Space–Time Radial Basis Function–Based Meshless Approach for Solving Convection–Diffusion Equations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Formulation
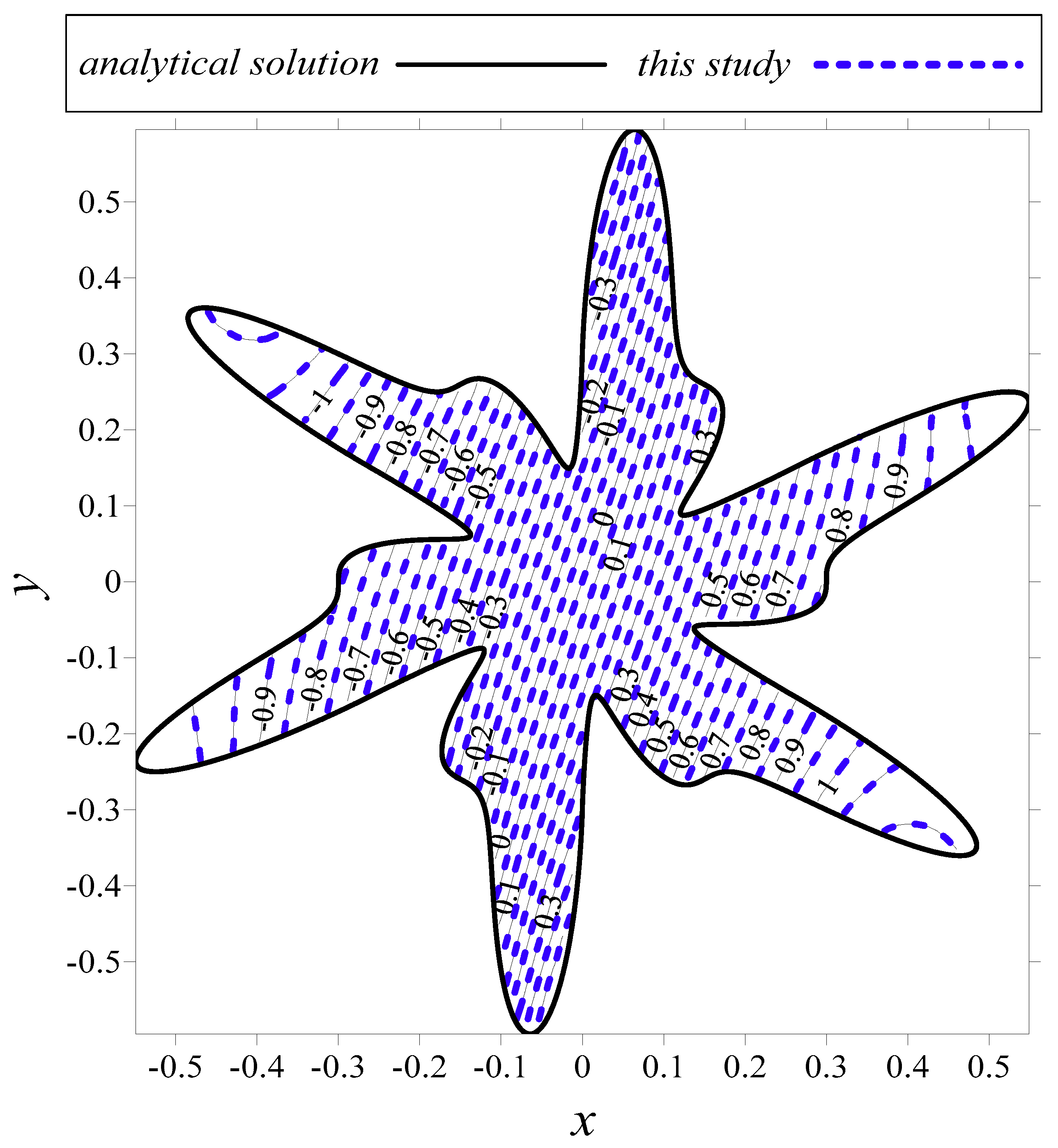
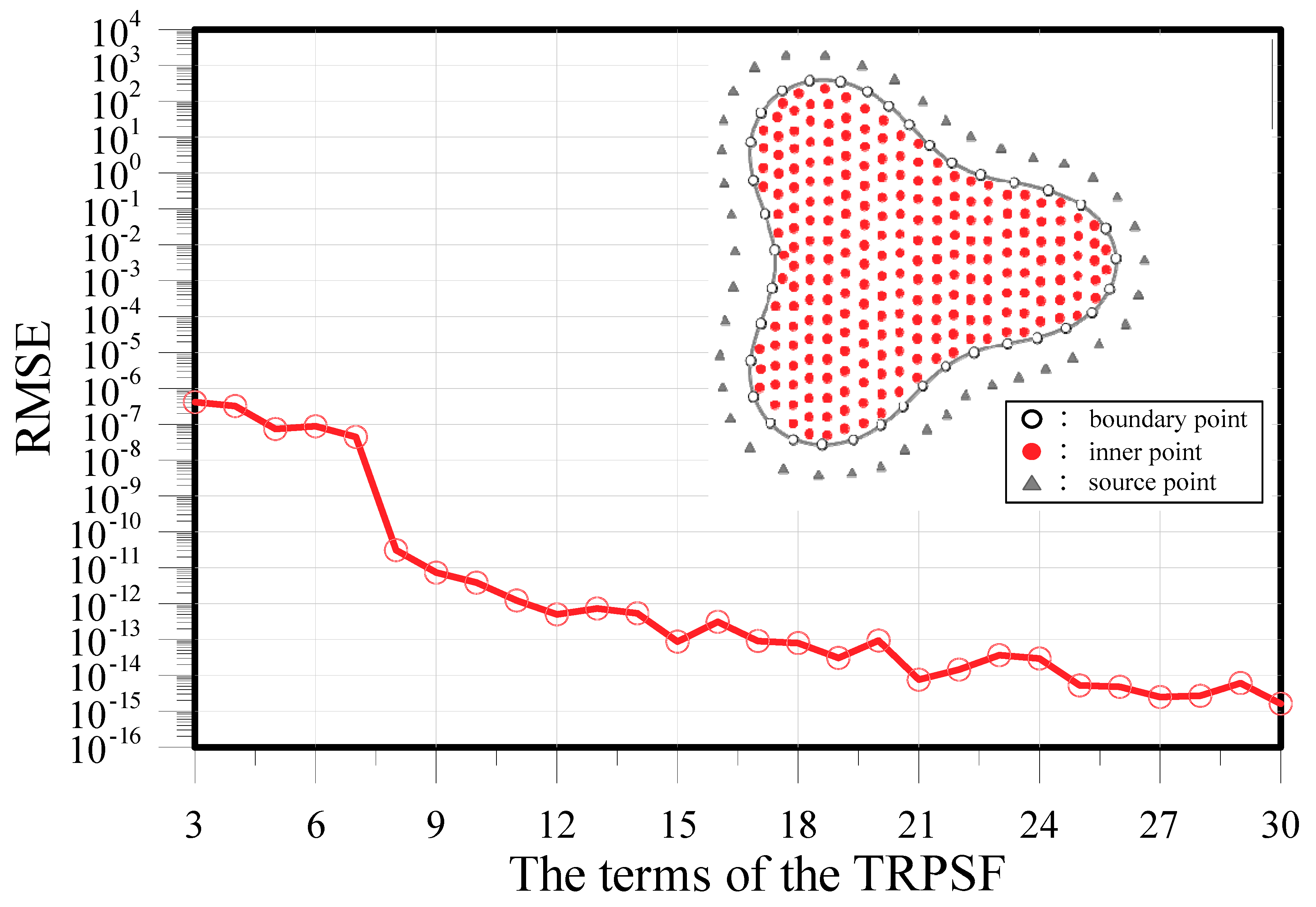
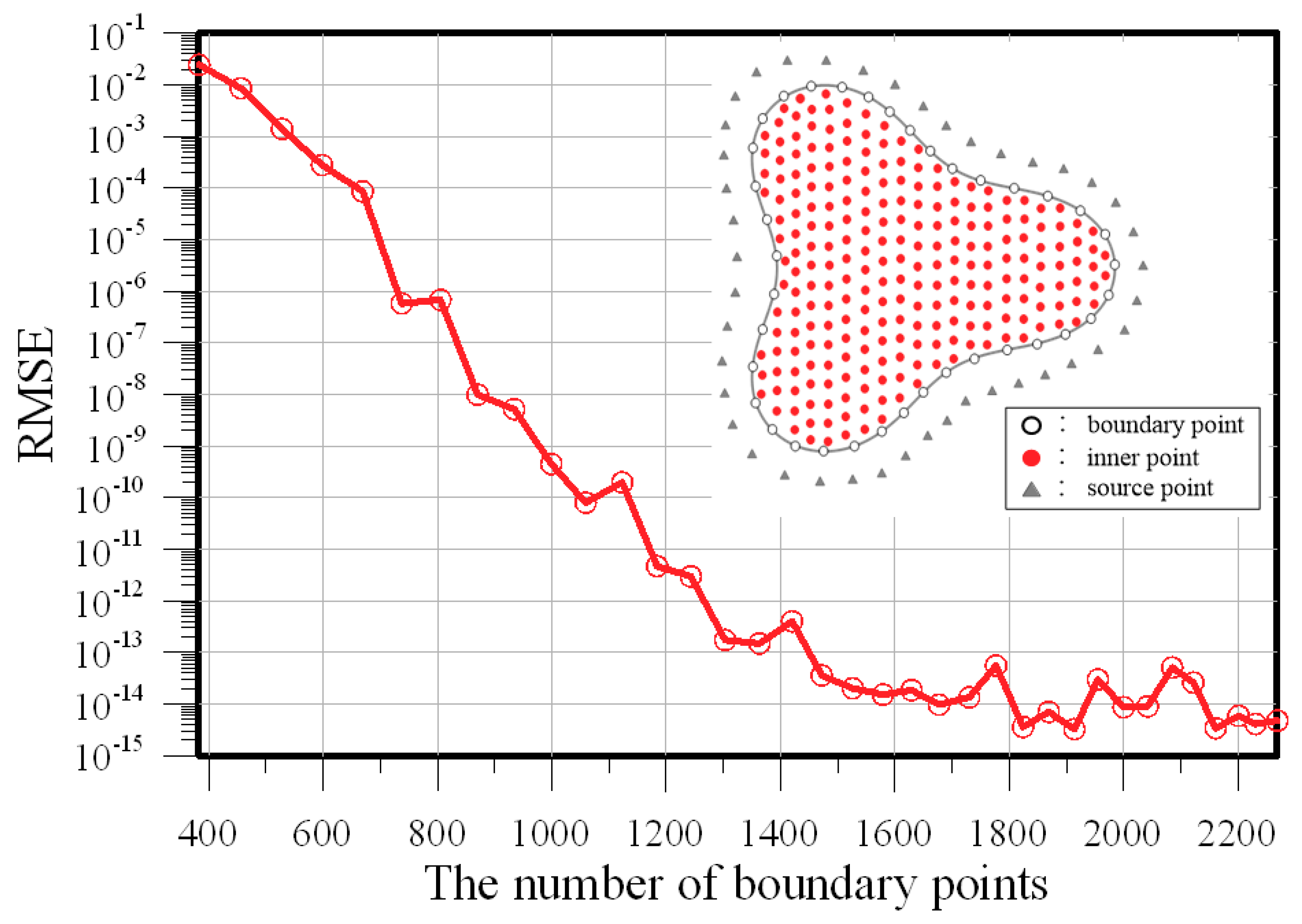
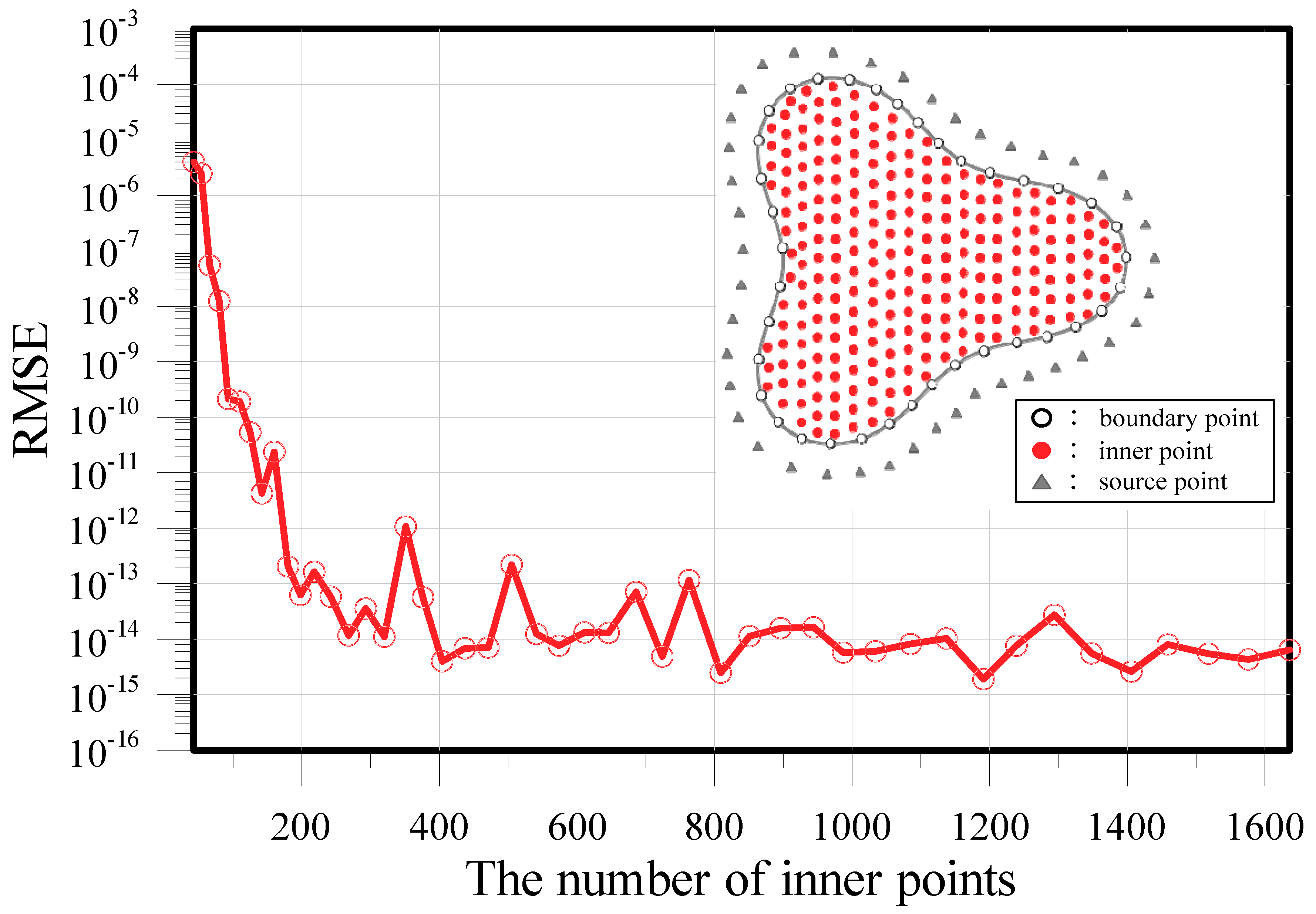
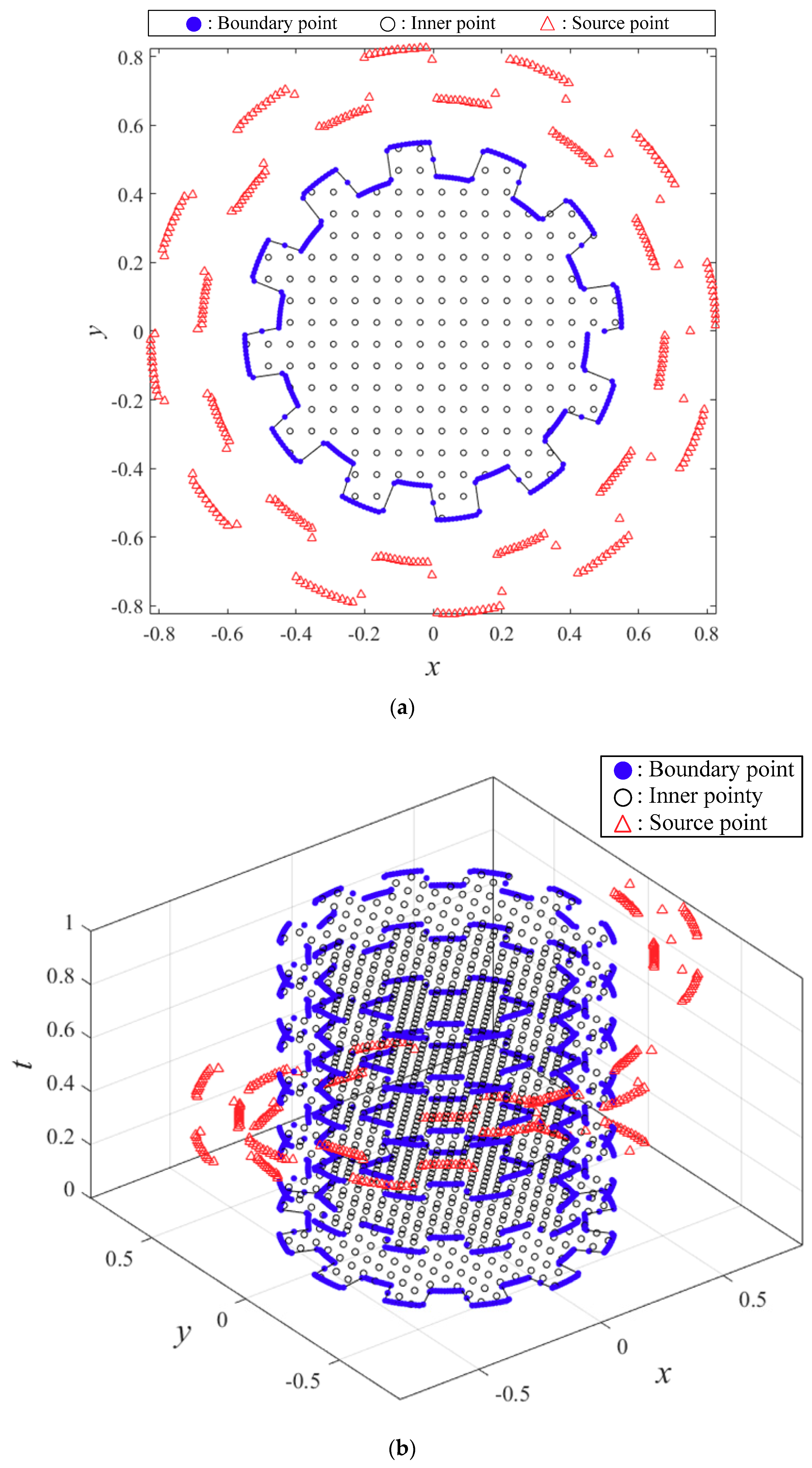
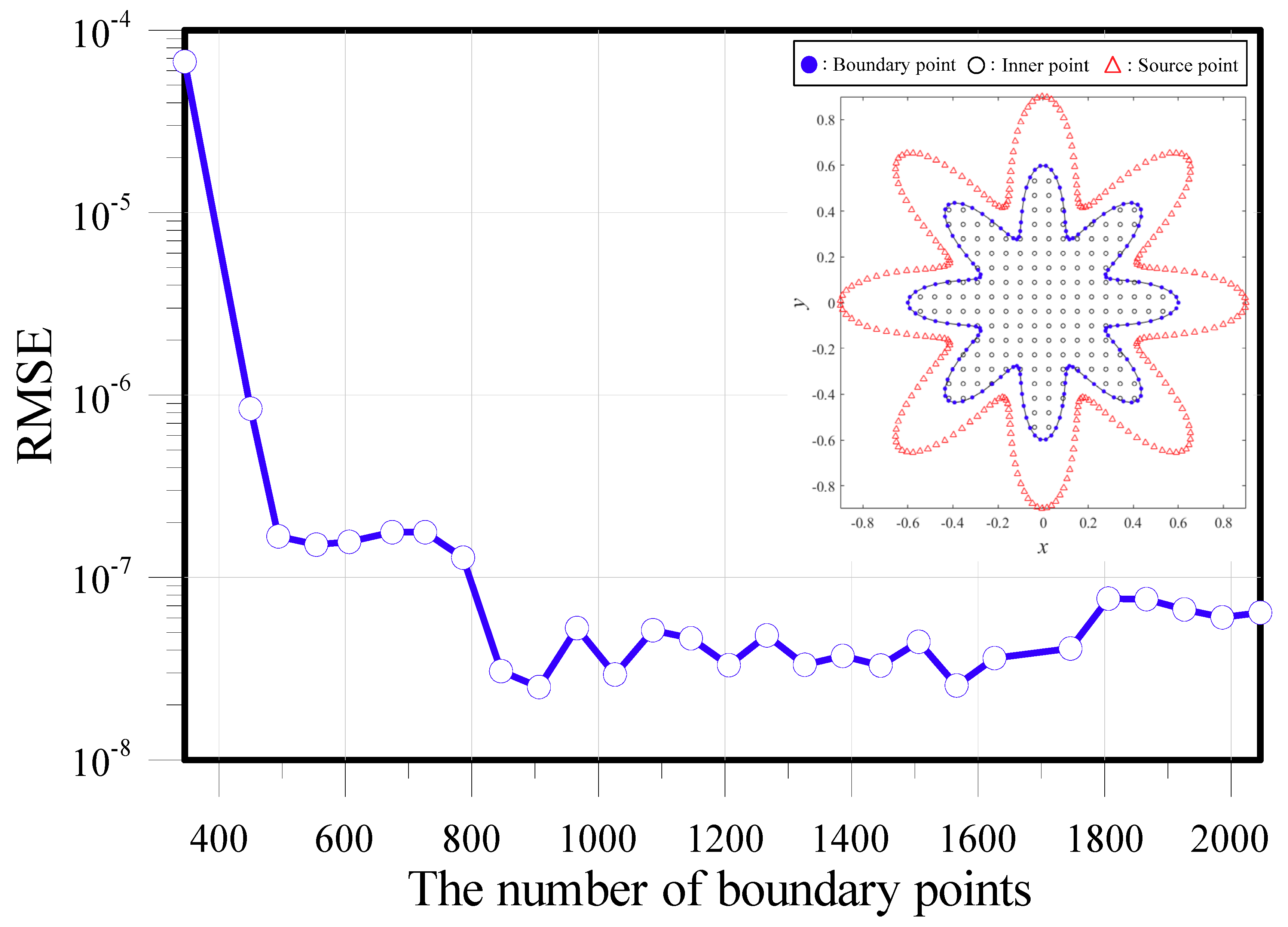
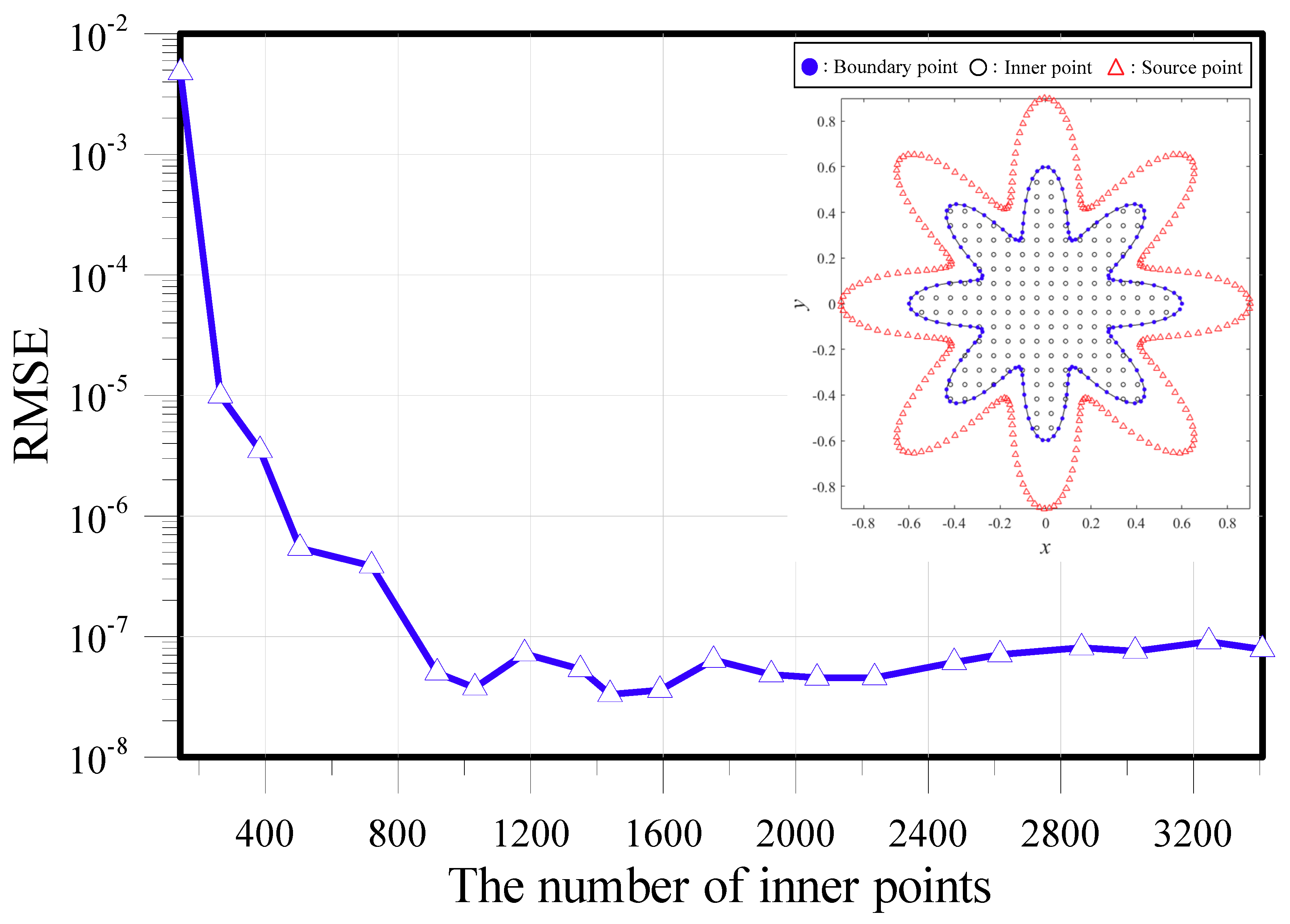
3. Validation and Convergence Analysis
4. Numerical Examples.
4.1. Diffusion Equation Modeling in Two Dimensions
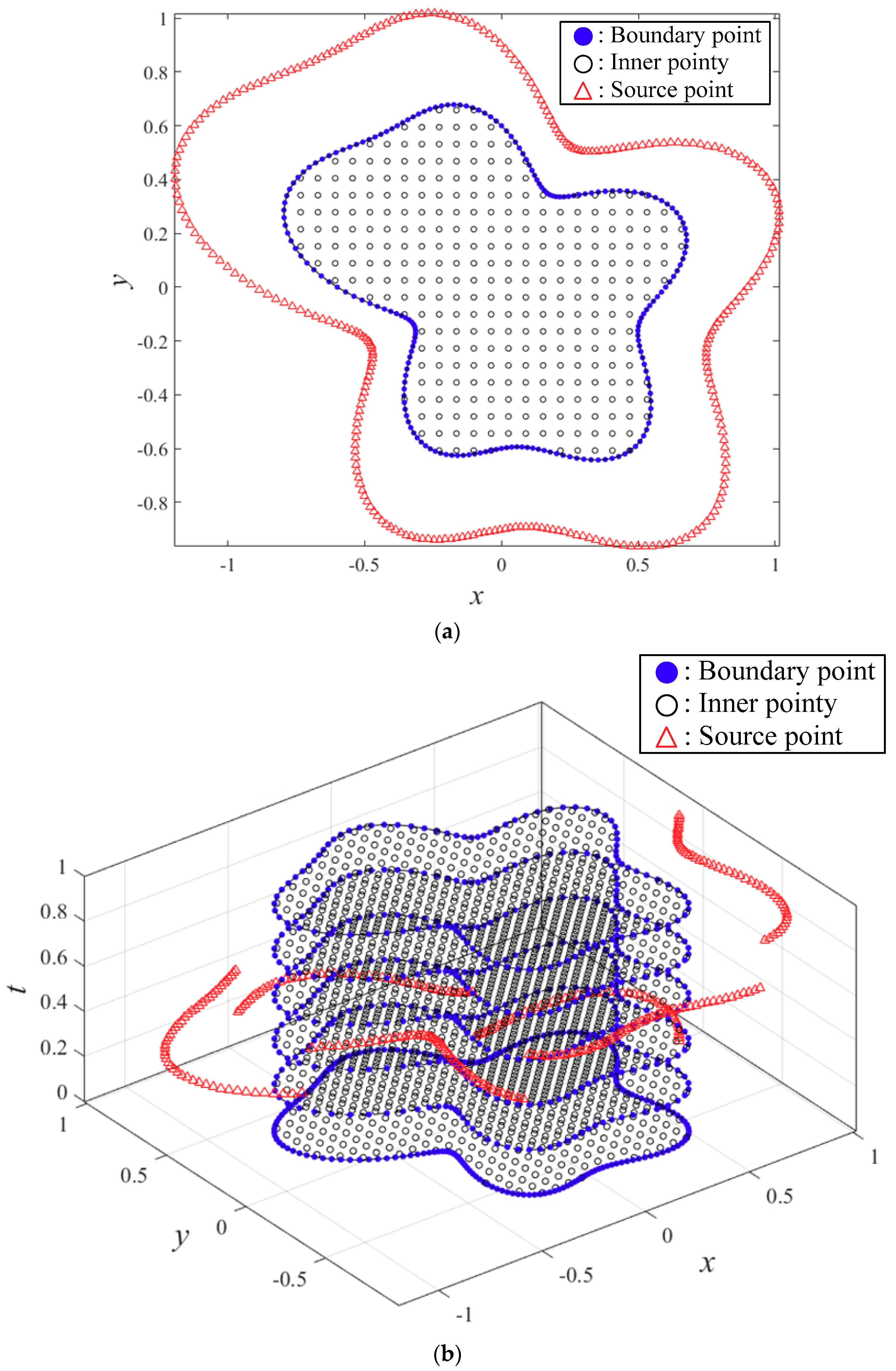
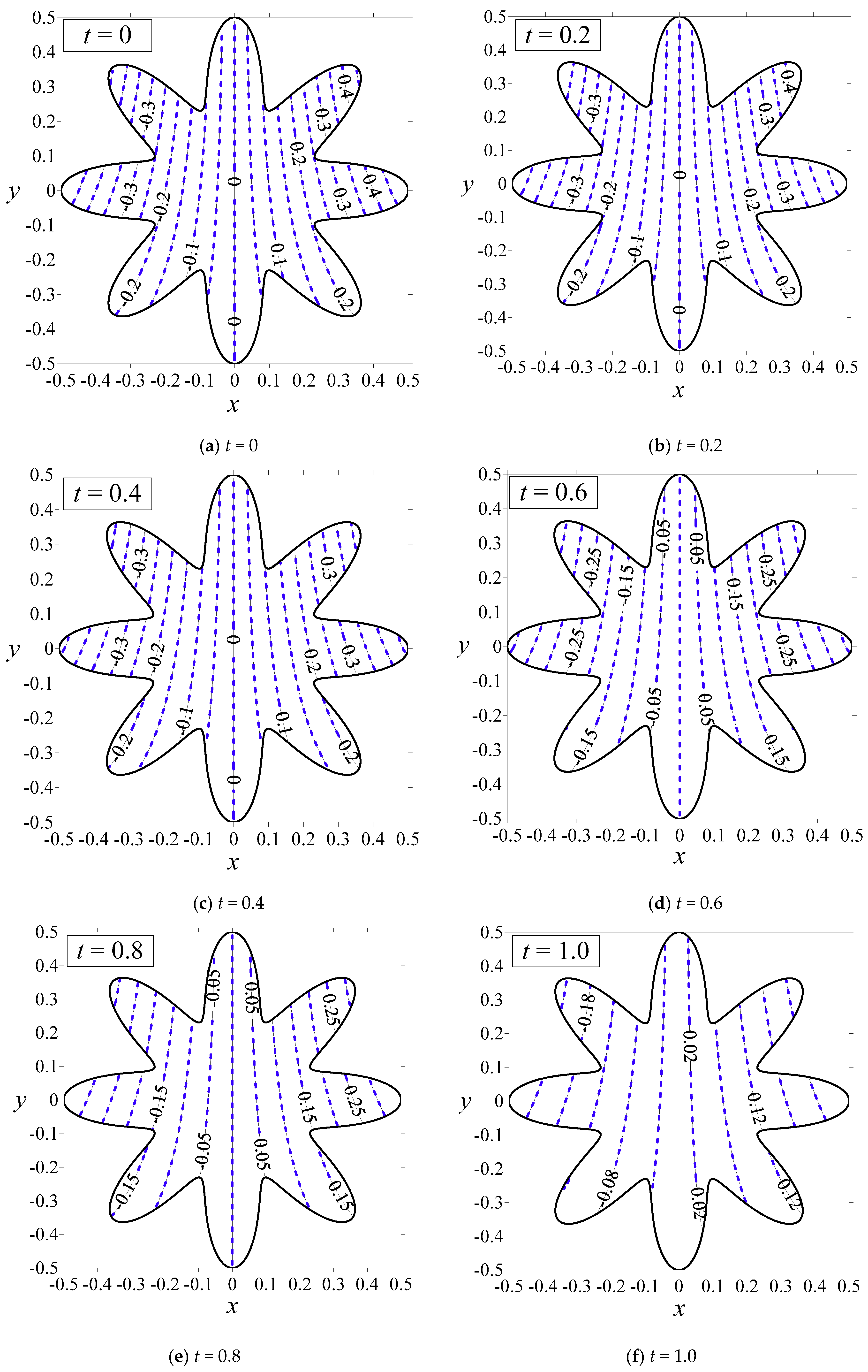
4.2. Modeling the Two-Dimensional Convection–Diffusion Equation: Case 1
4.3. Modeling the Two-Dimensional Convection–Diffusion Equation: Case 2
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, L.Y.; Jiang, Z.W.; Yin, Z. Fourth-order compact finite difference method for solving two-dimensional convection-diffusion equation. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2018, 234, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, I.; Hayes, R.E.; Nikrityuk, P. A new approach for the modeling of turbulent flows in automotive catalytic converters. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 140, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosetti, M.; Bracconi, M.; Maestri, M.; Groppi, G.; Tronconi, E. Packed foams for the intensification of catalytic processes: Assessment of packing efficiency and pressure drop using a combined experimental and numerical approach. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 122801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appadu, A.R. Numerical solution of the 1D advection-diffusion equation using standard and nonstandard finite difference schemes. J. Appl. Math. 2013, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tony, W.H.; Sheu, C.F.; Chen, W.S. A novel two-dimensional convection-diffusion finite-difference scheme. Numer. Heat Transf. B-Fundam. 2000, 38, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salkuyeh, D.K. On the finite difference approximation to the convection–diffusion equation. Appl. Math. Comput. 2000, 179, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, I.; Cornejo, G.; Nikrityuk, P.; Hayes, R.E. Entry length convective heat transfer in a monolith: The effect of upstream turbulence. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 138, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadhyani, S.; Patankar, S.V. Solution of the convection-diffusion equation by a finite-element method using quadrilateral elements. Numer. Heat Transf. A-Appl. 1985, 8, 595–612. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, C.L.N.; Carrer, J.A.M.; Oliveira, M.F.; Costa, V.L. A study concerning the solution of advection-diffusion problems by the boundary element method. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2016, 65, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, F.; Devals, C.; Vidal, D.; Préva, C.S.D.; Hayes, R.E. Towards the simulation of the catalytic monolith converter using discrete channel-scale models. Catal. Today. 2012, 188, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, R.; Prill, T.; Van Setten, B.A.A.L.; Votsmeier, M. Tomography based simulation of reactive flow at the micro-scale: Particulate filters with wall integrated catalyst. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 378, 121919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.Q.; Evans, J.W. Boundary element solution of heat convection-diffusion problems. J. Comput. Phys. 1991, 93, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, R.; Stynes, M. Finite element methods for convection-diffusion problems using exponential splines on triangles. Comput. Math. Appl. 1998, 35, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman, V.K.; Sengupta, T.K.; Jyothi Durga Prasad, C.; Surya Mohan, K.; Sanwalia, D. Spectral analysis of finite difference schemes for convection diffusion equation. Comput. Fluids. 2017, 150, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Fu, Z.J.; Chen, C.S. Recent Advances in Radial Basis Function Collocation Methods; Springer: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hardy, R.L. Multiquadric equations of topography and other irregular surfaces. J. Geophys, Res. 1971, 176, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansa, E.J. Multiquadrics—A scattered data approximation scheme with applications to computational fluid-dynamics—I surface approximations and partial derivative estimates. Comput. Math. Appl. 1990, 19, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansa, E.J. Multiquadrics—A scattered data approximation scheme with applications to computational fluid-dynamics—II solutions to parabolic, hyperbolic and elliptic partial differential equations. Comput. Math. Appl. 1990, 19, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.T.; Li, D.F. A meshless method for Burgers’ equation using MQ-RBF and high-order temporal approximation. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 9215–9222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.Y.; Liu, X.F.; Wen, P.H. The local Kansa’s method for solving Berger equation. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2015, 57, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Jiang, T.S.; Hon, Y.C. A meshless method based on RBFs method for nonhomogeneous backward heat conduction problem. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2010, 34, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabski, J.K.; Kołodziej, J.A. Laminar fluid flow and heat transfer in an internally corrugated tube by means of the method of fundamental solutions and radial basis functions. Comput. Math. Appl. 2018, 75, 1413–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Hon, Y.C.; Xiong, X.T. Numerical solution of two-dimensional radially symmetric inverse heat conduction problem. J. Inverse Ill-pose. P. 2015, 23, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Pepper, D. Radial basis function method for 1-D and 2-D groundwater contaminant transport modeling. Comput. Mech. 2003, 32, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayona, V.; Moscoso, M.; Kindelan, M. Optimal constant shape parameter for multiquadric based RBF-FD method. J. Comput. Phys. 2011, 230, 7384–7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbabai, A.; Mohebianfar, E.; Rabiei, H. On the new variable shape parameter strategies for radial basis functions. Comp. Appl. Math. 2002, 191, 2611–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.S.; Kolibal, J.; Li, M. The golden section search algorithm for finding a good shape parameter for meshless collocation methods. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2010, 34, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, Y.L.; Ng, K.C.; Sheu, T.W.H. A new higher-order RBF-FD scheme with optimal variable shape parameter for partial differential equation. Numer. Heat Transf. B-Fundam. 2019, 75, 289–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, H.; Codina, R.; Badia, S. On some time marching schemes for the stabilized finite element approximation of the mixed wave equation. Comput. Method Appl. M. 2015, 296, 295–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.L.; Gu, M.H.; Fan, C.M. The time-marching method of fundamental solutions for wave equations. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2009, 33, 1411–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.J.; Shu, C.W.; Zhang, Q. Stability analysis and error estimates of local discontinuous Galerkin methods with implicit-explicit time-marching for nonlinear convection-diffusion problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 2016, 272, 237–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.X.; Wang, F.J.; Hua, Q.S.; Qiu, X.Y. A novel space-time meshless method for nonhomogeneous convection-diffusion equations with variable coefficients. Appl. Math. Lett. 2019, 92, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
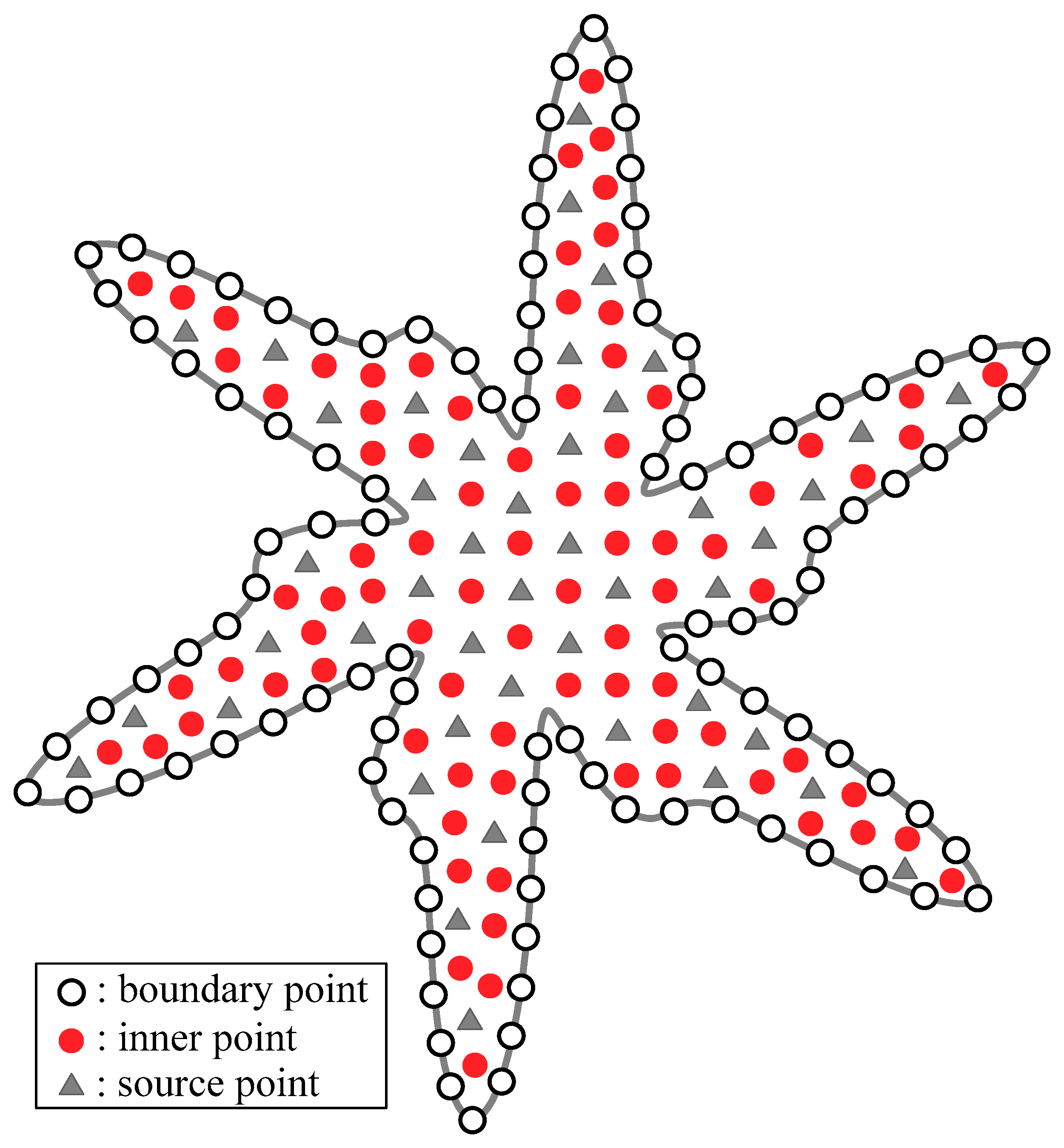
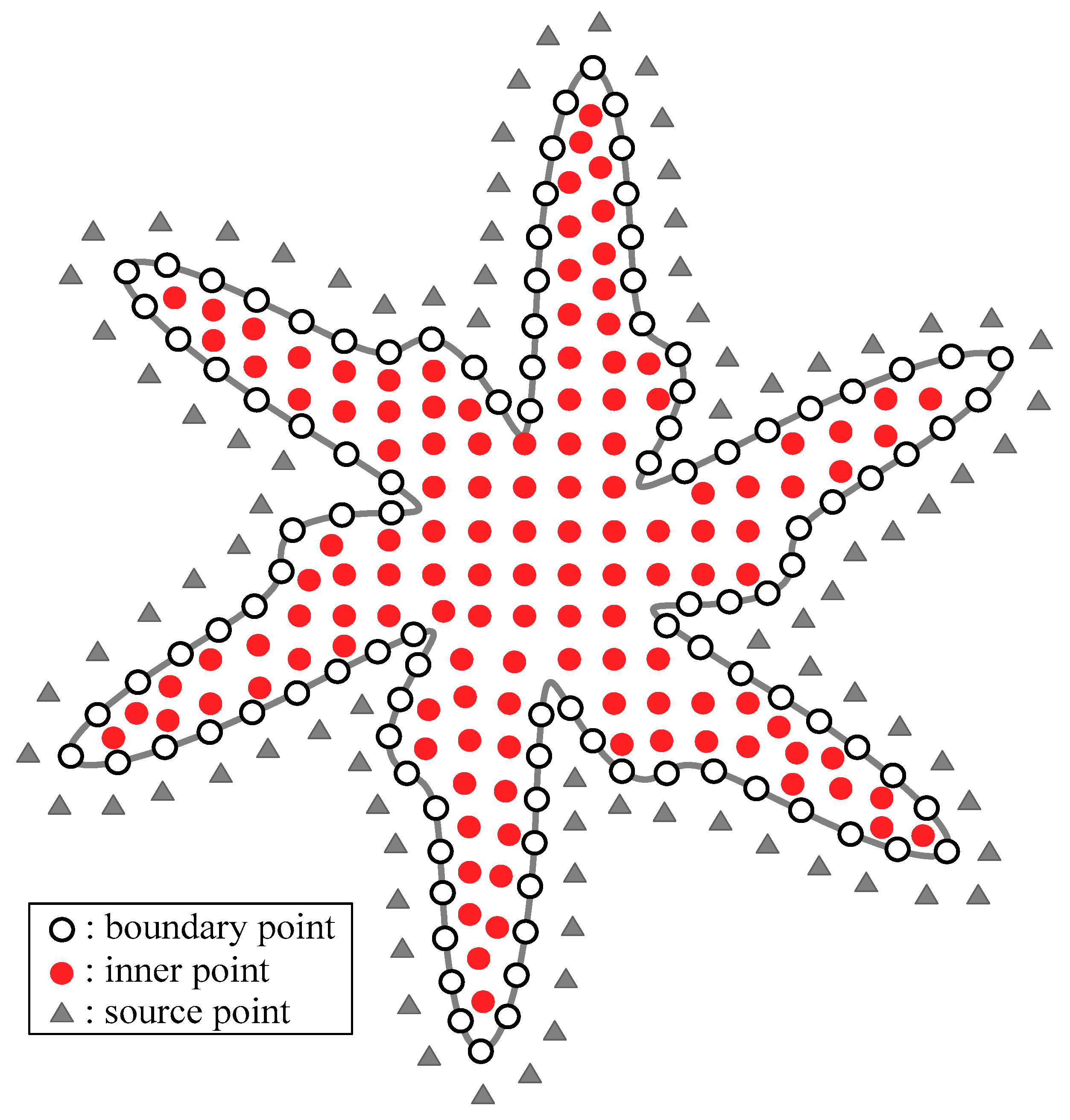
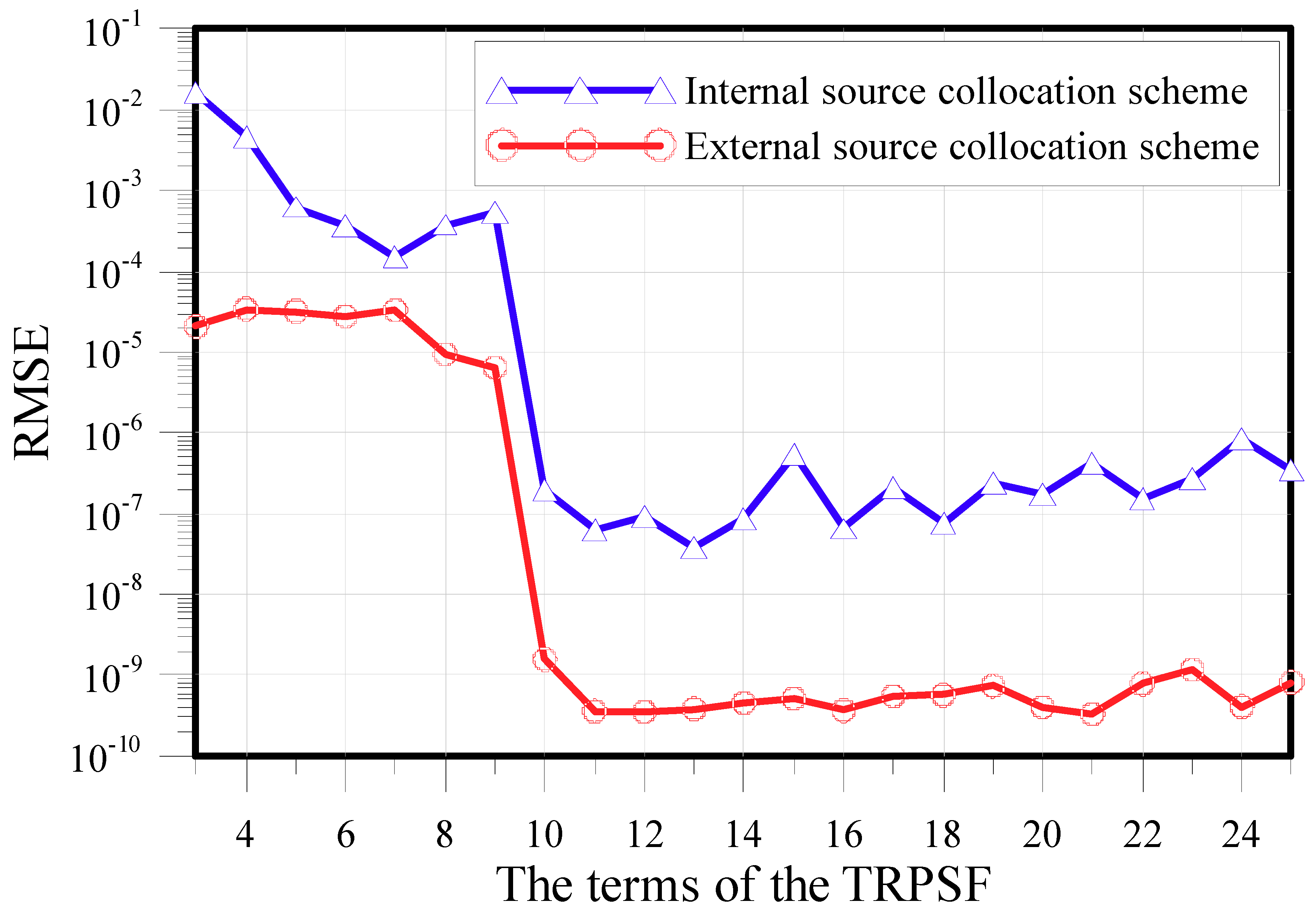
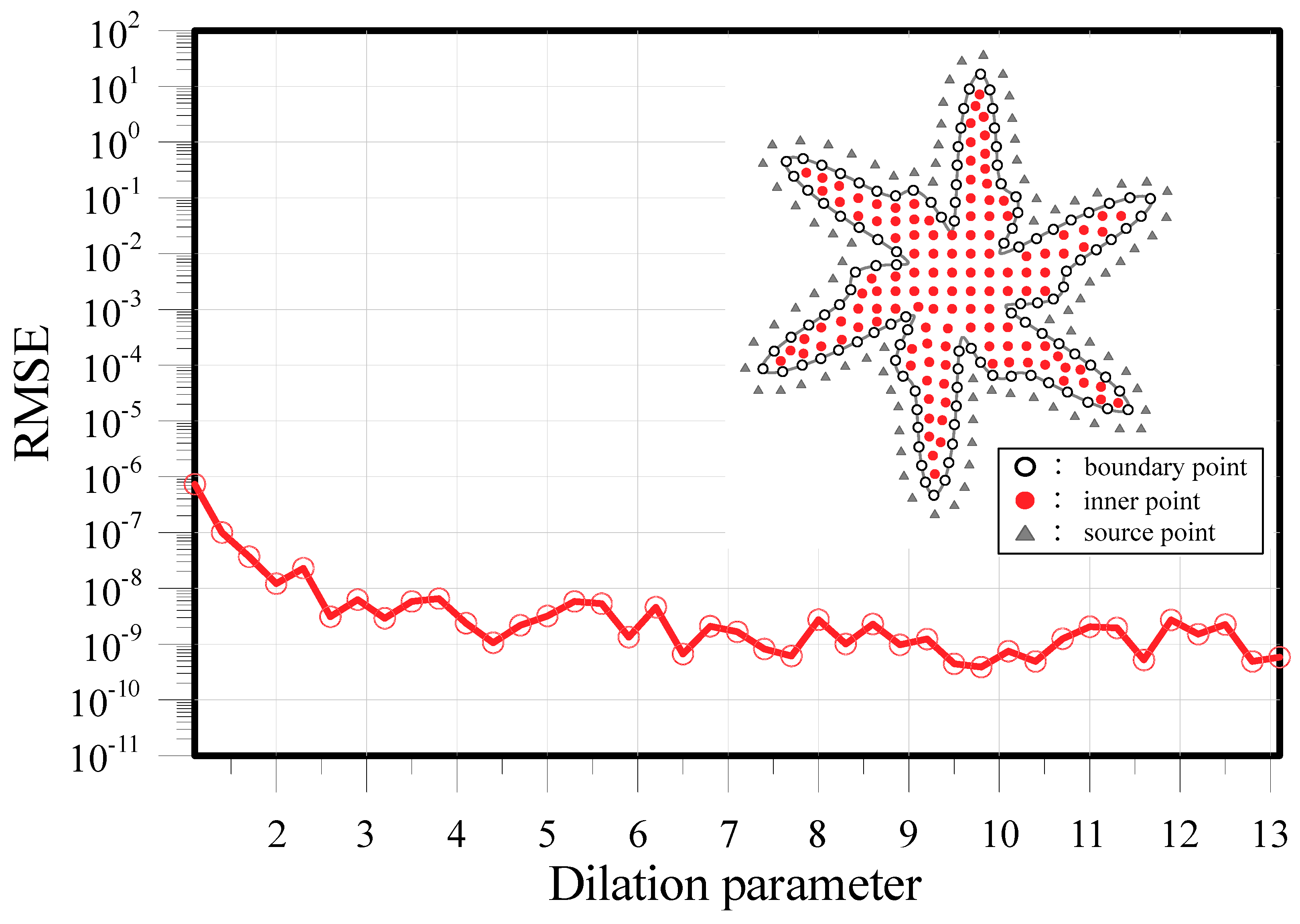




| RMSE | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| This Study | Multiquadratic (MQ) RBF | Inverse Multiquadriatic (IMQ) RBF | Gaussian | |||
| 1916 | 514 | |||||
| 2058 | 642 | |||||
| 2308 | 982 | |||||
| 2500 | 1280 | |||||
| 2642 | 1678 | |||||
| 2761 | 2369 | |||||
| RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|
| This Study | MQ RBF | |
| 0.001 | ||
| 0.01 | ||
| 0.1 | ||
| 1 | ||
| 10 | ||
| 100 | ||
| 1000 | ||
| Time | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | This Study | MQ RBF | STRBF [32] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 517 | (0.72 s) | (0.75 s) | (0.74 s) | (1.05 s) | |
| 987 | (2.77 s) | (2.88 s) | (3.05 s) | (4.43 s) | |
| 1722 | (15.55 s) | (16.05 s) | (16.22 s) | (25.43 s) | |
| 2730 | (64.08 s) | (65.11 s) | (74.82 s) | (100.81 s) | |
| 3380 | (133.71 s) | (135.43 s) | (146.92 s) | (217.36 s) | |
| 4179 | (249.42 s) | (253.92 s) | (258.64 s) | (378.69 s) | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ku, C.-Y.; Xiao, J.-E.; Liu, C.-Y. Space–Time Radial Basis Function–Based Meshless Approach for Solving Convection–Diffusion Equations. Mathematics 2020, 8, 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8101735
Ku C-Y, Xiao J-E, Liu C-Y. Space–Time Radial Basis Function–Based Meshless Approach for Solving Convection–Diffusion Equations. Mathematics. 2020; 8(10):1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8101735
Chicago/Turabian StyleKu, Cheng-Yu, Jing-En Xiao, and Chih-Yu Liu. 2020. "Space–Time Radial Basis Function–Based Meshless Approach for Solving Convection–Diffusion Equations" Mathematics 8, no. 10: 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8101735
APA StyleKu, C.-Y., Xiao, J.-E., & Liu, C.-Y. (2020). Space–Time Radial Basis Function–Based Meshless Approach for Solving Convection–Diffusion Equations. Mathematics, 8(10), 1735. https://doi.org/10.3390/math8101735







