Towards Robust Speech Models: Mitigating Backdoor Attacks via Audio Signal Enhancement and Fine-Pruning Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We introduce a backdoor defense framework specifically tailored for speech recognition systems, combining speech enhancement and fine-pruning to detect and eliminate backdoor triggers without prior knowledge of their structure or location.
- We optimize the fine-pruning process to minimize performance degradation, demonstrating through ablation experiments that our method maintains high accuracy even under aggressive pruning conditions.
- We validate our approach through extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets, showing superior defense performance against both conventional backdoor attacks and advanced steganographic techniques. Our method achieves a 99.4% clean accuracy while reducing the attack success rate to less than 1.5% in most scenarios.
2. Related Works
2.1. Speech Recognition
2.2. Speech Enhancement
2.3. Backdoor Attacks in SR
2.4. Backdoor Defense in SR
3. Problem Statement
3.1. System and Threat Model
3.2. Design Goals
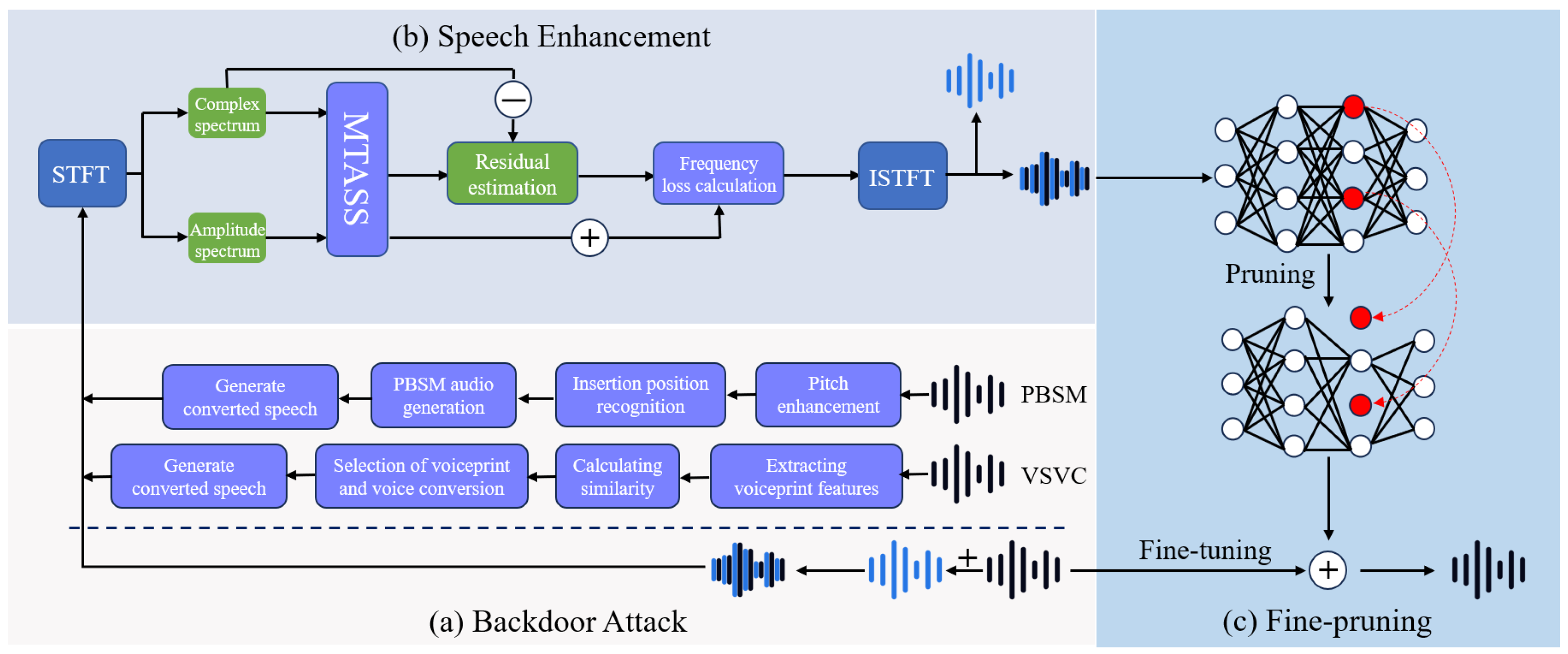
4. The Proposed Method
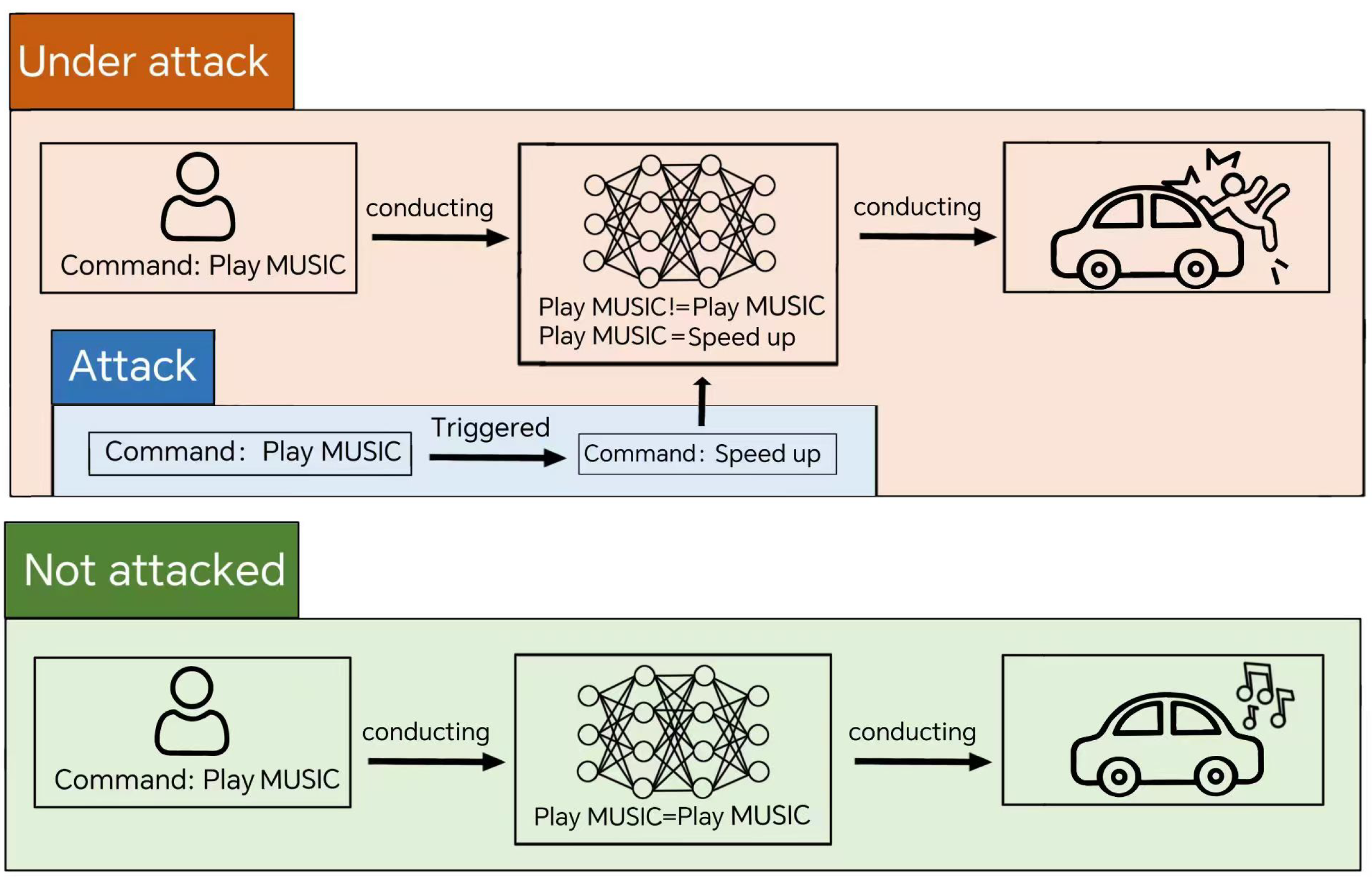
4.1. Backdoor Attack
4.2. Speech Enhancement Denoising
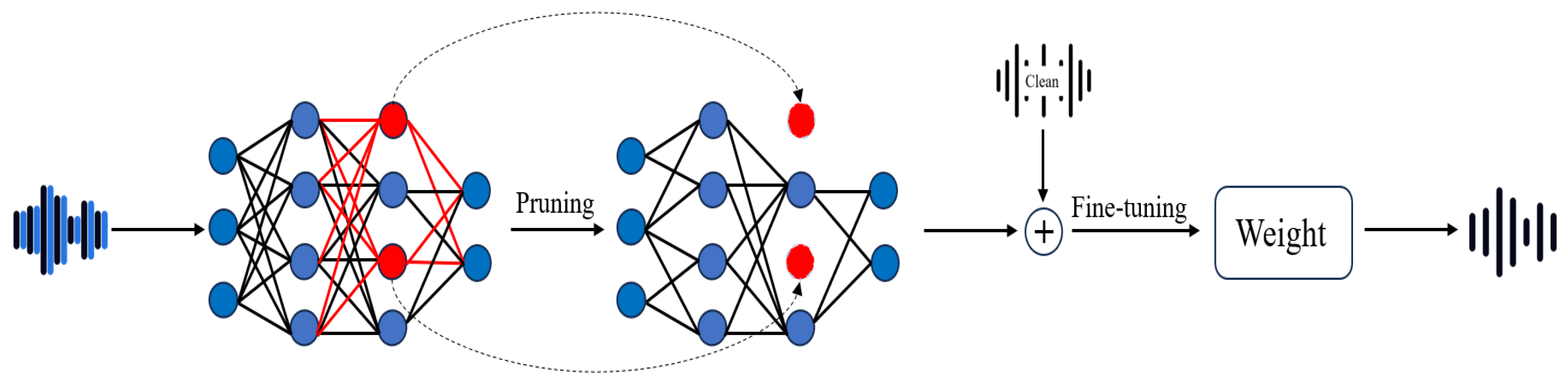
4.3. Fine-Pruning
5. Experiments
5.1. Datasets
5.2. Experiment Setting
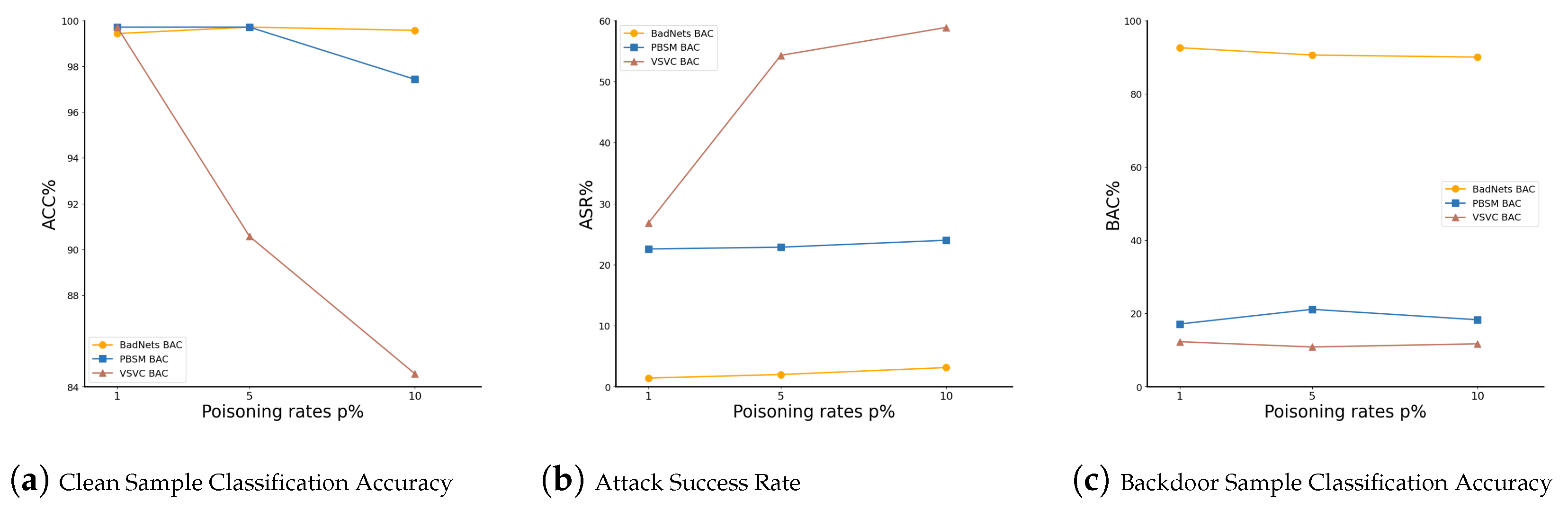
5.3. Experiment Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kheddar, H.; Hemis, M.; Himeur, Y. Automatic speech recognition using advanced deep learning approaches: A survey. Inf. Fusion 2024, 102422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isyanto, H.; Arifin, A.S.; Suryanegara, M. Performance of smart personal assistant applications based on speech recognition technology using IoT-based voice commands. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju-si, Republic of Korea, 21–23 October 2020; pp. 640–645. [Google Scholar]
- Girma, A.; Yan, X.; Homaifar, A. Driver identification based on vehicle telematics data using LSTM-recurrent neural network. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 31st International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), Portland, OR, USA, 4–6 November 2019; pp. 894–902. [Google Scholar]
- Church, K.W.; Chen, Z.; Ma, Y. Emerging trends: A gentle introduction to fine-tuning. Nat. Lang. Eng. 2021, 27, 763–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xie, Z.; Li, P. MultiAdapt: A neural network adaptation for pruning filters base on multi-layers group. Proc. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1873, 012062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldblum, M.; Tsipras, D.; Xie, C.; Chen, X.; Schwarzschild, A.; Song, D.; Mądry, A.; Li, B.; Goldstein, T. Dataset security for machine learning: Data poisoning, backdoor attacks, and defenses. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 1563–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yan, Z.; Choo, K.K.R.; Wang, G. Backdoor attacks and defenses targeting multi-domain ai models: A comprehensive review. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 57, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udeshi, S.; Peng, S.; Woo, G.; Loh, L.; Rawshan, L.; Chattopadhyay, S. Model agnostic defence against backdoor attacks in machine learning. IEEE Trans. Reliab. 2022, 71, 880–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Tondi, B.; Barni, M. An overview of backdoor attacks against deep neural networks and possible defences. IEEE Open J. Signal Process. 2022, 3, 261–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, P.; Dong, H.; Xiao, Y.; Koffas, S.; Li, Y. Towards stealthy backdoor attacks against speech recognition via elements of sound. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2024, 19, 5852–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togneri, R.; Pullella, D. An overview of speaker identification: Accuracy and robustness issues. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2011, 11, 23–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atayero, A.A.; Ayo, C.K.; Nicholas, I.O.; Ambrose, A. Implementation of ‘ASR4CRM’: An automated speech-enabled customer care service system. In Proceedings of the IEEE EUROCON 2009, IEEE, St. Petersburg, Russia, 18–23 May 2009; pp. 1712–1715. [Google Scholar]
- Nasereddin, H.H.; Omari, A.A.R. Classification techniques for automatic speech recognition (ASR) algorithms used with real time speech translation. In Proceedings of the 2017 Computing Conference, IEEE, London, UK, 18–20 July 2017; pp. 200–207. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Sharkh, O.M.; Surkhi, I.; Zabin, H.; Alhasan, M. SayHello: An intelligent peer-to-peer polyglot voice-to-voice conversation application. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.; Chakraborty, S.; Chaki, J.; Padhy, N.; Dey, N. Fundamentals, present and future perspectives of speech enhancement. Int. J. Speech Technol. 2021, 24, 883–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essaid, B.; Kheddar, H.; Batel, N.; Lakas, A.; Chowdhury, M.E. Advanced Artificial Intelligence Algorithms in Cochlear Implants: Review of Healthcare Strategies, Challenges, and Perspectives. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.15442. [Google Scholar]
- Haneche, H.; Ouahabi, A.; Boudraa, B. Compressed sensing-speech coding scheme for mobile communications. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2021, 40, 5106–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheddar, H.; Bouzid, M.; Megías, D. Pitch and fourier magnitude based steganography for hiding 2.4 kbps melp bitstream. IET Signal Process. 2019, 13, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheddar, H.; Megias, D.; Bouzid, M. Fourier magnitude-based steganography for hiding 2.4 kbps melp secret speech. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Applied Smart Systems (ICASS), Medea, Algeria, 24–25 November 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Rouhani, B.D.; Koushanfar, F. SpecMark: A spectral watermarking framework for IP protection of speech recognition systems. In Proceedings of the Interspeech, Shanghai, China, 25–29 October 2020; pp. 2312–2316. [Google Scholar]
- Yamni, M.; Karmouni, H.; Sayyouri, M.; Qjidaa, H. Efficient watermarking algorithm for digital audio/speech signal. Digit. Signal Process. 2022, 120, 103251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Xiao, A.; Wu, E.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y. Transformer in transformer. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 15908–15919. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, S.; Rastegari, M.; Caspi, A.; Shapiro, L.; Hajishirzi, H. Espnet: Efficient spatial pyramid of dilated convolutions for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 552–568. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, H.; Zeng, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, T.; Qiu, M.; Thuraisingham, B. Deepsweep: An evaluation framework for mitigating DNN backdoor attacks using data augmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Asia Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Hong Kong, China, 7–11 June 2021; pp. 363–377. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lv, S.; Xing, M.; Zhang, S.; Fu, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, B.; Xie, L. DCCRN: Deep complex convolution recurrent network for phase-aware speech enhancement. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.00264. [Google Scholar]
- Sivapatham, S.; Kar, A.; Bodile, R.; Mladenovic, V.; Sooraksa, P. A deep neural network-correlation phase sensitive mask based estimation to improve speech intelligibility. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 212, 109592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Ding, M.; Yi, J.; Li, J.; Lv, Z. Two-stage deep spectrum fusion for noise-robust end-to-end speech recognition. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 212, 109547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Dolan-Gavitt, B.; Garg, S. Badnets: Identifying vulnerabilities in the machine learning model supply chain. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1708.06733. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Liu, X.; You, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, B. DriNet: Dynamic backdoor attack against automatic speech recognization models. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, X.; Huo, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z. A novel trojan attack against co-learning based asr dnn system. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 24th International Conference on Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design (CSCWD), Dalian, China, 5–7 May 2021; pp. 907–912. [Google Scholar]
- Koffas, S.; Xu, J.; Conti, M.; Picek, S. Can you hear it? Backdoor attacks via ultrasonic triggers. In Proceedings of the 2022 ACM Workshop on Wireless Security and Machine Learning, San Antonio, TX, USA, 19 May 2022; pp. 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Xin, J.; Lyu, X.; Ma, J. Natural backdoor attacks on speech recognition models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning for Cyber Security, Guangzhou, China, 2–4 December 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 597–610. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, T.; Cai, Z.; Tang, Y. Opportunistic backdoor attacks: Exploring human-imperceptible vulnerabilities on speech recognition systems. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 2390–2398. [Google Scholar]
- Kaviani, S.; Sohn, I. Defense against neural trojan attacks: A survey. Neurocomputing 2021, 423, 651–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Carvalho, W.; Baracaldo, N.; Ludwig, H.; Edwards, B.; Lee, T.; Molloy, I.; Srivastava, B. Detecting backdoor attacks on deep neural networks by activation clustering. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.03728. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Ning, R.; Wang, C.; Xin, C.; Wu, H. Gangsweep: Sweep out neural backdoors by gan. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seattle, WA, USA, 12–16 October 2020; pp. 3173–3181. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Srivastava, A. Neural trojans. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Design (ICCD), Boston, MA, USA, 5–8 November 2017; pp. 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Dolan-Gavitt, B.; Garg, S. Fine-pruning: Defending against backdooring attacks on deep neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Research in Attacks, Intrusions, and Defenses, Limassol, Cyprus, 26–28 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 273–294. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Yao, Y.; Shan, S.; Li, H.; Viswanath, B.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, B.Y. Neural cleanse: Identifying and mitigating backdoor attacks in neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Symposium on Security and Privacy (SP), San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–22 May 2019; pp. 707–723. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Lyu, X.; Koren, N.; Lyu, L.; Li, B.; Ma, X. Neural attention distillation: Erasing backdoor triggers from deep neural networks. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.05930. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.; Wei, S.; Zha, H.; Wu, B. Neural polarizer: A lightweight and effective backdoor defense via purifying poisoned features. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 36, 1132–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Deng, F.; Wang, X. Multi-task audio source separation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding Workshop (ASRU), Cartagena, Colombia, 13–17 December 2021; pp. 671–678. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, H.; Du, J.; Na, X.; Wu, B.; Zheng, H. Aishell-1: An open-source mandarin speech corpus and a speech recognition baseline. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th Conference of the Oriental Chapter of the International Coordinating Committee on Speech Databases and Speech I/O Systems and Assessment (O-COCOSDA), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 1–3 November 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, D.; Chen, G.; Povey, D. Musan: A music, speech, and noise corpus. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1510.08484. [Google Scholar]

| Method | Dataset | Advantages | ASR↓ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aut. [37] | MNIST | No need to change the model | 0.2 |
| GS [36] | MNIST, CIFAR10 | No access to original training data needed | 0 |
| Prune [38] | LibriSpeech | Better than using pruning or fine-tuning alone | 2 |
| DS [24] | CIFAR-10 | Defense through data augmentation techniques | 5 |
| AC [35] | MNIST, LISA | No access to original training data needed, efficient backdoor repair | 0 |
| Method | BadNets | PBSM | VSVC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC↑ | ASR↓ | BAC↑ | ACC↑ | ASR↓ | BAC↑ | ACC↑ | ASR↓ | BAC↑ | |
| Baseline | 97.14 | 89.71 | 18.29 | 100.00 | 88.29 | 10.57 | 94.86 | 88.29 | 10.00 |
| Aut. [37] | 94.53 | 35.72 | 38.63 | 98.89 | 69.53 | 10.23 | 93.28 | 78.32 | 9.90 |
| GS [36] | 96.93 | 52.31 | 43.87 | 95.43 | 58.95 | 10.31 | 93.85 | 71.03 | 11.03 |
| Prune [38] | 96.86 | 38.14 | 51.29 | 99.37 | 79.43 | 10.86 | 92.86 | 80.86 | 9.71 |
| DS [24] | 94.91 | 41.37 | 56.78 | 96.51 | 71.23 | 11.23 | 92.95 | 74.32 | 10.07 |
| AC [35] | 95.34 | 46.72 | 62.23 | 98.43 | 62.68 | 11.05 | 91.85 | 69.24 | 10.31 |
| ASA(Ours) | 99.71 | 11.71 | 91.43 | 99.71 | 24.86 | 15.71 | 100.00 | 34.86 | 12.86 |
| ASAP(Ours) | 99.43 | 1.43 | 92.57 | 99.71 | 22.57 | 17.14 | 99.71 | 26.86 | 12.29 |
| Noise | ACC ↑ | ASR ↓ | BAC ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plane | 99.43 | 1.43 | 92.57 |
| Bird | 98.57 | 0.29 | 98.00 |
| Train | 98.86 | 2.14 | 90.23 |
| Buzzer | 99.14 | 0.00 | 97.14 |
| p | BadNets | PBSM | VSVC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC↑ | ASR↓ | BAC↑ | ACC↑ | ASR↓ | BAC↑ | ACC↑ | ASR↓ | BAC↑ | |
| 1% | 99.43 | 1.43 | 92.57 | 99.71 | 22.57 | 17.14 | 99.71 | 26.86 | 12.29 |
| 5% | 99.71 | 2.00 | 90.57 | 99.71 | 22.86 | 21.14 | 90.57 | 54.29 | 10.86 |
| 10% | 99.57 | 3.14 | 90.00 | 97.43 | 24.00 | 18.29 | 84.57 | 58.86 | 11.71 |
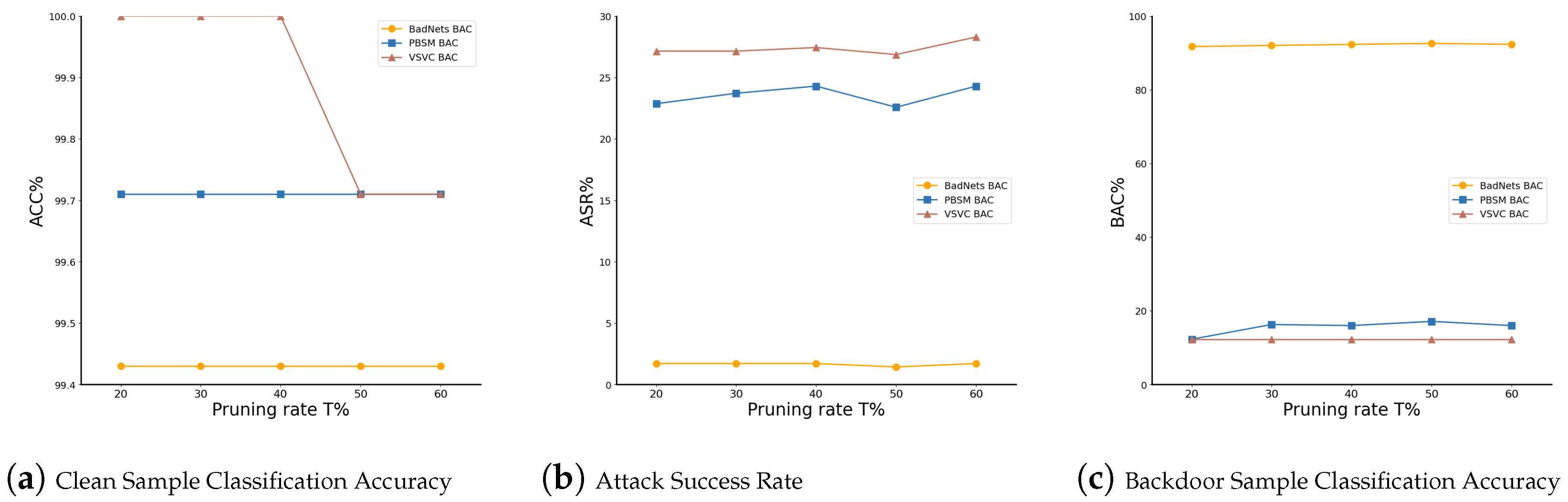
| T | BadNets | PBSM | VSVC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC↑ | ASR↓ | BAC↑ | ACC↑ | ASR↓ | BAC↑ | ACC↑ | ASR↓ | BAC↑ | |
| 0.2 | 99.43 | 1.71 | 91.71 | 99.71 | 22.86 | 12.29 | 100 | 27.14 | 12.29 |
| 0.3 | 99.43 | 1.71 | 92.00 | 99.71 | 23.71 | 16.29 | 100 | 27.14 | 12.29 |
| 0.4 | 99.43 | 1.71 | 92.29 | 99.71 | 24.29 | 16.00 | 100 | 27.43 | 12.29 |
| 0.5 | 99.43 | 1.43 | 92.57 | 99.71 | 22.57 | 17.14 | 99.71 | 26.86 | 12.29 |
| 0.6 | 99.43 | 1.71 | 92.29 | 99.71 | 24.29 | 16.00 | 99.71 | 28.29 | 12.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, H.; Zhong, Q.; Qi, M.; Fang, U.; Shi, G.; Cui, S. Towards Robust Speech Models: Mitigating Backdoor Attacks via Audio Signal Enhancement and Fine-Pruning Techniques. Mathematics 2025, 13, 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13060984
Sun H, Zhong Q, Qi M, Fang U, Shi G, Cui S. Towards Robust Speech Models: Mitigating Backdoor Attacks via Audio Signal Enhancement and Fine-Pruning Techniques. Mathematics. 2025; 13(6):984. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13060984
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Heyan, Qi Zhong, Minfeng Qi, Uno Fang, Guoyi Shi, and Sanshuai Cui. 2025. "Towards Robust Speech Models: Mitigating Backdoor Attacks via Audio Signal Enhancement and Fine-Pruning Techniques" Mathematics 13, no. 6: 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13060984
APA StyleSun, H., Zhong, Q., Qi, M., Fang, U., Shi, G., & Cui, S. (2025). Towards Robust Speech Models: Mitigating Backdoor Attacks via Audio Signal Enhancement and Fine-Pruning Techniques. Mathematics, 13(6), 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13060984






