Abstract
A digraph D is an efficient open domination digraph if there exists a subset S of for which the open out-neighborhoods centered in the vertices of S form a partition of . In this work we deal with the efficient open domination digraphs among four standard products of digraphs. We present a method for constructing the efficient open domination Cartesian product of digraphs with one fixed factor. In particular, we characterize those for which the first factor has an underlying graph that is a path, a cycle or a star. We also characterize the efficient open domination strong product of digraphs that have factors whose underlying graphs are uni-cyclic graphs. The full characterizations of the efficient open domination direct and lexicographic product of digraphs are also given.
1. Introduction
In this work we join two natural concepts. The first one is operations on digraphs (under some rules) that result in a bigger digraph than the starting ones. The second one is partitions of sets. There exist many digraph products for which the vertex set is the Cartesian product of vertex sets of its factors (there are also several operations which have (di)graph product in their name, but the vertex set is defined in a different manner). They differ by the definitions of the edge sets. Among them, four are called standard products. These are the Cartesian product, the strong product, the direct product and the lexicographic product. One can find a rich bibliography about them (see [1]). One standard approach of studying the digraph products is to study their structure and how to recognize them. Another approach is to deduce the properties of (di)graph products with respect to some properties of their factors. The later is also the topic of this work.
Partitions of objects are always interesting and useful as a mathematical concept, as every partition yields an equivalence relation. This further enables a factor structure of starting objects, which often brings simplification and deeper insight. Therefore, it is natural to study different kinds of partitions and the existence of them. Unfortunately, we are often not in the position to describe the mentioned relation with the properties of the investigated objects. This often disables further studies.
Graph theory offers a wide range of possibilities for partitions, one of them being the partitions of vertices. Open neighborhoods are a natural example for partitioning the set of vertices. Among graphs this was initiated in 1993 by Cockayne et al. in [2], where such partitions were named total perfect codes. The terminology efficient open domination graphs was introduced by Gavlas and Schultz in 2002 (see [3]). The study of efficient open domination of Cayley graphs can be found in [4]. Grid graphs, that is Cartesian products of two paths, were investigated in [5,6,7] and direct products of graphs with such a partition were characterized in [8]. Characterizations of efficient open domination graphs among lexicographic, strong and disjunctive product of two graphs can be found in [9]. In the same paper [9] the Cartesian products of some known families of graphs with respect to efficient open domination were also investigated. Later, in [10], one factor of a Cartesian product was fixed while the other factor was characterized in such a way that its Cartesian product is an efficient open domination graph.
Existence of a partition of vertices of a graph into closed neighborhoods was initiated even earlier by Biggs in 1976 (see [11]) under the name 1-perfect graphs. The name efficient (closed) domination graphs was proposed later by Bange et al. in [12]. This subject became quite popular and throughout the years several combinatorial and computational results were presented. One of the latest results of this type is that the problem of efficient closed domination is solvable in polynomial time for the class of -free graphs, as shown in [13] and independently in [14]. This was further investigated in [15] for some subclasses of -free graphs. The authors use the maximum weight independent set problem of a square graph to which the efficient closed domination of G can be reduced. Among products the strong product was treated in [16] and the direct product of (an arbitrary number of) cycles was covered in a series of papers [17,18,19]. For the lexicographic product the topic was covered in [20], while Mollard deals with the efficient closed domination Cartesian product in [21]. Recently, graphs that are both efficient open and efficient closed domination at the same time were considered in [22].
In the case of digraphs one can also distinguish between in- and out-neighborhoods besides open and closed neighborhoods. However, this dilemma is artificial because if we reverse the orientation of the digraph, then in-neighborhoods become out-neighborhoods and vice versa. Hence, we can deal with efficient open and efficient closed domination digraphs. Efficient open domination digraphs were introduced in [23] and studied further in [24,25,26,27]. In [28] Schaudt presented a useful characterization under the name of efficient total domination digraphs. See also [29] for more recent results. As in the case of graphs, there is more literature concerning efficient closed domination digraphs than that of efficient open domination digraphs. Here we mention only [30], a recent work that brings the results on the efficient closed domination among standard products of digraphs.
The paper is organized as follows. In the coming section we first settle the terminology. A section with several results on efficient open domination Cartesian products of digraphs follows. There we present a method for constructing an efficient open domination Cartesian product of digraphs with one fixed factor. Section four is devoted to the efficient open domination strong products of digraphs. We characterize those for which the factors have uni-cyclic graphs as their underlying graphs. Moreover, we conjecture that these are the only efficient open domination digraphs among strong products. The last section brings characterizations of the efficient open domination direct and lexicographic products of digraphs.
2. Preliminaries
The terminology and basic definitions in this section are summarized from [30] where the authors present the results on the efficient closed domination among standard products of digraphs.
Let D be a digraph with the vertex set and the arc set . For any two vertices , we write as the arc with direction or orientation from u to v, and say u is adjacent to v, or v is adjacent from u. For an arc we also say that u is the in-neighbor of v and that v is the out-neighbor of u. For a vertex , the open out-neighborhood of v (open in-neighborhood of v) is (). The in-degree of v is , the out-degree of v is and the degree of v is . Moreover, is the closed in-neighborhood of v ( is the closed out-neighborhood of v). In the above notation we omit D if there is no ambiguity with respect to the digraph D. We similarly proceed with any other notation which uses such a style of subscripts. Throughout the paper we use .
A vertex v of D with is called an out-universal vertex, and if , then v is called an in-universal vertex. A vertex v of D with is called a sink, and if , then v is called a source. If , then v is an isolated vertex or a singleton. An arc of the form is called a loop and can be considered as a directed cycle of length one. A vertex v with is called a leaf and is either a sink (if ) or a source (if ). Clearly, any vertex u with is either a sink, or a source, or .
The underlying graph of a digraph D is a graph with and for every arc from D we have an edge in . If and are both arcs, then we have two edges between u and v in the underlying graph. A directed path is a digraph with one source and one sink where its underlying graph is isomorphic to a path . Similarly, a directed cycle is a digraph without sinks and sources with a cycle as its underlying graph. We also consider a loop as a directed cycle of length one and double arc with different orientation as a directed cycle of length two. The distance between two vertices u and v is the minimum number of arcs on a directed path from u to v or ∞ if such a directed path does not exist. For we denote by a digraph obtained from D by deleting all vertices from A. By we denote the subdigraph of D that is induced on the vertices from A.
Let D be a digraph and let . The set S is called a total dominating set of D if the open out-neighborhoods centered in vertices of S cover , that is . Let S be a total dominating set of D. If for every two different vertices , then the set not only covers but also partitions . In this case we say that S is an efficient open dominating set (or an EOD set for short) of D. If there exists an EOD set S for the digraph D, then D is called an efficient open domination digraph (or an EOD digraph for short). For we say that is efficient open domination set only (or an EOD set only for short) for a digraph if every vertex from has exactly one in-neighbor in and in addition .
Let D and F be digraphs. Different products of digraphs D and F have, similarly as in graphs, their set of vertices equal to . We roughly and briefly discuss the four standard products of digraphs: the Cartesian product , the direct product , the strong product and the lexicographic product (sometimes also denoted ). Adjacency in different products is defined as follows.
- In the Cartesian product there exists an arc from vertex to vertex if there exists an arc from d to in D and or and there exists an arc from f to in F.
- If there is an arc from d to in D and an arc from f to in F, then there exists an arc from to in the direct product .
- In the strong product we have if ( and ) or ( and ) or ( and ).
- There is an arc in the lexicographic product from a vertex to a vertex , whenever or ( and ).
Some examples of the above mentioned products appear in Figure 1.
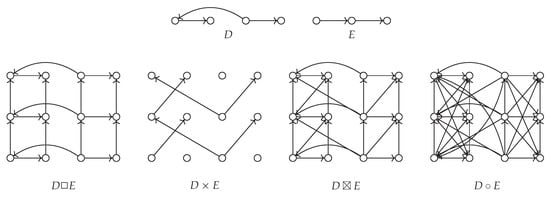
Figure 1.
The digraphs D and E, and their Cartesian, direct, strong and lexicographic products.
Let . The map defined by is called the projection map onto D. Similarly, we define as the projection map onto F. Projections are defined as maps between vertices, but frequently it is more convenient to see them as maps between digraphs. In this case we observe the subdigraphs induced by and for . Notice that in the Cartesian and in the strong product the arcs project either to arcs (with the same orientation) or to a vertex. In the case of the direct product arcs always project to arcs (with the same orientation). In the lexicographic product the projection maps arcs into arcs (with the same orientation) or into vertices. In the same product the projection maps arcs into vertices, into arcs with the same orientation, into arcs with different orientation or into two vertices without an arc between them.
For a fixed we call set a D-layer through f in , where . Symmetrically, an F-layer through d is defined for a fixed . Notice that for the Cartesian product, for the strong product and for the lexicographic product, is isomorphic to D and is isomorphic to F, respectively. In the case of the direct product loops play an important role. If there are no loops in f and in d, then the subdigraphs and are isomorphic to an empty digraph on and vertices, respectively. If we have and , then and are isomorphic to F and D, respectively.
It is easy to see that open out-neighborhoods in the direct product of digraphs satisfy
and for the lexicographic product of digraphs it holds that
Using these two equalities a complete characterization of the EOD digraphs among the direct and the lexicographic product is presented in the last section.
3. The Cartesian Product
Definition 1.
Let F be a digraph and let. Ifis an EOD set only for,, where, then we say that F is a k-EOD path divisible. Similarly, ifis an EOD set only for,, where, then we say that F is a k-EOD cycle divisible. We say that setsare k-EOD path or k-EOD cycle divisible sets of F.
Notice that every k-EOD path divisible digraph is also an EOD digraph, because is an EOD set only for . Therefore, an EOD digraph F with an EOD set is 1-EOD path divisible. Also if F is n-EOD path divisible, then it is also m-EOD path divisible for every . In particular, let F be a directed cycle, that is F is an EOD digraph with the EOD set . If we set and , then F is k-EOD path divisible for every positive integer k. If F is k-EOD path divisible, then it can happen that . See an example of this on Figure 2.
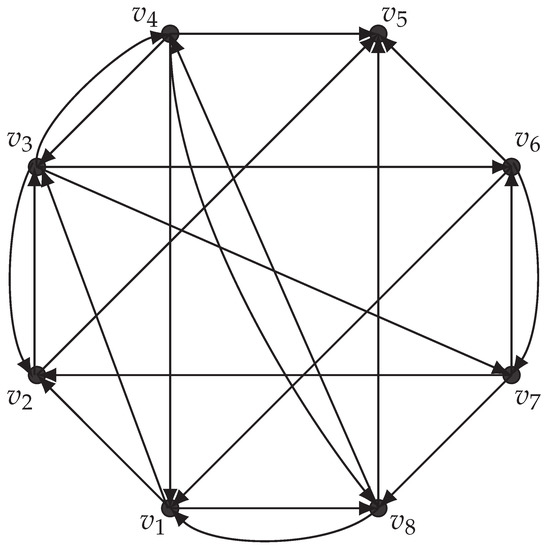
Figure 2.
4-EOD path divisible digraph with and with .
With the following example we underline the rich structure of n-EOD path (or cycle) divisible digraphs. We will show that every digraph can be an induced digraph of an n-EOD path (or cycle) divisible digraph. A complete digraph contains an arc in both directions between all different vertices of . Let . Digraph is obtained from by deleting all arcs , . For a digraph F we construct an n-EOD path divisible digraph in the folowing way. We take one copy of F and two copies of , the first copy containing the vertices and the second copy containing the vertices . The arc set of contains , all arcs from both copies of , the set , all arcs from the set and an arbitrary subset of . It is not hard to see that is an n-EOD path divisible digraph with n-EOD path divisible sets for every .
Similar construction can be done to get an n-EOD cycle divisible digraph. We only need to delete arcs and from . Also if F is an n-EOD cycle divisible digraph, then F is also an -EOD cycle divisible digraph, where -EOD cycle divisible sets are repeated cyclically k times.
Next we show that n-EOD path divisibility of F is essential for the Cartesian product to be an EOD digraph, where is a directed path.
Theorem 1.
Letbe a directed path and let F be a digraph. The Cartesian productis an EOD digraph if and only if F is an n-EOD path divisible digraph.
Proof.
Let be a directed path where is the source and is the sink and let F be an arbitrary digraph.
First assume that F is an n-EOD path divisible digraph. Denote by the subsets of that correspond with n-EOD path divisibility. We will show that is an EOD set of , meaning that for every and . For every it holds that because is an EOD set of F and therefore is an EOD set for . Since is a source of , there do not exist any other in-neighbors of vertices in except those already in , so . Next we observe for and . If , then has an in-neighbor in and if , then has an in-neighbor in . On the other hand these neighbors are unique in S, because and is an EOD set only for . Hence, S is an EOD set of , which is therefore an EOD digraph.
Now assume that is an EOD digraph and let S be its EOD set. Let for and let . Clearly, every vertex from must have exactly one in-neighbor in because is a source of . Therefore, is an EOD set of and . Now let . Vertices from have in-neighbors in and therefore do not have in-neighbors in , meaning that . On the other hand all other vertices in must have an in-neighbor in , because S is an EOD set of . Thus, is an EOD set only for . Therefore, yield that F is an n-EOD path divisible digraph. □
With n-EOD cycle divisibility one can describe all EOD digraphs among where is a directed cycle. The proof is very similar to the proof of Theorem 1 and is therefore omitted. The main difference is that we do not need to treat layer separately since everything follows from the general step.
Theorem 2.
Letbe a directed cycle and let F be a digraph. The Cartesian productis an EOD digraph if and only if F is an n-EOD cycle divisible digraph.
We continue with a path that is oriented in such a way, that it has exactly one source of degree two.
Theorem 3.
Let D be a digraph with an underlying graphwith such an orientation that,, is the only source, letand let F be a digraph. The Cartesian productis an EOD digraph if and only if F is an m-EOD path divisible digraph.
Proof.
Let be the only source of D. Thus is a directed path on k vertices, where is the source and is the sink, and is a directed path on vertices, where is the source and is the sink. Let . If F is m-EOD path divisible with sets , , then F is k-EOD path divisible with sets , and also -EOD path divisible with sets , . As shown in the proof of Theorem 1, sets and are EOD sets for and , respectively. Clearly, is an EOD set of because and is an EOD digraph.
Now assume that is an EOD digraph and let S be its EOD set. Since is a source, and are also EOD digraphs. By Theorem 1 F is a k-EOD path divisible digraph and an -EOD path divisible digraph. Hence, F is also m-EOD path divisible for . □
Before we deal with a path that is oriented in such a way, that it has exactly one sink of degree two, we need the following definition.
Definition 2.
Let F be a k-EOD and an ℓ-EOD path divisible digraph. We say that F is-sink friendly if there exist k-EOD path divisible setsand ℓ-EOD path divisible setssuch thatand there exists a set, which is an EOD set only for.
Theorem 4.
Let D be a digraph with an underlying graphwith such an orientation that,, is the only sink and let F be a digraph. The Cartesian productis an EOD digraph if and only if F is-sink friendly.
Proof.
Let F be digraph and let D be a digraph with an underlying graph where , , is the only sink. This means that and are the only sources of D.
First assume that F is -sink friendly. This means that there exist sets that yield -EOD path divisibility of F and sets that yield -EOD path divisibility of F. In addition, and there exists a set which is an EOD set only for . Let and . We will show that is an EOD set of . Let and be directed subpaths of D. By Theorem 1, and are EOD digraphs with EOD sets A and B, respectively. No vertex from is an in-neighbor of vertices from and , because is a sink. Therefore, there exists exactly one in-neighbor in S for every vertex from and . So, we only need to check for every . If , then is the in-neighbor of . On the other hand this is the only neighbor of from S because as and because is an EOD set only for . By symmetry we can see that has also exactly one in-neighbor in S whenever . So let . Clearly has no in-neighbor from S in and in . Since is an EOD set only for , there exists exactly one in-neighbor x of f in and is therefore the only neighbor of from S. Hence, S is an EOD set of which is therefore an EOD digraph.
Now assume that is an EOD digraph and let S be its EOD set. Again, for directed paths and , and are EOD digraphs with no influence from in a product . Sets for are -EOD path divisible sets by Theorem 1 and sets for (in reversed order) are -EOD path divisible sets by the same theorem. If , then has two in-neighbors and in S, a contradiction. Therefore, we have . Let and let f be an arbitrary vertex from . Clearly, has exactly one in-neighbor in because S is an EOD set. Also , , has no in-neighbor in as it has its unique in-neighbor either in S, in or in . Hence, is an EOD set only for and F is -sink friendly. □
The next challenge considering digraphs with an underlying graph isomorphic to a path or to a cycle is when we have more sinks and sources of degree two. Clearly, after every sink there comes a source and after each source there is a sink. In the case of a sink v of degree two digraph F must be -sink friendly by Theorem 4, where and are the distances to the sources that are closest to v. However this is not always enough. Let x and y be two sinks and let u be a source between them. By Theorem 4 digraph F must be -sink friendly and -sink friendly where and are the distances between u and x and u and y, respectively. We say that F is -source friendly if . Here, sets and are appropriate - and -EOD path divisible sets from -sink friendly and -sink friendly constellation, respectively. Now, if we can assure sink friendliness for each sink, and also source friendliness for each source of a digraph F, then this is characteristic for to be an EOD digraph. Here, the underlying graph of D is either or with more than one source or sink of degree two. Because the proof is very similar and the formal statement is problematic (it depends on the status of vertices of degree one in D), we omit the proof of this.
We end this section with another fixed factor which this time has a star as its underlying graph. Vertex of degree n is the source and all the others are sinks.
Theorem 5.
Let D be a digraph with an underlying graphwith the set of vertices, whereand let F be an arbitrary digraph. The Cartesian productis an EOD digraph if and only if F is a 2-EOD path divisible digraph.
Proof.
Let D be a digraph with an underlying graph with the set of vertices , where , which means that is the source. Clearly, and is a sink for every . Let F be an arbitrary digraph. Denote by A the set of vertices of .
First assume that F is 2-EOD path divisible with sets and . We will show that is an EOD set for , meaning that for every . For every it holds that since is an EOD set for F and therefore is an EOD set for . Since is a source, there do not exist any other in-neighbors of vertices except those from , so . Now let , . Vertices from are the in-neighbors of all of the vertices from and, since F is 2-EOD path divisible, vertices from are the in-neighbors of all of the vertices from . So . By the definition of 2-EOD path divisibility it holds that , meaning that .
Now assume that is an EOD digraph and let S be its EOD set. Let be an arbitrary vertex of the star D different from . Vertices from are in-neighbors of some (or all) of the vertices of . Denote the set of those vertices by . Vertices from have to have in-neighbors in , since they do not have in-neighbors in . Vertices from are not in-neighbors of any of the vertices from , since that would mean that there exists for which , a contradiction with S being an EOD set of . Let and . Clearly, is an EOD set of F and is an EOD set only for . Hence, F is a 2-EOD path divisible digraph. □
4. The Strong Product
In this section we first characterize all EOD strong product digraphs , such that the underlying graphs of D and F are cycles and , respectively. Then we extend this result to a characterization of all EOD digraphs where D and F have uni-cyclic graphs as their underlying graphs. We also conjecture that there are no more EOD digraphs among the strong product of digraphs. We start with several lemmas that come in handy later.
Lemma 1.
Let D and F be two digraphs without isolated vertices. If one of them has a source, thenis not an EOD digraph.
Proof.
Let D and F be two digraphs. If D has a source u and F has a source v, then vertex is a source in and it has no in-neighbor. Hence, there does not exist an EOD set for . Without loss of generality let D have a source u and let F be an arbitrary digraph without a source. We will try to construct an EOD set S for . Since u is a source, vertex has in-neighbors only in , and since F does not have a source at least one in-neighbor of exists. Let be the in-neighbor of . Again, since u is a source and F has no source, there exists an in-neighbor of . Denote by an out-neighbor of u in D. It exists since D contains no isolated vertices. By the definition of the strong product of two digraphs, both and are in-neighbors of and since vertex has two different in-neighbors in S. Meaning that S is not an EOD-set, so is not an EOD digraph. □
In the rest of this section we use the following notation and orientation for directed cycles and on m and n vertices, respectively, see Figure 3, and with we denote a vertex of a strong product of those two cycles. All operations on the first index i are via and on the second index j are via . We also partition into sets
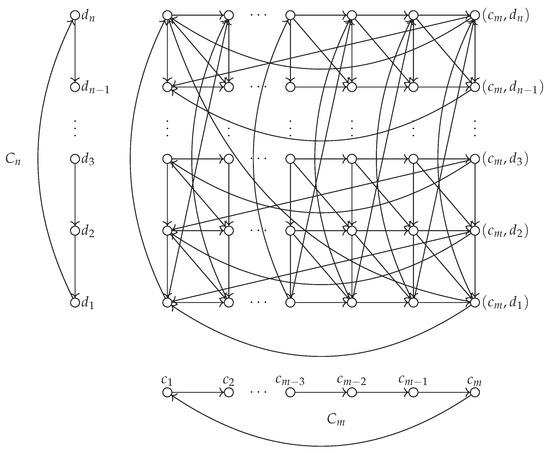
Figure 3.
The strong product of two directed cycles and .
Lemma 2.
If there exists an EOD set S for,, and, then.
Proof.
Let , , be an EOD digraph, let S be its EOD set and let . The vertex is an in-neighbor of and . On the other hand must also have an in-neighbor in S. The only in-neighbors of are and . If , then and are both in-neighbors of , a contradiction. Similarly, if , then and are both in-neighbors of , a contradiction again. Hence, must be in S. □
Lemma 3.
If there exists an EOD set S for,, and, then.
Proof.
Let , , be an EOD digraph and let S be its EOD set. With possible change of notation let . A vertex is an in-neighbor of the vertices , and . Vertex belongs to S by Lemma 2. Clearly, is also the in-neighbor of vertices and . So because otherwise has two in-neighbors in S. If , then has two in-neighbors in S again. So .
Vertex by Lemma 2 since and is an in-neighbor of and . One of the in-neighbors , or of the vertex must be in S. If , then has two in-neighbors in S. Similarly, if , then has two in-neighbors in S. Hence, .
We can exchange the role of factors and by symmetric arguments get that also belongs to S. □
Now we can characterize all EOD digraphs among strong product digraphs of two cycles.
Theorem 6.
Let D and F be digraphs with underlying graphsand, respectively. The strong productis an EOD digraph if and only if both D and F are directed cycles,andfor some.
Proof.
First, let and , , and let and be two directed cycles. Recall the sets and C from (3). We will show that A is an EOD set of . The in-neighbor of a vertex , , that is in A is , since . The in-neighbor of a vertex , , that is in A is , since . The in-neighbor of a vertex , , that is in A is , since . So every vertex v from is efficiently dominated by A. Moreover v has exactly one in-neighbor in A since exactly one in-neighbor of v has the sum of indices equal to .
To prove the contrary let D and F be two digraphs with underlying graphs and , respectively, such that is an EOD digraph with an EOD set S. If one of the cycles is not directed, then it has a source. By Lemma 1 the strong product is not an EOD digraph. So we may assume that both D and F are directed cycles. With possible change of notation we may assume that . By consecutive use of Lemma 3 we get that and that . If , then and by Lemma 3 again where . If , then and by Lemma 3 again where . Hence, and they are both the in-neighbors of , a contradiction. If , then and by Lemma 3 again where . Hence, and they are both the in-neighbors of , a contradiction again. Therefore, . By symmetric arguments we also get that and the proof is completed. □
Next we expand Theorem 6 and present a bigger class of EOD strong product digraphs. For this let be arbitrary trees with roots , respectively. We define an underlying graph such that we identify root with vertex of a cycle for every . Clearly, is exactly a uni-cyclic graph, but we need the before mentioned structure. Notice that if every tree is a one vertex tree. We say that a digraph with the underlying graph is well oriented if is a directed cycle and every edge from is oriented away from the root for every . We use the same notation for a digraph with the underlying graph .
Theorem 7.
Letbe two positive integers. The strong productis an EOD digraph if and only if bothandare well oriented,andfor some.
Proof.

First, let and , , and let and be well oriented. We show this direction in two steps. First let and we show that is an EOD digraph. By Theorem 6 is an EOD digraph with an EOD set A from (3). We extend set A to set for which we then show that it is an EOD set of . First we choose the notation for all the vertices from . With we denote all the vertices from with . Notice that different vertices from can have the same notation. Vertices from are then denoted as usual by . Furthermore, we denote sets , and . Now we partition into sets , and , where and C are from (3). We will show that is an EOD set of .
By Theorem 6 each vertex from A, B and C has exactly one in-neighbor in A. The in-neighbor of a vertex , , that is in is either or , since . The in-neighbor of a vertex , , that is in is , since . The in-neighbor of a vertex , , that is in is either or , since . So every vertex x from has an in-neighbor in . Moreover x has exactly one in-neighbor in since exactly one in-neighbor of x has the sum of indices equal to .
By symmetric arguments we can show that is an EOD digraph whenever . So, we can assume that and . We know by the above arguments that is an EOD digraph with an EOD set . Since there is no arc from vertices of to vertices of we will use the set for and enlarge it to that will be an EOD set of . For this we first need to present the following notation for vertices of D. By we denote all the vertices from D that belong to layers and and are at the distance k from . Similarly, we use for all the vertices from D that belong to layers and and are at the distance k from . Notice that different vertices from D can have the same notation. Beside we put and in if ( and ) or ( and ) or ( and ) for some .
We will show that is an EOD set of . We already know that is an EOD set of and we need to show that every vertex from D has exactly one in-neighbor in . Notice that every , where , has exactly three in-neighbors and . (If , then we put .) We need to consider nine cases. They are presented in the following Table 1.

Table 1.
Nine cases considered that show that every vertex from D has exactly one in-neighbor in .
In the first two columns we present all nine options. The middle column contains the in-neighbor of from and the last two columns show why this is the in-neighbor of in . Finally, we show that only one of the three in-neighbors of is in . If , then exactly one index of the other two in-neighbors differs by 1 from the same index of and they are therefore not in . By symmetry is also not in whenever either or is in . So let . In this case we can build a similar table as before, only that this table shows that is not in . Similarly, also when .
To prove the contrary let be an EOD digraph with an EOD set S. If there exists an arc in a tree that is not oriented away from the root, then we have a source in and with that a contradiction with Lemma 1. Hence, all arcs of trees from are oriented away from the root. If cycle is not a directed cycle, then we have a source on for some . Because all arcs of are oriented away from the root , we have a source in as well, a contradiction with Lemma 1 again. Hence, is well oriented. Also, must be well oriented by the same arguments. Next we observe a subdigraph of . By the orientation of all arcs of all the trees, we see that there does not exist an arc from vertices of to vertices of . Therefore, is an EOD digraph as well and by Theorem 6 we get and for some positive integers ℓ and k. □
The above results give rise to the following conjecture. We believe that it is true, but the proof is a challenge.
Conjecture 1.
The strong productis an EOD digraph if and only ifandare well oriented,andfor some.
5. The Direct and the Lexicographic Product
We conclude this paper with characterizations of the EOD digraphs among the direct and the lexicographic product. They follow from (1) and (2), respectively, and are no surprise. The following result for the direct product is an analogue of the result for the EOD graphs from [8] (under the name of total perfect codes).
Theorem 8.
Let D and F be digraphs. The direct productis an EOD digraph if and only if D and F are EOD digraphs.
Proof.
Let D and F be EOD digraphs with EOD sets and , respectively. We will show that is an EOD set of . By (1) it holds that
Suppose there exists a vertex that has two different in-neighbors and in . If , then , and by (1) we have
Thus, has two different in-neighbors f and in . That is a contradiction since in an EOD set of F. If , then and we obtain a contradiction by symmetric arguments. Meaning that and . Again by (1) the vertex has two different in-neighbors d and in and has two different in-neighbors f and in , a contradiction with and being EOD sets of D and F, respectively. Therefore, no two vertices from have a common out-neighbor, meaning that is an EOD digraph.
Now let be an EOD digraph and S be its EOD set. Let be an arbitrary vertex. Every vertex from has exactly one in-neighbor in S. Denote with the set of all those vertices. We will show that is an EOD set of D. Let d and be two different vertices from . Choose such that . If there exists such that d and are its in-neighbors, then has two in-neighbors and in S, a contradiction with S being an EOD set of . By (1) and because S is an EOD set of it also holds that . Therefore, is an EOD set of D, meaning that D is an EOD digraph. By symmetric arguments F is also an EOD digraph and with that the proof is completed. □
The result for EOD digraphs among the lexicographic product of digraphs is an analogue to the graph version from [9].
Theorem 9.
Let D and F be digraphs. The lexicographic productis an EOD digraph if and only if
- (i)
- D is a digraph without arcs and F is an EOD digraph, or
- (ii)
- D is an EOD digraph and F contains a sink.
Proof.
Let D be a digraph on n vertices without edges and F be an EOD digraph. Then is isomorphic to n copies of F and since F is an EOD digraph, n copies of F also form an EOD digraph.
Now, let D be an EOD digraph, let be its EOD set and let be a sink in F. We will show that is an EOD set of . By (2) it holds that since is a sink in F. So equals . If for and there exists a vertex in which in-neighbors are both and , then there also exists a vertex in D which in-neighbors are both d and . A contradiction with being an EOD set of D. Therefore, is an EOD digraph.
Conversely, let be an EOD digraph, S its EOD set and an arbitrary vertex. If f is not a sink in F, then there exists a vertex , such that is an in-neighbor of . Denote with the unique in-neighbor of from S. If , then has both and as its in-neighbors, which is not possible. Hence, . If d has any out-neighbors, then for every out-neighbor of d a vertex has both and as its in-neighbors, a contradiction. So no d such that has any out-neighbors. Since every vertex has exactly one in-neighbor , we conclude that yields that d has at least one out-neighbor, which is not possible. Therefore, and no has any out-neighbors. Meaning that D is a digraph without arcs. To prove that F is an EOD digraph choose an arbitrary F-layer (which always induces a digraph isomorphic to F). Clearly, the vertices in that are also in S form an EOD set of . So F is an EOD digraph and follows.
Now assume f is a sink. Notice that in this case is a subset of all out-neighbors of , where is an in-neighbor of d. We will prove that is an EOD set of D. Suppose it is not. Then there exist with a common out-neighbor. With this and (2) we have a contradiction with S being an EOD set of . Meaning that is an EOD set of D and follows. □
6. Conclusions
In this work we treated the four standard products of digraphs (the Cartesian, the strong, the direct and the lexicographic) with respect to the efficient open domination. The idea is to describe which digraphs among these products are efficient open domination digraphs and to describe them with the properties of their factors. We completely characterized such digraphs among the direct product (Theorem 8) and among the lexicographic product (Theorem 9). For the efficient open domination Cartesian product digraphs the characterizations are given for those for which the first factor has an underlying graph that is a path (Theorems 1, 3 and 4), a cycle (Theorem 2) or a star (Theorem 5). This yields an idea on how to deal with the Cartesian product of digraphs with one fixed factor and an arbitrary second one. Among the efficient open domination strong product of digraphs we characterized those in which both factors have uni-cyclic graphs as their underlying graphs (Theorems 6 and 7). We also conjecture that this are the only strong product digraphs that are the efficient open domination digraphs.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to this work. Conceptualization, D.B. and I.P.; methodology, D.B. and I.P.; formal analysis, D.B. and I.P.; validation, D.B. and I.P.; writing—original draft preparation, D.B. and I.P.; writing—review and editing, D.B. and I.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partially funded by Javna Agencija za Raziskovalno Dejavnost RS under grant numbers P1-0297 and J1-9109.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hammack, R.; Imrich, W.; Klavžar, S. Handbook of Product Graphs, Second Edition; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cockayne, E.J.; Hartnell, B.L.; Hedetniemi, S.T.; Laskar, R. Perfect domination in graphs. J. Comb. Inf. Syst. Sci. 1993, 18, 136–148. [Google Scholar]
- Gavlas, H.; Schultz, K. Efficient open domination. Electron. Notes Discret. Math. 2002, 11, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamizh Chelvam, T. Efficient open domination in Cayley graphs. Appl. Math. Lett. 2012, 25, 1560–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowen, R.; Hechler, S.H.; Kennedy, J.W.; Steinberg, A. Odd neighborhood transversals on grid graphs. Discret. Math. 2007, 307, 2200–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dejter, I.J. Perfect domination in regular grid graphs. Australas. J. Combin. 2008, 42, 99–114. [Google Scholar]
- Klostermeyer, W.F.; Goldwasser, J.L. Total Perfect Codes in Grid Graphs. Bull. Inst. Combin. Appl. 2006, 46, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Abay-Asmerom, G.; Hammack, R.H.; Taylor, D.T. Total perfect codes in tensor products of graphs. Ars Combin. 2008, 88, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Kuziak, D.; Peterin, I.; Yero, I.G. Efficient open domination in graph products. Discret. Math. Theoret. Comput. Sci. 2014, 16, 105–120. [Google Scholar]
- Kraner Šumenjak, T.; Peterin, I.; Rall, D.F.; Tepeh, A. Partitioning the vertex set of G to make G□H an efficient open domination graph. Discret. Math. Theoret. Comput. Sci. 2016, 18, 1503. [Google Scholar]
- Biggs, N. Perfect codes in graphs. J. Combin. Theory Ser. B 1973, 15, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bange, D.W.; Barkauskas, A.E.; Slater, P.J. Disjoint dominating sets in trees. Sandia Lab. Rep. SAND 1978, 78, 1087J. [Google Scholar]
- Lokshtanov, D.; Pilipczuk, M.; van Leeuwen, E.J. Independence and Efficient Domination on P6-free Graphs. ACM Trans. Algorithms 2017, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandstädt, A.; Mosca, R. Weighted Efficient Domination for P6-free Graphs. Tech. Rep. 2015, arXiv:1508.07733v2. [Google Scholar]
- Brandstädt, A.; Eschen, E.M.; Friese, E.; Karthick, T. Efficient domination for classes of P6-free graphs. Discret. Appl. Math. 2017, 233, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Abay-Asmerom, G.; Hammack, R.H.; Taylor, D.T. Perfect r-codes in strong products of graphs. Bull. Inst. Combin. Appl. 2009, 55, 66–72. [Google Scholar]
- Jerebic, J.; Klavžar, S.; Špacapan, S. Characterizing r-perfect codes in direct products of two and three cycles. Inf. Process. Lett. 2005, 94, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klavžar, S.; Špacapan, S.; Žerovnik, J. An almost complete description of perfect codes in direct products of cycles. Adv. Appl. Math. 2006, 37, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Žerovnik, J. Perfect codes in direct products of cycles—a complete characterization. Adv. in Appl. Math. 2008, 41, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.T. Perfect r-codes in lexicographic products of graphs. Ars Combin. 2009, 93, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- Mollard, M. On perfect codes in Cartesian products of graphs. Eur. J. Combin. 2011, 32, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Klavžar, S.; Peterin, I.; Yero, I.G. Graphs that are simultaneously efficient open domination and efficient closed domination graphs. Discret. Appl. Math. 2017, 217, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barkauskas, A.E.; Host, L.H. Finding efficient dominating sets in oriented graphs. Congr. Numer. 1993, 98, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Xu, J.-M. The bondage numbers and efficient dominations of vertex-transitive graphs. Discret. Math. 2008, 308, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Martinez, C.; Beivide, R.; Gabidulin, E. Perfect codes for metrics induced by circulant graphs. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2007, 53, 3042–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niepel, Ĺ.; Černý, A. Efficient domination in directed tori and the Vizing’s conjecture for directed graphs. Ars Combin. 2009, 91, 411–422. [Google Scholar]
- Schwenk, A.J.; Yue, B.Q. Efficient dominating sets in labeled rooted oriented trees. Discrete Math. 2005, 305, 276–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schaudt, O. Efficient total domination in digraphs. J. Discret. Algorithms 2012, 15, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sohn, M.Y.; Chen, X.-G.; Hu, F.-T. On efficiently total dominatable digraphs. Bull. Malays. Math. Sci. Soc. 2018, 41, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterin, I.; Yero, I.G. Efficient closed domination in digraph products. J. Combin. Optim. 2019, 38, 130–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).