A Study of an EOQ Model under Lock Fuzzy Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
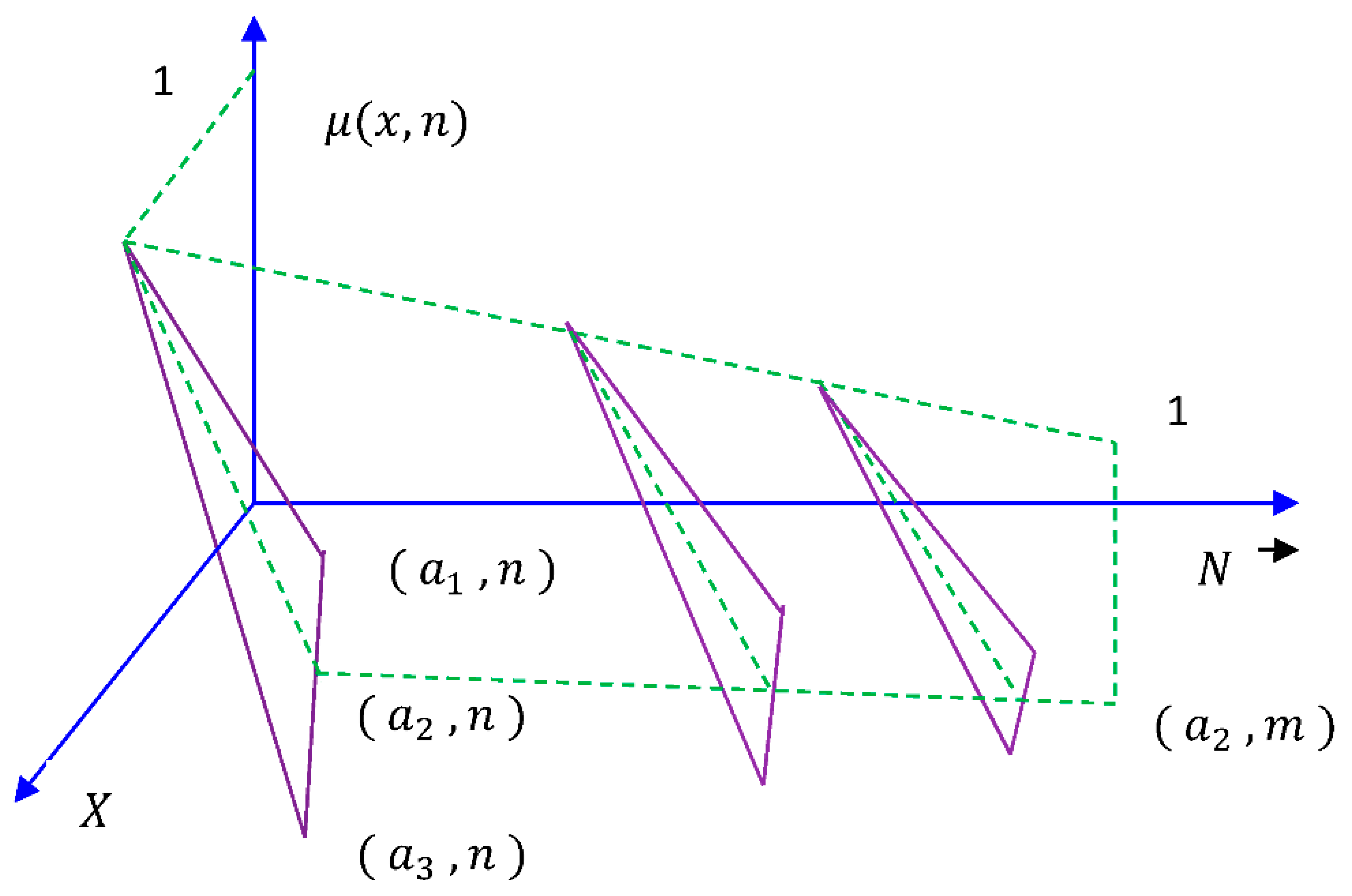
2.1. Triangular Dense Fuzzy Set (TDFS)
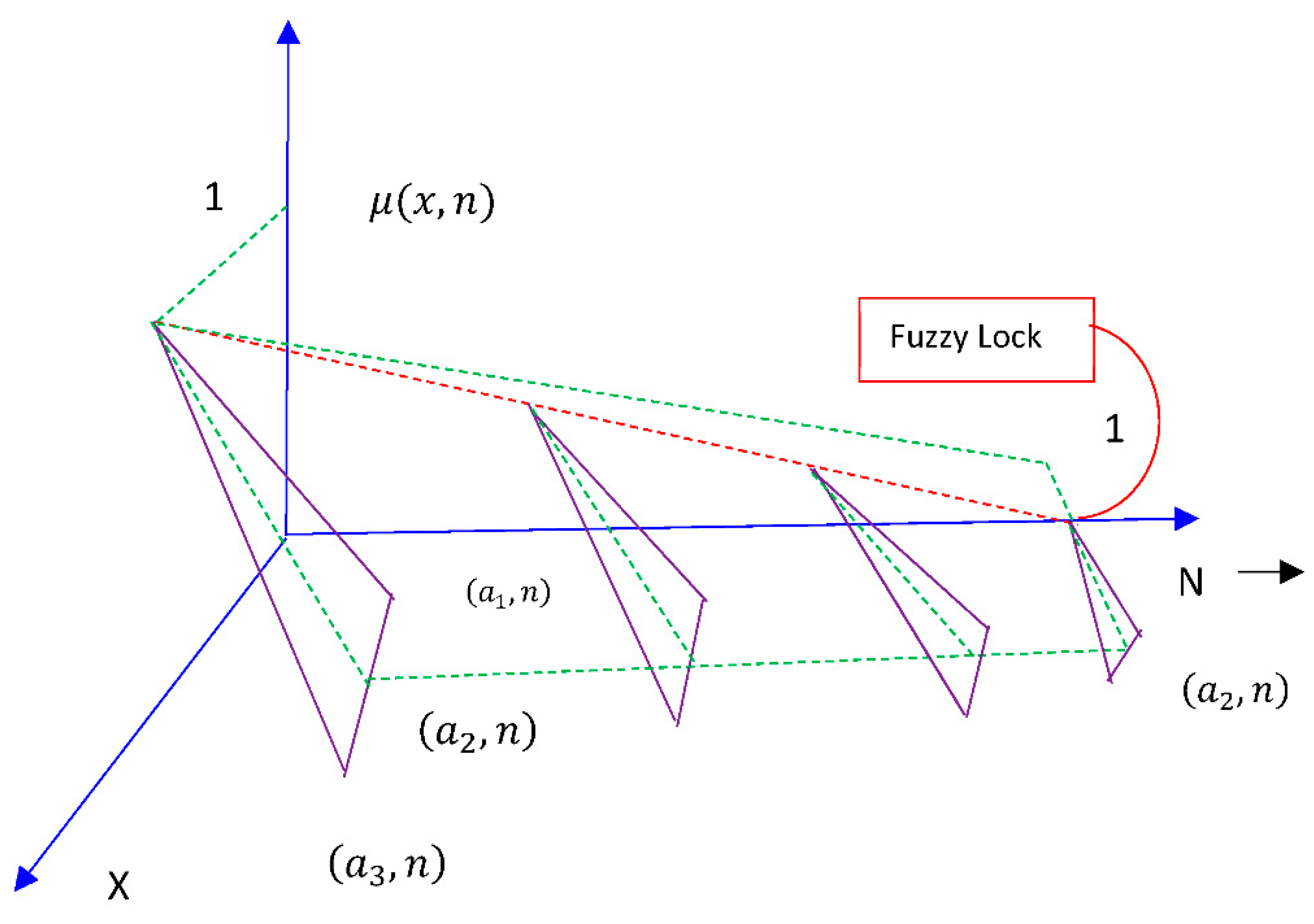
2.2. Triangular Dense Fuzzy Lock Sets (TDFLS)
2.3. Implication of TDFLS in Inventory Management Problems
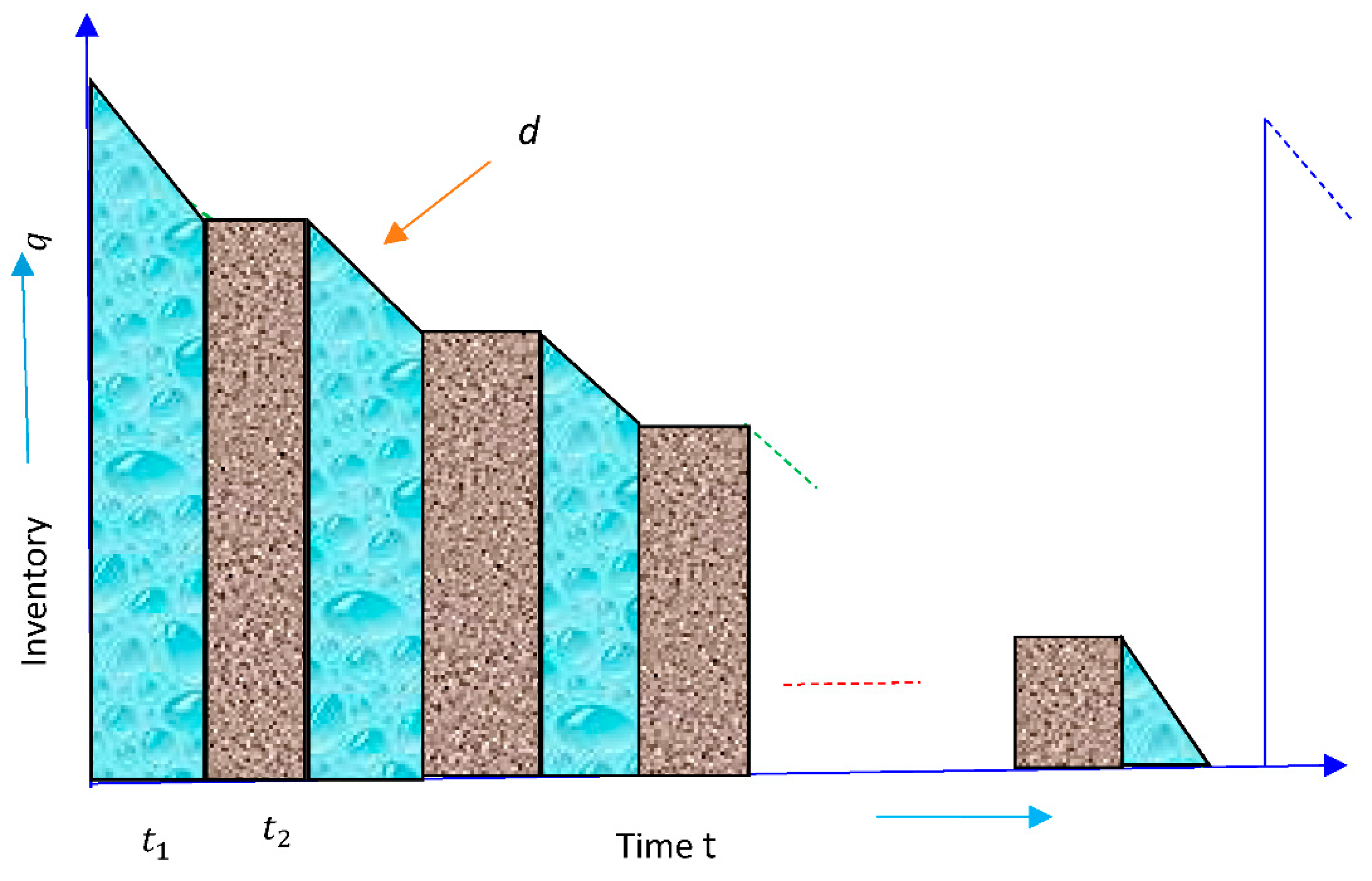
3. Crisp Mathematical Model
3.1. Assumptions and Notations
- Order quantity per cycle (decision variable)
- Inventory opening time per day (decision variable)
- Duration of closing/natural ideal time per day (decision variable)
- Inventory holding cost per unit quantity per day ($)
- Set up cost per cycle ($)
- Average natural idle time cost per unit idle time ($)
- selling price per unit ($)
- Cycle length (= n + 1) (days)
- Time horizon (days)
- Total average profit per cycle ($)
- Replenishments are instantaneous
- The time horizon is infinite
- The sum of opening and closing time period is unity
- Shortages are not allowed
- Holding cost is uniform over the cycle time
- Average natural idle time (leisure/pause) cost is constant per unit idle time
- The security charge, telephone charge, transportation cost (if any) etc., beyond the working hours may be considered as the idle time cost.
3.2. Formulation of the Crisp Mathematical Model
4. Fuzzy Mathematical Model
4.1. Model 1: When Demand Rate Assumes Dense Fuzzy Number
- (i)
- If in (22) then
- (ii)
- If in (i) then , the case of single key
- (iii)
- If in (ii) then , the case of general fuzzy number.
- (iv)
- If in (iii) then , the case of crisp model.
- (i)
- Problem of Dense fuzzy modelReferring (11), (16), and (18) the problem can be formulated as
- (ii)
- Problem of Dense fuzzy lock modelReferring to (19) and (22), the problem can be formulated asand the other parameters obtained in (23). Please note that for single key .
- (iii)
- Problem of general fuzzy modelTo set up the model considering then (24) becomesand the other parameters taken from (23).
Numerical Example 1
4.2. Model 2: When the Cost/Price Components Assume Fuzzy Number
- (i)
- If then gives the crisp problem.
- (ii)
- If for thengives the general fuzzy problem.
- (iii)
- If for thengives the problem of dense fuzzy model.
- (iv)
- If for thengives the problem of dense fuzzy lock model for single key.
- (v)
- If for thengives the problem of dense fuzzy lock model for double keys.
Numerical Example 2
4.3. Model 3: When Demand Rate and Cost/Price All Assume to Be Fuzzy Numbers
- (i)
- If then gives the crisp problem.
- (ii)
- If for thengives the general fuzzy problem.
- (iii)
- If for thengives the problem of dense fuzzy model.
- (iv)
- If for thengives the problem of dense fuzzy lock model for single key.
- (v)
- If for thengives the problem of dense fuzzy lock model for double keys.
Numerical Example 3
4.4. Discussion on Numerical Results Obtained in Model 1, Model 2, and Model 3
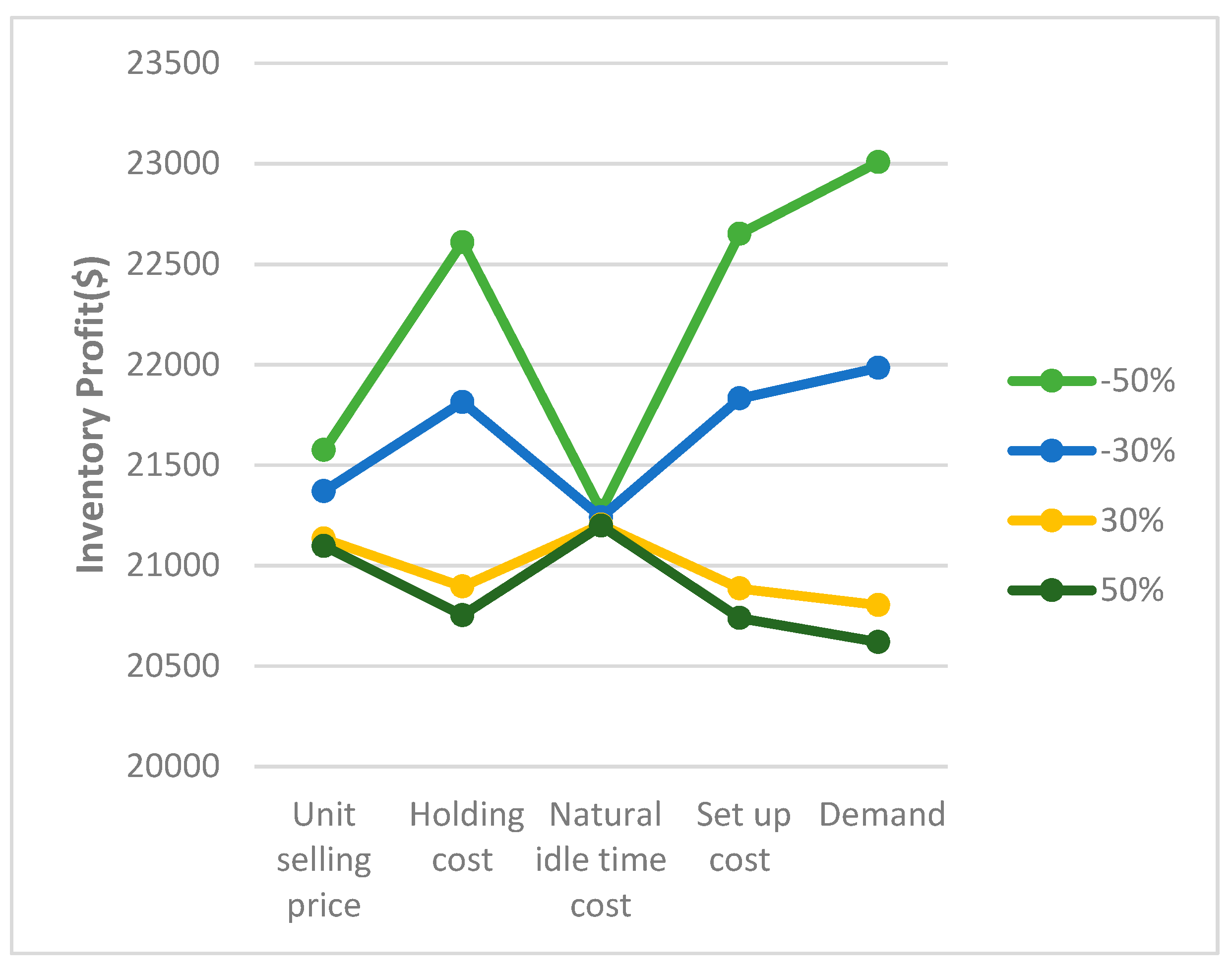
4.5. Sensitivity Analysis
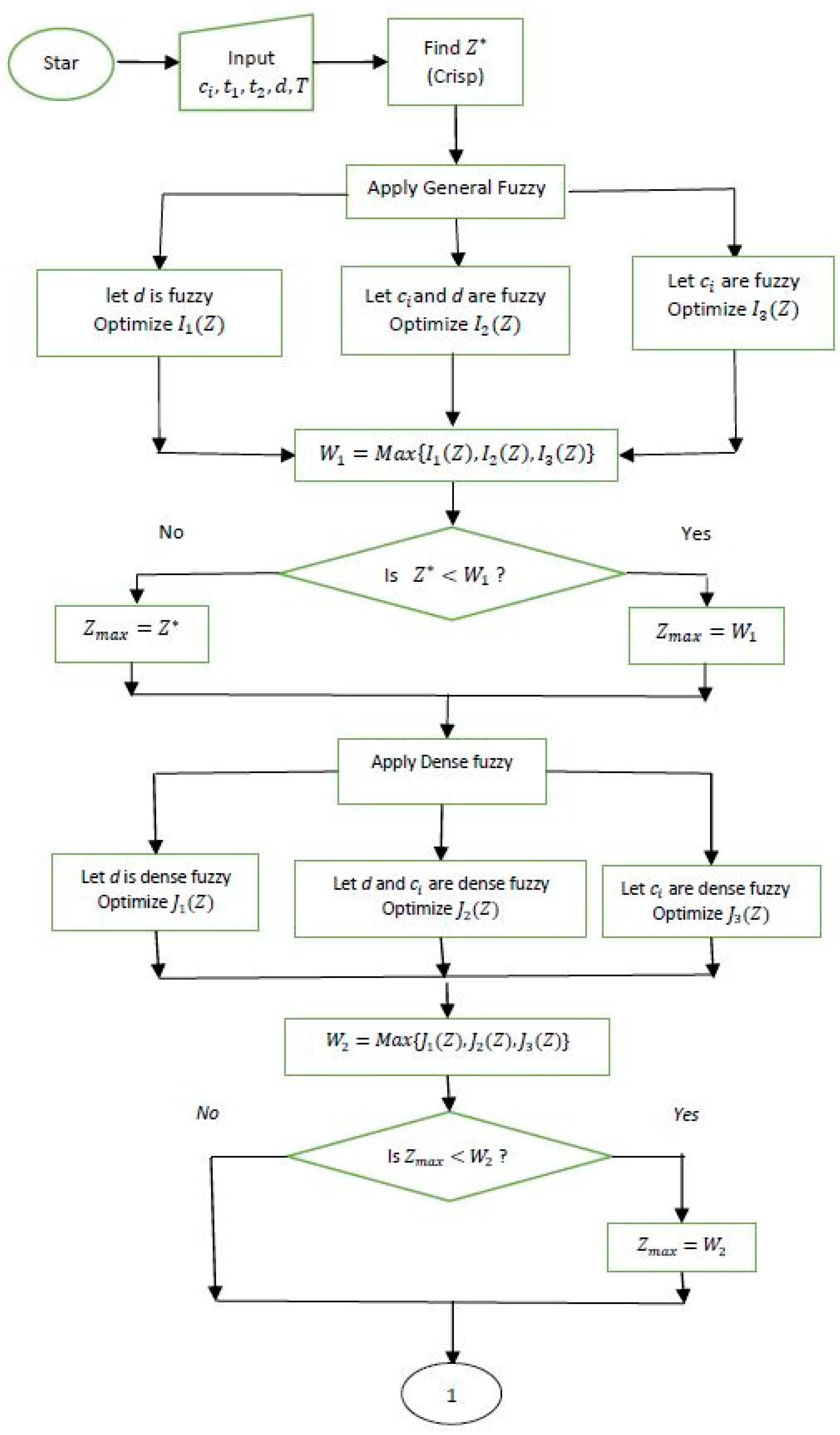
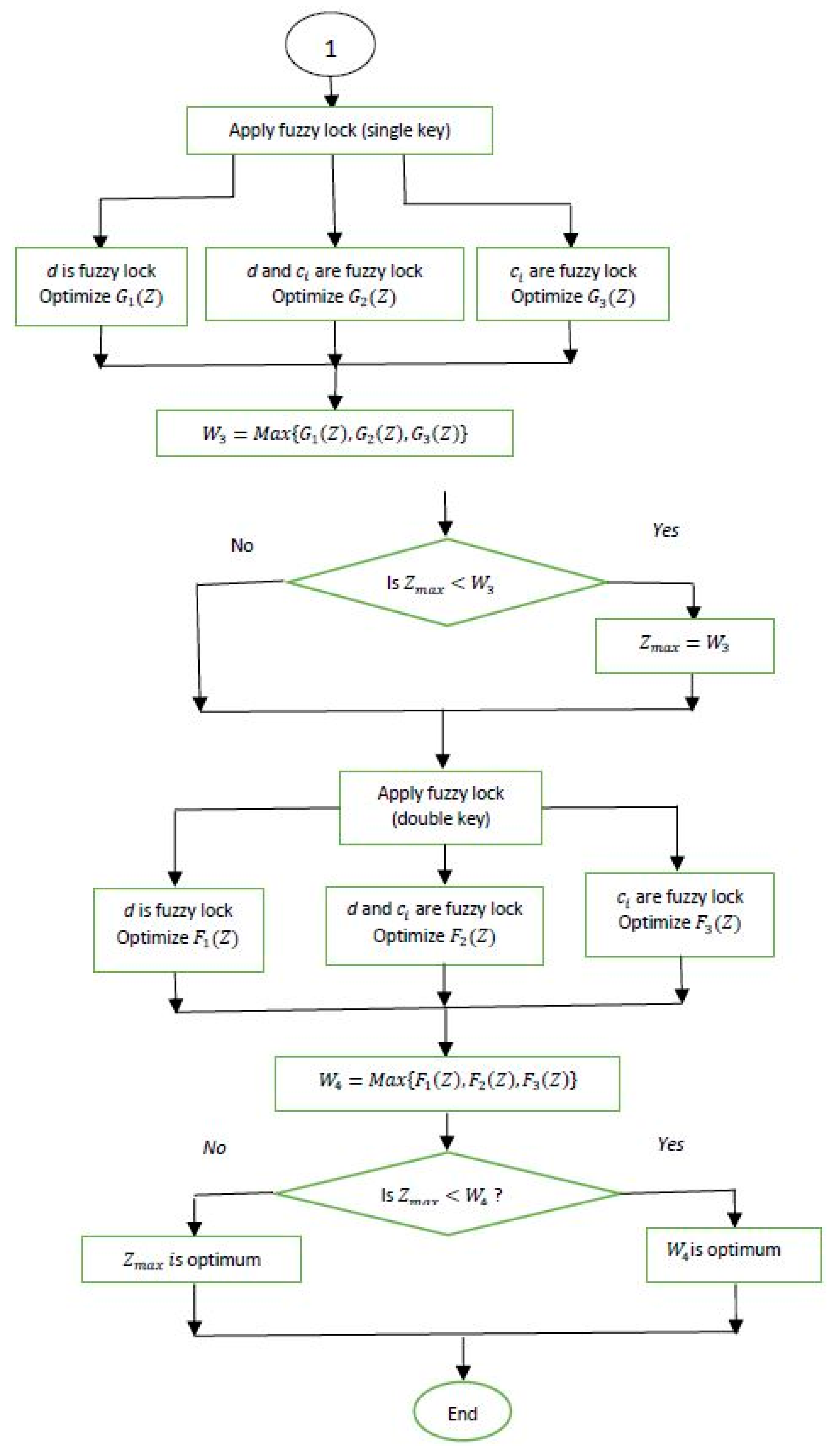
4.6. Solution Procedure for Dense Fuzzy Lock Set Model
Solution Algorithm and Flow Chart over Dense Fuzzy Lock Set Model
- Input .
- Find average profit (Crisp) using Equations (4), (5), (7), and (9).
- Apply general fuzzy (a) when d is fuzzy (b) when and d are fuzzy and (c) when are fuzzy only.
- Find corresponding average profit using Equations (25), (30), and (39), respectively.
- Find
- Check if yes go to step 7 else go to step 8.
- Set go to step 9.
- Set
- Apply dense fuzzy rule over the parameters.
- Consider three cases d is dense fuzzy, and d are dense fuzzy, are dense fuzzy.
- Find corresponding average profit respectively using Equations (23), (39), and (31).
- Find corresponding average profit .
- Check if yes go to step 14 else go to step 15.
- Set
- Apply fuzzy lock set of single key over the fuzzy parameters.
- Consider three cases d is fuzzy lock, and d are fuzzy lock, are fuzzy lock.
- Find corresponding average profit using Equations (24), (32), and (41), respectively.
- Find
- Check if yes go to step 20 else go to step 21.
- Set
- Apply fuzzy lock set of double keys over the fuzzy parameters.
- Consider three cases d is fuzzy lock, and d are fuzzy lock, are fuzzy lock.
- Find corresponding average profit using Equations (24), (33) and (42) respectively
- Find
- Check if yes go to step 26 else go to step 27.
- is optimum, go to step 25.
- is optimum.
- End.
4.7. Graphical Illustration
5. Conclusions
- (a)
- Inventory problems should be optimized with the help of dense fuzzy lock set rules instead of dense fuzzy rules.
- (b)
- Double key vectors may be able to maximize the average profit function instead of taking single key vectors for managerial decision-making.
- (c)
- Optimum results can be checked and updated through a computer-based algorithm.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- (i)
- Invested capital cost.
- (ii)
- Record-keeping and administrative cost.
- (iii)
- Handling cost.
- (iv)
- Storage cost.
- (v)
- Taxes and insurance costs.
References
- Nash, J.F. The bargaining problem. Econometrica 1950, 18, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 1965, 8, 338–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellman, R.E.; Zadeh, L.A. Decision making in a fuzzy environment. Manag. Sci. 1970, 17, 141–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, D.; Prade, H. Operations on fuzzy numbers. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 1978, 9, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, A.; Gupta, M.M. Introduction of Fuzzy Arithmetic Theory and Applications; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Baez-Sancheza, A.D.; Morettib, A.C.; Rojas-Medarc, M.A. On polygonal fuzzy sets and numbers. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2012, 209, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, I.; Ashraf, S. Fuzzy relational calculus. Bull. Malaysian Math. Sci. Soc. 2014, 37, 203–237. [Google Scholar]
- Deli, I.; Broumi, S. Neutrosophic soft matrices and NSM-decision making. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 28, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.S. Modelling a type-2 fuzzy inventory system considering items with imperfect quality ad shortage backlogging. Sadhana 2018, 43, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, P. The Structure of Type k Fuzzy Numbers, in the Coming of Age of Fuzzy Logic; Bezdek, J.C., Ed.; World Scientific Publishing: Seattle, WA, USA, 1989; pp. 671–674. [Google Scholar]
- Diamond, P. A note on fuzzy star shaped fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1990, 37, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutia, R.; Mahanta, S.; Baruah, H.K. An alternative method of finding the membership of a fuzzy number. Int. J. Latest Trends Comput. 2010, 1, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury, S.; Pedrycz, W. An alternative characterization of fuzzy complement functional. Soft Comput.—Fusion Found. Methodol. Appl. 2003, 7, 563–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobeylev, V.N. Cauchy problem under fuzzy control. BUSEFAL 1985, 21, 117–126. [Google Scholar]
- Bobeylev, V.N. On the reduction of fuzzy number to real. BUSEFAL 1988, 35, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Buckley, J.J. Generalized and extended fuzzy sets with applications. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 1988, 25, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.R.; Maji, P.K. A fuzzy soft theoretic approach to decision making problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2010, 203, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molodtsov, D. Soft set theory first result. Comput. Math. Appl. 1999, 37, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagman, N.; Enginoglu, S.; Citak, F. Fuzzy soft theory and its application. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2011, 8, 137–147. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak, Z. Rough sets. Int. J. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1982, 11, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torra, V. Hesitant fuzzy sets. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2010, 25, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, S.; De, S.K.; Goswami, A. A deteriorating EOQ model for natural idle time and imprecise demand: Hesitant fuzzy approach. Int. J. Syst. Sci. Oper. Logist. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.K.; Sana, S.S. Multi-criterion multi-attribute decision-making for an EOQ model in a hesitant fuzzy environment. Nat. Sci. Eng. 2015, 17, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- De, S.K.; Beg, I. Triangular dense fuzzy sets and new defuzzification methods. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 31, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.K.; Beg, I. Triangular dense fuzzy Neutrosophic sets. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 2016, 13, 24–37. [Google Scholar]
- De, S.K.; Mahata, G.C. Decision of a fuzzy inventory with fuzzy backorder model under cloudy fuzzy demand rate. Int. J. Appl. Comput. Math. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, S.; De, S.K.; Goswami, A. A pollution sensitive remanufacturing model with waste items: Triangular dense fuzzy lock set approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, S.; De, S.K.; Goswami, A. A pollution sensitive dense fuzzy economic production quantity model with cycle time dependent production rate. J. Clean. Prod. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; De, S.K.; Pal, M. Two decision makers’ single decision over a back order EOQ model with dense fuzzy demand rate. J. Financ. Mark. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccia, M.; Crainic, T.G.; Sforza, A.; Sterle, C. Multi-commodity location-routing: Flow intercepting formulation and branch-and-cut algorithm. Comput. Oper. Res. 2018, 89, 94–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkhgarda, H.; Savelsbergh, M.; Talebian, M. A linear programming-based algorithm to solve a class of optimization problems with a multi-linear objective function and affine constraints. Comput. Oper. Res. 2018, 89, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.F.; Shao, L.; Ehrgott, M. Primal and dual multi-objective linear programming algorithms for linear multiplicative programmes. Optimization 2016, 65, 415–431. [Google Scholar]
- Pelt, T.D.; Fransoo, J.C. A note on “Linear programming models for a stochastic dynamic capacitated lot sizing problem”. Comput. Oper. Res. 2018, 89, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.K. Triangular dense fuzzy lock set. Soft Comput. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
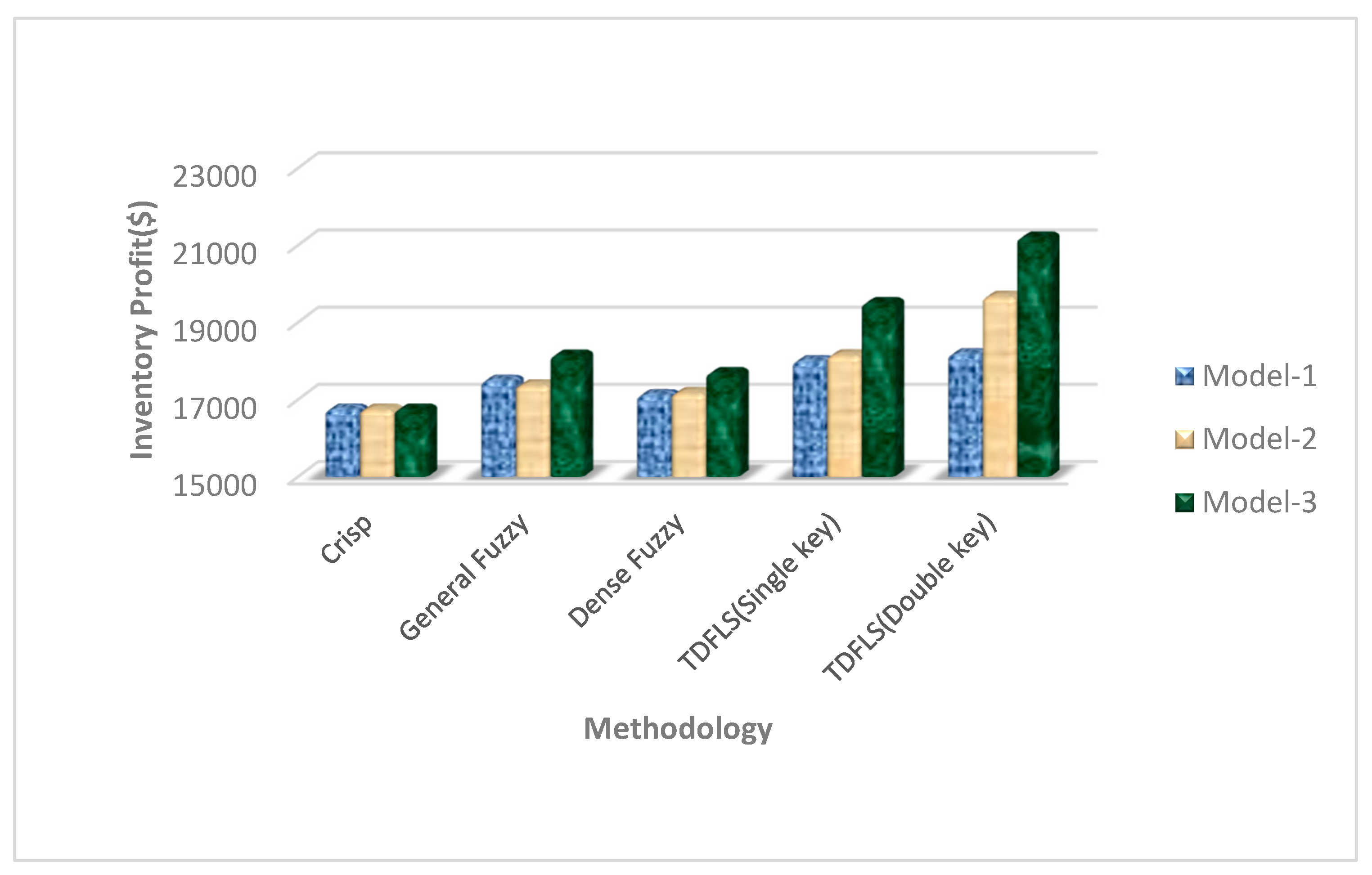
| Model | Learning Experiences | Cycle Time Days | Opening Time | Closing Time | Order Quantity | Average Profit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crisp | … | 3 | 0.505 | 0.495 | 75.75 | 16,759.89 | |
| General Fuzzy | … | 0.505 | 0.495 | 78.59 | 17,505.34 | ||
| Dense Fuzzy | 1 2 3 4 | 0.505 | 0.495 | 77.17 76.93 76.77 76.66 | 17,132.62 17,070.50 17,029.08 16,999.06 | ||
| TDFLS | Single Key | 1 2 3 4 | 0.505 | 0.495 | 80.01 80.24 80.40 80.51 | 17,878.07 17,940.19 17,981.61 18,011.63 | |
| Double Keys | 1 2 3 4 | 0.505 | 0.495 | 80.70 80.94 81.10 81.21 | 18,061.16 18,123.28 18,164.70 18,194.72 | ||
| Model | Keys | Learning Experiences | Cycle time Days | Opening Time | Closing Time | Order Quantity | Average Profit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crisp | … | … | 3 | 0.505 | 0.495 | 75.75 | 16,759.89 | |
| General Fuzzy | … | … | 17,388.39 | |||||
| Dense Fuzzy | … | 1 2 3 4 | 17,074.14 17,126.52 17,161.43 17,186.75 | |||||
| TDFLS | Single Key | 1 2 3 4 | 18,050.68 18,103.06 18,137.98 18,163.29 | |||||
| Double Keys | 1 2 3 4 | 19,568.17 19,621.15 19,656.07 19,681.38 | ||||||
| Model | Keys | Learning Experiences | Cycle Time Days | Opening Time | Closing Time | Order Quantity | Average Profit | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crisp | … | … | 3 | 16,759.89 | ||||
| General Fuzzy | … | … | 78.59 | 18,161.80 | ||||
| Dense Fuzzy | … | 1 2 3 4 | 0.505 | 0.495 | 77.17 77.40 77.56 77.67 | 17,453.86 17,570.88 17,649.10 17,705.93 | ||
| TDFLS | Single Key | 1 2 3 4 | 80.01 80.24 80.40 80.51 | 19,254.83 19,377.79 19,459.98 19,519.68 | ||||
| Double Keys | 1 2 3 4 | 80.70 80.94 81.10 81.21 | 20,952.53 21,075.22 21,157.24 21,216.80 | |||||
| Parameters | Associated Keys | % Change | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +50 +30 −30 −50 | 2 | 81.22 | 21,097.36 21,134.11 21,370.36 21,575.12 | +25.88 +26.09 +27.50 +28.73 | ||
| +50 +30 −30 −50 | 2 | 81.22 | 20,752.68 20,895.49 21,813.53 22,609.16 | +23.82 +24.67 +30.15 +34.90 | ||
| +50 +30 −30 −50 | 2 | 81.22 | 21,198.16 21,203.89 21,240.77 21,272.74 | +26.48 +26.51 +26.73 +26.92 | ||
| +50 +30 −30 −50 | 2 | 81.22 | 20,738.68 20,885.79 21,831.53 22,651.18 | +23.73 +24.61 +30.26 +35.15 | ||
| d | +50 +30 −30 −50 | 2 | 79.09 79.74 83.95 87.59 | 20,619.68 20,803.41 21,984.53 23,008.16 | +23.02 +24.12 +31.17 +37.28 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maity, S.; De, S.K.; Prasad Mondal, S. A Study of an EOQ Model under Lock Fuzzy Environment. Mathematics 2019, 7, 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7010075
Maity S, De SK, Prasad Mondal S. A Study of an EOQ Model under Lock Fuzzy Environment. Mathematics. 2019; 7(1):75. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7010075
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaity, Suman, Sujit Kumar De, and Sankar Prasad Mondal. 2019. "A Study of an EOQ Model under Lock Fuzzy Environment" Mathematics 7, no. 1: 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7010075
APA StyleMaity, S., De, S. K., & Prasad Mondal, S. (2019). A Study of an EOQ Model under Lock Fuzzy Environment. Mathematics, 7(1), 75. https://doi.org/10.3390/math7010075







