Abstract
In the realm of apple cultivation, the efficient and real-time monitoring of Gray Leaf Spot is the foundation of the effective management of pest control, reducing pesticide dependence and easing the burden on the environment. Additionally, it promotes the harmonious development of the agricultural economy and ecological balance. However, due to the dense foliage and diverse lesion characteristics, monitoring the disease faces unprecedented technical challenges. This paper proposes a detection model for Gray Leaf Spot on apple, which is based on an enhanced YOLOv8 network. The details are as follows: (1) we introduce Dynamic Residual Blocks (DRBs) to boost the model’s ability to extract lesion features, thereby improving detection accuracy; (2) add a Self-Balancing Attention Mechanism (SBAY) to optimize the feature fusion and improve the ability to deal with complex backgrounds; and (3) incorporate an ultra-small detection head and simplify the computational model to reduce the complexity of the YOLOv8 network while maintaining the high precision of detection. The experimental results show that the enhanced model outperforms the original YOLOv8 network in detecting Gray Leaf Spot. Notably, when the Intersection over Union (IoU) is 0.5, an improvement of 7.92% in average precision is observed. Therefore, this advanced detection technology holds pivotal significance in advancing the sustainable development of the apple industry and environment-friendly agriculture.
MSC:
68T45
1. Introduction
Apple, one of the most widely cultivated fruits globally, has solidified its significance among cash crops due to its abundant nutritional value, and it has become an integral part of daily diets. However, constant changes in climate and planting environments lead to an increasing number of disease problems in apple trees. Among these diseases, Gray Leaf Spot, which is generated by a fungus called Venturia inaequalis, is particularly noteworthy. It spreads rapidly under wet conditions and leads to lesions, early defoliation, and black spots on the surface of fruits [1]. Moreover, this fungus not only affects the normal growth cycle of apples but also directly impacts their yield and quality, ultimately posing a significant challenge to the income of fruit growers [2]. Therefore, its accurate identification and effective prevention in the early stage are of great importance to ensure the sustainable development of the apple industry.
At the turn of the 20th century, orchard managers found it difficult to achieve large-scale disease monitoring through manual inspection [3]. This reliance on human observation was time-consuming and prone to error, limiting the ability to manage diseases effectively. Since the early 1900s, with the development of computer technology, machine learning has been gradually applied to the visual recognition of agricultural diseases. It provided a new possibility for the auto-monitoring and detection of Gray Leaf Spot on apple [4]. Early machine learning approaches focused on handcrafted feature extraction, which required domain expertise and was often limited by the complexity of disease morphology and environmental variability. Ahmed Imtiaz et al. utilized machine learning to identify ideal large targets [5]. Mahvish Jan et al. used low-level and shape-based features to implement high-precision apple disease measurement in an ideal environment [6]. These studies laid the foundation for automated disease detection but were often constrained by the need for controlled conditions and the limitations of handcrafted features.
Subsequently, image recognition technology has undergone vital advancements as a result of the rapid advancement and widespread adoption of deep learning techniques. Researchers proposed the use of a convolutional neural network (CNN) to extract multi-level features automatically and increase the accuracy of detection remarkably [7]. Yadav Anju et al. exercised AFD-Net for the detection of apple leaf disease under ideal conditions [8]; Ayaz H. et al. introduced a nonlinear deep feature neural network for apple disease classification [9]; and Asif Iqbal Khan et al. utilized a CNN model, which was trained on a prepared dataset, for the automatic classification of apple diseases [10]. At the same time, the YOLO algorithm has drawn widespread attention due to its advantages in both accuracy and speed. It can directly predict the position and characteristics of targets through a single forward propagation, which makes it extremely suitable for applications. Zhao K. et al. proposed a field soybean flower and pod detection method based on an improved YOLOv8-VEW model, providing reliable technical support for field detection and high-yielding variety selection [11]; Niu S. et al. proposed a novel early drought detection method for maize using UAV images and an improved YOLOv8+ model, which incorporated various enhancements to achieve higher accuracy, faster detection speed, and better robustness compared to the original YOLOv8 model [12]; and Zhang L. et al. realized the monitoring of ginseng appearance quality under an ideal interference-free condition [13]. However, applying the YOLO algorithm to detect Gray Leaf Spot in apples poses several challenges [14]. For instance, leaves with small lesion areas, variable lesion morphologies, complex backgrounds, and an inconspicuous color contrast all pose difficulties to the analysis [15].
To enhance this, our study proposes a detection method for Gray Leaf Spot based on an improved YOLOv8 network. By optimizing the network structure and upgrading the feature extraction and fusion strategy, it greatly augments the accuracy and robustness of Gray Leaf Spot on apple under complex backgrounds [16]. The structure of this paper is as follows: Section 2 describes the preparation of the dataset and the design and implementation of the improved framework in detail; Section 3 presents and analyzes the experimental results; and Section 4 provides the concluding remarks.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Data Acquisition and Image Feature
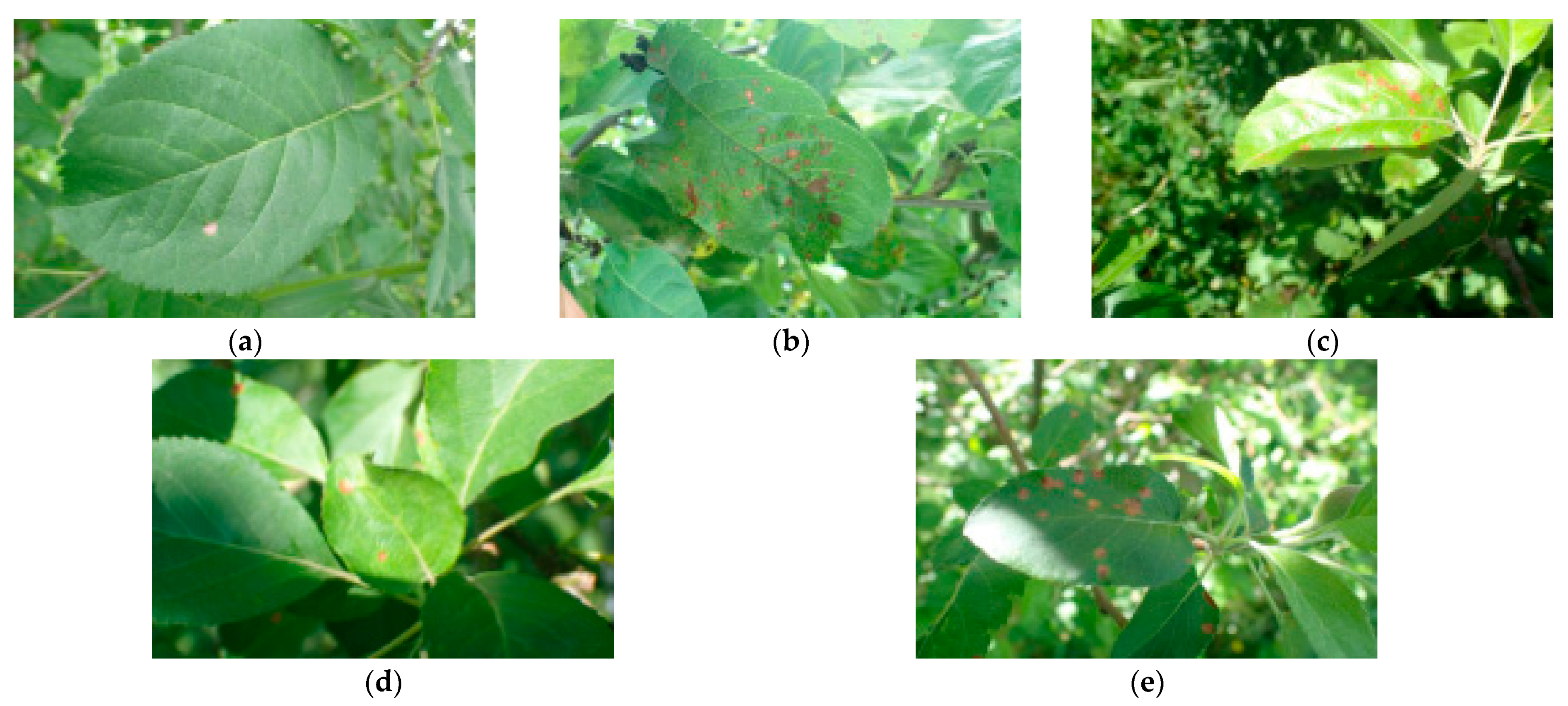
Our experimental image data originate from PaddlePaddle AI Studio (https://aistudio.baidu.com accessed on 9 September 2024). The image data of healthy apple leaves and 8 types of apple leaf diseases were obtained from the AppleLeaf9 dataset [17]. This article focuses on Gray Leaf Spot, the spots of which are smaller than other diseases, as shown in Figure 1 [18]. We set the image resolution to 960 × 40 pixels and ultimately generated 2010 images after de-duplication.
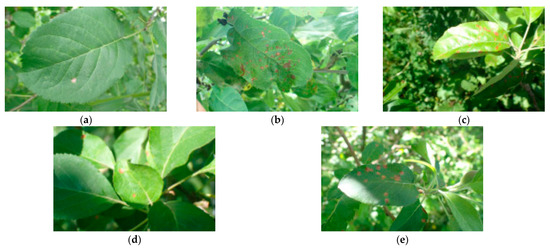
Figure 1.
Sample of detection images. (a) Leaf with single lesion; (b) leaf with high-density lesion; (c) overexposed leaf with lesions; (d) multi-layered leaves with lesions; (e) leaf with blurry lesions. The leaf size in this figure is approximately 10 cm in length and 6 cm in width.
Several challenges in detecting Gray Leaf Spot are as follows:
- A leaf with a single lesion: This is a single leaf with one spot, as shown in Figure 1a;
- A leaf with high-density lesions: Numerous spots will directly affect the performance of the YOLO-based algorithms in recognizing them [19], as shown in Figure 1b;
- An overexposed leaf with lesions: Excessive light can easily lead to missed detections, as shown in Figure 1c;
- Multi-layered leaves with lesions: Intertwined leaves cause a light blur, motion blur or out-of-focus target pixels [20], as shown in Figure 1d;
- A leaf with blurry lesions: Spots are far from the camera, which causes blur problems, as shown in Figure 1e.
2.1.2. Image and Data Augmentation
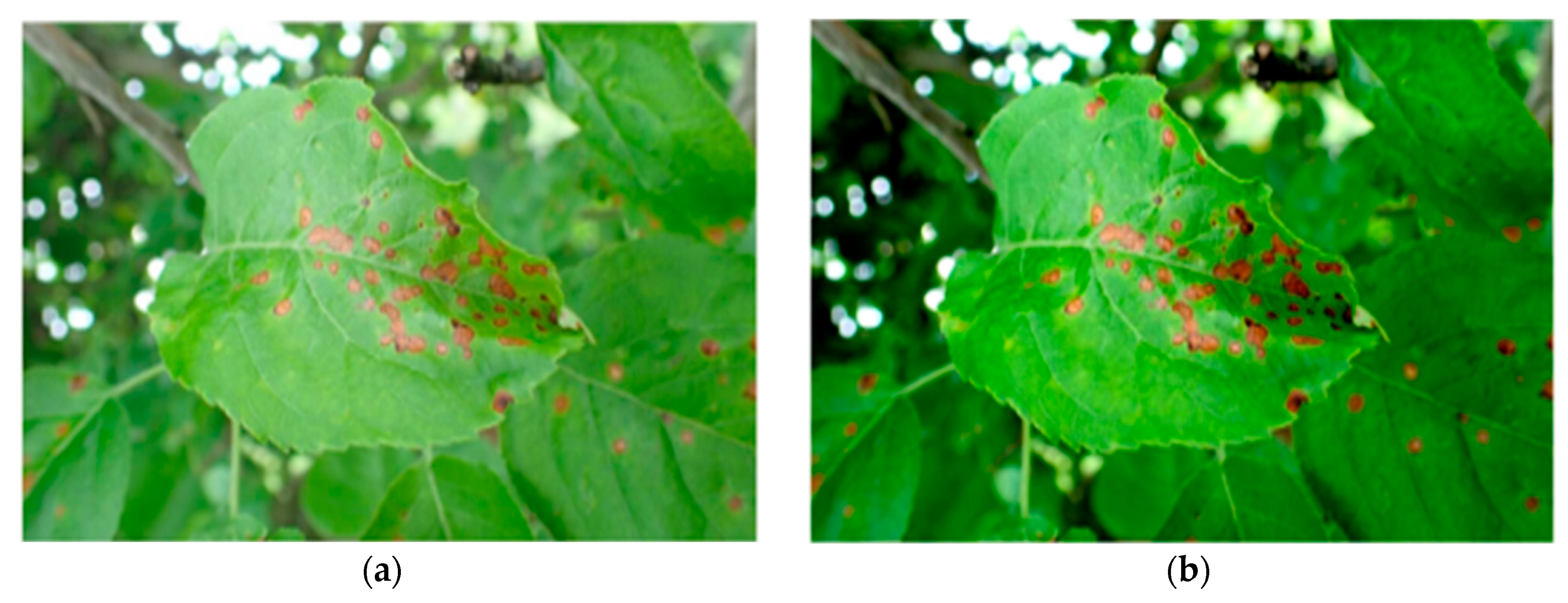
Contrast-Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE) was used to enhance image quality prior to the analysis [21]. CLAHE can effectively reduce image noise by limiting the range of contrast amplification while retaining the advantage of contrast improvement. Figure 2 shows a comparison after the enhancement, where the lesions in the right image are more prominent and obvious than those on the left. Based on these observations, our model is able to extract features from a clearer dataset with less noise.

Figure 2.
Comparison of images before and after CLAHE enhancement. (a) Original image (b) Image after data augmentation.
2.1.3. Image Annotation and Dataset Generation
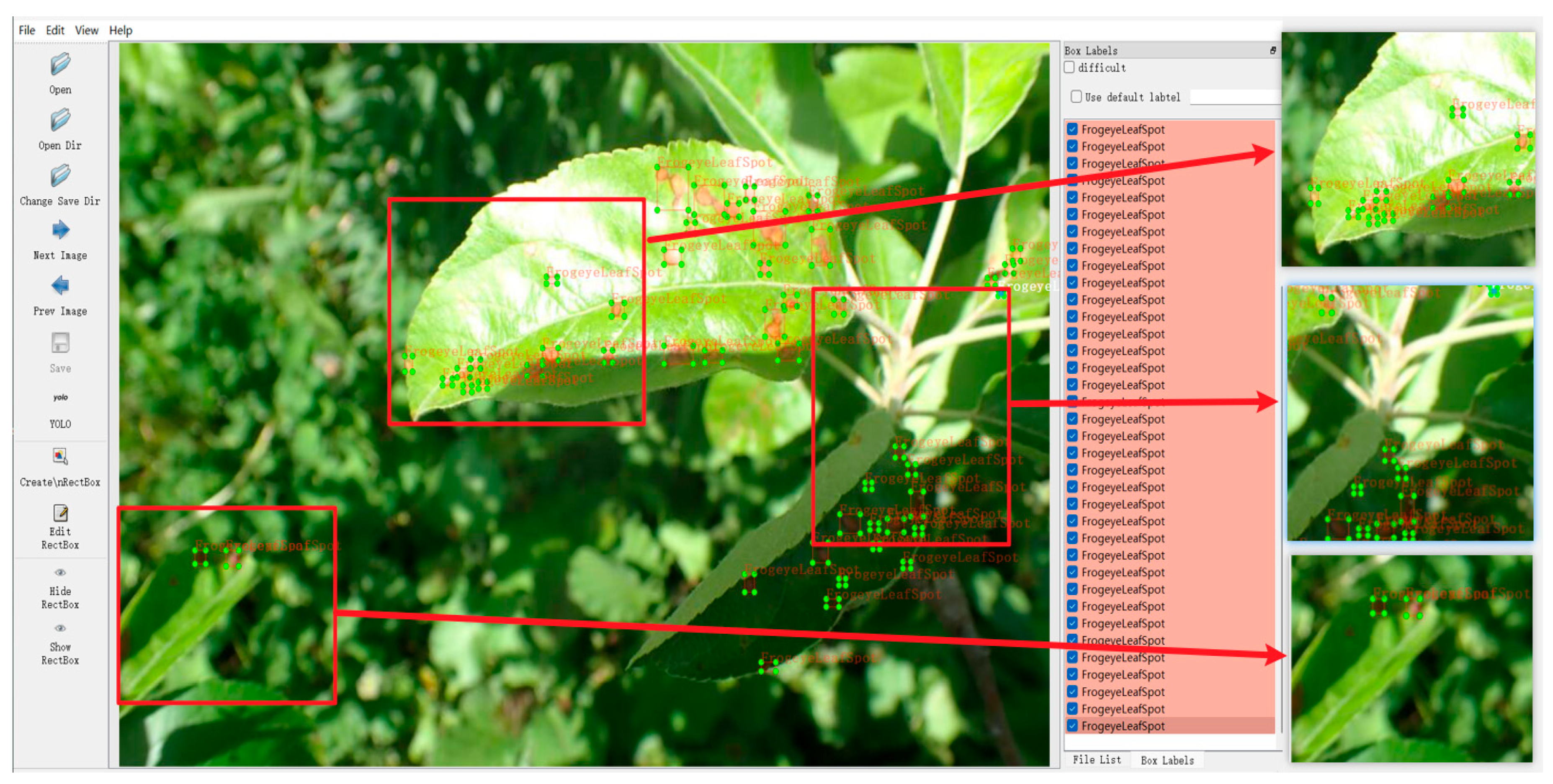
In the procedure of data pre-processing, LabelImg was used to annotate the dataset much more accurately. LabelImg is an open-source script on GitHub that accurately labels target samples in each image and generates XML files containing target type and coordinate information, thus laying the foundation for further training on the dataset. According to the distribution ratio of different class labels, the dataset was further divided into two subsets, training and validation, using the method of random sampling. In this paper, 1407 images were used for training and 603 images for validating, ensuring the effectiveness and generalization ability of the model training. An example of Gray Leaf Spot annotation on apple is shown in Figure 3.
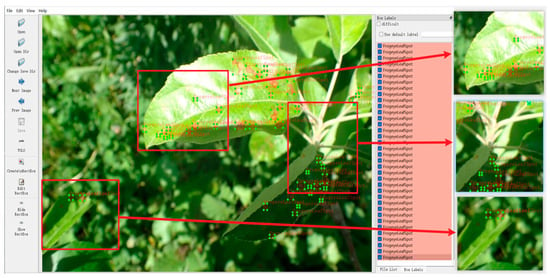
Figure 3.
Annotation of Gray Leaf Spot on apple.
2.2. Relevant Work
YOLOv8
YOLOv8 is built upon the success of previous YOLO versions and has a wide user base and strong community support [22]. This provides us with abundant resources and tools for model training, testing, and deployment. It also facilitates the implementation of our improved algorithms and the comparison of results with other state-of-the-art methods. YOLOv8 has demonstrated superior performance in terms of both speed and accuracy, which is crucial for detection tasks. It has achieved a better balance between these two aspects compared to many other architectures, making it the ideal choice for our study. Consequently, considering the requirements, complexity of detection tasks, and availability of resources, this paper chooses the YOLOv8 network model.
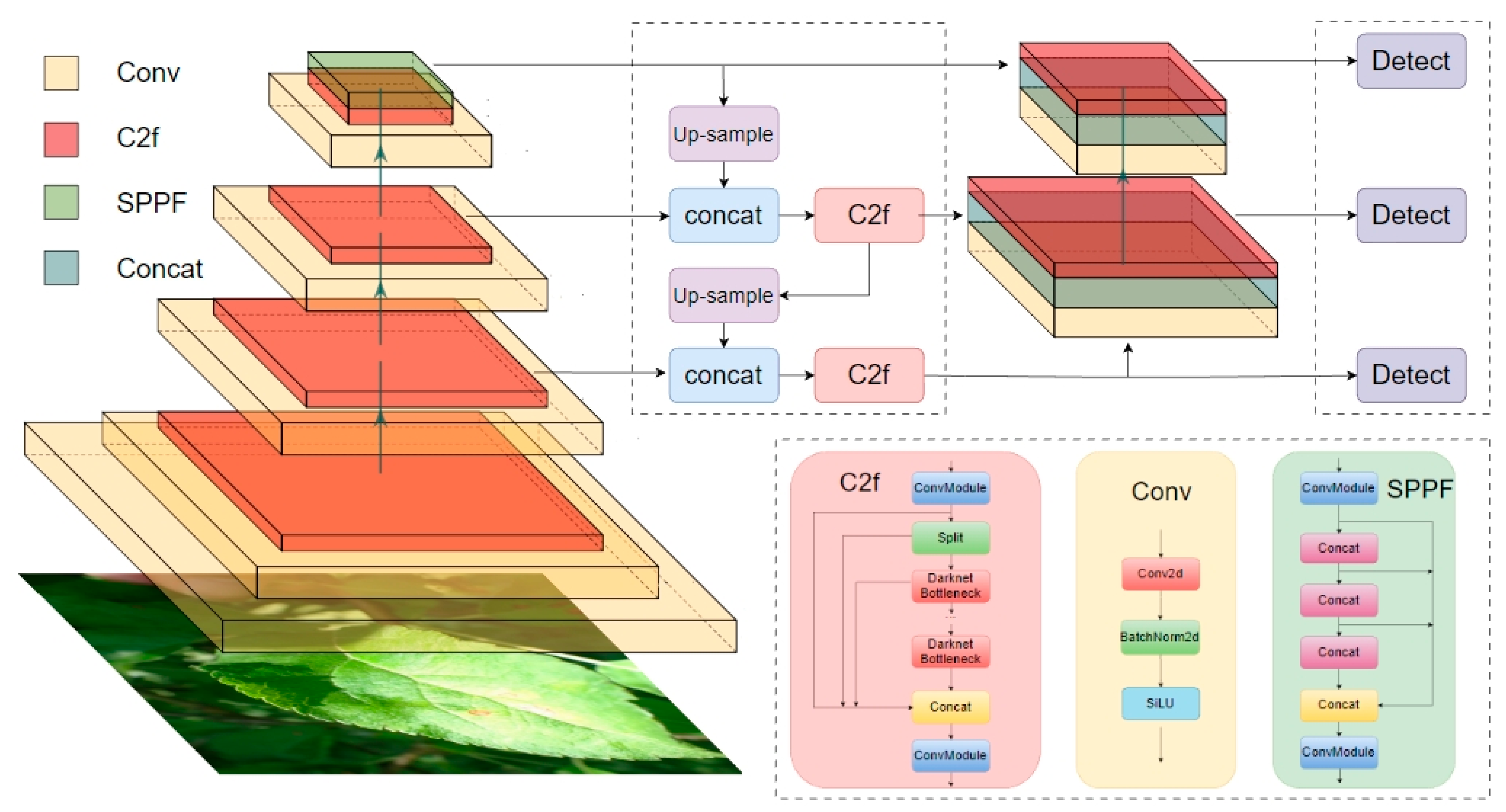
YOLOv8 adopts a high-efficiency feature extraction network, introducing a lightweight design concept and depth-wise separable convolution, which helps to reduce model parameters and computational complexity [23]. At the same time, it also retains a powerful capability of representation and faster inference speed under high-accuracy detection, satisfying the application scenario. In YOLOv8, multi-scale prediction and Feature Pyramid Networks (FPNs) have been utilized to precisely capture and recognize objects regardless of their size [24]. Additionally, it implements an advanced Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) algorithm to optimize detection results, further reducing false and missed detection rates [25]. In the training process, apart from the aforementioned techniques, YOLOv8 incorporates various advanced methods to enhance the stability and convergence speed, such as automatic learning rate adjustment [26] and weight decay optimization [27]. The combination of these strategies allows YOLOv8 to rapidly obtain high-quality model parameters in limited datasets, significantly promoting follow-up practical applications. The basic principle of YOLOv8 is illustrated in Figure 4.
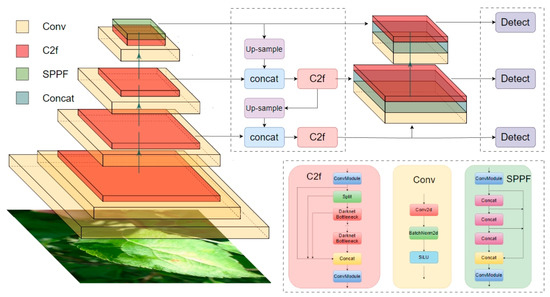
Figure 4.
YOLO-V8 algorithm structure diagram.
In this paper, we employed Precision, Recall, score, and Average Precision (AP) [28] as the evaluation metrics to examine the proposed network.
Precision indicates the fraction of true positive samples among all samples predicted as positive by the model. It reflects the accuracy of the model’s prediction, namely, the reliability of the model’s positive prediction. Higher Precision represents a more correct identification and a lower false detection rate. The calculation formula is shown in (1):
where TP is true positive, which refers to the samples correctly identified as Gray Leaf Spot on apple; FP is false positive, denoting the false identification of Gray Leaf Spot; TN means true negative, which refers to the samples correctly identified as background; and FN means false negative, representing the incorrect identification of samples as background. In this study, Precision represents the proportion of Gray Leaf Spot cases detected by the model that are actually Gray Leaf Spot. A high Precision value indicates that the model’s detection results are highly reliable.
Recall represents the proportion of actual positive samples that are correctly predicted as positive. It reflects the model’s ability to identify positive instances [29]. A higher Recall value indicates a lower probability of missing actual positive samples, meaning the model can detect the majority of Gray Leaf Spot cases. The calculation formula is shown in (2):
The score is the harmonic mean of Precision and Recall, providing a comprehensive measure of the model’s performance. It balances the importance of Precision and Recall, offering a single metric to evaluate the model. A higher F1 score indicates better overall performance and robustness. The score helps us find an optimal balance between Precision and Recall, ensuring the model’s effectiveness in practical applications. The calculation formula is shown in (3):
AP represents the average accuracy at different Recall levels that equals the area under the Precision–Recall curve (PR curve). It is a comprehensive metric for measuring model performance across different categories. It takes into account the changes in Precision at different Recall rates, thus providing a more holistic reflection of the model’s detection capabilities and ensuring its robustness across different confidence levels. The ‘r’ indicates the integral variable and determines the integral of Precision * Recall between 0 and 1. The calculation formula is shown in (4):
is the average value of AP calculated at multiple Intersection over Union (IoU) thresholds (ranging from 0.5 to 0.95, with a step size of 0.05). It thoroughly evaluates the model’s performance under varying detection challenges and provides a more comprehensive reflection of the model’s actual behavior compared to AP. Above all, it requires the model to maintain high accuracy under different IoU thresholds, which is particularly important for detection tasks in practical applications. The calculation formula is shown in (5):
2.3. The Proposed Algorithm
2.3.1. Dilated Reparam Block
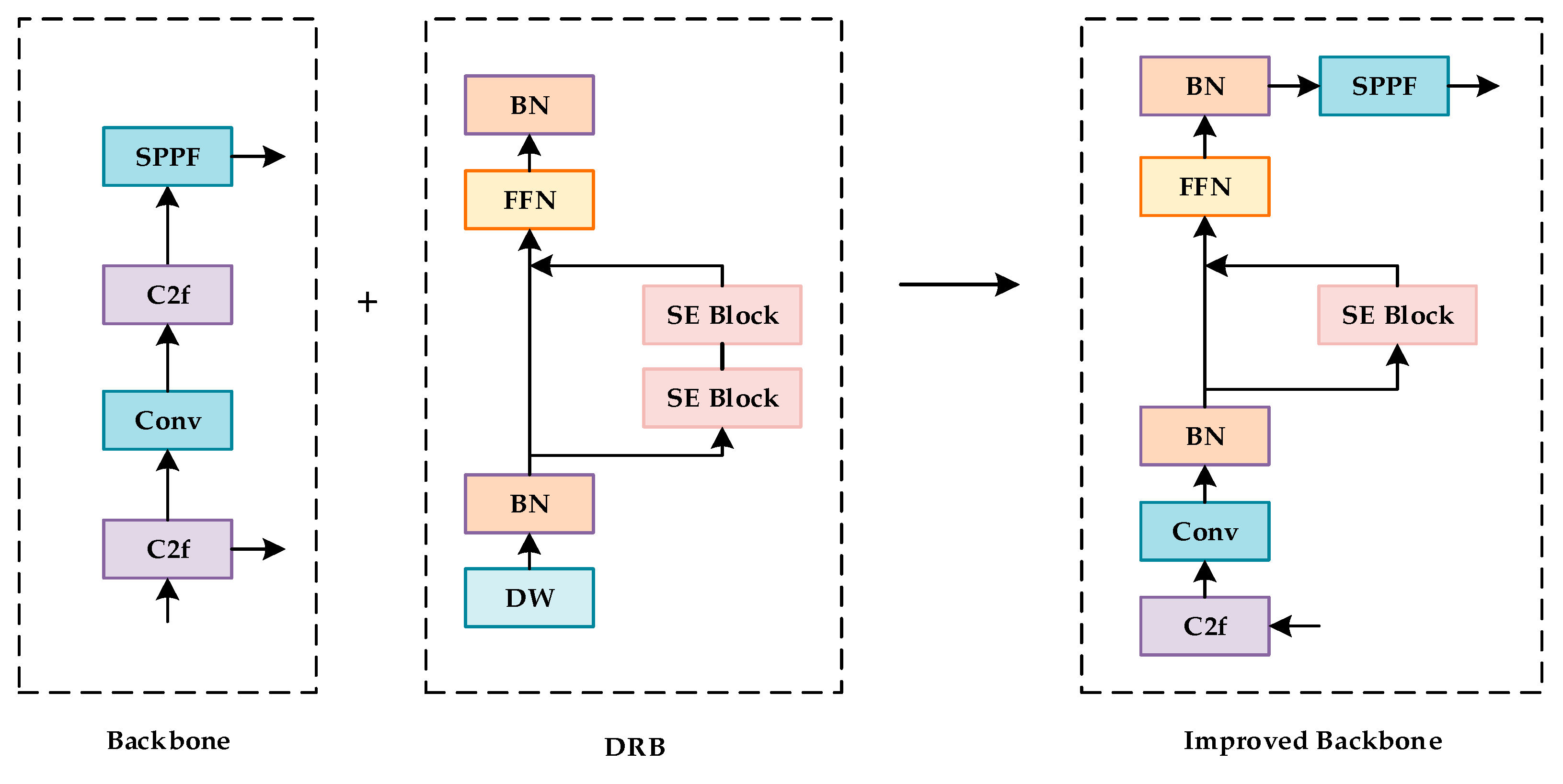
The Dilated Reparam Block (DRB) is an innovative design in deep learning, aimed at enhancing non-dilated large convolutional kernels. With the combination of parallel dilated convolutional layers and a sparse large kernel, the DRB effectively improves the performance of convolutional layers while maintaining relatively stable computational costs. Numerous parallel convolutional layers with different dilation rates were contained within the DRB model [30]. The DRB can increase the receptive field of the convolutional layers and keep the parameter count constant at the same time, thereby allowing more contextual information to be captured [31]. At the stage of inference, these parallel dilated convolutional layers are transformed equivalently into a non-dilated convolution with a sparse large kernel. Appropriate zero padding and function mapping were adopted to accomplish the transformation, ensuring that the large convolutional kernel could process to a similar capacity as small convolution. Furthermore, this contributes to a higher efficiency and a wider receptive field as well.
The application of DRBs in YOLOv8 dramatically advances the representation ability and efficiency of detection, thereby enhancing the feature extraction ability in complex scenes. The re-parameterization technique is utilized to fuse the outputs of multiple convolutional layers during the training process. Later, a single large kernel convolutional layer emerges throughout the inference. With this approach, the computational costs and inference speed are both promoted to a new height. The improved structural diagram is shown in Figure 5.
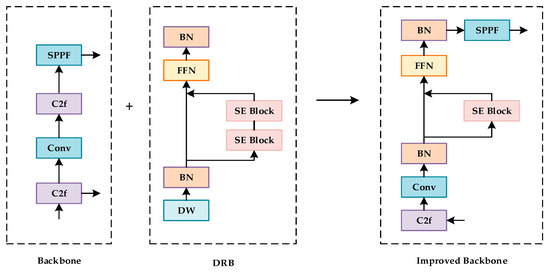
Figure 5.
Improved convolutional layer performance algorithm.
2.3.2. SBAY
The characteristics of Gray Leaf Spot include detailed boundaries, lesion edges, color, texture changes, etc., and their effective fusion is the key to augment accuracy [32]. Traditional Feature Pyramid Networks (FPNs) can partly fuse features at different levels. However, when an FPN fuses shallow and deep features directly, insufficient semantic information and the loss of details will result in redundancy and inconsistency [33].
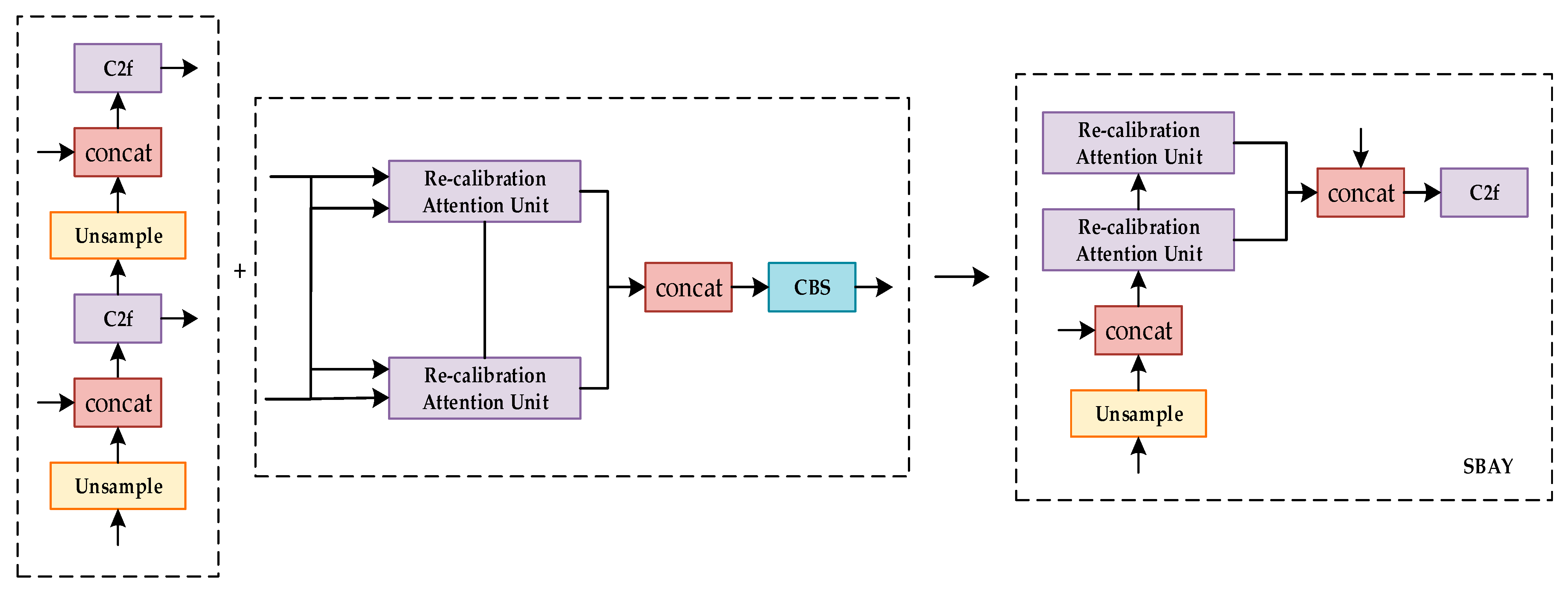
To address these challenges, the Selective Boundary Aggregation Module (SBAY) was used to correctly delineate the fine-grained contours of Gray Leaf Spot on apple and recalibrate the lesion position. The SBAY module is primarily designed to capture the delicate boundaries of lesions through high-resolution feature maps. In addition, it enhances the understanding of overall lesion characteristics with abundant semantic information provided by low-resolution feature maps. This bidirectional fusion not only facilitates the transfer of features but also dynamically adjusts feature weights based on concrete content through an adaptive mechanism. Ultimately, the proposed model can precisely capture multi-scale features of Gray Leaf Spot on apple. To sum up, SBAY shows great advantages in precise recognition and localization, and it opens up prospects for the intelligent detection and prevention of plant diseases [34]. The improved algorithm structure is illustrated in Figure 6.
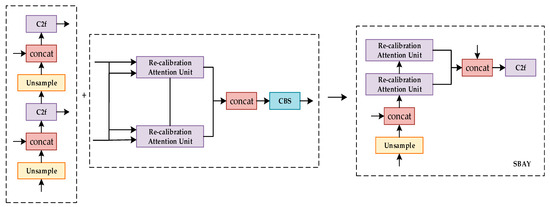
Figure 6.
Improved feature fusion algorithm.
2.3.3. Small Detection Head
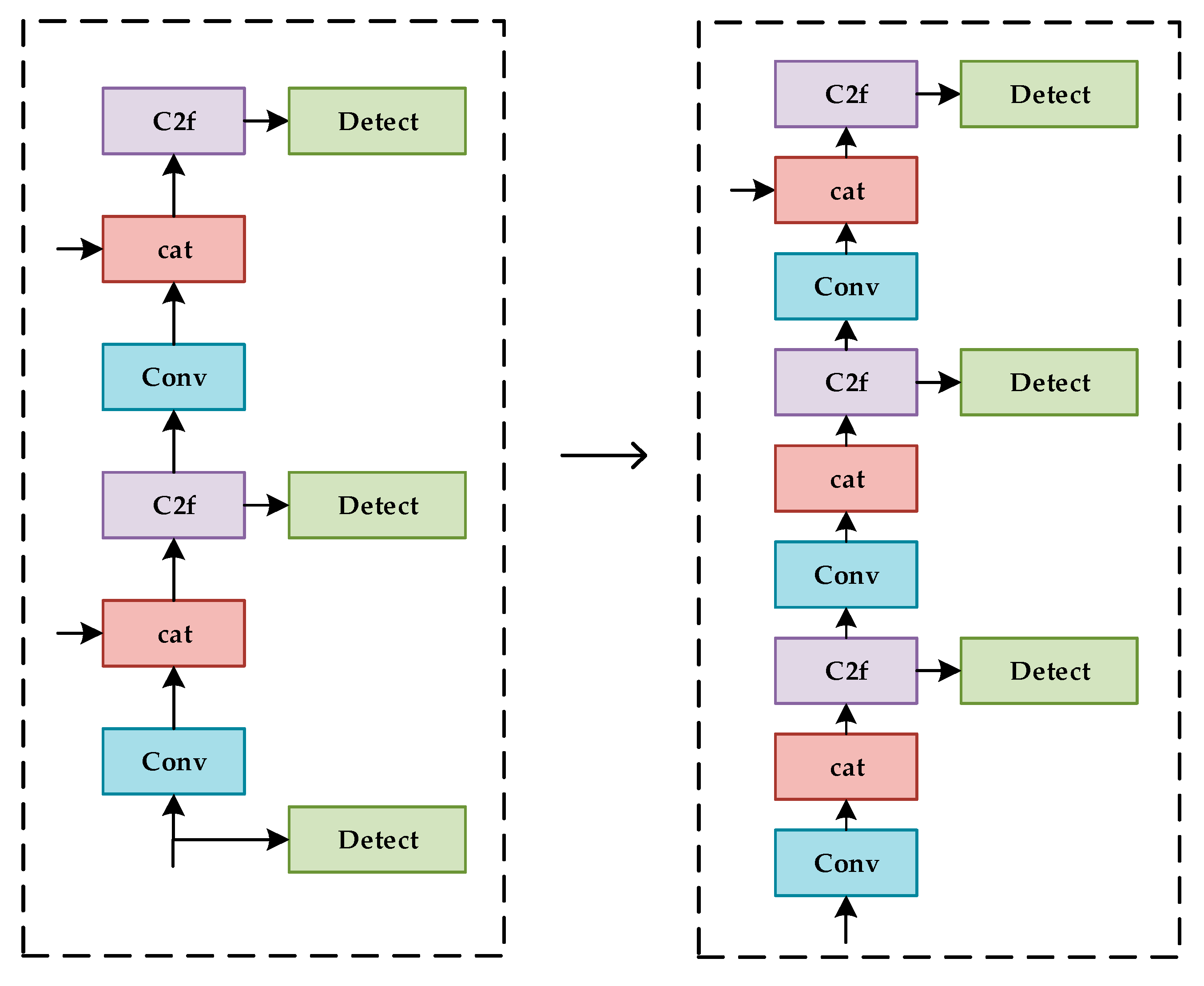
The original YOLOv8 algorithm has three types of detection heads, those being large, medium, and small [35]. On the basis of the actual distribution, feature omission caused by occlusion and nearby leaf interference will lead to high error rates in identifying Gray Leaf Spot on apple, thus decreasing the accuracy of the detection [36]. To overcome these problems, we replace the initial feature maps and add a layer on top of the original. This additional layer allows for the re-extraction of information flow, which can improve detection accuracy [37]. The improved algorithm structure is presented in Figure 7.
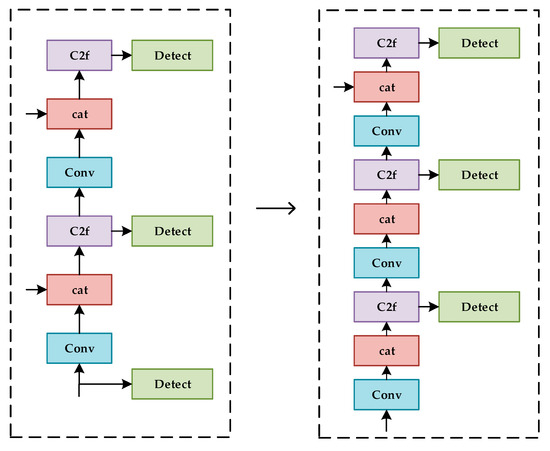
Figure 7.
Improvement in the detection head.
3. Results and Discussion
The experimental environment for this study is elaborated in Table 1. To achieve a preferable analysis, 200 iterations were executed. During the training process, relevant parameters were set to generate the pre-trained weight file, including a momentum of 0.949, an initial learning rate of 0.001, a weight decay coefficient of 0.0005, and a batch size of 16. The model was trained with the above settings, and the validating period used the same resolution images to validate the algorithm’s performance.

Table 1.
Experimental environment.
3.1. Training Result Analysis
Our study conducted a statistical analysis of the validation results that contained 28,190 Gray Leaf Spot samples. The confidence threshold (conf) was set to 0.25, and the IOU was set to 0.45. We examine the performance between the two YOLOv8 models, as summarized in Table 2. After the improvement, the model exhibits a notable increase in Precision, Recall, and F1 score. Specifically, Precision increased by 0.079, Recall increased by 0.13, and the F1 score increased by 0.12. The prominent changes in TPs (true positives) and FNs (false negatives) are the main reasons for the increased Recall. The results suggest that more samples were correctly identified, demonstrating the effectiveness of the improved algorithm.

Table 2.
Comparison of evaluation metrics before and after improvement.
3.2. Algorithm Performance Evaluation
3.2.1. Pre-Training
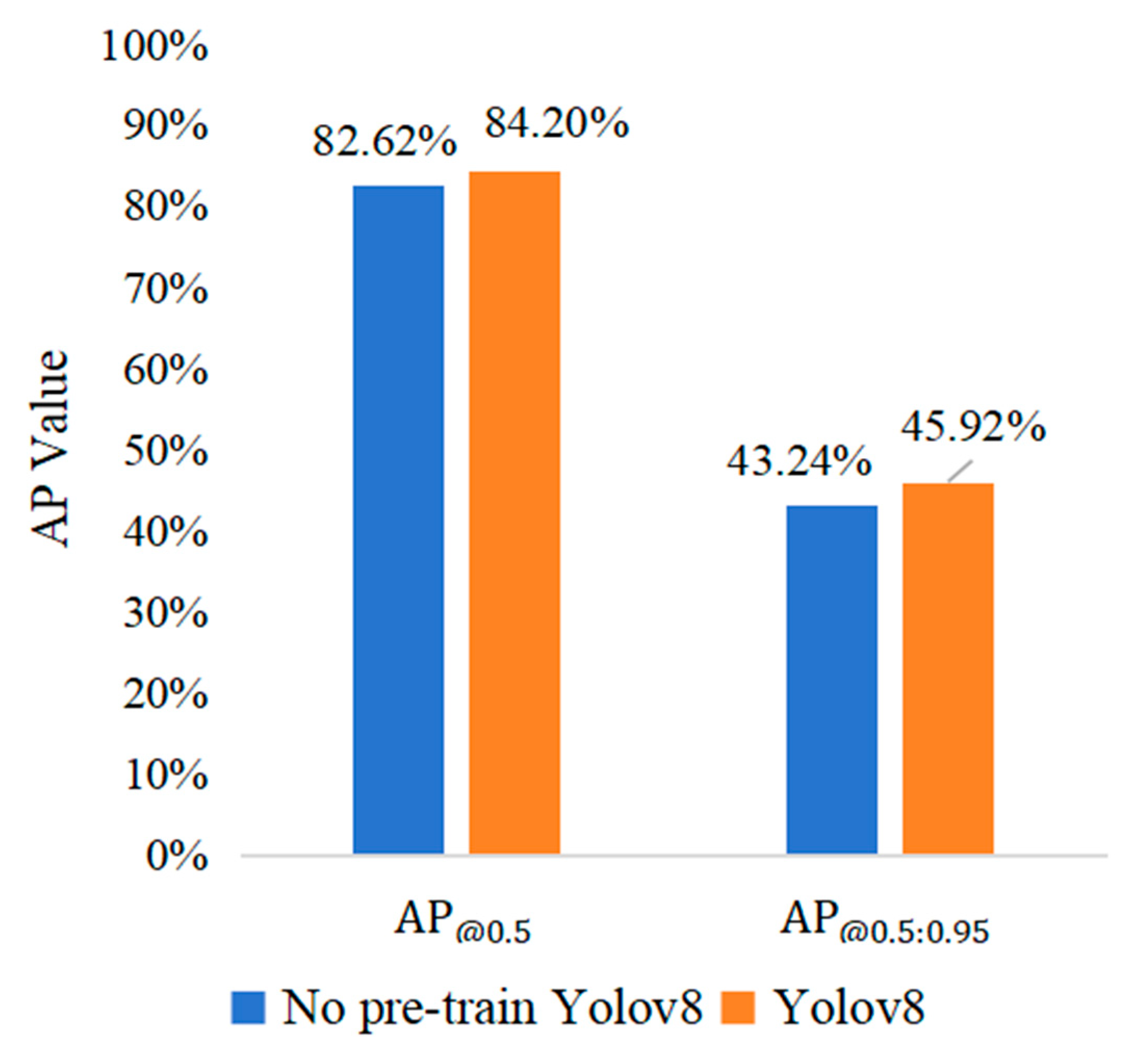
In this study, the pre-trained dataset was composed of 1407 images of Gray Leaf Spot on apple, eventually forming a pre-trained weight file, which was used to further learn the training dataset. This approach improved the model’s training performance and laid the foundation for recognizing Gray Leaf Spot on apple. As can be seen in Figure 8, the results with the transfer learning strategy are more effective, leading to a 1.58% improvement in AP.
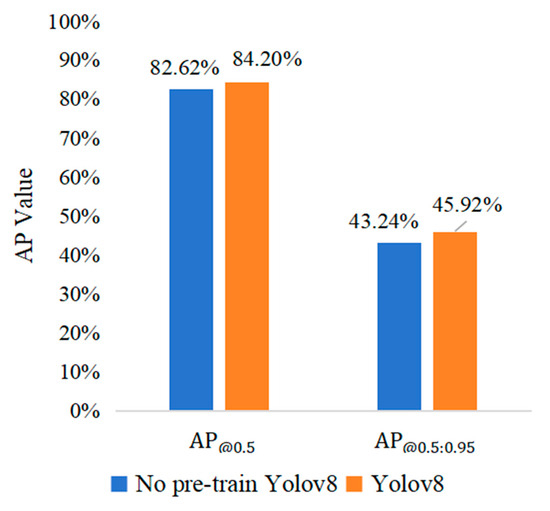
Figure 8.
Comparison of pre-training results.
3.2.2. Comparison of Improved Convolutional Layer
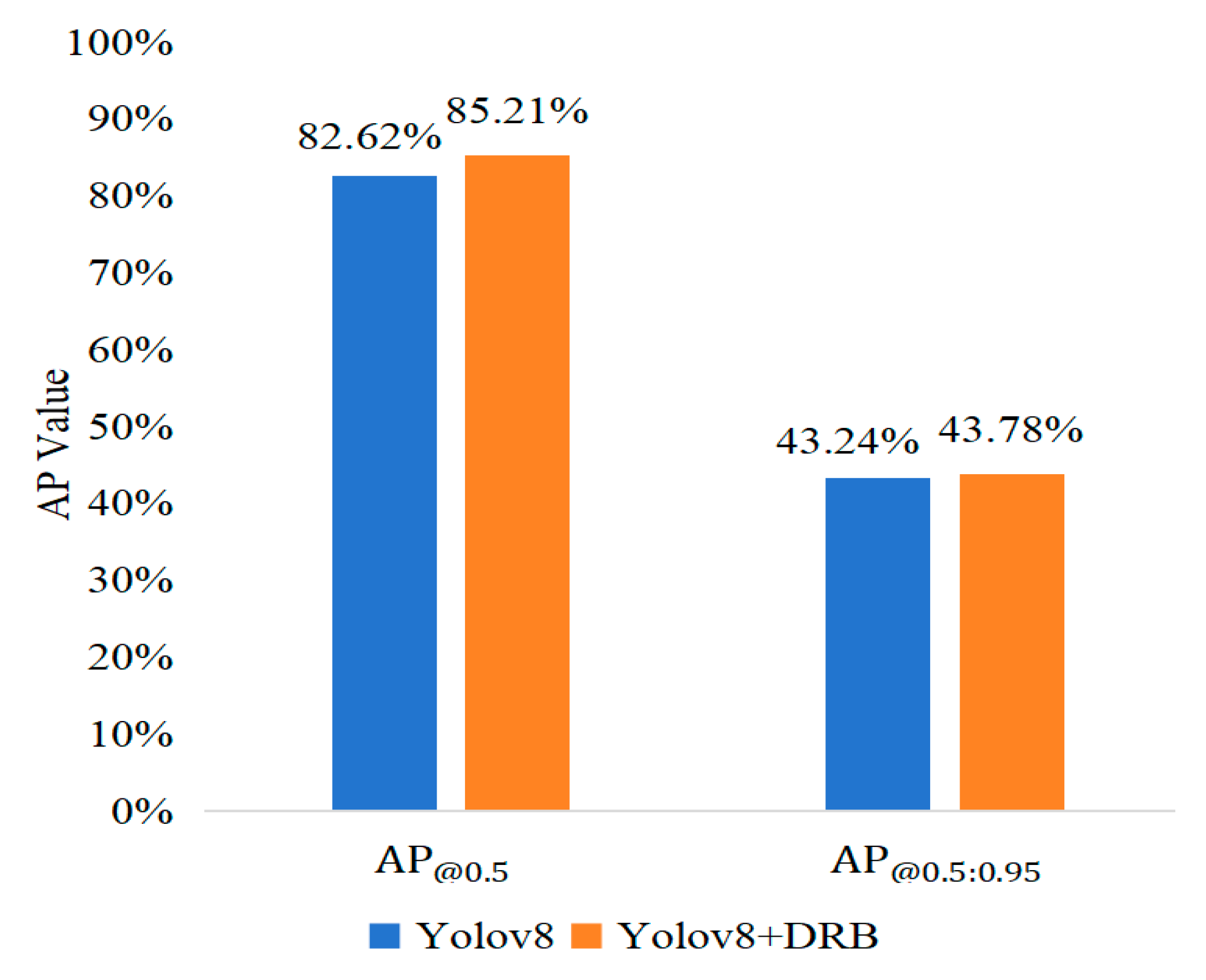
An improved DRB (Dilated Residual Block) was introduced into the YOLOv8 architecture. This enhancement optimized the receptive field of the convolutional layers and improved the ability to capture contextual information. Different dilation rates result in different fields of view; thus, more critical details and contextual information can be recognized after making appropriate adjustments. A comparison of the improvement results is shown in Figure 9, where AP increases from 82.62% to 84.21%. The results indicate that the enhanced non-dilated large convolutional layers have a positive effect on detection accuracy.
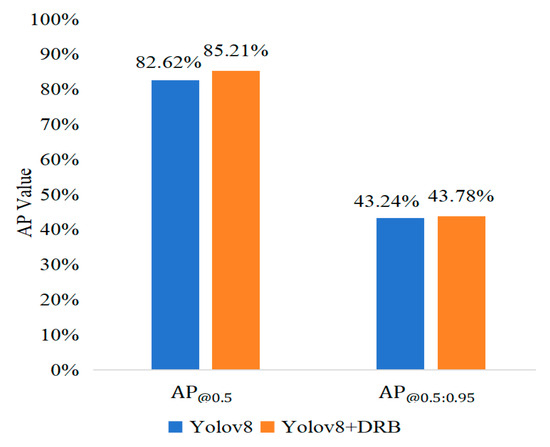
Figure 9.
Comparison of improved convolutional layer.
3.2.3. Comparison of Feature Fusion Strategy
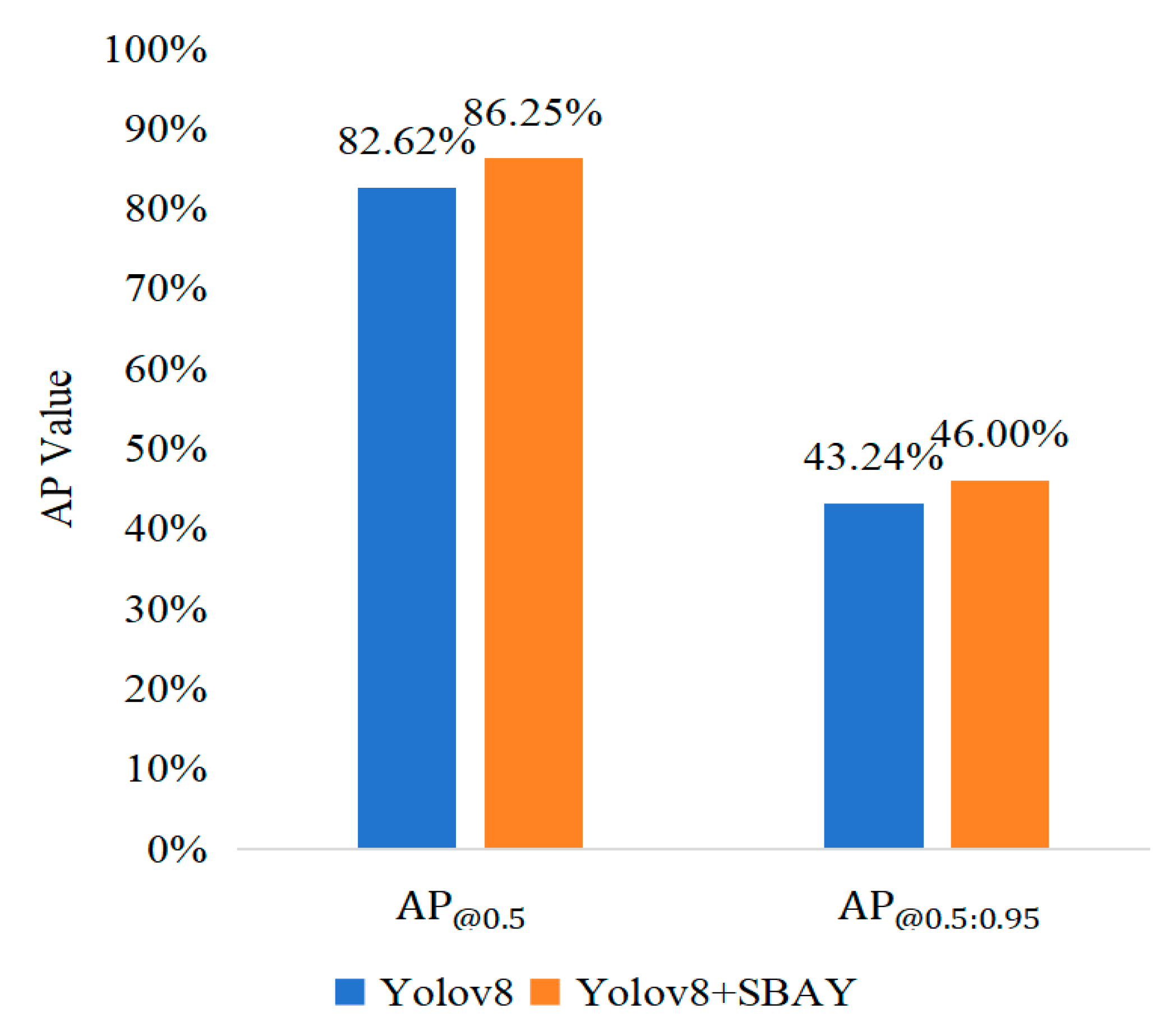
In the process of feature fusion between shallow and deep layers, problems such as insufficient semantic information and missing details occur frequently. Therefore, the Selective Boundary Aggregation Module (SBAY) was creatively implemented to capture subtle boundary information of the lesions. It also leveraged the complementary advantages of different resolution feature maps, realizing a deep fusion of lesion boundaries with features such as color and texture. The comparison results are shown in Figure 10, where mAP raises from 82.62% to 86.25%, demonstrating that the feature fusion strategy algorithm enhances the accuracy of detection.
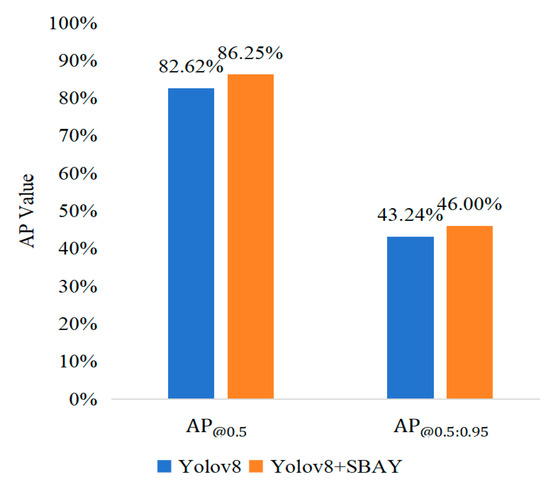
Figure 10.
Comparison of improved feature fusion strategy.
3.2.4. Comparison of Improved Detection Head
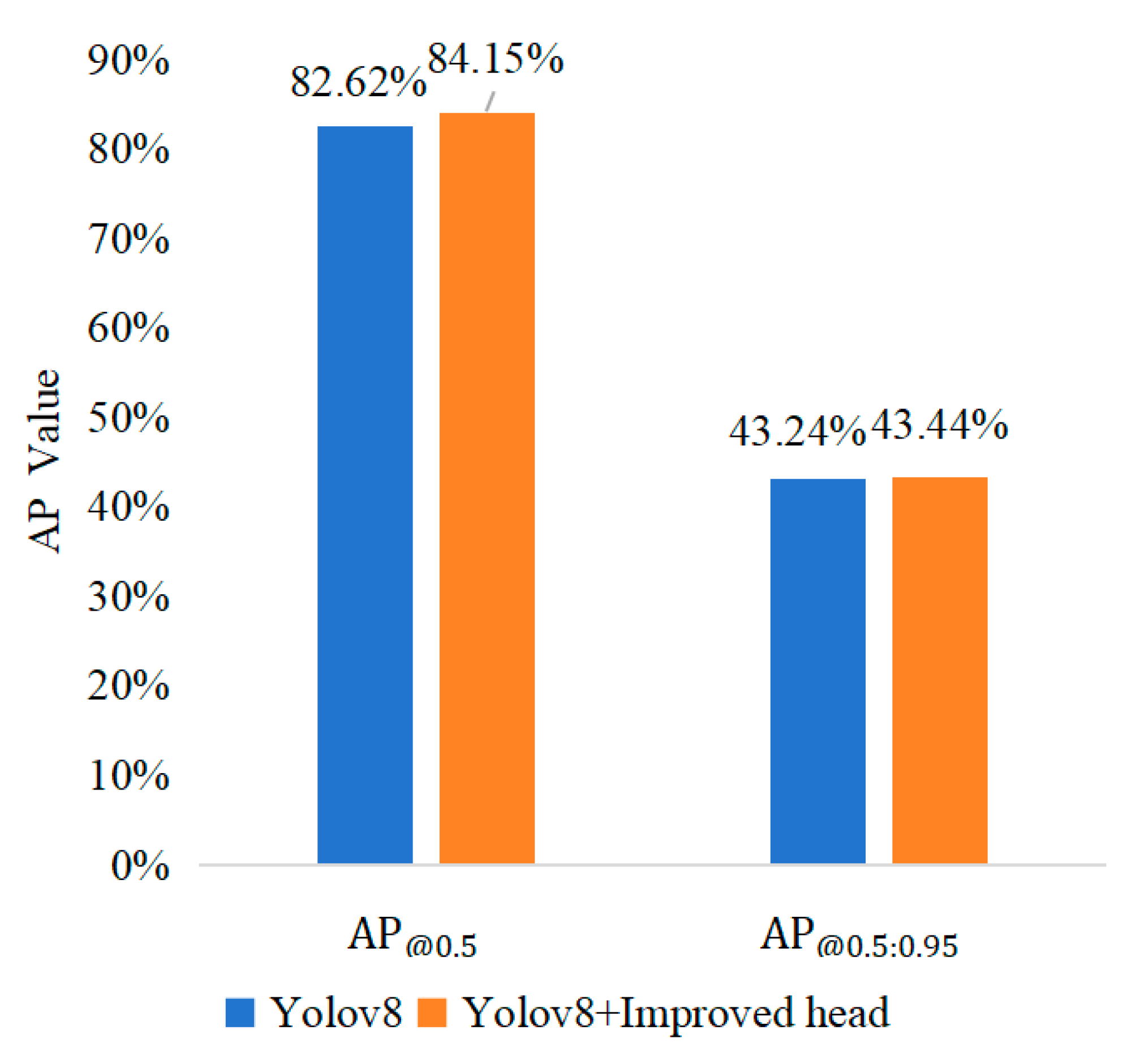
In this study, we used an improved detection head instead of the initial feature maps of the original. Based on a progressive information flow, the accuracy of detection was obviously increased, and issues like insufficient information and multi-scale analysis were effectively reduced. A comparison of the experimental results after the enhancement is shown in Figure 11, where mAP increases from 82.62% to 84.15%. In conclusion, the improved detection head achieves better identification performance.
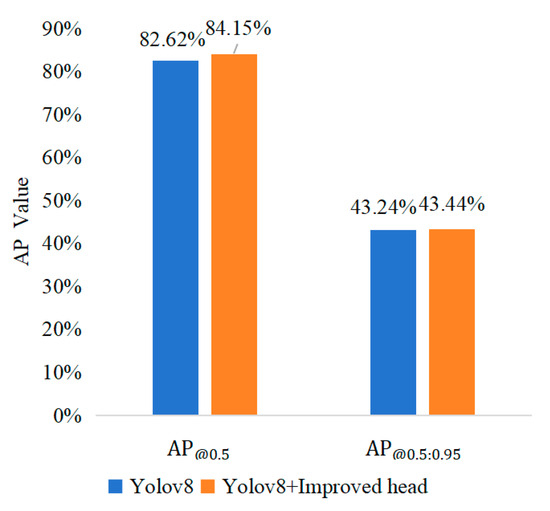
Figure 11.
Comparison of improved detection head.
3.3. Overall Algorithm Performance Comparison
Table 3 lists the results of different strategies. The results show a 7.92% increase in AP@0.5. The detection accuracy of Gray Leaf Spot on apples was effectively enhanced through a series of modifications.

Table 3.
Comparison of improved algorithm results.
To further analyze the performance of the proposed method, this study compares it to Faster R-CNN, SSD, YOLOv7, and YOLOv11. The same training, validation, and testing settings are applied to compare the performance of the five networks, and the results are shown in Table 4. The improved YOLOv8 outperforms the other models in terms of accuracy, further validating its strong adaptability and generalization ability in complex scenarios.

Table 4.
Comparison with current mainstream detection algorithms.
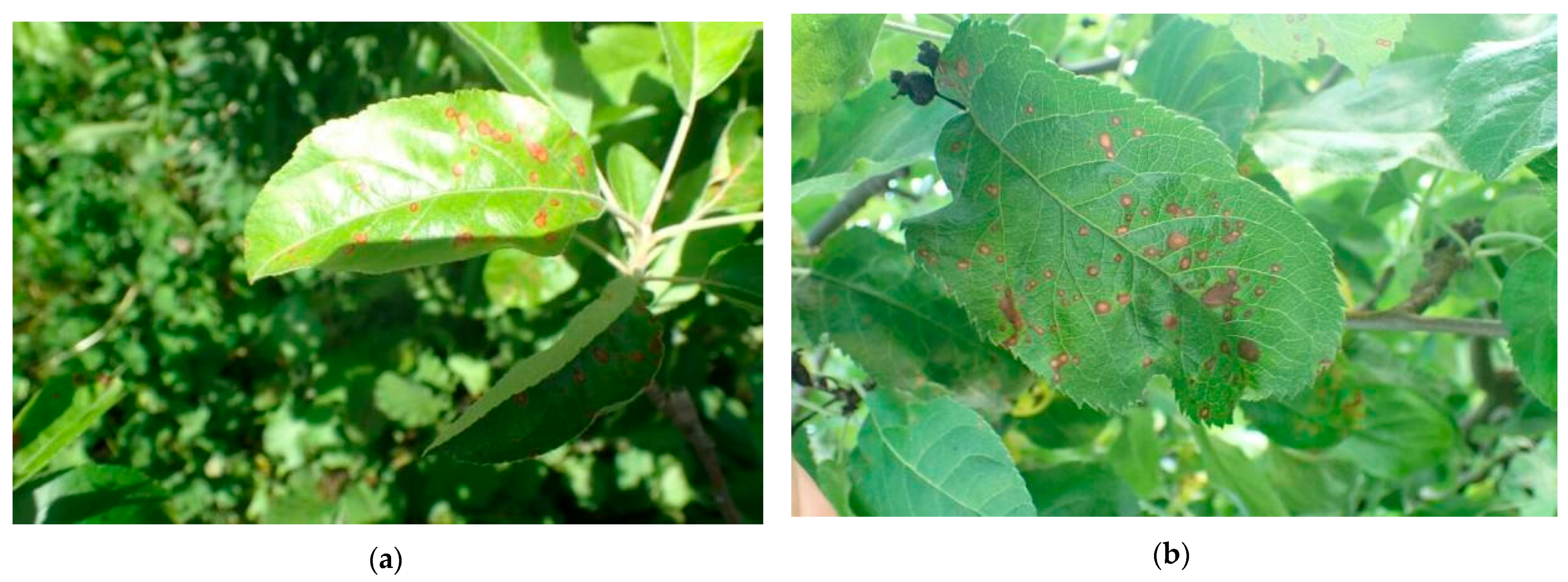
By comparing the detection results of the untrained YOLOv8 and the improved YOLOv8 models on gray spot disease images in a real-world environment, we select the diseased leaf shown in Figure 12.

Figure 12.
Diseased leaf. (a,b)are the leaf images to be identified.
This leaf contains small gray spot disease lesions. It encompasses various detection challenges encountered in real-world applications, such as high-density lesions, lesions under exposure conditions, multi-layered leaf lesions, and partially blurred lesions. The detection difficulty is high, with a significant level of complexity. The detection results of the entire image before and after the improvement are shown in Figure 13.

Figure 13.
Comparison of detection results. (a) Original YOLOv8 model recognition results; (b) recognition results after improvement.
4. Conclusions and Discussion
This paper proposes an improved YOLOv8 network for the detection of Gray Leaf Spot on apple leaves, which incorporates the parallel processing of dilated and non-dilated convolutions. This modification enhances YOLOv8’s precision in detecting complex scenes and objects through its feature map extraction network. Additionally, a bidirectional fusion mechanism is introduced to promote full information transfer between features. The adaptive attention mechanism dynamically adjusts feature weights based on the specific content of the feature maps, allowing for the more accurate capture of multi-scale features of apple leaf gray spot disease. This improves the detection accuracy and speed of apple gray spot disease lesions. The experimental results show that the proposed improved YOLOv8 network outperforms the original YOLOv8 network in apple gray spot disease detection tasks, with the average precision significantly increasing from 82.62% to 90.54%, representing an overall increase of 7.92%. The early and accurate detection of Gray Leaf Spot can help farmers take timely measures to control the spread of the disease, thereby reducing crop losses and improving the quality of agricultural products. The improved YOLOv8 network can be integrated into smart agriculture systems, providing real-time monitoring and early warning for apple leaf diseases. This can help farmers make more informed decisions and optimize their disease management strategies, ultimately leading to more efficient and sustainable agricultural practices.
In terms of future research directions, several areas warrant further exploration. First, we plan to further optimize the network structure to improve detection accuracy and speed. This may involve exploring more advanced attention mechanisms or incorporating other types of convolutional layers to better capture the complex features of plant diseases. Second, we aim to expand the dataset to include more diverse apple leaf images, including those under different lighting conditions and with varying degrees of disease severity. This will help improve the robustness and generalization ability of the model, making it more applicable in real-world scenarios. Third, we intend to explore the application of our improved YOLOv8 network in other types of plant disease detection, such as powdery mildew and black spot, to develop a more comprehensive plant disease detection system. This will contribute to the advancement of precision agriculture and help address the challenges of crop disease management on a larger scale.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.Z. and Y.H.; methodology, S.Z. and W.Y.; software, S.Z. and W.Y.; validation, S.Z. and Y.H.; formal analysis, S.Z. and Y.H.; writing—original draft preparation, S.Z. and W.Y.; writing—review and editing, W.Y. and X.L.; visualization, Y.H. and W.Y.; supervision, X.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Xin Li was employed by the company Dalian East Patent Agent Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Ayaz, F.K. Effect of climatic factors on sooty blotch, flyspeck intensity and fruit quality of apple. J. Pure Appl. Biol. 2018, 7, 727–735. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, P.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, S. Disease detection in apple leaves using deep convolutional neural network. Agriculture 2021, 11, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yağ, İ.; Altan, A. Artificial intelligence-based robust hybrid algorithm design and implementation for real-time detection of plant diseases in agricultural environments. Biology 2022, 11, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anupam, B.; Sunil, P.; Amandeep, K.; Shah, M.A. Exploring the trend of recognizing apple leaf disease detection through machine learning: A comprehensive analysis using bibliometric techniques. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Imtiaz, A.; Kumar, P.Y. Predicting Apple Plant Diseases in Orchards Using Machine Learning and Deep Learning Algorithms. SN Comput. Sci. 2024, 5, 700. [Google Scholar]
- Jan, M.; Ahmad, H. Image features based intelligent apple disease prediction system: Machine learning based apple disease prediction system. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Inf. Syst. 2020, 11, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Devaraj, M. Application of plant disease identification and detection based on deep learning. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Robotics, Artificial Intelligence and Intelligent Control (RAIIC), Mianyang, China, 5–7 July 2024; pp. 437–441. [Google Scholar]
- Anju, Y.; Udit, T.; Rahul, S.; Pal, V.; Bhateja, V. AFD-Net: Apple foliar disease multi-classification using deep learning on plant pathology dataset. Plant Soil 2022, 477, 595–611. [Google Scholar]
- Ayaz, H.; Rodríguez-Esparza, E.; Ahmad, M.; Oliva, D.; Pérez-Cisneros, M.; Sarkar, R. Classification of apple disease based on non-linear deep features. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.I.; Quadri, S.M.K.; Banday, S. Deep learning for apple diseases: Classification and identification. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Stud. 2021, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Li, J.; Shi, W.; Qi, L.; Yu, C.; Zhang, W. Field-based soybean flower and pod detection using an improved YOLOv8-VEW method. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Nie, Z.; Li, G.; Zhu, W. Early drought detection in maize using UAV images and YOLOv8+. Drones 2024, 8, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; You, H.; Wei, Z.; Li, Z.; Jia, H.; Yu, S.; Zhao, C.; Lv, Y.; Li, D. DGS-YOLOv8: A method for ginseng appearance quality detection. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhao, X.; Yue, X.; Yue, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X. A lightweight YOLOv8 model for apple leaf disease detection. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Xu, H.; Han, Y.; Lu, W.; Xu, L.; Rong, H.; Yang, B.; Zou, L.; Ma, Z. A visual identification method for the apple growth forms in the orchard. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 197, 106954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, K.; Xu, F.; Guo, H.; Tian, X.; Li, M.; Bao, Z.; Li, Y. An improved YOLOv5 model based on visual attention mechanism: Application to recognition of tomato virus disease. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 194, 106780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, K.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, L. A multi-scale cucumber disease detection method in natural scenes based on YOLOv5. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 202, 107363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Xu, X.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hua, Z.; Song, H. Using lightweight deep learning algorithm for real-time detection of apple flowers in natural environments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 207, 107765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, B.; He, D.; Liang, C. Real-time detection of apple leaf diseases using deep learning approach based on improved convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 59069–59080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ding, Z.; Tian, L.; He, D.; Li, S.; Wang, H. Grape leaf disease identification using improved deep convolutional neural networks. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manju, R.A.; Koshy, G.; Simon, P. Improved method for enhancing dark images based on CLAHE and morphological reconstruction. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 165, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terven, J.; Córdova-Esparza, D.-M.; Romero-González, J.-A. A comprehensive review of YOLO architectures in computer vision: From YOLOv1 to YOLOv8 and YOLO-NAS. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2023, 5, 1680–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, M. An improved YOLOv5-based vegetable disease detection method. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 202, 107345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Yu, X.; Ding, Y.; Peng, X.; Zhao, J.; Han, Z. Effective fusion factor in FPN for tiny object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, R.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, W.; Lv, Z.; Hou, J. Recognition method for potato buds based on improved Faster R-CNN. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 216–223. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, J.; Li, X.-L.; Han, H.-G. Design and Application of Deep Belief Network with Adaptive Learning Rate. Acta Autom. Sin. 2017, 43, 1339–1349. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, N.; Xin, J.; Xia, X.; Yang, X.; Gao, X. Learning lightweight super-resolution networks with weight pruning. Neural Netw. 2021, 144, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goutte, C.; Gaussier, E. A probabilistic interpretation of precision, recall, and F-score, with implication for evaluation. In Advances in Information Retrieval; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Losada, D.E., Fernández-Luna, J.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 345–359. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, D.; Chen, Z.; Gao, L. An improved object detection algorithm based on multi-scaled and deformable convolutional neural networks. Hum.-Cent. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2020, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wu, Z.; Wei, Z. CDE-DETR: A real-time end-to-end high-resolution remote sensing object detection method based on RT-DETR. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2024—2024 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Athens, Greece, 7–12 July 2024; pp. 8090–8094. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y. Receptive field block net for accurate and fast object detection. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision—ECCV 2018: 15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Part XI. Volume 11215, pp. 404–419. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z.; Zhong, G.; Yu, H. A review on the attention mechanism of deep learning. Neurocomputing 2021, 452, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiasi, G.; Lin, T.-Y.; Le, Q.V. NAS-FPN: Learning scalable feature pyramid architecture for object detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7029–7038. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Hu, X.; Li, F.; Xu, J. Lightweight recognition for multiple and indistinguishable diseases of apple tree leaf. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2023, 39, 184–190. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, J.; Cheng, Q.; Hu, X.; Liu, Z. YOLO adaptive developments in complex natural environments for tiny object detection. Electronics 2024, 13, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; He, M.; Luo, H. Occluded pedestrian detection algorithm based on improved YOLOv3. Acta Opt. Sin. 2022, 42, 1415003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Yan, J.; Qiu, X.; Yao, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W. A wheat spike detection method in UAV images based on improved YOLOv5. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).