Abstract
In this paper, unpredictable oscillations in Hopfield-type neural networks is under investigation. The motion strongly relates to Poincaré chaos. Thus, the importance of the dynamics is indisputable for those problems of artificial intelligence, brain activity and robotics, which rely on chaos. Sufficient conditions for the existence and uniqueness of exponentially stable unpredictable solutions are determined. The oscillations continue the line of periodic and almost periodic motions, which already are verified as effective instruments of analysis and applications for image recognition, information processing and other areas of neuroscience. The concept of strongly unpredictable oscillations is a significant novelty of the present research, since the presence of chaos in each coordinate of the space state provides new opportunities in applications. Additionally to the theoretical analysis, we have provided strong simulation arguments, considering that all of the assumed conditions are fulfilled.
1. Introduction
The Hopfield type neural networks were first developed in 1982 [1], through establishing the connection of neural networks with physical systems considered in statistical mechanics [2]. Hopfield neural network is an artificial neural network for storing and retrieving memory similar to the human brain. In the last decades, many works have been devoted to the study of Hopfield type neural networks. For example, periodic and almost periodic solutions [3,4], exponential stability [5,6,7], domain of attraction and convergence rate [8,9,10] have been deeply investigated.
The deterministic model proposed by J. Hopfield [11] is based on continuous variables and responses. The model contains a set of neurons and each neuron has the same architectural connection. More precisely, it is a single-layered and recurrent network where each neuron is connected to other neurons. Therefore, neurons are modeled as amplifiers combined with feedback circuits made up of wires, resistors and capacitors.
Oscillations are important in the human brain activity, they are relative to various cognitive tasks. The theory of oscillations in neural systems is widespread and successfully applied in the field of neuroscience [12]. The investigation of neural networks with chaotic oscillations has been of strong interest of numerous researchers [13,14,15]. Chaos is useful in many applications of neural networks such as separating image segments [16,17,18,19], synchronization [20,21,22], pattern recognition [23] and information processing [24].
Chaotic oscillations were widely studied in human physiological systems and particularly in the dynamics of human brain [24,25,26]. Chaotic behavior resulting from self-organized processes in the human brain could explain “randomness” of neural synchronization associated with cognitive functions and consciousness, as well as mental disorganization associated with psycho pathological phenomena [27,28,29].
The methodical background of the present research lies entirely in the theory of dynamical systems founded by H. Poincaré and G. Birkhoff [30,31]. It was the French genius, who determined that underneath of chaotic dynamics is the Poisson stable motion. In papers [32,33], we continue the line of different types of oscillations. It was proved that a Poisson stable motion equipped with the unpredictability property determines sensitivity in the quasi-minimal set. Thus, the painting of Poincaré on chaos dynamics, had been completed. It is usual that dynamical properties generate functional ones. For example, recurrent or almost periodic motions allow us to define recurrent and almost periodic functions, respectively. Similarly, issuing from the unpredictable point introduced in [32], in paper [33], the unpredictable function was defined as a point of the Bebutov dynamics, where the state space is a set of functions. In our next research [34], we have learned that the metrical state space of the Bebutov dynamics can be replaced with the topological space, where convergence of functions on compact sets of the real axis is applied. The space is metrizable. This made our suggestions more universal and effective in applications, since constructive verifiable conditions were proposed. The method has been realized in several papers [32,33,34,35,36,37,38] and the book [39]. In the present study it is applied in the circumstances of the Hopfield neural network with the unpredictability happen in each coordinate of the motion. This is why, besides new application opportunities, we meet additional theoretical challenges.
A new type of oscillations, which are described by unpredictable functions, was introduced in [32]. It relies on the dynamics of unpredictable points and Poincaré chaos [33]. Unpredictable points and unpredictable functions promise to be useful in the further development in theory of chaos. For instance, the unpredictable points are used by A. Miller in [40], R. Thakur and R. Das in [41], where they considered Poincaré chaos, strongly Ruelle–Takens chaos and strongly Auslander–Yorke chaos in semiflow. The study of unpredictable functions have been widely developed both theoretically [32,33,34,35,36,37,38], as well as in applications [39,42,43]. In paper [43], a new randomly defined unpredictable function was introduced. Thus, the list of unpredictable functions has been essentially extended. Now, it is possible to determine unpredictable functions by simulation discrete stochastic processes. Moreover, existence of unpredictable oscillations can be considered for differential equations of various types.
In this article, we have designed the new model of Hopfield type neural networks with unpredictable perturbations and derive sufficient conditions of the existence, uniqueness, and asymptotic stability of the strongly unpredictable oscillations, which develop previously known results in [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10], and others.
This paper is organized as follows. The main results of the present study are placed in Section 3, where the existence, uniqueness and stability of strongly unpredictable oscillations of Hopfield-type neural networks systems are investigated. The topology of uniform convergence on compact sets and the contraction mapping principle are utilized to prove the existence of the unpredictable motions. In Section 4, we demonstrate examples of unpredictable solutions, which support theoretical discussions of the paper. Finally, in Section 5, the results of the article are outlined.
2. Preliminaries
The main subjects under investigation in this paper are the following Hopfield-type neural networks:
where t is the time variable, p denotes the number of neurons in the network, corresponds to the membrane potential of the unit i, at time Moreover, are constant rates with which the units self-regulate or reset their potential when isolated from other units and inputs, with , denotes the measures of activation to its incoming potentials of the unit i at time t, the constants , , denote the synaptic connection weight of the unit j on the unit i. The function corresponds to the external input from outside the network to the unit i, for .
Let and be the set of real and natural numbers, respectively.
We assume that the coefficients are real numbers, the activation functions , and perturbations are continuous functions. Additionally, we introduce the norm where is the absolute value, and .
Let us commence with a preliminary definition of the unpredictable sequence.
Definition 1.
[35] A bounded sequence , in is called unpredictable if there exist a positive number and sequences , , , of positive integers both of which diverge to infinity such that as for each k in bounded intervals of integers and for each .
The following definition is one of the main in our study.
Definition 2.
[32] A uniformly continuous and bounded function is unpredictable if there exist positive numbers and sequences , both of which diverge to infinity such that as uniformly on compact subsets of and for each and .
From the last definition, it implies that some coordinates may not be scalar valued unpredictable functions. That is why it is of significant importance for applications to consider functions with unpredictability in all their coordinates—strongly unpredictable functions.
Definition 3.
A uniformly continuous and bounded function , , is strongly unpredictable if there exist positive numbers and sequences , both of which diverge to infinity such that as uniformly on compact subsets of and for each and .
Based on the Definition 2, it is easy to indicate that any strongly unpredictable function is an unpredictable function, but not vice versa. Furthermore, each of the functions , in the Definition 3 are unpredictable in the sense of the Definition 2.
3. Main Results
Denote by the space of vector-functions, , , with norm , satisfying the following conditions:
- (U1) are uniformly continuous;
- (U2) there exists a positive number H such that for all
- (U3) there exists a sequence , as , such that for each the sequence uniformly converges to on compact subsets.
We will need the following conditions:
- (C1) the function , in (1) belongs to space and there exist positive numbers and sequences as , which satisfy for each , and such that the function is strongly unpredictable;
- (C2) there exists a positive number L, such that , , for all ;
- (C3) the inequalities , are valid with positive numbers and ;
- (C4) and where is a positive number, for all and
- (C5);
- (C6).
In the following, the next assertion is used:
Lemma 1.
[44] A function is a bounded solution of Equation (1), if and only if it is a solution of the following integral equation:
for all
Let us introduce in the space the following operator, where
for all
Lemma 2.
The operator Π is invariant in .
Proof.
To prove the lemma, one needs to verify conditions (U1)–(U3).
One can check that
for all and . That is, the derivatives are bounded and consequently the condition (U1) for is valid.
Now, we will demonstrate that satisfies the condition . For a function and fixed , we have that
The last inequality and condition (C5) imply that
Next, will show that the sequence as uniformly on compact subsets.
Fix an arbitrary and a section
Choose numbers and such that
and
for all .
Consider the number n large enough for and on . For a function belonging to and fixed , it is true that
Lemma 3.
If conditions – are valid, then Π is a contraction operator.
Proof.
Let us take two functions such that , and We have that for a fixed
Therefore, , and condition (C6) imply that is a contraction operator in . □
Theorem 1.
Proof.
are valid.
Firstly, let us check the completeness of the space . Consider a Cauchy sequence in , which converges to a limit function on . We start with the condition because other two properties can be easily checked. Fix a closed, bounded interval We get that
Choose sufficiently large n and k, so that each term on the right side of (6) is smaller than for an arbitrary and . Thus, one can conclude that the sequence is uniformly converging to on We have shown that the space is complete. Apply the contraction mapping theorem, duo to Lemmas 2 and 3, there exists a unique solution of the Equation (1).
Further, applying the relations
and
we obtain that
One can fix a natural numbers l and k, and positive number such that
Let the numbers and a number , be fixed.
Denote Consider the following two alternatives: (i) (ii) , and consequently, the rest of the proof falls into two parts.
(ii) For the case , we get that
if . Thus, it can be inferred that solution is strongly unpredictable.
At last, we shall prove the stability of the solution . It is true that
for all
Let be another solution of system (1). Then
for all
Making use of the relation
for all we have that
for all
Thus, it is shown that
where , and multiplying both sides of this inequality by we get
Next, applying Gronwall–Belman Lemma, one can obtain
Therefore, (C6) implies that is a uniformly exponentially stable solution of the system (1). The theorem is proved. □
4. Examples
It is not possible to find the initial data of unpredictable solutions. Therefore, in the present examples, we visualize unpredictable oscillations through graphs of attracted neighbor solutions.
Example 1.
At first, we will design an unpredictable function. To that end, we use the dynamics of the logistic map in the same way as in [32]. Let us keep in mind the logistic map
where , and for [45]. According to Theorem 4.1 [32], for each the logistic map (11) possesses an unpredictable solution.
Let us denote by the unpredictable solution of the logistic map (11) with . The sequence inside the unit interval .
Since the sequence , there exist a positive number and sequences , both of which diverge to infinity such that as for each i in bounded intervals of integers and for each
Consider the function
where the function is defined by for The function is bounded on the whole real axis such that .
Next, we will show that is an unpredictable function. Consider a bounded and closed interval , and a number . Assume, without loss of generality, that α and β are integers. Choose a positive number ξ and an integer such that the following inequalities and are satisfied. Moreover, let n be a large natural number such that on .
Then, for all , we obtain that
Thus, as uniformly on the interval .
The following inequalities are valid, There exists a positive number such that
Let us fix the number κ and and consider two cases: (i) and (ii)
In what follows, we need the relation
(i) From the last relation, it implies that
for
Thus, is unpredictable function with positive numbers , and sequences and .
Let us rewrite the integral (12) as
where . It is worth noting that the simulation of an unpredictable function is impossible, since the initial value is not known.
That is why we will simulate a function which approaches to with increasing time. Let us determine
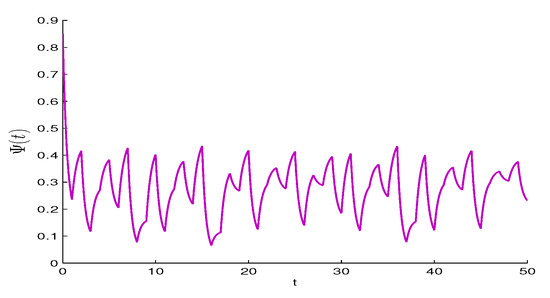
where is a fixed number, which is not necessarily equal to . Subtract (15) from (14) to obtain that , . That is, the difference exponentially diminishes. This means that the function exponentially tends to the unpredictable function , i.e., the graphs of these functions approach, as time increases. Instead of the curve describing the unpredictable solution, we can take the graph of . In Figure 1, we depict the graph defined by the initial value .

Figure 1.
The graph of function , which approximates the unpredictable function .
Example 2.
Let us introduce the following Hopfield type neural network:
where and
where is the unpredictable function from Example 1.
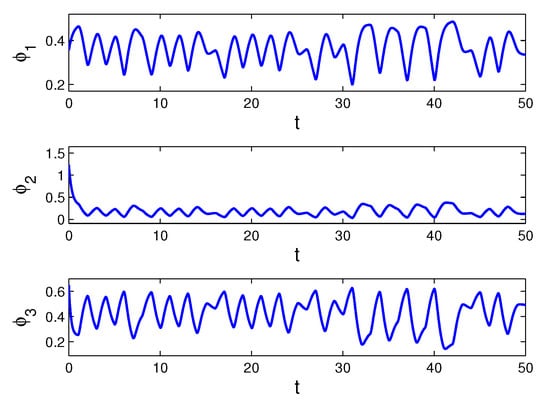
The perturbation function is unpredictable in accordance with Lemmas 1.4 and 1.5 [36]. The properties (C1)–(C6) hold for the system (16) with and The simulation results of solution for the system with the initial conditions , , , are shown in Figure 2. Similarly to Example 1, one can show that the solution approaches to the unpredictable solution as t increases. Additionally, from the graph it is seen that the maximum value does not exceed . Thus, if we take , then all conditions in Theorem 1 are fulfilled. According to the theorem, system (16) possesses a unique asymptotically stable unpredictable solution. The irregular behavior of the solution indicates the presence of an unpredictable solution in the dynamics of (16).

Figure 2.
The time series of the coordinates , and of the solution of system (16) with the initial conditions , , .
In the next example, we utilize the unpredictable solution for system (16) to form new perturbations.
Example 3.
Consider the system
where and
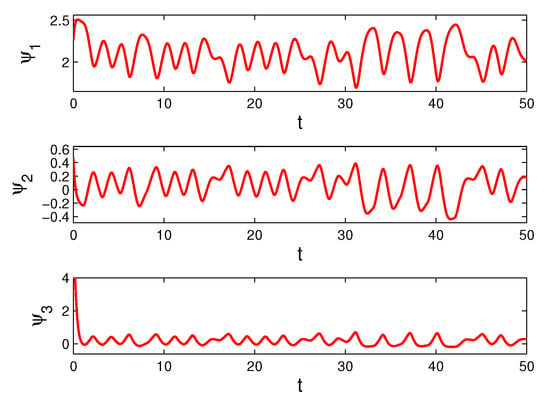
where is the solution of (16). The properties (C1)–(C6) hold for the system (17) with and That is why, according to the Theorem 1, system (17) possesses the unique asymptotically stable unpredictable solution. If one accepts , then the solutions of system (17) satisfy all conditions of the theorem. The simulation result of system (17), with the initial conditions , is shown in Figure 3. Likewise, in Example 2, the solution approaches to the unpredictable solution as time increases.

Figure 3.
The time series of the coordinates , and of the solution of system (17) with the initial conditions .
5. Conclusions
This is the first time that the Hopfield-type neural networks are considered for existence, uniqueness and asymptotic stability of unpredictable oscillations. The strength of the actuality of the research is increased as the oscillations are strongly related to the new type of dynamics, Poincaré chaos. Consequently, all the benefits, which are connected with chaos applications for artificial intelligence, robotics and engineering are extended for unpredictable oscillations. In the present research, the motions are specified with the condition of strong unpredictability, when the property is true for all coordinates of the dynamics. Thus, the chaos applications became more effective, since the motions are observable in each parameter of a process, and the phenomenon can be extended, if one applies the results of the paper for models with larger dimensions. Correspondingly, one can say about such effective methods of chaos analysis and applications as synchronization, control, stabilization of periodic solutions in future researches [20,21,22,24,29,46]. In addition, indication of unpredictable oscillations can be improved by application of the sequential test for the Poincaré chaos, which is developed in the paper [47].
Author Contributions
M.A.: conceptualization, methodology, investigation. M.T.: investigation, supervision, writing—review and editing. Z.N.: software, investigation, writing—original draft. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
M. Akhmet has been supported by a grant (118F161) from TÜBİTAK, the Scientific and Technological Research Council of Turkey. M. Tleubergenova and Z. Nugayeva have been supported by the MES RK grant No. AP05132573 “Cellular neural networks with continuous/discrete time and singular perturbations” (2018–2020) of the Committee of Science, Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hopfield, J.J. Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 2554–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramya, C.; Kavitha, G.; Shreedhara, K.S. Recalling of images using Hopfield neural network model. Natl. Conf. Comput. Commun. Controls 2011, 11, 2–4. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Q.; Matsui, K.; Huang, X. Existence and stability of periodic solutions for Hopfield neural network equations with periodic input. Nonlinear Anal. 2002, 49, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Huang, L. Existence and attractivity of almost periodic solutions of Hopfield Neural Networks. Math. Acta Sci. 2001, 21, 505–511. [Google Scholar]
- Akhmet, M.; Karacaören, M. A Hopfield neural network with multi-compartmental activation. Neural Comput. Appl. 2018, 29, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J. Global exponential stability of Hopfield neural networks. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2001, 32, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmet, M.U.; Arugaslan, D.; Yilmaz, E. Stability analysis of recurrent neural networks with piecewise constant argument of generalized type. Neural Netw. 2010, 23, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Tao, Q. Estimation of the domain of attraction and the convergence rate of a Hopfield associative memory and an application. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 2000, 60, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J. An estimation of the domain of attraction and convergence rate for Hopfield continuous feedback neural networks. Phys. Lett. A 2004, 325, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Peng, J. A New Approach for Estimating the Attraction Domain for Hopfield-Type Neural Networks. Neural Comput. 2009, 21, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfield, J.J. Neurons with graded response have collective computational properties like those of two-stage neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 81, 3088–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwin, P.; Coombes, S.; Nicks, R. Mathematical Frameworks for Oscillatory Network Dynamics in Neuroscience. J. Math. Neurosci. 2016, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aihara, K.; Takabe, T.; Toyoda, M. Chaotic Neural Networks. Phys. Lett. A 1990, 6, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Roy, A.B.; Das, P. Chaos in a three dimensional neural network. Appl. Math. Model. 2000, 24, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Li, Q.D.; Yang, X.-S. Horseshoe chaos in a class of simple Hopfield neural networks. Chaos Solit. Fract. 2009, 39, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibasaki, M.; Adachi, M. Response to external input of chaotic neural networks based on Newman—Watts model. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Brisbane, Australia, 10–15 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sang, N.; Zhang, T. Segmentation of FLIR images by Hopfield neural network with edge constraint. Pattern Recognit. 2001, 34, 811–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raiko, T.; Valpola, H. Oscillatory neural network for image segmentation with biased competition for attention. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2011, 718, 75–85. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.C.; Lin, Z.C.; Mao, C.W. The Application of Competitive Hopfield Neural Network to Medical Image Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1996, 15, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, S. Adaptive lag synchronization of chaotic Cohen–Grossberg neural networks with discrete delays. Chaos 2012, 22, 033123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.P.; Wen, S.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, T.; Meng, Q.; Yao, W. Lag synchronization of switched neural networks via neural activation function and applications in image encryption. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 26, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales-Miranda, J.M. Synchronization and Control of Chaos; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, Q.; Oommen, J. Logistic Neural Networks: Their chaotic and pattern recognition propertie. Neurocomputing 2014, 125, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Chen, L.; Aihara, K. Associative memory with a controlled chaotic neural network. Neurocomputing 2008, 71, 2794–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erchova, I.; McGonigle, D.J. Rhythms of the brain: An examination of mixed mode oscillation approaches to the analysis of neurophysiological data. Chaos 2008, 18, 015115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, H.M.; Córdova, F.M.; Cañete, L.; Palominos, F.; Cifuentes, F.; Sánchez, C.; Herrera, M. Order and chaos in the brain: Fractal time series analysis of the EEG activity during a cognitive problem solving task. Proc. Comput. Sci. 2015, 55, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.; Avitabile, D.; Montbrio, E.; Roxin, A. Network mechanisms underlying the role of oscillations in cognitive tasks. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, M.; Abel, A. What changes in neural oscillations can reveal about developmental cognitive neuroscience: Language development as a case in point. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2013, 6, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, C.; Bergman, H.; Brown, P. Pathological synchronization in Parkinson’s disease: Networks, models and treatments. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poincaré, H. Les Methodes Nouvelles De La Mecanique Celeste; Gauthier-Villars: Paris, France, 1899; reprint Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1957; Volume III. [Google Scholar]
- Birkhoff, G.D. Dynamical Systems; Colloquium Publications: Providence, RI, USA, 1927. [Google Scholar]
- Akhmet, M.; Fen, M.O. Poincaré chaos and unpredictable functions. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Nr. Simul. 2017, 48, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmet, M.; Fen, M.O. Unpredictable points and chaos. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Nr. Simul. 2016, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmet, M.; Fen, M.O. Existence of unpredictable solutions and chaos. Turk. J. Math. 2017, 41, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmet, M.; Fen, M.O. Non-autonomous equations with unpredictable solutions. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Nr. Simul. 2018, 59, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmet, M.; Fen, M.O.; Tleubergenova, M.; Zhamanshin, A. Unpredictable solutions of linear differential and discrete equations. Turk. J. Math. 2019, 43, 2377–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmet, M.; Tleubergenova, M.; Zhamanshin, A. Quasilinear differential equations with strongly unpredictable solutions. Carpathion J. Math. 2020, 36, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Akhmet, M.; Tleubergenova, M.; Zhamanshin, A. Poincaré chaos for a hyperbolic quasilinear system. Miskolc Math. Notes 2019, 20, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmet, M.U.; Fen, M.O.; Alejaily, E.M. Dynamics with Chaos and Fractals; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, A. Unpredictable points and stronger versions of Ruelle–Takens and Auslander–Yorke chaos. Topol. Appl. 2019, 253, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R.; Das, R. Strongly Ruelle-Takens, strongly Auslander-Yorke and Poincaré chaos on semiflows. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simulat. 2019, 81, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmet, M.U.; Fen, M.O.; Alejaily, E.M. Extension of sea surface temperature unpredictability. Ocean Dyn. 2019, 69, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmet, M.; Fen, M.O.; Alejaily, E.M. A randomly determined unpredictable function. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.12758. [Google Scholar]
- Hartman, P. Ordinary Differential Equations; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Hale, J.; Koçak, H. Dynamics and Bifurcations; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Akhmet, M.; Fen, M.O. Replication of Chaos in Neural Networks, Economics and Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Akhmet, M.; Fen, M.O.; Tola, A. The Sequential Test for Chaos. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.09127. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).