Modified Proximal Algorithms for Finding Solutions of the Split Variational Inclusions
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Algorithm 1: |
| [11]. For , set as where is chosen such that The iterative is generated by where and |
- (i)
- ; ; ;
- (ii)
- , , .
2. Preliminaries
- ⇀ stands for the weak convergence,
- → stands for the strong convergence.
- (1)
- nonexpansive if, for all ,
- (2)
- firmly-nonexpansive if, for all ,
- (i)
- is single-valued and firmly nonexpansive for each ;
- (ii)
- and ;
- (iii)
- for all and for all ;
- (iv)
- If , then we have for all , each , and each ;
- (v)
- If , then we have for all , each , and each .
- (i)
- If is a solution of (SVIP), then .
- (ii)
- Suppose that and the solution set of (SVIP) is nonempty. Then, is a solution of (SVIP).
- (i)
- for all ;
- (ii)
- for all .
- (i)
- exists for each ;
- (ii)
- every sequential weak limit point of is in C.
- (i)
- ;
- (ii)
- ;
- (iii)
- implies for any subsequence of .
3. Weak Convergence Result
| Algorithm 2: |
| Choose and define where and |
4. Strong Convergence Result
- (a1)
- and ;
- (a2)
- ;
- (a3)
- ;
- (a4)
- .
| Algorithm 3: |
| Choose and let . Let be a real sequence in . Let be iteratively generated by where and |
5. Numerical Experiments
- Case 1:
- , , , and
- Case 2:
- , , , and
- Case 3:
- , , , and
- Case 4:
- , , , and .
- Case 1:
- , and
- Case 2:
- , and
- Case 3:
- , and
- Case 4:
- , and .
6. Split Feasibility Problem
- (a1)
- and ;
- (a2)
- ;
- (a3)
- .
- (i)
- ; ; ;
- (ii)
- and
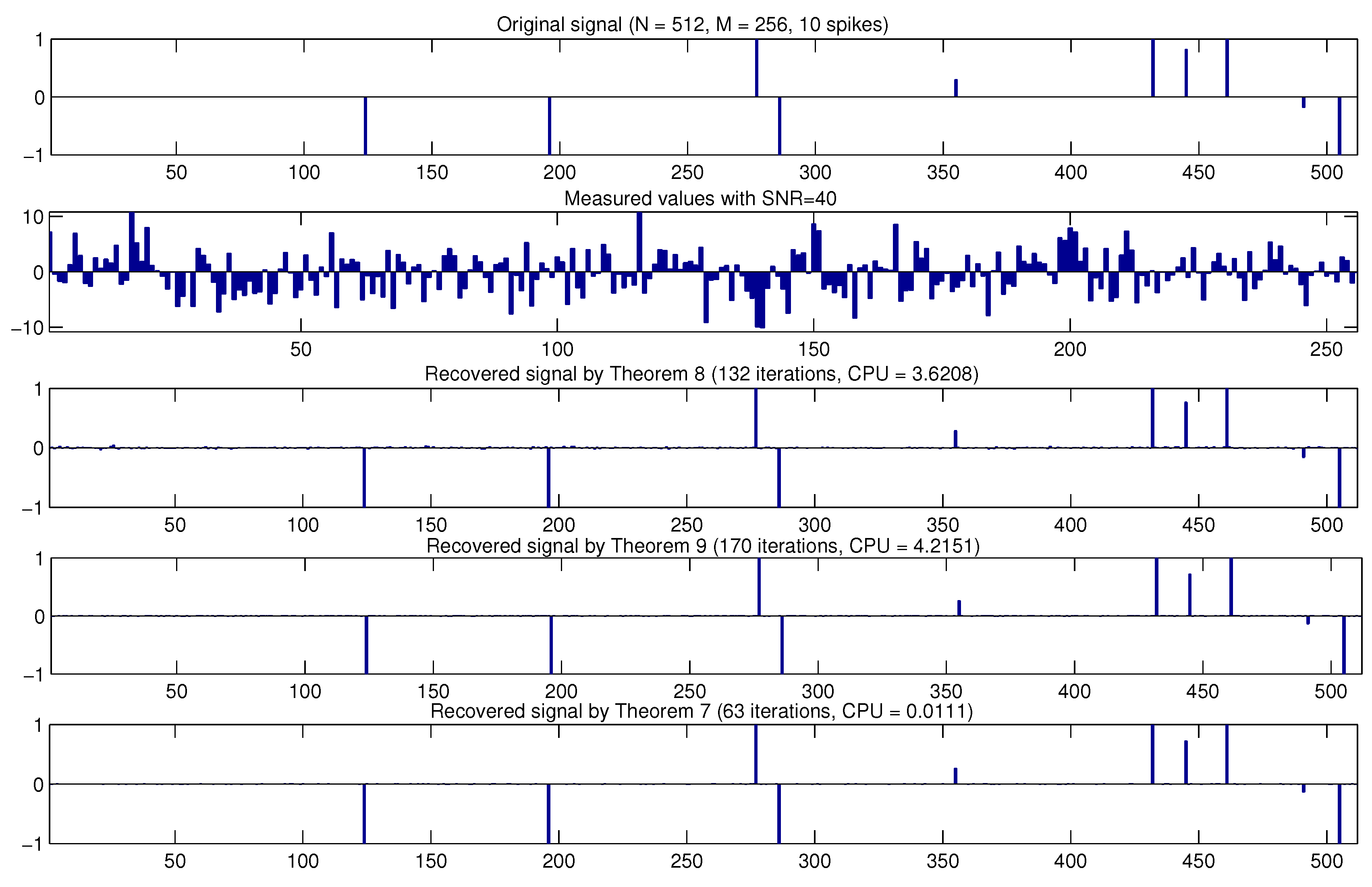
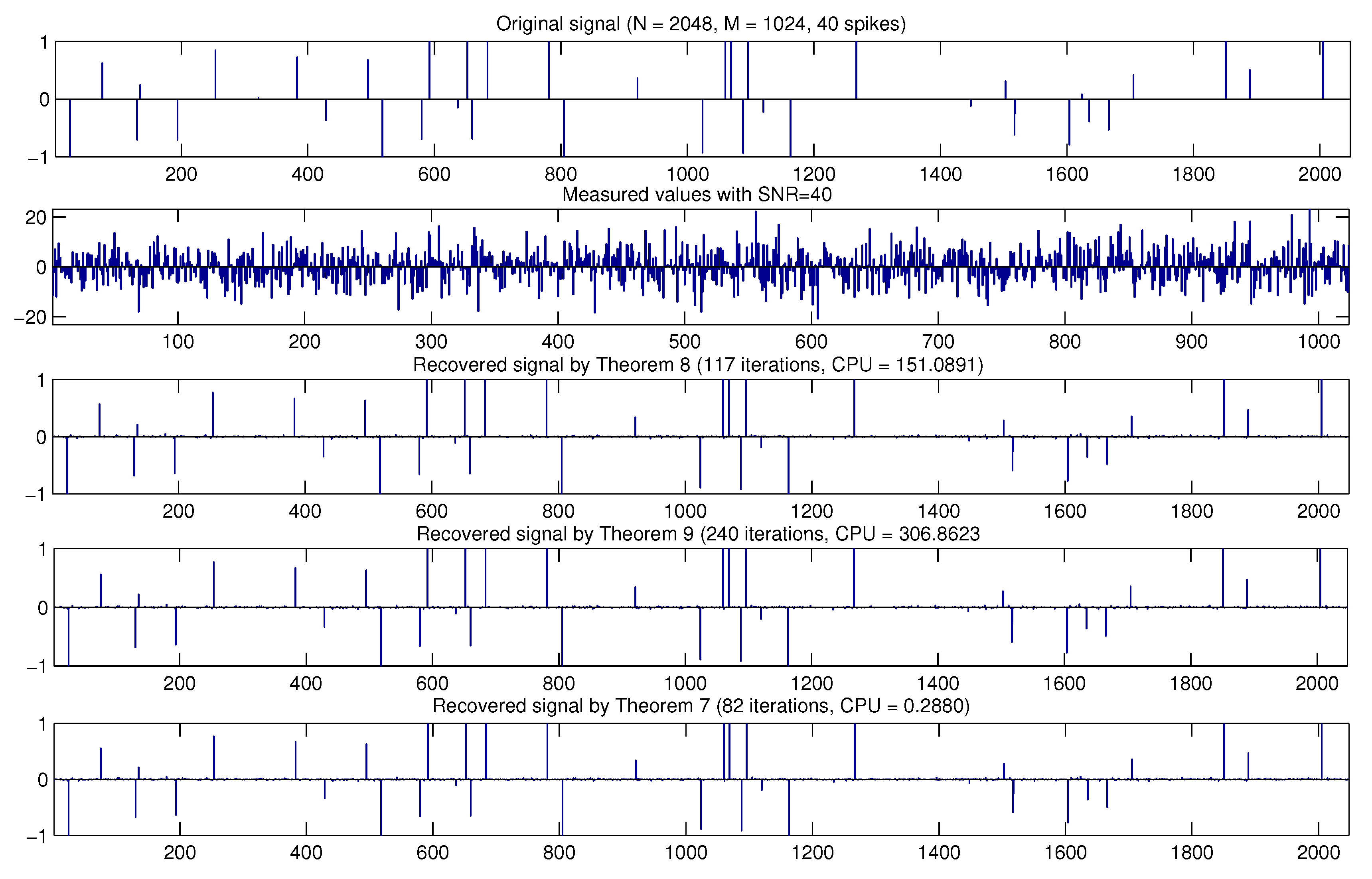
7. Applications to Compressed Sensing
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinet, B. Régularisation d’inéquations variationnelles par approximations successives. Revue Francaise d’Informatique et de Recherche Operationelle 1970, 4, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Rockafellar, R.T. Monotone operators and the proximal point algorithm. SIAM J. Control Optim. 1976, 14, 877–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudafi, A. Split monotone variational inclusions. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2011, 150, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censor, Y.; Elfving, T. A multiprojection algorithm using Bregman projections in a product space. Numer Algor. 1994, 8, 221–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, C. Iterative oblique projection onto convex sets and the split feasibility problem. Inverse Probl. 2002, 18, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, C.; Censor, Y.; Gibali, A. Weak and strong convergence of algorithms for the split common null point problem. J. Nonlinear Convex Anal. 2011, 13, 759–775. [Google Scholar]
- Censor, Y.; Bortfeld, T.; Martin, B. A unified approach for inversion problems in intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Phys. Med. Biol. 2006, 51, 2353–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, G.; Martín-Márquez, V.; Xu, H.K. Iterative algorithms for the multiple-sets split feasibility problem. In Biomedical Mathematics: Promising Directions in Imaging, Therapy Planning and Inverse Problems; Censor, Y., Jiang, M., Wang, G., Eds.; Medical Physics Publishing: Madison, WI, USA, 2010; pp. 243–279. [Google Scholar]
- Stark, H. Image Recovery: Theory and Applications; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, C.S. Algorithms with new parameter conditions for split variational inclusion problems in Hilbert spaces with application to split feasibility problem. Optimization 2016, 65, 859–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.S. Strong convergence theorems for the split variational inclusion problem in Hilbert spaces. Fixed Point Theory Appl. 2013, 2013, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Goebel, K.; Kirk, W.A. Topics in Metric Fixed Point Theory; Cambridge Studies in Advanced Mathematics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990; Volume 28. [Google Scholar]
- Marino, G.; Xu, H.K. Convergence of generalized proximal point algorithms. Commun. Pure Appl. Anal. 2004, 3, 791–808. [Google Scholar]
- Opial, Z. Weak convergence of the sequence of successive approximations for nonexpansive mappings. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 1967, 73, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Yang, C. Solving the variational inequality problem defined on intersection of finite level sets. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Gao, Y. The strong convergence of a KM-CQ-like algorithm for a split feasibility problem. Inverse Prob. 2011, 27, 015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, H.K. Approximating curve and strong convergence of the CQ algorithm for the split feasibility problem. J. Inequal. Appl. 2010, 2010, 102085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.K. Iterative methods for the split feasibility problem in infinite-dimensional Hilbert spaces. Inverse Prob. 2010, 26, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q. Modified projection methods for the split feasibility problem and multiple-sets feasibility problem. Appl. Math. Comput. 2012, 219, 1644–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.P.; O’Regan, D.; Sahu, D.R. Fixed Point Theory for Lipschitzian-Type Mapping with Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, W. Introduction to Nonlinear and Convex Analysis; Yokohama Tokohama Publishers, Inc.: Yokohama, Japan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Tibshirani, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1996, 58, 267–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Method | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | Iter | CPU | Iter | ||
| Case 1 | Theorem 1 | 0.1091 | 3657 | 0.2763 | 7688 |
| Theorem 2 | 0.0078 | 131 | 0.0778 | 1272 | |
| Theorem 3 | 0.0452 | 777 | 0.0699 | 1186 | |
| Theorem 5 | 0.0017 | 66 | 0.0023 | 86 | |
| Case 2 | Theorem 1 | 0.1565 | 4645 | 0.5374 | 8388 |
| Theorem 2 | 0.0276 | 454 | 0.3143 | 4357 | |
| Theorem 3 | 0.0368 | 609 | 0.0487 | 860 | |
| Theorem 5 | 0.0011 | 39 | 0.0028 | 48 | |
| Case 3 | Theorem 1 | 0.1390 | 4572 | 0.3172 | 8219 |
| Theorem 2 | 0.0280 | 471 | 0.2936 | 4510 | |
| Theorem 3 | 0.0635 | 1048 | 0.0905 | 1541 | |
| Theorem 5 | 0.0014 | 45 | 0.0016 | 55 | |
| Case 4 | Theorem 1 | 0.1189 | 4069 | 0.2849 | 7668 |
| Theorem 2 | 0.0213 | 345 | 0.2092 | 3307 | |
| Theorem 3 | 0.0686 | 1159 | 0.1046 | 1768 | |
| Theorem 5 | 0.0011 | 34 | 0.0011 | 43 | |
| Method | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | Iter | CPU | Iter | ||
| Case 1 | Theorem 4 | 0.0310 | 714 | 0.0871 | 2256 |
| Theorem 6 | 0.0068 | 273 | 0.0240 | 860 | |
| Case 2 | Theorem 4 | 0.0225 | 685 | 0.0790 | 2166 |
| Theorem 6 | 0.0038 | 142 | 0.0117 | 448 | |
| Case 3 | Theorem 4 | 0.0204 | 675 | 0.0727 | 2135 |
| Theorem 6 | 0.0043 | 156 | 0.0132 | 492 | |
| Case 4 | Theorem 4 | 0.0241 | 671 | 0.0677 | 2120 |
| Theorem 6 | 0.0038 | 140 | 0.0156 | 441 | |
| m-Sparse | Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | Iter | CPU | Iter | ||
| Theorem 8 | 0.9662 | 44 | 3.6208 | 132 | |
| Theorem 9 | 1.3204 | 58 | 4.2151 | 170 | |
| Theorem 7 | 0.0054 | 26 | 0.0111 | 63 | |
| Theorem 8 | 1.3082 | 57 | 2.8470 | 124 | |
| Theorem 9 | 1.8984 | 84 | 3.7938 | 170 | |
| Theorem 7 | 0.0058 | 36 | 0.0099 | 72 | |
| Theorem 8 | 1.4928 | 65 | 3.5994 | 161 | |
| Theorem 9 | 2.7294 | 122 | 5.7801 | 251 | |
| Theorem 7 | 0.0070 | 42 | 0.0143 | 99 | |
| Theorem 8 | 2.2008 | 98 | 6.0600 | 275 | |
| Theorem 9 | 4.1730 | 183 | 18.6269 | 824 | |
| Theorem 7 | 0.0107 | 67 | 0.0323 | 227 | |
| m-Sparse | Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | Iter | CPU | Iter | ||
| Theorem 8 | 47.6530 | 41 | 119.9776 | 101 | |
| Theorem 9 | 67.6869 | 57 | 157.1087 | 134 | |
| Theorem 7 | 0.0807 | 25 | 0.1899 | 58 | |
| Theorem 8 | 47.7347 | 41 | 151.0891 | 117 | |
| Theorem 9 | 93.1898 | 79 | 306.8623 | 240 | |
| Theorem 7 | 0.1007 | 31 | 0.2880 | 82 | |
| Theorem 8 | 65.1771 | 55 | 136.1508 | 115 | |
| Theorem 9 | 99.0021 | 83 | 188.9366 | 158 | |
| Theorem 7 | 0.1227 | 35 | 0.2203 | 67 | |
| Theorem 8 | 76.7457 | 64 | 163.8805 | 138 | |
| Theorem 9 | 127.5520 | 106 | 209.5990 | 177 | |
| Theorem 7 | 0.1401 | 43 | 0.2449 | 75 | |
| m-Sparse | Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | Iter | CPU | Iter | ||
| Theorem 11 | 5.8869 | 237 | 28.2850 | 863 | |
| Theorem 10 | 0.0296 | 157 | 0.1232 | 551 | |
| Theorem 11 | 6.1204 | 245 | 38.9049 | 1561 | |
| Theorem 10 | 0.0260 | 155 | 0.1550 | 950 | |
| Theorem 11 | 9.3238 | 376 | 116.7590 | 4613 | |
| Theorem 10 | 0.0377 | 233 | 0.4484 | 2730 | |
| Theorem 11 | 9.3206 | 379 | 32.8208 | 1255 | |
| Theorem 10 | 0.0420 | 252 | 0.1578 | 858 | |
| m-Sparse | Method | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | Iter | CPU | Iter | ||
| Theorem 11 | 131.3365 | 111 | 578.6894 | 490 | |
| Theorem 10 | 0.2419 | 74 | 0.9969 | 305 | |
| Theorem 11 | 184.8031 | 157 | 616.7051 | 526 | |
| Theorem 10 | 0.3274 | 101 | 1.0929 | 339 | |
| Theorem 11 | 262.3976 | 224 | 1.3220 × 103 | 503 | |
| Theorem 10 | 0.4633 | 141 | 1.4516 | 339 | |
| Theorem 11 | 282.6013 | 237 | 1.6136 × 103 | 1326 | |
| Theorem 10 | 0.5393 | 158 | 2.6758 | 791 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suantai, S.; Kesornprom, S.; Cholamjiak, P. Modified Proximal Algorithms for Finding Solutions of the Split Variational Inclusions. Mathematics 2019, 7, 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7080708
Suantai S, Kesornprom S, Cholamjiak P. Modified Proximal Algorithms for Finding Solutions of the Split Variational Inclusions. Mathematics. 2019; 7(8):708. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7080708
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuantai, Suthep, Suparat Kesornprom, and Prasit Cholamjiak. 2019. "Modified Proximal Algorithms for Finding Solutions of the Split Variational Inclusions" Mathematics 7, no. 8: 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7080708
APA StyleSuantai, S., Kesornprom, S., & Cholamjiak, P. (2019). Modified Proximal Algorithms for Finding Solutions of the Split Variational Inclusions. Mathematics, 7(8), 708. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7080708





