Hybrid Microgrid Power Management via a CNN–LSTM Centralized Controller Tuned with Imperialist Competitive Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Proposed MG Model
MG Components
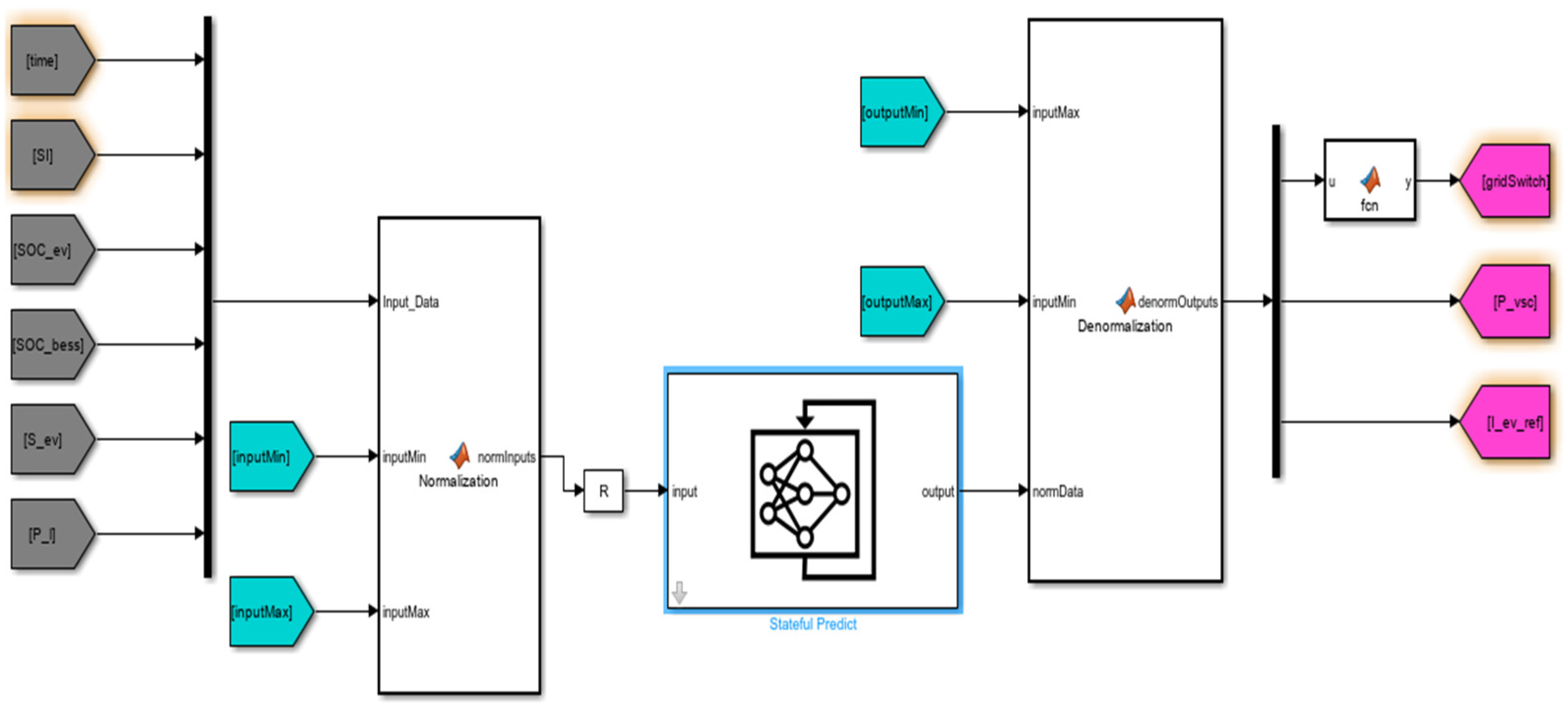
3. Centralized Controller
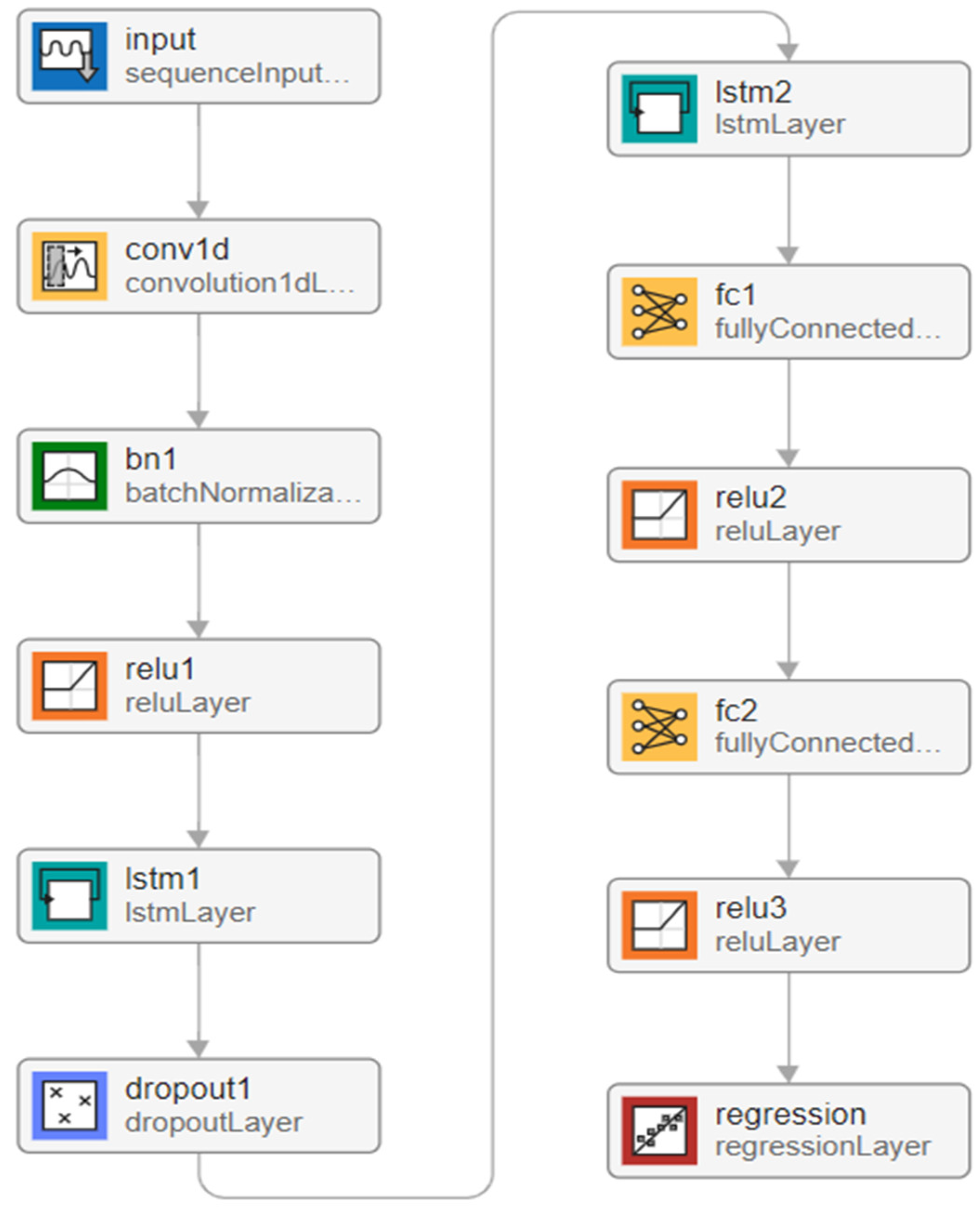
3.1. ICA-Optimized CNN–LSTM Controller
3.2. CNN Principles
3.3. LSTM Framework
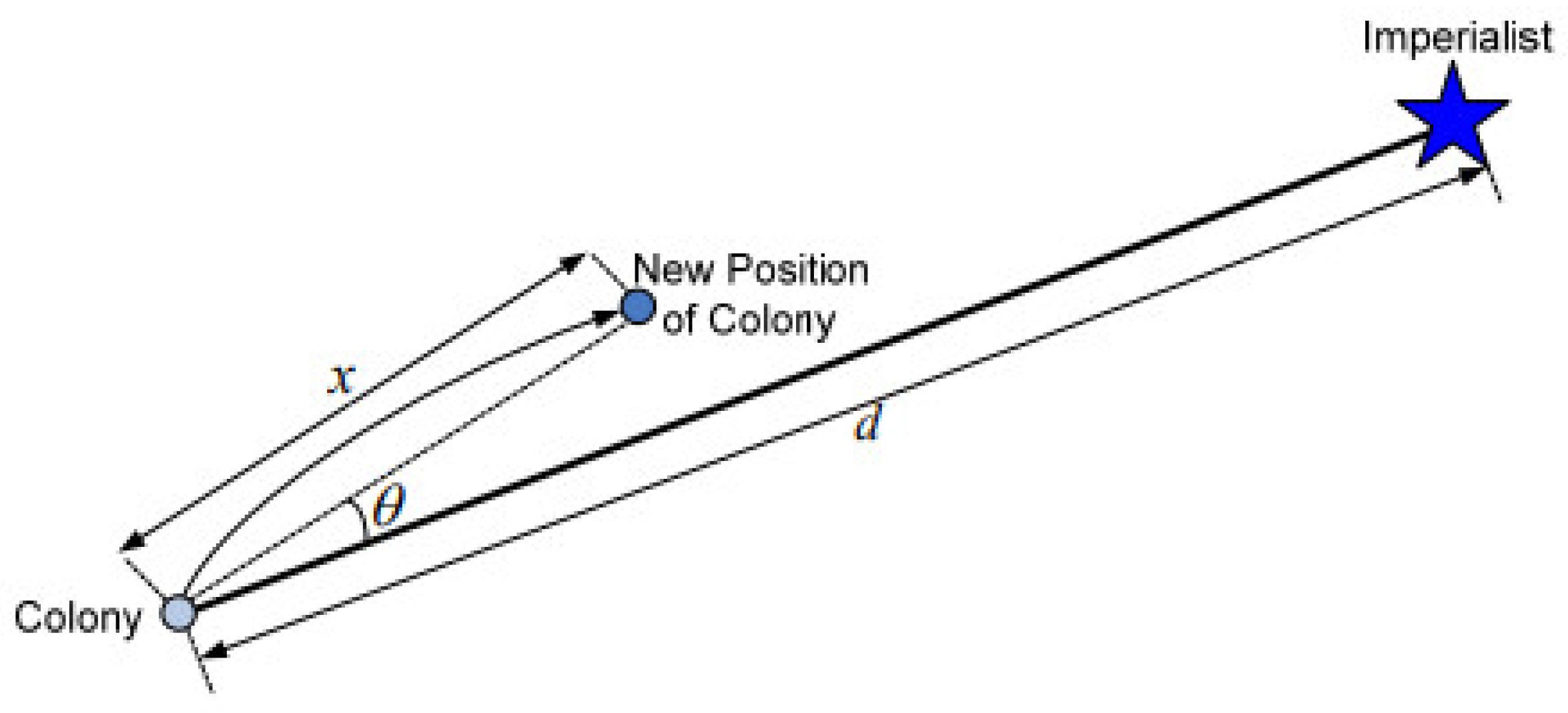
3.4. Imperialist Competitive Algorithm
3.5. Integrated Network Configuration
3.6. Assessment Measure
3.7. Power Management
4. MG Mode Functionalities
5. Simulation Outcomes
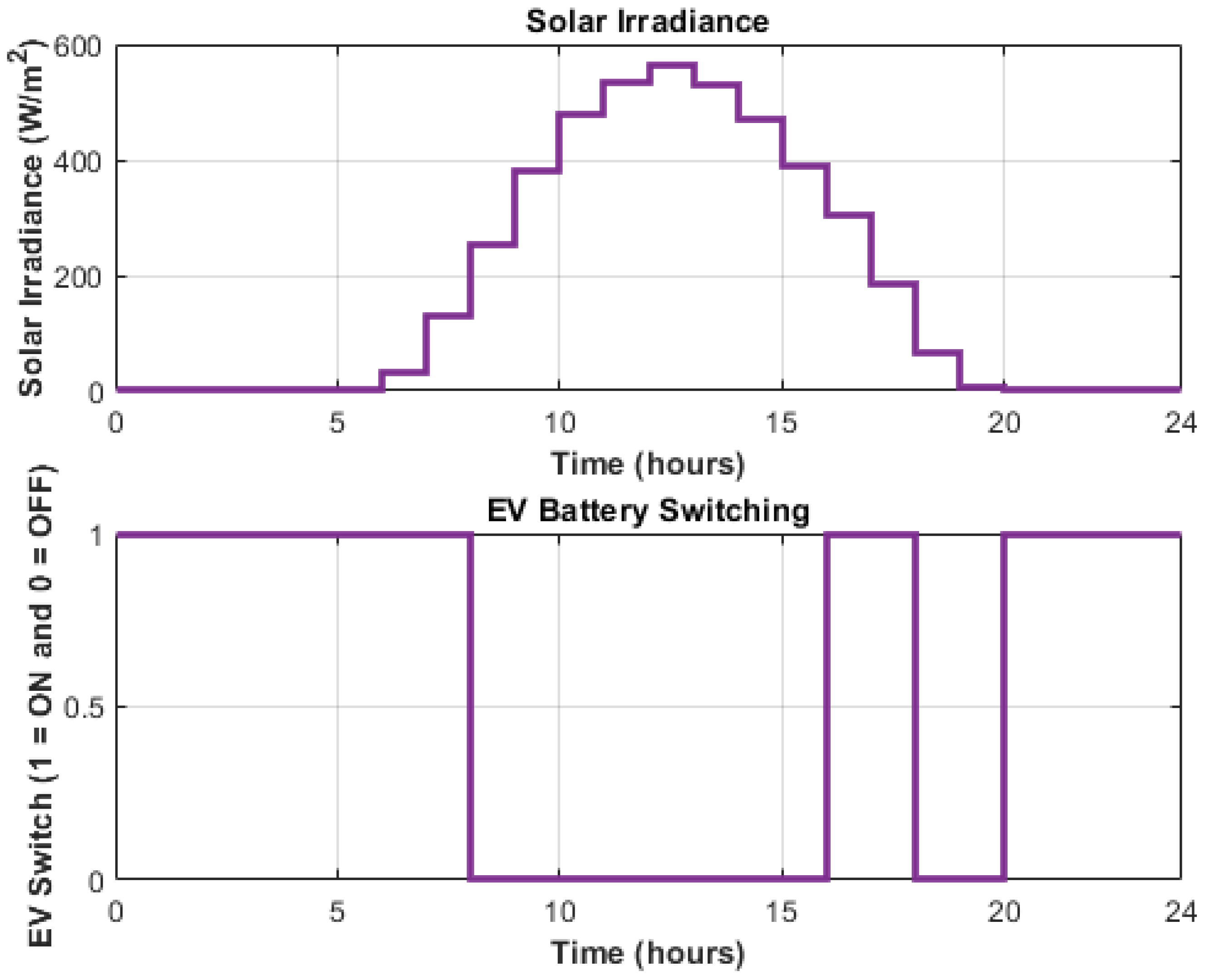
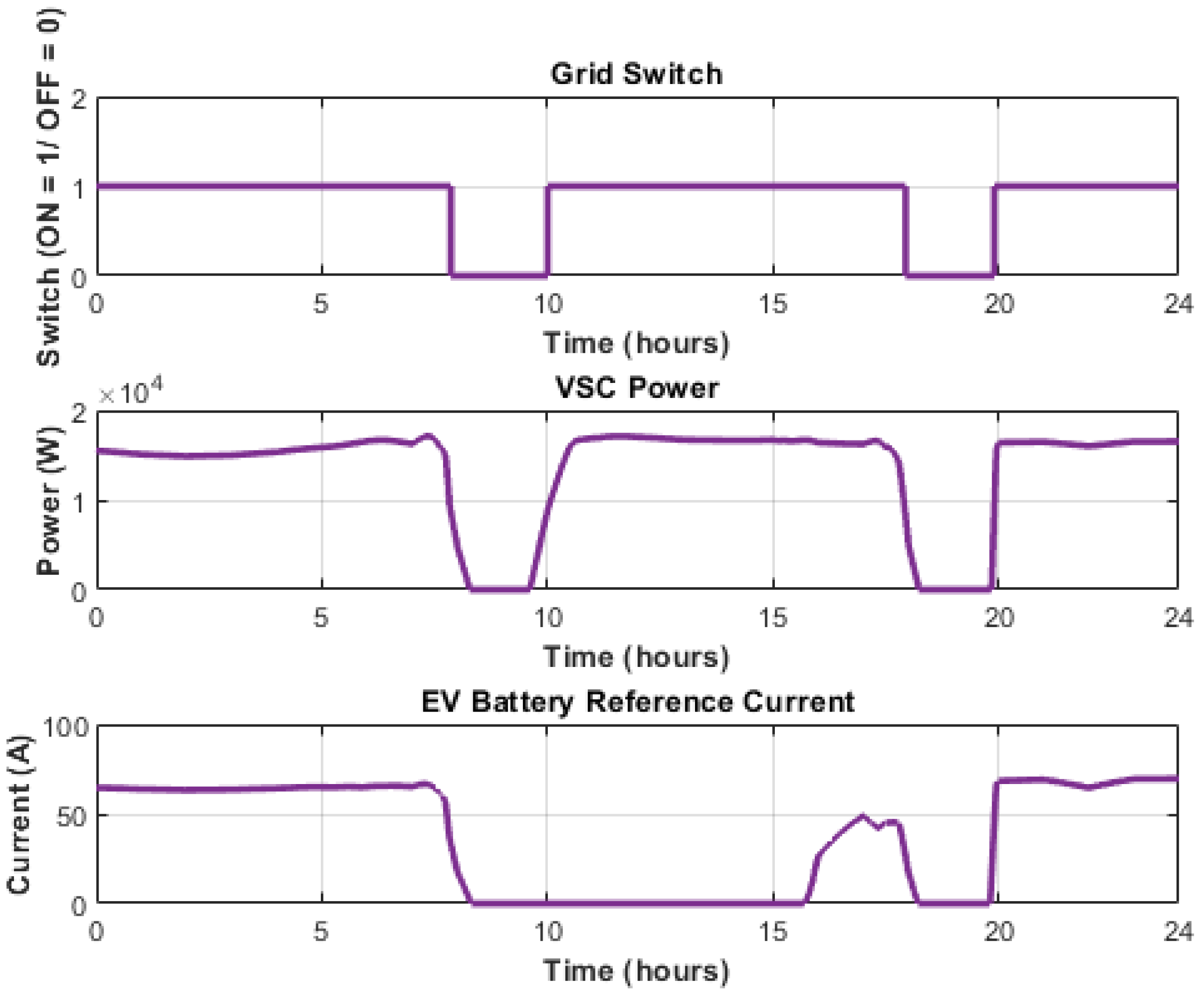
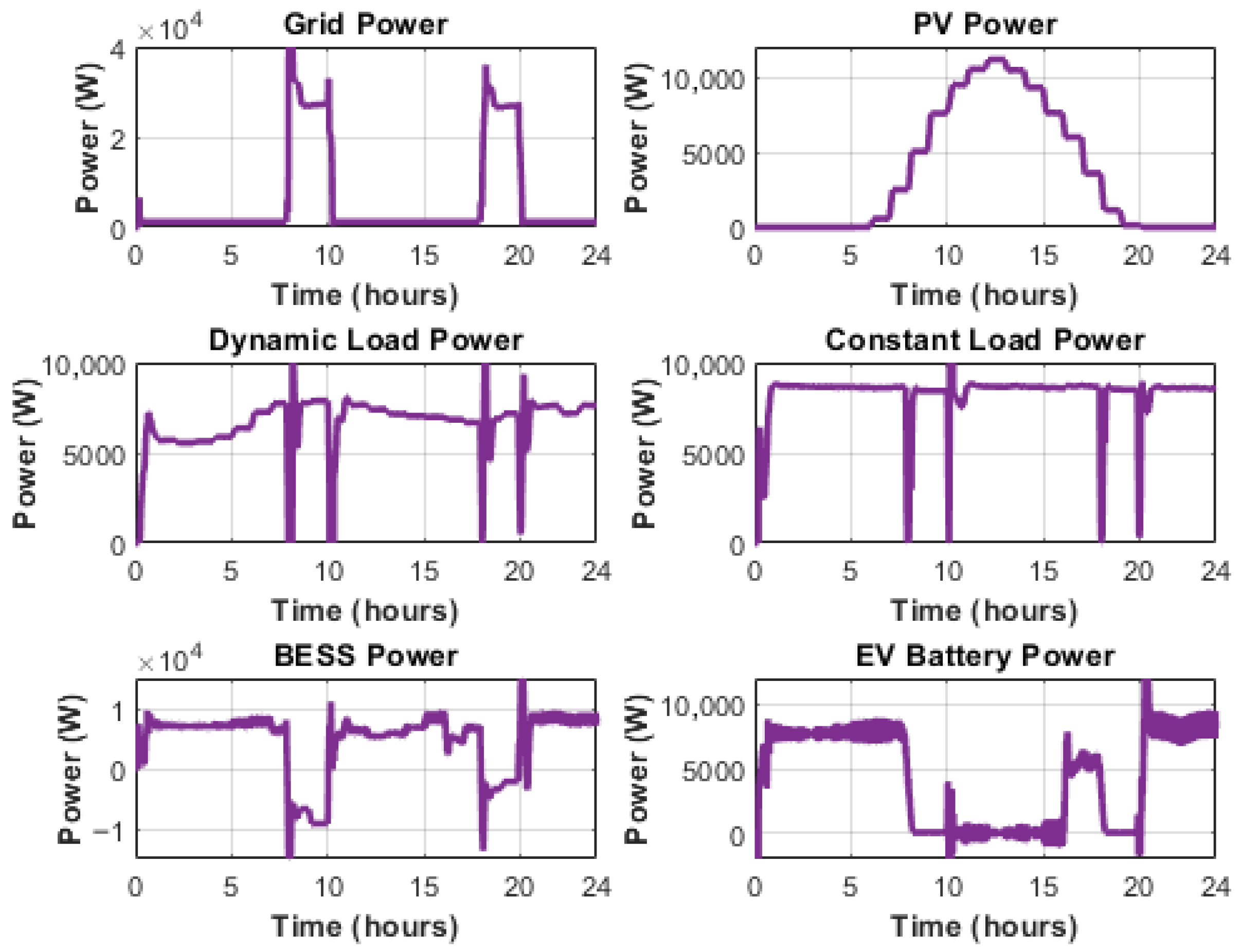
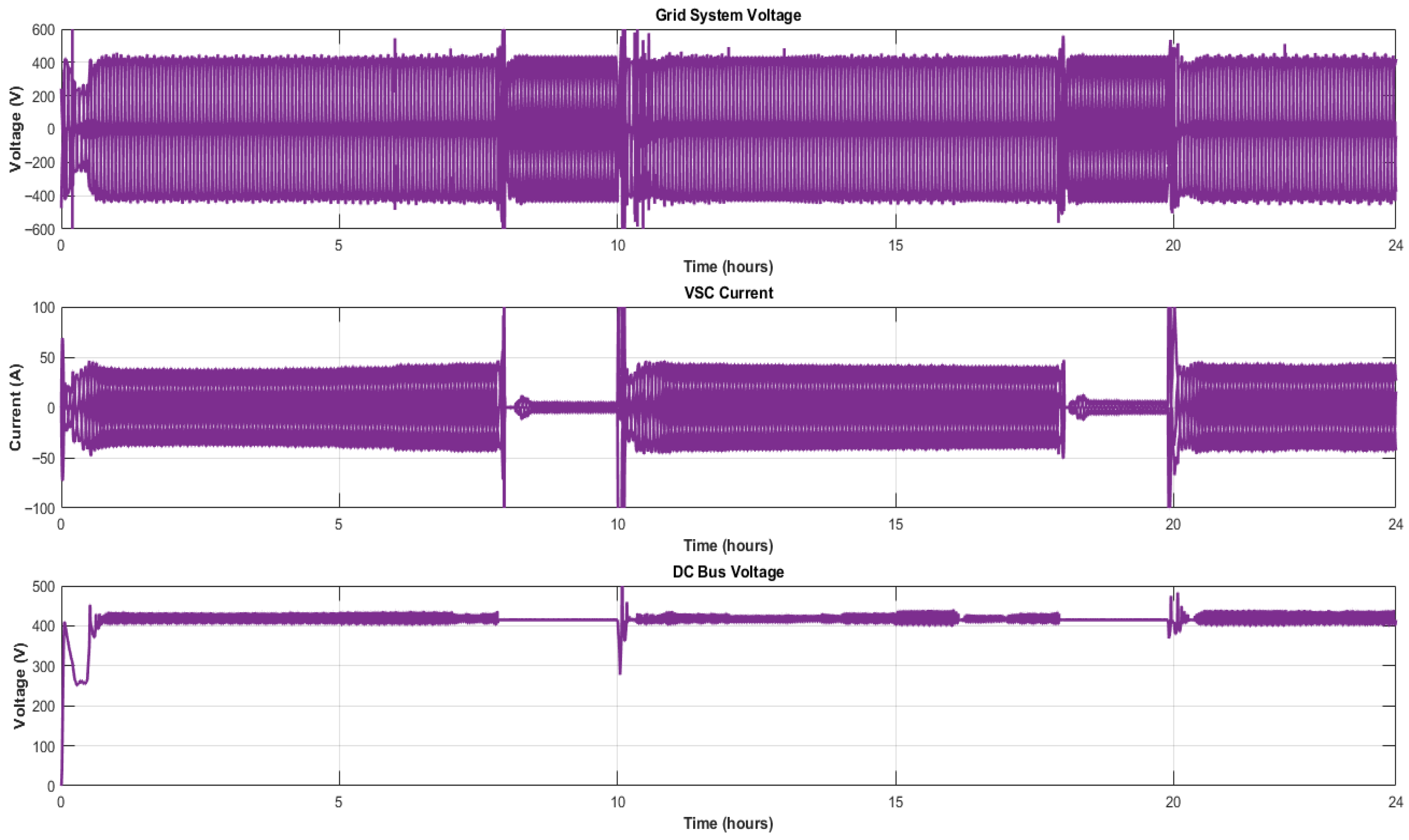
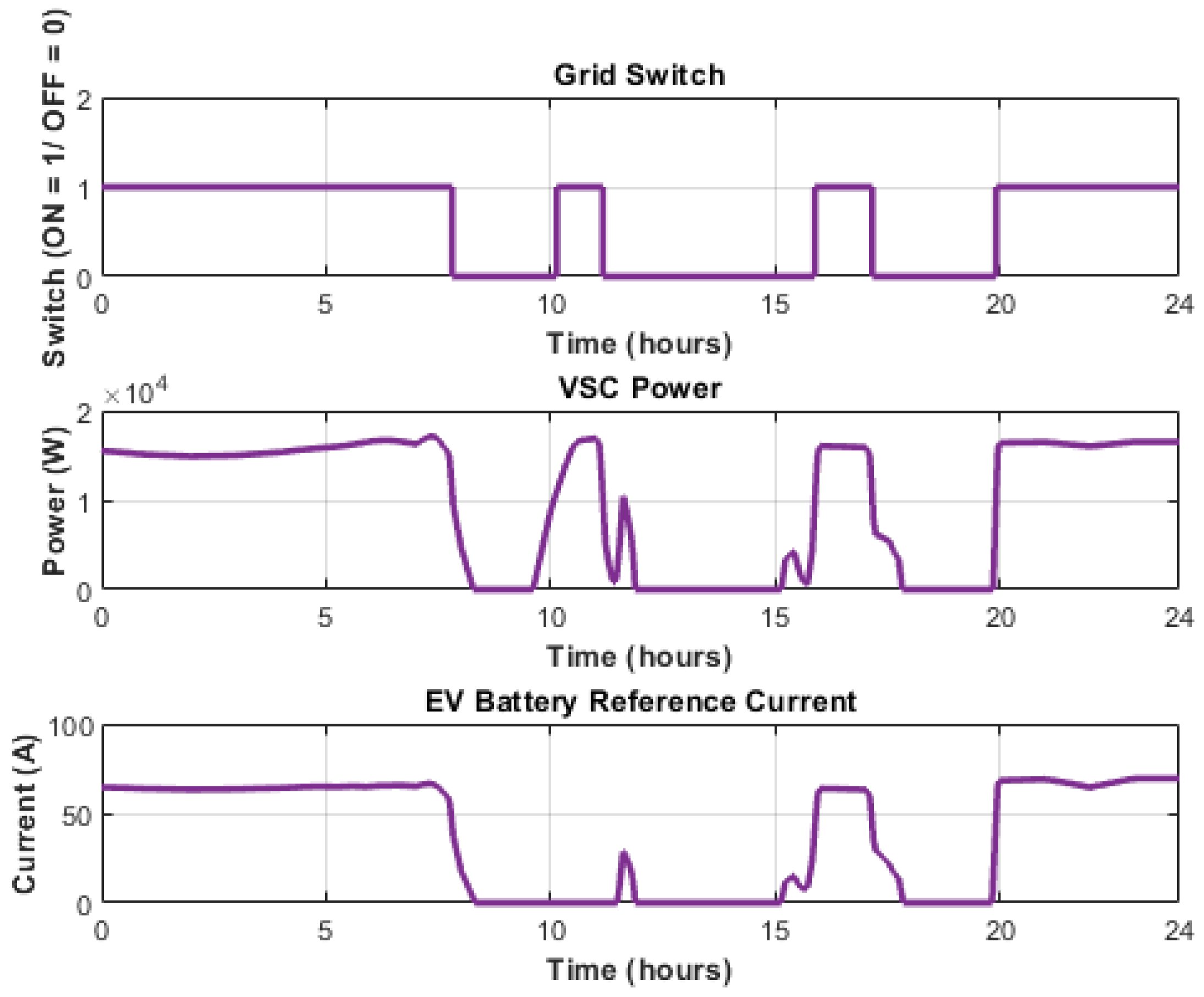
5.1. Normal Operating Condition
5.2. Solar Irradiance Drop Scenario
5.3. BESS and EV with 0% Initial SoC
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Dinata, N.F.P.; Ramli, M.A.M.; Jambak, M.I.; Sidik, M.A.B.; Alqahtani, M.M. Designing an optimal microgrid control system using deep reinforcement learning: A systematic review. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2024, 51, 101651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agupugo, C.P.; Tochukwu, M.F.C.; Ogunmoye, K.A.; Mosha, A.S.; Sabbih, F. Review of Smart Microgrid Platform Integrating AI and Deep Reinforcement Learning for Sustainable Energy Management. Int. J. Future Eng. Innov. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Dong, W.; Lv, Z.; Gu, Y.; Singh, S.; Kumar, P. Hybrid microgrid many-objective sizing optimization with fuzzy decision. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 28, 2702–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Hu, J.; Qiu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ghosh, B.K. A distributed economic dispatch strategy for power–water networks. IEEE Trans. Control Netw. Syst. 2021, 9, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Cai, Y.; Li, X. Process arrangement and multi-aspect study of a novel environmentally-friendly multigeneration plant relying on a geothermal-based plant combined with the goswami cycle booted by kalina and desalination cycles. Energy 2024, 299, 131381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, M.A.; Nallathambi, K.; Vishnuram, P.; Rathore, R.S.; Bajaj, M.; Rida, I.; Alkhayyat, A. A novel technological review on fast charging infrastructure for electrical vehicles: Challenges, solutions, and future research directions. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 82, 260–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lund, P.D. Peer-to-peer energy sharing and trading of renewable energy in smart communities─trading pricing models, decision-making and agent-based collaboration. Renew. Energy 2023, 207, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gbadega, P.A.; Sun, Y.; Akindeji, K.T. A modified droop control technique for accurate power-sharing of a resilient stand-alone micro-grid. In Proceedings of the 2023 31st Southern African Universities Power Engineering Conference (SAUPEC), Johannesburg, South Africa, 24–26 January 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Thirumalai, M.; Hariharan, R.; Yuvaraj, T.; Prabaharan, N. Optimizing distribution system resilience in extreme weather using prosumer-centric microgrids with integrated distributed energy resources and battery electric vehicles. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.R.; Haider, Z.M.; Malik, F.H.; Almasoudi, F.M.; Alatawi, K.S.S.; Bhutta, M.S. A comprehensive review of microgrid energy management strategies considering electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and AI techniques. Processes 2024, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazari-Heris, M.; Mohammadi-Ivatloo, B.; Anvari-Moghaddam, A.; Razzaghi, R. A bi-level framework for optimal energy management of electrical energy storage units in power systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 216141–216150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, J. An initialization-free distributed algorithm for dynamic economic dispatch problems in microgrid: Modeling, optimization and analysis. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2023, 34, 101004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.A.; Jyothi, B.; Rathore, R.S.; Singh, A.R.; Kumar, B.H.; Bajaj, M. A novel framework for enhancing the power quality of electrical vehicle battery charging based on a modified Ferdowsi Converter. Energy Rep. 2023, 10, 2394–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Yanrong, C.; Hai, T.; Ren, G.; Wenhuan, W. DGNet: An adaptive lightweight defect detection model for new energy vehicle battery current collector. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 29815–29830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaroual, M.; Hermann, D.T.; Ouassaid, M.; Bajaj, M.; Maaroufi, M.; Alsaif, F.; Alsulamy, S. Optimal solution of peer-to-peer and peer-to-grid trading strategy sharing between prosumers with grid-connected photovoltaic/wind turbine/battery storage systems. Int. J. Energy Res. 2023, 2023, 6747936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.; Varghese, G.T.; Mohanty, S.; Kolluru, V.R.; Bajaj, M.; Blazek, V.; Prokop, L.; Misak, S. Energy management and power quality improvement of microgrid system through modified water wave optimization. Energy Rep. 2023, 9, 6020–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Mohammed, A.N.; Mishra, S.; Sharma, N.K.; Selim, A.; Bajaj, M.; Rihan, M.; Kamel, S. Optimal real-time tuning of autonomous distributed power systems using modern techniques. Front. Energy Res. 2023, 11, 1055845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbabak, H.; Alsafasfeh, Q.; Su, W. A distributed consensus-based algorithm for optimal power flow in DC distribution grids. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2020, 35, 3506–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ma, H. Distributed Real-time Optimal Power Flow Strategy for DC Microgrid Under Stochastic Communication Networks. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2022, 11, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Narayanan, V.; Singh, B.; Panigrahi, B.K. Multiple voltage source converters based microgrid with solar photovoltaic array and battery storage. E-Prime-Adv. Electr. Eng. Electron. Energy 2024, 7, 100408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugumaran, G. An efficient buck-boost converter for fast active balancing of lithium-ion battery packs in electric vehicle applications. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2024, 118, 109429. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Moneim, M.G.; Hamad, M.S.; Abdel-Khalik, A.S.; Hamdy, R.R.; Hamdan, E.; Ahmed, S. Analysis and control of split-source current-type inverter for grid-connected applications. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 96, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayeghi, H.; Rahnama, A.; Takorabet, N.; Thounthong, P.; Bizon, N. Designing a multi-stage PD (1 + PI) controller for DC–DC buck converter. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Nasir, M.; Schulz, N.N. An optimal neighborhood energy sharing scheme applied to islanded DC microgrids for cooperative rural electrification. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 116956–116966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheradmandi, M.; Hamzeh, M.; Hatziargyriou, N.D. A hybrid power sharing control to enhance the small signal stability in DC microgrids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2022, 13, 1826–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.S.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Das, A.; Medikondu, N.R.; Almawgani, A.H.; Alhawari, A.R.; Das, S. Wavelet-based rapid identification of IGBT switch breakdown in voltage source converter. Microelectron. Reliab. 2024, 152, 115283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, H.; Jokar, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Kavousi Fard, A.; Dabbaghjamanesh, M.; Karimi, M. A Deep Learning-to-learning Based Control system for renewable microgrids. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2025, 19, e12727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi, N.; Dowlatabadi, M.; Sabzevari, K. A hierarchical deep learning approach to optimizing voltage and frequency control in networked microgrid systems. Appl. Energy 2025, 377, 124313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arévalo, P.; Cano, A.; Benavides, D.; Jurado, F. Fault analysis in clustered microgrids utilizing SVM-CNN and differential protection. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 164, 112031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, T.N.; Cho, M.Y.; Thanh, P.N. Hourly load prediction based feature selection scheme and hybrid CNN-LSTM method for building’s smart solar microgrid. Expert Syst. 2024, 41, e13539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcanli, A.K.; Baysal, M. Islanding detection in microgrid using deep learning based on 1D CNN and CNN-LSTM networks. Sustain. Energy Grids Netw. 2022, 32, 100839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ismail, F.S. A critical review on DC microgrids voltage control and power management. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 30345–30361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Sattar, H.; Hassan, M.H.; Vera, D.; Jurado, F.; Kamel, S. Maximizing hybrid microgrid system performance: A comparative analysis and optimization using a gradient pelican algorithm. Renew. Energy 2024, 227, 120480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.R.; Sarker, S.; Halim, M.A.; Ibrahim, S.; Haque, A. A Comprehensive Review of Techno-Economic Perspective of AC/DC Hybrid Microgrid. Control Syst. Optim. Lett. 2024, 2, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnayak, S.K.; Choudhury, S.; Nayak, N.; Bagarty, D.P.; Biswabandhya, M. Maximum power tracking & harmonic reduction on grid PV system using chaotic gravitational search algorithm based MPPT controller. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Smart Power System and Sustainable Energy (CISPSSE), Keonjhar, India, 29–31 July 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Phogat, P.; Dey, S.; Wan, M. Powering the sustainable future: A review of emerging battery technologies and their environmental impact. RSC Sustain. 2025, 3, 3266–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conzen, J.; Lakshmipathy, S.; Kapahi, A.; Kraft, S.; DiDomizio, M. Lithium ion battery energy storage systems (BESS) hazards. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2023, 81, 104932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Coimbra, C.F. Hybrid solar irradiance nowcasting and forecasting with the SCOPE method and convolutional neural networks. Renew. Energy 2024, 232, 121055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, T.; Wang, H.; Tahir, M.; Zhang, Y. Wind and solar power forecasting based on hybrid CNN-ABiLSTM, CNN-transformer-MLP models. Renew. Energy 2025, 239, 122055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Peng, X.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, W. Dynamic fusion LSTM-Transformer for prediction in energy harvesting from human motions. Energy 2025, 327, 136192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.C.; Prusty, U.C.; Prusty, R.C.; Panda, S. Imperialist competitive algorithm optimized cascade controller for load frequency control of multi-microgrid system. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2025, 47, 5538–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khujaev, A.; Uğurenver, A. Centralized controller-based on optimal power flow (OPF) algorithm for power management in microgrid systems. Sigma J. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2025, 43, 2279–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao-Van, K.; Minh, T.C.; Tan, H.M. Prediction of heart failure using voting ensemble learning models and novel data normalization techniques. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 154, 110888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghojoghi, E.; Farsangi, M.A.E.; Mansouri, H.; Rashedi, E. Prediction and minimization of blasting flyrock distance, using deep neural networks and gravitational search algorithm, JAYA, and multi-verse optimization algorithms. Heliyon 2024, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayat, A.; Kissaoui, M.; Bahatti, L.; Raihani, A.; Errakkas, K.; Atifi, Y. Efficient Day-Ahead Energy Forecasting for Microgrids Using LSTM Optimized by Grey Wolf Algorithm. E-Prime-Adv. Electr. Eng. Electron. Energy 2025, 13, 101054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Frequency | 50 Hz |
| AC Nominal Voltage | 400 V |
| DC Nominal Voltage | 400 V |
| Grid Resistance | 1.8 Ω |
| Grid Inductance | 4 μH |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| 218.871 (W) | |
| Number of parallel strings | 6 |
| Number of modules connected in series | 15 |
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Nominal Voltage | 120 V |
| Nominal Capacity | 180 Ah |
| Response Time of Battery | 0.1 s |
| No. | Parameter | Description | Optimized Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NumUnits1 | Number of hidden units in the first LSTM layer. | 57 |
| 2 | NumUnits2 | Number of hidden units in the second LSTM layer. | 28 |
| 3 | LearnRate | Learning rate for training. | 2.91 × 10−4 |
| 4 | DropoutRate | Dropout fraction to prevent overfitting. | 0.0155 |
| 5 | MiniBatchSize | Number of sequences per mini-batch. | 45 |
| 6 | NumFilters | Number of convolutional filters in the CNN layer. | 24 |
| 7 | FilterSize | Size of convolutional filters. | 3 |
| Sr. No. | Item | Explanation | Selected Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Optimizer | Optimization algorithm used for training. | Adam |
| 2 | GradientDecayFactor (β1) | The decay factor applied to the first moment estimate in Adam. | 0.9 |
| 3 | SquaredGradientDecayFactor (β2) | The decay factor applied to the second moment estimate in Adam. | 0.999 |
| 4 | Epsilon (ε) | Small constant to prevent division by zero in Adam optimizer. | 1.0 × 10−8 |
| 5 | InitialLearnRate | Starting learning rate for training. | 2.91 × 10−4 |
| 6 | MaxEpochs | Number of times the training algorithm iterates over the dataset. | 100 |
| 7 | MiniBatchSize | Sequences allocated to each mini-batch during training. | 45 |
| 8 | Shuffle | Rearranging the order of the training samples randomly. | One-time |
| 9 | L2Regularization | L2 penalty factor to avoid overfitting. | 1.0 × 10−4 |
| 10 | ValidationFrequency | Number of iterations between validations on validation data. | Every 10 iterations |
| 11 | Validation Data | Data reserved for monitoring validation performance during training. | 698 Sequences |
| Network Architecture | (Output 1) | (Output 2) | (Output 3) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE | |
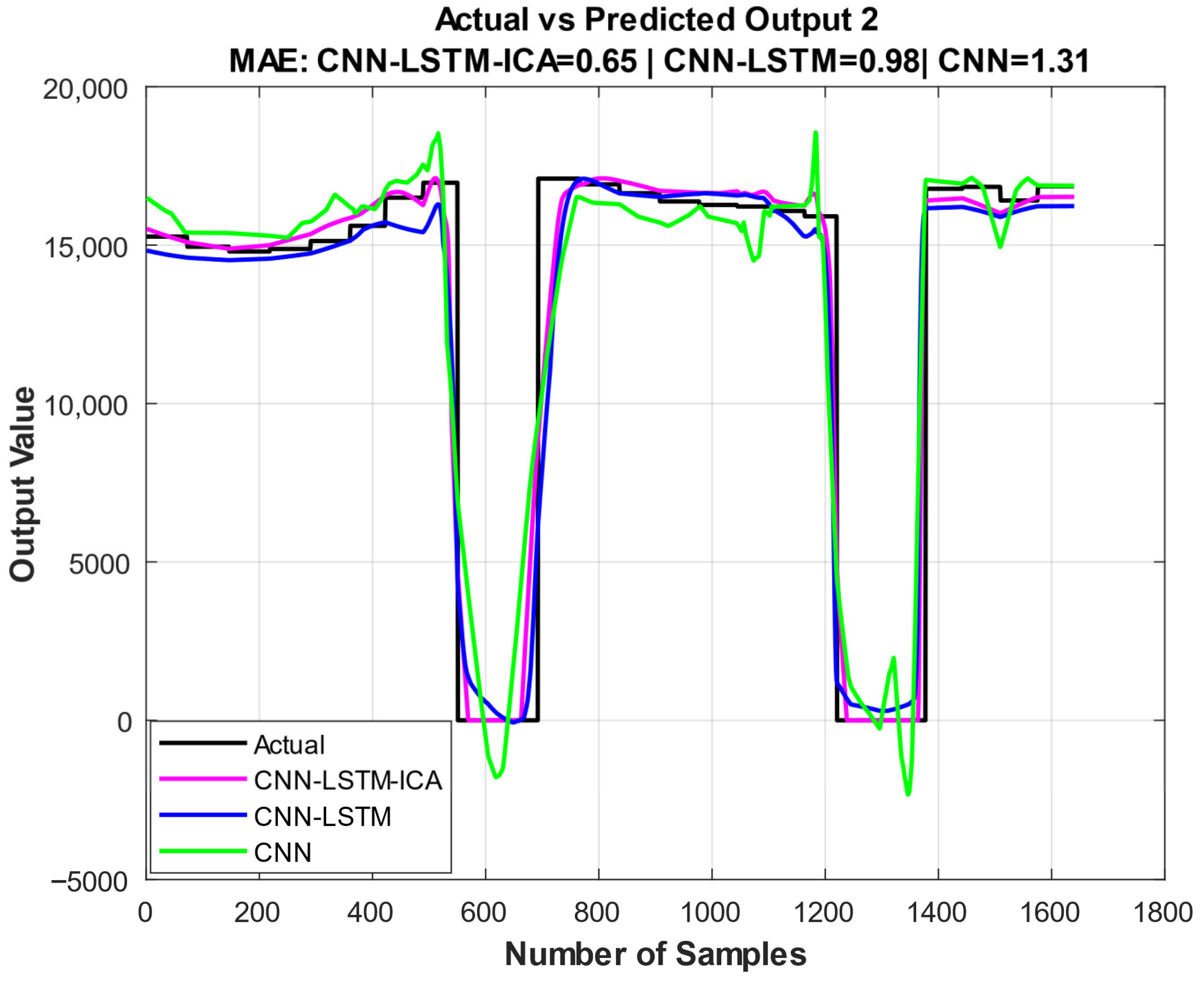
| CNN | 0.8789 | 0.1740 | 0.0786 | 0.8721 | 2.8901 | 1.3150 | 0.9168 | 9.0163 | 3.8283 |
| CNN-LSTM | 0.9025 | 0.1558 | 0.0615 | 0.8980 | 2.5724 | 0.9810 | 0.9250 | 8.6863 | 3.4661 |
| CNN-LSTM-PSO | 0.9442 | 0.1169 | 0.0462 | 0.9394 | 1.9032 | 0.7190 | 0.9511 | 6.1851 | 1.8442 |
| CNN-LSTM-ICA | 0.9602 | 0.1075 | 0.0370 | 0.9512 | 1.7817 | 0.6507 | 0.9618 | 6.0829 | 1.9227 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Behgouy, P.; Ugurenver, A. Hybrid Microgrid Power Management via a CNN–LSTM Centralized Controller Tuned with Imperialist Competitive Algorithm. Mathematics 2025, 13, 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13244030
Behgouy P, Ugurenver A. Hybrid Microgrid Power Management via a CNN–LSTM Centralized Controller Tuned with Imperialist Competitive Algorithm. Mathematics. 2025; 13(24):4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13244030
Chicago/Turabian StyleBehgouy, Parastou, and Abbas Ugurenver. 2025. "Hybrid Microgrid Power Management via a CNN–LSTM Centralized Controller Tuned with Imperialist Competitive Algorithm" Mathematics 13, no. 24: 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13244030
APA StyleBehgouy, P., & Ugurenver, A. (2025). Hybrid Microgrid Power Management via a CNN–LSTM Centralized Controller Tuned with Imperialist Competitive Algorithm. Mathematics, 13(24), 4030. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13244030








