Progressive Policy Learning: A Hierarchical Framework for Dexterous Bimanual Manipulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
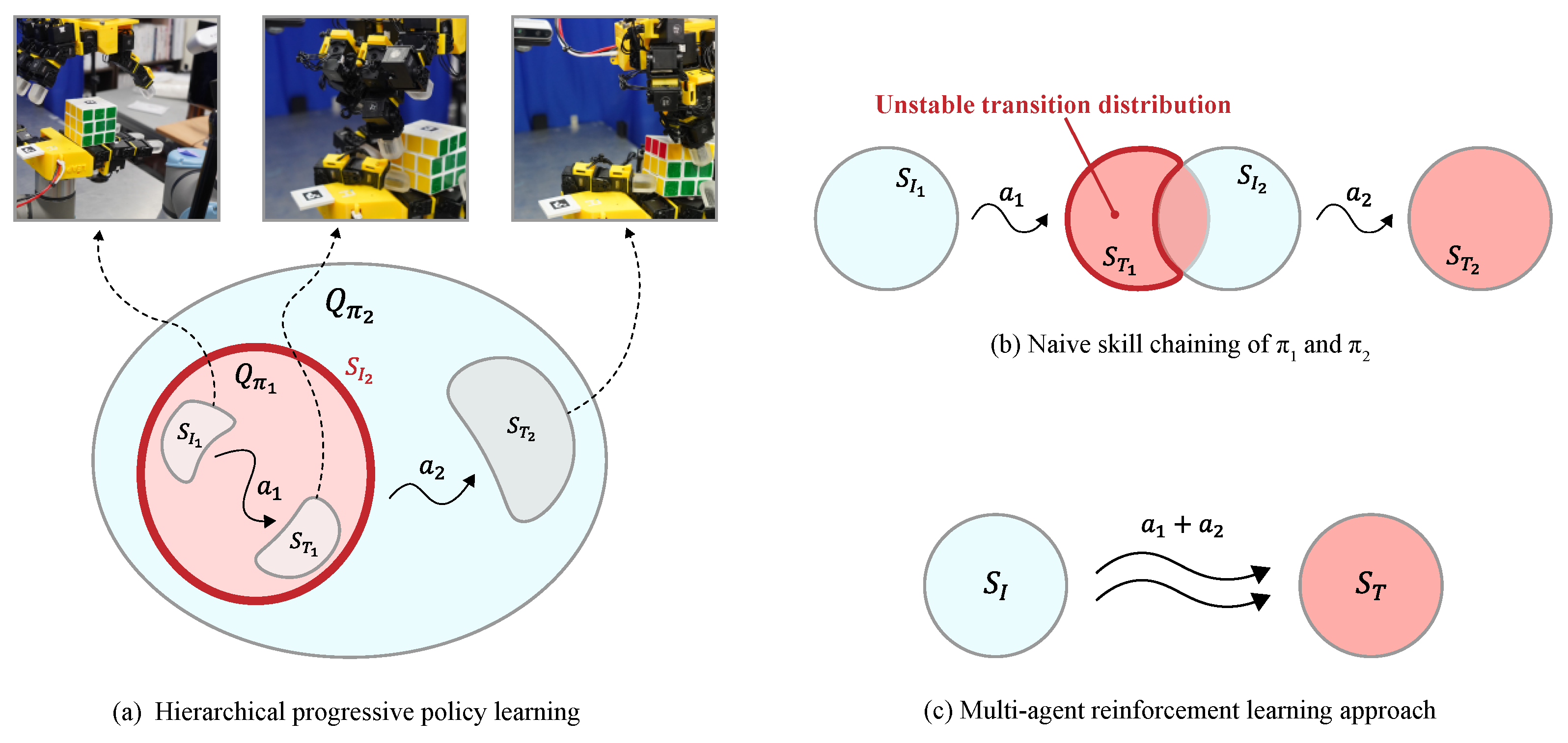
- A novel framework (HPPL) combining hierarchical task decomposition with progressive policy learning for dexterous bimanual manipulation is proposed.
- A solution to the policy connectivity problem is presented by utilizing the state generated by the preceding policy as a condition for the subsequent policy’s action generation.
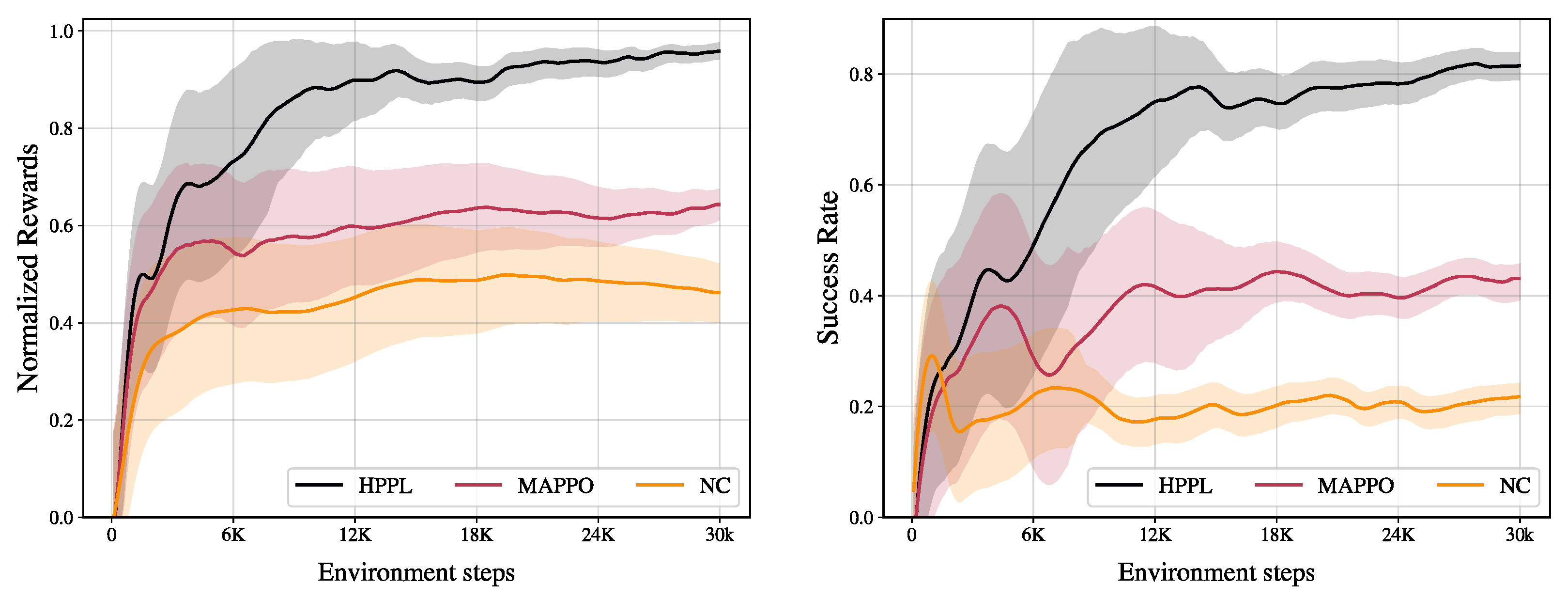
- The HPPL framework outperforms end-to-end and multi-agent RL baselines and is empirically validated on a bimanual cube manipulation task via transfer to a real bimanual robot system.
2. Related Work
3. Methodology
3.1. Problem Formulation
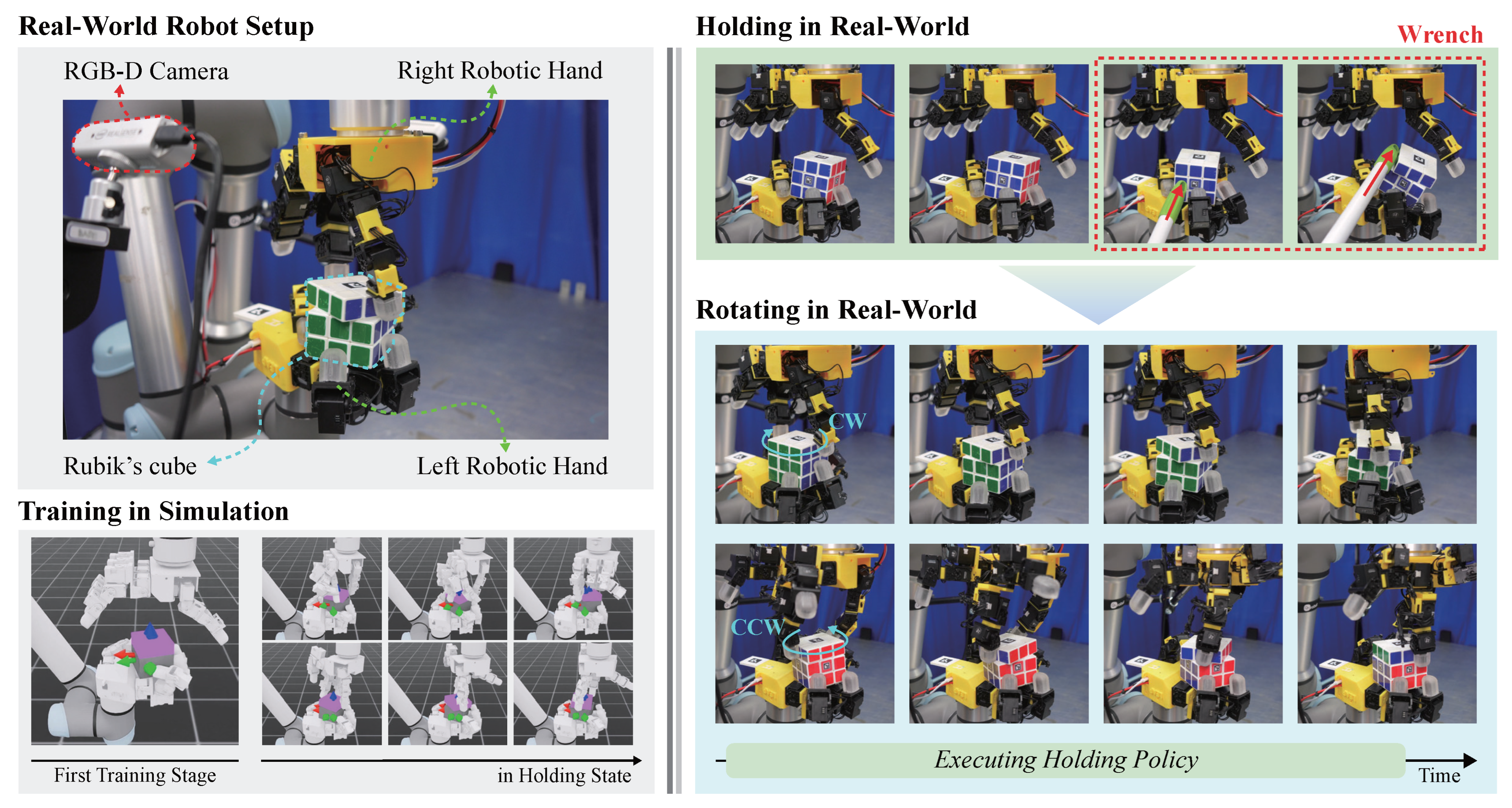
3.2. System Setup
3.3. Task Description
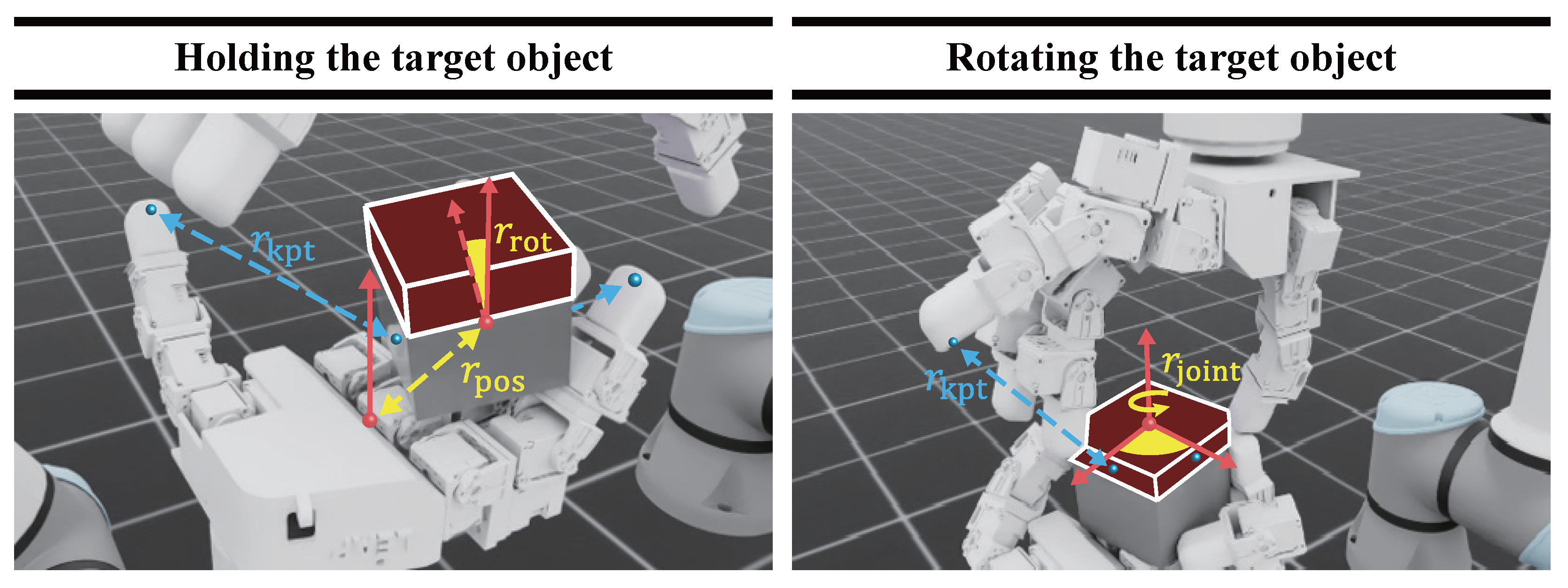
3.4. Reward Design
3.5. Training Procedure
4. Experiments
4.1. Baselines
- (1)
- Naive skill chaining (NC). The holding policy is trained first; an independent rotating policy is then trained, and the two are executed sequentially. The reward functions used for training are configured identically.
- (2)
- Multi-agent proximal policy optimization (MAPPO). This reinforcement-learning approach treats the two hands as independent agents trained concurrently. Both hands observe a shared state and produce separate actions.
4.2. Ablation 1: Distribution Mismatch at the Chaining Boundary
4.3. Ablation 2: Limitations of Simultaneous Training
4.4. Bimanual Manipulation in the Real World
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, K.W.; Qin, Y.; Wang, X.; Lim, S.C. Dextouch: Learning to seek and manipulate objects with tactile dexterity. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 10772–10779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Giudici, G.; Coppola, C.; Althoefer, K.; Farkhatdinov, I.; Li, Z.; Jamone, L. Dexskills: Skill segmentation using haptic data for learning autonomous long-horizon robotic manipulation tasks. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 18–24 October 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 5104–5111. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Che, H.; Qin, Y.; Huang, B.; Yin, Z.H.; Lee, K.W.; Wu, Y.; Lim, S.C.; Wang, X. Robot synesthesia: In-hand manipulation with visuotactile sensing. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 13–17 May 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 6558–6565. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Shi, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Li, F.; Liu, K. DexCap: Scalable and Portable Mocap Data Collection System for Dexterous Manipulation. In Proceedings of the RSS Workshop: Data Generation for Robotics, Cologne, Germany, 15–19 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Qi, H.; Yi, B.; Levine, S.; Malik, J. Learning visuotactile skills with two multifingered hands. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Atlanta, GA, USA, 19–23 May 2025; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 5637–5643. [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen, M.; Karayiannidis, Y.; Kyrki, V. A survey of robot manipulation in contact. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2022, 156, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Varava, A.; Kragic, D. Modeling, learning, perception, and control methods for deformable object manipulation. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, eabd8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, F.; Asfour, T. A bimanual manipulation taxonomy. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 11031–11038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, Y.; Jiang, S.; He, B.; Cheng, Q. Robot learning in the era of foundation models: A survey. Neurocomputing 2025, 638, 129963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Wei, T.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H. Learning to Manipulate Anywhere: A Visual Generalizable Framework For Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–30 September 2025; pp. 1815–1833. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.; Yin, Z.H.; Qi, H.; Abbeel, P.; Malik, J. Twisting Lids Off with Two Hands. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–30 September 2025; pp. 5220–5235. [Google Scholar]
- Urain, J.; Mandlekar, A.; Du, Y.; Shafiullah, M.; Xu, D.; Fragkiadaki, K.; Chalvatzaki, G.; Peters, J. Deep Generative Models in Robotics: A Survey on Learning from Multimodal Demonstrations. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.04380v3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Che, H.; Qi, H.; Ma, Y.; Malik, J.; Wang, X. Lessons from Learning to Spin “Pens”. In Proceedings of the 8th Annual Conference on Robot Learning, Munich, Germany, 6–9 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Foerster, J.; Farquhar, G.; Afouras, T.; Nardelli, N.; Whiteson, S. Counterfactual multi-agent policy gradients. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, T.; Samvelyan, M.; De Witt, C.S.; Farquhar, G.; Foerster, J.; Whiteson, S. Monotonic value function factorisation for deep multi-agent reinforcement learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sunehag, P.; Lever, G.; Gruslys, A.; Czarnecki, W.M.; Zambaldi, V.; Jaderberg, M.; Lanctot, M.; Sonnerat, N.; Leibo, J.Z.; Tuyls, K.; et al. Value-Decomposition Networks For Cooperative Multi-Agent Learning Based On Team Reward. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and MultiAgent Systems, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 2085–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Mulyana, B.; Stankovic, V.; Cheng, S. A survey on deep reinforcement learning algorithms for robotic manipulation. Sensors 2023, 23, 3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutsebaut-Buysse, M.; Mets, K.; Latré, S. Hierarchical reinforcement learning: A survey and open research challenges. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2022, 4, 172–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soviany, P.; Ionescu, R.T.; Rota, P.; Sebe, N. Curriculum learning: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 1526–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X. Reinforcement Learning with Value Function Decomposition for Hierarchical Multi-Agent Consensus Control. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xia, F.; Martin-Martin, R.; Savarese, S. Hrl4in: Hierarchical reinforcement learning for interactive navigation with mobile manipulators. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 16–18 November 2020; pp. 603–616. [Google Scholar]
- Hakhamaneshi, K.; Zhao, R.; Zhan, A.; Abbeel, P.; Laskin, M. Hierarchical few-shot imitation with skill transition models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08981. [Google Scholar]
- Nasiriany, S.; Gao, T.; Mandlekar, A.; Zhu, Y. Learning and Retrieval from Prior Data for Skill-based Imitation Learning. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Atlanta, GA, USA, 6–9 November 2023; pp. 2181–2204. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Fei-Fei, L.; Liu, K. Sequential Dexterity: Chaining Dexterous Policies for Long-Horizon Manipulation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Atlanta, GA, USA, 6–9 November 2023; pp. 3809–3829. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Lim, J.J.; Anandkumar, A.; Zhu, Y. Adversarial Skill Chaining for Long-Horizon Robot Manipulation via Terminal State Regularization. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Auckland, New Zealand, 14–18 December 2022; pp. 406–416. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, U.A.; Xue, S.; Chen, Y.; Xu, D. Generative skill chaining: Long-horizon skill planning with diffusion models. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Atlanta, GA, USA, 6–9 November 2023; pp. 2905–2925. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Mao, J.; Du, Y.; Wu, J.; Tenenbaum, J.B.; Lozano-Pérez, T.; Kaelbling, L.P. Compositional Diffusion-Based Continuous Constraint Solvers. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Atlanta, GA, USA, 6–9 November 2023; pp. 3242–3265. [Google Scholar]
- Mendez-Mendez, J.; Kaelbling, L.P.; Lozano-Pérez, T. Embodied lifelong learning for task and motion planning. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Atlanta, GA, USA, 6–9 November 2023; pp. 2134–2150. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, J.B.; Lau, N.; Silva, F. Curriculum-guided skill learning for long-horizon robot manipulation tasks. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2025, 192, 105032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayar, E.; Iacca, G.; Knoll, A. Curriculum learning for robot manipulation tasks with sparse reward through environment shifts. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 46626–46635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motes, J.; Sandström, R.; Lee, H.; Thomas, S.; Amato, N.M. Multi-robot task and motion planning with subtask dependencies. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3338–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shome, R.; Bekris, K.E. Synchronized multi-arm rearrangement guided by mode graphs with capacity constraints. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on the Algorithmic Foundations of Robotics, Oulu, Finland, 21–23 June 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 243–260. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, V.N.; Orthey, A.; Driess, D.; Oguz, O.S.; Toussaint, M. Long-horizon multi-robot rearrangement planning for construction assembly. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2022, 39, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Cousineau, E.; Kuppuswamy, N.; Agrawal, P. Vegetable peeling: A case study in constrained dexterous manipulation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.07884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pan, C.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y. Efficient bimanual handover and rearrangement via symmetry-aware actor-critic learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 3867–3874. [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka, S.; Ghasemipour, S.K.S.; Freeman, D.; Mordatch, I. Bi-manual manipulation and attachment via sim-to-real reinforcement learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.08277. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Qin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Atanasov, N.; Wang, X. Dynamic handover: Throw and catch with bimanual hands. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.Z.; Tompson, J.; Driess, D.; Florence, P.; Ghasemipour, S.K.S.; Finn, C.; Wahid, A. ALOHA Unleashed: A Simple Recipe for Robot Dexterity. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 4–6 June 2025; pp. 1910–1924. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, D.; Walke, H.R.; Pertsch, K.; Black, K.; Mees, O.; Dasari, S.; Hejna, J.; Kreiman, T.; Xu, C.; Luo, J.; et al. Octo: An Open-Source Generalist Robot Policy. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems, Delft, The Netherlands, 15–19 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wu, L.; Li, B.; Tan, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Xu, K.; Su, H.; Zhu, J. RDT-1B: A Diffusion Foundation Model for Bimanual Manipulation. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations, Singapore, 24–28 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Yang, G.; Wang, X. Open-TeleVision: Teleoperation with Immersive Active Visual Feedback. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 4–6 June 2025; pp. 2729–2749. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Cheng, X.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Ji, M.; Yuan, C.; Yang, G.; Yi, S.; Wang, X. Mobile-television: Predictive motion priors for humanoid whole-body control. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.07773. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, D.J.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Simchi-Levi, D.; Xu, Y. Offline Reinforcement Learning: Fundamental Barriers for Value Function Approximation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Learning Theory, PMLR, London, UK, 2–5 July 2022; p. 3489. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, W.; Huang, B.; Huang, A.; Jiang, N.; Lee, J. Offline reinforcement learning with realizability and single-policy concentrability. In Proceedings of the Conference on Learning Theory, PMLR, London, UK, 2–5 July 2022; pp. 2730–2775. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Galván, B.; López-Rentería, J.; Aguirre-Hernández, B.; Fernández-Anaya, G. Robust stability in discrete control systems via linear controllers with single and delayed time. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 3674628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, K.J.; McClellan, R. Time-varying filter stability and state matrix products. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Digital Audio Effects, Vienna, Austria, 6–10 September 2022; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, M.; Yu, C.; Yu, Q.; Liu, J.; Rudin, N.; Hoeller, D.; Yuan, J.L.; Singh, R.; Guo, Y.; Mazhar, H.; et al. Orbit: A unified simulation framework for interactive robot learning environments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 3740–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Jurado, S.; Muñoz-Salinas, R.; Madrid-Cuevas, F.J.; Marín-Jiménez, M.J. Automatic generation and detection of highly reliable fiducial markers under occlusion. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 47, 2280–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrenko, A.; Allshire, A.; State, G.; Handa, A.; Makoviychuk, V. DexPBT: Scaling up Dexterous Manipulation for Hand-Arm Systems with Population Based Training. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.12127. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, V.; Hinton, G.E. Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In Proceedings of the 27th international conference on machine learning (ICML-10), Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 807–814. [Google Scholar]
- Schulman, J.; Wolski, F.; Dhariwal, P.; Radford, A.; Klimov, O. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.06347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Verma, A.; Orosz, G.; Chaudhuri, S.; Yue, Y.; Burdick, J. Control regularization for reduced variance reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 1141–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, S.; Arlaud, E.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Vividex: Learning vision-based dexterous manipulation from human videos. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Atlanta, GA, USA, 19–23 May 2025; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 3336–3343. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Li, S.; Lyu, C.; Sou, K.W.; Chan, W.S.; Ding, W. MoDex: Planning High-Dimensional Dexterous Control via Learning Neural Hand Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.10983. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter | Range |
|---|---|
| Mass | [0.05, 0.3] kg |
| External Force | [−0.1, 0.1] N |
| External Torque | [−0.1, 0.1] Nm |
| Action Noise | N(0, 0.02) rad |
| Joint Observation Noise | N(0, 0.4) rad |
| Cube Position Observation Noise | N(−0.5, 0.5) cm |
| Method | Norm. Reward ↑ | Success Rate ↑ |
|---|---|---|
| NC | [0.414, 0.504] | [0.205, 0.245] |
| MAPPO | [0.613, 0.668] | [0.412, 0.455] |
| HPPL (Ours) | [0.948, 0.975] | [0.803, 0.840] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.-W.; Lee, J.-W.; Kim, S.; Lim, S.-C. Progressive Policy Learning: A Hierarchical Framework for Dexterous Bimanual Manipulation. Mathematics 2025, 13, 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13223585
Lee K-W, Lee J-W, Kim S, Lim S-C. Progressive Policy Learning: A Hierarchical Framework for Dexterous Bimanual Manipulation. Mathematics. 2025; 13(22):3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13223585
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kang-Won, Jung-Woo Lee, Seongyong Kim, and Soo-Chul Lim. 2025. "Progressive Policy Learning: A Hierarchical Framework for Dexterous Bimanual Manipulation" Mathematics 13, no. 22: 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13223585
APA StyleLee, K.-W., Lee, J.-W., Kim, S., & Lim, S.-C. (2025). Progressive Policy Learning: A Hierarchical Framework for Dexterous Bimanual Manipulation. Mathematics, 13(22), 3585. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13223585







