Abstract
We introduce a new methodology for anomaly detection (AD) in multichannel fast oscillating signals based on nonparametric penalized regression. Assuming the signals share similar shapes and characteristics, the estimation procedures are based on the use of the Rational-Dilation Wavelet Transform (RADWT), equipped with a tunable Q-factor able to provide sparse representations of functions with different oscillations persistence. Under the standard hypothesis of Gaussian additive noise, we model the signals by the RADWT and the anomalies as additive in each signal. Then we perform AD imposing a double penalty on the multiple regression model we obtained, promoting group sparsity both on the regression coefficients and on the anomalies. The first constraint preserves a common structure on the underlying signal components; the second one aims to identify the presence/absence of anomalies. Numerical experiments show the performance of the proposed method in different synthetic scenarios as well as in a real case.
1. Introduction
Anomaly detection (AD) is an important problem that has received much attention in recent years. It consists of establishing whether a given data deviates from nominal shape or form. It is not possible to establish a single mathematical framework to deal with AD because it depends on the type of application. There are a lot of surveys in the literature, some of them specific to certain applications and some others are broader and application-free. See, for example, the review by [1] regarding the Intrusion Detection Systems, or the paper by [2] providing an overview on AD, analysis, and prediction in Internet of Things (IoT) systems or the paper by [3] considering the application of AD techniques to aviation and how they improve the safety and service of flight operations, just to cite some. However, a milestone of the literature is the paper by Chandola et al. [4], where the authors offer a very good understanding of the subject, defining anomalies, describing its challenges, depicting a relevant taxonomy of the different techniques, and illustrating the various domains of applications. As well explained by the authors, the AD problem depends on the nature of input data (points, sequence, functions, graphs, objects of different nature), on the type of anomaly (point anomalies, contextual or behavioral anomalies, or their combination), on the availability of labeled data for training/validation of the AD techniques (leading to unsupervised AD and supervised AD), and on the type of output of AD (scores or label). Two more recent reviews are the ones by Pimentel et al. [5] and by Ahmed et al. [6], where the authors display a huge and comprehensive number of references on the topic. In particular, reference [5] is devoted to novelty detection, where the distinction with the word anomaly is that the former considers, as normal, the data after their detection. Another important and very recent paper is the one by Thudumu et al. [7], which reviews AD in the context of big data where a curse of dimensionality occurs, bringing the failure of different methodologies.
We can broadly divide the AD techniques into four categories as very well represented by the taxonomy of Figure 3 in [6]: classification techniques, statistical techniques, clustering techniques, and information theory techniques.
In this paper, we focus on statistical techniques, whose recipe is to fit a statistical model to the given data and then check if some of them do not fit this model. We think that a good survey on statistical methods is given by Rousseeuw and Hubert in [8], where they consider robust regression techniques, signal processing techniques, and robust principal component analysis (PCA) techniques.
Our paper is placed in the context of statistical signal processing techniques, where the data are indeed time series, signals, or functions. It is worth observing that signal processing is synonymous with functional data analysis in more classical statistics nomenclature, as well as outliers and anomalies. In particular, we can distinguish between isolated and persistent outliers, see [9]. The isolated outliers insist on a small part of the signal, while the persistent outliers insist on most of their domain. It is important to stress that the literature on AD in functional data is quite recent and is mainly devoted to univariate functions.
In this paper, we deal with the AD problem for multichannel (i.e., multivariate) data affected by persistent outliers and approach it from the perspective of penalized multiple regression framework. We model the nominal shape as K multiple signals from K channels sharing a joint sparse representation into a special dictionary, and then we add a possible anomaly term of any form and shape to each signal component. This framework represents situations where we expect similar shapes for the components of the signal, but some components can undergo anomaly behavior for some unpredictable reason. In particular, we consider nominal signals with a fast oscillating characteristic that can be well represented only by using an appropriate dictionary, namely a RADWT, as done in the context of multiple regression in [10]. A RADWT is a modern and fast computational tool for analyzing signals which are a mixture of oscillatory and nonoscillatory transient behaviors. Such kinds of signals are not periodic and may describe many physiological and physical signals (for example, speech, stock-market, biomedical EEG, etc.) which could not be represented sparsely in the classic orthogonal bases such as Fourier, wavelet, etc. The request of joint sparse representation formalizes the hypothesis that the signal components are expected to have the same spectral characteristics while preserving numerical differences. The idea we develop in our work is the following: a linear model is applied to simultaneously estimate the signal by using its sparse representation in this special dictionary and detect potential anomalies modeled as residuals in this sparse representation.
A similar idea has been already applied in the literature under different model assumptions, for example in [11,12,13]. Specifically, in [11] the authors propose to learn the dictionary by using a set of nominal signals through PCA, as well as in [12] the authors learn the dictionary by using a training set of “normal” nominal signals, i.e., not affected by anomalies, under the specific hypothesis that they are multivariate mixtures of discrete and continuous signals and applying their sparse coding algorithm to select the training signals having the highest residuals. Subsequently, in both papers, the authors detect anomalies for a new signal occurrence by evaluating the residual of its sparse representation in this dictionary. On the other hand, in [13], the authors face the univariate AD problem considering a linear regression model where the univariate signal is expressed as a linear combination of columns of a given design matrix without the sparseness hypothesis. The authors propose detecting anomalies by simultaneously estimating both the nominal signal and its residual using nonconvex penalized regression with the constraint on the outliers vector.
Our paper stands in between these recent proposals [11,12,13] for two reasons. First, we use a dictionary for sparsely representing functions (as in [11,12]) but without requiring a training set of “normal” nominal signals for dictionary learning because we rely on an innovative instrument such as the RADWT transform to deal with fast oscillating signals. Second, we look for anomalies by simultaneously estimating both the nominal signal and its residual (as in [13]) but imposing a double constraint on the regression coefficients and the anomalies, taking into account that few RADWT coefficients are necessary to represent the signals. To ensure that the residuals can preserve information about the outliers/anomalies, we must use robust regression techniques. As we will clarify later on, a good AD undergoes a good robust regression analysis, because the procedure aims simultaneously to detect the anomalies and to estimate the signal’s components, the success of the first goal ensuring the success of the second and vice versa. Hence, our paper can be also considered as part of the literature on robust regression in the high-dimensional setting, see [14,15]. In this perspective, we also refer to [16], from which we were inspired to use robust losses, such as the Huber loss and the skipped mean loss.
The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 describes the data model with the working hypothesis. Section 3 presents and discusses the proposed AD procedure within the paradigm of group-lasso regression, enlightening the connections with other existing procedures. Section 4 describes some important implementation issues. Section 5 shows numerical experiments on synthetic and real data and finally, the last section discusses conclusions.
2. The Data Model and Problem Setting
We will consider hereafter a functional dataset consisting of K curves , observed on a set of equispaced grid points and resulting in observed K dimensional response vectors , , …,. The observed curves are composed by nominal signals , , … which may have some functional properties to which are eventually added anomaly signals , , …, which may appear as functional outliers , . Once the data is discretized our data model becomes
where, for each , is the underlying unknown nominal signal, is the potential anomaly, and is the additive white noise. Note that if the Gaussian noise in some channel is correlated with known covariance structure, we can easily manage this situation reparametrizing the data.
The mathematical hypothesis is that, while the K components have a nominal behavior which results in a joint sparse representation into a RADWT dictionary, the anomalies can be of any shape, so they have no sparse representation in the same dictionary, and they are independent of each other, so an anomaly can be detected in any, some, or all components.
We do not hypothesize functions belong to some functional Sobolev space as it is usually done in functional nonparametric regression setting, instead we let these functions be much more general and we restrict our attention to their finite-dimensional representation. Since many physiological and physical signals exhibit a mixture of oscillatory and nonoscillatory behaviors (for example, speech, stock-market, biomedical, EEG, etc.), we suppose that each component is a “high resonance” signal or a “low resonance” signal or a sum of both types of signal. By a high-resonance component, we mean a signal consisting of multiple simultaneous sustained oscillations; in contrast, by a low-resonance component, we mean a signal consisting of nonoscillatory transients of unspecified shape and duration. We stress that the high and low resonance components of a signal can not be extracted from its high and low frequencies components in a time-scale decomposition, but they can be well represented by a high-Q factor RADWT and a low-Q factor RADWT respectively, see [17]. The RADWT is a normalized tight dictionary of defined as where is a wavelet function and () is a triplet of parameters that gives the time-scale characteristic of the dictionary. In particular, the ratio is closely related to the scale (or frequency) dilatation factor, the parameter s is closely related to the time dilatation factor, and is the redundant factor. The Q-factor depends on these parameters although there is not an explicit formula, in particular setting the dilatation factor between 1 and 2 and gives a RADWT with high Q-factor, while setting we obtain a low Q-factor RADWT with time-scale characteristic similar to the dyadic wavelet transform. In particular, when , and , the dictionary reduces to the classical wavelet basis. Given a finite energy signal of length n and levels of decomposition, the RADWT transform is obtained by a sequence of proper downsampling operations and fast Fourier transforms; it ends up with scaling coefficients (low-pass filtering) and wavelet coefficients (high-pass filtering) at each level . See [18] for details on fast analysis and synthesis schemes.
In the following, we will use these signal processing results in order to formulate our working setup. Let be the finite matrix representation of the low Q-factor analysis filter, where indicates the cardinality of the low Q-factor RADWT, and let be the finite matrix representation of the high Q-factor analysis filter (the synthesis operators being just the transpose matrices), where indicates the cardinality of the high Q-factor RADWT. Let us define the dictionary , with , then our working hypothesis is the following:
- (H1)
- signals have a jointly sparse representation in , i.e., setting , , the coefficients matrixhas a minimal number of rows different from zero. This means considering the following constraintwhere counts the number of non zero rows, T is the a priori parameter indicating the expected degree of sparsity level, and is the indicator function:
It is worth observing that the role of dictionary matrix could be played by any other dictionary in which the nominal signals have a sparse joint representation. What we will expose in the following is not related to the nature of the dictionary and can therefore be considered a valid method for other types of signals as long as there is a dictionary that sparsely represents them. For example, could be made up of only if it is known that the f signals have only a high resonance component, or it could be made up of the union of other types of basis, frames, or dictionaries. However, when and are the finite representation of RADWT, they constitute thigh frames, i.e., and , so and then, once we obtain the estimate of the coefficients it is straightforward to obtain the estimate of the signal. When the choice of the dictionary change, and is not necessarily satisfied, and hence signal reconstruction is not obvious.
3. Proposed Procedures
The linear model in (1) can be rewritten in terms of dictionary coefficients as follows
which turns out to be a linear multiple regression model with a special common design matrix. A first and somewhat naive approach, but sub-optimal, would consist of treating each channel separately, ignoring the underlying common structure. This is the reason why such kind of problem is reformulated in terms of a unique regression problem in the following form:
with obvious correspondence between elements of the two expressions. So, is a column vector of response variables, a design matrix of dimension , an unknown regression coefficients column vector of length , is an unknown anomalies column vector of length , and, finally without loss of generality, we let be a -variate Gaussian random column vector with zero mean and covariance matrix . Our regression problem (5) has regression parameters and only data point, so it clearly falls into the class of high-dimensional regression problems. Under the working hypothesis (H1), we expect to be group sparse, i.e., for many we expect that , for all . This provides the following nonoverlapping group structure for the whole vector
with
group of size K. Let us define the following norm
with denoting the reduction of vector to the subset of index . The problem we are dealing with is not a classic regression problem, because our interest is to simultaneously estimate the vector , more specifically the , …, anomalies that compose it, and the vector. For example, if an anomaly is present in the first channel, the vector , representing the residual of the linear regression of on will have a -norm much higher than the residual in another channel with no anomaly. While the anomalies vectors are not connected, because the anomalies can appear in any, some, or all channels, the underlying signals are not independent since by hypothesis they share the same spectral characteristic. For these reasons, we propose solving the following convex minimization problem
where is a regularization parameter that controls the group sparsity of vector , while is a regularization parameter that controls the number of expected anomalies. Both the regularization parameters represent a trade-off between the fit and the complexity of the model. Being fixed, implies a non sparse , generalizing the model proposed in [13] to the multichannel setting, on the contrary implies a sparser vector, increasing the energy of the anomalies. On the other hand, being fixed, detects anomalies in each channel, while brings to a model without anomalies. Their choice is a delicate point and we will discuss it in the Implementation, Section 4. Finally, for each we detect an anomaly if the obtained estimate , where is the solution of the optimization problem (7). Moreover, the intensity of the detected anomaly, measured as , can be considered as a score for the anomaly and treated as an incipient level of fault according to the specific application which defines an alarm threshold.
From a statistical perspective, the problem given in Equation (7) falls into the class of group lasso regression problem applied to the augmented parameter vector and augmented design matrix . Indeed, the problem in Equation (7) can be rewritten as
with group Lasso penalty . If the unknown vector is sparse, under appropriate hypothesis on the design matrix , consistency of the proposed estimator is guaranteed, see [19,20,21].
From a numerical perspective, problem (7) is jointly convex in and , and its simple form suggests that we can apply an alternating optimization given initial estimates for and . Of course, we need an estimate for that takes into account the potential presence of the anomaly, i.e., robust.
Given an initial robust estimate for , i.e., , we define , then at each iteration the procedure solves the following two sub-problems,
- given , estimate
- given , estimate
Iteration stops when a given number of maximum iteration is reached or when the relative error on the anomaly vector is below a fixed threshold. Let us give a closer look at the two sub-problems. Function is separable in each channel, i.e.,
where is the current residual of the regression of on ; so the solution of sub-problem (9) is obtained by the multivariate-Soft thresholding rule
where the directional vector plays the rule of function in classical one dimensional setting, see [22]. In Equation (10), the Soft thresholding operator acts on the vector by shortening it towards 0 by an amount if its norm is greater than , by setting it to zero if its norm is less than . For the seek of completeness, we sketch below how to derive the above statement. Vector in Equation (10) is the solution of the following convex problem
Considering the case and setting the derivative with respect to to zero, we obtain
from which the following two equations derive:
by solving the second equation in and substituting into the first we get,
Now, consider the case . We need to impose that the vector belongs to the pseudogradient evaluated at , i.e., there exists a vector , and such that . This is possible only if . Finally, combining both cases into a single equation, we get exactly the expression in Equation (10).
Let us now consider sub-problem (8). It is possible to prove that minimization of , where is the solution of Equation (9), i.e., vectors given by Equation (10), is equivalent to solve the following Huber’s cost functional with parameter plus a group lasso penalty. i.e.,
Here the mutivariate Huber cost function is given by the following rule:
for any .
For the sake of completeness, we sketch below how to derive the above statement. Let and be its complement.
In robust regression, i.e., regression in presence of outliers, it is well known that Huber loss is less sensitive to outliers than quadratic loss because it combines the squared loss and the absolute loss in an adaptive way. Intuitively, when the data points are not too big, Huber’s loss function penalizes like the squared loss; otherwise, it penalizes like the absolute loss. However, it is not resistant to high leverage outliers (outliers in the predictors) because it never rejects gross outliers that have moderate or high leverage. Its breakdown point is . Indeed, according to [23], a convex criterion is inherently incompatible with robustness.
The proposed procedure is summarized in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 Calculate with the Soft Thresholding operator |
Input data:
Output: |
Possible Improvements
In this section we explore the possibility to improve our estimator, adopting a different type of threshold operator. We are inspired by [13], where the authors deal with the outliers detection problem in the case of one channel. In the paper they propose a two step procedure: after a proper initialization for , in the first step, they apply a Soft thresholding operator to the residual, in the second step they use Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) to update vector . The main difference with our procedure is in the second step, where we perform a group lasso regression instead of an OLS to face the multitask regression. Although in [13] the authors deal with the outliers detection, looking for pointwise anomalies, the philosophy of their estimator is comparable to ours. Moreover, they note that in the presence of multiple outliers, the Soft threshold is not able to deal with masking and swamping effects, and propose to replace Soft-thresholding with Hard-thresholding obtaining a great improvement. Then they generalize the idea and introduce an entire class of methods, namely which uses a general thresholding operator instead of the Soft thresholding operator, discovering important results and outstanding performance. In this direction of research, we explore the possibility to improve our estimator, substituting the first step of our procedure, i.e., the multivariate Soft thresholding operator expressed in Equation (10), by an appropriate operator as done by the authors of [13]. Specifically, we substitute Equation (10), by the following Hard-thresholding operator
where is the indicator function defined in Equation (3). We stress that substituting Equation (13) into the first step of our procedure, the second step becomes equivalent to a skipped-mean loss penalized with a group lasso penalty. We sketch below how to derive it.
where and its complement.
Hence, substituting Soft threshold with Hard threshold automatically makes the second step equivalent to the following penalized skipped-mean loss
with loss defined as:
for any . Note that skipped-mean loss is not-convex and is a special case of Hampel loss, that belongs to the family of redescending M-estimators, see [24], with high breakdown point, close to 0.5. This means that is robust to outliers. For a summary, see Appendix 1 in [16].
Figure 1 shows a comparison between quadratic loss, Huber loss , and skipped-mean loss .
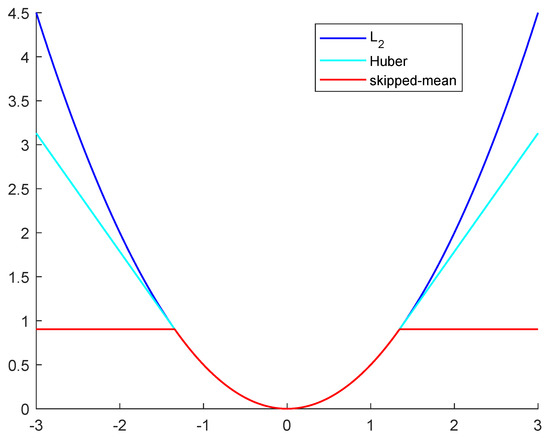
Figure 1.
Loss functions: L2, Huber and skipped-mean.
We can conclude that, when using Hard threshold instead of Soft threshold, we solve the following problem instead of the problem in Equation (7)
with , the grouped norm.
Of course, the problem in Equation (16) is not convex, because the complexity penalty is not convex; therefore, we can only aspire to find one of the possible local minima of the objective function. Nonconvex functions may possess local optima that are not global optima, and our iterative method may terminate undesirably in one of these local optima. From a statistical perspective, although theoretical results for nonconvex penalties have been studied in [14,15] proving that all local optima are essentially as good as a global optimum, we cannot apply those results because our penalty does not satisfy their hypothesis. Therefore, our finding for this second procedure is purely empirical and we include the side condition to guarantee the existence of at least one local/global optima. In addition, we will require so that the true regression vector and the true anomaly vector , that satisfy Equation (4), are feasible.
The proposed procedure is summarized in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 2 Calculate with the Hard Thresholding operator |
Input data:
Output: |
4. Implementation
In this section, we describe all the issues that make the proposed procedure effective: namely the initialization step, the numerical algorithm, and the choice of the regularization parameters and .
As described in Section 3, we need to initialize the two step procedure by a robust estimator of parameters which gives a robust estimator of to plug into expression of Equation (9). First, we note that vector , hence to initialize our procedure is enough to establish a robust estimator for each of the signal component . In our procedure, under the prior knowledge that the number of channels with anomaly are less then the half number of channels, we initialize by the median of the data channels, namely
As regards the numerical algorithm we note that the first step described in Equation (9) has a closed-form solution given in Equation (10) and Equation (13) in the case of Soft and Hard threshold respectively; the second step in Equation (8) requires the solution of a linear regression problem with a group Lasso penalty. Hence for the solution of the second step we employed the grpreg R package that implements the efficient Group Descendent Algorithm presented in [25,26]. This algorithm works groupwise by using the separability of the model (5) in terms of a group of variables, i.e., it updates each group of variables freezing the other groups to their current value until convergence. The updating of each group of variables is performed through a multivariate soft-thresholding operator, under the assumption of “orthonormal groups”. We stress that the “orthonormal group” property refers to the condition , with denoting the reduction of design matrix to columns of the subset of index . When this condition is not satisfied the grpreg automatically orthonormalizes the design matrix, but this practice leads to a slight modification of the -norm contained in the penalty, as pointed out in [27,28]. However, this is not our case, because the design matrix defined in Equation (5) satisfies the “orthonormal groups” property by construction, and hence, we can take complete advantage of the Group Descendent Algorithm implemented in the grpreg package.
As in any penalized regression approach, the choice of the regularization parameter is really strategic. In particular, in the proposed procedure the regularization parameter has two components, namely and . The latter controlling the degree of regularization in the regression model on parameter , the last controlling the threshold over which the residual of the previous regression is considered not acceptable. Under the data model described in Equation (1), the expected size of the residual , in absence of anomaly in channel k, is given by , hence it is natural to fix where is an estimator of the noise variance. In particular, we adopt where is the residual after having initialized as described above. The choice of the regularization is more demanding; we avoided CV criterion since it is quite computationally heavy and in principle when applied on the data, a large prediction error can be due to both a suboptimal as well as to the presence of an anomaly. Hence we suggest tuning parameter by the BIC criterion, which is much less computationally demanding and easily modifiable to our setting. In particular, we adopted the following formula
where is evaluated according to formula (22) in [26] and , with and estimates obtained for . The grid of values has been obtained as in Section 3.5 of [26].
5. Simulations and Real Examples
To show the performance of the proposed methodology, we performed numerical experiments both in a simulation setting and in a real dataset case.
5.1. Synthetic Data
We generated data according to the model in Equation (1) with some known functions and some known anomalies and evaluated the performance of the proposed techniques in terms of signals reconstruction and anomalies detection.
Since the proposed method deals with nominal signals with fast oscillating characteristics, we choose the HiSine and the TwoChirp signals (represented in Figure 2 and Figure 3) among the classical signals employed in the literature. Both can be well represented by using an appropriate RADWT. In particular, a RADWT with Q-factor almost 5 (, , and ) is appropriate for their sparse representation.
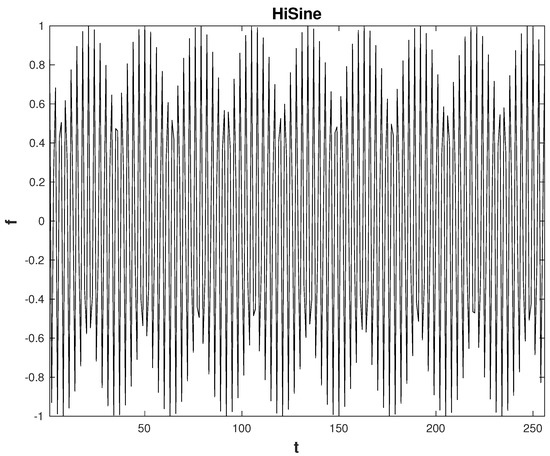
Figure 2.
HiSine signal.
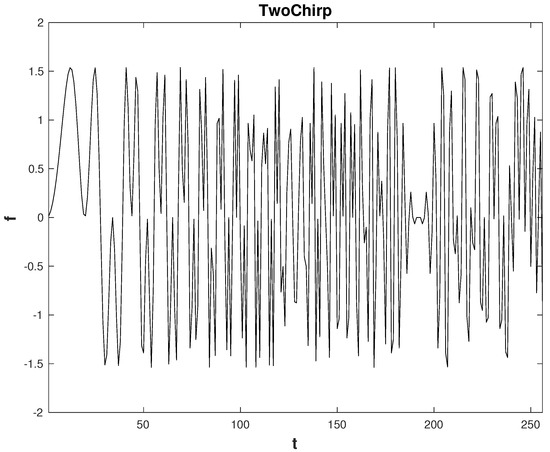
Figure 3.
TwoChirp signal.
As regards the anomalies, there are no assumptions on their shape, i.e., they can be of any duration and shape and they can appear in any of the signal components, so we decided to model them by the following formula
to represent situations where the mean of the signal undergoes to a shift during a specific interval of time ; where the shift with , to mimic situation where the anomaly is weak or strong with respect to the underlying signals. We generated data according to model (1), building K signals, of length and for such a choice the W matrix has dimension . Each signal has been generated randomizing the original signal ( or ) by the formula , where u is a vector of i.i.d. variables with distribution . These generations guarantee that the true underlying signals have similar shape and the same sparsity patterns. According to the model in Equation (1), we added noise to each channel as with related to the variance of the true underlying signal realizing three different type of to mimic situations of different severity of noise. For completeness, here is the expression
Finally, we added anomalies to some channels as in Formula (17).
To sketch, we have considered two settings:
To summarize, for each of these two settings ( and ), we analyzed two different levels of anomalies ( and in Formula (17)) and three different levels of SNR ( and 6). These choices are arbitrary but they were dictated by the idea of understanding a sort of breakdown point of our procedure. Naturally, we expect that the weaker the anomalies and the stronger the noise, the worse the problem. Finally, we evaluated performance by computing the MSE for each signal’s component as
with estimate of , and by computing the relative number of (falsely) detected anomalies (FPR) as well as the relative number of not detected anomalies (FNR), namely
A being the true number of channel with anomalies. In addition, we evaluated the intensity of the estimated anomalies to compare with the intensity of the simulated ones and to analyze the detection capabilities of both our proposals as
To be robust to the particular realization in generating synthetic data (and corresponding noise), each experiment was run several times. In particular, we ran 10 instances for each of the 12 considered cases (2 (function settings) × 2 (levels of anomaly) × 3 (SNRs)). For the sake of exposition, in the following we show separately results obtained for each function’s settings. Specifically, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 and Table 1 and Table 2 show results of the 6 different combinations of levels of anomaly and SNRs obtained when the function is and Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13, Figure 14 and Figure 15 and Table 3 and Table 4 show analogous results when the function is . Moreover, we show in Figure 5 and Figure 6 the plots of the shape of the unknown signals and the goodness of reconstructions by the Hard thresholding procedure in the two extreme cases, weak anomaly () with highest noise () and strong anomaly () with lowest noise level () for the first setting ; while in Figure 7 and Figure 8 we show the same results obtained by the Soft thresholding procedure. For the second setting , four analogous plots are given in Figure 11 and Figure 12 and Figure 13 and Figure 14 for the Hard and Soft thresholding procedures respectively.
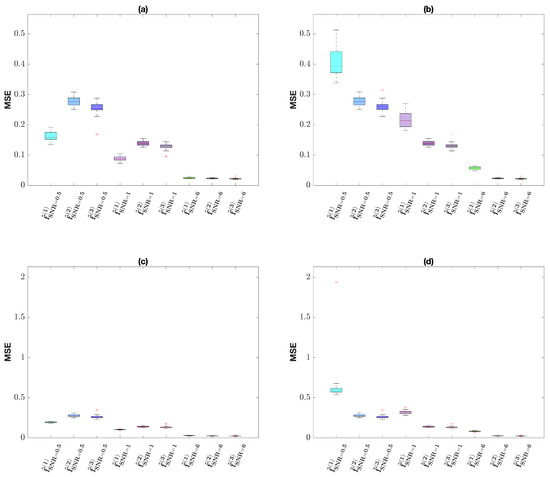
Figure 4.
Mean Square Error for the estimated signals , , for the HiSine. First row: (a) Hard and (b) Soft estimators for . Second Row: (c) Hard and (d) Soft estimators for . Blue colors refer to (first 3 boxes), violet colors refer to (second 3 boxes), green colors refer to (last 3 boxes).
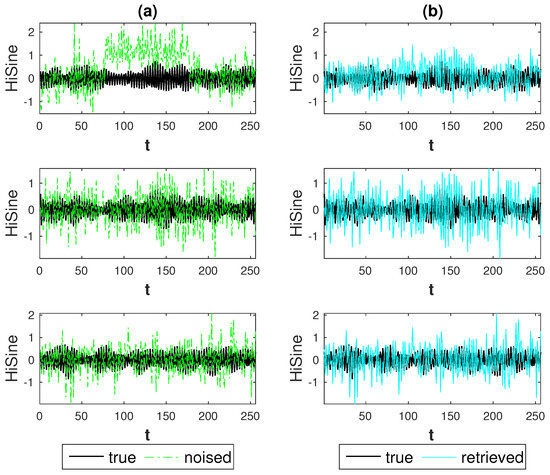
Figure 5.
First setting: HiSine signals, weak anomaly (), highest noise level (). Result for Hard thresholding procedure: (a) true signals (black) and noised signals (green); (b) true signals (black) and retrieved signals (cyan).
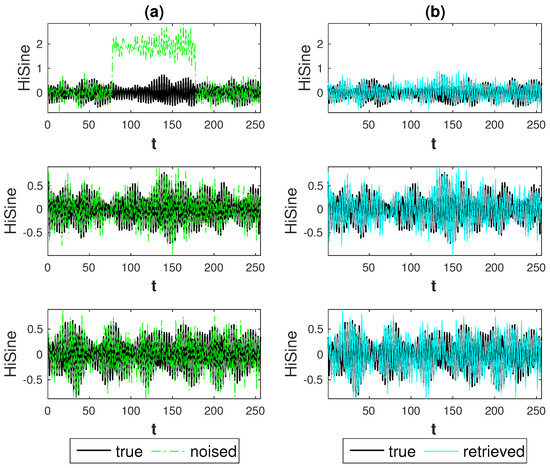
Figure 6.
First setting: HiSine signals, strong anomaly (), lowest noise level (). Result for Hard thresholding procedure: (a) true signals (black) and noised signals (green); (b) true signals (black) and retrieved signals (cyan).
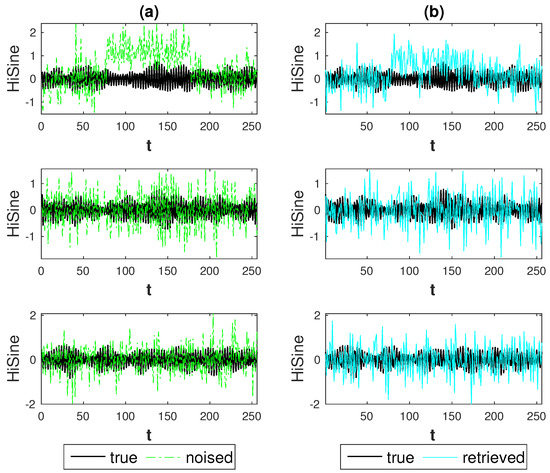
Figure 7.
First setting: HiSine signals, weak anomaly (h = 0.5), highest noise level (SNR = 0.5). Result for Soft thresholding procedure: (a) true signals (black) and noised signals (green); (b) true signals (black) and retrieved signals (cyan).
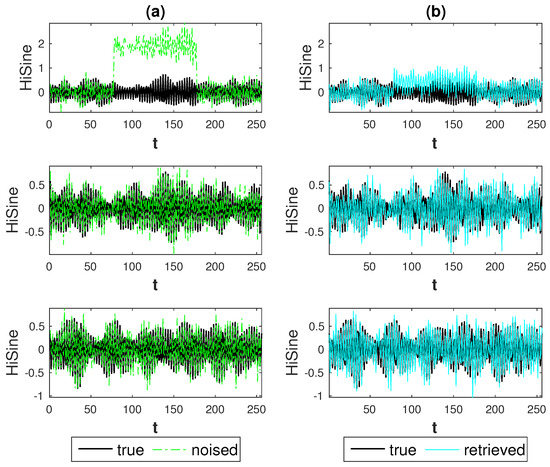
Figure 8.
First setting: HiSine signals, strong anomaly (h = 2), lowest noise level (SNR = 6). Result for Soft thresholding procedure:(a) true signals (black) and noised signals (green); (b) true signals (black) and retrieved signals (cyan).
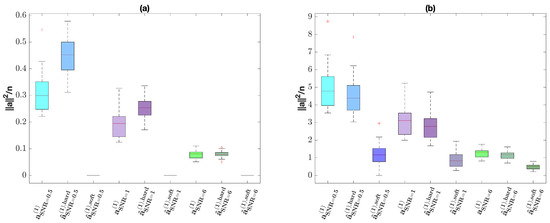
Figure 9.
Intensity of the simulated anomaly , of the estimated anomaly by Hard thresholding and, of the estimated anomaly by Soft thresholding for the HiSine. Panel (a) refers to and anomaly in channel 1, panel (b) refers to and anomaly in channel 1. Blue colors refer to (first 3 boxes), violet colors refer to (second 3 boxes), green colors refer to (last 3 boxes).

Table 1.
False positives rates FPR (%) and false negatives rates FNR (%) for the simulations carried out on HiSine signals, . We report average values of the indicators over 10 simulations.

Table 2.
False positives rates FPR (%) and false negatives rates FNR (%) for the simulations carried out on HiSine signals, . We report average values of the indicators over 10 simulations.
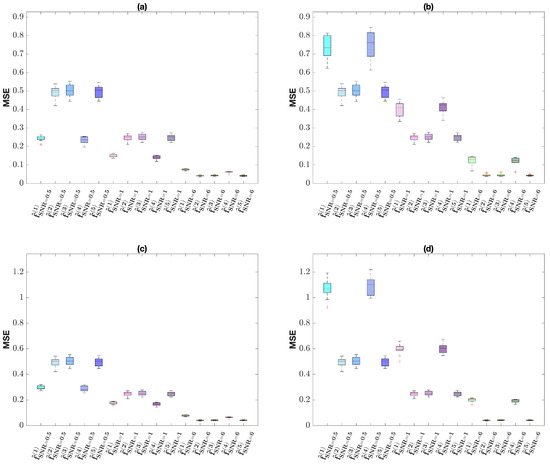
Figure 10.
Mean Square Error for the estimated signals , , , , for the TwoChirp. First row: (a) Hard and (b) Soft estimators for . Second Row: (c) Hard and (d) Soft estimators for . Blue colors refer to (first 5 boxes), violet colors refer to (second 5 boxes), green colors refer to (last 5 boxes).
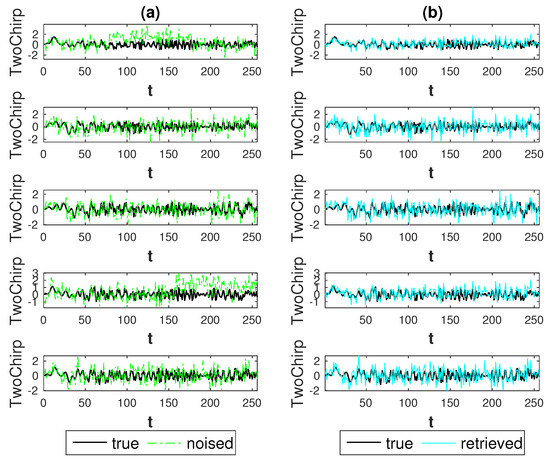
Figure 11.
Second setting: TwoChirp signals, weak anomaly (h = 0.5), highest noise level (SNR = 0.5). Result for Hard thresholding procedure: (a) true signals (black) and noised signals (green); (b) true signals (black) and retrieved signals (cyan).
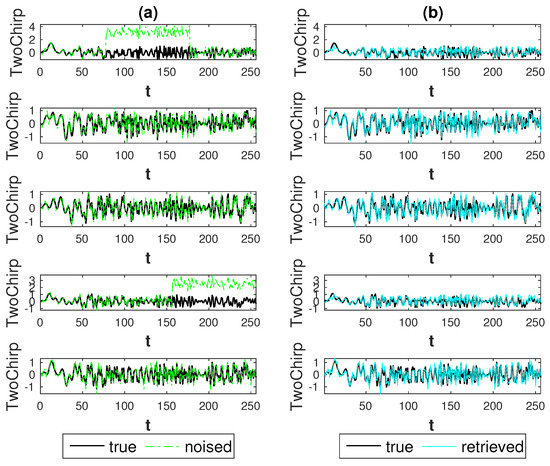
Figure 12.
Second setting: TwoChirp signals, strong anomaly (), lowest noise level (). Result for Hard thresholding procedure: (a) true signals (black) and noised signals (green); (b) true signals (black) and retrieved signals (cyan).
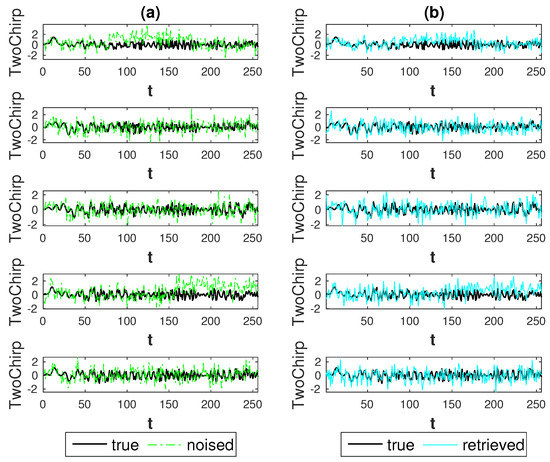
Figure 13.
Second setting: TwoChirp signals, weak anomaly (h = 0.5), highest noise level (SNR = 0.5). Result for Soft thresholding procedure: (a) true signals (black) and noised signals (green); (b) true signals (black) and retrieved signals (cyan).
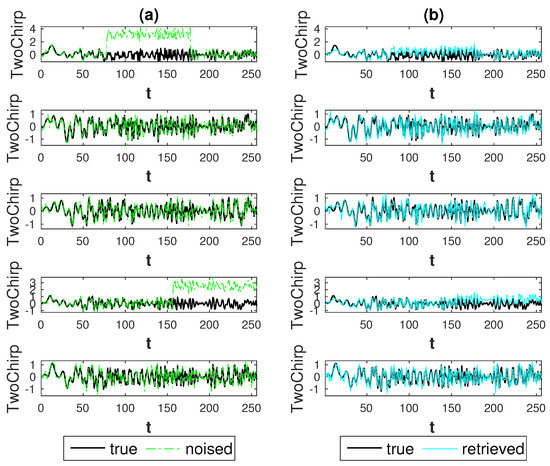
Figure 14.
Second setting: TwoChirp signals, strong anomaly (), lowest noise level (). Result for Soft thresholding procedure: (a) true signals (black) and noised signals (green); (b) true signals (black) and retrieved signals (cyan).
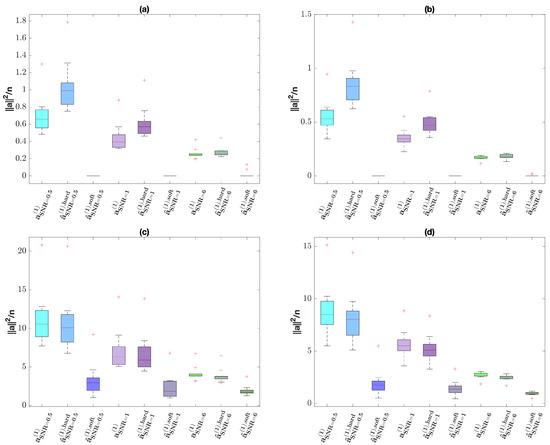
Figure 15.
Intensity of the simulated anomaly , of the estimated anomaly by Hard thresholding and, of the estimated anomaly by Soft thresholding for the TwoChirp. Panel (a) refers to and anomaly in channel 1, panel (b) refers to and anomaly in channel 4, panel (c) refers to and anomaly in channel 1, panel (d) refers to and anomaly in channel 4. Blue colors refer to (first 3 boxes), violet colors refer to (second 3 boxes), green colors refer to (last 3 boxes).

Table 3.
False positives rates FPR (%) and false negatives rates FNR (%) for the simulations carried out on TwoChirp signals, . We report average values of the indicators over 10 simulations.

Table 4.
False positives rates FPR (%) and false negatives rates FNR (%) for the simulations carried out on TwoChirp signals, . We report average values of the indicators over 10 simulations.
Comment on the results. Concerning anomaly detection performance, we observe that for both procedures, Hard and Soft, and both settings, and , it is worst in the case of weak anomaly (, Table 1 and Table 3) with respect to the case of strong anomaly (, Table 2 and Table 4). This is a consequence of the masking effect: the weaker the anomaly the easier the noise, and the anomalies can mask each other. However, there is an interesting difference between the two procedures. In particular, for the Hard thresholding, we observe that is always zero, while there can be some in the more difficult setting, i.e., when the anomalies are weaker and the level of noise is higher. This means that the Hard thresholding procedure always detects the true anomalies, being prone to some false positives detection when stressing the problem setting. This observation is relevant from the practical point of view because in such extreme cases one can always adopt a post-processing rule to classify the detected anomalies, being confident enough not to miss any anomaly. On the contrary, the Soft thresholding is much more conservative, hence when stressing the setting, i.e., when the anomalies are weaker () and the level of noise higher, the Soft thresholding procedure is more prone to false negatives detection. Indeed, for the Soft we always get , while stressing the setting we get some (the opposite of Hard). This is not a drawback, rather a different way of reacting to the difficulty of the problem. However, from a practical point of view, when using Soft instead of Hard it can be a disadvantage to have false-negative detection because when the result undergoes post-processing the anomalies not detected are not further analyzed. However, although our two procedures are not the definitive answer to the AD problem, it is important from a practical point of view to be aware that the Hard thresholding tends to select more anomalies (and therefore to have some false positives) while the Soft threshold tends to select fewer anomalies (and therefore to have some false negatives). In addition, Figure 9 and Figure 15 show the boxplots of the intensity of the simulated anomalies and of the estimated anomalies by both Hard and Soft thresholding. We can note the good performance of the Hard thresholding procedure with respect to the Soft thresholding one, both in the case of weak anomalies and strong anomalies, with a better intensities estimate in the last case.
As regards the estimation performance, we observe that for both procedures, Hard and Soft, and both settings, , and , it decreases when increasing the level of noise (i.e., decreasing the SNR). In fact, the significantly decreases when moving from the left to the right in all box-plot shown in Figure 4 for the first setting and in Figure 10 for the second setting ; panels (a)–(c) refer to Hard thresholding for and , respectively, and panels (b) and (d) refer to Soft thresholding for and , respectively. Interestingly, in line with what we observed on the detection performance results, we have significant differences in terms of MSE performance on the anomalous channels between the Hard and the Soft. See box-plots in positions 1, 4, 7, corresponding to the first channel for the signal and box-plots in positions 1, 4, 6, 9, 11, 14, corresponding to the first and the fourth channels for the signal. The anomalous channels always have a better MSE for the Hard than for the Soft. This is a direct consequence of our double-step procedure: when we correctly detect the anomaly (in the first step), we correctly adjust the residual (in the second step) and hence we obtain a better estimation. On the channels without anomaly, detection performance is comparable.
Finally, we stress that what we have observed on average (looking at box-plots) about estimation performance, can be inspected visually for a randomly chosen realization looking at the first channel in Figure 5 (Hard thresholding, , ), Figure 6 (Hard thresholding, , ), Figure 7 (Soft thresholding, , ) and Figure 8 (Soft thresholding, , ), which refer to and looking at the first and fourth channels in Figure 11 (Hard thresholding, , ), Figure 12, (Hard thresholding, , ), Figure 13 (Soft thresholding, , ) and Figure 14 (Soft thresholding, , ), which refer to .
5.2. Real Data
To illustrate the performance of our procedures on a real example, we considered the problem of detecting anomalies for signals recording measurements on a water pump. The signals represent the behavior of the pump in both normal and abnormal conditions and a complete description of it is given in [29]. The dataset is part of a repository managed by the Delft University of Technology and is freely available at http://homepage.tudelft.nl/n9d04/occ/index.html (accessed on the 18 February 2021) (dataset 541: Delft pump AR app). Each signal has a length and has been obtained by first fitting an AutoRegressive model of order 32 (AR(32)) to each of 5 vibration measurements and then by combining the coefficients in a single vector.
This dataset has been previously analyzed in [30]. In that paper, the authors proposed a data domain description, named the Support Vector Data Description (SVDD) to find the finest representation of the data such that the normal target signals are optimally clusterized and can be distinguished as best as possible from the abnormal ones. Their approach has a good performance and in some sense, it is another perspective for looking at the detection of anomalies. However, the data representation proposed in [30] does not take into account the longitudinal shape of the data, which are ordered coefficients; hence the method proposed in [30] is expected to be invariant under permutation of the data. On the other hand, our analysis is truly functional, since we treat the data as functions/signals; moreover, the dataset satisfies the hypothesis of our model. Since the underlying signals have a fast oscillating characteristic, they share a similar shape which presupposes the same sparsity pattern into the RADWT dictionary and the signals measured under abnormal conditions can be modeled as the signals measured under normal conditions plus some shift in the first part of the interval.
We considered 20 signals, 12 nominal and 8 with the anomaly, randomly chosen from the whole dataset, see Figure 16. We applied both procedures, Hard and Soft thresholding, obtaining reconstruction shown in Figure 17, panels (a) and (b). In the same figure, panels (c) and (d), we also display the retrieved residuals which represent anomalies. While the Soft thresholding has no false positives neither false negatives, the Hard thresholding has 2 false positives (channel 10 and 11), with the norm of the order of the estimated variance 0.0035, see Table 5. However, the Hard thresholding estimates better the intensity of the anomalies (which represent residuals for the regression on ), permitting a better signals reconstruction. This does not happen for the Soft thresholding, which results in over-smoothed signal reconstruction. Finally, we can conclude that the Hard thresholding procedure has a better performance although it has two false positives, which could be easily detected by standard post-processing.
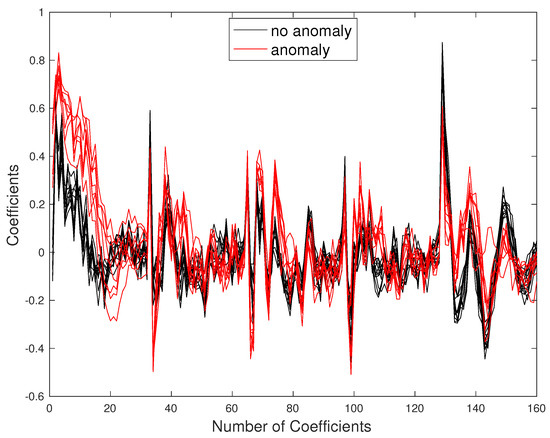
Figure 16.
Pump data: red color indicates anomaly signals, black color indicates normal signals.
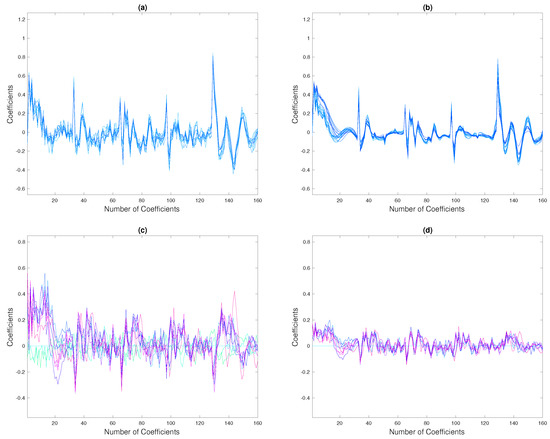
Figure 17.
First row: (a) Pump data estimated by the Hard thresholding procedure (b) Pump data estimated by the Soft thresholding procedure. Second Row: (c) Anomalies estimated by the Hard thresholding procedure (d) Anomalies estimated by the Soft thresholding procedure.

Table 5.
for the Hard estimator.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we presented two procedures for anomaly detection in multichannel signals under a structural hypothesis on the underlying signals covering some specific real-life situations. In particular, we dealt with fast oscillating signals under the assumption that they share a common specific sparsity pattern in a given dictionary. The construction of the dictionary leverages on a complete filter bank (RADWT) of which guarantees a perfect reconstruction property and a tunable Q-factor. We based the two procedures on group penalized regression methods and we implemented them by a two-step iterative algorithm. The two methods differ in the second step iteration, the first applying Soft thresholding to the residual vectors, the second one applying Hard thresholding. Moreover, we made connections between them and the robust regression literature in a high dimensional setting obtaining interesting interpretations. From the computational point of view, we observed that the Hard thresholding procedure reveals some advantages to the Soft thresholding procedure, confirming some previous results on nonconvex robust regression.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.D.C. and I.D.F.; methodology, D.D.C. and I.D.F.; validation, D.D.C. and I.D.F.; formal analysis, D.D.C. and I.D.F.; visualization, D.D.C. and I.D.F.; funding acquisition, I.D.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Project Piattaforma Tecnologica ADVISE-Regione Campania; project “TAILOR” (H2020-ICT-48 GA: 952215).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The pump dataset is part of a repository managed by the Delft University of Technology and is freely available at http://homepage.tudelft.nl/n9d04/occ/index.html accessed on 20 April 2021 (dataset 541: Delft pump AR app).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to anonymous reviewers for improving the overall manuscript. We thank Anestis Antoniadis for the fruitful discussions that helped to improve the manuscript. This work was partially supported by the grant INdAM-GNCS Project 2020.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Agrawal, S.; Agrawal, J. Survey on Anomaly Detection using Data Mining Techniques. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 60, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahim, M.; Sillitti, A. Anomaly Detection, Analysis and Prediction Techniques in IoT Environment: A Systematic Literature Review. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 81664–81681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basora, L.; Olive, X.; Dubot, T. Recent Advances in Anomaly Detection Methods Applied to Aviation. Aerospace 2019, 6, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandola, V.; Banerjee, A.; Kumar, V. Anomaly Detection: A Survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2009, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, M.A.F.; Clifton, D.A.; Clifton, L.; Tarassenko, L. A review of novelty detection. Signal Process. 2014, 99, 215–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Mahmood, A.N.; Hu, J. A survey of network anomaly detection techniques. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2016, 60, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thudumu, S.; Branch, P.; Jin, J.; Singh, J.J. A comprehensive survey of anomaly detection techniques for high dimensional big data. J. Big Data 2020, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseeuw, P.; Hubert, M. Anomaly detection by robust statistics. WIREs Data Mining Knowl. Discov. 2018, 8, e1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, M.; Rousseeuw, P.; Segaert, P. Multivariate functional outlier detection. Stat. Methods Appl. 2015, 24, 177–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Canditiis, D.; De Feis, I. Simultaneous nonparametric regression in RADWT dictionaries. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2019, 134, 36–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, A.; Elad, M.; Hel-Or, Y. Sparse Coding with Anomaly Detection. J. Signal Process. Syst. 2015, 79, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilastre, B.; Boussouf, L.; D’Escriv, S.; Tourneretca, J.Y. Anomaly detection in mixed telemetry data using a sparse representation and dictionary learning. Signal Process. 2020, 168, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.; Owen, A. Outlier Detection Using Nonconvex Penalized Regression. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2011, 106, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, P.; Wainwright, M.J. Regularized M-estimators with Nonconvexity: Statistical and Algorithmic Theory for Local Optima. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2015, 16, 559–616. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, P. Statistical consistency and asymptotic normality for high-dimensional robust M-estimators. Ann. Stat. 2017, 45, 866–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, U.; Antoniadis, A.; De Feis, I.; Gijbels, I. Penalised robust estimators for sparse and high-dimensional linear models. Stat. Methods Appl. 2021, 30, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selesnick, I.W. Resonance-Based Signal Decomposition: A New Sparsity-Enabled Signal Analysis Method. Signal Process. 2011, 91, 2793–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayram, I.; Selesnick, I.W. Frequency-Domain design of overcomplete rational-dilation wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 2957–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J. On the L1-Lq Regularized Regression; Technical Report; Department of Statistics, Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, F.R. Consistency of the Group Lasso and Multiple Kernel Learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 1179–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J. Estimation Consistency of the Group Lasso and its Applications. In Artificial Intelligence and Statistics; van Dyk, D., Welling, M., Eds.; PMLR: Clearwater Beach, FL, USA, 2009; Volume 5, pp. 376–383. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.; Lin, Y. Model selection and estimation in regression withgrouped variables. J. R. Statist. Soc. B 2006, 68, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseeuw, P.J.; Leroy, A.M. Robust Regression and Outlier Detection; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, P. Robust Statistics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Breheny, P.; Huang, J. Group descent algorithms for nonconvex penalized linear and logistic regression models with grouped predictors. Stat. Comput. 2015, 25, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breheny, P.; Huang, J. Penalized methods for bi-level variable selection. Stat. Its Interface 2009, 2, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Breheny, P.; Ma, S. A selective review of group selection in high-dimensional models. Stat. Sci. 2012, 27, 481–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, N.; Tibshirani, R. Standardization and the group lasso penalty. Stat. Sin. 2012, 22, 983–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ypma, A. Learning Methods for Machine Vibration Analysis and Health Monitoring. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Tax, D.M.J.; Ypma, A.; Duin, R.P. Pump Failure Detection Using Support Vector Data Descriptions. In International Symposium on Intelligent Data Analysis; Advances in Intelligent Data Analysis, IDA 1999, Lecture Notes in Computer Science Volume 1642; Hand, D.J., Kok, J.N., Berthold, M.R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).