A Hierarchical Approach for Joint Parameter and State Estimation of a Bilinear System with Autoregressive Noise
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We present a bilinear state estimator on the basis of the Kalman filtering algorithm.
- We derive a state estimator-based RGLS algorithm for joint state and parameter estimation of bilinear state space models on the basis of the hierarchical identification principle.
- We derive a filtering-based two-stage RGLS (F-TS-RGLS) algorithm using the state estimates for improving the parameter estimation accuracy by introducing the data filtering technique.
2. System Description
3. The RGLS Algorithm Using the Bilinear State Estimates
4. The F-TS-RGLS Algorithm Using the Bilinear State Estimator
- To initialize: let , , , , , , , , , , , , , .
- Increase t by one, and turn to Step 2.
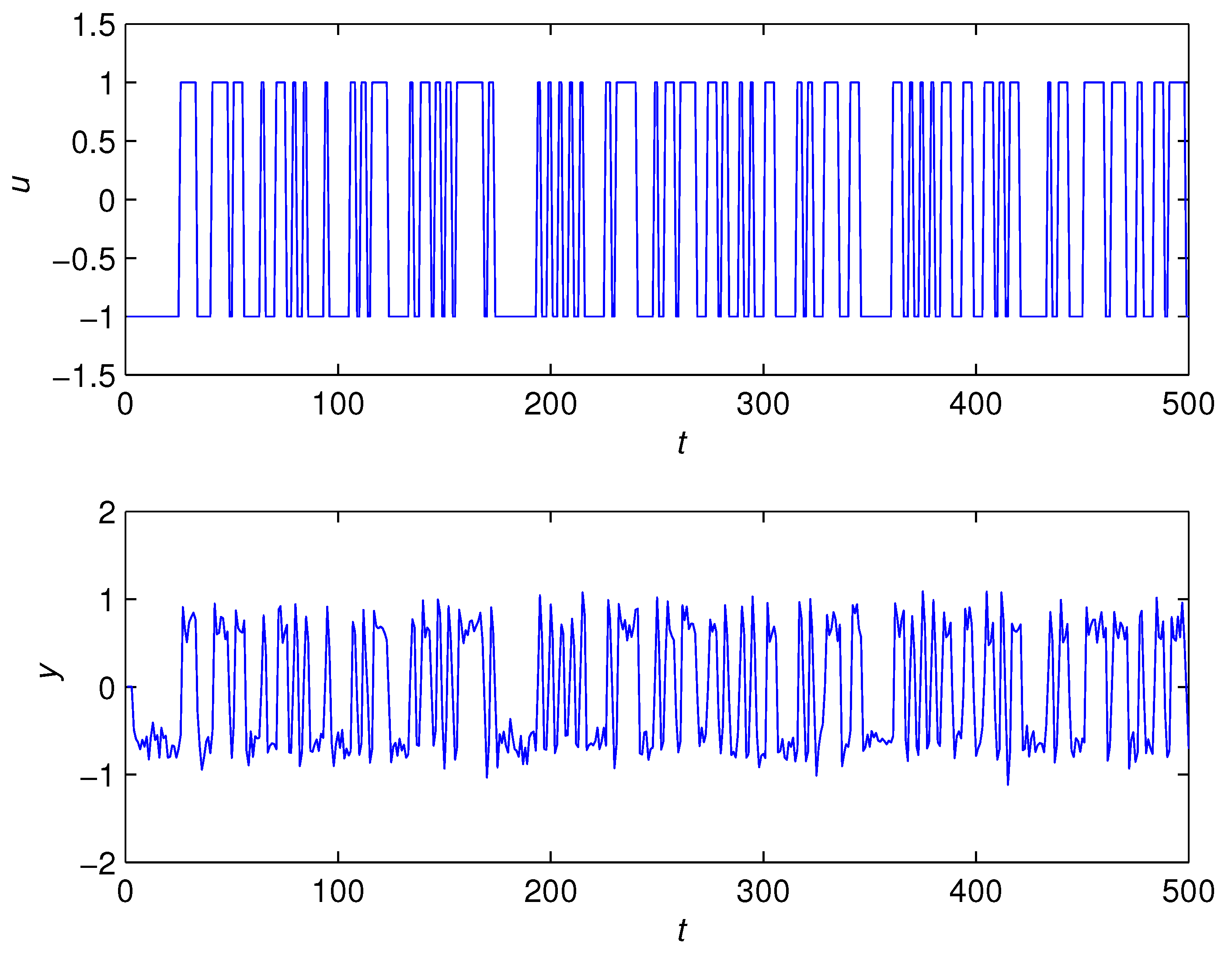
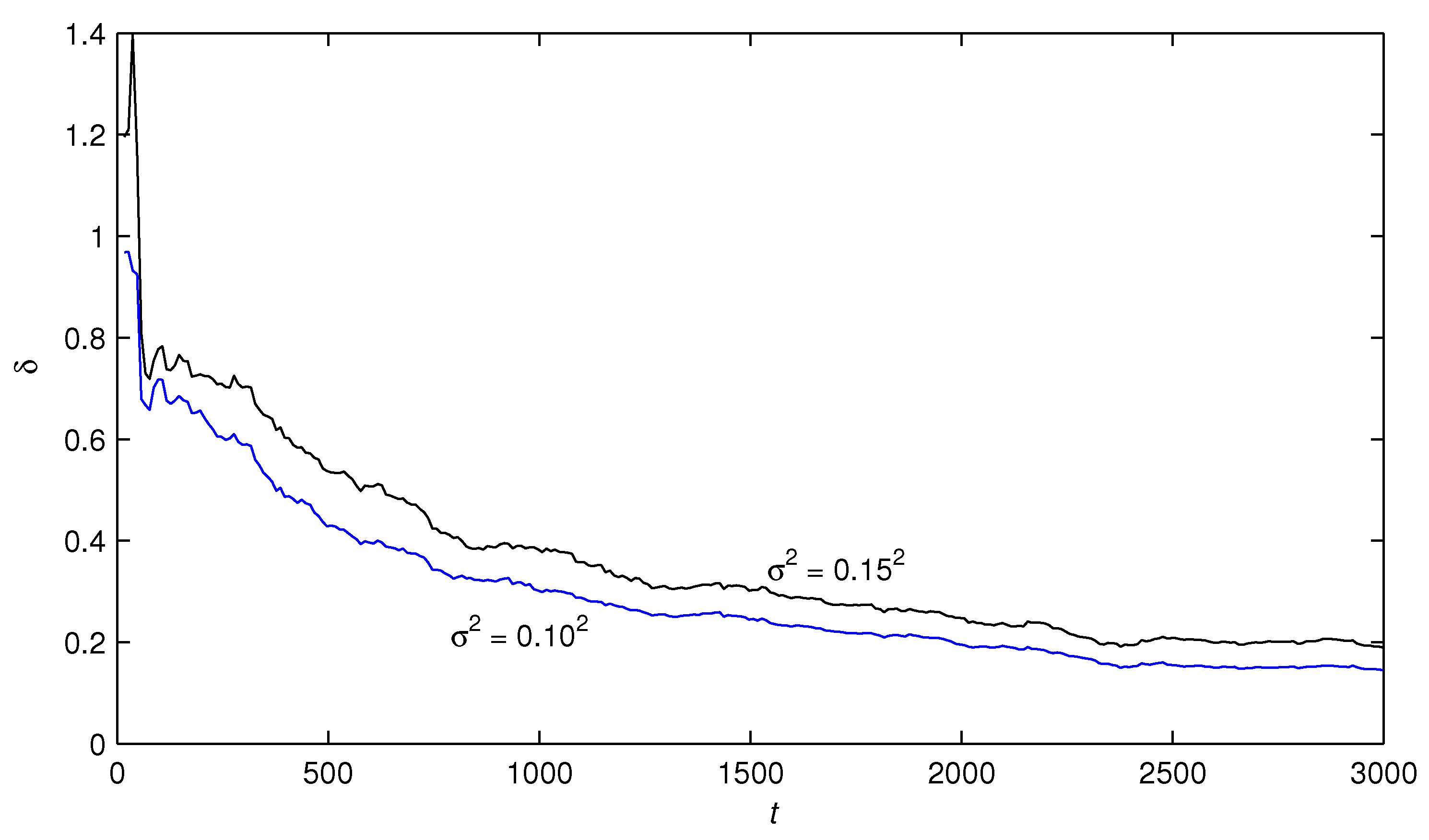
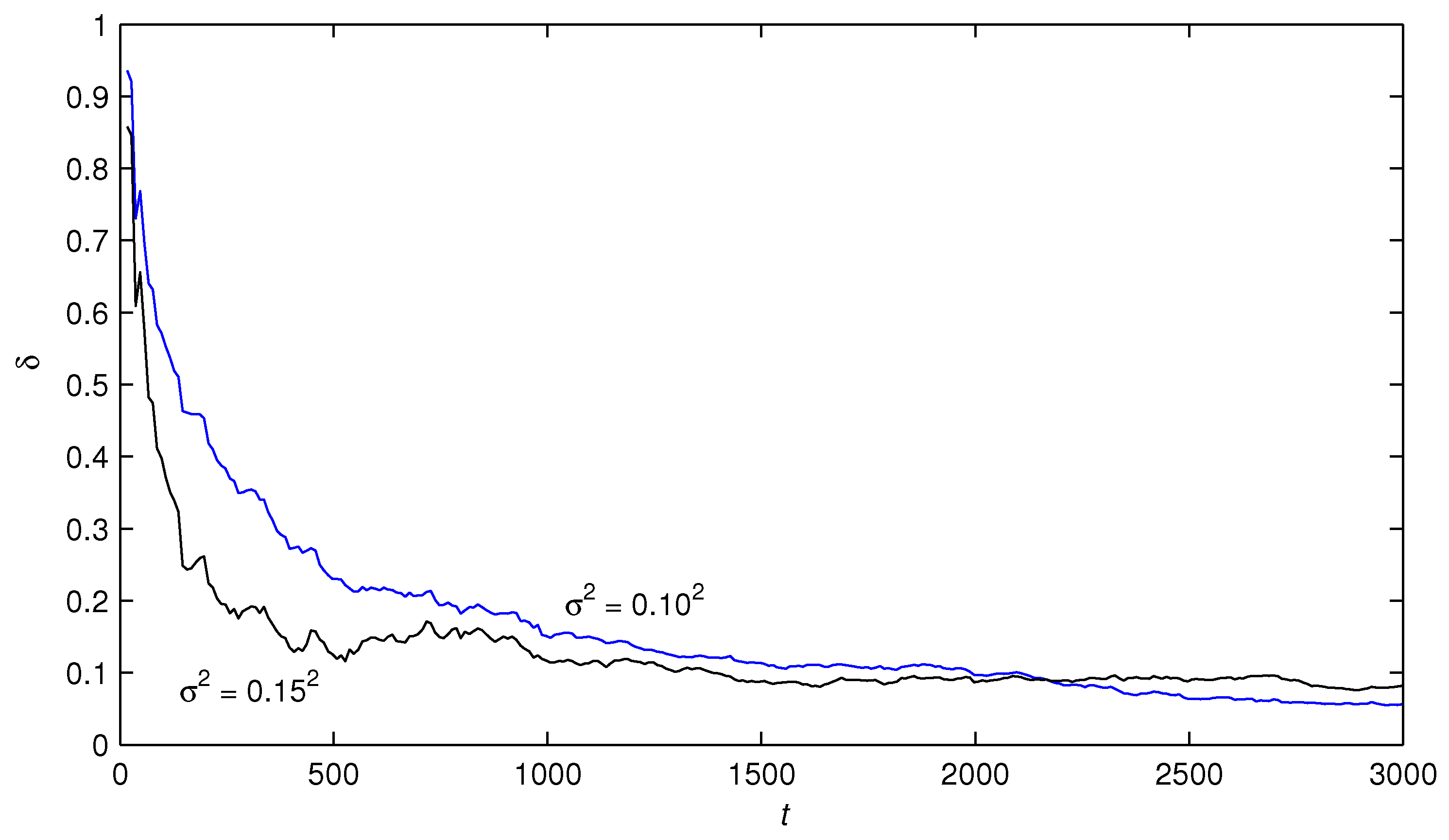
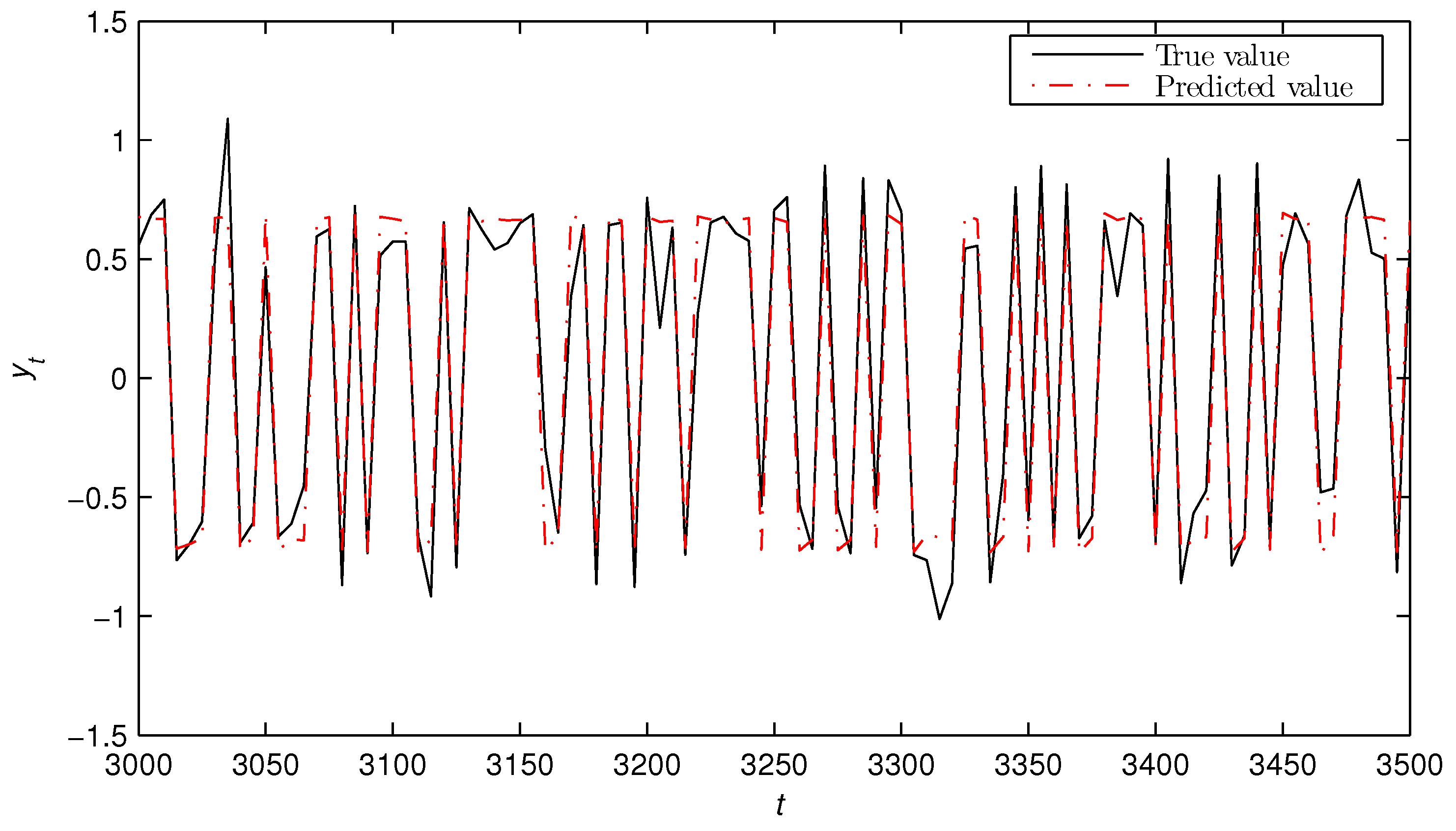
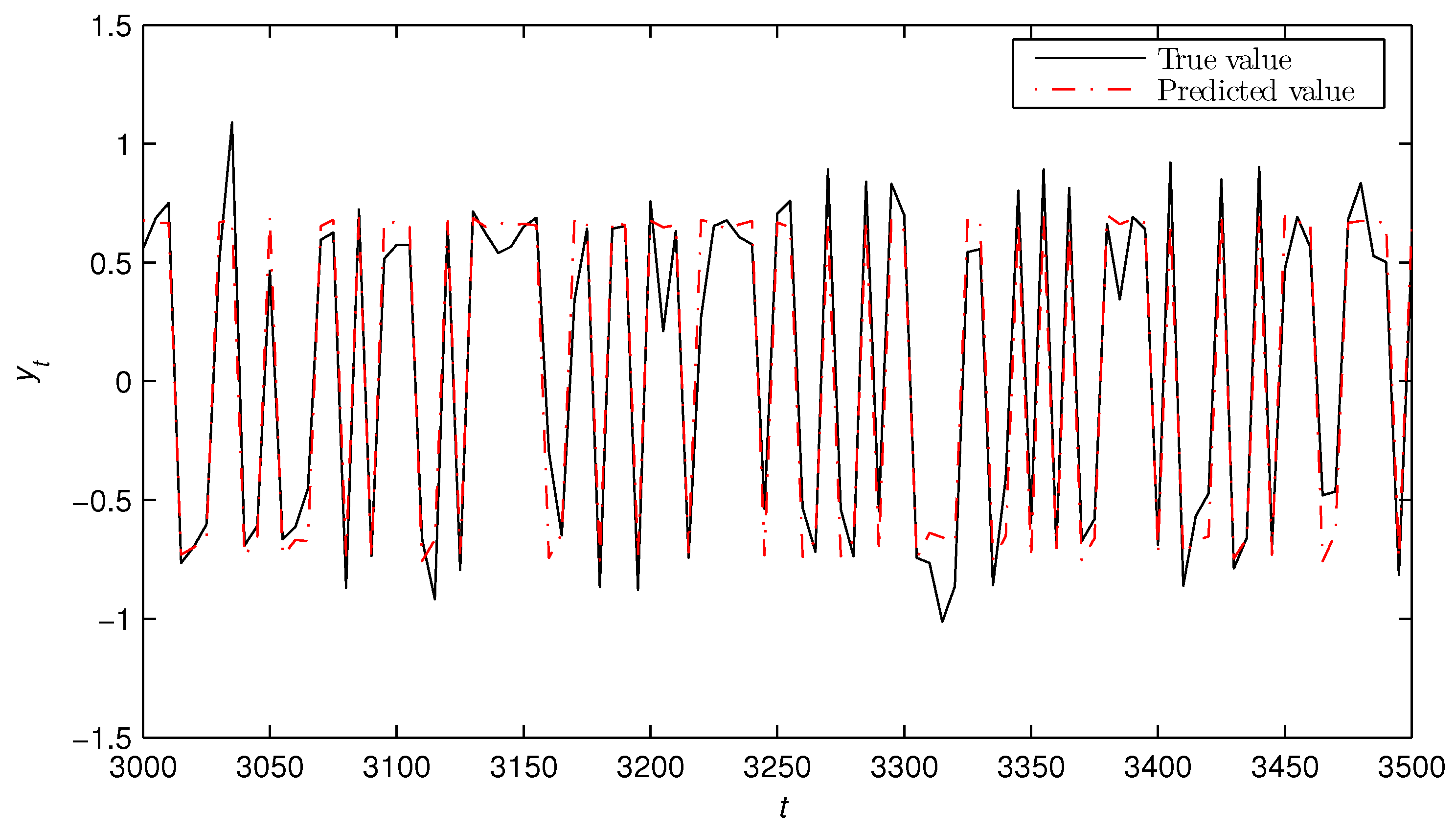
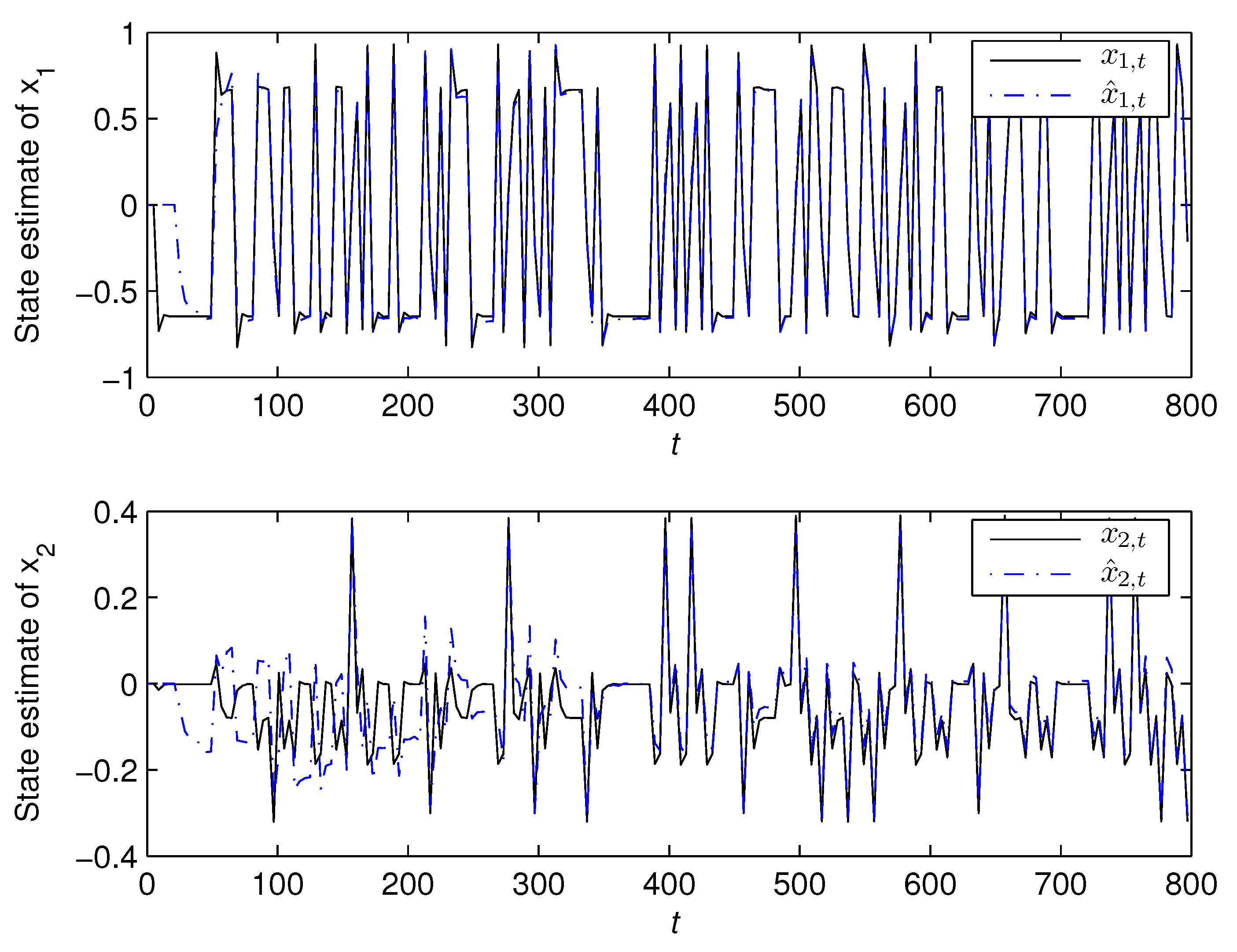
5. Numerical Example
- The estimation errors of the RGLS algorithm and the F-TS-RGLS algorithm became smaller with the data length increasing. This means that the proposed algorithms are effective.
- Under the same noise levels, the state estimator-based F-TS-RGLS algorithm could generate more accurate parameter estimates than the state estimator-based RGLS algorithm.
- The F-TS-RGLS algorithm could decrease the dimensions of the covariance matrices and improve the computational efficiency.
- The state estimates obtained from the bilinear state estimator could track their true values as t increased.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, K.; Jiang, B.; Shi, P. Adjustable parameter-based distributed fault estimation observer design for multiagent systems with directed graphs. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 47, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L. A proportional differential control method for a time-delay system using the Taylor expansion approximation. Appl. Math. Comput. 2014, 236, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. Application of the Newton iteration algorithm to the parameter estimation for dynamical systems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2015, 288, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, L.; Xiong, W.L. Parameter estimation and controller design for dynamic systems from the step responses based on the Newton iteration. Nonlinear Dyn. 2015, 79, 2155–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ding, F. Parameter estimation for control systems based on impulse responses. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2017, 15, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.Z.; Yin, C.C. Solution of Hamilton-Jacobi-Bellman equation in optimal reinsurance strategy under dynamic VaR constraint. J. Funct. Spaces 2019, 2019, 6750892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. The parameter estimation algorithms based on the dynamical response measurement data. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ding, F. Iterative parameter estimation for signal models based on measured data. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2018, 37, 3046–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Xiong, W.L.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T. Hierarchical parameter estimation for the frequency response based on the dynamical window data. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2018, 16, 1756–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, F.; Xu, L.; Yang, E.F. Highly computationally efficient state filter based on the delta operator. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; Gan, M.; Chen, C.L.P.; Li, H.X. A regularized variable projection algorithm for separable nonlinear least-squares problems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2019, 64, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; Gan, M.; Ding, F.; Chen, C.L.P. Modified Gram-Schmidt method-based variable projection algorithm for separable nonlinear models. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Li, H.X. An efficient variable projection formulation for separable nonlinear least squares problems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 44, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Liu, X.P.; Liu, G. Gradient based and least-squares based iterative identification methods for OE and OEMA systems. Digit. Signal Process. 2010, 20, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Liu, X.G.; Chu, J. Gradient-based and least-squares-based iterative algorithms for Hammerstein systems using the hierarchical identification principle. IET Control Theory Appl. 2013, 7, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F. Decomposition based fast least squares algorithm for output error systems. Signal Process. 2013, 93, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F. Two-stage least squares based iterative estimation algorithm for CARARMA system modeling. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 4798–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Wang, D.Q.; Ding, F. Least squares based iterative algorithms for identifying Box-Jenkins models with finite measurement data. Digit. Signal Process. 2010, 20, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ding, F.; Yang, E.F. Modeling a nonlinear process using the exponential autoregressive time series model. Nonlinear Dyn. 2019, 95, 2079–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Y.; Ding, F. Auxiliary model-based recursive generalized least squares algorithm for multivariate output-error autoregressive systems using the data filtering. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 38, 590–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.W.; Ding, F.; Xu, L.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T. Gradient-based iterative identification method for multivariate equation-error autoregressive moving average systems using the decomposition technique. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 1658–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.P.; Niu, H.M. A bi-objective model with sequential search algorithm for optimizing network-wide train timetables. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 127, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.X. The truncation method for the Cauchy problem of the inhomogeneous Helmholtz equation. Appl. Anal. 2019, 98, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Wu, M.; Jiang, Y.; Xiong, W.; Liu, C. Contract design for relay incentive mechanism under dual asymmetric information in cooperative networks. Wirel. Netw. 2018, 24, 3029–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.H.; Shekofteh, Y.; Akgul, A.; Li, C.B.; Panahi, S. A new chaotic system with a self-excited attractor: Entropy measurement, signal encryption, and parameter estimation. Entropy 2018, 20, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Li, H.X.; Wu, B.Y. Piecewise reproducing kernel method for linear impulsive delay differential equations with piecewise constant arguments. Appl. Math. Comput. 2019, 349, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, C.; Dipillo, G.; Koch, G. Bilinear systems: An appealing class of nearly linear systems in theory and applications. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1974, 19, 334–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D. Observation of bilinear systems with application to biological control. Automatica 1977, 13, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Shields, D.N. A bilinear fault detection observer. Automatica 1996, 32, 1597–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohler, R.R.; Kolodziej, W.J. An overview of bilinear system theory and applications. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 2007, 10, 683–688. [Google Scholar]
- Favoreel, W.; De Moor, B.; Van Overschee, P. Subspace identification of bilinear systems subject to white inputs. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1999, 44, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdult, V.; Verhaegen, M. Identification of multivariable bilinear state space systems based on subspace techniques and separable least squares optimization. Int. J. Control 2001, 74, 1824–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkowski, T.; Linden, J.G.; Vinsonneau, B.; Burnham, K.J. Frisch scheme identification for dynamic diagonal bilinear models. Int. J. Control 2009, 82, 1591–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hizir, N.B.; Phan, M.Q.; Betti, R.; Longman, R.W. Identification of discrete-time bilinear systems through equivalent linear models. Nonlinear Dyn. 2012, 69, 2065–2078. [Google Scholar]
- Vicario, F.; Phan, M.Q.; Betti, R.; Longman, R.W. Linear state representations for identification of bilinear discrete-time models by interaction matrices. Nonlinear Dyn. 2014, 77, 1561–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L. The damping iterative parameter identification method for dynamical systems based on the sine signal measurement. Signal Process. 2016, 120, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ding, F. Parameter estimation algorithms for dynamical response signals based on the multi-innovation theory and the hierarchical principle. IET Signal Process. 2017, 11, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ding, F. Recursive least squares and multi-innovation stochastic gradient parameter estimation methods for signal modeling. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 36, 1735–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Chen, C.L.P.; Chen, G.Y.; Chen, L. On some separated algorithms for separable nonlinear squares problems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 48, 2866–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.P. Parameter estimation with scarce measurements. Automatica 2011, 47, 1646–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.P. Partially coupled stochastic gradient identification methods for non-uniformly sampled systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2010, 55, 1976–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Y.; Shmaliy, Y.S.; Ahn, C.K.; Liu, F. Adaptive-horizon iterative UFIR filtering algorithm with applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 6393–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.Y.; Huang, B.; Liu, F. Linear optimal unbiased filter for time-variant systems without apriori information on initial conditions. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2017, 62, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Ding, F.; Gu, Y.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T. A multi-innovation state and parameter estimation algorithm for a state space system with d-step state-delay. Signal Process. 2017, 140, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopin, N.; Jacob, P.E.; Papaspiliopoulos, O. SMC2: An efficient algorithm for sequential analysis of state space models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2013, 75, 397–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wingerden, J.W.; Verhaegen, M. Subspace identification of bilinear and LPV systems for open-and closed-loop data. Automatica 2009, 45, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroud, J.R.; Katzfuss, M.; Wikle, C.K. A Bayesian adaptive ensemble Kalman filter for sequential state and parameter estimation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2018, 46, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urteaga, I.; Bugallo, M.F.; Djurić, P.M. Sequential Monte Carlo methods under model uncertainty. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop (SSP), Palma de Mallorca, Spain, 26–29 June 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Martino, L.; Read, J.; Elvira, V.; Louzada, F. Cooperative parallel particle filters for online model selection and applications to urban mobility. Digit. Signal Process. 2017, 60, 172–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schön, T.B.; Wills, A.; Ninness, B. System identification of nonlinear state-space models. Automatica 2011, 47, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.H.; Liu, X.M. The least squares based iterative algorithms for parameter estimation of a bilinear system with autoregressive noise using the data filtering technique. Signal Process. 2018, 147, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, M.Q.; Vicario, F.; Longman, R.W.; Betti, R. Optimal bilinear observers for bilinear state-space models by interaction matrices. Int. J. Control 2015, 88, 1504–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, F.; Alsaadi, F.E.; Hayat, T. Recursive parameter identification of the dynamical models for bilinear state space systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 89, 2415–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, F.; Xu, L.; Yang, E.F. State filtering-based least squares parameter estimation for bilinear systems using the hierarchical identification principle. IET Control Theory Appl. 2018, 12, 1704–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Ding, F.; Hayat, T. Combined state and parameter estimation for a bilinear state space system with moving average noise. J. Frankl. Inst. 2018, 355, 3079–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, L.; Elvira, V.; Camps-Valls, G. Distributed Particle Metropolis-Hastings schemes. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Statistical Signal Processing Workshop, Freiburg, Germany, 10–13 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, C.M.; Johannes, M.S.; Lopes, H.F.; Polson, N.G. Particle learning and smoothing. Stat. Sci. 2010, 25, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.Y.; Yin, Y.K.; Li, M. Start-up process modelling of sediment microbial fuel cells based on data driven. Math. Probl. Eng. 2019, 2019, 7403732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Ma, H.; Jiang, X.; Ding, W.; Ding, F. Adaptive gradient-based iterative algorithm for multivariate controlled autoregressive moving average systems using the data filtering technique. Complexity 2018, 2018, 9598307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.P. Control algorithms of magnetic suspension systems based on the improved double exponential reaching law of sliding mode control. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2018, 16, 2878–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.H.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, M.; Zhao, N.; Wang, J.; Wan, X.; Rao, Z.; Zhu, L. Robust global motion estimation for video security based on improved k-means clustering. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2019, 10, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.K.; Wu, H.; Qiao, F.; Li, F.C.; Li, Y.; Yan, Y.W.; Wei, J.X. Electrocardiogram baseline wander suppression based on the combination of morphological and wavelet transformation based filtering. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2019, 2019, 7196156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Schaeffer, E.; Wang, Y. A M-EKF fault detection strategy of insulation system for marine current turbine. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 115, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Si, Y.; Huang, B.; Lou, Z. Survey on the theoretical research and engineering applications of multivariate statistics process monitoring algorithms: 2008–2017. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 96, 2073–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Chou, Y.; Liu, J.; Ji, Y. Moving horizon estimation for multirate systems with time-varying time-delays. J. Frankl. Inst. 2019, 356, 2325–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Ding, F. Iterative estimation for a non-linear IIR filter with moving average noise by means of the data filtering technique. IMA J. Math. Control Inf. 2017, 34, 745–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Lu, H.; Wen, T. A safety computer system based on multi-sensor data processing. Sensors 2019, 19, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, T.; Li, P. Research on dynamic nonlinear input prediction of fault diagnosis based on fractional differential operator equation in high-speed train control system. Chaos 2019, 29, 013130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, Y. Parallel processing algorithm for railway signal fault diagnosis data based on cloud computing. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 88, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ma, L.C.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W. Standard analysis for transfer delay in CTCS-3. Chin. J. Electron. 2017, 26, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.M.; Zhang, F.F.; Li, T.X. Synchronization and antisynchronization of N-coupled fractional-order complex chaotic systems with ring connection. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2018, 41, 2625–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.H.; Xue, L.; Jiang, X. Global stabilization for a class of stochastic nonlinear systems with SISS-like conditions and time delay. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2018, 28, 3909–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Chen, Y.; Liu, R.; Wu, M.H.; Xiong, W. Monitoring strategy for relay incentive mechanism in cooperative communication networks. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2017, 60, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Wu, M.H.; Chen, J.J. Android-based mobile educational platform for speech signal processing. Int. J. Electr. Eng. Edu. 2017, 54, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Ding, F. Multiperiodicity and exponential attractivity of neural networks with mixed delays. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 36, 2558–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Algorithms | Number of Multiplications | Number of Additions | Total Flop |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGLS | |||
| F-TS-RGLS | |||
| Algorithms | t | c | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGLS | 100 | −0.00316 | 0.05268 | 0.07544 | 0.05230 | −0.06414 | −0.05137 | 0.42414 | 0.34337 | 0.09662 | 77.79370 |
| 200 | −0.02327 | 0.12465 | 0.06667 | 0.02426 | −0.06804 | −0.03437 | 0.41314 | 0.31430 | −0.00151 | 73.30282 | |
| 500 | −0.16392 | 0.16651 | 0.03428 | 0.08494 | −0.05452 | −0.03641 | 0.42364 | 0.26468 | 0.02093 | 53.53272 | |
| 1000 | −0.26324 | 0.20629 | 0.03025 | 0.11604 | −0.04730 | −0.07382 | 0.41937 | 0.22896 | 0.01985 | 38.31102 | |
| 2000 | −0.36424 | 0.23406 | 0.03468 | 0.13072 | −0.04674 | −0.10435 | 0.41210 | 0.19167 | 0.03129 | 24.68460 | |
| 3000 | −0.40788 | 0.25214 | 0.04352 | 0.12255 | −0.04747 | −0.12509 | 0.40931 | 0.18628 | 0.05481 | 18.65007 | |
| F-TS-RGLS | 100 | −0.17207 | 0.13225 | 0.08149 | 0.04762 | −0.08050 | −0.06387 | 0.38554 | 0.24812 | −0.24016 | 67.37094 |
| 200 | −0.26379 | 0.21163 | 0.05110 | 0.10094 | −0.07089 | −0.08449 | 0.39815 | 0.22078 | −0.20425 | 51.91655 | |
| 500 | −0.41609 | 0.27122 | 0.04448 | 0.17605 | −0.04003 | −0.19822 | 0.40894 | 0.15549 | −0.06009 | 20.84531 | |
| 1000 | −0.44506 | 0.28907 | 0.05723 | 0.16636 | −0.05408 | −0.19663 | 0.40519 | 0.15223 | −0.00605 | 12.54315 | |
| 2000 | −0.45785 | 0.28984 | 0.06293 | 0.16491 | −0.06176 | −0.19095 | 0.40193 | 0.14834 | 0.02730 | 8.43565 | |
| 3000 | −0.45744 | 0.29468 | 0.06717 | 0.15764 | −0.06434 | −0.19611 | 0.40149 | 0.14983 | 0.05888 | 4.92240 | |
| True values | −0.46000 | 0.30000 | 0.08000 | 0.17000 | −0.07000 | −0.22000 | 0.40000 | 0.15000 | 0.08000 | ||
| Algorithms | t | c | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RGLS | 100 | −0.01344 | 0.08368 | 0.04929 | 0.12366 | −0.04534 | −0.08160 | 0.42729 | 0.30373 | 0.01047 | 71.76858 |
| 200 | −0.04819 | 0.15699 | 0.03634 | 0.12767 | −0.03469 | −0.10328 | 0.41799 | 0.25865 | −0.09361 | 65.81981 | |
| 500 | −0.21525 | 0.21335 | 0.02114 | 0.18346 | −0.02157 | −0.15342 | 0.42234 | 0.19440 | −0.08012 | 42.77206 | |
| 1000 | −0.31044 | 0.24492 | 0.03458 | 0.18170 | −0.03375 | −0.16150 | 0.41530 | 0.17384 | −0.06081 | 30.24311 | |
| 2000 | −0.39697 | 0.26064 | 0.04731 | 0.17039 | −0.04645 | −0.16265 | 0.40883 | 0.15616 | −0.02604 | 19.40043 | |
| 3000 | −0.42738 | 0.27001 | 0.05540 | 0.15703 | −0.05159 | −0.16863 | 0.40674 | 0.15902 | 0.00337 | 14.22233 | |
| F-TS-RGLS | 100 | −0.17072 | 0.12873 | 0.08786 | 0.04669 | −0.08179 | −0.08320 | 0.39734 | 0.23700 | −0.08772 | 56.19069 |
| 200 | −0.26673 | 0.21478 | 0.05515 | 0.09642 | −0.07483 | −0.09063 | 0.40715 | 0.20974 | −0.07335 | 40.40498 | |
| 500 | −0.45453 | 0.28197 | 0.04590 | 0.18588 | −0.04140 | −0.21202 | 0.41195 | 0.13243 | 0.04761 | 8.46768 | |
| 1000 | −0.46578 | 0.29562 | 0.05933 | 0.17264 | −0.05829 | −0.20062 | 0.40718 | 0.14093 | 0.06403 | 4.89664 | |
| 2000 | −0.47371 | 0.29198 | 0.06315 | 0.17165 | −0.06534 | −0.19084 | 0.40294 | 0.13951 | 0.06910 | 5.33512 | |
| 3000 | −0.46830 | 0.29693 | 0.06704 | 0.16129 | −0.06756 | −0.19803 | 0.40240 | 0.14385 | 0.08923 | 4.02737 | |
| True values | −0.46000 | 0.30000 | 0.08000 | 0.17000 | −0.07000 | −0.22000 | 0.40000 | 0.15000 | 0.08000 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Ding, F.; Xu, L.; Alsaedi, A.; Hayat, T. A Hierarchical Approach for Joint Parameter and State Estimation of a Bilinear System with Autoregressive Noise. Mathematics 2019, 7, 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7040356
Zhang X, Ding F, Xu L, Alsaedi A, Hayat T. A Hierarchical Approach for Joint Parameter and State Estimation of a Bilinear System with Autoregressive Noise. Mathematics. 2019; 7(4):356. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7040356
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiao, Feng Ding, Ling Xu, Ahmed Alsaedi, and Tasawar Hayat. 2019. "A Hierarchical Approach for Joint Parameter and State Estimation of a Bilinear System with Autoregressive Noise" Mathematics 7, no. 4: 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7040356
APA StyleZhang, X., Ding, F., Xu, L., Alsaedi, A., & Hayat, T. (2019). A Hierarchical Approach for Joint Parameter and State Estimation of a Bilinear System with Autoregressive Noise. Mathematics, 7(4), 356. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7040356






