The Impact of Viscous Dissipation on the Thin Film Unsteady Flow of GO-EG/GO-W Nanofluids
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Formulation
3. Method of Solution
4. Table Discussion
5. Result and Discussion
6. Conclusions
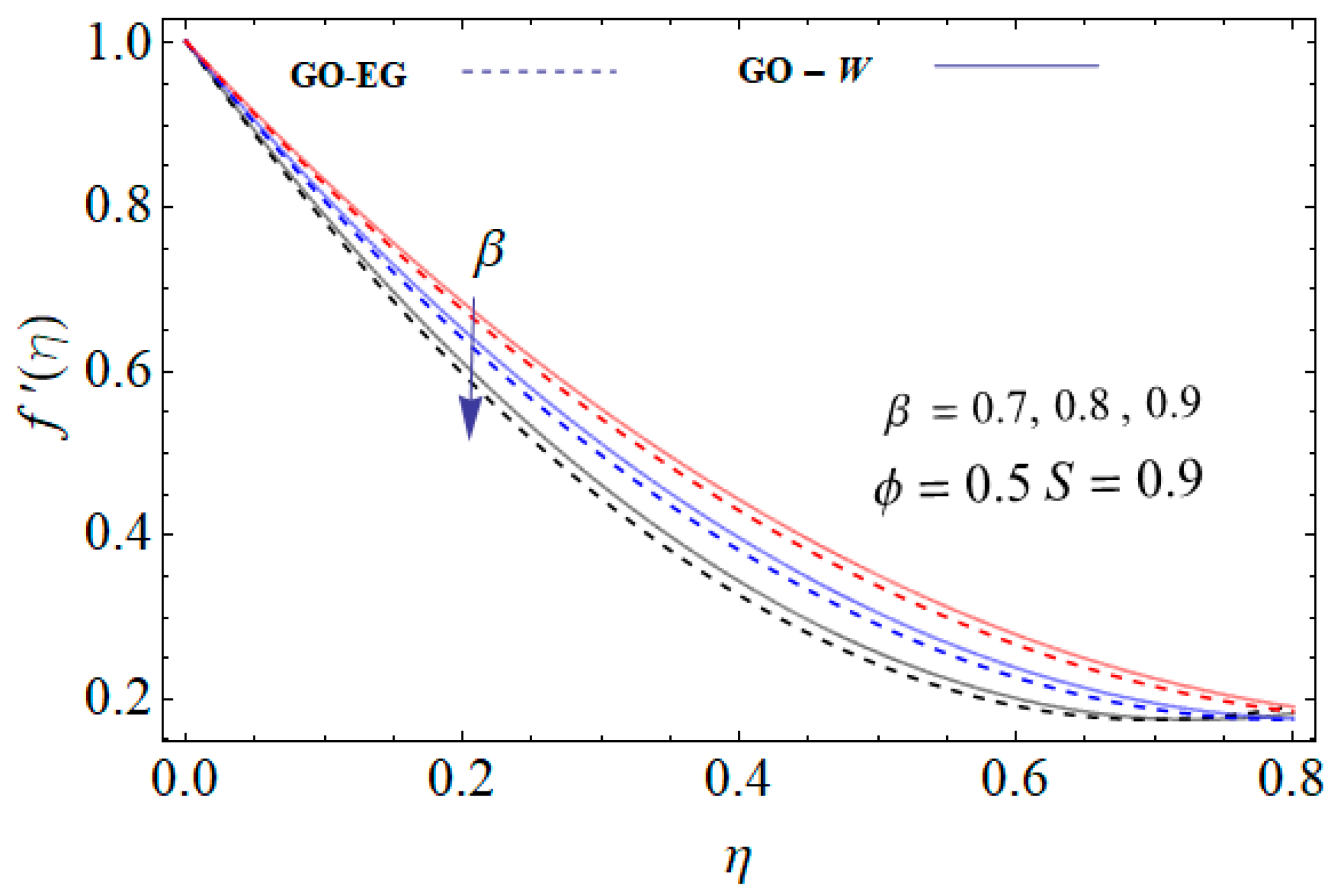
- By increasing the unsteadiness parameter the velocity profile decreases and this effect is comparatively strong in the GO-EG nanofluid.
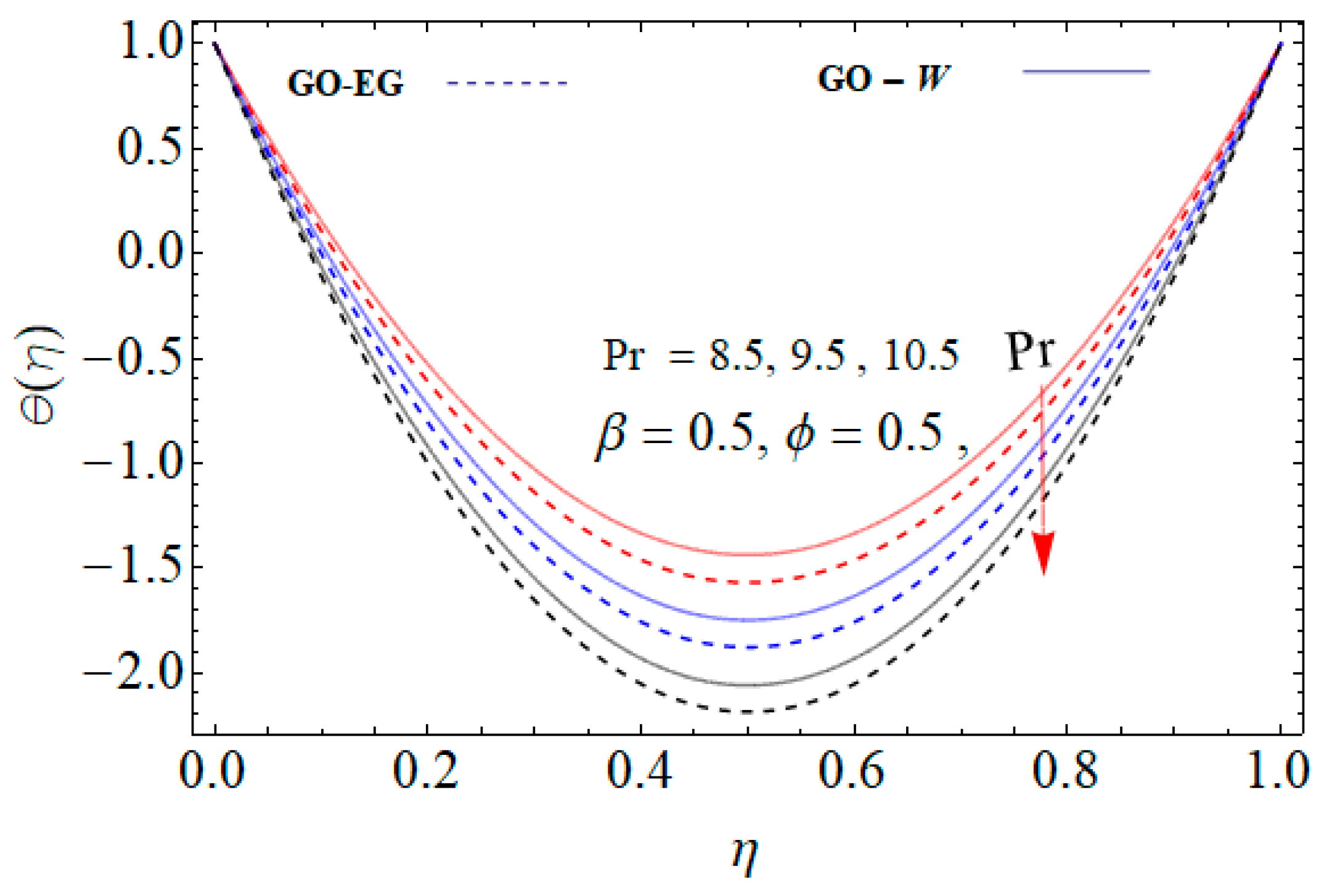
- The increasing value of the Prandtl number reduces the temperature profile. The effect is comparatively strong using the GO-EG nanofluid.
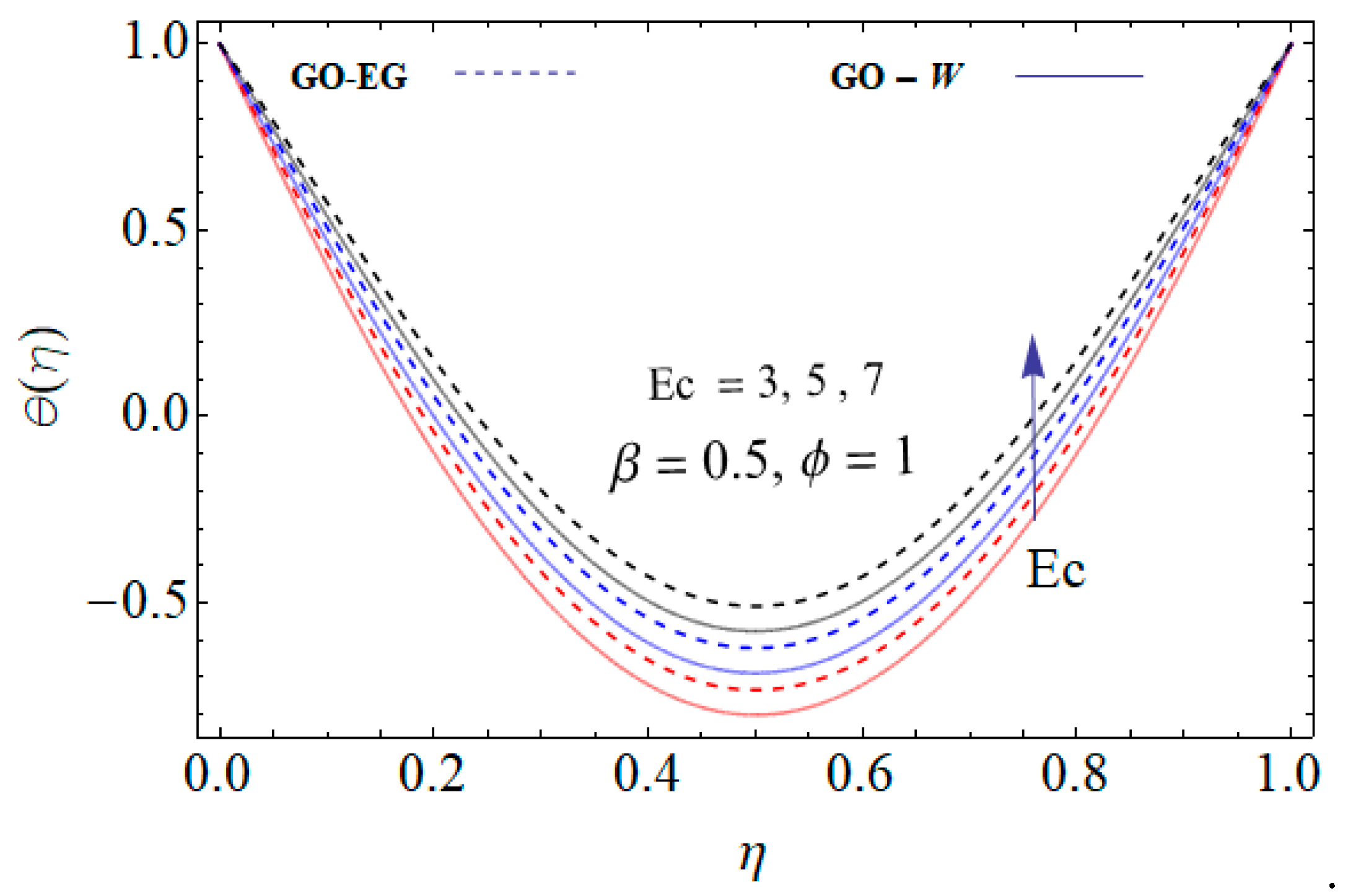
- Increasing the Eckert number increases the kinetic energy to enhance the temperature field.
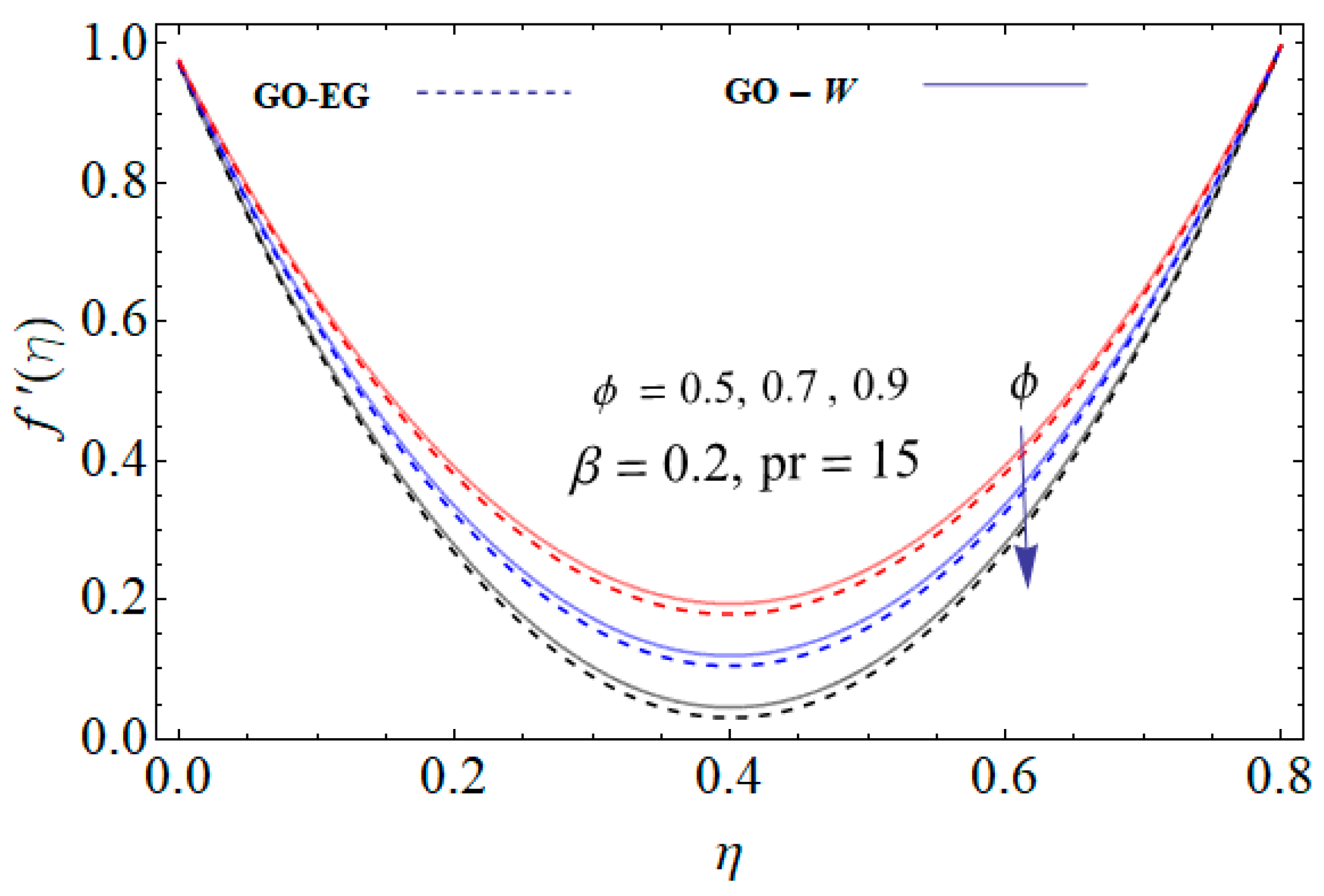
- The increasing thickness of the thin film reduces the fluid motion.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclatures
| Acceleration due to gravity | |
| Dynamic viscosity of the nanofluids axial directions | |
| Density of the nanofluids | |
| Eckert number | |
| Heat generation/absorption parameter | |
| Local temperature | |
| Non-dimensional thickness of the liquid film | |
| Nusselt number | |
| Prandtl number | |
| Specific heat | |
| Stretching velocity | |
| Similarity variable | |
| Skin friction | |
| Solid particle volume fraction | |
| Thickness of the liquid film | |
| Temperature at the free surface | |
| Thermal conductivity of the nanoparticles | |
| Velocity components |
References
- Choi, S.U.S.; Estman, J.A. Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME Publ. Fed 1995, 231, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.U.; Zhang, Z.G.; Yu, W.; Lockwood, F.E.; Grulke, E.A. Anomalous thermal conductivity enhancement in nanotube suspensions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 79, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, R.U.; Kazmi, S.N.; Mekkaoui, T. Thermal management of water based SWCNTs enclosed in a partially heated trapezoidal cavity via FEM. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2017, 112, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, F.A.; Haq, R.U.; Khan, Z.H.; Zhang, Q. Passive control of nanoparticle due to convective heat transfer of Prandtl fluid model at the stretching surface. Chin. J. Phys. 2017, 55, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Xie, H.Q.; Chen, L.F.; Li, Y. Investigation on the thermal transport properties of ethylene glycol-based nanofluids containing copper nanoparticles. Powder Technol. 2010, 197, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.Q.; Chen, L.F.J. Review on the preparation and thermal performances of carbon nanotube contained nanofluids. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 1030–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L. Developing a novel form of thermal conductivity of nanofluids with Brownian motion effect by means of fractal geometry. Powder Technol. 2013, 239, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buongiorno, J. Convective transport in nanofluids. ASME J. Heat Transf. 2006, 128, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.A.; Pop, I. Boundary layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2010, 53, 2477–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Z.; Gul, T.; Khan, M.A.; Ali, I.; Islam, S.; Hussain, F. Effects of hall current on steady three dimensional non-Newtonian nanofluid in a rotating frame with Brownian motion and thermophoresis effects. J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 6, 280–296. [Google Scholar]
- Balandin, A.A.; Ghosh, S.; Bao, W. Superior thermal conductivity of single-layer graphene. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Huaqing, X.; Dan, B. Enhanced thermal conductivities of nanofluids containing graphene oxide nanosheets. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 055705. [Google Scholar]
- Gul, T.; Firdous, K. The experimental study to examine the stable dispersion of the graphene nanoparticles and to look at the GO-H2O nanofluid flow between two rotating disks. Appl. Nanosci. 2018, 8, 1711–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, T.; Noman, W.; Sohail, M.; Khan, M.A. Impact of the Marangoni and thermal radiation convection on the graphene-oxide-water-based and ethylene-glycol-based nanofluids. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, M.; Khan, Z.H.; Lopez, R.J.; Khan, W.A. Heat and mass transfer in nanofluid thin film over an unsteady stretching sheet using Buongiorno’s model. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2016, 131, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshomrani, A.S.; Gul, T. The convective study of the Al2O3-H2O and Cu-H2O nano-liquid film sprayed over a stretching cylinder with viscous dissipation. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2017, 132, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, T.; Nasir, S.; Islam, S.; Shah, Z.; Khan, M.A. Effective Prandtl number model influences on the γAl2O3-C2H6O2 and γAl2O3-H2O nanofluids spray along a stretching cylinder. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 44, 1601–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, R.C.; Hashim, I.; Alomari, A.K. Thin film flow and heat transfer on an unsteady stretching sheet with internal heating. Meccanica 2011, 46, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, M.S.; Nassab, S.G. Numerical investigation of forced laminar convection flow of nanofluids over a backward facing step under bleeding condition. J. Mech. 2012, 28, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Nada, E. Numerical prediction of entropy generation in separated flows. Entropy 2005, 7, 234–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Nada, E. Application of nanofluids for heat transfer enhancement of separated flows encountered in a backward facing step. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2008, 29, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.J. The Proposed Homotopy Analysis Method for the Solution of Nonlinear Problems. Ph.D. Thesis, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China, June 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.J. Advances in the Homotopy Analysis Method; World Scientific Press: Singapore, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rehman, A.; Gul, T.; Salleh, Z.; Mukhtar, S.; Hussain, F.; Nisar, K.S.; Kumam, P. Effect of the Marangoni convection in the unsteady thin film spray of CNT nanofluids. Processes 2019, 7, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, T.; Sohail, M. Marangoni liquid film scattering over an extending cylinder. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 2019, 9, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.S.; Gul, T.; Kumam, P. Influence of inclined magnetic field on Carreau nanoliquid thin film flow and heat transfer with graphene nanoparticles. Energies 2019, 12, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, V.; Gul, T.; Afridi, S.; Ali, F.; Alharbi, S.O.; Khan, I. Thin film flow of micropolar fluid in a permeable medium. Coatings 2019, 9, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, T.; Khan, W.A.; Tahir, M.; Bilal, R.; Khan, I.; Nisar, K.S. Unsteady Nano–Liquid spray with thermal radiation comprising CNTs. Processes 2019, 7, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, T.; Khan, A.S.; Islam, S. Heat transfer investigation of the unsteady thin film flow of Williamson fluid past an inclined and oscillating moving plate. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.; Gul, T.; Idrees, M.; Islam, S.; Khan, I.; Dennis, L.C.C. Thin film Williamson nanofluid flow with varying viscosity and thermal conductivity on a time-dependent stretching sheet. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





GO-W | GO-W | GO-EG | GO-EG | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 30.3264 | 30.3335 | 28.7696 | 30.4545 |
| 0.2 | - | 30.3140 | 30.3412 | 30.3040 | 30.3414 |
| - | 0.2 | 30.2883 | 30.3261 | 30.2830 | 30.3264 |
| - | 0.3 | 30.7430 | 28.7777 | 28.1609 | 28.7778 |
GO-W | GO-W | GO-EG | GO-EG | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.5 | −0.1437 | −0.4409 | −0.62116 | −0.4411 |
| 0.2 | - | −1.2456 | −1.2571 | −1.2458 | −1.2576 |
| 0.3 | - | −1.8697 | −1.8869 | −1.8700 | −1.8875 |
| - | 0.6 | 0.6026 | −1.8337 | −0.6027 | −0.6098 |
| - | 0.7 | 0.5870 | −1.8875 | −0.5871 | −0.5952 |
| GO-W | GO-W | |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | ||
| 12 | ||
| 18 | ||
| 24 | ||
| 30 |
| GO-EG | GO-EG | |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | ||
| 12 | ||
| 18 | ||
| 24 | ||
| 30 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rehman, A.; Salleh, Z.; Gul, T.; Zaheer, Z. The Impact of Viscous Dissipation on the Thin Film Unsteady Flow of GO-EG/GO-W Nanofluids. Mathematics 2019, 7, 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7070653
Rehman A, Salleh Z, Gul T, Zaheer Z. The Impact of Viscous Dissipation on the Thin Film Unsteady Flow of GO-EG/GO-W Nanofluids. Mathematics. 2019; 7(7):653. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7070653
Chicago/Turabian StyleRehman, Ali, Zabidin Salleh, Taza Gul, and Zafar Zaheer. 2019. "The Impact of Viscous Dissipation on the Thin Film Unsteady Flow of GO-EG/GO-W Nanofluids" Mathematics 7, no. 7: 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7070653
APA StyleRehman, A., Salleh, Z., Gul, T., & Zaheer, Z. (2019). The Impact of Viscous Dissipation on the Thin Film Unsteady Flow of GO-EG/GO-W Nanofluids. Mathematics, 7(7), 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7070653





