DA-TransResUNet: Residual U-Net Liver Segmentation Model Integrating Dual Attention of Spatial and Channel with Transformer
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- We propose DA-TransResUNet, a novel liver segmentation network that adopts Res U-Net as the baseline architecture and integrates residual learning, dual-attention (DA) blocks, and Transformer encoders in a unified framework. Instead of a simple aggregation of existing modules, each component is carefully embedded into the network to enhance feature representation at different semantic levels, thereby improving segmentation accuracy.
- (2)
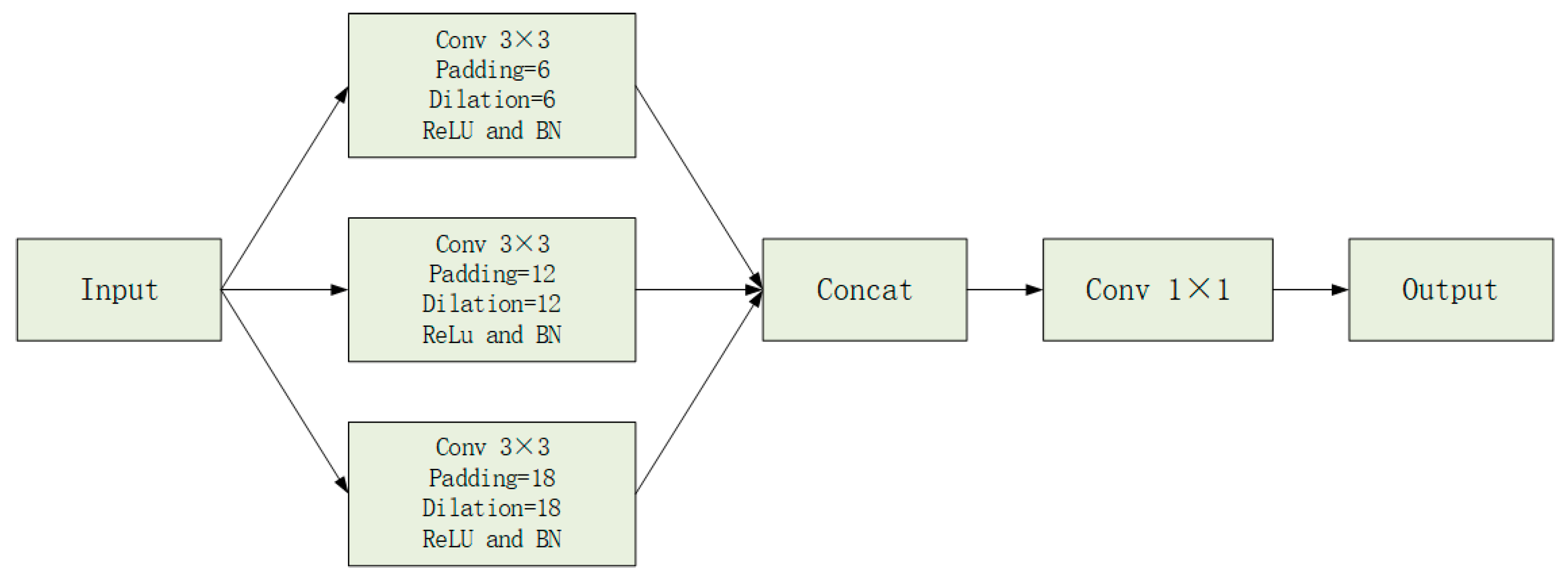
- We design a task-oriented hybrid encoder in which DA blocks are employed to explicitly model spatial and channel-wise dependencies in convolutional feature maps, while the Transformer encoder focuses on capturing global contextual information. This complementary design enables effective interaction between local detail preservation and global dependency modeling. In addition, Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP) is introduced between the encoder and decoder to further enhance multi-scale feature representation. Moreover, each skip connection is refined by a DA block to reduce feature redundancy and alleviate the semantic gap between encoder and decoder features.
- (3)
- Unlike existing approaches such as TransUNet, DA-TransUNet, and SAR-U-Net, which mainly emphasize either global modeling or attention-enhanced convolutional features, DA-TransResUNet explicitly explores the synergistic collaboration among residual learning, dual attention, and Transformer-based global modeling within a Res U-Net framework. Experimental results on two public benchmark datasets show that DA-TransResUNet delivers competitive performance and further improves segmentation accuracy compared with several existing methods.
2. Related Work
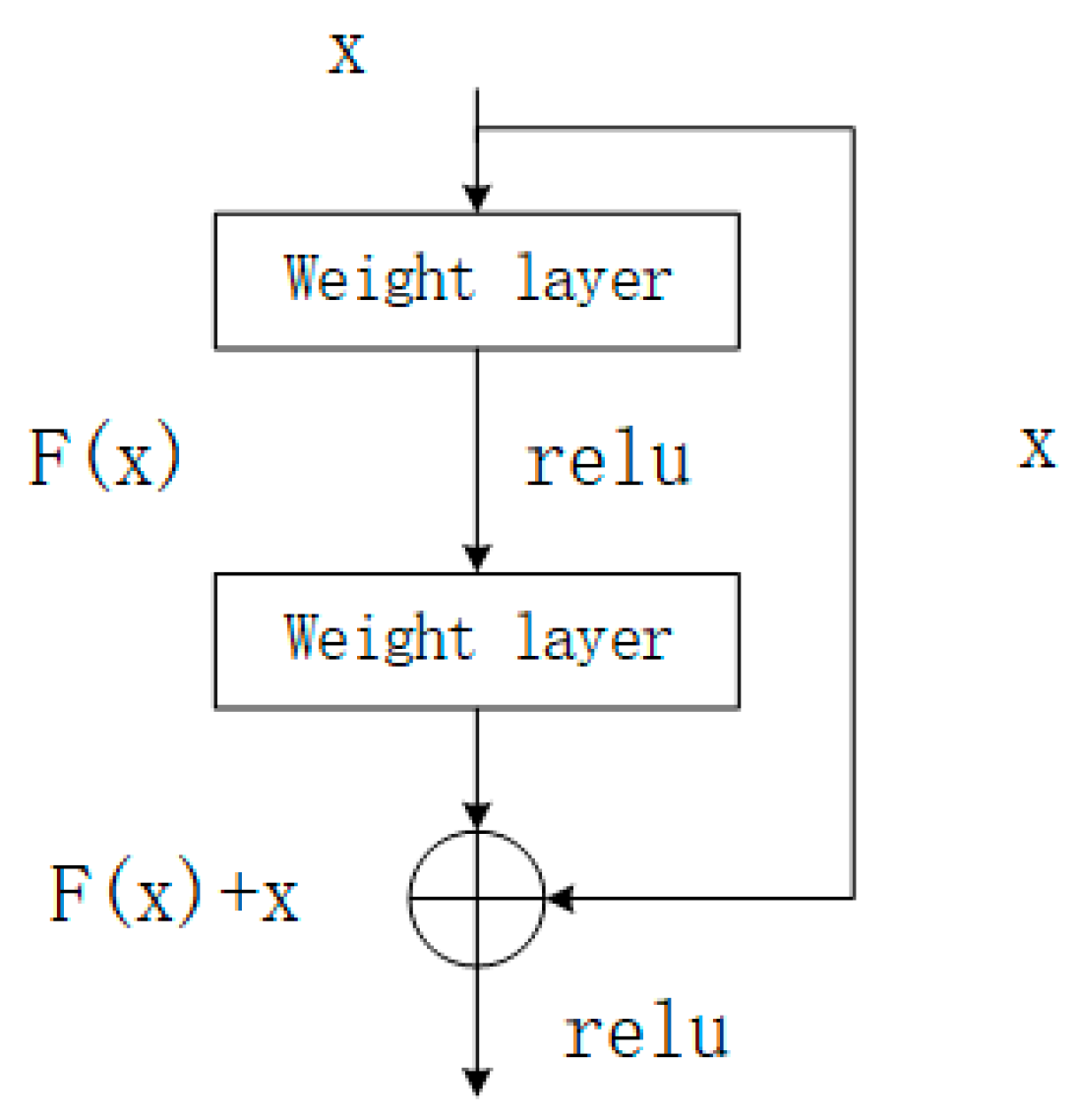
2.1. Residual Structure
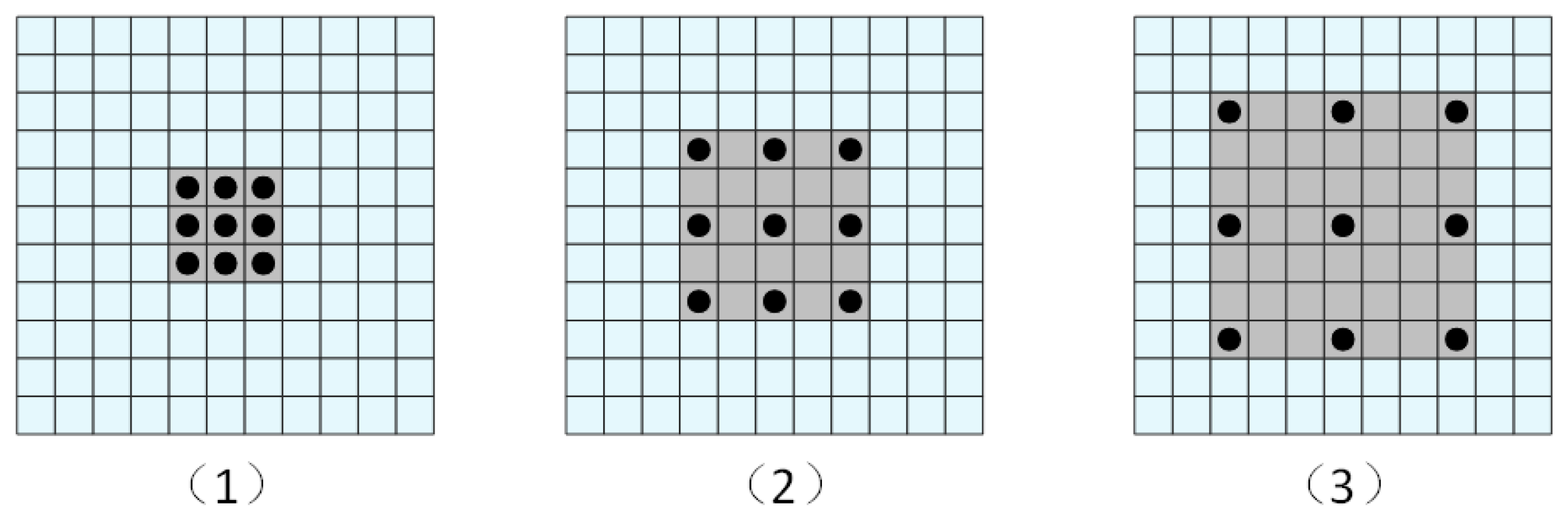
2.2. Dilated Convolution
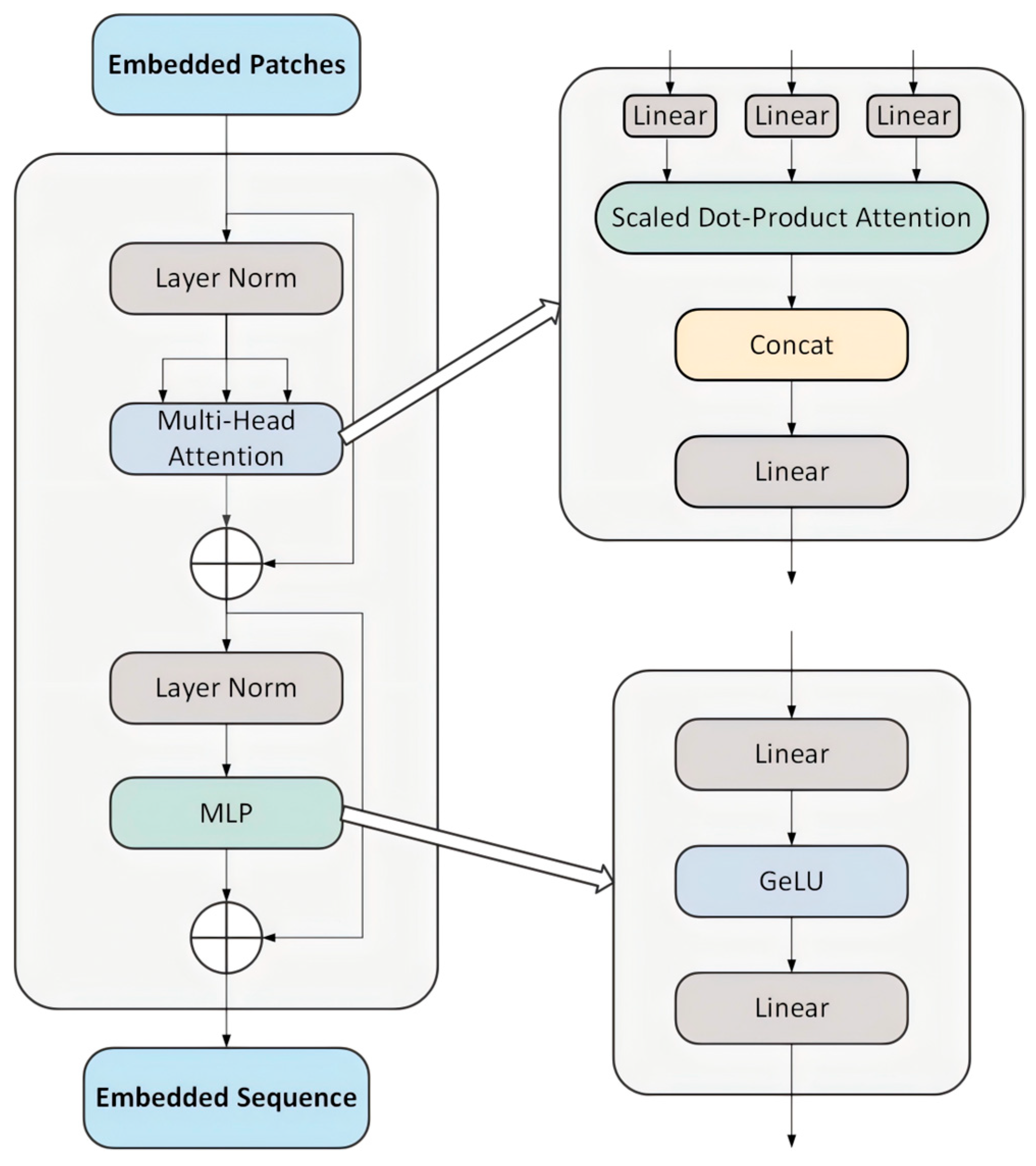
2.3. Transformer Encoder
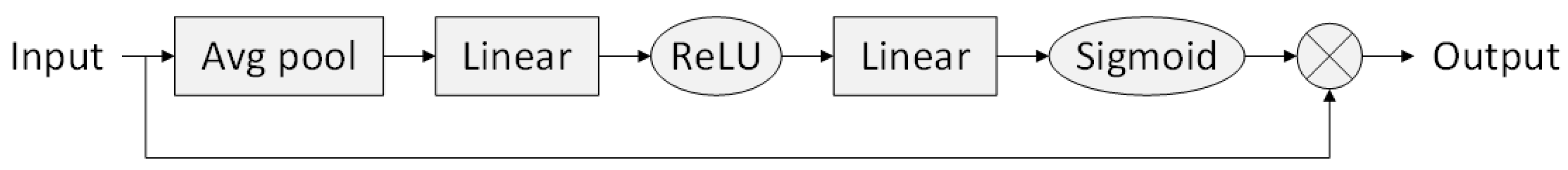
2.4. Squeeze-and-Excitation Blocks
3. Methodology
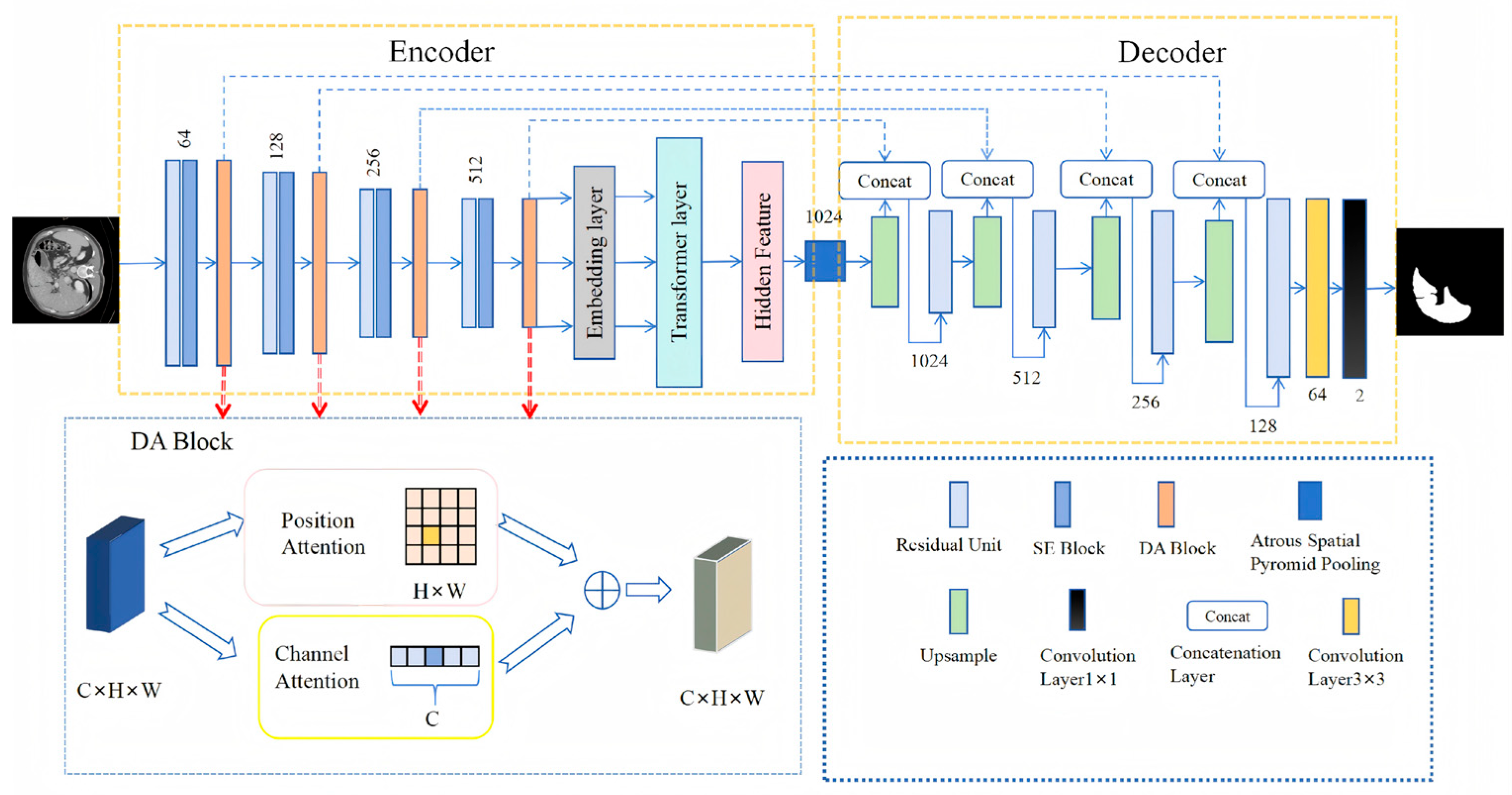
3.1. Architecture
3.2. Encoder Combining Transformer, Residual Blocks and Dual-Attention Modules
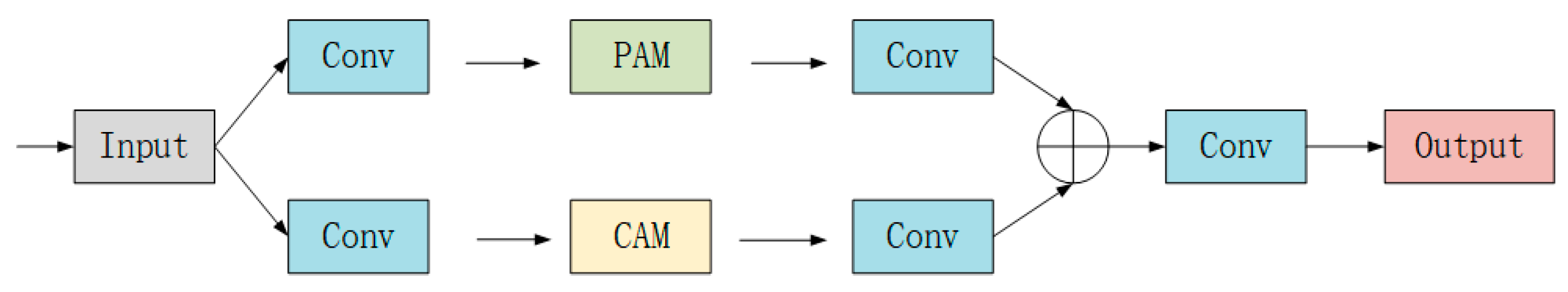
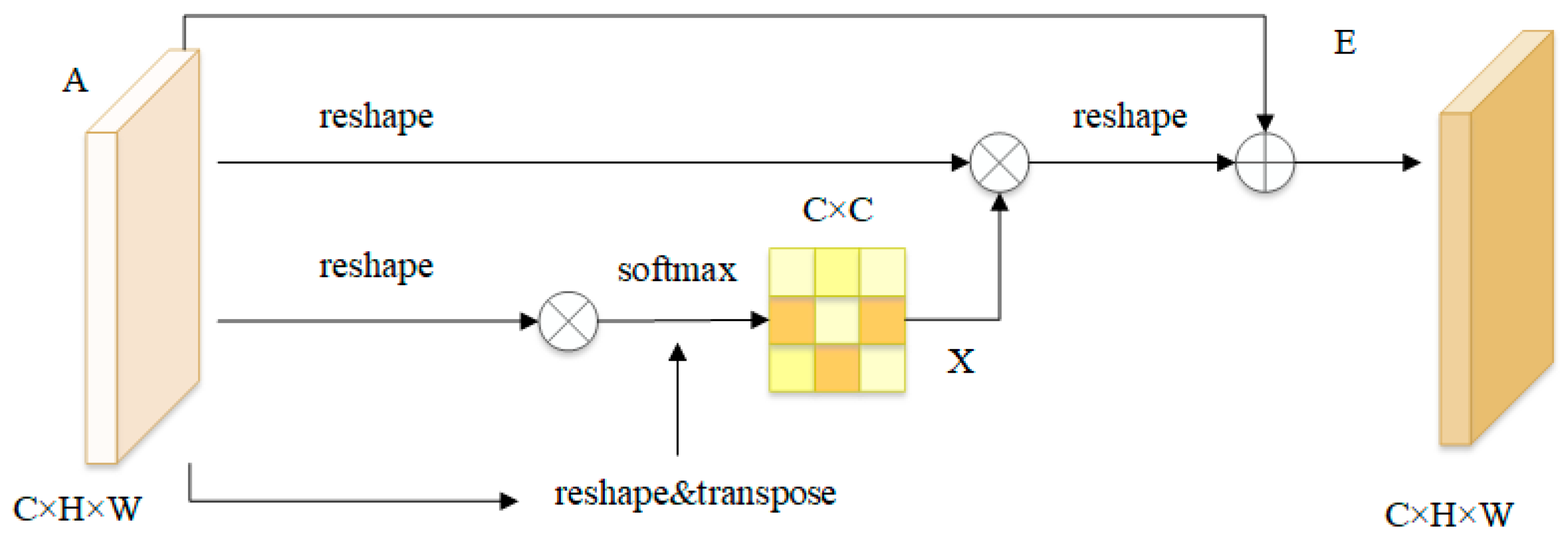
3.3. Dual Attention Block
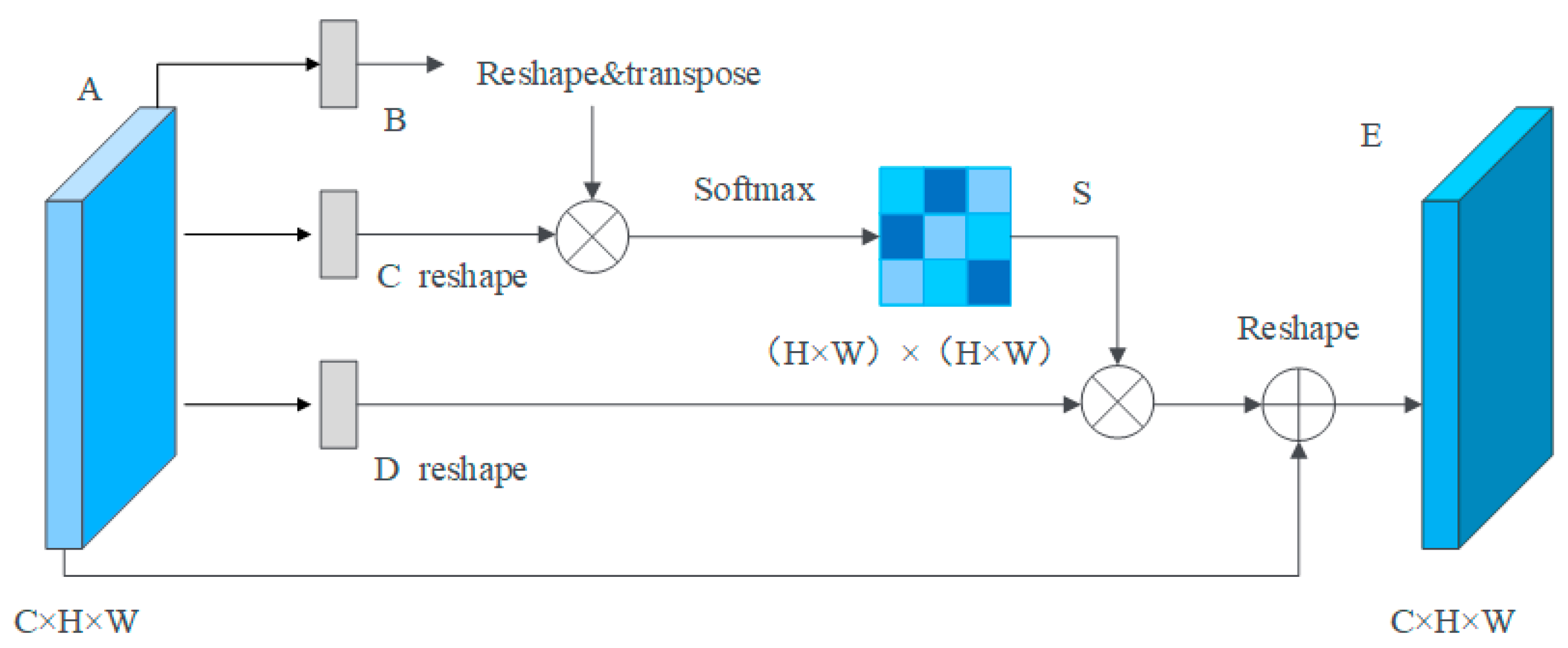
3.3.1. Position Attention Module
3.3.2. Channel Attention Module
3.4. Decoder
4. Experiment
4.1. Dataset and Experimental Environment
4.1.1. LiTS2017 Dataset
4.1.2. Sliver07 Dataset
4.1.3. Data Split Strategy and Overfitting Analysis
4.2. Experimental Environment and Parameters
4.3. Image Preprocessing
4.4. Loss Function
4.5. Evaluation Metrics
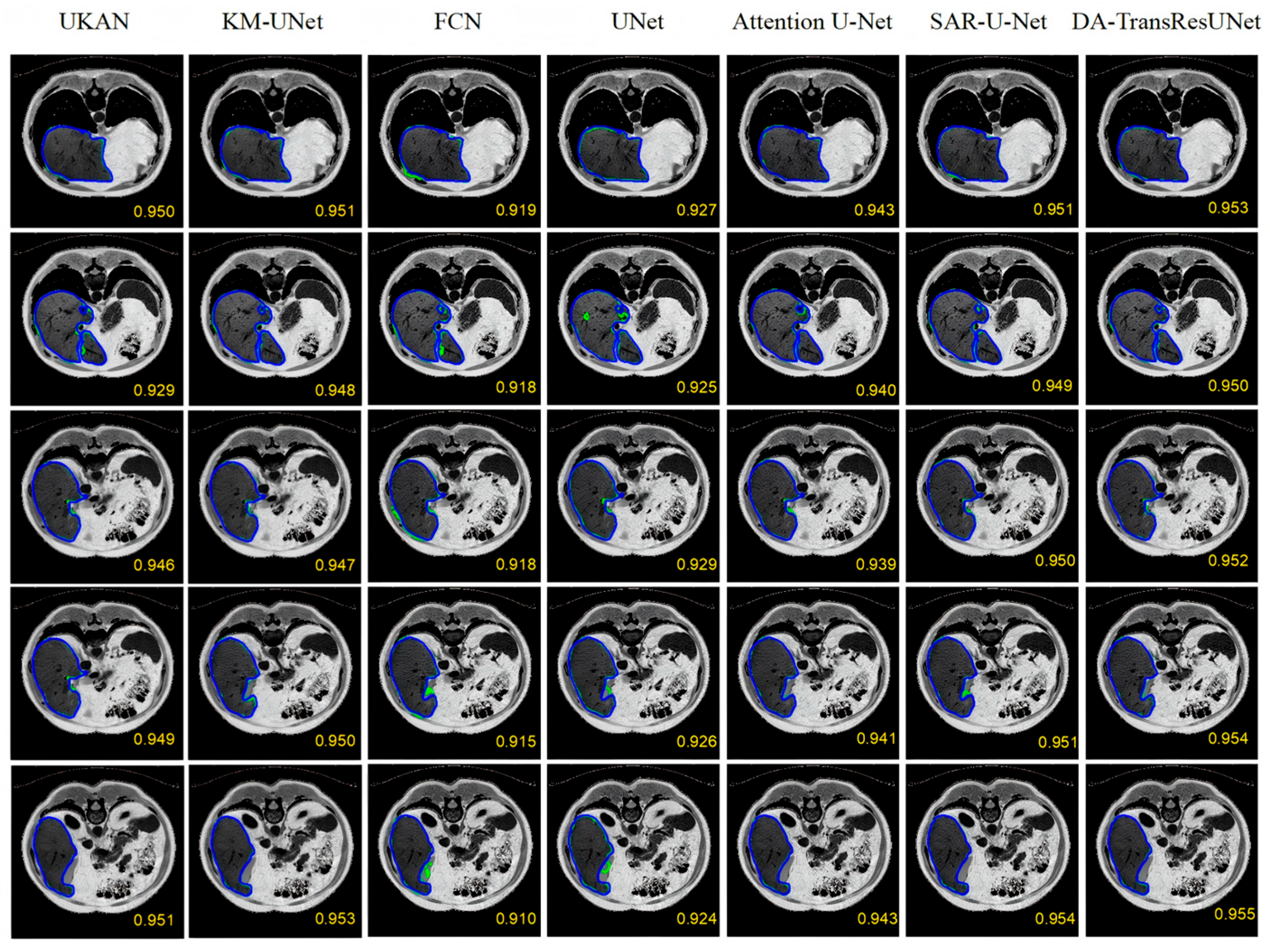
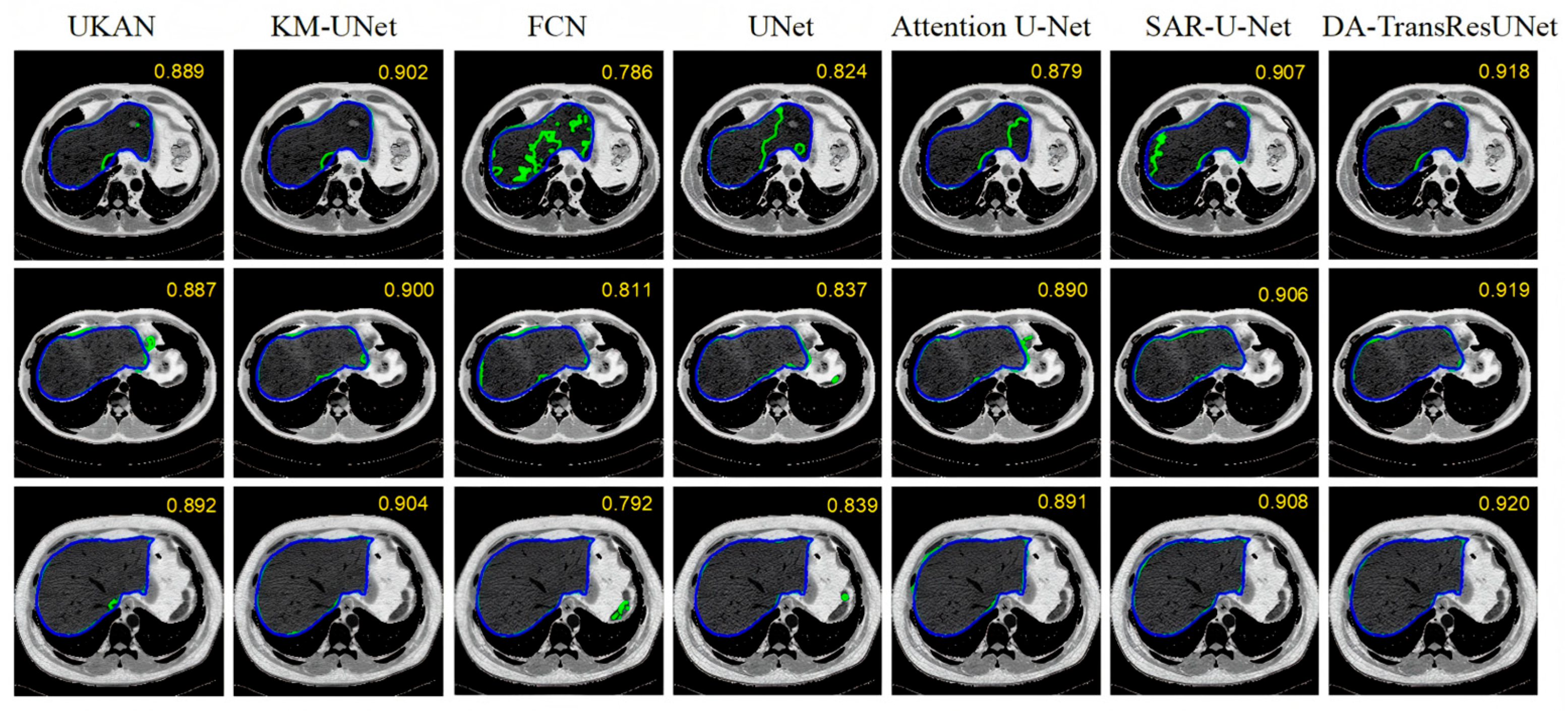
5. Experimental Results and Analysis
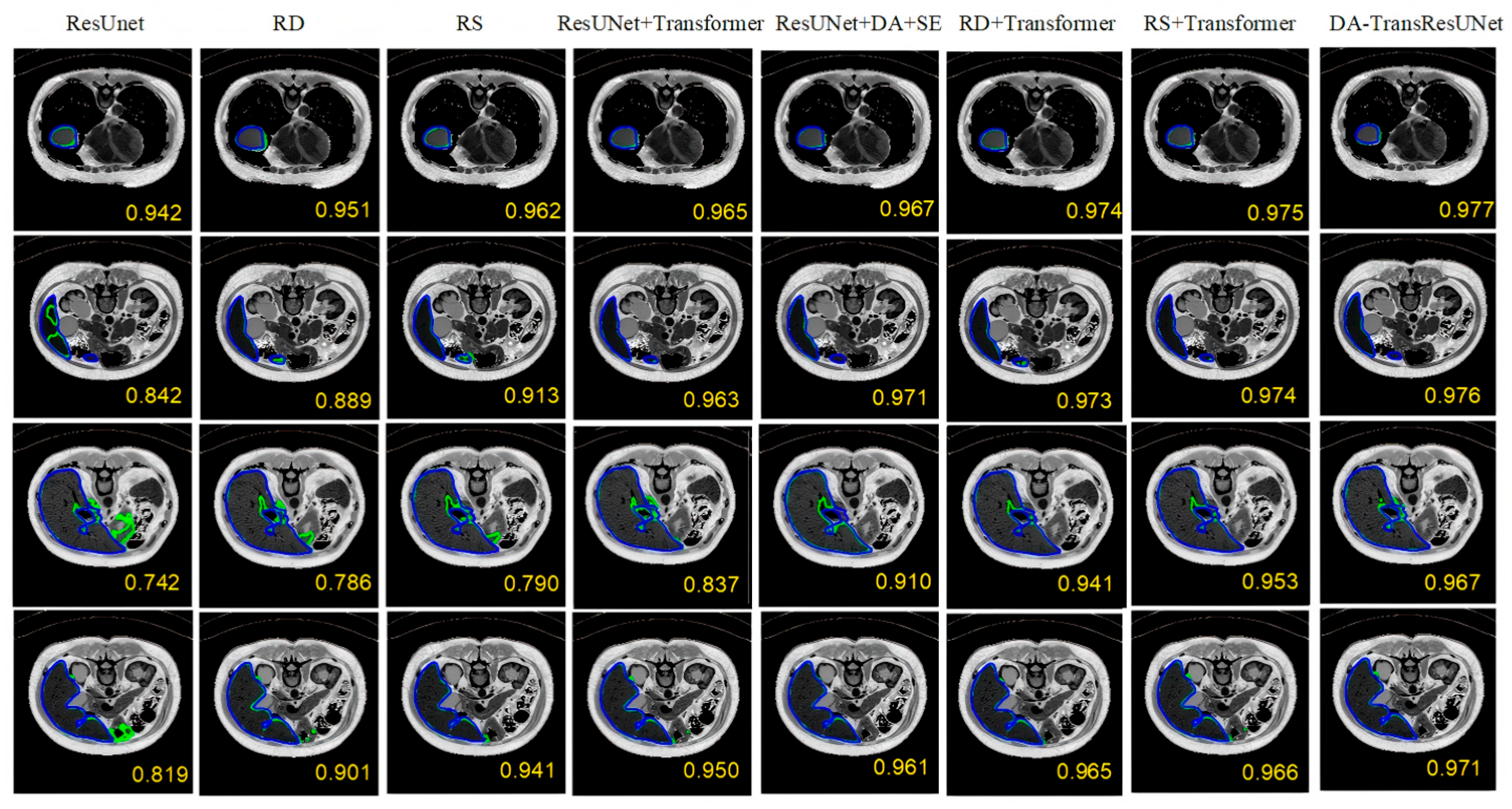
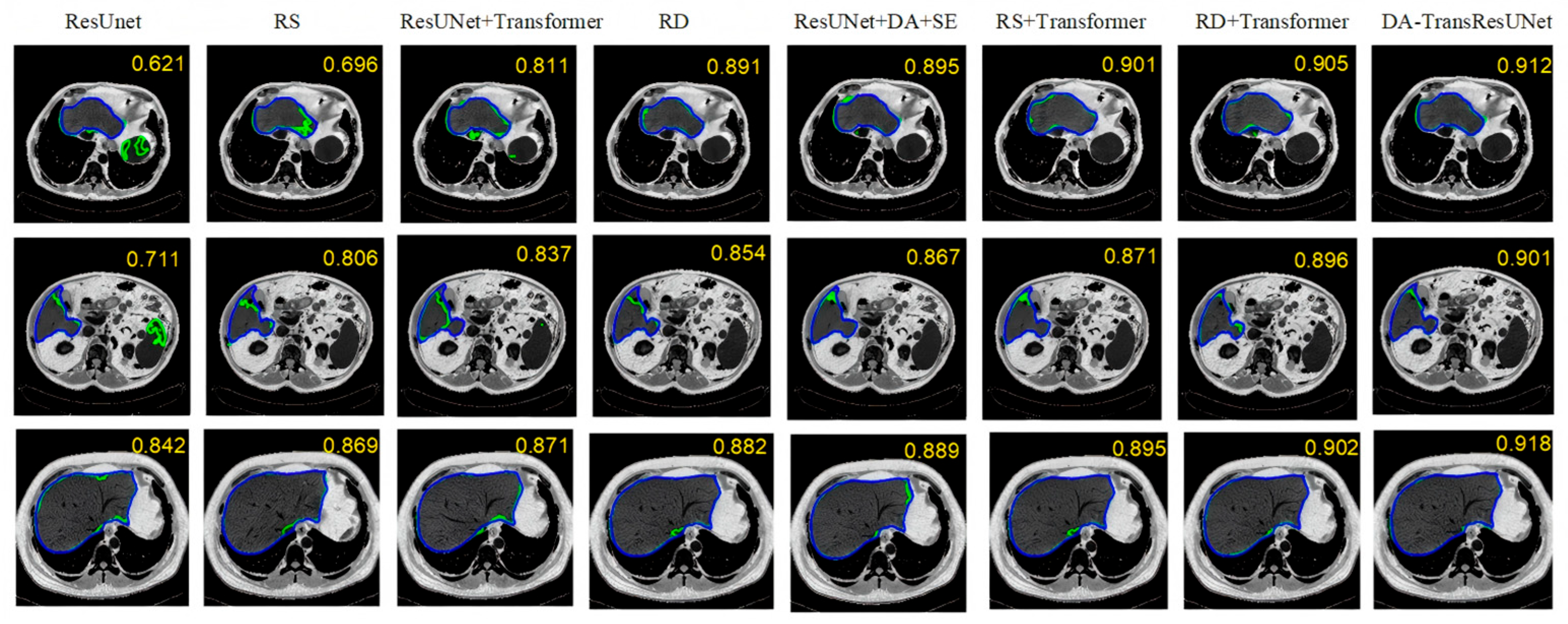
5.1. Ablation Experiment
5.2. Comparative Experiment
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DA | Dual Attention |
| PAM | Position Attention Module |
| CAM | Channel Attention Module |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| FCN | Fully Convolutional Network |
| ViT | Vision Transformer |
| SAR | Spatial Attention Residual |
| SE | Squeeze-and-Excitation |
References
- Sattari, M.A.; Zonouri, S.A.; Salimi, A.; Izadi, S.; Rezaei, A.R.; Ghezelbash, Z.; Hayati, M.; Seifi, M.; Ekhteraei, M. Liver margin segmentation in abdominal CT images using U-Net and Detectron2: Annotated dataset for deep learning models. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaitner, N.; Ludwig, J.; Meyer, T.; Boehm, O.; Anders, M.; Huang, B.; Jordan, J.; Schaeffter, T.; Sack, I.; Reiter, R. Automated liver and spleen segmentation for MR elastography maps using U-Nets. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 10762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayantara, P.V.; Kamath, S.; Kadavigere, R.; Manjunath, K.N. Automatic liver segmentation from multiphase CT using modified SegNet and ASPP module. SN Comput. Sci. 2024, 5, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmoral, J.C.; Tavares, J.M.R.S. Semantic segmentation of CT liver structures: A systematic review of recent trends and bibliometric analysis: Neural network-based methods for liver semantic segmentation. J. Med. Syst. 2024, 48, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakogiannis, F.I.; Waldner, F.; Caccetta, P.; Wu, C. ResUNet-a: A deep learning framework for semantic segmentation of remotely sensed data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 162, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A. Attention is all you need. In NIPS’17: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2017; Available online: https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1370849946232757637 (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Dosovitskiy, A. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Luo, X.; Adeli, E.; Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yuille, A.L.; Zhou, Y. Transunet: Transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2102.04306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q.; Wang, M. Swin-unet: Unet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2022 Workshops, Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; Proceedings, Part III; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2016/html/He_Deep_Residual_Learning_CVPR_2016_paper.html (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V.; Funkhouser, T. Dilated residual networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 472–480. Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2017/html/Yu_Dilated_Residual_Networks_CVPR_2017_paper.html (accessed on 2 April 2025).
- Guo, X.; Wang, Z.; Wu, P.; Li, Y.; Alsaadi, F.E.; Zeng, N. ELTS-Net: An enhanced liver tumor segmentation network with augmented receptive field and global contextual information. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 169, 107879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. Deeplab: Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected crfs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lv, P.; Wang, H.; Shi, C. SAR-U-Net: Squeeze-and-excitation block and atrous spatial pyramid pooling based residual U-Net for automatic liver segmentation in Computed Tomography. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2021, 208, 106268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual attention network for scene segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3146–3154. Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_CVPR_2019/html/Fu_Dual_Attention_Network_for_Scene_Segmentation_CVPR_2019_paper.html (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- Sun, G.; Pan, Y.; Kong, W.; Xu, Z.; Ma, J.; Racharak, T.; Nguyen, L.-M.; Xin, J. DA-TransUNet: Integrating spatial and channel dual attention with transformer U-net for medical image segmentation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1398237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Ou, J.; Liu, R.; Zou, Y.; Xie, T.; Xiao, H.; Bai, T. RMAU-Net: Residual multi-scale attention U-Net for liver and tumor segmentation in CT images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 158, 106838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Fang, J. GCHA-Net: Global context and hybrid attention network for automatic liver segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Model | DICE (%) | VOE (%) | RVD (%) | ASD (mm) | MSD (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Res U-Net | 96.93 | 9.84 | −2.78 | 8.06 | 46.11 |
| ResU-Net + DA | 97.39 | 7.86 | 1.31 | 8.10 | 38.49 |
| ResU-Net + SE | 97.59 | 7.7 | −1.66 | 8.11 | 39.83 |
| ResU-Net + Transformer | 97.64 | 8.99 | −1.88 | 8.03 | 38.12 |
| ResU-Net + DA + SE | 97.67 | 7.62 | −0.95 | 8.02 | 38.70 |
| ResU-Net + DA + Transformer | 97.74 | 7.55 | −1.10 | 7.99 | 37.90 |
| ResU-Net + SE + Transformer | 97.76 | 7.48 | −1.25 | 7.98 | 37.80 |
| DA-TransResUNet | 97.79 | 7.52 | −1.02 | 7.97 | 37.58 |
| Model | DICE (%) | VOE (%) | RVD (%) | ASD (mm) | MSD (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Res U-Net | 83.53 | 24.97 | −7.61 | 13.88 | 155.50 |
| ResU-Net + SE | 83.87 | 19.13 | 5.19 | 11.36 | 149.04 |
| ResU-Net + Transformer | 86.19 | 17.79 | 4.65 | 9.73 | 138.61 |
| ResU-Net + DA | 86.87 | 16.72 | 3.16 | 9.69 | 101.43 |
| ResU-Net + DA + SE | 87.35 | 16.10 | 2.45 | 9.42 | 100.10 |
| ResU-Net + SE + Transformer | 88.30 | 16.35 | 2.10 | 9.05 | 105.40 |
| ResU-Net + DA + Transformer | 89.62 | 15.55 | 1.85 | 8.92 | 99.20 |
| DA-TransResUNet | 91.79 | 15.17 | 1.10 | 8.45 | 98.51 |
| Model | DICE (%) | VOE (%) | RVD (%) | ASD (mm) | MSD (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UKAN | 94.63 | 9.81 | −2.30 | 8.26 | 53.15 |
| KM-UNet | 94.88 | 9.22 | −1.95 | 8.20 | 51.97 |
| FCN | 91.83 | 14.64 | −6.91 | 9.03 | 58.59 |
| U-Net | 92.67 | 13.20 | −5.41 | 8.30 | 55.81 |
| Attention U-Net | 94.12 | 10.93 | −3.58 | 8.21 | 54.47 |
| RMAU-Net [18] | 95.21 | 8.19 | −0.40 | - | - |
| GCHA-Net [19] | 92.68 | 11.85 | −1.50 | - | - |
| SAR-U-Net | 94.98 | 9.42 | −2.15 | 8.08 | 52.61 |
| DA-TransResUNet | 95.22 | 7.52 | −1.02 | 7.97 | 37.58 |
| Model | DICE (%) | VOE (%) | RVD (%) | ASD (mm) | MSD (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UKAN | 89.18 | 18.31 | −3.19 | 9.90 | 145.13 |
| KM-UNet | 90.05 | 17.44 | −2.11 | 9.06 | 135.47 |
| FCN | 78.57 | 35.29 | −12.36 | 15.54 | 174.04 |
| U-Net | 82.69 | 27.66 | −8.93 | 12.51 | 167.20 |
| Attention U-Net | 88.81 | 20.12 | −4.09 | 10.04 | 147.75 |
| SAR-U-Net | 90.51 | 17.11 | −1.51 | 8.98 | 129.14 |
| DA-ResTransUNet | 91.79 | 15.17 | 1.10 | 8.45 | 98.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Wang, K.; Lu, X.; Li, J.; Lu, Y. DA-TransResUNet: Residual U-Net Liver Segmentation Model Integrating Dual Attention of Spatial and Channel with Transformer. Mathematics 2026, 14, 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/math14030575
Wang K, Lu X, Li J, Lu Y. DA-TransResUNet: Residual U-Net Liver Segmentation Model Integrating Dual Attention of Spatial and Channel with Transformer. Mathematics. 2026; 14(3):575. https://doi.org/10.3390/math14030575
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kunzhan, Xinyue Lu, Jing Li, and Yang Lu. 2026. "DA-TransResUNet: Residual U-Net Liver Segmentation Model Integrating Dual Attention of Spatial and Channel with Transformer" Mathematics 14, no. 3: 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/math14030575
APA StyleWang, K., Lu, X., Li, J., & Lu, Y. (2026). DA-TransResUNet: Residual U-Net Liver Segmentation Model Integrating Dual Attention of Spatial and Channel with Transformer. Mathematics, 14(3), 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/math14030575





