Hedging Risks in the Loss-Averse Newsvendor Problem with Backlogging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Presentation and Motivation
2.2. Risk Measure: CVaR
2.3. The Model
3. Results
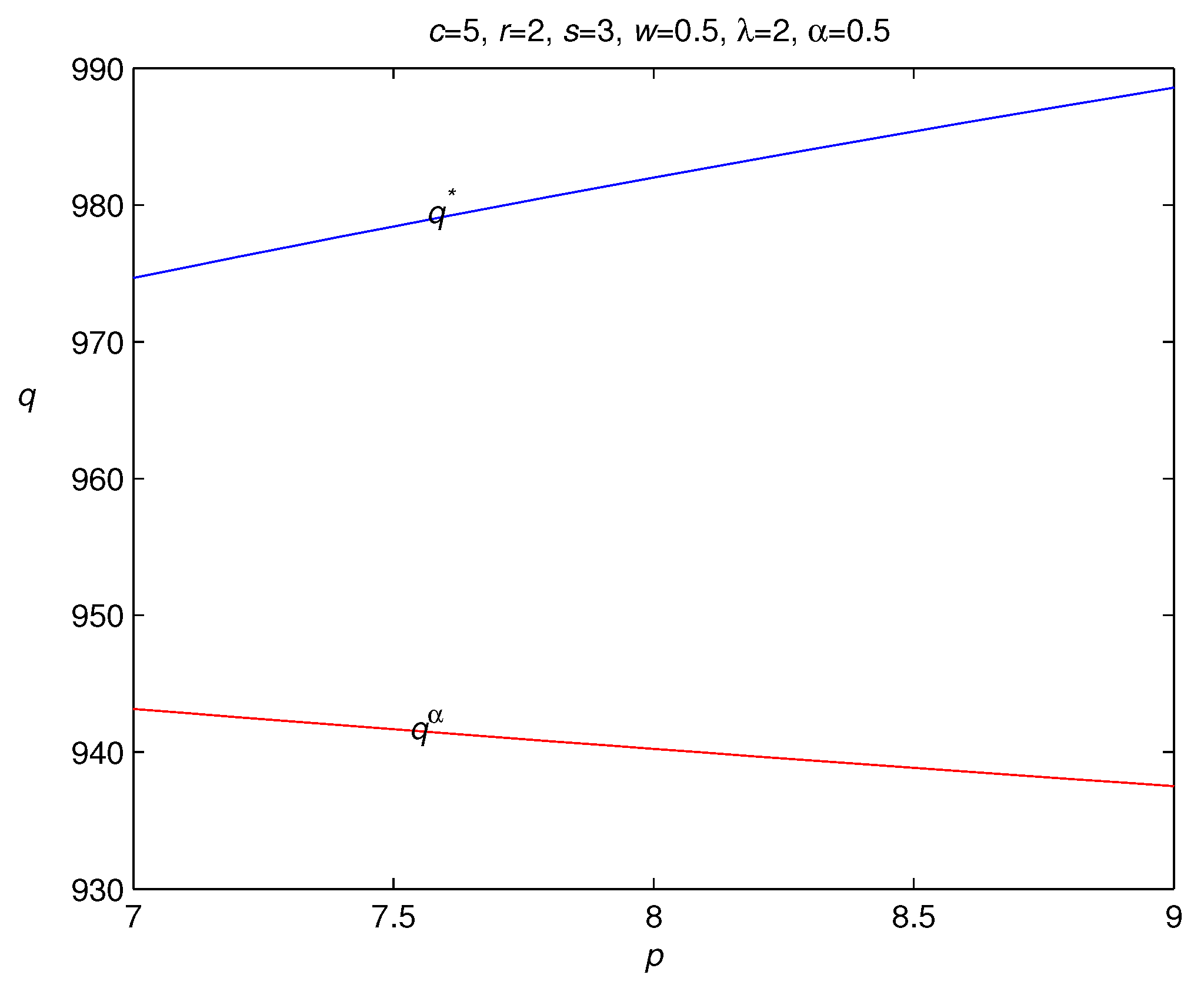
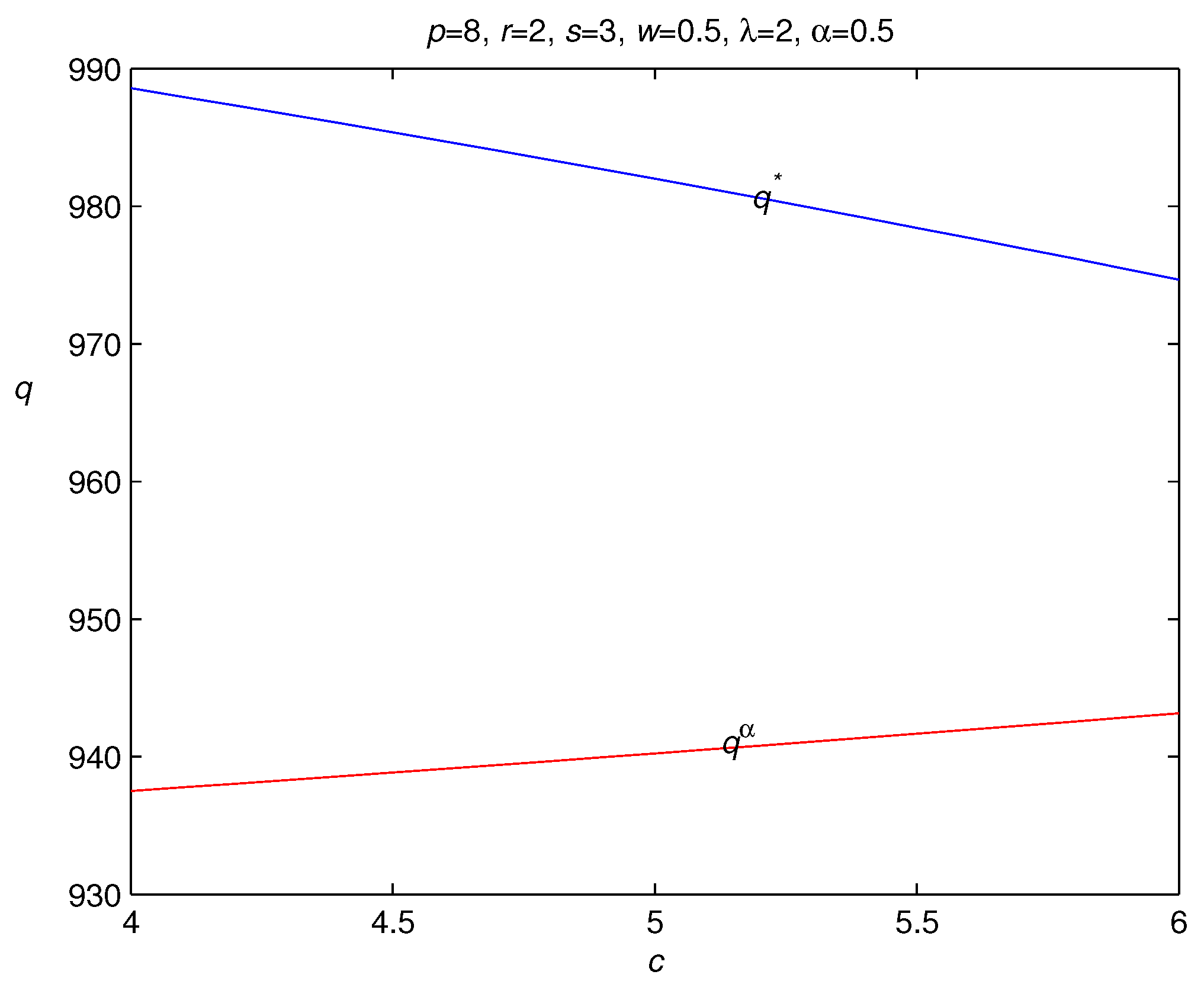
3.1. Optimal Order Quantity to Maximize Expected Utility
- (i)
- is increasing in the retail price p;
- (ii)
- is increasing in the salvage price r;
- (iii)
- is increasing in the shortage cost s; and
- (iv)
- is decreasing in the wholesale price c.
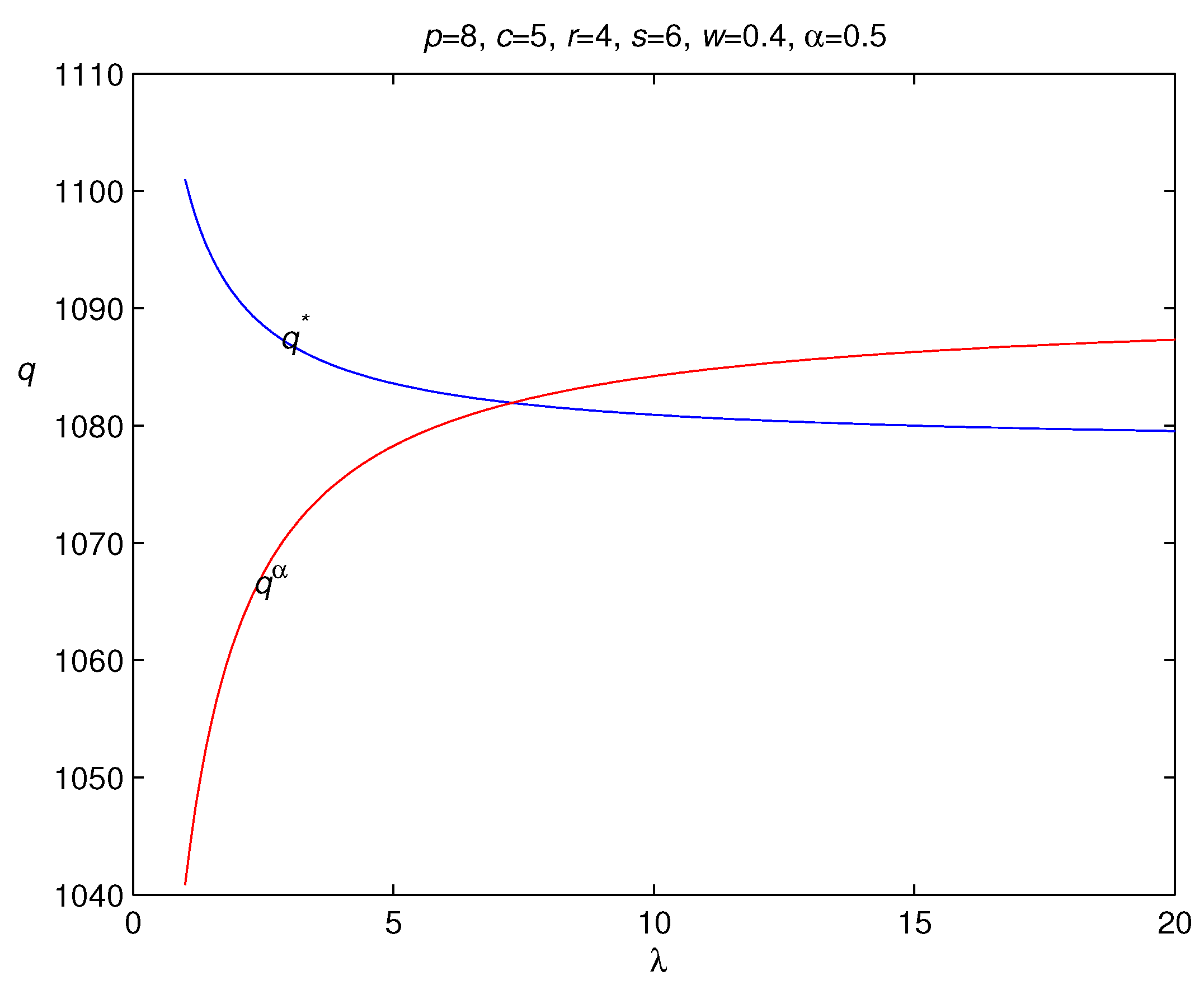
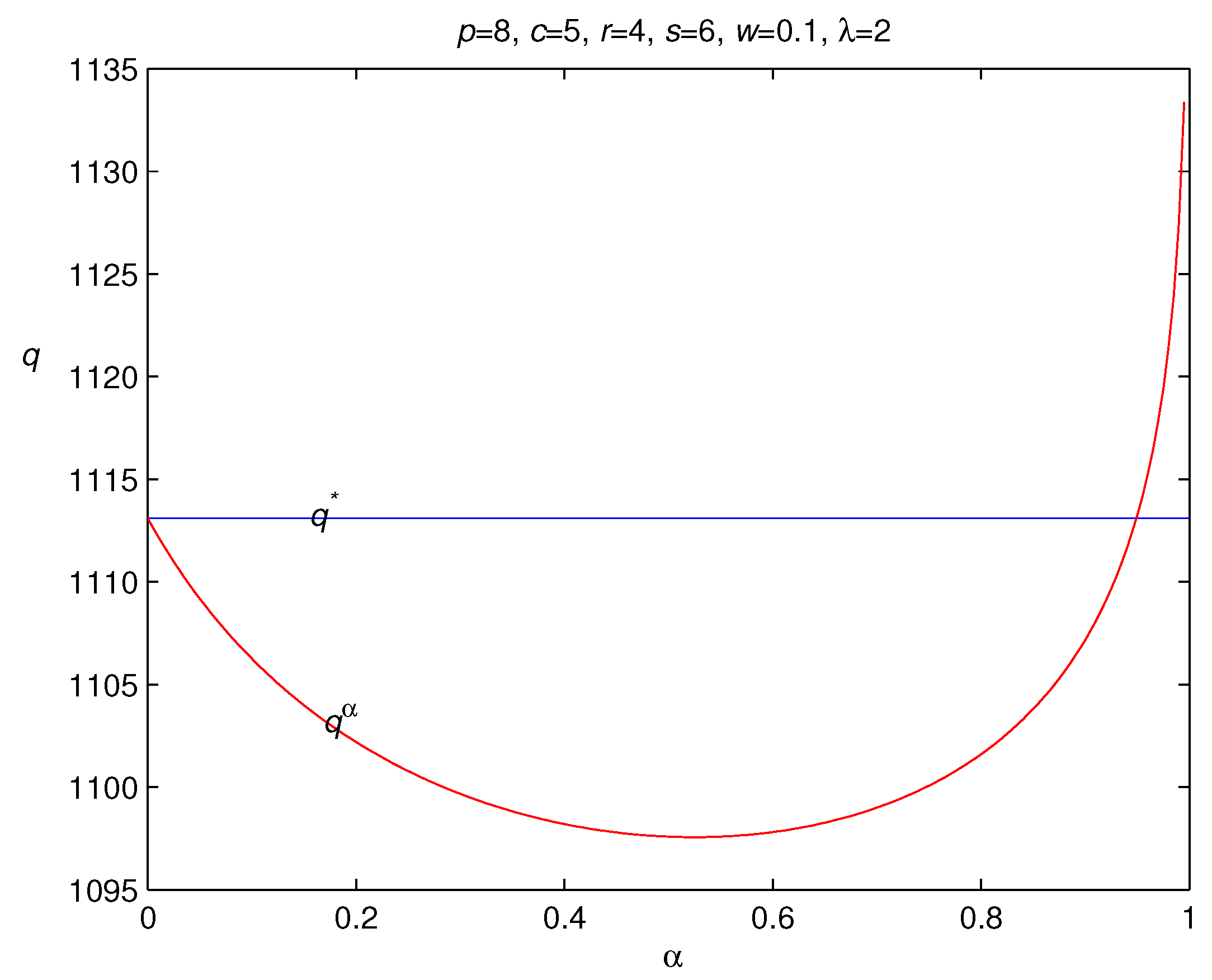
3.2. Risk Hedging in Loss-Averse Newsvendor Model with Backordering
- (i)
- is increasing in the salvage price r; and
- (ii)
- is increasing in the shortage cost s.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- (i)
- , that is . For this case, for any fixed q, we consider the following three cases:
- (a)
- .
- (b)
- .
- (ii)
- , that is .
- (a)
- .
- (b)
- .
References
- Gruen, T.; Corsten, D. Rising to the challenge of out-of-stocks. ECR J. 2002, 2, 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery, D.C.; Bazaraa, M.S.; Keswani, A.K. Inventory models with a mixture of backorders and lostsales. Naval Res. Logist. Q. 1973, 20, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pando, V.; San, J.L.A.; García-Laguna, J.; Sicilia, J. A newsboy problem with an emergency order under a general backorder rate function. Omega 2013, 41, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San José, L.A.; Sicilia, J.; Garciá-Laguna, J. Analysis of an inventory system with exponential partial backordering. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2006, 100, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodree, J.E.J. Advanced supply chain planning with mixture of backorders, lost sales, and lost contract. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 181, 168–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodree, J.E.J.; Kim, Y.; Jang, W. Time and quantity dependent waiting costs in a newsvendor problem with backlogged shortages. Math. Comput. Model. 2008, 47, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, S. Manufacturer-buyer coordination for newsvendor-type-products with two ordering opportunities and partial backorders. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 198, 958–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, S.; Hassin, R.; Zhang, N. Two backorder compensation mechanisms in inventory systems with impatient customers. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2015, 24, 1640–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.D.; Song, M.; Tan, K.C.; Zhang, C.Y. Multi-class dynamic inventory rationing with stochastic demands and backordering. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 244, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.F.; Hsu, J.T. Economic production quantity (EPQ) models under an imperfect production process with shortages backordered. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2016, 47, 852–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braglia, M.; Castellano, D.; Gallo, M. Approximate d close d-form minimum-cost solution to the (r,q) policy with complete backordering and further developments. Appl. Math. Model. 2016, 40, 8406–8423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.N.; Liu, Z.Y.; Yu, Y.M.; Zhang, W. On the decomposition property for a dynamic inventory rationing problem with multiple demand classes and backorder. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 265, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khouja, M. The single-period (news-vendor) problem: Literature review and suggestions for further research. Omega 1999, 27, 537–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Wang, R.; Vakharia, A.J.; Chen, Y.; Michelle, M.H.S. The newsvendor problem: Review and directions for further research. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 213, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahneman, D.; Tversky, A. Prospect theory: An analysis of decision under risk. Econometrica 1979, 47, 263–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, M.E.; Cachon, G.P. Decision bias in the newsvendor problem with a known demand distribution: Experimental evidence. Manag. Sci. 2000, 46, 404–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.X.; Webster, S. The loss-averse newsvendor problem. Omega 2009, 37, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.F.; Wu, D.S.; Liang, L.; Olson, D.L. Supply chain loss averse newsboy model with capital constraint. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2016, 46, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xu, Q.Y.; Xu, B.; Wu, P.K. Supply chain coordination in quality improvement with reference effects. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2016, 67, 1158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vipin, B.; Amit, R.K. Loss aversion and rationality in the newsvendor problem under recourse option. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 261, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chan, C.K.; Langevin, A. Coping with risk management and fill rate in the loss-averse newsvendor model. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 195, 296–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artzner, P.; Delbaen, F.; Eber, J.M.; Heath, D. Coherent measures of Risk. Math. Finance 1999, 9, 203–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauser, H.; Rosen, D. Beyond VaR: From measuring risk to managing risk. ALGO Res. Q. 1999, 1, 5–20. [Google Scholar]
- Rockafellar, R.T.; Uryasev, S. Optimization of Conditional Value-at-Risk. J. Risk 2000, 2, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockafellar, R.T.; Uryasev, S. Conditional value-at-risk for general loss distributions. J. Bank. Finance 2002, 26, 1443–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yu, G.; Zhang, H. CVaR in a newsvendor model with lost sale penalty cost. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 2006, 26, 1–8. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh, J.; Takano, Y. Newsvendor solutions via conditional value-at-risk minimization. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 179, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, J. Optimal decisions when balancing expected profit and conditional value-at-risk in newsvendor models. J. Syst. Sci. Complex. 2010, 23, 1054–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sim, M.; Simichi-levi, D.; Sun, P. Risk Aversion in Inventory Management; MIT: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Z.G. A risk-averse newsvendor model under the CVaR criterion. Oper. Res. 2009, 57, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lin, Q.; Ye, F. Pricing and promised delivery lead time decisions with a risk-averse agent. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2014, 52, 3518–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Ayuso, A.; Escudero, L.F.; Guignard, M.; Weintraub, A. Risk management for forestry planning under uncertainty in demand and prices. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 267, 1051–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, H.W.; Lu, H. Coordination of supply chains with a retailer under the mean-CVaR criterion. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018, 48, 1039–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Meng, Z.; Shen, R. A tri-level programming model based on Conditional Value-at-Risk for three-stage supply chain management. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2013, 66, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Meng, Z.; Shen, R.; Jiang, M.; Ji, P. Optimal decisions for the loss-averse newsvendor problem under CVaR. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 164, 146–159. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Meng, Z.; Ji, P.; Dang, C.; Wang, H. On the newsvendor model with conditional Value-at-Risk of opportunity loss. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2016, 54, 2449–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Dang, C.; Ji, P. The loss-averse newsvendor model with backordering. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 188, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, S.G.; Thorstenson, A. Emergency orders in the periodic-review inventory system with fixed ordering costs and compound Poisson demand. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014, 157, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, J.; Wang, Y.; Chan, F.T.S.; Hu, X.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, F.; Shi, B.; Shi, Y.; Lin, F. A life-cycle framework of green IoT based agriculture and its finance, operation and management issues. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019, 57, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chan, F.T.S.; Chan, C.K. Optimal option purchase decision of a loss-averse retailer under emergent replenishment. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Optimal Order Quantity (OOQ) q | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPM order quantity in newsvendor model | + | − | + | + | n/a | n/a | n/a | |
| OOQ in Chen et al. [29] | + | − | + | n/a | − | n/a | n/a | |
| OOQ in Gotoh and Takano [27] | + | − | + | + | n/a | n/a | ||
| OOQ in Schweitzer and Cachon [16] | + | − | + | n/a | n/a | − | n/a | |
| OOQ in Wang and Webster [17] | + | + | n/a | n/a | ||||
| in this paper | + | − | + | + | n/a | − | − | |
| in this paper | + | + | − |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Chan, F.T.S.; Xu, X. Hedging Risks in the Loss-Averse Newsvendor Problem with Backlogging. Mathematics 2019, 7, 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7050429
Liu X, Chan FTS, Xu X. Hedging Risks in the Loss-Averse Newsvendor Problem with Backlogging. Mathematics. 2019; 7(5):429. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7050429
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoqing, Felix T. S. Chan, and Xinsheng Xu. 2019. "Hedging Risks in the Loss-Averse Newsvendor Problem with Backlogging" Mathematics 7, no. 5: 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7050429
APA StyleLiu, X., Chan, F. T. S., & Xu, X. (2019). Hedging Risks in the Loss-Averse Newsvendor Problem with Backlogging. Mathematics, 7(5), 429. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7050429






