A Fuzzy-Statistical Tolerance Interval from Residuals of Crisp Linear Regression Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Crisp Linear Regression
3. Fuzzy Linear Regression
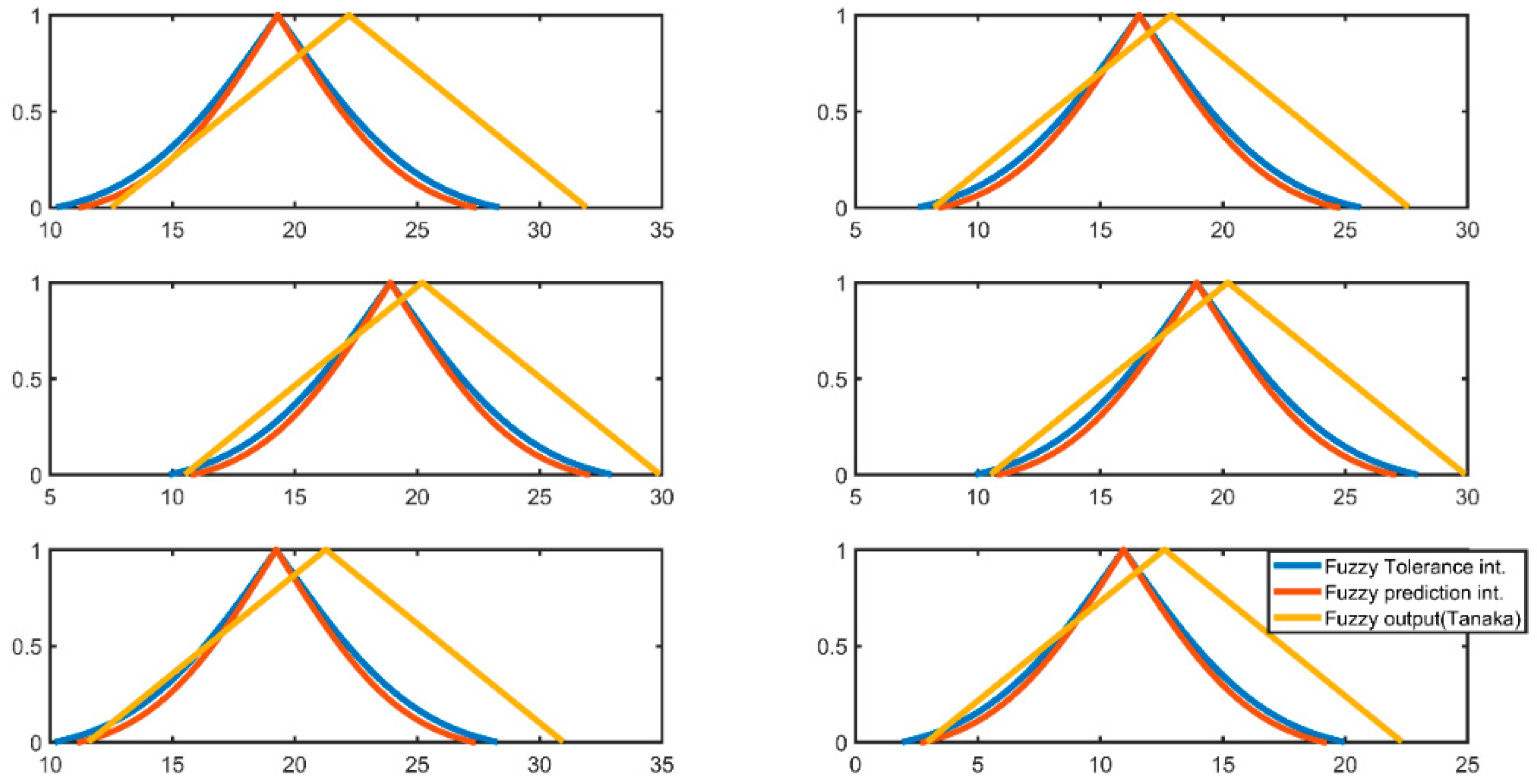
4. Proposed Method
5. Case Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tanaka, H.; Uegima, S.; Asai, K. Linear regression analysis with fuzzy model. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybernet. 1982, 12, 903–907. [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka, H.; Watada, J. Possibilistic linear systems and their application to the linear regression model. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1988, 27, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savić, D.; Pedrycz, W. Evaluation of fuzzy linear regression models. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1991, 39, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, J.J. Fuzzy statistics: Hypothesis testing. Soft Comput. 2004, 9, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-H.O.; Ayyub, B.M. Fuzzy regression methods—A comparative assessment. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2001, 119, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Moskowitz, H.; Köksalan, M. Fuzzy versus statistical linear regression. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1996, 92, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjenughwure, K.; Papadopoulos, B. Constructing fuzzy-statistical prediction intervals from crisp linear regression models. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference of Numerical Analysis and Applied Mathematics, Rhodes, Greece, 13–18 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Adjenughwure, K.; Papadopoulos, B. Constructing fuzzy numbers from arbitrary statistical intervals. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Evolving and Adaptive Intelligent Systems (EAIS), Rhodes, Greece, 25–27 May 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kao, C.; Chyu, C.-L. A fuzzy linear regression model with better explanatory power. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2002, 126, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, W.A. Tolerance intervals for linear regression. In Proceedings of the Second Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability, Berkeley, CA, USA, 31 July–12 August 1950; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1951. [Google Scholar]
- Young, D.S. tolerance: An R Package for Estimating Tolerance Intervals. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, A.; Wolfowitz, J. Tolerance Limits for a Normal Distribution. Ann. Math. Stat. 1946, 17, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, W.G. Two-sided Tolerance Limits for Normal Populations—Some Improvements. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1969, 64, 610–620. [Google Scholar]
- Sfiris, D.; Papadopoulos, B. Non-asymptotic fuzzy estimators based on confidence intervals. Inf. Sci. 2014, 279, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, D.; Foulloy, L.; Mauris, G.; Prade, H. Probability-Possibility Transformations, Triangular Fuzzy Sets, and Probabilistic Inequalities. Reliab. Comput. 2004, 10, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Y. A systematic approach to optimizing h value for fuzzy linear regression with symmetric triangular fuzzy numbers. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichman, M. UCI Machine Learning Repository; School of Information and Computer Science, University of California: Irvine, CA, USA, 2013; Available online: http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml (accessed on 24 August 2020).
- Woods, H.; Steinour, H.H.; Starke, H.R. Effect of composition of Portland cement on heat evolved during hardening. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1932, 24, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C.; Peck, E.A. Introduction to Linear Regression Analysis, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Adjenughwure, K.; Papadopoulos, B. Fuzzy-statistical prediction intervals from crisp regression models. Evol. Syst. 2019, 11, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 29.50 | 31.30 | 37.60 | 39.90 | 39.90 | 40.30 | 41.50 | 43.60 | 45.70 | 47.80 | 49.50 | |
| 79.99 | 75.63 | 69.25 | 62.75 | 64.66 | 63.09 | 61.51 | 60.07 | 58.22 | 58.43 | 60.57 | |
| 133.60 | 137.63 | 147.86 | 196.76 | 220.53 | 223.25 | 233.19 | 265.67 | 335.16 | 411.29 | 460.68 |
| 50.10 | 50.20 | 49.90 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 50.00 | 50.90 | 53.10 | 55.20 | |
| 58.23 | 58.03 | 57.53 | 55.68 | 55.24 | 54.51 | 50.08 | 50.05 | 49.72 | |
| 477.96 | 474.02 | 466.80 | 466.16 | 469.80 | 468.95 | 476.24 | 499.39 | 521.20 |
| 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 16 | 18 | |
| 14 | 16 | 14 | 18 | 18 | 22 | 18 | 22 |
| Hvalue | A | Total Credibility |
|---|---|---|
| 0.3148 | y ∗ = (−610.8251, 0.0000) + (19.1484, 0.0000)x1 + (1.4018, 1.2301)x2 | 0.1371 |
| 0 | y = (−610.8233, 0.0000) + (19.1484, 0.0000)x1 + (1.4017, 0.8429)x2 | 0.1082 |
| 0.5 | y = (−610.8240, 0.0000) + (19.1484, 0.0000)x1 + (1.4017, 1.6857)x2 | 0.1271 |
| Confidence Level | Linear Model Based on Fuzzy Prediction Intervals (Data from Liu and Chen, 2013) | Total Credibility | Lowest Membership Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90% | y = (−1590.9) + (29.6726)x1 + (9.9906)x2 | 0.2153 | 0 |
| 95% | y = (−1590.9) + (29.6726)x1 + (9.9906)x2 | 0.2056 | 0.0169 |
| 99% | y = (−1590.9) + (29.6726)x1 + (9.9906)x2 | 0.1949 | 0.0566 |
| Proportion | Linear Model Based on Fuzzy Tolerance Interval (Data from Liu and Chen 2013) | Total Credibility | Lowest Membership Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90% | y = (−1590.9) + (29.6726)x1 + (9.9906)x2 | 0.2029 | 0 |
| 95% | y = (−1590.9) + (29.6726)x1 + (9.9906)x2 | 0.1871 | 0.0793 |
| 99% | y = (−1590.9) + (29.6726)x1 + (9.9906)x2 | 0.1631 | 0.1794 |
| Hvalue | Fuzzy Model (Data from Liu and Chen 2013) | Total Credibility |
|---|---|---|
| 0.2666 | y ∗ = (12.0000, 1.3635) + (0.6250,0.1704)x | 1.4960 |
| 0 | y = (12.0000, 1.000) + (0.6250,0.1300)x | 1.2984 |
| 0.7 | y = (12.0000, 3.330) + (0.6250,0.4200)x | 0.9736 |
| Confidence Level | Linear Model Based on Fuzzy Prediction Interval (Data from Liu and Chen 2013) | Total Credibility | Lowest Membership Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90% | y = (12.93) + (0.54)x | 1.5612 | 0.1371 |
| 95% | y = (12.93) + (0.54)x | 1.4698 | 0.1825 |
| 99% | y = (12.93) + (0.54)x | 1.3651 | 0.2155 |
| Proportion | Linear Model Based on Fuzzy Tolerance Interval (Data from Liu and Chen 2013) | Total Credibility | Lowest Membership Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90% | y = (12.93) + (0.54)x | 1.3813 | 0.2921 |
| 95% | y = (12.93) + (0.54)x | 1.1850 | 0.4034 |
| 99% | y = (12.93) + (0.54)x | 0.8866 | 0.5627 |
| Hvalue | Fuzzy Model (Car Data UCI Repository) | Total Credibility |
|---|---|---|
| 0.3 | y = (45.4865, 13.8711) + (−0.0026, 0.0000)x1 + (−1.091, 0.0000)x2 | 4.4629 |
| 0 | y * = (45.4865, 9.7097) + (−0.0026, 0.0000)x1 + (−1.091, 0.0000)x2 | 5.4725 |
| 0.5 | y = (45.4865, 19.4195) + (−0.0026, 0.0000)x1 + (−1.091, 0.0000)x2 | 3.7626 |
| Confidence Level | Linear Model Based on Fuzzy Prediction Intervals (Car data UCI Repository) | Total Credibility | Lowest Membership Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90% | y = (47.7694) + (−0.0066)x1 + (−0.0420)x2 | 7.9395 | 0 |
| 95% | y = (47.7694) + (−0.0066)x1 + (−0.0420)x2 | 7.6792 | 0 |
| 99% | y = (47.7694) + (−0.0066)x1 + (−0.0420)x2 | 7.3592 | 0 |
| Proportion | Linear Model Based on Fuzzy Tolerance Interval (Car data UCI Repository) | Total Credibility | Lowest Membership Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90% | y = (47.7694) + (−0.0066)x1 + (−0.0420)x2 | 7.7065 | 0 |
| 95% | y = (47.7694) + (−0.0066)x1 + (−0.0420)x2 | 7.4172 | 0 |
| 99% | y = (47.7694) + (−0.0066)x1 + (−0.0420)x2 | 7.0796 | 0 |
| Hvalue | Fuzzy Model (Hald Cement Dataset [17]) | Total Credibility |
|---|---|---|
| 0.2487 | y ∗ = (79.3955, 0.0000) + (1.5212, 0.2474)x1 + (0.3238, 0.0000)x2 + (−0.0839, 0.1453)x3 + (0.3187, 0.0000)x4 | 1.9208 |
| 0 | y = (79.3955, 0.0000) + (1.5212, 0.1859)x1 + (0.3238, 0.0000)x2 + (−0.0839, 0.1091)x3 + (0.3187, 0.0000)x4 | 1.7102 |
| 0.5 | y ∗ = (79.3955, 0.0000) + (1.5212, 0.3718)x1 + (0.3238, 0.0000)x2 + (−0.0839, 0.2183)x3 + (0.3187, 0.0000)x4 | 1.7059 |
| Confidence Level | Linear Model Based on Fuzzy Prediction Intervals (Hald Cement Dataset [17]) | Total Credibility | Lowest Membership Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90% | y = (62.4054) + (1.5511)x1 + (0.5102)x2 + (0.1091)x3 + (−0.1441)x4 | 1.8326 | 0.0762 |
| 95% | y = (62.4054) + (1.5511)x1 + (0.5102)x2 + (0.1091)x3 + (−0.1441)x4 | 1.7302 | 0.1248 |
| 99% | y = (62.4054) + (1.5511)x1 + (0.5102)x2 + (0.1091)x3 + (−0.1441)x4 | 1.6160 | 0.1602 |
| Proportion | Linear Model Based on Fuzzy Tolerance Interval (Hald Cement Dataset [17]) | Total Credibility | Lowest Membership Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 90% | y = (62.4054) + (1.5511)x1 + (0.5102)x2 + (0.1091)x3 + (−0.1441)x4 | 1.7655 | 0.1870 |
| 95% | y = (62.4054) + (1.5511)x1 + (0.5102)x2 + (0.1091)x3 + (−0.1441)x4 | 1.6683 | 0.2298 |
| 99% | y = (62.4054) + (1.5511)x1 + (0.5102)x2 + (0.1091)x3 + (−0.1441)x4 | 1.5724 | 0.2609 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Kandari, M.; Adjenughwure, K.; Papadopoulos, K. A Fuzzy-Statistical Tolerance Interval from Residuals of Crisp Linear Regression Models. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8091422
Al-Kandari M, Adjenughwure K, Papadopoulos K. A Fuzzy-Statistical Tolerance Interval from Residuals of Crisp Linear Regression Models. Mathematics. 2020; 8(9):1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8091422
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Kandari, Maryam, Kingsley Adjenughwure, and Kyriakos Papadopoulos. 2020. "A Fuzzy-Statistical Tolerance Interval from Residuals of Crisp Linear Regression Models" Mathematics 8, no. 9: 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8091422
APA StyleAl-Kandari, M., Adjenughwure, K., & Papadopoulos, K. (2020). A Fuzzy-Statistical Tolerance Interval from Residuals of Crisp Linear Regression Models. Mathematics, 8(9), 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8091422






