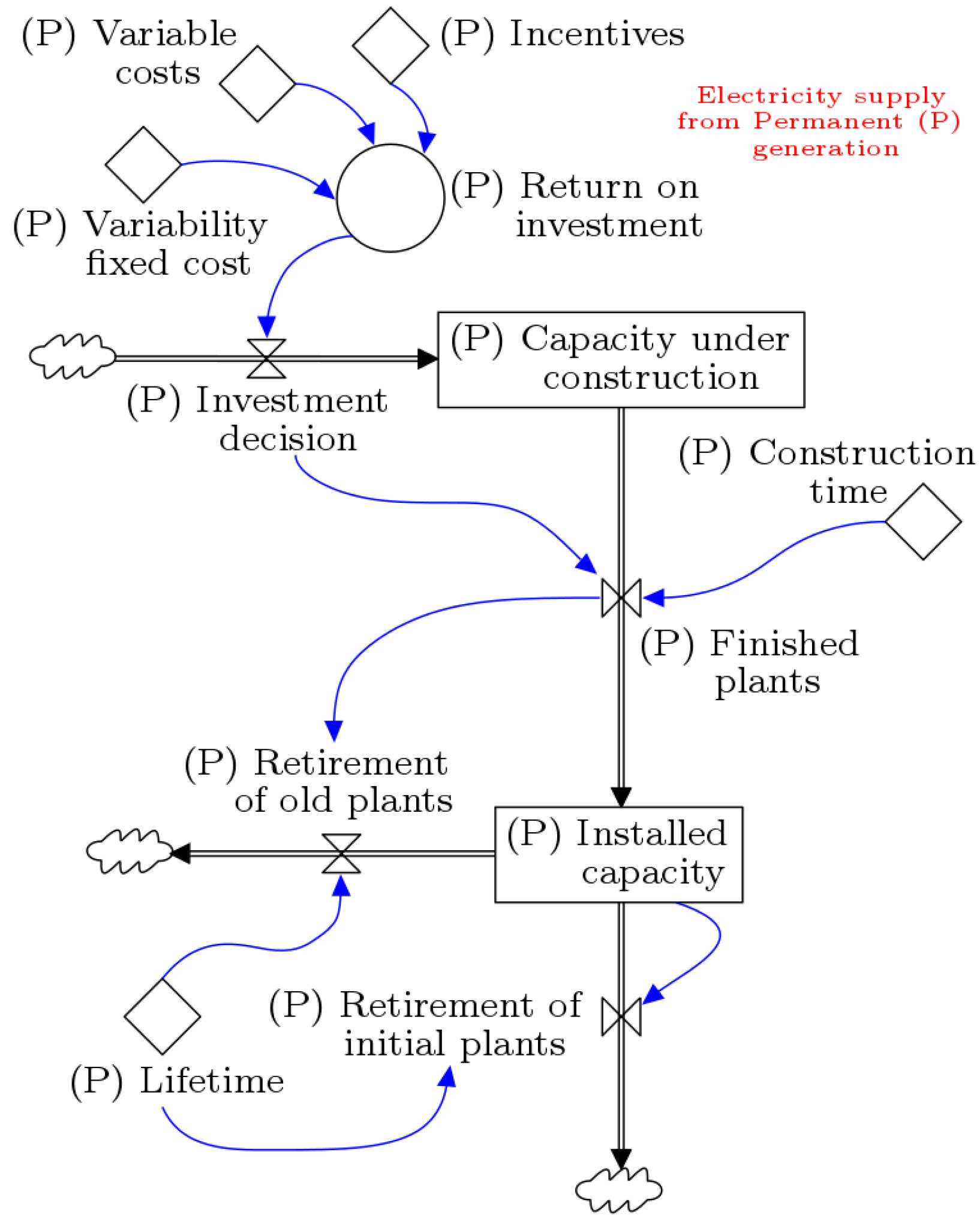
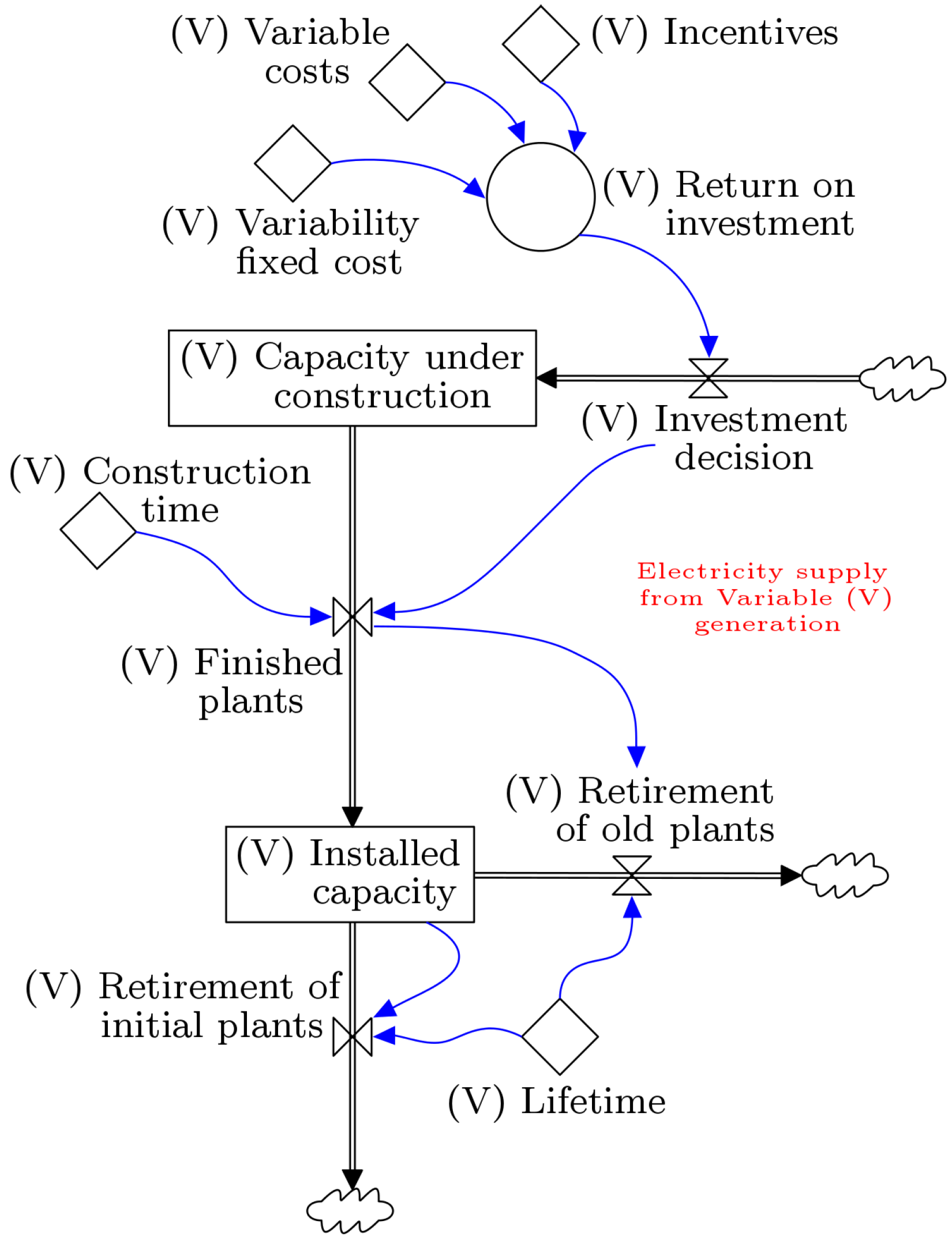
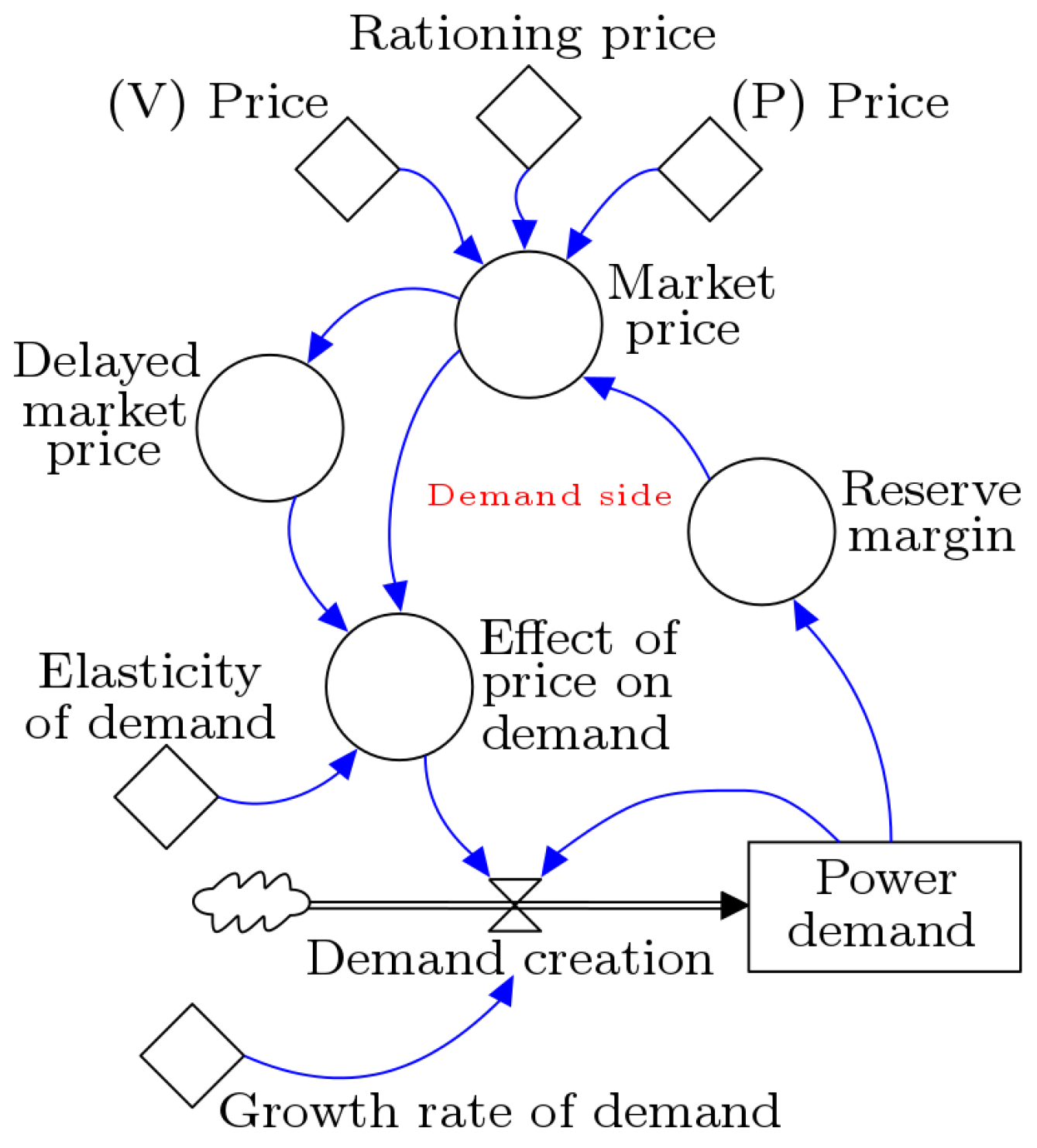
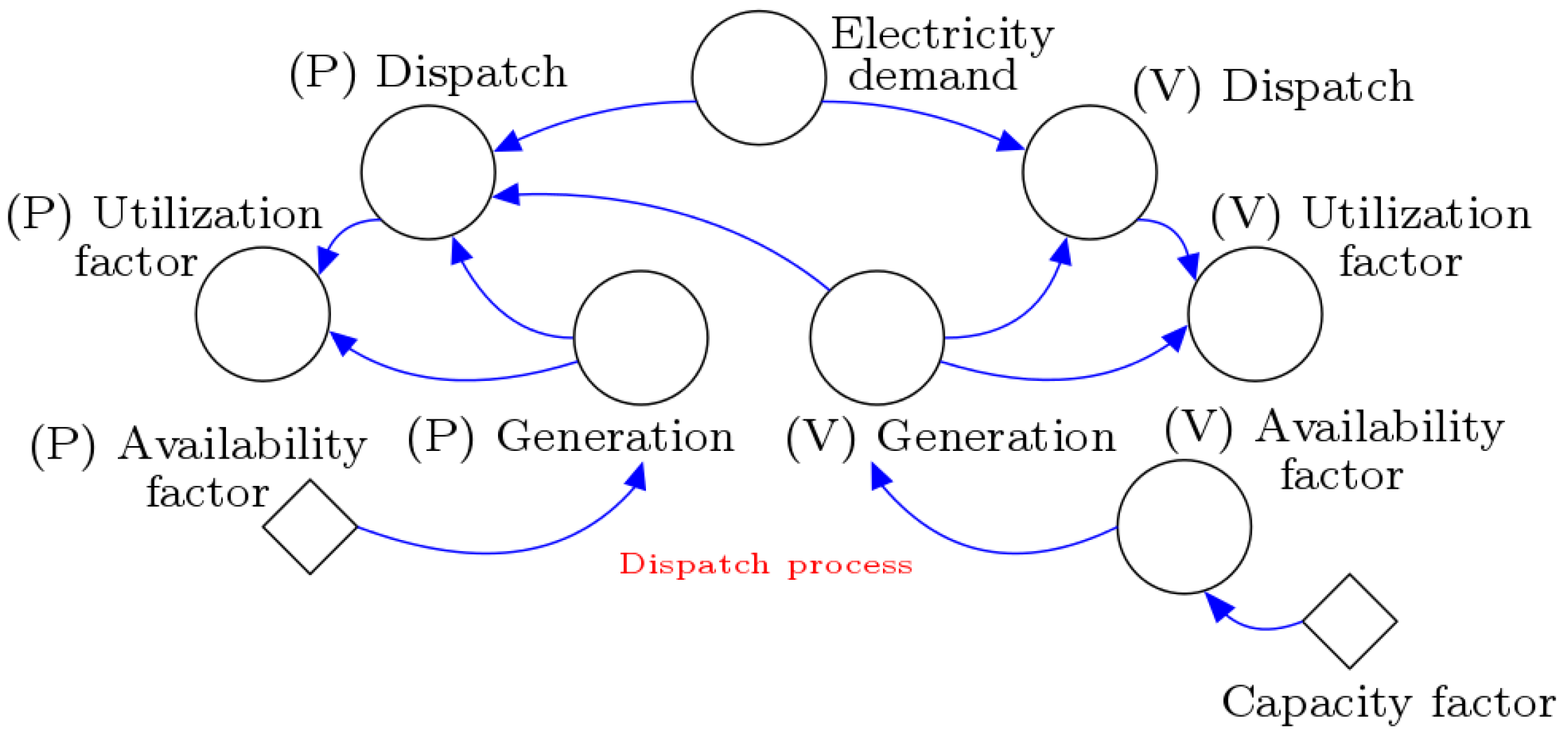
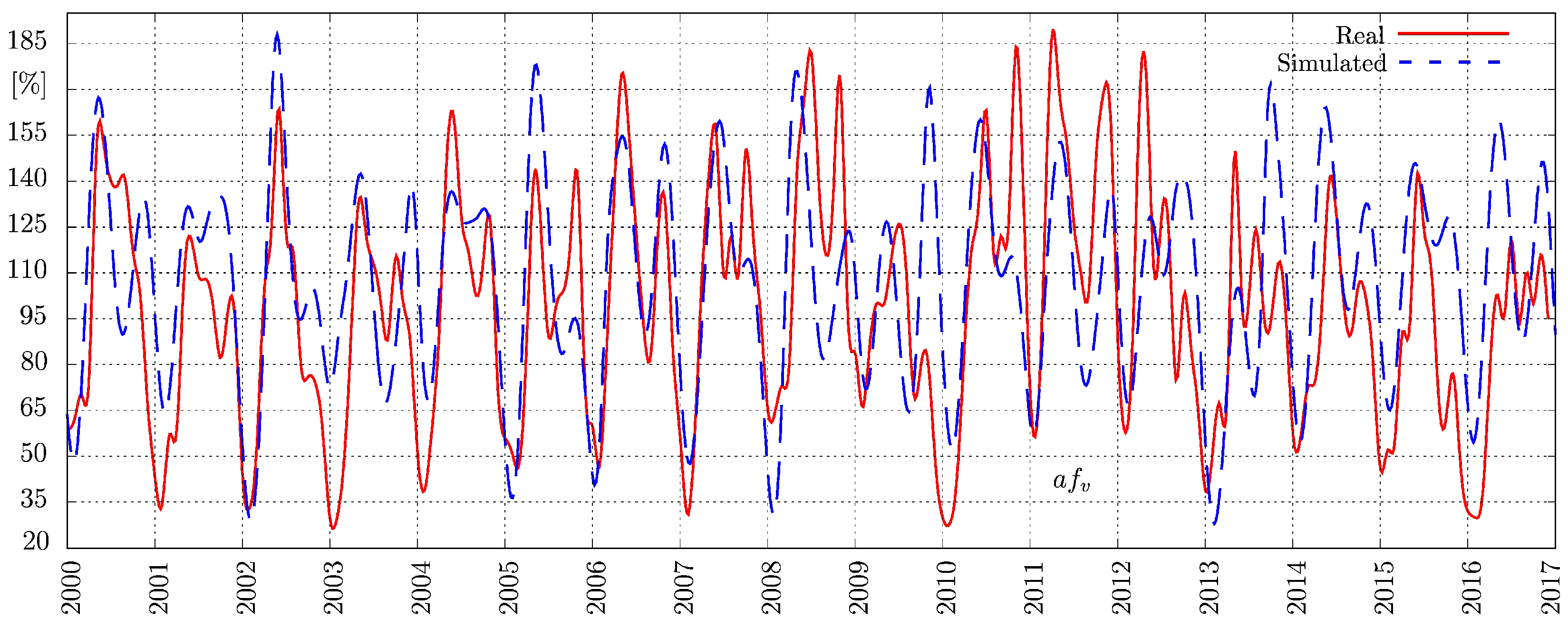
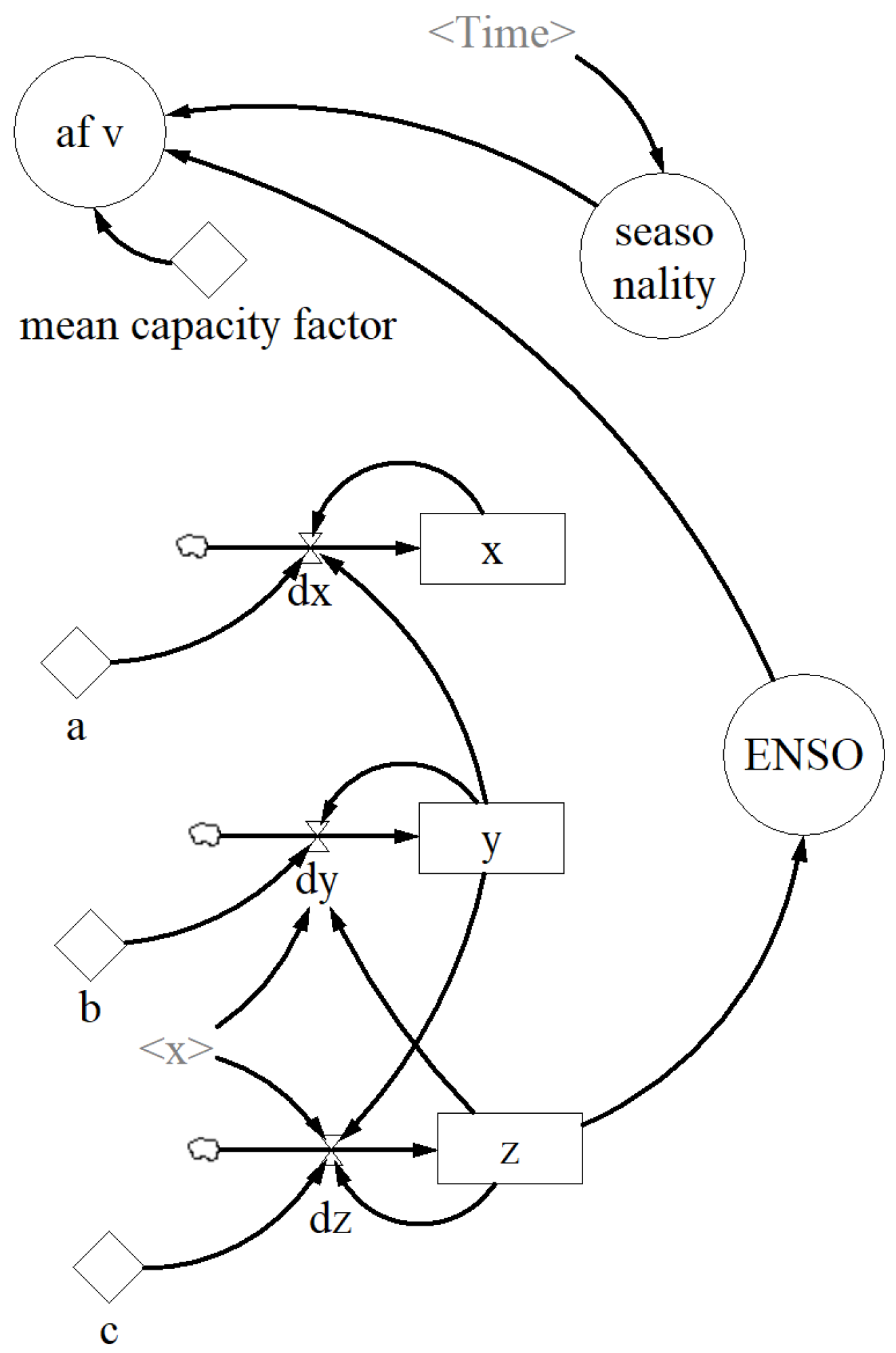
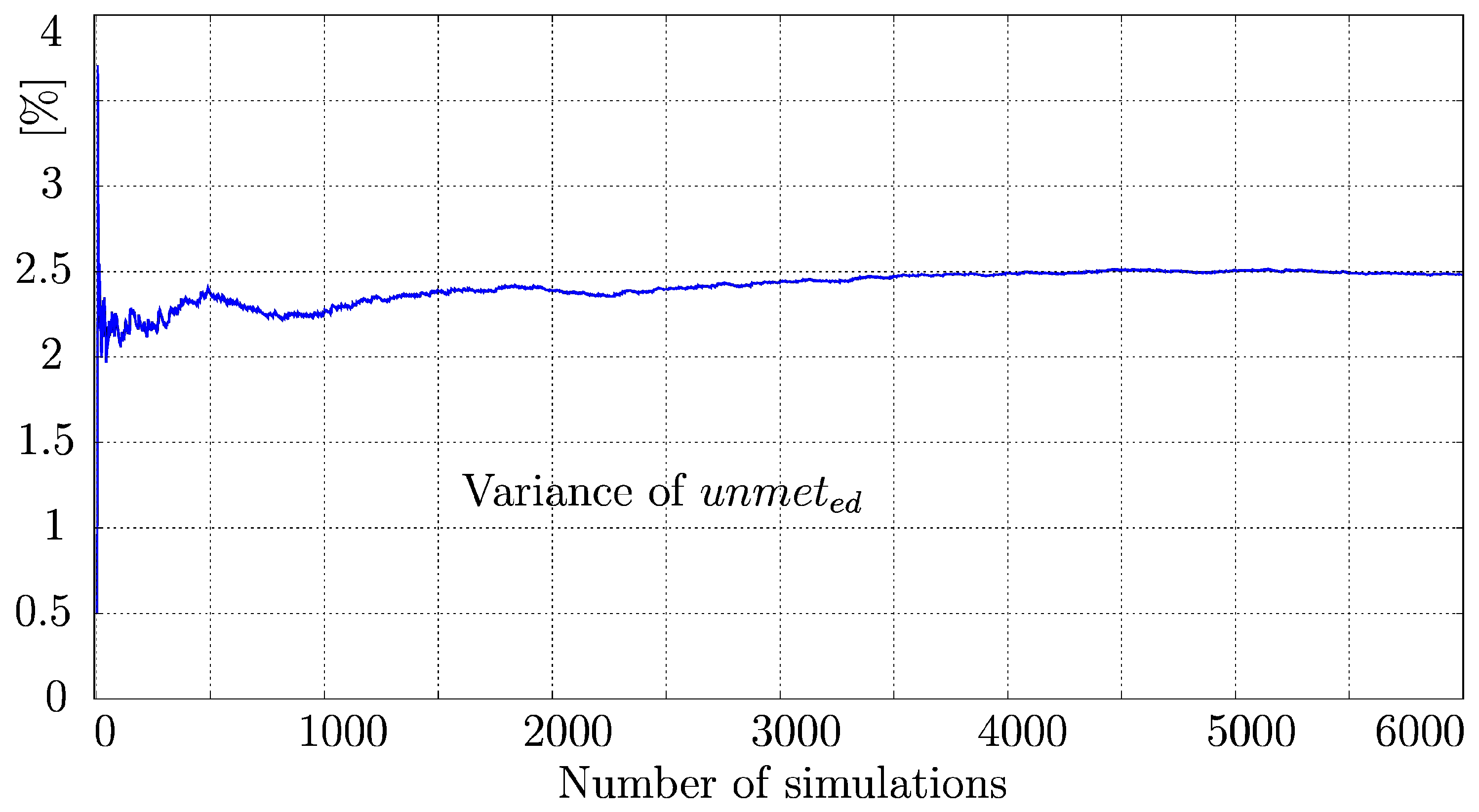
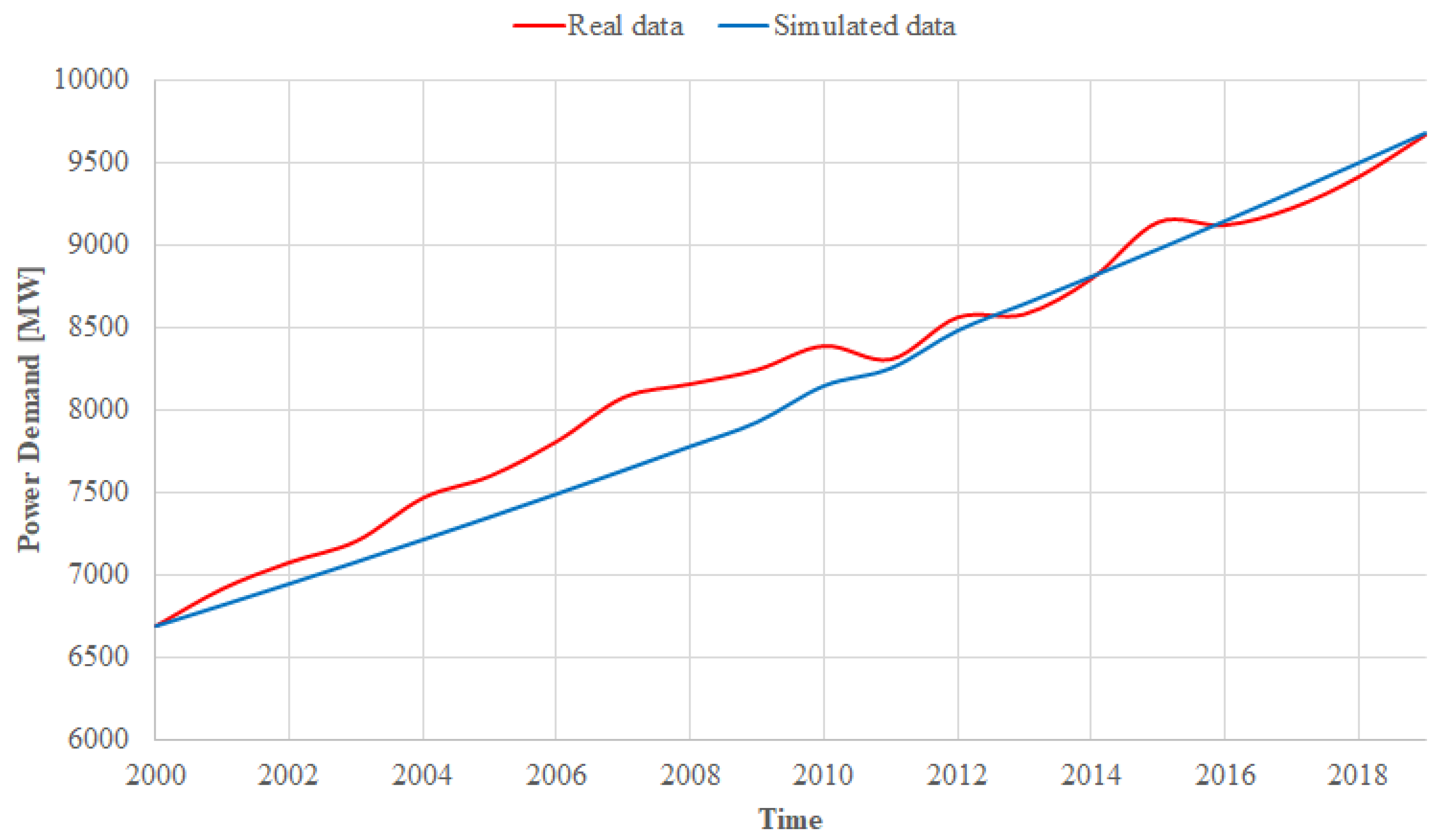
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| a | 10 |
| b | 28 |
| c | 2.6667 |
| 10 | |
| 5 | |
| 20 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morcillo, J.D.; Angulo, F.; Franco, C.J. Simulation and Analysis of Renewable and Nonrenewable Capacity Scenarios under Hybrid Modeling: A Case Study. Mathematics 2021, 9, 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9131560
Morcillo JD, Angulo F, Franco CJ. Simulation and Analysis of Renewable and Nonrenewable Capacity Scenarios under Hybrid Modeling: A Case Study. Mathematics. 2021; 9(13):1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9131560
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorcillo, José D., Fabiola Angulo, and Carlos J. Franco. 2021. "Simulation and Analysis of Renewable and Nonrenewable Capacity Scenarios under Hybrid Modeling: A Case Study" Mathematics 9, no. 13: 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9131560
APA StyleMorcillo, J. D., Angulo, F., & Franco, C. J. (2021). Simulation and Analysis of Renewable and Nonrenewable Capacity Scenarios under Hybrid Modeling: A Case Study. Mathematics, 9(13), 1560. https://doi.org/10.3390/math9131560







