Edge-Aware Illumination Enhancement for Fine-Grained Defect Detection on Railway Surfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
- AIE using CLAHE and gamma correction effectively improves local contrast and adjusts global brightness distributions under low-light conditions.
- ESE, based on a morphological edge-focused enhancement strategy, preserves fine defect contours and sharpens structural boundaries to support high-fidelity feature extraction.
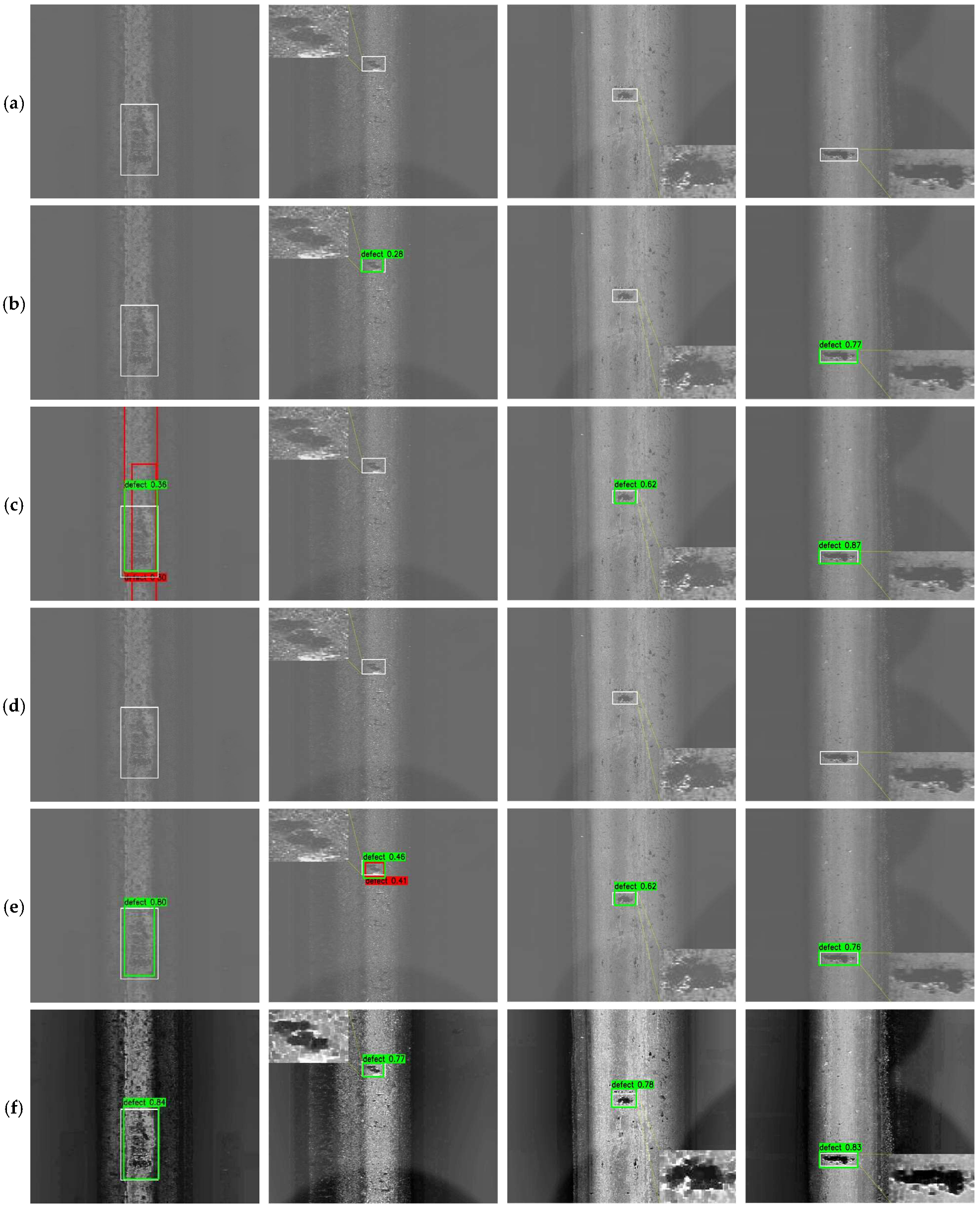
- When integrated with YOLOv11, the proposed preprocessing framework leverages its modular and adaptive design to enhance defect detection performance across diverse low-light and degraded-visibility conditions, achieving up to 7% increases in mAP over the baseline model.
2. Related Works
2.1. Vision-Based Rail Defect Detection
2.2. Low-Light Image Enhancement for Industrial Applications
2.3. Research Gap and Our Approach
- Global enhancement techniques often fail to preserve fine textures and boundary features essential for detecting microdefects.
- Most detection models are not optimized for illumination variability, which limits their effectiveness in real-world low-light scenarios.
- Few works combine local contrast enhancement and structural edge reinforcement within a unified preprocessing framework.
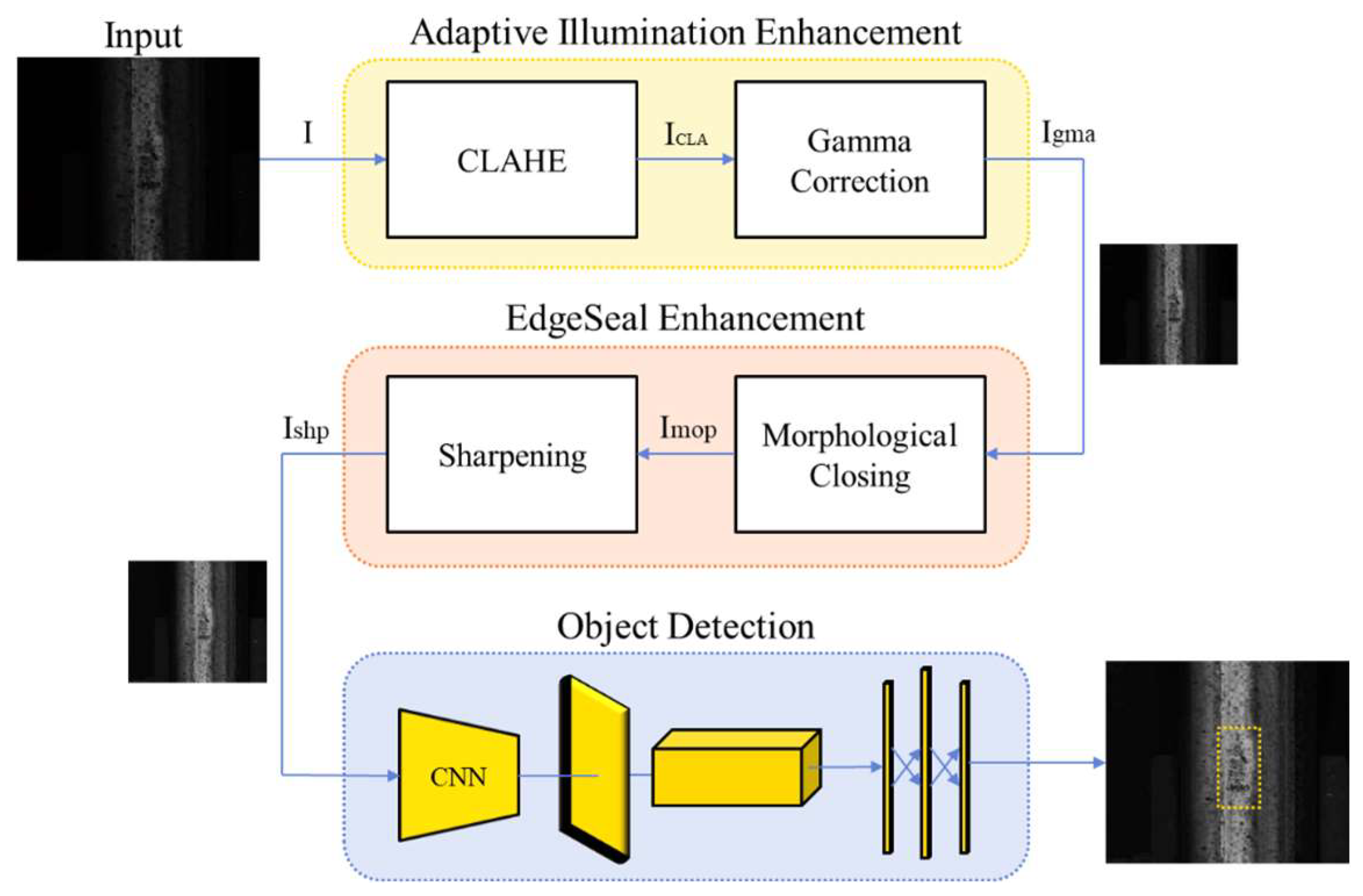
3. Methodology
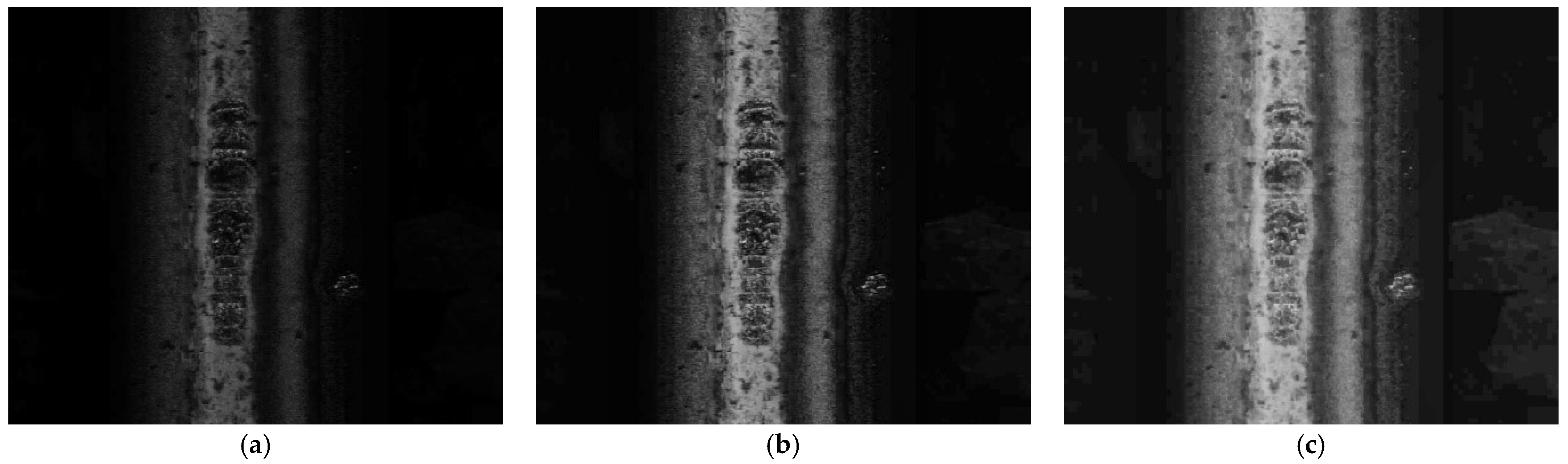
3.1. Adaptive Illumination Enhancement
3.1.1. CLAHE
3.1.2. Gamma Correction
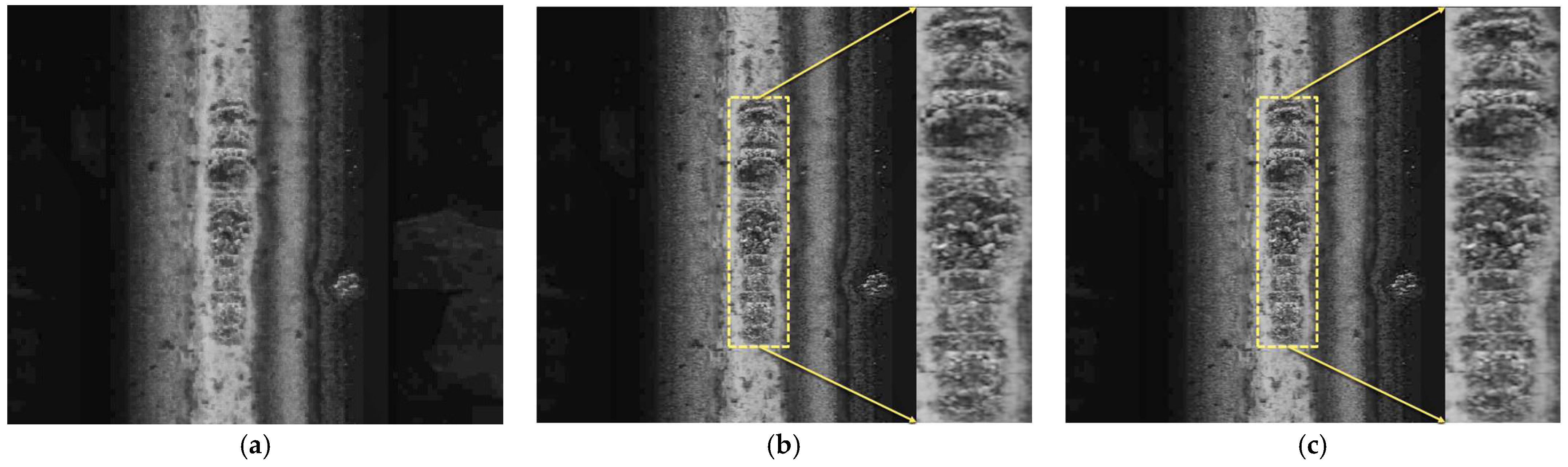
3.2. EdgeSeal Enhancement
3.2.1. Morphological Closing
3.2.2. Sharpening
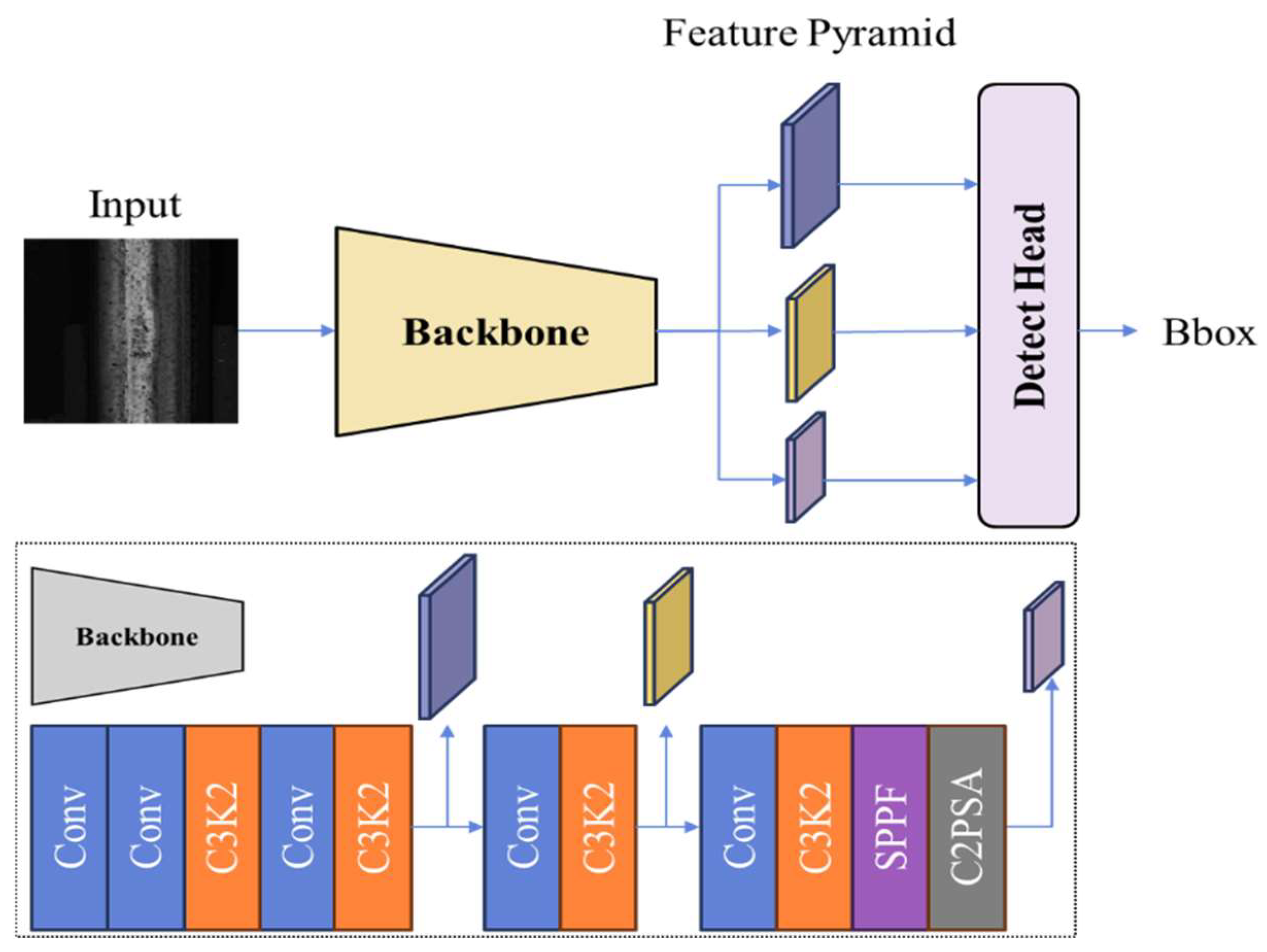
3.3. Object Detection
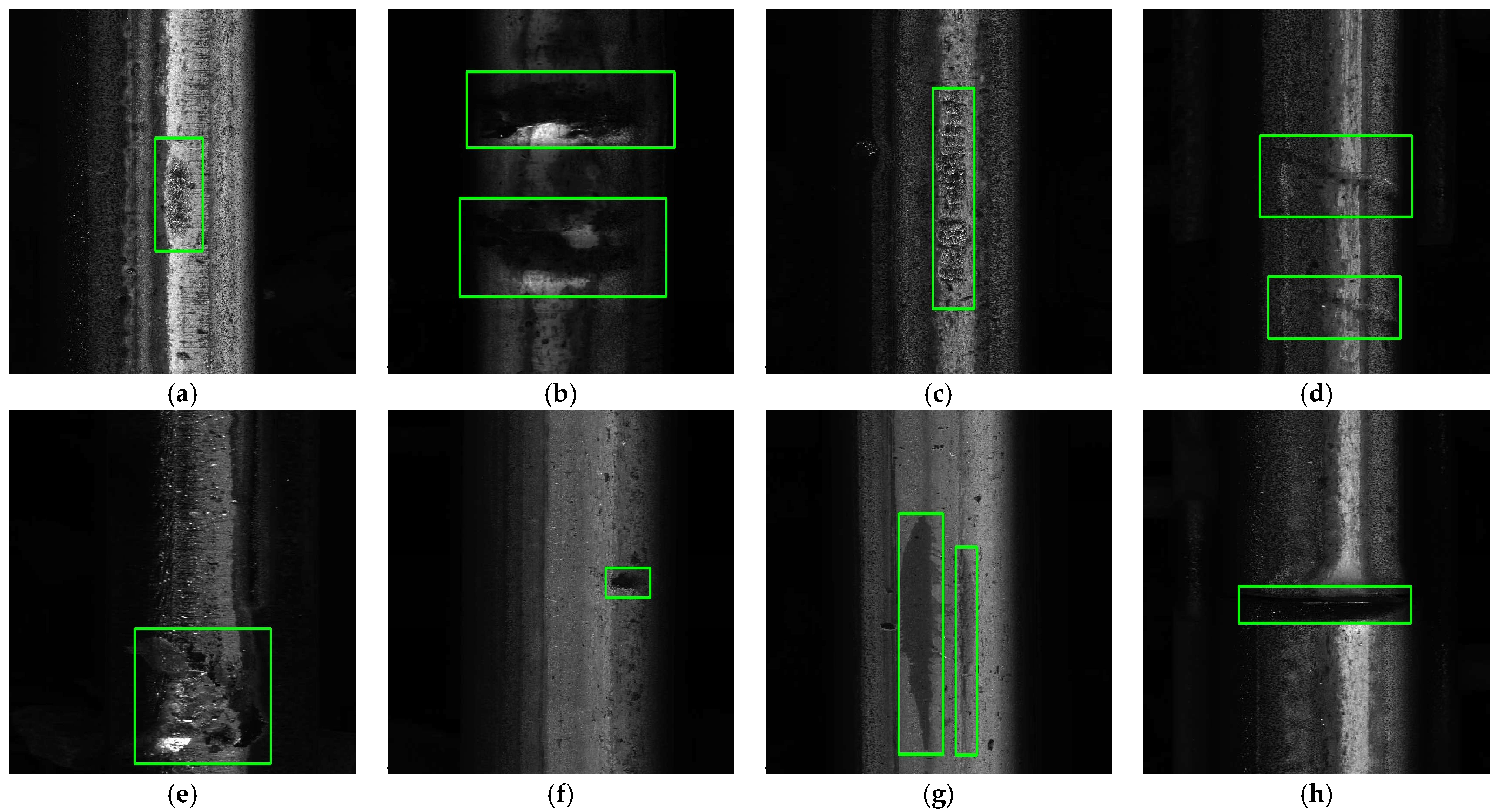
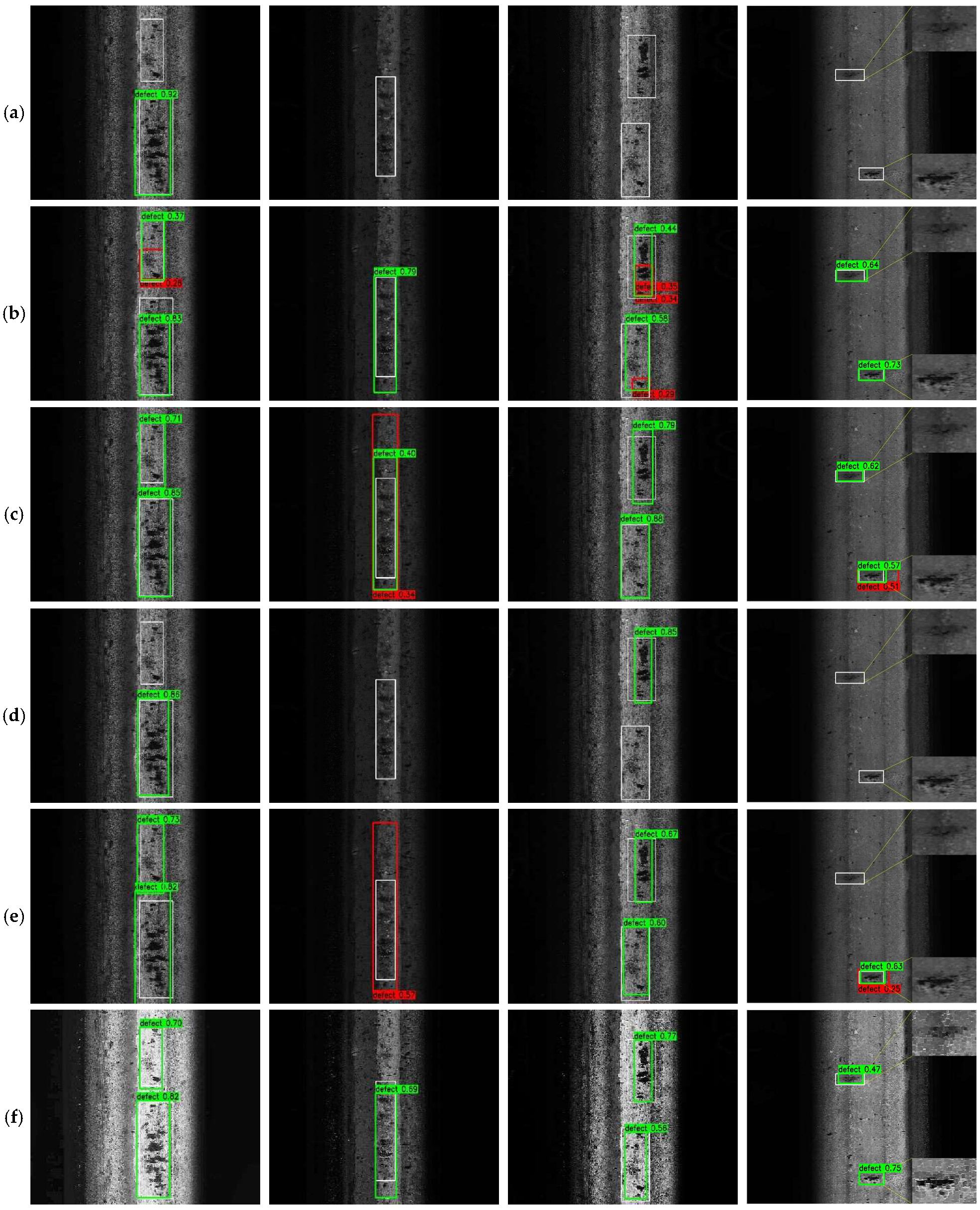
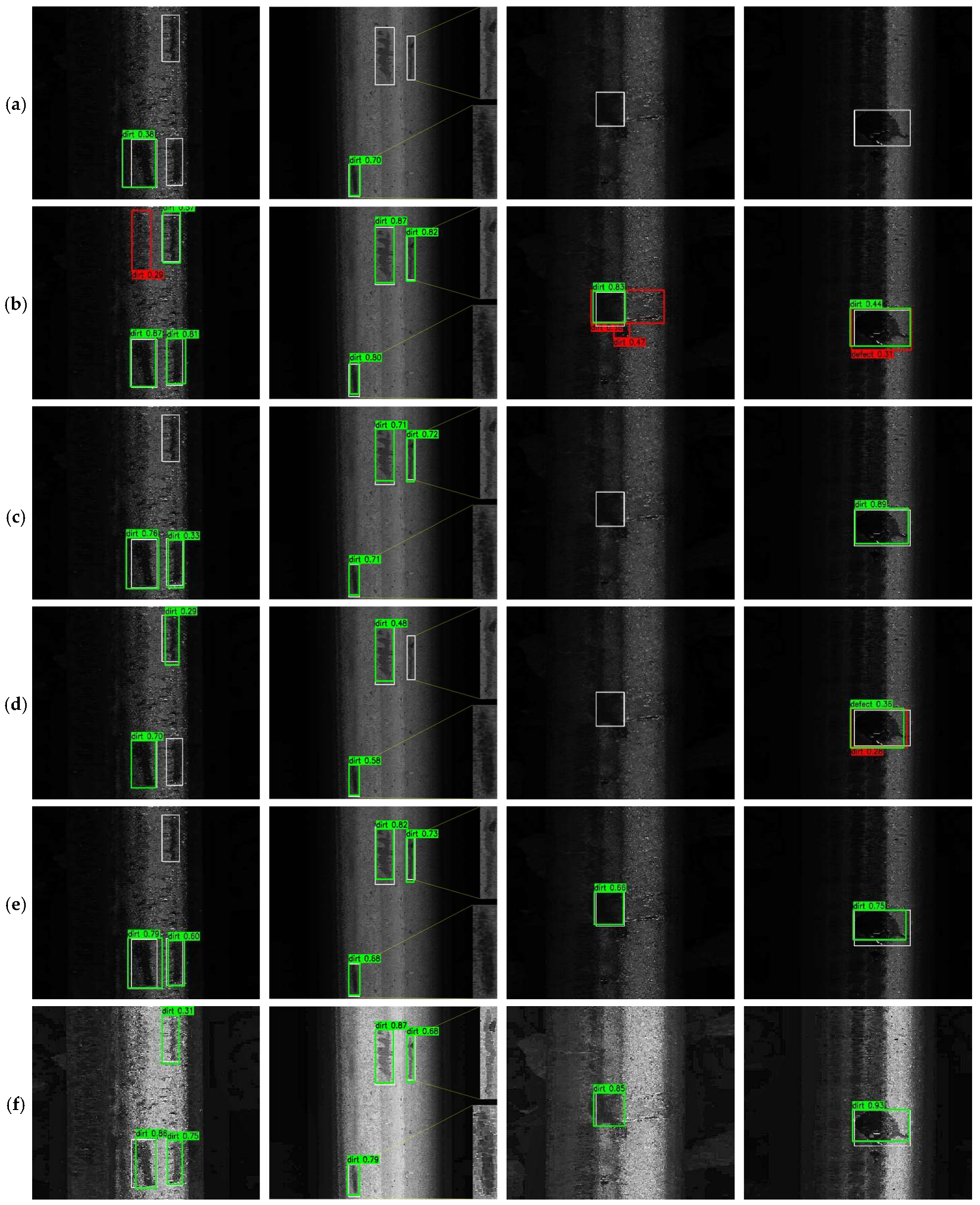
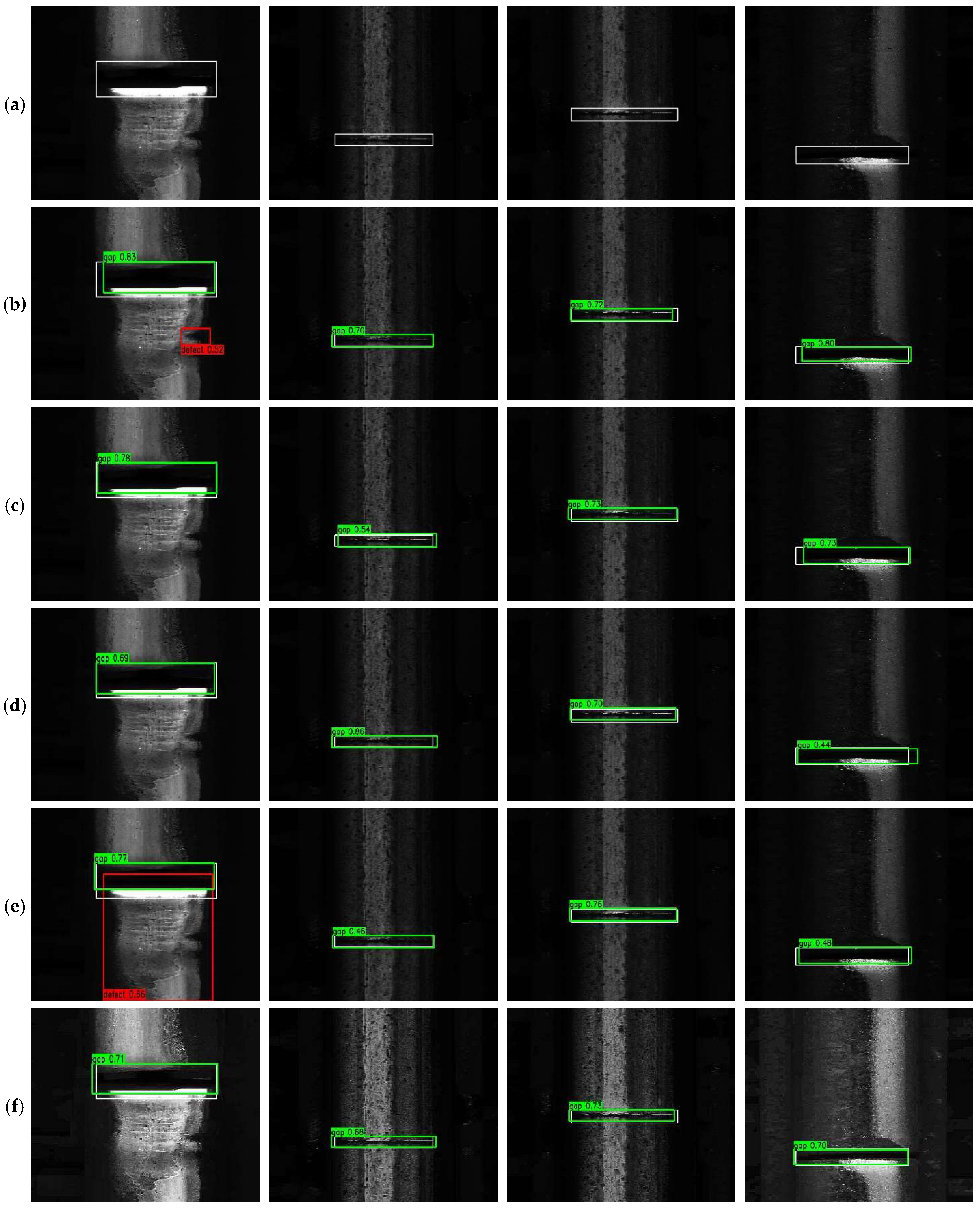
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Ablation Study
4.3. Comparative Evaluation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Silva, P.; Ribeiro, D.; Pratas, P.; Mendes, J.; Seabra, E. Indirect assessment of railway infrastructure anomalies based on passenger comfort criteria. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Han, X.; Zhang, K.; Lin, S.; Jin, J. Application of YOLO11 model with spatial pyramid dilation convolution (SPD-Conv) and effective squeeze-excitation (EffectiveSE) fusion in rail track defect detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Jing, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y. Detection of rail defects using NDT methods. Sensors 2023, 23, 4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Kan, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhang, W.; Kang, G. SH Guided wave excitation in rails for defect and stress monitoring. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2025, 224, 112064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, B.; Kang, Y.; Cai, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Duan, Z. Automatic crack identification using a novel 3D profilometry-based magnetic particle testing method. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 200, 110720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quercio, M.; Santoro, L.; Sesana, R.; Fulginei, F.-R. Advanced feature analysis of eddy current testing signals for rail surface defect characterization. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 141156–141169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Harsha, S.-P. A systematic literature review of defect detection in railways using machine vision-based inspection methods. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2024, 13, 100–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-Y.; Han, J.-M. Deep learning (Fast R-CNN)-based evaluation of rail surface defects. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, A.; Yang, X.; Diao, W. An improved lightweight deep learning model and implementation for track fastener defect detection with unmanned aerial vehicles. Electronics 2024, 13, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, K.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, Y. Detection of surface defects on railway tracks based on deep learning. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 126451–126465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Cai, L.; Li, C. Rail surface defect detection based on an improved YOLOv5s. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D.; He, Y.; Zhang, J. A deep learning-driven framework for real-time recognition and quantification of subway tunnel surface defects using high-resolution imaging. Urban Rail Transit 2025, 11, 279–299. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.; Qu, P.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, W. A survey of deep learning-based low-light image enhancement. Sensors 2023, 23, 7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Pan, K.; Lu, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z. Large–small-scale structure blended U-net for brightening low-light images. Sensors 2025, 25, 3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munaf, S.; Bharathi, A.; Jayanthi, A.-N. FPGA-based low-light image enhancement using Retinex algorithm and coarse-grained reconfigurable architecture. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J.A.; López-Rubio, E.; Ángel-Ruiz, J.A.; Molina-Cabello, M.A. The impact of noise and brightness on object detection methods. Sensors 2024, 24, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Shao, F.; Zhang, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, Q. Advanced object detection in low-light conditions: Enhancements to YOLOv7 framework. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Chang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H. Research on low-light environment object detection algorithm based on YOLO_GD. Electronics 2024, 13, 3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. YOLOv11: An overview of the key architectural enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Yu, S. Research on the lightweight detection method of rail internal damage based on improved YOLOv8. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2025, 72, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, R.; Guo, T. Lightweight rail surface defect detection algorithm based on an improved YOLOv8. Measurement 2025, 232, 115739. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Zheng, S.; Li, L.; Shi, R.; An, X. Research on rail surface defect detection based on improved CenterNet. Electronics 2024, 13, 3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, Q.; Han, Z.; Zhai, F. DP-YOLO: A lightweight real-time detection algorithm for rail fastener defects. Sensors 2025, 25, 2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Li, R.; Hu, H. PGCI-YOLO: A railway fastener detection algorithm based on improved YOLOv8n. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2025, 22, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, M.; Peng, J.; Huang, J.; Li, H. A multi-category defect detection model for rail fastener based on optimized YOLOv8n. Machines 2025, 13, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukov, A.; Benois-Pineau, J.; Youssef, A.; Zemmari, A.; Mosbah, M.; Taillandier, V. FusWay: Multimodal hybrid fusion approach. Application to railway defect detection. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2509.06987. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Shen, Y.; Zhong, S. SCRNet: A Retinex structure-based low-light enhancement model guided by spatial consistency. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.08053. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Bian, H.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Timofte, R.; Zhang, Y. Retinexformer: One-stage retinex-based transformer for low-light image enhancement. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.06705. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Lu, F.; Gu, X.; Qin, K. Research on unsupervised low-light railway fastener image enhancement method based on contrastive learning GAN. Sensors 2024, 24, 3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, J.; Yang, C. BrightsightNet: A lightweight progressive low-light image enhancement network and its application in “rainbow” maglev train. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2023, 35, 101814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; He, M.; Chen, B. Efficient deep learning based rail fastener screw detection method for fastener screw maintenance robot under complex lighting conditions. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, S.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.; Jiang, Q.; Kou, Y. Tunnel lining crack detection model based on improved YOLOv5. Tunn. Under. Space Technol. 2024, 147, 105713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wang, R.; Zhang, M.; Lv, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Bian, X. SwinLightGAN a study of low-light image enhancement algorithms using depth residuals and transformer techniques. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Z.; Chen, R.; Zhao, S. Research on steel rail surface defects detection based on improved YOLOv4 network. Front. Neurorobot. 2023, 17, 1119896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Han, C.; Liu, Z. No-Service Rail Surface Defect Segmentation via Normalized Attention and Dual-scale Interaction. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2306.15442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Kim, G.T.; Kim, M.; Jang, J. Contrast Enhancement-Based Preprocessing Process to Improve Deep Learning Object Task Performance and Results. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. YOLOv10: Real-time end-to-end object detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.14458. [Google Scholar]
- Sirlis. RailDefect Dataset. Available online: https://github.com/sirlis/RailDefect (accessed on 29 November 2024).
- Tao, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Yung, K.L.; Ip, W.H. LEGAN: A low-light image enhancement generative adversarial network for industrial internet of smart-cameras. Internet Things 2024, 25, 101054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. YOLOX: Exceeding YOLO series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lv, W.; Xu, S.; Wei, J.; Wang, G.; Dang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. DETRs beat YOLOs on real-time object detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.08069. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, D.; Zhang, L.; Deng, W. Rail surface defect detection based on image enhancement and improved YOLOX. Electronics 2023, 12, 2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, D.; Gong, L.; Jin, C.; Cui, X.; Yang, T.; Qin, J. SMI-YOLOv8: Intelligent detection of tunnel lining cracks via multiscale feature attention fusion. Measurement 2025, 257, 118833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Module | Precision | Recall | mAP @50 | mAP @50~95 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIE | ESE | Defect | Dirt | Gap | Defect | Dirt | Gap | ||
| - | - | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.98 | 0.79 | 0.61 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 0.55 |
| √ | - | 0.88 | 0.82 | 0.94 | 0.65 | 0.78 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 0.56 |
| - | √ | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.66 | 0.78 | 1.00 | 0.88 | 0.56 |
| √ | √ | 0.86 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.59 |
| Model | mAP@0.50 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run 1 | Run 2 | Run 3 | Run 4 | Run 5 | Mean ± Std | |
| YOLOv11 | 85.5 | 85.8 | 85.2 | 85.3 | 85.4 | 85.4 ± 0.2 |
| Proposed model | 92.9 | 92.5 | 92.6 | 92.4 | 92.8 | 92.6 ± 0.2 |
| Image Enhancement | Precision | Recall | mAP @50 | mAP @50–95 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Defect | Dirt | Gap | Defect | Dirt | Gap | |||
| - | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.98 | 0.79 | 0.61 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 0.55 |
| HE | 0.89 | 1.00 | 0.79 | 0.62 | 0.68 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 0.57 |
| CLAHE | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.86 | 0.65 | 0.78 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 0.57 |
| DCP | 0.83 | 0.93 | 0.80 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 0.56 |
| LEGAN [39] | 0.79 | 0.93 | 0.88 | 0.72 | 0.74 | 1.00 | 0.86 | 0.55 |
| Proposed AIE + ESE | 0.86 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.59 |
| Model | Precision | Recall | mAP @50 | mAP @50–95 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Defect | Dirt | Gap | Defect | Dirt | Gap | |||
| YOLOX [40] | 0.53 | 0.88 | 0.57 | 0.42 | 0.57 | 0.57 | 0.53 | 0.26 |
| RT-DETR [41] | 0.89 | 0.77 | 0.94 | 0.73 | 0.62 | 1.00 | 0.84 | 0.51 |
| YOLOv11 [19] | 0.84 | 0.85 | 0.98 | 0.79 | 0.61 | 1.00 | 0.85 | 0.55 |
| Improved YOLOX [42] | 0.53 | 0.88 | 0.63 | 0.45 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.56 | 0.27 |
| SMI-YOLOv8 [43] | 0.88 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.57 | 0.78 | 1.00 | 0.90 | 0.55 |
| Proposed model | 0.86 | 0.92 | 0.99 | 0.90 | 0.89 | 1.00 | 0.92 | 0.59 |
| Model | Precision | Recall | mAP @50 | mAP @50–95 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Defect | Dirt | Gap | Defect | Dirt | Gap | |||
| YOLOX [40] | 0.85 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.42 | 0.26 | 0.05 |
| RT-DETR [41] | 0.51 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.02 | 0.10 | 0.73 | 0.39 | 0.13 |
| YOLOv11 [19] | 0.76 | 0.31 | 0.76 | 0.28 | 0.10 | 0.75 | 0.39 | 0.20 |
| Improved YOLOX [42] | 0.70 | 0.17 | 0.91 | 0.42 | 0.10 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.32 |
| SMI-YOLOv8 [43] | 0.84 | 0.87 | 1.00 | 0.59 | 0.68 | 0.73 | 0.85 | 0.46 |
| Proposed model | 0.95 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.64 | 0.73 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 0.52 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, G.; Yoon, S.; Cho, J. Edge-Aware Illumination Enhancement for Fine-Grained Defect Detection on Railway Surfaces. Mathematics 2025, 13, 3780. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233780
Bae G, Yoon S, Cho J. Edge-Aware Illumination Enhancement for Fine-Grained Defect Detection on Railway Surfaces. Mathematics. 2025; 13(23):3780. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233780
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Geuntae, Sungan Yoon, and Jeongho Cho. 2025. "Edge-Aware Illumination Enhancement for Fine-Grained Defect Detection on Railway Surfaces" Mathematics 13, no. 23: 3780. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233780
APA StyleBae, G., Yoon, S., & Cho, J. (2025). Edge-Aware Illumination Enhancement for Fine-Grained Defect Detection on Railway Surfaces. Mathematics, 13(23), 3780. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13233780






