Lie Symmetry, Conservation Laws, and Dynamical Analysis of Ionic Currents in the Microtubule Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Applying the Lie symmetry method to obtain symmetry reductions and invariant solutions.
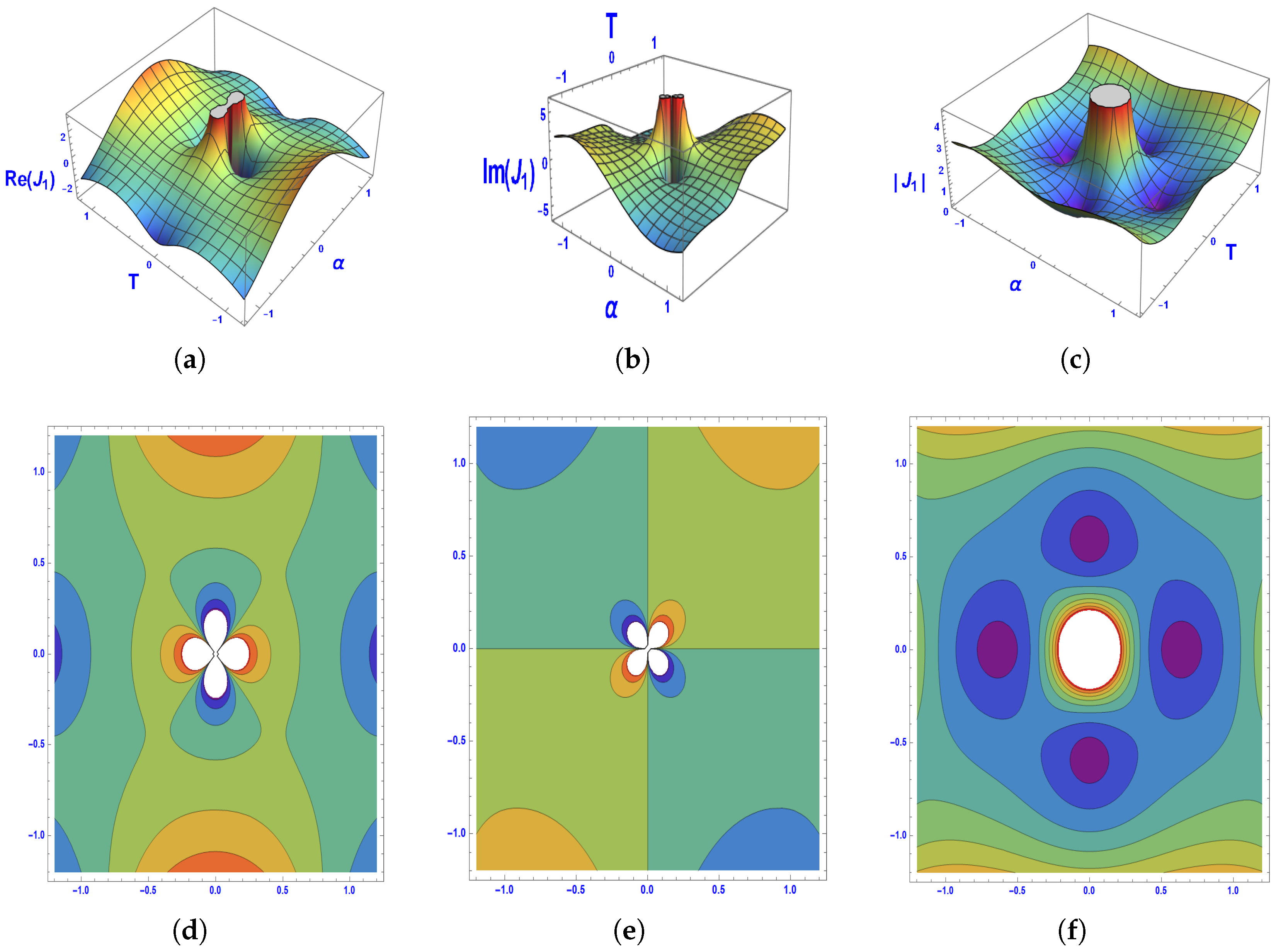
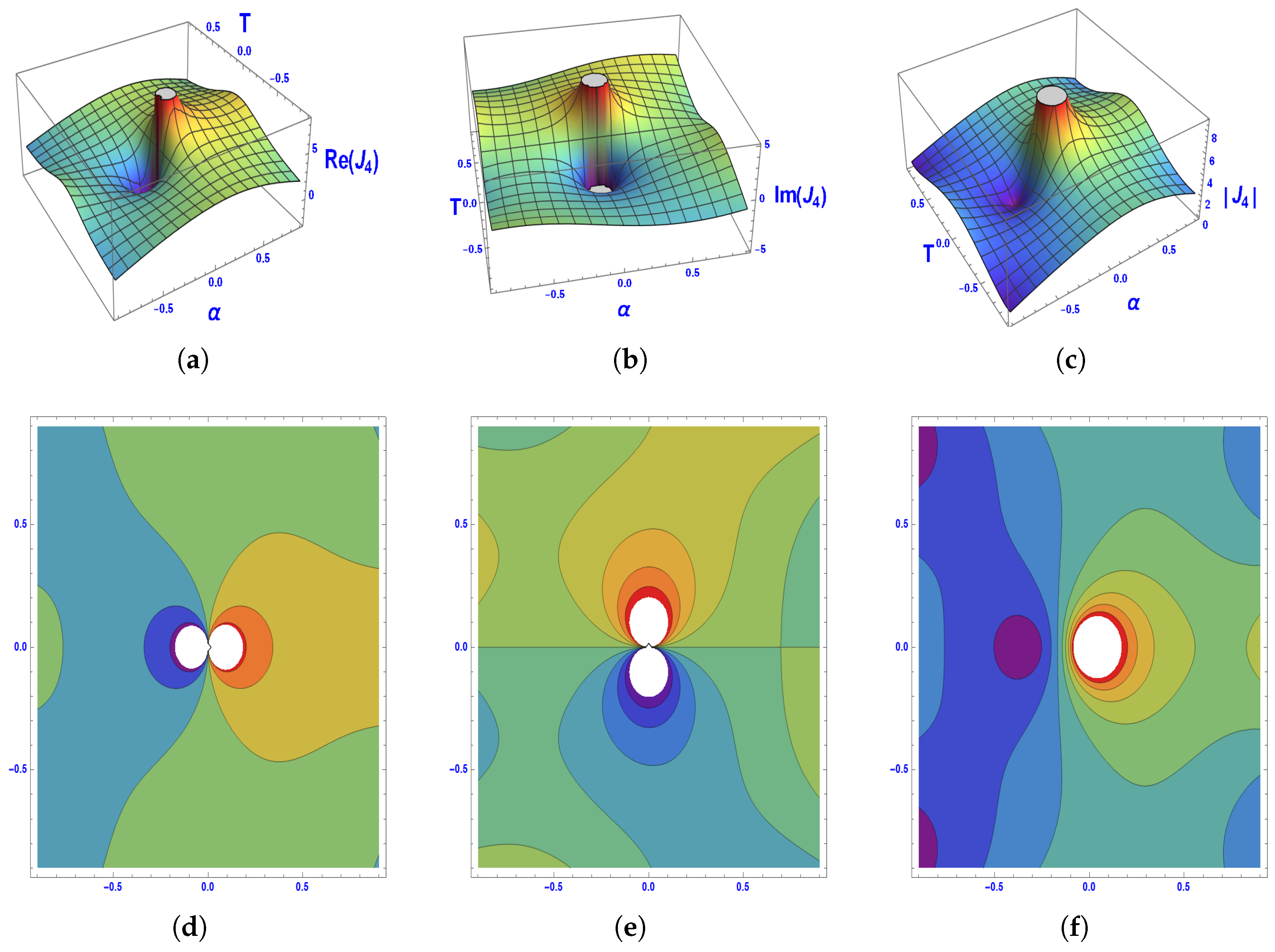
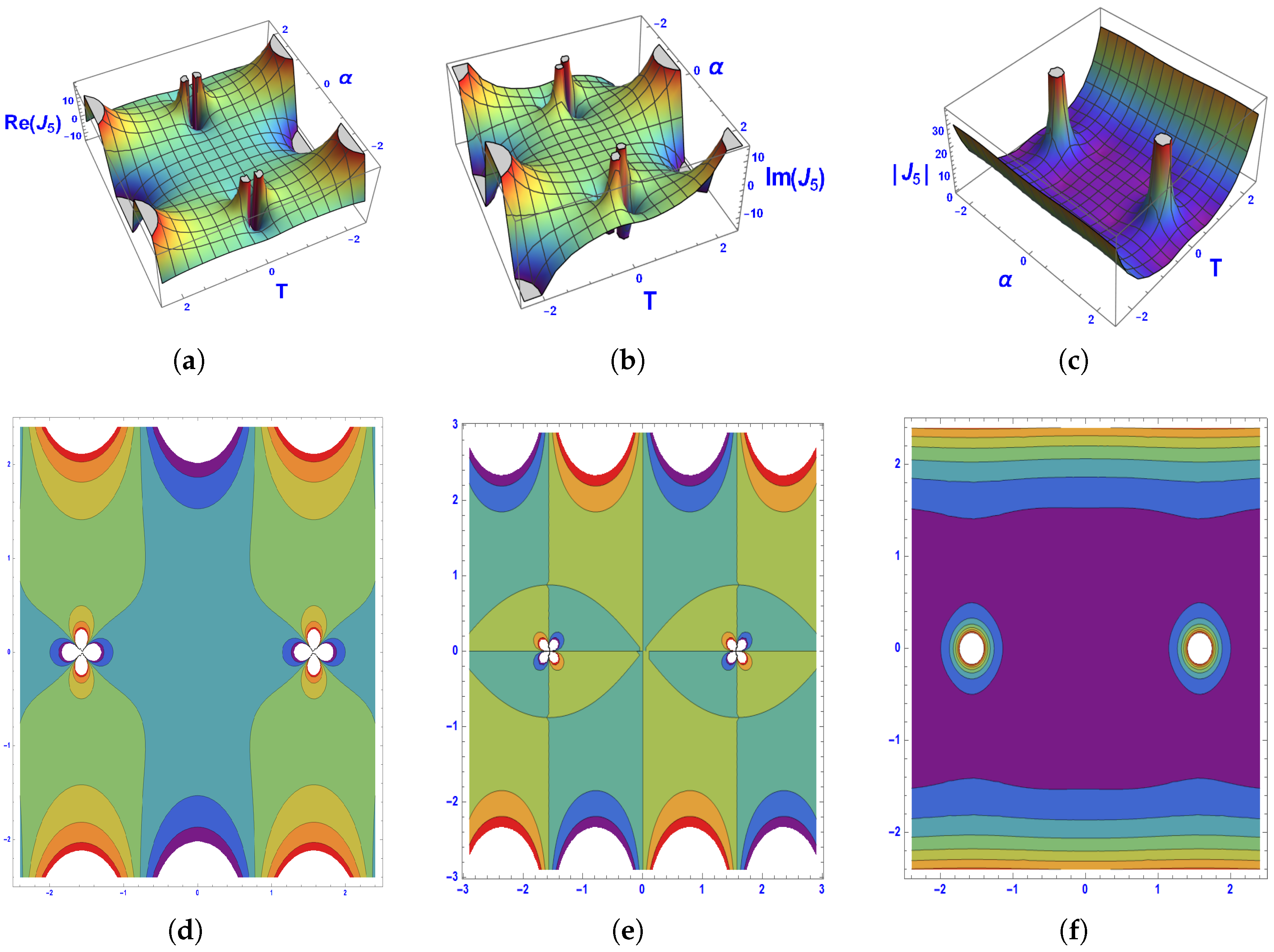
- Deriving exact soliton solutions using the multivariate generalized exponential rational integral function method, illustrated through 3D and contour plots.
- Performing bifurcation and chaos analyses to explore periodic, quasi-periodic, and chaotic behaviors using 2D phase portraits, time series, fractal dimension, return maps, and power spectram.
- Find the conservation laws of consider equation
- Finally, discuss the multi-stability analysis of the model.
2. Exploring Lie Symmetries of Equation (1)
3. Symmetry Reduction of Equation (1)
4. Analytical Solutions for the Equation (1)
4.1. Methodology of MGERIFM
4.2. Analytical Solutions of the Equation (1) via MGERIFM
4.2.1. Established Sine Representation
4.2.2. Established Cosine Representation:
4.2.3. Established Exponential Representation
4.2.4. Established Cosine Hyperbolic Representation
4.2.5. Established Sine Hyperbolic Representation
5. Physical Interpretation of the Solutions
6. Conservation Laws of Equation (1)
7. Exploring the Qualitative Characteristics of Equation (1)
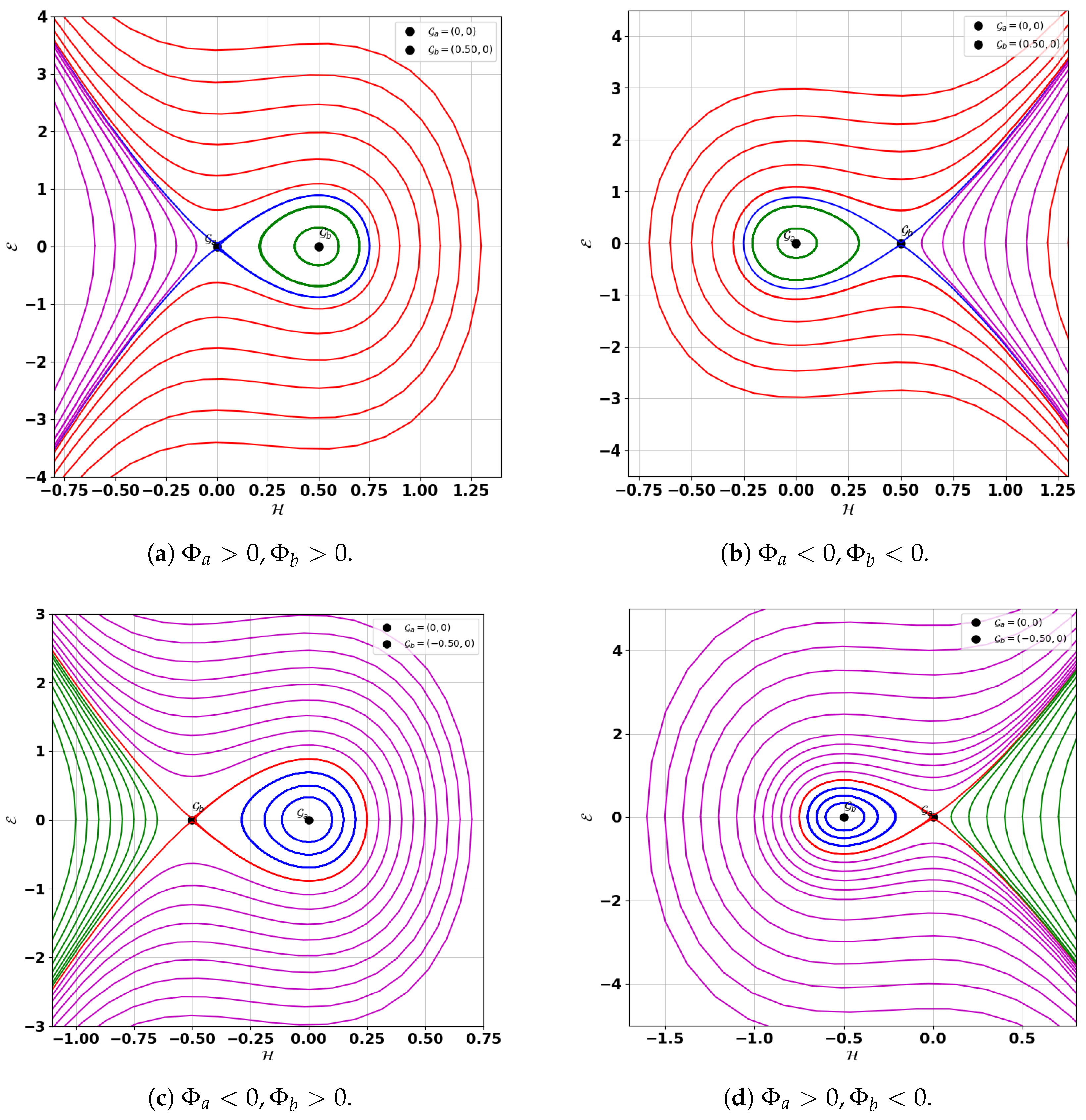
7.1. Hamiltonian Analysis
- If and , the point is a center.
- If and , the point is a saddle.
- If and , the point is a cusp.
7.2. Fixed Points of System (86)
7.3. Phase Portrait Analysis
- If :
- 1.
- For , the equilibrium points are and . The point is a saddle and exhibits unstable behavior, while is a center and exhibits stable behavior. This result is illustrated in Figure 7a.
- 2.
- If :
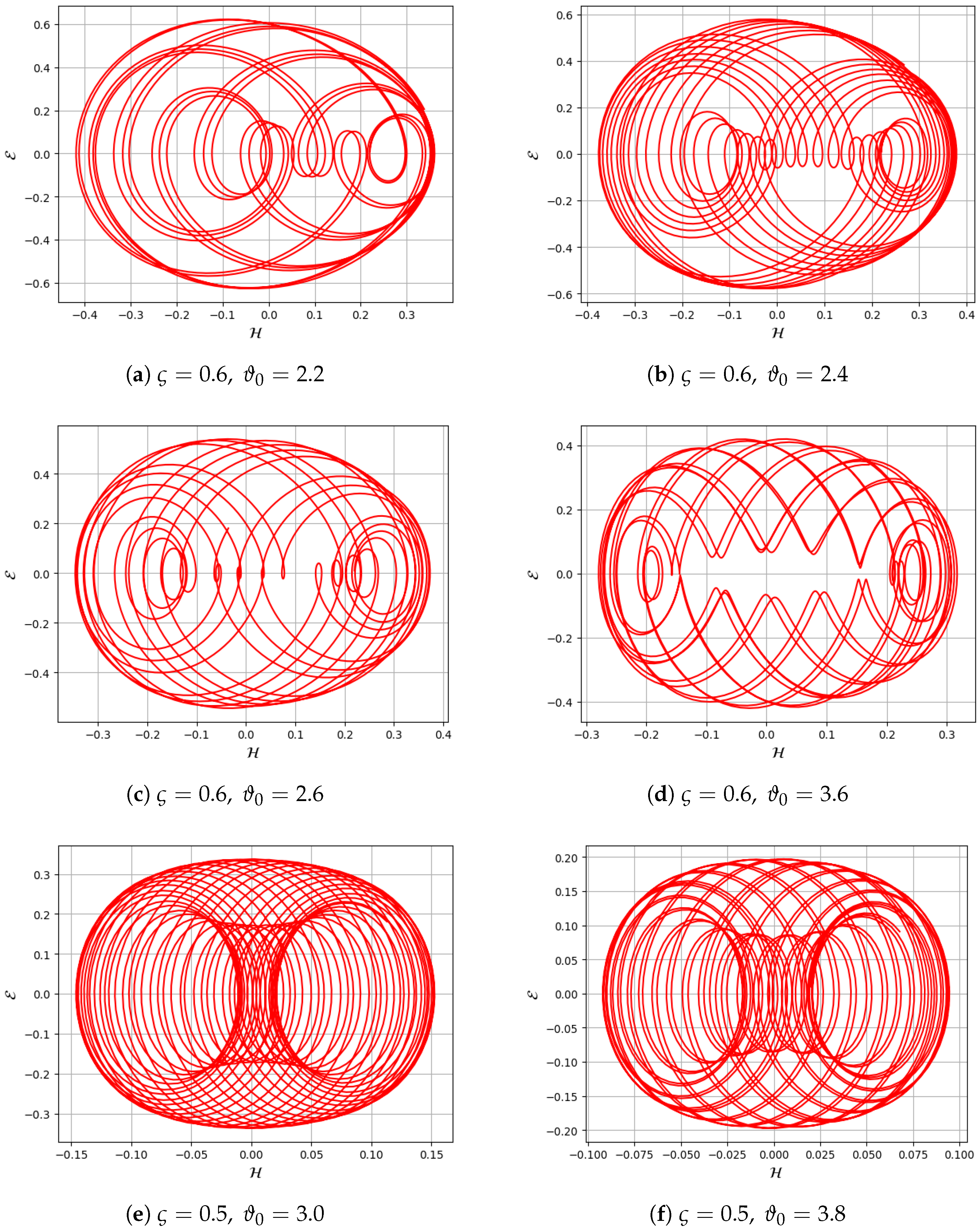
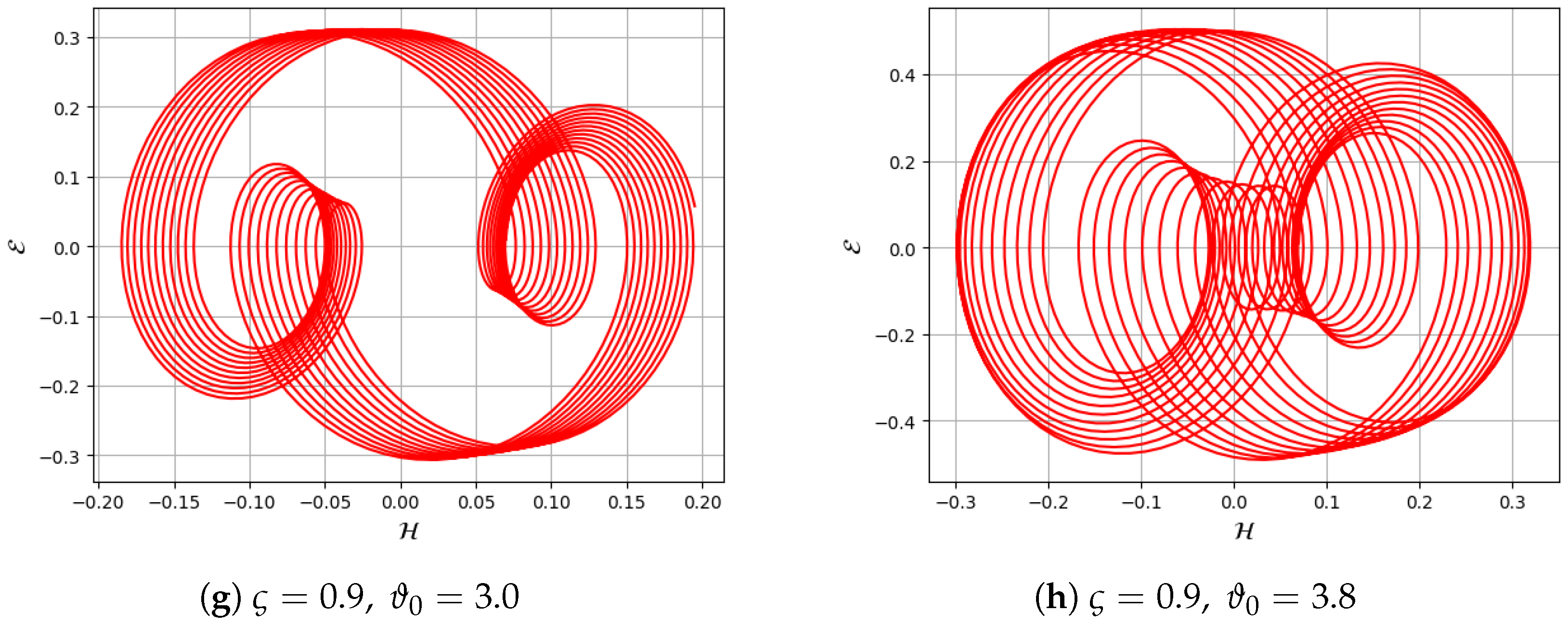
8. Chaotic and Quasi-Periodic Behaviors
8.1. 2D Phase Portrait Analysis
8.2. Poincare Map Analysis
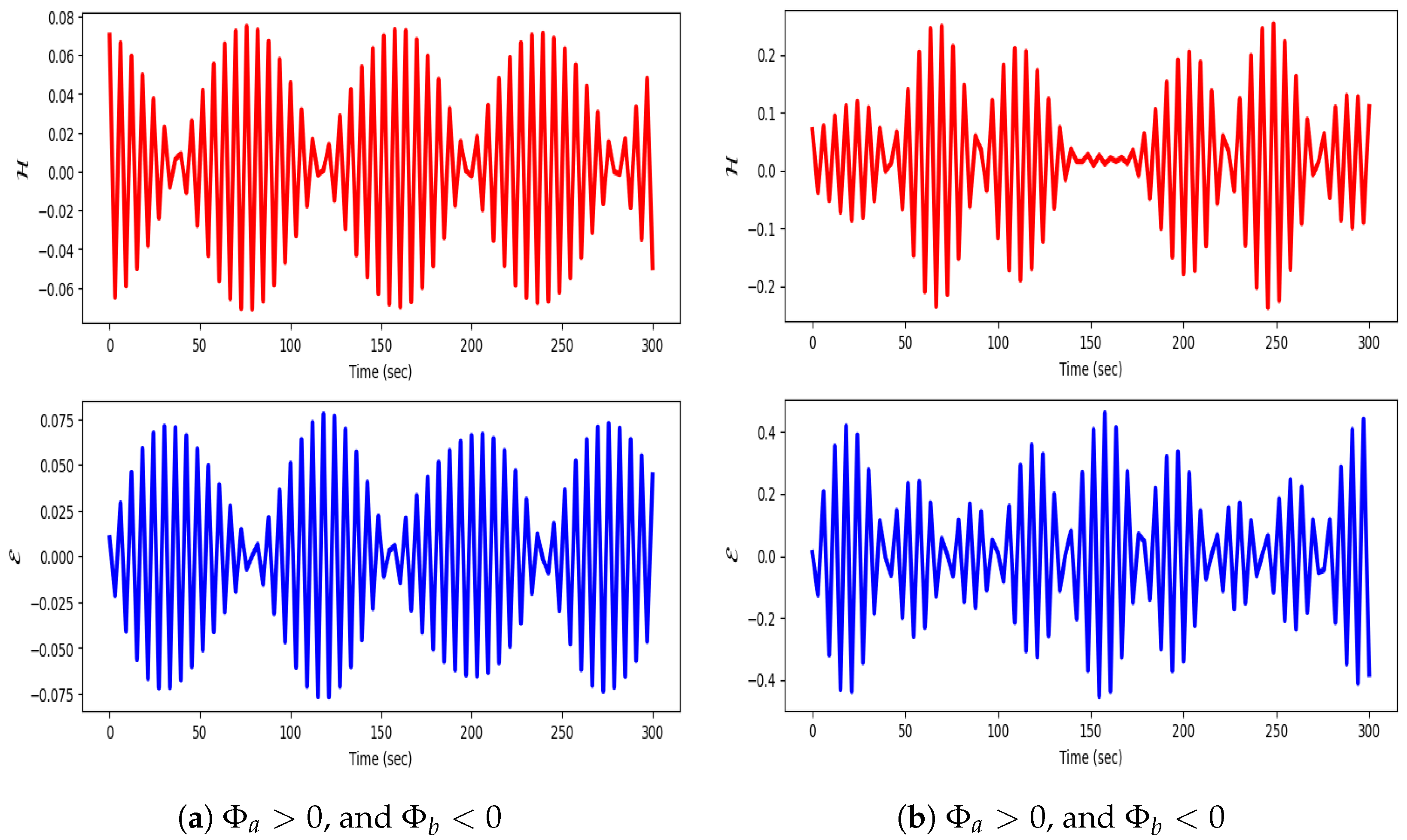
8.3. Time Series Analysis
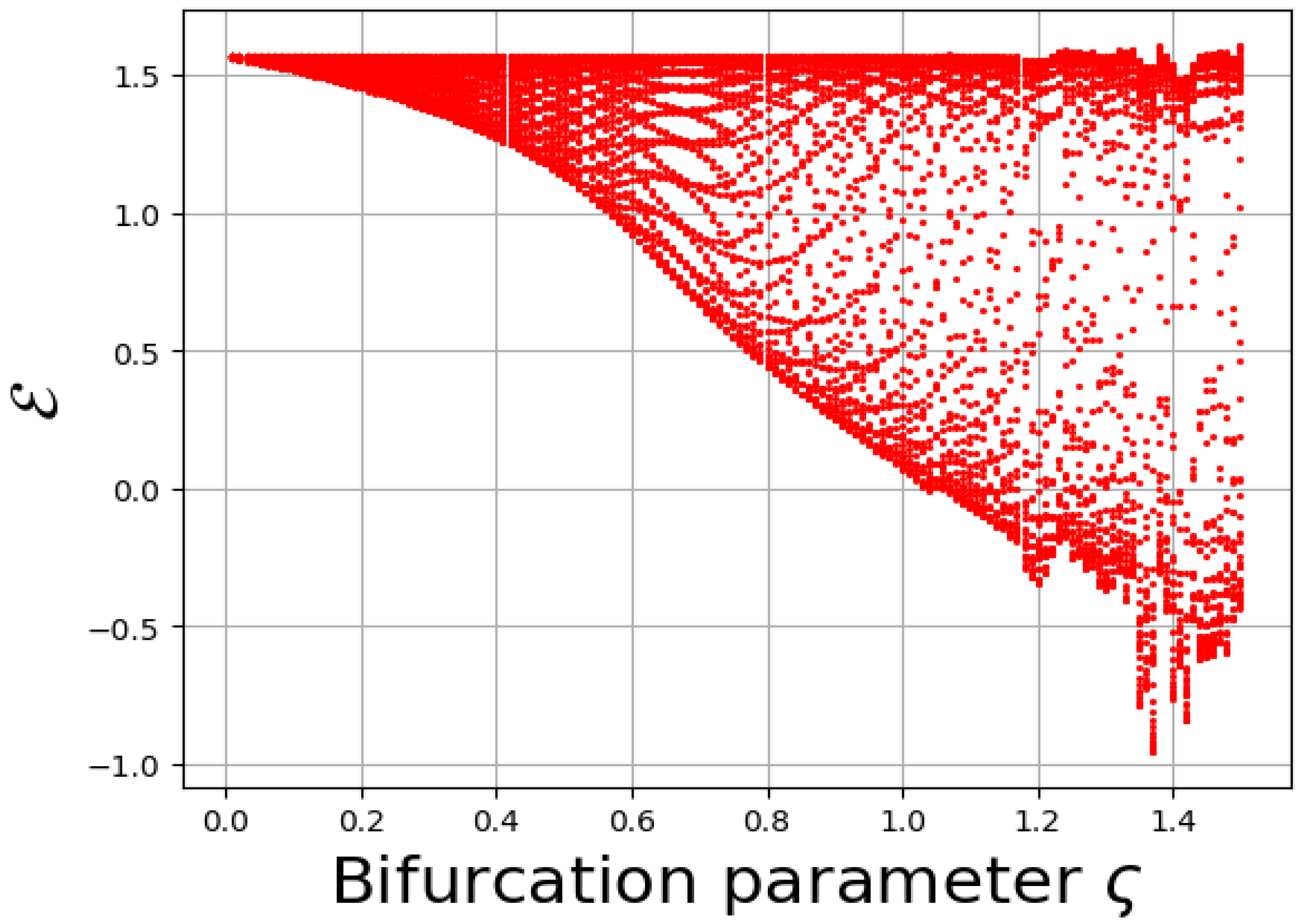
8.4. Bifurcation Diagram
8.5. Lyapunov Exponents
8.6. Fractal Dimension
8.7. Return Map
8.8. Chaotic Attractor
8.9. Power Spectrum
9. Multistability Analysis
10. Comparison with Existing Literature
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, S.; Niwas, M. Exact closed-form solutions and dynamics of solitons for a (2+1)-dimensional universal hierarchy equation via Lie approach. Pramana 2021, 95, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, U.; Hussain, E.; Muhammad, J.; Sharaf, M.; Meligy, M.E. Chaotic Structure, Sensitivity Analysis and Dynamics of Solitons to the Nonlinear Fractional Longitudinal Wave Equation. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2025, 64, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, E.; Tedjani, A.H.; Farooq, K.; Beenish. Modeling and Exploration of Localized Wave Phenomena in Optical Fibers Using the Generalized Kundu–Eckhaus Equation for Femtosecond Pulse Transmission. Axioms 2025, 14, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopçasız, B.; Yaşar, E. Inquisition of optical soliton structure and qualitative analysis for the complex-coupled Kuralay system. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2025, 39, 2450512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopçasız, B. Unveiling new exact solutions of the complex-coupled Kuralay system using the generalized Riccati equation mapping method. J. Math. Sci. Model. 2024, 7, 146–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipu, G.H.; Faridi, W.A.; Yao, F.; Garayev, M. Uncovering nonlinear dynamics in shallow water: An analytic approach to the (1+1)-dimensional Estevez–Mansfield–Clarkson equation. J. Ocean. Eng. Mar. Energy 2025, 11, 799–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Fan, L.; Chen, C.; Lu, G.; Li, B.; Tu, T. Study on fuel injection stability improvement in marine low-speed dual-fuel engines. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 253, 123729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinat, N.; Hussain, A.; Kara, A.H.; Zaman, F.D. On the analysis and integrability of the time-fractional stochastic potential-KdV equation. Quaest. Math. 2025, 48, 909–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Lai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Tian, J.; Du, Y.; Gao, J. Targeted sonodynamic therapy platform for holistic integrative Helicobacter pylori therapy. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2408583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Sun, Q.; Ge, J.; Wang, H.; Qi, J. Multidimensional Engineering of Nanoconfined Catalysis: Frontiers in Carbon-Based Energy Conversion and Utilization. Catalysts 2025, 15, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Gao, Z.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, L.; Guo, G.; Mumtaz, S. Compensator-Based Fixed-Time Prescribed Performance Control of Vehicular Platoon with Input Nonlinearities: A Performance Boundary Self-Adjusting Approach. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 14823–14837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, M.M.; Mohamed, M.S.; Attia, R.A. On semi analytical and numerical simulations for a mathematical biological model; the time-fractional nonlinear Kolmogorov–Petrovskii–Piskunov (KPP) equation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2021, 144, 110676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, M.M.; Ahmed, A.E.S.; El-Shorbagy, M.A. Abundant stable computational solutions of Atangana–Baleanu fractional nonlinear HIV-1 infection of CD4+ T-cells of immunodeficiency syndrome. Results Phys. 2021, 22, 103890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, M.M.; Nisar, K.S.; Mohamed, M.S. Numerical investigation for the fractional nonlinear space-time telegraph equation via the trigonometric Quintic B-spline scheme. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2021, 44, 4598–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, M.M.; Nofal, T.A.; Abu-Zinadah, H.; Lotayif, M.S.; Lu, D. Novel computational and accurate numerical solutions of the modified Benjamin–Bona–Mahony (BBM) equation arising in the optical illusions field. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 1797–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, B.; Chen, L.; Tian, F.; Xu, J.; Liu, J.; Zhu, B. Effect of lateral stress and loading paths on direct shear strength and fracture of granite under true triaxial stress state by a self-developed device. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2025, 318, 110952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wei, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Wen, S.; Guo, G. Global prescribed performance control for 2-D plane vehicular platoons with small overshoot: A fixed-time composite sliding mode control approach. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 18789–18804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Li, M.; Qi, Z.; Yang, X.; Lin, Y.; Cao, S. A review on curve edge based architectures under lateral loads. Thin-Walled Struct. 2025, 217, 113849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Huang, S.; Li, M.; He, J.; Totis, G.; Hua, C.; Weng, S. Highly efficient heat dissipation method of grooved heat pipe for thermal behavior regulation for spindle system working in low rotational speed. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2025, 169, 109575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; He, J.; Totis, G.; Weng, S. High-efficiency topology optimization method for thermal-fluid problems in cooling jacket of high-speed motorized spindle. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2025, 169, 109533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, L.; Cui, R.; Lv, B.; Xiao, Z.; Xu, X. Light modulated magnetism and spin–orbit torque in a heavy metal/ferromagnet heterostructure based on van der Waals-layered ferroelectric materials. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 123, 092406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, M.M.; Lu, D.; Inc, M. Diverse novel solutions for the ionic current using the microtubule equation based on two recent computational schemes. J. Comput. Electron. 2021, 20, 2604–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Alshammari, F.S.; Yasin, S. Exact Solitary Wave Solutions and Sensitivity Analysis of the Fractional (3+1) D KdV–ZK Equation. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San, S.; Alshammari, F.S. Analytical and Dynamical Study of Solitary Waves in a Fractional Magneto-Electro-Elastic System. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Ali, U. Novel Exact Solutions of a Higher-Dimensional Complex KdV System with Conformable Derivative Using the Generalized Expansion Method. J. Math. Anal. Model. 2025, 6, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Xiao, X.; Li, J.; Guo, H. Design and fabrication of a chalcogenide hollow-core anti-resonant fiber for mid-infrared applications. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 7659–7670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, B. Robust stability design for inverters using phase lag in proportional-resonant controllers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2025, 72, 2655–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xia, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ye, Y. Equivalence relation analysis and design of repetitive controllers and multiple quasi-resonant controllers for single-phase inverters. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2025, 13, 3338–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Lin, Q.; Liu, M.; Liu, H. Electromechanical braking systems and control technology: A survey and practice. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J. Automob. Eng. 2025, 239, 4551–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, J.K.; Koçak, H. Dynamics and Bifurcations; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Li, M.; Song, Z.; Fu, T.; Hao, X.; Li, Y.; Sotskov, Y. An Integrated MILP Model for Scheduling of Steelmaking-Continuous Casting with Cranes. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2025, 10, 10426–10433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Ding, S.; Ho-Ching Iu, H.; Erkan, U.; Toktas, A.; Simsek, C.; Mou, J. A three-dimensional memristor-based hyperchaotic map for pseudorandom number generation and multi-image encryption. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2025, 35, 073105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhsine, H.; Mokni, K.; Ch-Chaoui, M. Exploring multi-parameter bifurcations and immigrationdriven dynamics in a discrete-time Bazykin–Berezovskaya prey–predator model. Nonlinear Dyn. 2025, 113, 34101–34131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Current Study | Khater et al.’s Work [22] |
|---|---|
| Investigates the Lie symmetry structure of the model to reveal invariant properties. | No analysis based on Lie symmetry. |
| Derives and verifies conservation laws to identify conserved physical quantities. | Does not explore conservation laws. |
| Employs the multivariate generalized exponential rational integral function method for obtaining diverse soliton solutions. | Utilizes the extended simple equation, homotopy perturbation and adomian decomposition for soliton solutions. |
| Performs comprehensive Hamiltonian and bifurcation analyses to understand system stability and dynamics. | Lacks Hamiltonian and bifurcation evaluations. |
| Conducts chaos detection through computational tools such as phase portraits, Lyapunov exponents, and bifurcation diagrams. | No investigation of chaos analysis. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beenish; Alsharidi, A.K. Lie Symmetry, Conservation Laws, and Dynamical Analysis of Ionic Currents in the Microtubule Model. Mathematics 2025, 13, 3891. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233891
Beenish, Alsharidi AK. Lie Symmetry, Conservation Laws, and Dynamical Analysis of Ionic Currents in the Microtubule Model. Mathematics. 2025; 13(23):3891. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233891
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeenish, and Abdulaziz Khalid Alsharidi. 2025. "Lie Symmetry, Conservation Laws, and Dynamical Analysis of Ionic Currents in the Microtubule Model" Mathematics 13, no. 23: 3891. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233891
APA StyleBeenish, & Alsharidi, A. K. (2025). Lie Symmetry, Conservation Laws, and Dynamical Analysis of Ionic Currents in the Microtubule Model. Mathematics, 13(23), 3891. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233891







