1. Introduction
Large-scale dynamical systems with time delays, characterized by functional differential equations [
1,
2], are frequently used to represent models of engineering systems or physical phenomena, capturing processes that occur in a non-instantaneous manner. Time-delay systems (TDSs) are commonly found in numerous applications, including biology, control of communication networks, mechanical tool vibrations, and population dynamics [
3,
4,
5]. This paper focuses on second-order TDSs of the following form:
where
is the state vector,
are constant time delays in the states,
is the controlled input, and
is the output function.
,
, and
are constant matrices, with
M invertible. In the subsequent analysis, we consider a zero initial condition, i.e.,
. The transfer functions corresponding to the second-order TDSs (
1) can be described as follows:
The dimension of differential equations,
n, depicting the system states can become exceedingly high for complex engineering systems. The increased complexity of utilizing the model for simulating and designing controllers arises from the high computational resource requirements, including time and memory costs. Thus, model order reduction (MOR) [
6,
7,
8] has demonstrated great potential in generating a simplified system with substantially fewer equations (
) that imitates the input-to-output response of the original system. To ensure compatibility with the original system and enable the use of the same tools, it is essential that the substitute model possesses the identical structure as the original system, meaning the reduced-order model (ROM) should take the following form:
with the resulting reduced system matrices
,
, and
.
As a result of its importance in numerous applications, MOR techniques for systems described by delay differential equations have been extensively studied in the literature, largely by building upon methods for systems without delays. For TDSs, finite-dimensional approximation-based MOR methods through rational approximations are well developed [
9,
10]. The motivation for this approach is that the present evaluation and simulation design, based on models with finite dimensions, is generally more attractive, as it allows the use of mature classical feedback control and systems theory. Some researchers have also devised methods to project TDSs onto a lower-dimensional subspace while still preserving time delays in ROMs. These structure-preserving methods have garnered significant attention, as they maintain the infinite-dimensional nature of the delay system, including the orthogonal polynomial techniques [
11,
12,
13], the multi-order Arnoldi MOR method [
14], balanced truncation (BT) methods [
7,
15], and the approach of solving delay Lyapunov equations [
16]. The authors of [
17,
18] presented an overview of various reduction methods, along with additional references on the topic. For second-order TDSs, [
19] extended the dominant pole algorithm to second-order TDSs, and a deflation strategy was devised to ensure that the residues remain in close proximity to their original values, subject to specific conditions. In addition, the Krylov subspace method has been successfully utilized in the analysis of second-order TDSs in [
13,
20,
21], and moment-matching methods can be employed to ensure that the transfer function of the ROMs matches a specific number of moments. Furthermore, a BT approach utilizing approximate Gramians for second-order TDSs was presented in [
22].
BT is recognized as one of the most frequently employed and highly effective MOR techniques, as it offers a global computable error bound and is well grounded [
23]. BT was initially amplified to handle the reduction of second-order form systems in [
24], i.e., second-order balanced truncation (SOBT). The Gramians of an equivalent first-order model were utilized to define the free and zero-velocity Gramians for systems in second-order form. Similar to the approximate BT procedures [
25,
26] for linear time-invariant (LTI) systems, some MOR approaches can be extended to TDSs to construct the ROMs via those low-rank time-delay Gramians, such as the approach using Poor Man’s truncated balanced realization (PMTBR) for TDSs [
7]. It presents an efficient low-rank Gauss–Kronrod quadrature procedure to approximate the controllability and observability time-delay Gramians defined in the frequency domain, and then the ROMs are obtained by balancing and truncating the low-rank Gramians. The PMTBR was also extended to second-order TDSs in [
22], where the connection between the time-delay Gramians of the corresponding first-order system was demonstrated. By employing the approximate Gramians and BT procedures, it was anticipated that the resulting ROM would provide a good approximation of the original system. Although the PMTBR method for TDSs can reduce the complexity of solving Lyapunov-type equations, it still requires the selection of the frequency-sampling points. As a consequence, some researchers have improved and extended PMTBR-related methods for TDSs based on these approximate Gramians [
27,
28].
The main contribution of this paper is the proposal of a novel structure-preserving MOR approach for second-order TDSs utilizing the low-rank approximation of the Gramians based on Laguerre functions. By utilizing the low-rank Gramians obtained and incorporating the concept of the low-rank square root method (LRSRM) [
29], our proposed structure-preserving algorithms produce ROMs by truncating the states associated with the smaller estimated singular values. In contrast to BT-related methods, which require solving Lyapunov-type equations to calculate the full Gramians, the proposed method is more efficient, involving matrix recursive calculation and a single singular-value decomposition (SVD) for a considerably smaller-dimensional matrix.
This paper is arranged as follows. In
Section 2, some important properties of Laguerre functions are briefly introduced. In
Section 3, the first-order MOR is presented based on the LRSRM and the position and velocity Gramians introduced in [
30]. In addition, several structure-preserving algorithms for second-order TDSs are proposed. In
Section 4, the second-order MOR using direct projection is also proposed, and the corresponding MOR algorithm is presented. In
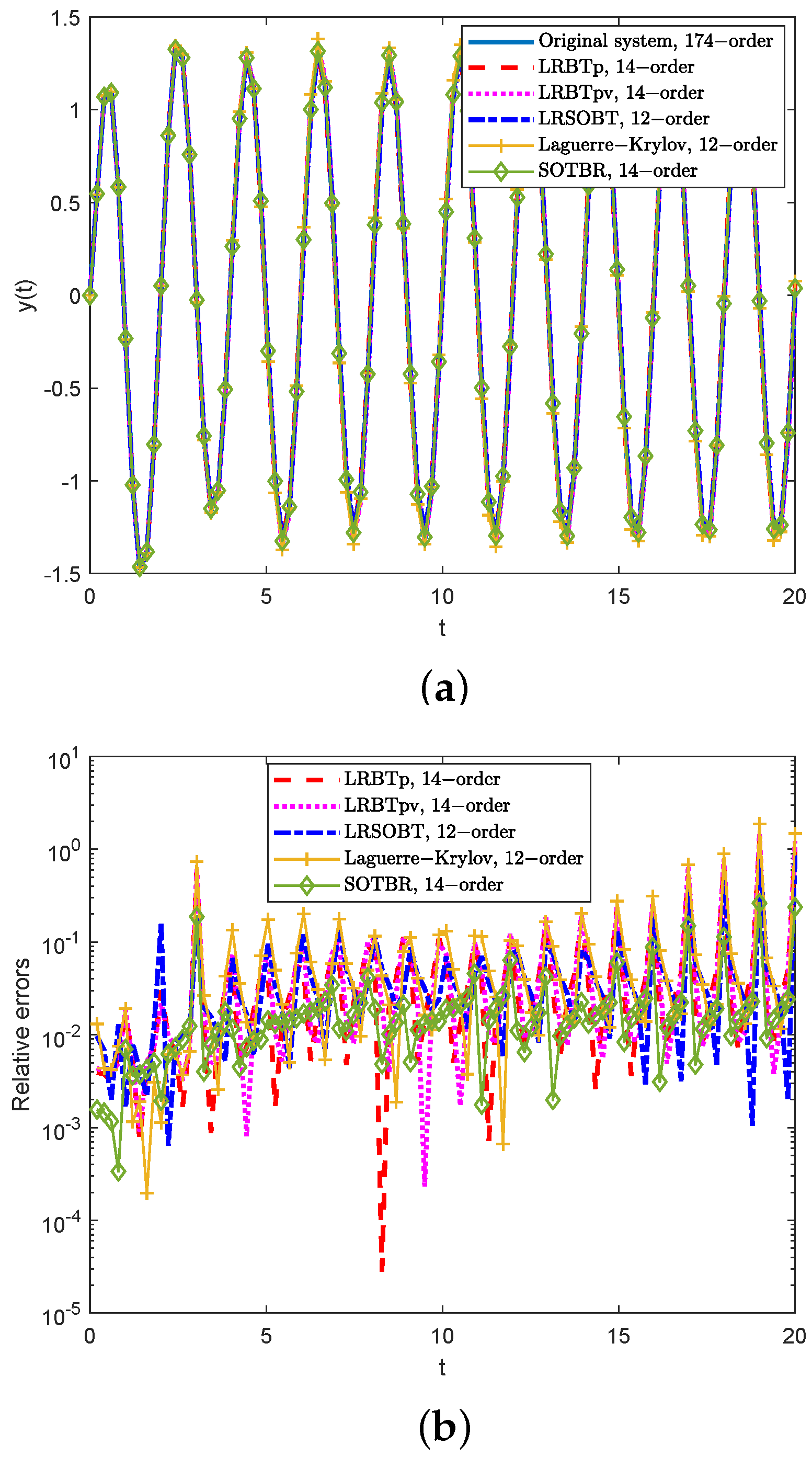
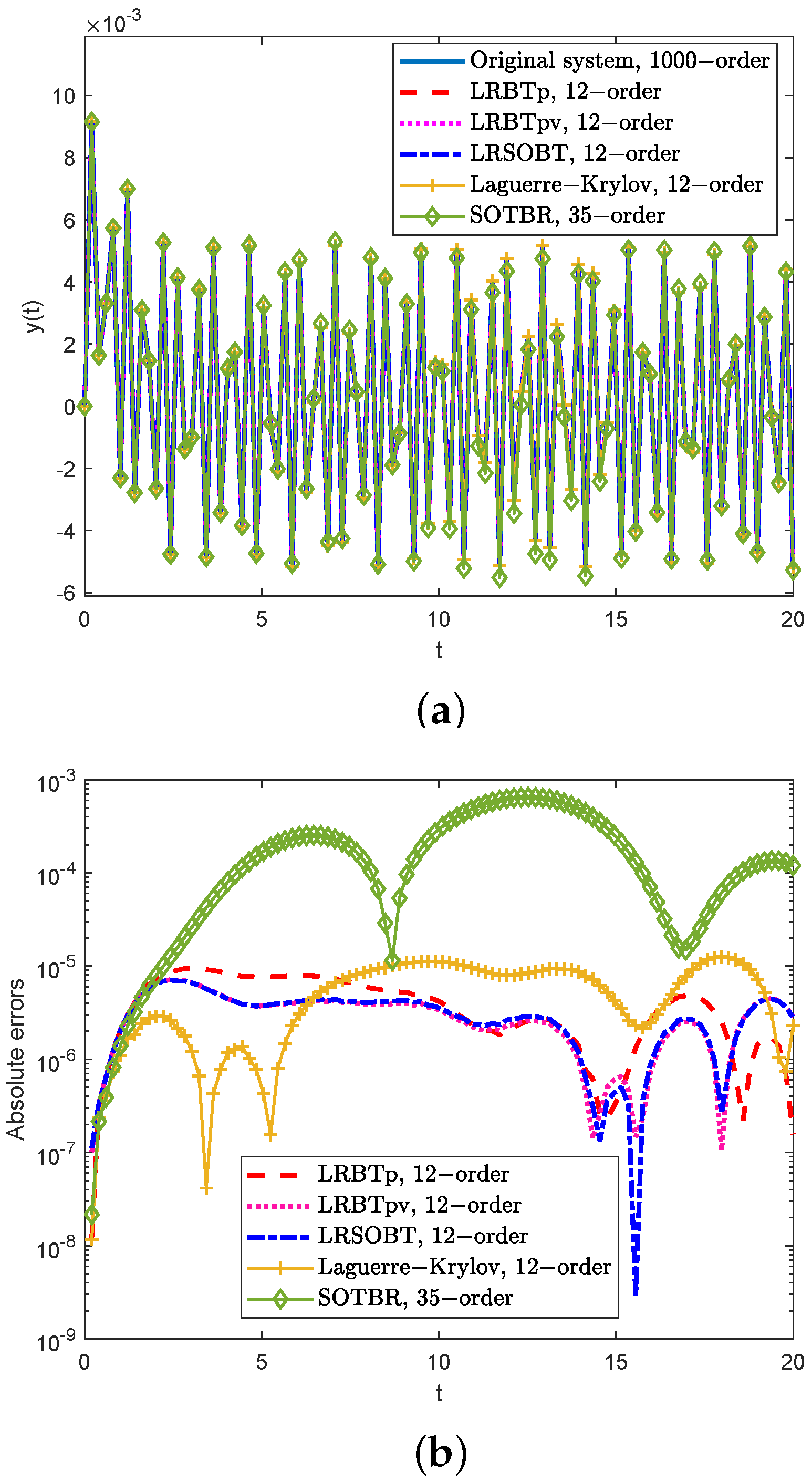
Section 5, the effectiveness of our approaches is demonstrated through two numerical examples. This paper concludes with summarizing remarks in
Section 6.
2. Preliminary
As one of the most classical orthogonal polynomials, the Laguerre polynomials have often been used to solve control problems by many researchers, and their important properties can help in obtaining effective MOR methods [
31]. In this part, we briefly introduce some important properties of Laguerre functions.
The Laguerre polynomials are defined as
The polynomials
are orthogonal with respect to the weight function
in the time interval
, with
The Laplace transform of the Laguerre polynomials is given by
In addition, the scaled Laguerre functions are expressed as
where
is a positive scaling parameter called the Laguerre parameter or time-scale factor [
11].
From (
3), the Laguerre functions also have the property of orthogonality in the time domain, as follows:
The Laplace transform of
is given by
Furthermore (see [
32]), the sequence
forms a uniformly bounded orthonormal basis for the Hilbert space
, so the Laguerre functions also have the property of orthogonality in the frequency domain, as follows:
3. Second- to First-Order MOR for Second-Order TDSs
Considering the SOBT method [
24], a similar MOR procedure for second-order TDSs is presented, which first converts the original second-order system into a first-order form and then uses the low-rank Gramians to obtain the ROMs.
As a specific category of TDSs with a newly defined state
, the second-order TDS (
1) can be rewritten as
with coefficient matrices
,
, and
where
I is the identity matrix of dimension
n. Performing the Laplace transform on the state equation of (
5) results in
and the transfer function from
to
is expressed as
where
is the identity matrix of
dimension. The controllability and observability Gramians
, corresponding to the system (
5), are provided in the frequency domain [
7,
22] as
Calculating the Gramians from time-domain Lyapunov-type equations [
7] is as difficult as calculating the Gramians from their time-domain definitions. In our experiments, the orthogonality of the Laguerre functions in the frequency domain is used to obtain the low-rank decomposition of controllability and observability Gramians, and this motivates us to calculate the Gramians in the frequency domain for computational efficiency.
3.1. Low-Rank Decomposition of the First-Order Gramians via Laguerre Functions
Since our method uses the approximate Gramians in the frequency domain, similar to the PMTBR method, in this part, we present an approach for obtaining the low-rank decomposition of the Gramians in the frequency domain using the Laguerre expansions, which is the main task of the first-order MOR.
For the equivalent first-order original TDS (
5), the transfer function (
6) can be developed into a Laguerre series:
and
By applying (
11) to the controllability Gramian
of Formula (
8), we obtain
Considering the orthogonality of the Laguerre functions in the frequency domain (
4), the low-rank decomposition of the controllability Gramian
is given by
where
.
Analogously, expanding
using the Laguerre functions yields
and by substituting (
13) into the observability Gramian
in (
9), the observability Gramian
is able to be decomposed into the following low-rank approximation:
where
.
Remark 1. The Laguerre function sequence forms a uniformly bounded orthogonal basis in the Hilbert space . Under this set of bases, any function can be expanded as . The expansion coefficient of f is calculated by . According to [33], the above expansion in the Lebesgue sense converges uniformly, and the approximation is optimal in the sense of the least-squares error . Meanwhile, the sequence forms a uniformly bounded orthogonal basis for the Hardy space , equipped with the inner product and norm [31]. Therefore, the truncated Fourier–Laguerre expansions of and are optimally approximated in the sense of the -norm. 3.2. Calculating the Low-Rank Decomposition Factors and
After the time-delay Gramians and are decomposed into low-rank approximations, we calculate the low-rank factors and , which are constructed using the Laguerre coefficients and for . Here, we provide an approach to obtain the Laguerre coefficient ; the can be computed in a similar way.
Assume that
and
are expressible as a series of Laguerre functions:
where
and
are scalar coefficients. In the interest of maintaining clear notation, we use the bilinear transformation
According to the relation
derived from (
16), (
15) can be rewritten as
and
Consider the generating function associated with the Laguerre polynomials [
34], which yields
where
is the
i-th Laguerre polynomial. Note that when
,
, it has the following expression:
Substituting (
19) into (
18), we obtain
Ultimately, the coefficients
can be calculated as
Similar to (
15),
can be expressed as
Subsequently, by substituting (
16) into the preceding equation, the following equation can be derived:
Since
is invertible, it is clear that Formula (
6) can be expressed as
Substituting (
17) and (
20) into (
21) leads to
Then, the above equation can be written as
where
and
. The Laguerre coefficients
can be determined by setting the coefficients of
(
) equal, resulting in the following linear systems:
and the elements of the coefficient matrix are as follows:
Provided that
is invertible, the low-rank factor
can be obtained using the following recurrence formulas:
Analogously, the low-rank factor
can also be computed by
3.3. Structure-Preserving Low-Rank BT Algorithms
In this subsection, a series of structure-preserving low-rank BT algorithms for second-order TDSs are presented, based on the low-rank factors of Gramians and the LRSRM.
For the second- to first-order MOR approach, the low-rank factors of Gramians
and
are obtained from (
22) and (
23). The transformation matrices can be constructed directly from them for the corresponding first-order system and then used to generate the ROMs. However, the method has the drawback that it generally does not preserve the second-order structure of the original system. Given the importance of preserving structure in engineering control and design, this part focuses on the controllability and observability Gramians for second-order position and velocity and introduces some structure-preserving MOR algorithms for second-order TDSs. Partition the Gramians
and
as follows:
where all the blocks have a size of
.
and
are the second-order position Gramians of the system (
1), whereas
and
are the second-order velocity Gramians of (
1). We can then define the position-balanced
, velocity-balanced
, position-velocity-balanced
, and velocity-position-balanced
ROMs [
35,
36]. To reduce the computation cost of obtaining the second-order Gramians from the full first-order Gramians
and
, we perform all computations using a low-rank approach. Partition the low-rank factors
and
as
,
, and we can obtain
Subsequently, the approximate low-rank factors of the second-order position and velocity Gramians can be directly derived by
Next, based on the LRSRM [
29], only two algorithms utilizing the position and position-velocity balanced ROMS are proposed, representing clear extensions of the reduction technique through the Laguerre functions for the second-order TDS (
1). Other algorithms can be formulated in a similar manner.
By computing the SVD of the matrix
, we obtain
where
is the rank of the matrix
,
is invertible, with singular values
in non-increasing order, and
Let
and
be the first
r columns of the matrices
and
, respectively. Define the projection matrices
and
as
where
is the
r-order leading principal submatrix of
. We can the obtain the reduced second-order TDS (
2) with
,
,
,
,
,
, and
. The above reduction procedure can be described by Algorithms 1 and 2.
| Algorithm 1 Low-rank BT for second-order TDSs with position balancing (LRBTp) |
Input: The coefficient matrices and ; Output: The coefficient matrices of the r-order ROM: ; 1. Compute and via ( 22) and ( 23); 2. Compute the SVD: , , , and ; r is adaptively chosen by the given tolerance: ; 3. Compute projection matrices: ; 4. Construct the reduced model: , , , , , , .
|
| Algorithm 2 Low-rank BT for second-order TDSs with position-velocity balancing (LRBTpv) |
Input: The coefficient matrices and ; Output: The coefficient matrices of the r-order ROM: ; 1. Compute and via ( 22) and ( 23); 2. Compute the SVD: , , , and ; r is adaptively chosen by the given tolerance: ; 3. Compute projection matrices: ; 4. Construct the reduced model: , , , , , , .
|
In Algorithms 1 and 2, the parameter
N indicates the number of Laguerre function expansion terms, typically ranging from 10 to 30 to achieve a satisfactory ROM in most cases. With the given error threshold “
”, the adaptive reduced-order
r can be obtained via the approximate error indicator
, which is valid for LTI systems with no time delays. In our numerical experiments, we utilize this approximate error indicator for TDSs, and the simulation results demonstrate its effectiveness in determining the corresponding value of
r for the ROM. In addition, the Laguerre parameter
is an important factor that directly impacts the stability of the ROM and the accuracy of the approximation. For LTI systems, determining the optimal
involves addressing the minimax optimal problem [
31,
37]
where
represents the eigenvalues of the matrix
. Although the method for obtaining the optimal
is only applicable to LTI systems, in the examples presented later, the value of
is determined through the optimization problem (
24), and the experimental outcomes imply that the above
is also effective.