Abstract
Dexterous bimanual manipulation remains a challenging task in reinforcement learning (RL) due to the vast state–action space and the complex interdependence between the hands. Conventional end-to-end learning struggles to handle this complexity, and multi-agent RL often faces limitations in stably acquiring cooperative movements. To address these issues, this study proposes a hierarchical progressive policy learning framework for dexterous bimanual manipulation. In the proposed method, one hand’s policy is first trained to stably grasp the object, and, while maintaining this grasp, the other hand’s manipulation policy is progressively learned. This hierarchical decomposition reduces the search space for each policy and enhances both the connectivity and the stability of learning by training the subsequent policy on the stable states generated by the preceding policy. Simulation results show that the proposed framework outperforms conventional end-to-end and multi-agent RL approaches. The proposed method was demonstrated via sim-to-real transfer on a physical dual-arm platform and empirically validated on a bimanual cube manipulation task.
Keywords:
reinforcement learning; robot manipulation; artificial intelligence; machine learning; dexterous robotic hand MSC:
68T40
1. Introduction
Dexterous manipulation has emerged as a core capability for enabling robots to perform complex tasks in diverse and unstructured environments [1,2,3]. Robotic hands with high degrees of freedom (DoF), resembling the human hand, can perform delicate and dexterous operations that are difficult to achieve with simple end-effectors such as parallel grippers. In particular, bimanual manipulation extends basic actions such as grasping and moving into higher-level tasks, including tool use, assembly, and other forms of coordinated operations [4,5]. Through the cooperative motion of both hands, these skills can be applied across various domains, including industrial assembly, service robotics, and assistive devices [6,7,8].
Reinforcement learning (RL) has been widely utilized as an effective approach for dexterous manipulation tasks. RL enables the learning of action strategies through exploratory interactions and reward-based feedback, making it possible to achieve effective control even in complex and uncertain environments where explicit modeling is difficult [9]. These characteristics complement the limitations of traditional control algorithms, which require precise mathematical modeling and pre-designed control rules, by allowing the acquisition of generalized manipulation skills that can adapt to external disturbances and variations in object properties. This adaptability makes RL particularly valuable in complex manipulation settings where ensuring modeling accuracy is challenging [1,10,11].
However, learning bimanual dexterous manipulation with reinforcement learning (RL) remains a challenging problem [4,5]. Combining two robotic hands creates a vast state–action space, making the search for optimal actions inefficient, and the complex interdependence between the hands makes it difficult to stably generate cooperative motions in which one hand’s actions are highly dependent on the state of the other [12].
For example, manipulating a cube may appear to be a relatively simple action for a human, but it is a challenging task for a robot. In this task, one hand must stably grasp the cube while the other hand rotates one layer of the cube to a target angle, requiring cooperative motion between both hands. In particular, due to contact changes and slippage during the rotation process, as well as various disturbances such as external forces that continuously occur during object manipulation, the actions of each hand must adapt in real time to the state of the other [13]. These characteristics further complicate the state–action space and make it difficult for reinforcement learning-based policies to acquire stable cooperative behaviors.
To address these challenges, various approaches have been proposed. End-to-end learning jointly optimizes both hands, but the high-dimensional search space often results in low learning efficiency and unstable convergence. Multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) treats each hand as an independent agent, sharing values to improve efficiency, but it often suffers from the limitation that each policy tends to focus on its own rewards, making it difficult to learn fine-grained cooperative behaviors. In addition, long-horizon bimanual tasks consist of sequences of interdependent actions, making exploration and reward function design more complex [14,15,16].
To reduce learning complexity, curriculum learning and hierarchical reinforcement learning (HRL) have been employed [17,18]. Curriculum learning gradually increases task difficulty, which can improve initial learning stability and convergence speed; however, its performance and efficiency are highly dependent on carefully designed difficulty schedules and reward functions, which significantly influence the final outcome [19]. Hierarchical RL decomposes complex tasks into sub-policies, reducing the search space and improving learning efficiency. However, in bimanual manipulation tasks where sub-skills are strongly interdependent, smooth transitions between stages are difficult to achieve, and most existing studies have been limited to single-hand manipulation or relatively simple tasks [18].
To overcome these limitations, we propose a Hierarchical Progressive Policy Learning (HPPL) framework for dexterous bimanual manipulation. The proposed method decomposes the task into sequential sub-policies: first, a policy for one hand is trained to achieve a stable grasp, and then, while this state is maintained, a policy for the other hand is progressively trained for manipulation. This hierarchical structure effectively reduces the exploration space for each policy and enhances learning stability. In particular, by ensuring the state space of the subsequent policy includes the state of the preceding policy, the proposed approach improves the connectivity between the two policies and enables stable learning.
The main contributions of this work are as follows:
- A novel framework (HPPL) combining hierarchical task decomposition with progressive policy learning for dexterous bimanual manipulation is proposed.
- A solution to the policy connectivity problem is presented by utilizing the state generated by the preceding policy as a condition for the subsequent policy’s action generation.
- The HPPL framework outperforms end-to-end and multi-agent RL baselines and is empirically validated on a bimanual cube manipulation task via transfer to a real bimanual robot system.
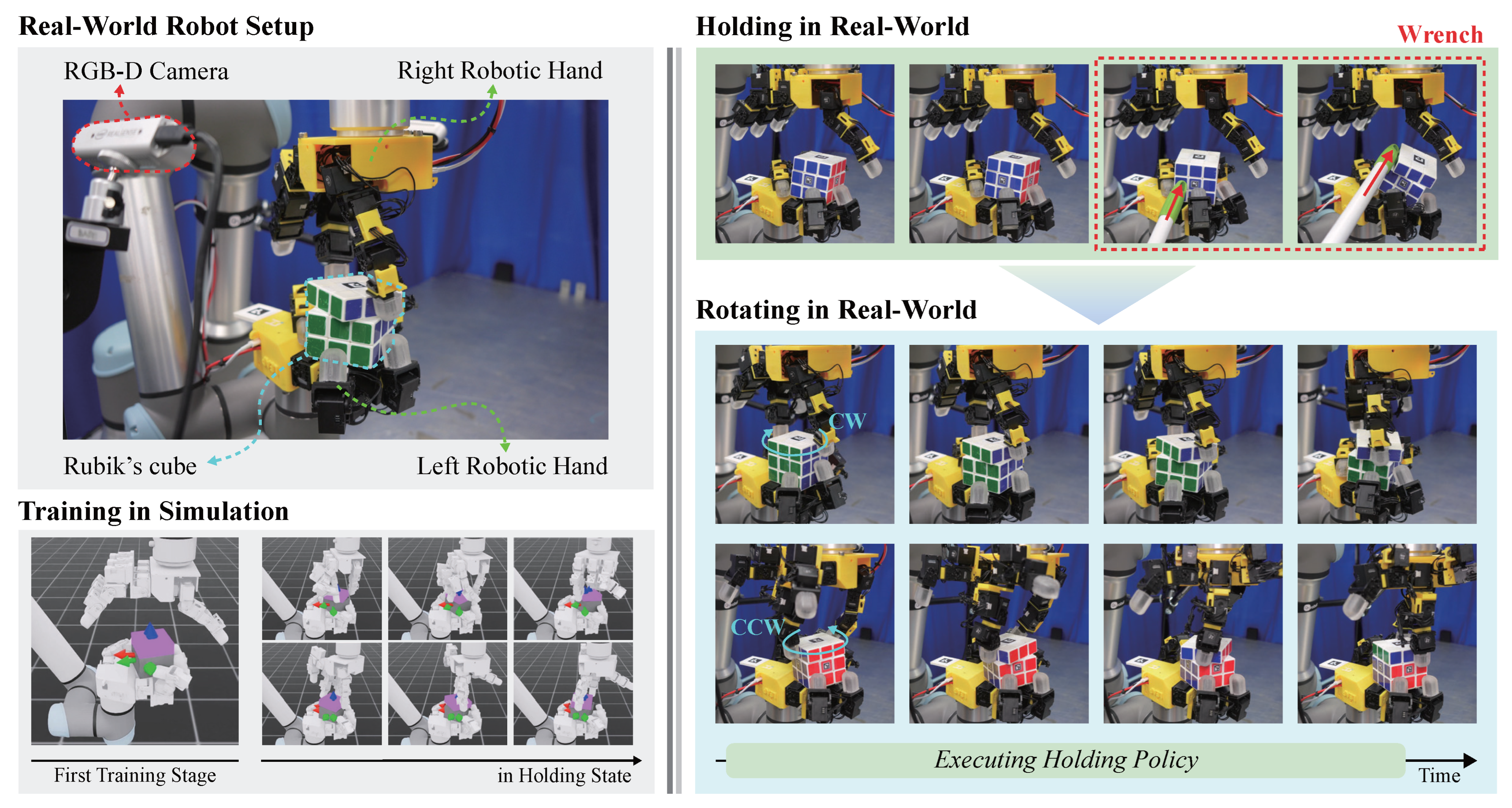
Figure 1 illustrates the proposed training pipeline and robot system. This framework provides a structured and scalable approach to learning complex cooperative skills in bimanual dexterous manipulation. By integrating hierarchical decomposition with progressive policy training, the method enables efficient exploration, stable coordination. The effectiveness of the proposed approach was established via quantitative comparisons against baselines and empirically validated on a bimanual cube manipulation task through sim-to-real transfer on a dual-arm system.
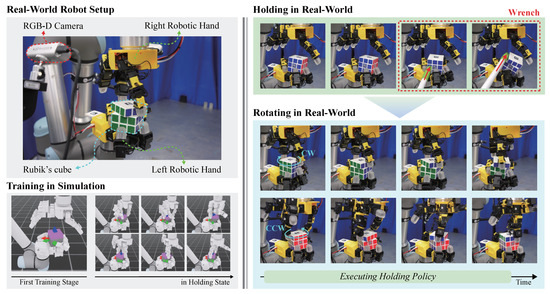
Figure 1.
System and training overview with a real-world demonstration. (Left) Hardware setup (two robot arm-hands and RGB-D cameras) and the simulation-based training pipeline. (Right) With the Holding policy active, the left hand maintains a stable grasp even under external wrench disturbances, while the Rotating policy rotates the cube in the CW/CCW direction.
2. Related Work
Hierarchical and curriculum learning have been studied as representative approaches to address the inefficient exploration problems in high-dimensional and long-horizon RL tasks. Hierarchical reinforcement learning (HRL) decomposes complex long-horizon tasks into higher-level and lower-level policies, improving efficiency by reducing the exploration space. Such modularization also allows learned sub-policies to be reused across tasks [20]. This approach has been leveraged to enable exploration and manipulation tasks in conjunction with mobile manipulators [21], and to facilitate adaptation to novel tasks when combined with few-shot imitation [22,23]. To sequentially integrate subtasks decomposed from long-horizon problems, skill chaining methods have been proposed, where individual skills are linked in sequence to complete the overall task while ensuring smooth transitions between skills. This has enabled challenging applications such as block assembly with dexterous hands [24] and furniture assembly [25]. More recently, diffusion-based models have been explored to address instability in skill transitions [26,27,28]. However, sequential chaining approaches still face limitations when applied to highly cooperative and complex tasks, as instability in skill transitions remains a major challenge.
Curriculum learning gradually increases task difficulty, starting from simpler problems, to ensure stable initial learning and faster convergence. This approach contributes to the stability of long-horizon training, and has been combined with skill chaining to bridge gaps between skills through transition policies [29], or to achieve increasingly complex tasks under sparse rewards [30]. Nevertheless, curriculum learning heavily depends on the manual design of task difficulty levels and reward structures, which becomes even more challenging in complex bimanual cooperation scenarios. In this work, we introduce a progressive and hierarchical learning framework that decomposes long-horizon policies and incrementally learns subsequent policies conditioned on states generated by preceding policies. This approach enhances training stability while improving connectivity across policies.
Bimanual manipulation enables the execution of more complex and diverse tasks compared to single-arm manipulation by allowing cooperative use of both hands. To implement coordinated movements in robots, approaches based on task and motion planning have been proposed [31,32,33]. More recently, learning-based approaches leveraging reinforcement learning (RL) in large-scale simulators capable of parallel training have been explored. These methods have been applied to task-specific scenarios such as peeling vegetables with dexterous hands [34], twisting lids off containers [11], and performing rearrangement, handover, and assembly tasks [35,36,37]. However, they often remain limited to learning a single control policy optimized for a single task, making it challenging to address tasks that require continuous interaction between two hands. To improve learning efficiency, expert demonstrations have been widely used to constrain the exploration space and accelerate policy training [38,39,40,41,42]. Nevertheless, generating large-scale demonstrations remains a demanding problem, and applying trained policies to environments beyond the distribution of the demonstration data is still limited. In this work, instead of relying on predefined motion primitives or pre-collected demonstrations, we directly train low-level control through deep RL and focus on the challenge of enabling each policy to adapt to states that dynamically change due to the actions of the other hand during task execution.
3. Methodology
3.1. Problem Formulation
The objective of this study is to learn a policy that, in bimanual dexterous manipulation, simultaneously achieves a stable grasp with the left hand and a rotation of the cube layer with the right hand. Inter-hand interactions are highly coupled: an action by one hand instantaneously changes the object’s state and thus influences the control of the other. For efficient learning, we decompose the overall task into two subtasks, which we formalize as the following two Markov Decision Processes (MDPs):
In this Equation (1), denotes the state space, the action space, the reward function, and the transition dynamics. Each policy () is conditioned on its observation (), as expressed in . The two observations (one per hand) consist of each hand’s local information and the cube information, with the cube information shared between the two. The action () is generated by the policy () conditioned on the observation.
The action space is decomposed as , where controls only and controls only . This separation of control channels prevents any overlap or redundancy in the action space. Both policies’ observations commonly include the object state . However, includes the target pose error for stable grasping and the fingertip-to-cube keypoint distances, whereas includes the layer joint positions and angular velocities for rotation, as well as the fingertip-to-layer keypoint distances. Therefore, shared information is confined to a single object state, while derived relative features differ, minimizing observation redundancy.
Left-hand MDP (): transition kernel under the idle-right-hand assumption. During training of the left-hand policy, the right hand is kept idle with . To simulate potential contact changes and reaction forces that may arise in subsequent interaction, we apply a random external wrench (force/torque) to the manipulated object. The disturbance is sampled from a predefined Gaussian distribution and the resulting transition kernel is expressed as follows:
denotes the next state obtained after applying an action in the current state s. Accordingly, the left hand is trained independently, and the grasp policy is optimized with respect to the reward , which promotes a stable grasp. During left-hand training, truncated-Gaussian wrenches are applied at random intervals (0.5–1.5 s), with magnitudes bounded to N, and Nm, reflecting hardware limits. By design, the policy responds primarily to disturbance scale and activation boundaries rather than the precise distributional shape, thereby preventing over-reliance on the exact Gaussian parameters.
Right-hand MDP: transition kernel with respect to the left-hand policy. After the left hand has been pre-trained, the right hand learns its manipulation policy over the state distribution induced by the executing left-hand policy. Accordingly, the transition kernel of the right-hand MDP is defined by marginalizing over the left-hand action policy as follows:
Equation (3) defines the right-hand transition kernel by marginalizing over the fixed left-hand policy. The expectation in Equation (3) is implemented via a single-sample Monte Carlo estimator in a vectorized simulation. During right-hand training, the left-hand policy is frozen and executed as part of the environment, and is sampled from in each parallel environment. Consequently, no explicit integration is required, and the transition is realized by the simulator/environment under a fixed left-hand control policy. The initial state distribution of the right hand, , is defined by restricting the left-hand on-policy distribution to the grasp-success set , and is expressed as follows:
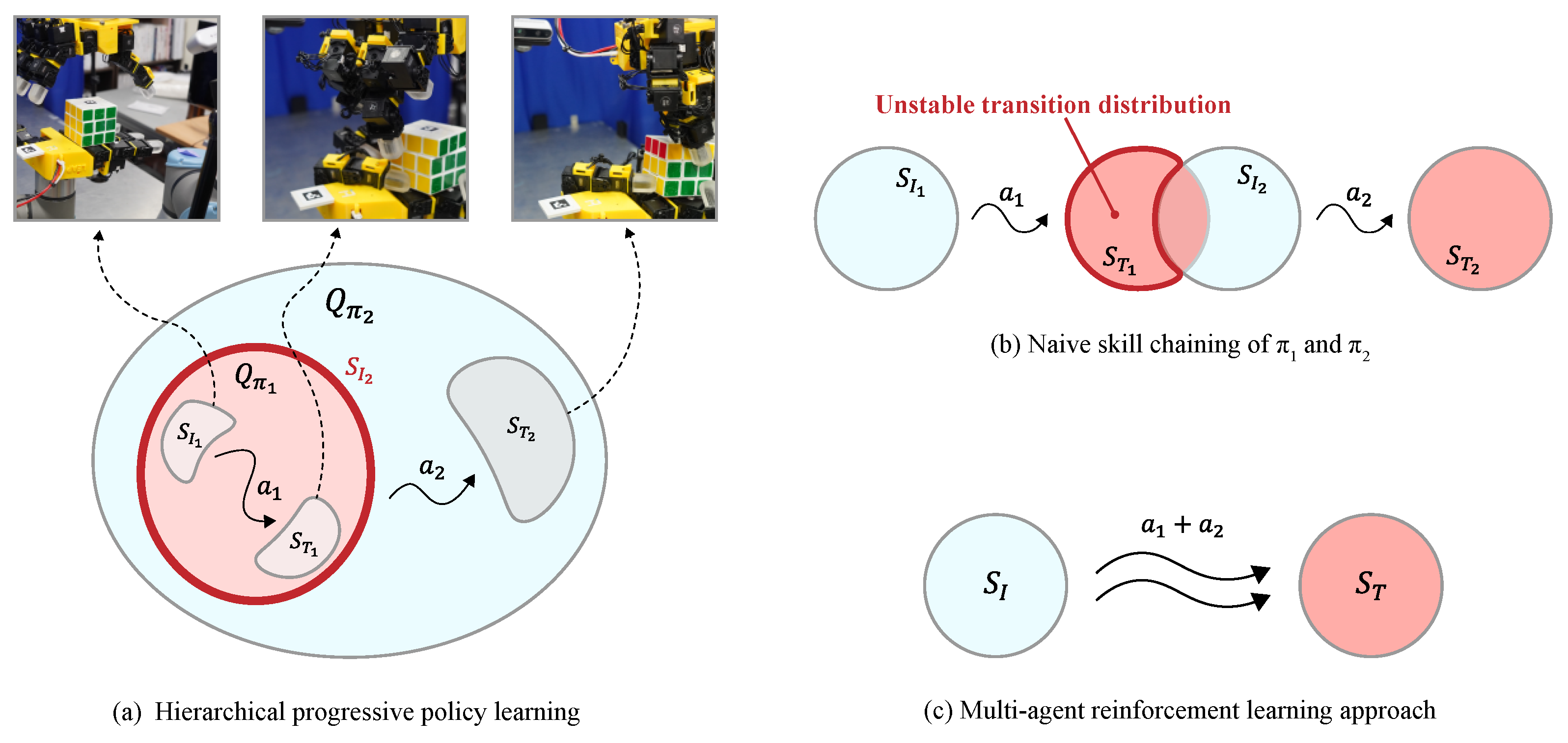
This is a normalized restriction of the actual deployment distribution and thus preserves policy connectivity. Moreover, for any rotation-relevant subset if then uaranteeing adequate coverage over the task-relevant manifold. In terms of concentrability, choosing proportional to yields a finite, typically smaller coefficient which improves sample efficiency and numerical stability [43,44]. This construction ensures that the right hand learns manipulation while the left hand maintains a stable grasp on the cube, thereby reducing the exploration space and improving policy connectivity. Figure 2 illustrates the proposed hierarchical progressive learning process.
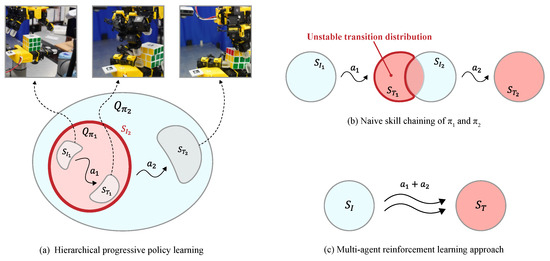
Figure 2.
Comparison of policy-design paradigms for bimanual manipulation. denotes the initial state distribution of task i, denotes the terminal state distribution reached after executing the action , and denotes the on-policy state distribution actually experienced under policy . (a) Hierarchical progressive policy learning: train first, then train on the state distribution induced by , mitigating distribution mismatch between skills. (b) Naive skill chaining: a mismatch between the terminal distribution of and the initial distribution of yields unstable transition distributions. (c) Multi-agent reinforcement learning: the two hands act as independent agents, but mutual interference makes learning unstable.
(1) State: The environment uses a shared base state space . Specifically, comprises: left-hand joint positions (16), right-hand joint positions (17, including the wrist), cube body pose (7), cube layer pose (7), cube-body keypoints (12), cube-layer keypoints (12), cube-layer joint position (1), holding-goal pose (7), each fingertip position (24) and the previous action (16 + 17). Here, the keypoints are virtual locations inside the cube, predefined to facilitate cube manipulation and used to guide each policy toward appropriate manipulation behaviors.
For reward computation, additionally include relative features: two scalars for the position error and the z-axis alignment error between the cube body and the holding goal, and four scalars for the minimum relative distances between the fingertips and the keypoints. Moreover, to compensate for partially unobserved dynamics, the joint angles of both hands and the previous action include a 3-step history. From the common state space , the left- and right-hand policies use different observations tailored to their respective tasks.
(2) Action: At each step, the left and right hand action provied by the each policy network is a relative target position. Actions take values in . The left hand joint position () uses a 16-dimensional vector, and the right hand joint position () uses a 17-dimensional vector that includes one wrist joint. The action a is converted to physical units using an action scale and added to the previous joint position; the resulting position command is defined as:
In this Equation (5), t denotes the time step, and constrains joint commands to remain within joint limits. To suppress abrupt changes, a first-order exponential moving average (EMA) low-pass filter is applied to , and the command is converted into desired torques via low-level PD control and applied to the robot. In practice, exponential moving-average (EMA) smoothing and incremental joint position control are widely adopted stabilization techniques in RL-based robot [1,3,13,24,34]. They act as lightweight low-pass filters on policy outputs, reducing command jitter and making the subsequent PD tracking more robust without introducing additional dynamics or tuning complexity [45,46].
3.2. System Setup
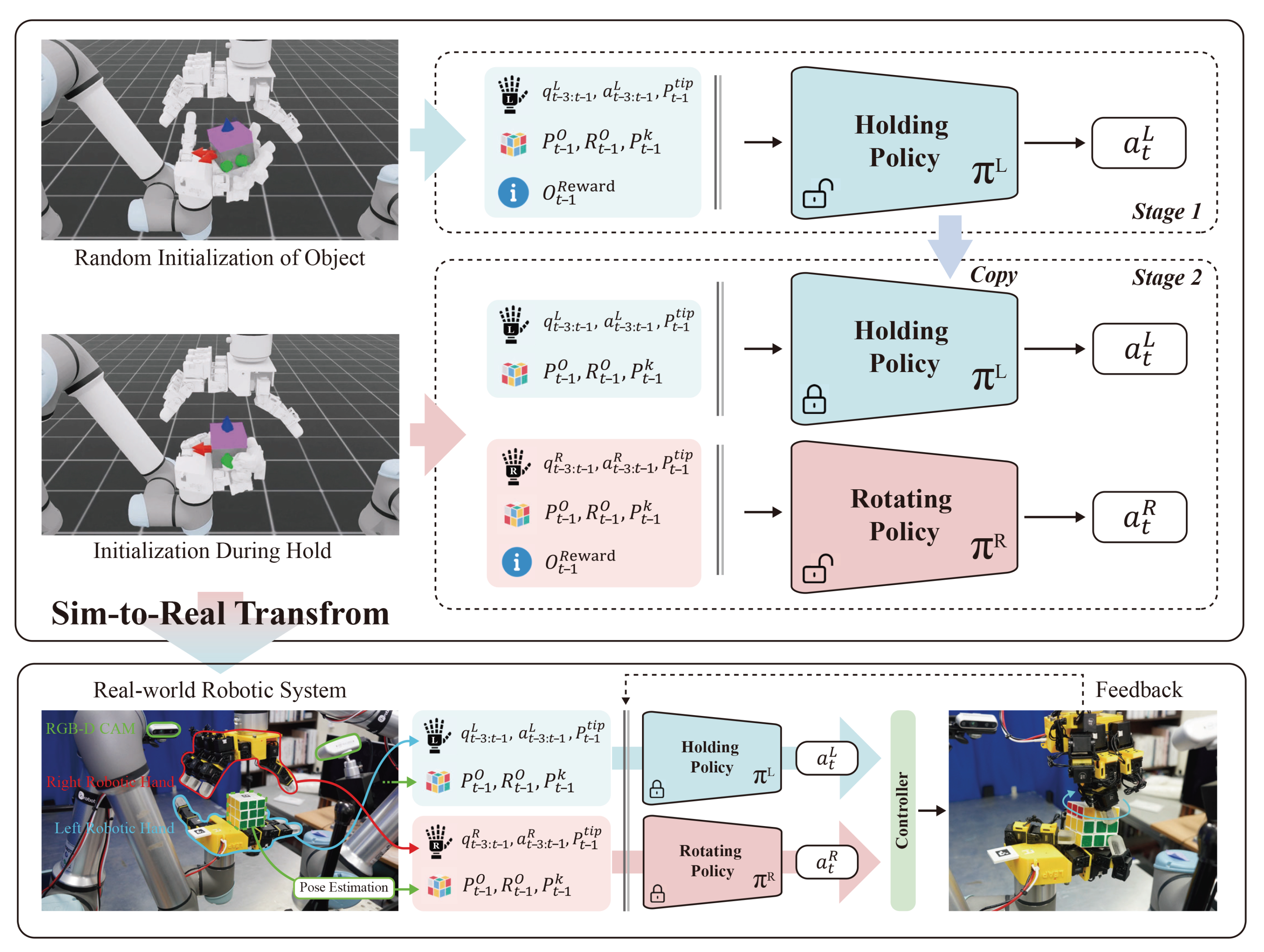
Figure 3 illustrates the training of each policy in simulation and the sim-to-real transfer process. The system is a bimanual robot in which each arm provides 22 DoF—a UR5e (6 DoF) (Universal Robots, Odense, Denmark) coupled with a LEAP-Hand (16 DoF)—for a total of 44 DoF. To improve contact stability and grasp quality, the default rigid fingertips on the LEAP-Hand were replaced with elastomer fingertips of identical geometry. Commands from the trained policies are executed through a ROS-based low-level controller, which converts policy actions into control signals. Reinforcement learning is conducted in the IsaacLab simulator [47]. We instantiate a digital twin of the real bimanual system and model the manipulated object as a cube with a rotatable layer matching the real setup. The control rate is set to 60 Hz in both simulation and the physical system.
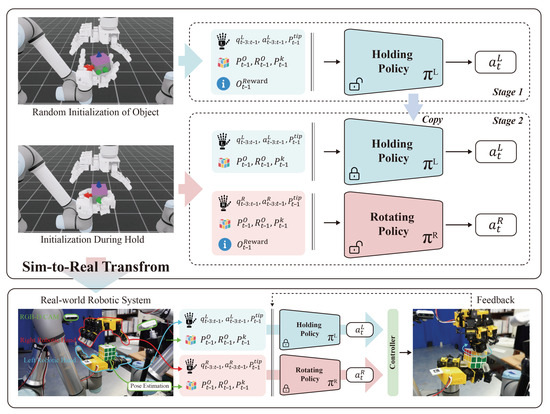
Figure 3.
Two-stage training and zero-shot sim-to-real transfer. denotes the 3-step history of the robot’s joint angles, and denotes the 3-step history of actions. P denotes position: is the 3D position of the cube body/layer, the predefined keypoint positions, and the fingertip positions. R denotes rotation: is the quaternion of the cube body/layer. Finally, denotes the relative features used for reward computation (e.g., distance to the goal, z-axis alignment error, keypoint distances, joint progress/velocity, etc.). Stage 1 trains the Holding policy from random initializations. Stage 2 initializes from random holding states and trains the Rotating policy while executing the frozen Holding policy. During transfer, both policies run concurrently, and the controller maps their actions to low-level commands that drive the real robot.
For robust sim-to-real transfer, the policy observations include the centroids of the cube body and the rotatable layer as key inputs. Additional keypoints are defined with respect to these two centroids. In the real environment, ArUco markers [48] are attached to the cube and the robot hands; we estimate each marker’s pose and compute the centroids and keypoints from these estimates. The pose estimation pipeline is synchronized with the policy loop and operates at 60 Hz.
3.3. Task Description
We focus on a cube-manipulation task that simultaneously requires multi-finger dexterity and bimanual coordination. To reduce the training complexity of this problem, which requires explicit consideration of inter-hand interactions and the resulting changes in the object’s state, we decompose the overall task into two stages. The subsequent policy is trained on the stable state distribution induced by the preceding policy, thereby improving policy connectivity and training stability. The objective is to rotate a designated cube layer by 90 (deg) about its axis in either clockwise or counterclockwise (CW/CCW) direction, while maintaining a stable grasp and avoiding collisions between the hands and fingers throughout the process.
Holding object (left hand) The goal is to establish a stable grasp on the object and to align and maintain the cube’s pose. A robust grasp policy is required that can withstand disturbances caused by external wrenches (forces/torques) arising during subsequent manipulation.
Rotating layer (right hand) The goal is to rotate the designated cube layer by 90(deg) in the commanded direction. This task is executed while the preceding policy holds the cube; the controller must avoid exerting excessive forces that could destabilize the cube’s pose and must perform the manipulation while avoiding collisions with the left hand.
At the start of each episode, the two robotic hands are initialized in a static configuration with their palms facing each other, and the cube is spawned at a random location within the left palm. In the Holding object scenario, the right hand is fixed in the static pose and only the left-hand manipulation motion is trained. In the Rotating layer scenario, the right hand is trained while the preceding holding policy is active. During bimanual interaction with the cube, various events may occur. Among these, failure modes, such as object drops, finger–finger interference, and jamming, provide little informative learning signal. To avoid unproductive, high-dimensional exploration, we therefore introduce early-termination criteria to promote efficient exploration. An episode is reset if the cube falls to the floor or the pose-alignment error exceeds a tolerance. Episodes are also reset if the cube cannot be aligned or the layer cannot be rotated within the time limit.
3.4. Reward Design
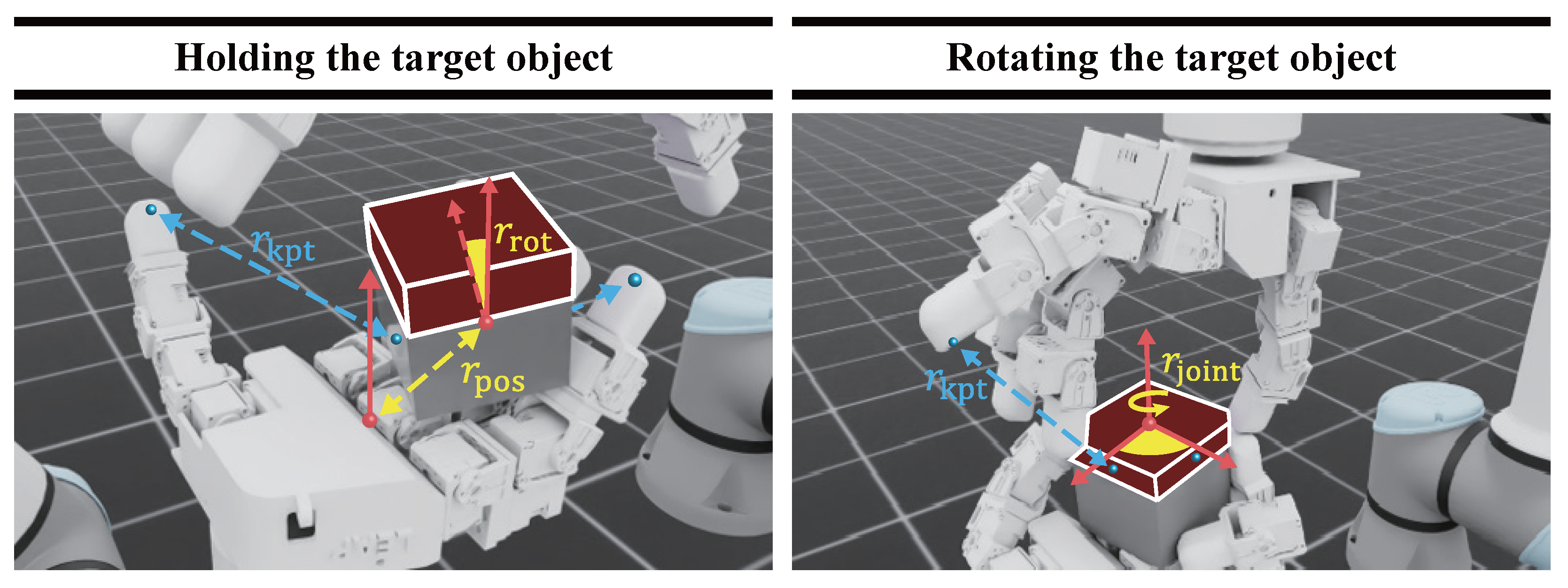
In reinforcement learning, training a successful control policy requires reward signals that are sufficiently dense to make exploration tractable. Dense rewards are a key factor that enables the agent to acquire the intended behavior more quickly and efficiently [49]. However, applying a single reward function to a complex task such as bimanual manipulation can destabilize training due to conflicts among sub-goals and diffuse exploration. Therefore, we decompose the overall task into two subtasks and, for each subtask, design an intuitive, dense reward function to promote efficient learning. Figure 4 illustrates the reward components for each subtask. The proposed reward functions are designed to correspond directly to the target metrics, thereby guiding the agent to converge toward the desired behaviors. Additionally, inspired by [49], a reward function is designed such that the agent can only receive rewards for movements toward the goal.
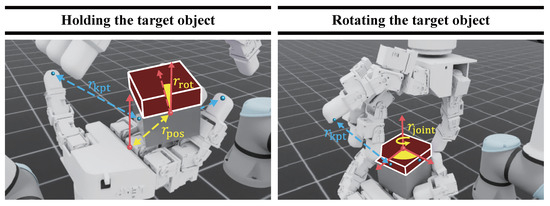
Figure 4.
Visualization of reward components by task. (Left) Holding: Yellow arrows indicate the rewards and based on target position error and z-axis alignment error, respectively, and blue arrows indicate the keypoint reward based on the distance between fingertips and keypoints. (Right) Rotating: Yellow arrows indicate the rotation reward for the layer, and blue arrows indicate based on fingertip–keypoint distances.
Holding the target object: The role of the left hand is to maintain a stable grasp on the cube so that the right hand can rotate the layer. At the same time, it must withstand wrenches (forces/torques) induced by the right-hand manipulation. To realize these capabilities, the holding reward is designed as follows:
In this Equation (6), is a reward that reduces the rotational error for z-axis alignment between the object and the target pose, and is a reward that reduces the position alignment error. is is a terminal reward granted upon achieving the alignment goal, and is an energy penalty, , that suppresses excessive joint commands, thereby reducing oscillations and improving energy efficiency and stability. Among these components, is designed as follows:
In this Equation (7), is defined as z-axis alignment error between the object and the goal. We set as a constant for numerical stability. was set considering the position/rotation errors observed in the task and the success tolerance, chosen to retain informative reward values near the goal and to avoid gradient vanishing. If the z-axis alignment error is within the tolerance , the rotation alignment is deemed successful and a bonus is awarded. In our experiments, (rad). The position alignment reward is designed as follows:
In this Equation (8), is defined as the euclidean distance between the object and the goal. We use the same value . If the position alignment error is within the tolerance , the position alignment is deemed successful and a bonus is awarded. In our experiments, (m). This value accounts for (i) centimeter-level errors induced by perception, contact, and control in the real system, and (ii) numerical noise in the simulator. It provides a dense signal during the approach phase without reward saturation while defining a physically achievable success region. Additionally, the bonus weights in the reward function were used to provide each agent with an intuitive signal toward the final objective, thereby accelerating policy convergence. To prevent excessive variance, a continuous reward served as the primary learning signal, and the bonus scale was set with respect to the total reward each agent receives at each time step. When both the rotation- and position-alignment success conditions are satisfied, a success bonus is granted to accelerate convergence to the neighborhood of the goal.
The keypoint term is designed as follows:
In this Equation (9), is defined based on the nearest distance between each fingertip and the cube’s predefined keypoints. First, the keypoints are transformed from the object’s local frame to the world frame using the current object pose. Then, for each finger, we compare the euclidean distances to up to four keypoints and select the nearest one; the corresponding distance is used as that finger’s value . This procedure is applied independently for each finger. We use the same , and a per-finger bonus is awarded when the distance falls within the tolerance (m). For holding, we aggregate fingertip-keypoint terms with uniform per-finger weights and a contact-count bonus, which consistently promotes multi-contact grasps and avoids bias toward any single digit under randomized initial states and disturbances.
The final reward is computed by applying weights to the above components, with . In addition, if the object deviates significantly from the goal or drops from the palm, we assign a separate penalty and reset the environment to limit exploration of unstable states.
Rotating the target object: The role of the right hand is to grasp the layer and rotate it. To realize these capabilities, the rotating reward is designed as follows:
In this Equation (10), is a reward that encourages a monotonic decrease in the layer’s error relative to the target joint angle, and is defined as follows:
In this Equation (11), is the success indicator for the holding the target object condition, encouraging manipulation only while the cube is stably maintained. denotes the current error with respect to the goal joint angle, and is the minimum error observed up to time t. Thus, the agent receives a reward when the target angle error drops below its previous minimum. denotes the layer’s angular velocity and encourages maintaining rotation.
When the angle error does not exceed 0.088 (rad) (5.0 deg), a success bonus is awarded, accelerating convergence to the neighborhood of the goal. Because dense rewards persist up to completion in the holding task, we set . For the rotating task, we set to compensate for the pre-completion reward drop that occurs when the monotonic progress/velocity gate ceases operating at the target. Since the two tasks are trained separately and independently, this does not induce bias toward any particular subtask. The terms and are configured as in the holding the target object task but evaluated from the right-hand perspective. Specifically, is defined based on the nearest distance between each right-hand fingertip and the layer’s keypoints, and is the right hand’s action-magnitude penalty. The weights are set to . As in the previous task, if the cube is dropped, a penalty of is applied and the environment is reset.
3.5. Training Procedure
Each policy is trained from simulated experience in IsaacLAB [47], a highly parallel, GPU-accelerated physics engine. Training was conducted on a computer equipped with an NVIDIA RTX 4090, and the process lasted approximately 7.0 h. Both the policy and value networks are three-layer MLPs with hidden sizes 256-256-128 and ELU [50] activations. To train the control policy, we use Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) [51] with the following hyper-parameters: clipping , discount factor and 0.016 KL threshold. Simulations run with 2048 parallel environments, a simulator time step of (s), and four physics substeps per step.
A two-stage progressive training scheme is employed: (i) the left-hand grasp policy is first trained under external wrenches with the right hand kept idle; (ii) the trained left-hand policy is then frozen, and the right-hand rotation policy is trained. To facilitate domain transfer, domain randomization is applied to the object’s mass, position, and keypoints. Instead of a separate probabilistic state-estimation model, domain randomization was applied during training by injecting bounded noise into the object/layer pose and keypoints, as well as the mass. Table 1 shows the domain randomization parameters applied. The noise ranges were set considering ArUco accuracy, calibration quality, and sensor noise, thereby enhancing the policy’s robustness to observation errors.

Table 1.
Domain Randomization Parameters. Observation and action randomizations follow a Gaussian distribution. Other randomizations are uniformly sampled from the specified range.
4. Experiments
This section validates the proposed method through a quantitative comparison against baselines. The primary evaluation criterion is policy connectivity between the two skills, assessed by the success rate on the final rotating task. In other words, we evaluate whether the two policies can be connected to accomplish the final task. All methods are evaluated under the same reward functions, observations, policy parameterization, and training environment. Normalized return and success rate are used as evaluation metrics.
Experiments and analyses are mainly conducted on the following perspectives: (i) Analyze how distribution mismatch at the policy-chaining boundary affects performance. (ii) Compare performance against approaches that train multiple agents concurrently.
4.1. Baselines
- (1)
- Naive skill chaining (NC). The holding policy is trained first; an independent rotating policy is then trained, and the two are executed sequentially. The reward functions used for training are configured identically.
- (2)
- Multi-agent proximal policy optimization (MAPPO). This reinforcement-learning approach treats the two hands as independent agents trained concurrently. Both hands observe a shared state and produce separate actions.
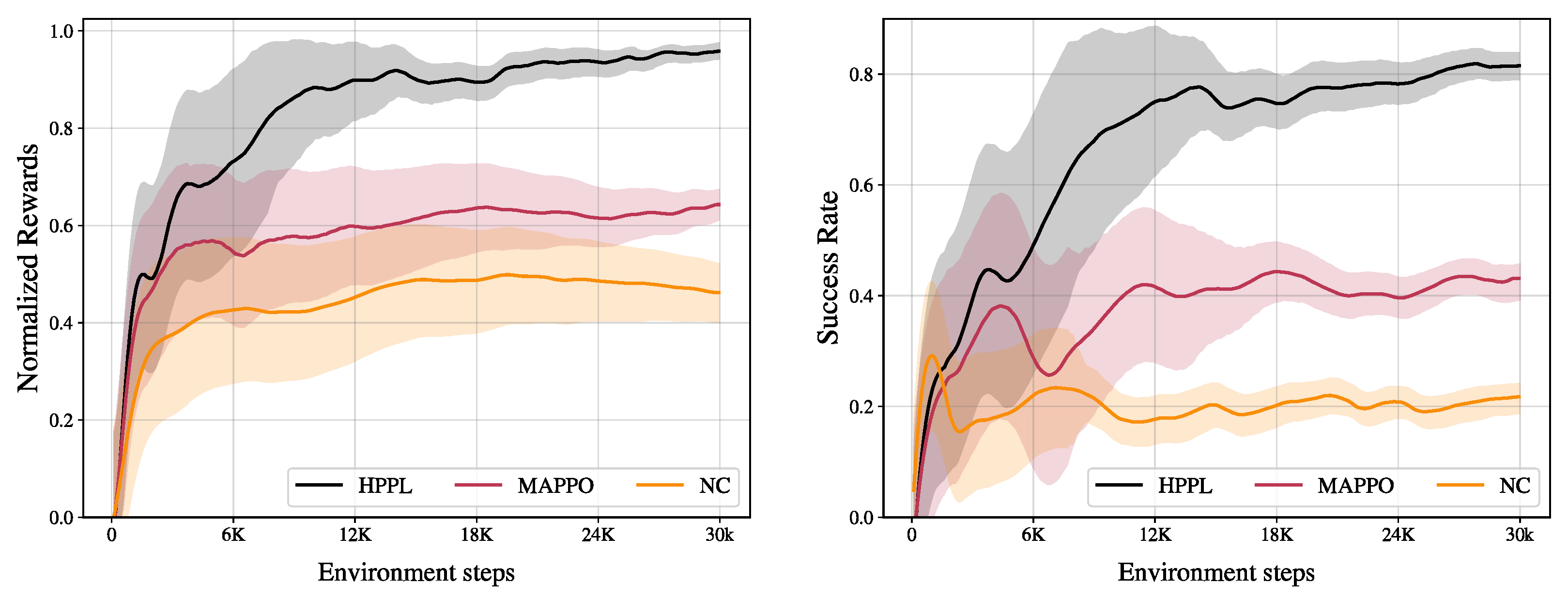
Figure 5 and Table 2 compare performance up to 30,000 environment steps, averaged over 12 random seeds. All results are reported as the mean ± standard deviation over 12 random seeds under identical settings. Each seed was evaluated on a large number of episodes via 2048 parallel environments, reducing uncertainty in the estimate of the final success rate. Because the between-method mean gaps observed during training were large, using seeds allowed us to clearly distinguish performance trends. HPPL achieves a final success rate of (mean ± sd; ; 95% CI ), normalized reward of (95% CI ). NC achieves a final success rate of (95% CI ), normalized reward of (95% CI ). MAPPO achieves a final success rate of (95% CI ), normalized reward of (95% CI ). CIs computed across seeds using two-sided t-intervals.
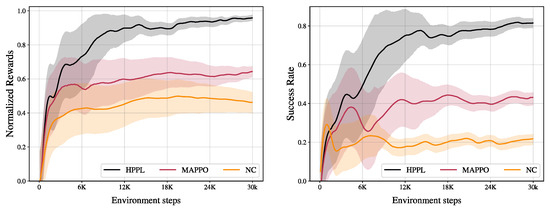
Figure 5.
Training performance comparison. (Left) Normalized reward and (Right) success rate plotted against environment steps. Each curve is the mean over 12 random seeds, and the shaded area indicates the standard deviation across seeds. HPPL shows the best final performance and faster convergence on both metrics.

Table 2.
Quantitative comparison in simulation. Normalized reward and success rate (higher is better) are reported as mean, standard deviation and 95% confidence interval over 12 seeds. The upward arrow indicates that larger values correspond to higher performance.
The mean denotes the arithmetic average of the final task success rates across random seeds, and the deviation denotes the standard deviation of success rates across random seeds under the same setting. The proposed HPPL outperforms the baselines in both sample efficiency and final performance. The normalized reward reaches 0.8 within the first 6k steps and gradually converges near 0.95, while the success rate rises to 0.8. In contrast, MAPPO plateaus at a reward of about 0.6 and a success rate of 0.4, and NC remains around a 0.45 reward and 0.2 success rate. The early-training variance band is also narrowest for HPPL, indicating greater training stability. These results suggest that the improvements are not due to exceptional outcomes from particular seeds but are reproducible across random seeds.
4.2. Ablation 1: Distribution Mismatch at the Chaining Boundary
NC trains the holding policy and the rotating policy independently and then connects them sequentially at execution time. PPO is used identically to train each policy. However, at the chaining boundary a distribution mismatch arises because the initial distribution of , does not encompass the terminal distribution actually induced by , . When rewards are bounded by and the discount factor is , the distance between the two distributions can be measured by total variation:
That is, the larger the distance between the two distributions, the greater the performance gap of the subsequent policy becomes [52]. The proposed HPPL aligns the initial training distribution with the left hand’s stable holding distribution, thereby reducing and, consequently, strengthening inter-policy consistency. In contrast, under NC, tends to be large, which makes policy composition unstable and ultimately degrades final task performance.
In deployment, small errors from accumulate and may cause to start from states outside its training distribution or to encounter such states during execution. Under nonlinear dynamics with contact and friction, this increases transition instability and reduces the success rate.
By contrast, the proposed approach trains while executing a frozen , ensuring and thus guaranteeing policy connectivity. As a result, for the same number of steps, the proposed method achieves significantly higher normalized return and success rate than NC, with lower variance.
4.3. Ablation 2: Limitations of Simultaneous Training
MAPPO treats the holding policy and the rotating policy as independent agents and trains them concurrently. The same reward function as in the proposed method is used. However, each agent receives a shared reward for the overall task rather than an individual reward based on its own action. Because each policy outputs a lower-dimensional action than a single agent that controls both hands at once, this approach can improve training efficiency.
However, when the two policies are updated at the same time, the counterpart policy makes the environment nonstationary. As the counterpart changes during training, the induced distribution shifts, which leads to instability. Because each policy must both succeed at its own task and adapt to the motions generated by the other policy, the effective product space of states and actions becomes larger and exploration becomes more difficult. Moreover, informative rewards occur only when the behaviors of both hands are appropriate at the same time, so the density of useful samples is low early in training. This reduces sample efficiency and slows initial convergence.
In contrast, the proposed method addresses these issues with a staged training strategy. To chain the two policies, it first establishes a stable state distribution for the holding task and then trains the rotating task on top of it. Because the subsequent policy is trained while the counterpart policy is fixed, training is stable and the two policies remain well connected. In addition, policy-specific rewards are applied directly, which effectively guide appropriate motions. Consequently, the proposed method outperforms MAPPO in both initial sample efficiency and final performance, and it exhibits lower variance.
4.4. Bimanual Manipulation in the Real World
The holding policy and the rotating policy trained in simulation were transferred to the real robot in a zero-shot. Without any additional fine-tuning or parameter changes, the system executed the entire task on the physical robotic system. Among the observations, the poses of the cube body and the layer and the positions of the keypoints were estimated using ArUco markers attached to the cube and the robot. As shown in Figure 3, two RGB-D cameras (Intel RealSense D435, Intel Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA) detected the markers, and robot-camera extrinsic calibration mapped them to the world frame.
In transfer, the left hand maintained a stable grasp while the right hand rotated the layer by 90 (deg) in the clockwise and counterclockwise directions. Notably, the grasp remained stable under external disturbances during holding, and the object pose recovered, which enabled the right hand to perform the layer-manipulation task. These results demonstrate the sim-to-real feasibility of the proposed approach.
The real-world experiments show that the proposed hierarchical progressive learning approach—by separating the grasp-and-rotate roles for cube manipulation—mitigates excessive expansion of the combined state–action space and the ambiguity arising from a shared reward, improves policy connectivity, and thereby enables sim-to-real transfer to a physical robot. The primary failure modes were slip under large external forces and contact failures, which we expect can be mitigated via tactile-vision fusion and more robust contact-planning strategies.
The holding policy and the rotating policy trained in simulation were transferred to the real robot in a zero-shot. Without any additional fine-tuning or parameter changes, the system executed the entire task on the physical robotic system. As described in Section 3.2 (System Setup), the system configuration implements the same bimanual robot as in the simulator, and the experiments follow the same initialization protocol as in simulation. Both hands are initialized to the joint angles used in simulation, and the cube is randomly placed within the region at the base of the left hand. Among the observations, the poses of the cube body and the layer and the positions of the keypoints were estimated using ArUco markers attached to the cube and the robot. As shown in Figure 3, two RGB-D cameras (Intel RealSense D435) detected the markers, and robot-camera extrinsic calibration mapped them to the world frame. The proprioceptive position data of each robotic hand are collected in the same format as in simulation and included in the observations. All coordinates are transformed with respect to the world frame, consistent with the simulation, with the origin at the base of the left arm.
The episode length was set to 10 s, as in simulation, and experiments were conducted for both CW and CCW directions. The success criterion for each episode is to reach the target layer’s angle within tolerance by the right hand within 10 s while maintaining a stable grasp with the left hand. The tolerance is 0.088 rad (5.0 deg), identical to the simulation. A trial is deemed a failure if any predefined failure mode occurs—such as a timeout, dropping the cube, or loss of contact. Additionally, during the holding stage, light disturbances such as taps and pulls were applied by a human hand to verify grasp stability.
Quantitative evaluation uses the success rate over the number of trials per condition as the primary metric. In real-world transfer, only the HPPL model that achieved the highest performance in simulation was tested, with a total of 65 trials. A total of 41 successes were observed, corresponding to an overall success rate of 63.08%. All experiments were conducted zero-shot without additional tuning, and the reported success rate suggests that transfer performance was retained despite observation and contact discrepancies between simulation and the real environment. It was also observed that the grasp was maintained when disturbances were applied during the holding stage, and that a stable grasp was maintained during the right hand’s rotation as well. The real-world experiments show that the proposed hierarchical progressive learning approach—by separating the grasp-and-rotate roles for cube manipulation—mitigates excessive expansion of the combined state–action space and the ambiguity arising from a shared reward, improves policy connectivity, and thereby enables sim-to-real transfer to a physical robot. Nevertheless, policies trained in simulation generally experience reduced performance upon transfer to the real environment. These performance losses are primarily due to the sim-to-real gap, encompassing physical-model discrepancies, sensor noise and timing delays, and calibration errors [11,24,34,35,36,37]. To mitigate this, domain randomization and a displacement-based joint action generation are employed [1,3,13,24,34]. Nevertheless, a reduction in success rate relative to simulation is observed, though the magnitude of the transfer loss was broadly comparable to that reported in prior work [24,53,54].
The primary failure factors observed were (i) unintended cube displacements caused by excessive contact and (ii) increased pose-estimation errors due to marker occlusions from the motion of the cube or the hand, both of which lowered the transfer success rate. Limitations include the dependence of each policy’s performance on hand-crafted reward design and reduced success rates in real-world transfer due to marker pose-estimation errors. First, these limitations stem from the absence of physical interaction information due to the constraints of vision-centric state estimation. To overcome these limitations, we plan to implement robust control policies that leverage tactile-vision fusion in future work. A robotic hand equipped with tactile sensors can detect contact states and slip, and can generate the torques and motions required for manipulation. It can compensate when visual information is limited.
In addition, by extending the proposed framework (HPPL) to inverse reinforcement learning (IRL) and imitation learning (IL), reliance on hand-crafted rewards for training each subtask can be reduced while preserving HPPL’s core, interpolicy connectivity. In future work, dexterous manipulation performance is expected to be enhanced and transfer success rates increased by leveraging a tactile-equipped system. Along with these enhancements, extending the scope of domain randomization to include tactile sensing and friction variations, and incorporating contact-aware rewards, is expected to further improve success rates and robustness in real-world settings.
In conclusion, the framework reuses the stabilized states generated by the preceding policy as the initialization distribution for the subsequent policy. This enables effective exploration without relying on fine-grained reward shaping, reduces initial exploration variance, and stably drives learning in rotation-centric manipulation using only intuitive, general-purpose rewards. The proposed HPPL enhances connectivity between policies by aligning a subsequent policy’s initial state distribution with its predecessor’s stabilized state distribution. This approach was empirically validated on bimanual cube manipulation through sim-to-real transfer on a bimanual robotics arm-hand system. However, there are limitations in verifying extensibility and generalization across diverse tasks. To address this, future work will systematically evaluate the extensibility of the approach on a broad set of tasks that differ in task type, reward function, and observation design.
5. Conclusions
This paper proposes a Hierarchical Progressive Policy Learning (HPPL) framework that decomposes bimanual cube manipulation into two stages—grasping and rotating—and progressively trains the subsequent policy on the stable execution distribution induced by the preceding policy to ensure strong connectivity between policies. Each policy is trained in a simulation environment matched to the real robot system and is transferred zero-shot to the physical robot, demonstrating stable holding and clockwise/counterclockwise rotations without additional tuning (Video S1).
We compare against naive skill chaining and multi-agent proximal policy optimization, and the proposed method exhibits superior sample efficiency and final performance with lower variance, indicating more stable learning. The results suggest that staged training with a frozen preceding policy mitigates distribution mismatch at the chaining boundary, nonstationarity arising from simultaneous training, and credit-assignment ambiguities under shared rewards.
Limitations include the dependence of each policy’s performance on hand-crafted reward design and reduced success rates in real-world transfer due to marker pose-estimation errors. Future work will focus on establishing more robust learning via tactile-vision fusion, alleviating the reward-design burden through reward learning/inverse reinfocement learning, and investigating generalization by expanding task types and robotic platforms.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/math13223585/s1, Video S1: Demonstration of bimanual cube manipulation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.-W.L. and S.-C.L.; methodology, K.-W.L.; software, K.-W.L., J.-W.L. and S.K.; validation, K.-W.L., J.-W.L. and S.K.; formal analysis, K.-W.L.; investigation, K.-W.L., J.-W.L. and S.K.; data curation, J.-W.L., S.K.; writing—original draft preparation, K.-W.L.; writing—review and editing, K.-W.L.; visualization, K.-W.L. and J.-W.L.; supervision, K.-W.L. and S.-C.L.; project administration, K.-W.L. and S.-C.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (RS-2025-00562981, RS-2025-25433409).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lee, K.W.; Qin, Y.; Wang, X.; Lim, S.C. Dextouch: Learning to seek and manipulate objects with tactile dexterity. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 10772–10779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Giudici, G.; Coppola, C.; Althoefer, K.; Farkhatdinov, I.; Li, Z.; Jamone, L. Dexskills: Skill segmentation using haptic data for learning autonomous long-horizon robotic manipulation tasks. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 18–24 October 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 5104–5111. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Che, H.; Qin, Y.; Huang, B.; Yin, Z.H.; Lee, K.W.; Wu, Y.; Lim, S.C.; Wang, X. Robot synesthesia: In-hand manipulation with visuotactile sensing. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 13–17 May 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 6558–6565. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Shi, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Li, F.; Liu, K. DexCap: Scalable and Portable Mocap Data Collection System for Dexterous Manipulation. In Proceedings of the RSS Workshop: Data Generation for Robotics, Cologne, Germany, 15–19 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Qi, H.; Yi, B.; Levine, S.; Malik, J. Learning visuotactile skills with two multifingered hands. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Atlanta, GA, USA, 19–23 May 2025; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 5637–5643. [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen, M.; Karayiannidis, Y.; Kyrki, V. A survey of robot manipulation in contact. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2022, 156, 104224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Varava, A.; Kragic, D. Modeling, learning, perception, and control methods for deformable object manipulation. Sci. Robot. 2021, 6, eabd8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, F.; Asfour, T. A bimanual manipulation taxonomy. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 11031–11038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, Y.; Jiang, S.; He, B.; Cheng, Q. Robot learning in the era of foundation models: A survey. Neurocomputing 2025, 638, 129963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Wei, T.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H. Learning to Manipulate Anywhere: A Visual Generalizable Framework For Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–30 September 2025; pp. 1815–1833. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.; Yin, Z.H.; Qi, H.; Abbeel, P.; Malik, J. Twisting Lids Off with Two Hands. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–30 September 2025; pp. 5220–5235. [Google Scholar]
- Urain, J.; Mandlekar, A.; Du, Y.; Shafiullah, M.; Xu, D.; Fragkiadaki, K.; Chalvatzaki, G.; Peters, J. Deep Generative Models in Robotics: A Survey on Learning from Multimodal Demonstrations. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.04380v3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Che, H.; Qi, H.; Ma, Y.; Malik, J.; Wang, X. Lessons from Learning to Spin “Pens”. In Proceedings of the 8th Annual Conference on Robot Learning, Munich, Germany, 6–9 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Foerster, J.; Farquhar, G.; Afouras, T.; Nardelli, N.; Whiteson, S. Counterfactual multi-agent policy gradients. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, T.; Samvelyan, M.; De Witt, C.S.; Farquhar, G.; Foerster, J.; Whiteson, S. Monotonic value function factorisation for deep multi-agent reinforcement learning. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 1–51. [Google Scholar]
- Sunehag, P.; Lever, G.; Gruslys, A.; Czarnecki, W.M.; Zambaldi, V.; Jaderberg, M.; Lanctot, M.; Sonnerat, N.; Leibo, J.Z.; Tuyls, K.; et al. Value-Decomposition Networks For Cooperative Multi-Agent Learning Based On Team Reward. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and MultiAgent Systems, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 2085–2087. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D.; Mulyana, B.; Stankovic, V.; Cheng, S. A survey on deep reinforcement learning algorithms for robotic manipulation. Sensors 2023, 23, 3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutsebaut-Buysse, M.; Mets, K.; Latré, S. Hierarchical reinforcement learning: A survey and open research challenges. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2022, 4, 172–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soviany, P.; Ionescu, R.T.; Rota, P.; Sebe, N. Curriculum learning: A survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 1526–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X. Reinforcement Learning with Value Function Decomposition for Hierarchical Multi-Agent Consensus Control. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xia, F.; Martin-Martin, R.; Savarese, S. Hrl4in: Hierarchical reinforcement learning for interactive navigation with mobile manipulators. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 16–18 November 2020; pp. 603–616. [Google Scholar]
- Hakhamaneshi, K.; Zhao, R.; Zhan, A.; Abbeel, P.; Laskin, M. Hierarchical few-shot imitation with skill transition models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08981. [Google Scholar]
- Nasiriany, S.; Gao, T.; Mandlekar, A.; Zhu, Y. Learning and Retrieval from Prior Data for Skill-based Imitation Learning. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Atlanta, GA, USA, 6–9 November 2023; pp. 2181–2204. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Fei-Fei, L.; Liu, K. Sequential Dexterity: Chaining Dexterous Policies for Long-Horizon Manipulation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Atlanta, GA, USA, 6–9 November 2023; pp. 3809–3829. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.; Lim, J.J.; Anandkumar, A.; Zhu, Y. Adversarial Skill Chaining for Long-Horizon Robot Manipulation via Terminal State Regularization. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Auckland, New Zealand, 14–18 December 2022; pp. 406–416. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, U.A.; Xue, S.; Chen, Y.; Xu, D. Generative skill chaining: Long-horizon skill planning with diffusion models. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Atlanta, GA, USA, 6–9 November 2023; pp. 2905–2925. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Mao, J.; Du, Y.; Wu, J.; Tenenbaum, J.B.; Lozano-Pérez, T.; Kaelbling, L.P. Compositional Diffusion-Based Continuous Constraint Solvers. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Atlanta, GA, USA, 6–9 November 2023; pp. 3242–3265. [Google Scholar]
- Mendez-Mendez, J.; Kaelbling, L.P.; Lozano-Pérez, T. Embodied lifelong learning for task and motion planning. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Atlanta, GA, USA, 6–9 November 2023; pp. 2134–2150. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, J.B.; Lau, N.; Silva, F. Curriculum-guided skill learning for long-horizon robot manipulation tasks. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2025, 192, 105032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayar, E.; Iacca, G.; Knoll, A. Curriculum learning for robot manipulation tasks with sparse reward through environment shifts. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 46626–46635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motes, J.; Sandström, R.; Lee, H.; Thomas, S.; Amato, N.M. Multi-robot task and motion planning with subtask dependencies. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3338–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shome, R.; Bekris, K.E. Synchronized multi-arm rearrangement guided by mode graphs with capacity constraints. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on the Algorithmic Foundations of Robotics, Oulu, Finland, 21–23 June 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 243–260. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, V.N.; Orthey, A.; Driess, D.; Oguz, O.S.; Toussaint, M. Long-horizon multi-robot rearrangement planning for construction assembly. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2022, 39, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Cousineau, E.; Kuppuswamy, N.; Agrawal, P. Vegetable peeling: A case study in constrained dexterous manipulation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2407.07884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pan, C.; Xu, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y. Efficient bimanual handover and rearrangement via symmetry-aware actor-critic learning. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 3867–3874. [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka, S.; Ghasemipour, S.K.S.; Freeman, D.; Mordatch, I. Bi-manual manipulation and attachment via sim-to-real reinforcement learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.08277. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, B.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Qin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Atanasov, N.; Wang, X. Dynamic handover: Throw and catch with bimanual hands. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.Z.; Tompson, J.; Driess, D.; Florence, P.; Ghasemipour, S.K.S.; Finn, C.; Wahid, A. ALOHA Unleashed: A Simple Recipe for Robot Dexterity. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 4–6 June 2025; pp. 1910–1924. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, D.; Walke, H.R.; Pertsch, K.; Black, K.; Mees, O.; Dasari, S.; Hejna, J.; Kreiman, T.; Xu, C.; Luo, J.; et al. Octo: An Open-Source Generalist Robot Policy. In Proceedings of the Robotics: Science and Systems, Delft, The Netherlands, 15–19 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wu, L.; Li, B.; Tan, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Xu, K.; Su, H.; Zhu, J. RDT-1B: A Diffusion Foundation Model for Bimanual Manipulation. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations, Singapore, 24–28 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Yang, G.; Wang, X. Open-TeleVision: Teleoperation with Immersive Active Visual Feedback. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning, PMLR, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 4–6 June 2025; pp. 2729–2749. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Cheng, X.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Ji, M.; Yuan, C.; Yang, G.; Yi, S.; Wang, X. Mobile-television: Predictive motion priors for humanoid whole-body control. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.07773. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, D.J.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Simchi-Levi, D.; Xu, Y. Offline Reinforcement Learning: Fundamental Barriers for Value Function Approximation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Learning Theory, PMLR, London, UK, 2–5 July 2022; p. 3489. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, W.; Huang, B.; Huang, A.; Jiang, N.; Lee, J. Offline reinforcement learning with realizability and single-policy concentrability. In Proceedings of the Conference on Learning Theory, PMLR, London, UK, 2–5 July 2022; pp. 2730–2775. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Galván, B.; López-Rentería, J.; Aguirre-Hernández, B.; Fernández-Anaya, G. Robust stability in discrete control systems via linear controllers with single and delayed time. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 3674628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, K.J.; McClellan, R. Time-varying filter stability and state matrix products. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Digital Audio Effects, Vienna, Austria, 6–10 September 2022; pp. 6–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, M.; Yu, C.; Yu, Q.; Liu, J.; Rudin, N.; Hoeller, D.; Yuan, J.L.; Singh, R.; Guo, Y.; Mazhar, H.; et al. Orbit: A unified simulation framework for interactive robot learning environments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 3740–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido-Jurado, S.; Muñoz-Salinas, R.; Madrid-Cuevas, F.J.; Marín-Jiménez, M.J. Automatic generation and detection of highly reliable fiducial markers under occlusion. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 47, 2280–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrenko, A.; Allshire, A.; State, G.; Handa, A.; Makoviychuk, V. DexPBT: Scaling up Dexterous Manipulation for Hand-Arm Systems with Population Based Training. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.12127. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, V.; Hinton, G.E. Rectified linear units improve restricted boltzmann machines. In Proceedings of the 27th international conference on machine learning (ICML-10), Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 807–814. [Google Scholar]
- Schulman, J.; Wolski, F.; Dhariwal, P.; Radford, A.; Klimov, O. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.06347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, R.; Verma, A.; Orosz, G.; Chaudhuri, S.; Yue, Y.; Burdick, J. Control regularization for reduced variance reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 1141–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, S.; Arlaud, E.; Laptev, I.; Schmid, C. Vividex: Learning vision-based dexterous manipulation from human videos. In Proceedings of the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Atlanta, GA, USA, 19–23 May 2025; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2025; pp. 3336–3343. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, T.; Li, S.; Lyu, C.; Sou, K.W.; Chan, W.S.; Ding, W. MoDex: Planning High-Dimensional Dexterous Control via Learning Neural Hand Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.10983. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).