Abstract
On-demand urban delivery increasingly relies on electric delivery bicycles (EDBs), yet their limited battery capacity creates coupled challenges of routing efficiency and energy replenishment. We study a novel battery swapping cabinet location-routing problem (BSC-LRP) with multiple depots, which jointly optimizes routing and modular energy infrastructure deployment under time-window and battery constraints. To address the problem’s complexity, we design an improved branch-and-price algorithm enhanced with adaptive heuristic-exact labeling (IBP-HL) and a robust arc-based branching scheme. This hybrid framework accelerates column generation while preserving exactness, representing a methodological advancement over standard B&P approaches. Computational experiments on modified Solomon instances show that IBP-HL consistently outperforms Gurobi in both runtime and solution quality on small cases, and achieves substantial speedups and improved bounds over baseline B&P on medium and large cases. These results demonstrate not only the scalability of IBP-HL but also its practical relevance: the framework provides decision support for operators and planners in designing cost-efficient, reliable, and sustainable last-mile delivery systems with battery-swapping infrastructure.
Keywords:
on-demand delivery; battery swapping cabinet; electric delivery bicycle; location-routing problem; branch-and-price; heuristic labeling MSC:
90B06; 90B80; 90C11
1. Introduction
The rapid growth of urban instant delivery services has led to the widespread adoption of electric delivery bicycles (EDBs) due to their low cost, high flexibility, and environmental advantages. However, the limited battery capacity of EDBs imposes strict constraints on service range and operational continuity. To address the issue of range anxiety and reduce service interruptions, battery swapping cabinets (BSCs) have emerged as a critical component of the urban logistics infrastructure. Figure 1a illustrates a spatial distribution of BSCs in the Xiasha area of Hangzhou city, China, where several universities and business zones generate high demand for on-demand delivery services. Figure 1b illustrates a typical battery swapping operation conducted by an EDB rider. The integration of BSCs into last-mile on-demand delivery systems introduces new operational complexities, especially in coordinating vehicle routing and energy replenishment decisions. In particular, mid-route battery swapping operations require explicit consideration in the optimization model to accurately capture their influence on routing efficiency.
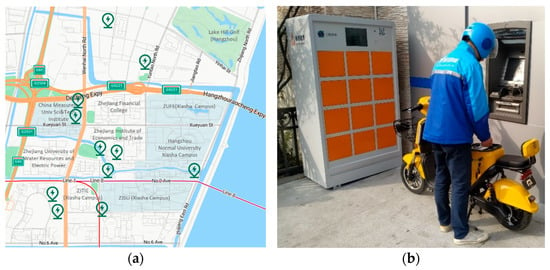
Figure 1.
(a) Spatial distribution of BSCs (map scale 1:60,000). (b) Mid-route battery swapping operations.
Despite the growing relevance of EDB-based urban delivery systems, few optimization frameworks systematically capture the interdependencies among depots, BSC siting, and routing under energy constraints. In practice, neglecting these couplings may lead to infeasible or suboptimal operations. Moreover, due to the limited battery capacity of EDBs and the spatial distribution of customer demands, integrated and energy-aware planning strategies are increasingly essential. These considerations motivate the development of a comprehensive optimization framework to support both tactical and operational decisions in EDB-based delivery systems. This paper formulates a battery swapping cabinet location-routing problem (BSC-LRP), arising in urban on-demand logistics, which jointly optimizes the siting of BSCs and the routing of EDBs to meet customer demands under battery constraints. The problem setting involves multiple depots, candidate BSC locations, and spatially distributed customers, with tight coupling between routing and energy replenishment decisions. EDBs need to complete delivery tasks within battery capacity limits, potentially recharging mid-route at selected BSCs. The integration of facility location, vehicle routing, and battery constraints renders the problem highly complex and combinatorially difficult.
Recent advancements in the electric vehicle routing problem (EVRP) or electric location-routing problems (ELRPs) have focused primarily on integrating charging or swapping infrastructure with vehicle routing decisions, often under time window and energy constraints. For instance, Xiao, Liu [1] proposed an EVRP model with synchronized mobile partial recharging and flexible waiting strategies, reflecting the increasing need for temporal flexibility in charging-aware vehicle routing. From the infrastructure side, Aghalari, Salamah [2] formulated a two-stage stochastic ELRP with fast charging stations, incorporating demand uncertainty and charging station placement into a unified decision-making framework. However, these models are primarily designed for electric vans or trucks operating from centralized depots and rely on large-scale energy facilities with ample capacity. In contrast, this study considers light electric vehicles, specifically, EDBs, which are widely used in on-demand urban delivery but face more stringent battery and routing constraints. The proposed model introduces BSCs as modular and capacity-limited infrastructure components, suitable for flexible deployment in dense urban settings. Additionally, our problem incorporates multiple depots and strict customer time windows, which are often simplified or omitted in traditional ELRP formulations. These distinctions necessitate a tailored modeling framework to capture the operational characteristics of EDB-based last-mile delivery systems more accurately.
This study investigates a novel LRP that arises in on-demand last-mile delivery systems using EDBs. The problem involves the joint optimization of routing plans and the deployment of modular BSCs, which serve as mid-route energy replenishment infrastructure with limited capacity. To accurately capture the operational characteristics of such systems, we formulate a mixed-integer linear programming (MILP) model that integrates battery constraints, time windows, multiple depots, and BSC siting decisions into a unified optimization framework. To solve this problem efficiently, we develop an improved branch-and-price algorithm enhanced with adaptive heuristic labeling strategies (IBP-HL). The algorithm incorporates both exact and heuristic labeling routines under a unified framework, and employs a performance-based adaptive selection mechanism to balance exploration efficiency and solution quality. A robust arc-based branching scheme ensures compatibility with the column generation process and accelerates convergence. The main contributions of this study are threefold: First, we propose the BSC-LRP, a novel extension of the ELRP tailored to EDB-based delivery systems. The model explicitly considers modular energy infrastructure, limited swapping capacities, multiple depots, and customer time windows, features often simplified or ignored in existing ELRP literature. Second, we design a hybrid branch-and-price (B&P) framework that integrates exact and heuristic labeling algorithms through an adaptive selection mechanism, enabling efficient solution of medium- and large-scale instances. Third, extensive computational experiments based on modified Solomon benchmarks demonstrate that IBP-HL consistently outperforms commercial solvers (e.g., Gurobi) and baseline B&P implementations in both runtime and solution quality, underscoring its practical applicability in energy-aware urban logistics planning.
The remainder of the paper is structured as follows: Section 2 reviews the related literature. Section 3 formulates the BSC-LRP using a MILP model. Section 4 describes the IBP-HL algorithm, including key components of the solution strategy. Section 5 presents computational experiments and performance comparisons. Section 6 concludes the study and suggests future research directions.
2. Literature Review
This section reviews the relevant literature on the application of electric vehicles in urban logistics, with a particular focus on on-demand delivery systems, EVRP, and ELRP. These three strands of research provide the foundation for understanding how electric vehicle technologies are being integrated into modern delivery systems and where potential research opportunities remain.
2.1. On-Demand Delivery
On-demand delivery services have gained significant attention in urban logistics due to the growing demand for fast and flexible delivery options. These services, often employed for meal delivery and e-commerce, have promoted numerous studies on optimizing delivery systems, with a particular focus on reducing carbon emissions and improving operational efficiency. Recent studies have emphasized the environmental impact of on-demand deliveries, specifically the CO2 emissions associated with traditional delivery methods. For example, Allen, Piecyk [3] conducted a case study on the transport and CO2 impacts of on-demand meal deliveries in London, highlighting the environmental cost of conventional delivery fleets. Schnieder, Hinde [4] further examined the emission estimates of such services using macroscopic simulation models, emphasizing the need for cleaner delivery solutions.
As the demand for on-demand delivery grows, the need for efficient and environmentally sustainable solutions has grown correspondingly. In response, numerous studies have examined the use of electric vehicles, drones, and other low-emission technologies to enhance delivery system efficiency. Tu, Zhao [5] proposed a crowdsourced delivery system for on-demand meals, utilizing a dynamic optimization framework that incorporates order collection and sequential delivery, aiming to reduce operational inefficiencies and environmental impacts. Simoni and Winkenbach [6] further developed an order batching and assignment algorithm for crowdsourced on-demand food delivery, highlighting the operational gains achievable through intelligent task aggregation and worker coordination. In parallel, UAVs have been explored as a promising solution for last-mile delivery, offering substantial reductions in traffic congestion and carbon emissions. Liu, Yan [7] presented a multi-depot two-tier parcel transit location-routing problem involving autonomous delivery robots for last-mile services, while Huang, Hu [8] investigated dynamic task scheduling in UAV-based meal delivery systems, emphasizing the need for effective scheduling to handle random task arrivals and time windows. Liu [9] also developed an optimization-driven fleet scheduling approach for UAV-based instant food delivery. More recently, Chen and Hu [10] examined courier dispatch decisions in on-demand delivery platforms, considering customer sensitivity to service delay and proposing a dynamic pricing and allocation mechanism that balances responsiveness with system efficiency.
Despite these advancements in electric vehicles and autonomous delivery systems, few studies have specifically addressed the integration of light electric vehicles, such as EDBs, into on-demand delivery systems. This gap in the literature, particularly in the context of energy replenishment through battery swapping, represents a significant opportunity for research. This study aims to address this gap by optimizing both the deployment of BSCs and the routing of EDBs, aiming to enhance overall delivery efficiency while promoting environmental sustainability and operational effectiveness within the on-demand delivery system.
2.2. Electric VRP
The EVRP initially emerged as an adaptation of the classical VRP, integrating EV characteristics such as limited driving range and the need for recharging. A seminal contribution by Schneider, Stenger [11] extended the traditional VRP with time windows by incorporating recharging stations into the model, establishing a foundational framework for EVRP research. Their formulation considers routing constraints, battery range limitations, and service time requirements, and has since served as a benchmark for many subsequent studies. Building on this foundation, Felipe, Ortuño [12] introduced a green VRP that allows for heterogeneous vehicle technologies and partial recharges, expanding the model’s flexibility to reflect realistic operational environments. Their heuristic method accounts for both environmental and operational trade-offs, emphasizing the importance of charging strategies. Keskin and Çatay [13] further examined partial recharge strategies within an EVRP-TW context, showing that the ability to partially recharge can lead to significant efficiency improvements in routing decisions. Meanwhile, Montoya, Guéret [14] incorporated nonlinear charging functions into the EVRP, reflecting the diminishing marginal gains of charging over time and highlighting the nontrivial interactions between route planning and charging behavior.
While early EVRP studies focused on modeling charging constraints and operational feasibility, subsequent research has emphasized more accurate representations of energy consumption and the incorporation of uncertainty. Basso, Kulcsár [15] advanced the modeling framework by integrating a data-driven energy consumption estimation into the EVRP. Their approach captures the nonlinear relationship between energy usage and vehicle dynamics, such as load, speed, and route profile, thereby enhancing the model’s predictive capability. Addressing the inherent variability in EV operations, Pelletier, Jabali [16] proposed a stochastic version of the EVRP that accounts for uncertainty in energy consumption. By modeling energy usage as a random variable and incorporating risk-averse constraints, their work extends the deterministic formulation to more robust, real-world scenarios. In a similar direction, Keskin, Çatay [17] examined the effects of stochastic waiting times at recharging stations, which can significantly impact route feasibility and service quality. Their simulation-based heuristic demonstrates how operational uncertainties in charging infrastructure can be explicitly considered to ensure reliable EV deployment. Zhang, Zhou [18] contributed to this stream by incorporating prioritized time windows and time-dependent hybrid recharging options, including fast, standard, and mobile recharge modes, into a collaborative EVRP model. Their study emphasizes customer-centric routing strategies in combination with dynamic energy planning.
As EVRP models matured in terms of operational detail and uncertainty handling, recent research has expanded the problem scope to encompass system-level considerations such as fleet configuration and infrastructure collaboration. Hiermann, Puchinger [19] proposed an extension of the EVRP that jointly optimizes fleet size and vehicle type selection under time window and recharging constraints. Their formulation enables operators to balance acquisition costs, charging logistics, and service requirements, providing a comprehensive view of electric fleet management. Focusing on energy efficiency, Zhang, Gajpal [20] formulated an EVRP variant aimed at minimizing total energy consumption rather than merely distance or cost, highlighting the growing emphasis on sustainability metrics in electric logistics. More recently, Wang, Zhou [21] introduced a collaborative multi-depot EVRP with shared charging stations, reflecting the challenges and opportunities of inter-depot coordination and infrastructure sharing in densely networked logistics systems. Souza, Papini [22] further addressed the need for flexible solution methods by designing a variable neighborhood search algorithm capable of handling multiple EVRP variants, including those with partial recharging, heterogeneous fleets, and dynamic charging options. Jiang, Hu [23] proposed a multi-mode hybrid EVRP with time windows, accounting for different propulsion types and energy-switching strategies along routes. Their model reflects the operational challenges of coordinating various vehicle modes under strict temporal constraints.
In addition to routing-focused studies, another research stream in the electric vehicle domain emphasizes vehicle dynamics and control, such as fuzzy or quantized feedback control for lateral stability [24] and model-predictive control driving [25]. These studies mainly address continuous-time vehicle dynamics and safety control, which are important for general EV operation. However, their scope differs fundamentally from our setting of electric delivery bicycles in urban on-demand services, where vehicles operate independently at low speed, and the primary challenges arise from routing and energy replenishment under time-window constraints.
2.3. Electric LRP
Building on the EVRP literature that addresses energy constraints through fixed charging infrastructure, a growing body of research has focused on the joint optimization of facility location and vehicle routing in electric vehicle systems. One of the earliest contributions in this domain is the battery swap station location-routing problem (BSS-LRP) proposed by Yang and Sun [26], which integrates the siting of swap stations with vehicle routing decisions for capacitated electric fleets. This model emphasizes the importance of infrastructure availability in ensuring route feasibility and service efficiency. Extending this framework, Hof, Schneider [27] introduced an adaptive variable neighborhood search algorithm tailored for BSS-LRP, incorporating intermediate stops and demonstrating the practical relevance of flexible routing through dynamic charging interventions. Chen, Li [28] further generalized the problem setting by considering a mixed fleet of electric and conventional vehicles. Their heuristic B&P algorithm with an adaptive selection scheme reflects the increasing complexity of urban logistics, where legacy fleets coexist with electric alternatives. More recently, Guo, Zhang [29] enriched the modeling landscape by integrating nonlinear partial charging behaviors and battery degradation into the location-routing formulation, thereby capturing important operational nuances related to battery health and charging efficiency. Aghalari, Salamah [2] formulated a two-stage stochastic location-routing problem for electric vehicles with fast charging, incorporating demand-side uncertainty and charging behavior into the planning process. Their study highlights how probabilistic factors can affect infrastructure deployment and routing robustness.
Complementing the infrastructure-focused stream of ELRP research, another line of studies has emphasized system-level coordination and environmental considerations in electric vehicle logistics. Schiffer and Walther [30] formulated an ELRP that incorporates time windows and partial recharging, highlighting the operational trade-offs between service punctuality and flexible energy replenishment. Their work captures the intricacies of synchronizing customer service requirements with the dynamic constraints of electric fleets. Addressing demand-side uncertainty, Zhang, Chen [31] proposed a stochastic ELRP model in which customer demands are random variables. This formulation significantly enhances model realism and decision robustness, particularly in urban delivery environments characterized by fluctuating order volumes. Çalık, Oulamara [32] extended the ELRP framework to accommodate heterogeneous vehicle fleets, proposing a mixed-integer programming model and a Benders decomposition algorithm to solve large-scale instances efficiently. Their approach reflects the growing diversity in vehicle technologies and the computational challenges posed by joint location-routing decisions. Furthermore, Wang, Miao [33] tackled the design of green logistics networks by integrating multiple types of charging infrastructure, such as fast and slow chargers, into the ELRP framework. Using a branch-and-price algorithm, they demonstrated how infrastructure heterogeneity affects both routing efficiency and environmental impact. In a related effort, Aghalari, Salamah [34] also examined the EV location-routing problem under ambient temperature variations, showing that temperature significantly affects charging efficiency and battery performance. Their findings suggest that environmental parameters should be integrated into location-routing frameworks for more accurate and sustainable electric logistics planning.
As summarized in Table 1, existing studies have addressed various aspects of electric vehicle routing and location problems, including charging and swapping infrastructure, multi-depot systems, and time window constraints. However, most of these works focus on either charging stations or conventional large-scale infrastructure, while the specific context of deploying BSCs in urban on-demand delivery scenarios remains largely unexplored. Conventional ELRP models lack adaptability to the operational characteristics of BSCs, such as modular deployment and limited-service capacity. Therefore, this research proposes an exact optimization framework tailored to the integrated location-routing design of BSCs and EDBs, aiming to complement and extend the current ELRP literature.

Table 1.
Overview of relevant studies.
3. Model Formulation
In this section, we first describe the studied problem, followed by some necessary notations and symbols to formulate the corresponding mathematical model.
3.1. Problem Description
The BSC-LRP studied in this paper arises in the context of on-demand last-mile delivery using EDBs, which can be viewed as a novel variant of the ELRP, adapted to the specific operational characteristics of EDB-based distribution systems. In the studied setting, multiple depots are available for dispatching EDBs to serve spatially distributed customers. Each EDB departs from its assigned depot with a fully charged battery and is subject to both energy and payload capacity constraints. To extend the operational range and mitigate range anxiety, BSCs are tactically deployed across the delivery region. These cabinets provide pre-charged replacement batteries and enable mid-route energy replenishment. Each BSC has a limited number of battery slots, and its capacity configuration, i.e., the number of batteries stored, directly affects system feasibility and delivery efficiency. Therefore, the problem entails an intricate integration of facility location decisions, energy-constrained vehicle routing, and capacity constraints for the deployed BSCs. A representative delivery scenario is illustrated in Figure 2, where three EDB routes are supported by one activated BSC that provides mid-route battery swapping services.
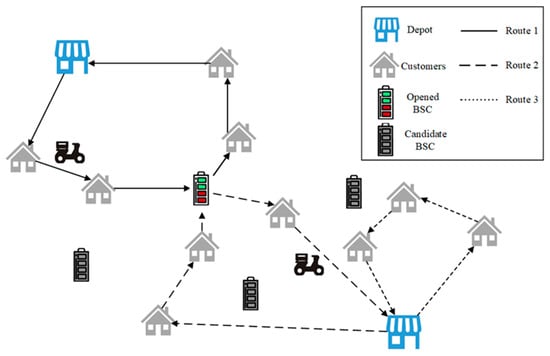
Figure 2.
An illustration of the proposed BSC-LRP.
The following modeling assumptions are introduced to define the problem scope and ensure computational tractability. (i) Each depot is equipped with a charging facility, and all EDBs depart fully charged at the beginning of the planning horizon. (ii) All EDBs are homogeneous in terms of battery specifications and payload capacity. (iii) Each deployed BSC has a fixed swapping capacity (i.e., a limited number of fully charged batteries available for mid-route exchange), and the recharging or reuse of depleted batteries is not considered within the same operational day. (iv) Battery procurement and recharging costs are excluded from the objective function, as these costs are amortized over longer time periods and have limited influence on the short-term routing and siting decisions considered in this study.
3.2. Mathematical Model
The following sets, parameters, and decision variables are defined to formalize the mathematical model of the problem.
| Sets | Explanations |
| The set of all customers | |
| The set of all candidate BSCs | |
| The set of all depots | |
| The set of all nodes, as | |
| The set of all arcs, | |
| The set of EDBs assigned to depot | |
| The set of all EDBs, | |
| Parameters | Explanations |
| The distance from node to node | |
| The delivery cost per unit distance | |
| A sufficiently large positive constant | |
| The demand of customer | |
| The maximum loading capacity of EDBs | |
| The maximum driving range of EDBs | |
| The safety level of the remaining power of EDBs | |
| The time window requirement of customer | |
| The battery usage cost | |
| Decision Variables | |
| 1 if EDB travels from node directly to node , 0 otherwise | |
| 1 if candidate BSC is deployed, 0 otherwise | |
| Auxiliary Variables | |
| The remaining loading capacity of EDB leaving from node | |
| The remaining battery power of EDB when it arrives at node | |
| The remaining battery power of EDB when it departs from node | |
| The arrival time of EDB at node | |
With the notations defined, the mathematical formulation of the problem is given below.
Mathematical model:
Subject to:
The objective function (1) is designed to minimize the total cost, comprising the battery replacement cost at BSCs and the travel cost of EDBs. Constraint (2) ensures that each customer is served exactly once. Constraint (3) restricts battery swapping operations to activated BSCs. Constraint (4) ensures route continuity via flow conservation at each node. Constraint (5) requires each EDB to return to its originating depot after completing deliveries. Constraint (6) limits each EDB to operate on at most one delivery route. Constraint (7) denotes that the total number of EDBs departing from a depot does not exceed its available fleet size. Constraint (8) tracks the changes in the remaining loading capacity along the route based on the sequence of its delivery route. Constraint (9) enforces the loading capacity limits at each node. Constraint (10) ensures time feasibility by updating arrival times based on route sequence and service times. Constraint (11) enforces the customer time window constraints. Constraint (12) updates the remaining battery level after each travel segment. Constraint (13) indicates that the EDB depart from the depot with fully charged batteries. Constraint (14) resets the battery to full capacity upon visiting an activated BSC. Constraint (15) implies that the battery level remains unchanged during customer service. Constraint (16) ensures that the battery level cannot fall below the safety threshold α. Constraint (17) specifies the binary nature of the decision variables. These constraints jointly ensure the feasibility and safety of the integrated delivery and battery swapping operations.
4. Solution Approach
Over the past decades, the B&P algorithm has become a state-of-the-art method for solving large-scale VRPs, particularly those involving complex combinatorial structures such as EVRPs and LRPs. The B&P algorithm integrates column generation within the B&B framework to efficiently solve large-scale integer programming models [37]. In this study, we adapt and extend the B&P framework to address the proposed BSC-LRP, which generalizes classical ELRP by incorporating multiple depots, limited battery-swapping capacities, and time-sensitive on-demand delivery requirements. The algorithm starts from a restricted master problem (RMP) initialized with a feasible column set. A labeling-based pricing subproblem is formulated using the dual information from the relaxed RMP to identify new columns (i.e., feasible delivery routes) with negative reduced cost. Both exact and heuristic labeling rules are employed to efficiently explore the solution space. New columns are iteratively generated and added to the RMP until no further improving routes can be identified. If the final solution remains fractional, a problem-specific branching strategy is invoked to obtain an integer-optimal solution. The overall algorithmic framework is illustrated in Figure 3. Based on this general B&P framework, our IBP-HL introduces two key enhancements: (i) an adaptive mechanism that alternates between heuristic and exact labeling to accelerate pricing, and (ii) a robust arc-based branching scheme compatible with column generation.
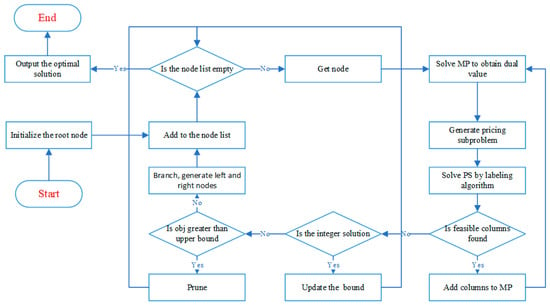
Figure 3.
The flowchart of the B&P algorithm.
4.1. Model Reformulation
To enable the application of the B&P algorithm, the original MILP is reformulated into a set-partitioning formulation, which decomposes the problem into a RMP and a pricing subproblem. The RMP selects a combination of feasible delivery routes that collectively satisfy all customer and operational constraints. The pricing subproblem is designed to identify new routes with negative reduced cost, thereby improving the objective value of the RMP.
4.1.1. Master Problem
Let denote the set of all feasible delivery routes that satisfy the operational constraints defined in the pricing subproblem. For each depot , let represent the subset of routes originating from depot . Each route is associated with a specific set of customers and a unique originating depot, and its total operational cost is denoted by . We introduce binary parameter , where if customer is served by route , and 0 otherwise. Similarly, indicates that arc is included in route , and 0 otherwise. A new binary decision variable is defined to indicate whether route is selected for execution from depot . Based on these notations, the following linking constraints are introduced.
These constraints link the arc-based formulation of the original model to the route-based variables in the master problem. Specifically, constraint (18) aggregates the arc-level decisions from selected routes to derive the values of , while constraint (19) defines customer inclusion within routes based on the underlying node connections.
Given these definitions, the master problem is expressed as follows:
Master problem:
Subject to:
In this master problem, objective function (20) minimizes the total system cost by selecting an optimal set of delivery routes. Constraint (21) guarantees that each customer is assigned to exactly one route. Constraint (22) enforces the fleet size limitation at each depot. Constraint (23) defines the binary nature of the route selection decisions.
The computational complexity of the master problem stems from the exponential number of feasible routes in , rendering direct enumeration and full model solution infeasible for practical instances. To overcome this, the column generation method is employed. The algorithm begins with a RMP initialized by a small set of feasible routes . At each iteration, a pricing subproblem is solved to identify new columns (routes) with negative reduced costs. These columns are added dynamically to the RMP, and the process continues until no further improving columns can be found. This iterative strategy ensures both computational efficiency and solution optimality in the presence of large-scale routing configurations.
4.1.2. Pricing Subproblem
The pricing subproblem serves as the core of the column generation procedure. Its primary objective is to generate new feasible routes with negative reduced cost, which are then incorporated into the RMP to improve the current solution. Mathematically, this subproblem can be viewed as a resource-constrained shortest path problem (RCSPP), where each feasible path need to satisfy all operational constraints related to time, load, and energy while potentially offering cost improvement to the master problem. Let and denote the dual variables associated with constraints (21) and (22) in the RMP, respectively. The reduced cost of arc is defined as: , where is the original cost of traveling from node to node . Using this modified arc cost, the pricing subproblem can be formulated as follows:
Pricing subproblem:
Subject to:
Constraints (4)–(6) and (8)–(16)
In this pricing subproblem, the first term accounts for the dual-adjusted cost of the selected arcs and the second term penalizes overuse of depot resources based on the dual variable . The constraint set (25) includes: flow conservation constraints (4)–(6), ensuring route continuity; load feasibility constraints (8) and (9), ensuring vehicle capacity is not exceeded; time window and service synchronization constraints (10) and (11); battery dynamics and recharging rules (12)–(16), ensuring that energy requirements are respected along the route. A feasible route with negative objective value in (24) indicates a promising column that can potentially improve the current RMP solution. Such a route is then added to the RMP, and the dual variables are updated accordingly. The procedure iterates: solving the RMP, extracting updated dual values, reformulating the pricing subproblem, and searching for improving routes, until no negative reduced cost column can be identified. This iterative mechanism ensures convergence to the optimal solution of the original model, leveraging the decomposition structure to efficiently handle the large solution space inherent in VRPs with energy and resource constraints.
4.2. Column Generation Procedure
To efficiently solve the RMP within the B&P framework, we employ an iterative column generation procedure to dynamically enrich the solution space with high-quality routes. The core mechanism involves dynamically generate promising delivery routes (columns) that can potentially improve the objective value of the RMP by contributing negative reduced cost. At each iteration, a labeling algorithm is used to solve the pricing subproblem and identify a set of feasible paths with negative reduced cost. To improve computational efficiency, a termination criterion is imposed. The labeling process terminates once the number of feasible columns with negative reduced cost reaches a predetermined threshold, which is empirically set to four times the number of customers. The identified paths are added to the RMP as new columns. The updated RMP is then solved using the commercial solver Gurobi to obtain revised dual prices and , corresponding to the customer coverage and vehicle capacity constraints, respectively. These dual values are used to reprice the subproblem and guide the generation of additional promising columns. This iterative process continues until no feasible path with negative reduced cost can be found. To further enhance efficiency, the selection of the labeling algorithm at each iteration is determined by an adaptive mechanism, as elaborated in Section 4.3.4.
4.3. Labeling Algorithm
To solve the RCSPP arising in the pricing subproblem, we develop both exact and heuristic labeling algorithms within a unified label management framework. This section first introduces the generalized label structure and extension procedure, followed by the specification of dominance rules and pruning criteria tailored to the exact and heuristic variants.
4.3.1. Labeling Framework
To address the RCSPP, we adopt a labeling-based dynamic programming approach. This section introduces the unified label representation, which serves as the foundation for both exact and heuristic variants of the labeling algorithm. A label encodes a partial delivery route originating from a depot and is defined as a tuple , where
- : the origin depot from which the delivery route is initiated;
- : the current vertex (i.e., the last visited customer);
- : the set of visited customers;
- : the cumulative customer demand served;
- : the remaining battery level of the EDB after leaving vertex ;
- : the earliest service start time at vertex ;
- : the accumulated reduced cost associated with this delivery route.
The labeling process begins by constructing a root label for each depot , given as , with denoting the initial energy level of the EDB at departure.
Label extension is performed iteratively. Given a label ending at node , feasible extensions to unvisited customers are conducted. The resulting label is defined as follows.
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
where and respectively denote the demand of customer , energy consumption between nodes and , travel time between nodes and , service duration at , and the earliest service start time at .
Let denote the set of unprocessed labels, and denote the set of feasible complete paths found so far. The labeling algorithm proceeds as follows:
- (1)
- Initialization: Generate root labels for all depots and set , .
- (2)
- Label selection: While , select a label for expansion.
- (3)
- Label extension: For each unvisited customer , extend label to if resource constraints are satisfied. Add feasible to .
- (4)
- Dominance check: Apply dominance rules to prune inferior labels with the same depot and end node.
- (5)
- Completion check: If corresponds to a complete and feasible route with negative reduced cost, add the corresponding path to .
- (6)
- Path selection: Select the most cost-effective path from for inclusion in the RMP.
This unified labeling framework provides the computational foundation for both the exact and heuristic algorithms developed in subsequent sections. The primary distinction between these variants lies in the dominance rules and pruning strategies applied during label expansion.
4.3.2. Exact Labeling Algorithm
The exact labeling algorithm serves as the core routine for solving the RCSPP within the pricing subproblem. Each label encodes a partial path originating from a depot and terminating at an intermediate node, along with accumulated resource attributes. A label is considered feasible if it satisfies the following conditions: (a) the cumulative demand does not exceed the loading capacity, (b) the remaining battery level is sufficient for reaching the next node, (c) the arrival time respects the time window at the current node.
To mitigate the combinatorial explosion of labels during extension, a dominance rule is applied to eliminate inferior labels. Consider two labels and that originate from the same depot and terminate at the same vertex, i.e., and . Label is said to dominate if the following conditions hold:
- (non-redundant customer coverage);
- (non-increasing cumulative demand);
- (non-decreasing residual power);
- (non-delayed arrival);
- (non-increasing reduced cost).
When these conditions are satisfied, can be safely discarded, as ensures at least equal feasibility and cost efficiency. This exact dominance criterion effectively eliminates suboptimal labels, substantially reducing the solution space and improving the computational performance of the B&P algorithm.
4.3.3. Heuristic Labeling Strategies
The exact labeling algorithm guarantees optimality by exhaustively enumerating all feasible extensions of partial paths. However, this exhaustive approach often leads to a combinatorial explosion of labels, incurring substantial computational burden, especially when the pricing subproblem is solved repeatedly within the B&P framework. To improve computational efficiency while maintaining acceptable solution quality, we propose four heuristic labeling strategies. These heuristics either relax strict dominance conditions or perform early pruning of unpromising labels during extension. The goal is to accelerate label generation by directing the search toward promising regions of the solution space.
Heuristic rule 1: Early pruning of non-improving labels.
This rule introduces a pruning criterion during label extension. When extending a label to a new node , the resulting label is immediately discarded if its reduced cost exceeds both zero and the reduced cost of the parent label, i.e., and . This eliminates extensions that are unlikely to yield paths with negative reduced cost. For instance, if extending a label leads to labels with , , , and , then is discarded. The remaining labels are further filtered using the exact dominance rule.
Heuristic rule 2: Relaxed energy-based dominance.
This rule modifies the exact dominance criterion by relaxing the constraint on the remaining battery level. A label is said to dominate if both originate from the same depot and terminate at the same node, and the following conditions hold: , , , . The battery level is omitted from comparison, thereby allowing more aggressive pruning in scenarios where battery consumption is less critical.
Heuristic rule 3: Relaxed load-based dominance.
This rule relaxes the dominance condition on the remaining load capacity of the vehicle. Specifically, label dominates if , , , . Here, the vehicle load is not included in the dominance condition, which helps preserve more feasible labels when load constraints are relatively loose.
Heuristic rule 4: Relaxed time-window dominance.
This rule targets scenarios where time window constraints are less restrictive. A label dominates if , , , . By relaxing the condition on the arrival time , the algorithm tolerates less favorable timing in favor of improved cost efficiency or reduced pruning.
Each of the above heuristics offers a distinct trade-off between solution quality and computational efficiency. During the column generation process, these strategies can be selectively employed to guide the labeling algorithm toward diverse yet tractable solution paths, improving overall performance in large-scale instances.
4.3.4. Adaptive Selection Mechanism
The performance of the column generation algorithm is heavily influenced by the choice of labeling algorithm used to solve the pricing subproblem. While exact labeling ensures optimality, it is computationally expensive. In contrast, heuristic labeling strategies are faster but may occasionally fail to identify negative reduced cost columns. To strike a balance between efficiency and solution quality, we propose an adaptive selection mechanism that dynamically chooses among multiple labeling algorithms based on their historical performance during the column generation process.
Let denote the adaptive weight of labeling algorithm after column generation iterations, and let represent its usage count. Initially, all algorithms (including the exact and four heuristic variants) are assigned equal weights , usage counts , and cumulative performance scores . After each iteration, the weights are updated according to the observed effectiveness of the selected algorithms. Specifically, the weight update rule is defined as follows:
where is a responsiveness parameter controlling the adaption rate. A higher enables faster adaptation to recent performance, while a lower emphasizes long-term stability. After each use, and the performance score is incremented by a fixed reward if the algorithm successfully identifies feasible paths with negative reduced cost; otherwise, the score remains unchanged.
At each iteration, a roulette wheel selection mechanism is used to probabilistically select one labeling algorithm based on the current normalized weights:
This approach allows the algorithm to favor more effective heuristics while retaining the possibility of exploring others. In each iteration, if any of the heuristic labeling algorithms finds feasible paths with negative reduced cost, the corresponding columns are added to the restricted master problem, and the process continues. To guarantee convergence of the column generation process, a safeguard mechanism is introduced. Specifically, if all heuristic labeling algorithms fail to identify any feasible column, the exact labeling algorithm is mandatorily invoked. The column generation process is terminated only when the exact algorithm also fails to find any column with negative reduced cost, thereby confirming the optimality of the RMP. This adaptive strategy enhances algorithm robustness and scalability by effectively allocating computational effort across competing labeling algorithms. It accelerates convergence by exploiting fast heuristics while preserving solution quality through the fallback to exact labeling when needed.
4.4. Branching Rules
In the context of B&P algorithms, the classical branching strategy based on path variables (i.e., branching on whether a specific path is selected) is known to cause severe imbalance in the branching tree. This imbalance arises because prohibiting a single path has limited impact, as there remain a large number of feasible paths satisfying the same constraints, while enforcing a specific path drastically reduces the problem size. Consequently, such strategies tend to generate highly asymmetric trees and may lead to inefficient exploration of the solution space. To address this issue, we adopt the arc-based branching scheme originally proposed by Ryan and Foster [38], which has been widely recognized as an effective and robust branching strategy in column generation contexts. In this scheme, branching is performed on whether a given arc is used in the solution.
Let denote the total usage of arc by routes originating from depot , where indicates whether arc is used in route generated from depot , and is the associated path variable. The arc with fractional usage value closest to 0.5 in the current LP solution is selected as the branching candidate. Two child nodes are then created as follows:
- Left child node: Impose . All columns (paths) in the current RMP that include arc are removed. In the pricing subproblem, arc is eliminated from the graph , without changing the subproblem formulation structure.
- Right child node: Impose . All columns that do not include arc but pass through either vertex or vertex are removed from the RMP. In the pricing subproblem, a path is required to traverse arc . To enforce this, all arcs with and with are removed from the graph , ensuring that any feasible path visiting vertex must subsequently visit vertex . Depending on the position of arc in the path, three cases are distinguished to implement the above logic.
- as the starting node: remove paths not containing but passing through ; in the graph, delete all arcs for .
- as the terminal node: remove paths not containing but passing through ; in the graph, delete all arcs for .
- as intermediate nodes: remove all arcs , and , to ensure the traversal of arc .
The complete B&B framework with arc-based branching is structured as follows.
| Step | Description |
| 1. Initialization | Construct an initial pool of feasible paths and formulate the root node RMP. |
| 2. Search tree management | Create a depth-first search tree and insert the root node. |
| 3. Node selection | Select an unexplored node from the tree. Retrieve its associated RMP and arc removal constraints. |
| 4. Solve the RMP | Apply column generation to solve the RMP, yielding LP solution . |
| 5. Check integrality | If is integer feasible, compare its objective value with the incumbent upper bound and update if better; otherwise, prune the node. If is fractional, proceed to next step. |
| 6. Branch | If the objective value is less than the current upper bound, identify arc with usage closest to 0.5, and generate two child nodes as described above. Otherwise, prune the node. |
| 7. Termination | Repeat Steps 3–6 until the search tree is empty. |
| 8. Output | Return the best integer solution identified during the search. |
5. Computational Experiments
This section presents the computational experiments conducted to evaluate the performance of the proposed IBP-HL algorithm. We begin by describing the instance generation procedure and parameter settings. Then, we compare the solution quality and computational efficiency of IBP-HL with the commercial solver Gurobi 9.1.2 on small-scale instances. Subsequently, we assess the scalability of IBP-HL on medium- and large-scale instances. All algorithms were implemented in Python 3.8 and executed on a Windows 10 PC equipped with an Intel Core i9-9900 CPU and 16 GB of RAM.
5.1. Instance Generation and Parameter Settings
To evaluate the performance of the proposed model and algorithm, three categories of problem instances, i.e., small, medium, and large, were constructed based on modified Solomon benchmark datasets. These instances were tailored to reflect the specific features of the BSC-LRP. In particular, additional input elements were incorporated to accommodate the operational characteristics of BSCs, including the coordinates of candidate BSC sites, the capacity limits of BSCs, the unit travel cost of EDBs, and their battery range constraints. Candidate BSC sites were generated following the station-generation guidelines proposed by Schneider, Stenger [11]. For each candidate BSC, the capacity limit was determined proportionally to the average daily demand of its surrounding customers, with values ranging from 9 to 15 battery units depending on instance size. Customer nodes were categorized into three spatial distributions, consistent with standard Solomon benchmarks: clustered (C), random (R), and mixed (RC), reflecting typical urban and suburban demand distribution. Customer time windows were inherited from the Solomon dataset, and to reflect different service stringencies, we considered both tight and relaxed window settings, where the upper bound was adjusted by ±20% around the original value. For all instances, the unit travel cost was set to . The maximum battery range of EDBs was defined as where denotes the farthest Euclidean distance from the depot to any node in the network. This adaptive setting ensures that the battery range scales appropriately with instance size. These parameter settings follow established practices in EVRP/ELRP studies and aim to maintain consistency across instances while preserving realistic cost and range considerations.
5.2. Performance on Small-Scale Instances
To verify the correctness of the proposed model and evaluate the effectiveness of the IBP-HL algorithm, computational experiments were first conducted on small-scale instances. These instances were deliberately constructed to be solvable by both commercial solvers and customized algorithms, enabling a direct and meaningful comparison between the proposed method and the off-the-shelf MILP solver Gurobi 9.1.2. Table 2 presents a detailed summary of the tested instance sets. Each group comprises three randomly selected instances derived from Solomon-type customer distributions as clustered (C), random (R), and mixed (RC). The “Description” section of the table provides the structural characteristics of each group, including the number of customers , candidate BSC locations , and depot locations . The “Num” column indicates the number of instances per group. The “Performance” section reports the computational results for both the IBP-HL algorithm and Gurobi. Specifically, “Optimal (Num)” denotes the number of instances where a proven optimal solution was obtained within the given time limit; “Feasible (Num)” indicates the number of instances for which a feasible solution was identified; “Avg Gap (%)” reports the average optimality gap at termination, computed as , where and represent the best upper and lower bounds, respectively. “Avg Time (s)” provides the average computation time (in seconds) across the three instances. All experiments were subject to a uniform time limit of 1800 CPU seconds, ensuring a fair assessment of both computational efficiency and solution quality.

Table 2.
Comparative results for small-scale instances.
As shown in Table 2, the proposed IBP-HL algorithm consistently outperforms Gurobi in terms of both optimality and efficiency across all tested small-scale instances. For instance groups with up to 12 customers, both algorithms were able to solve all instances to optimality. However, the IBP-HL algorithm demonstrated clear advantages in computation time. For example, when , the average runtime of IBP-HL was 9.79 s, compared to 44.27 s required by Gurobi. As the problem size increased, the performance gap between the two methods became more pronounced. In the instance groups with 15 customers, the IBP-HL algorithm successfully solved all instances to optimality with average runtimes of 74.35 and 78.18 s, respectively. In contrast, Gurobi failed to reach optimality in two out of three instances for each group, with average optimality gaps of 12.33% and 15.32%, respectively, and runtimes approaching the imposed time limit. The performance gap becomes more pronounced as the problem size increases. In the instance groups with , the IBP-HL algorithm successfully solved all instances to optimality within average runtimes of 74.35 and 78.18 s, respectively. In contrast, Gurobi only solved one out of three instances in each group within the time limit and exhibited average optimality gaps of 12.33% and 15.32%. These findings underscore the robustness and scalability of the proposed IBP-HL algorithm, particularly in handling integrated location-routing problems with complex battery-swapping constraints. The synergy of intelligent branching strategies, tailored labeling heuristics, and efficient pricing subproblem resolution enables the IBP-HL algorithm to achieve superior performance compared to general-purpose solvers, especially as instance complexity grows.
5.3. Performance on Medium-Scale Instances
To further evaluate the scalability and effectiveness of the proposed IBP-HL algorithm, we conducted computational experiments on a set of medium-scale benchmark instances. These instances are significantly larger than those in the small-scale tests and represent more practically challenging scenarios. Given the considerable computational burden associated with solving such instances using general-purpose MILP solvers, and the superior performance of the IBP-HL algorithm demonstrated previously, we focus here on assessing the internal enhancements of IBP-HL by comparing it with its baseline version, i.e., standard B&P without heuristic labeling (HL) and adaptive column selection. The middle-scale test set includes 24 instances categorized into three groups based on customer size: 20, 25, and 30. Each group contains 8 instances with heterogeneous customer distributions (R, C, and RC types), consistent with Solomon’s classification. All instances include 5 candidate BSCs and 2 depots. A runtime limit of 7200 CPU seconds was imposed for each instance to ensure comparability.
The detailed computational results for each medium-scale instance are summarized in Table 3. For each instance, the table reports the lower bound (LB) and upper bound (UB) obtained at the root node of the B&B tree, corresponding to the objective values of the linear relaxation and the best integer solution, respectively. The root node solution time () indicates the computational effort required to solve the RMP at the root node, while the number of nodes explored (node) reflects the complexity of the branching process. The best integer objective value (best obj) represents the final solution obtained by the IBP-HL algorithm, and the total computation time () denotes the overall runtime for solving each instance (up to the imposed time limit). Furthermore, the number of columns generated in the final RMP (col) reflects the degree of pricing activity and instance complexity. For comparison, we also report the total runtime () of a baseline B&P algorithm without heuristic labeling and adaptive selection strategies. Instances that failed to complete within the time limit are marked with an asterisk (*).

Table 3.
Comparative results for middle-scale instances.
The computational results presented in Table 3 reveal the effectiveness and scalability of the proposed IBP-HL algorithm across medium-scale instances. For the group with 20 customers, the algorithm solved all eight instances to proven optimality within the time limit with an average runtime of 1062.73 s. In all cases, the IBP-HL outperformed the baseline B&P algorithm without heuristic enhancement, showcasing the benefits of heuristic labeling and adaptive selection strategies. As the problem size increased to 25 customers, the IBP-HL algorithm maintained strong performance by solving six out of eight instances to optimality. Although two instances were not solved to optimality within the limit, high-quality feasible solutions were still obtained. The average runtime for this group was 2413.16 s. Compared with the baseline B&P, the IBP-HL exhibited faster convergence, particularly in structurally regular or less congested instances. For the group of 30 customers, the IBP-HL algorithm solved five out of eight instances to optimality with an average runtime of 3600.41 s. The increased computational burden was due to the larger solution space and a higher number of generated columns. Nonetheless, even when optimality was not achieved, the IBP-HL algorithm outperformed the baseline B&P in both solution quality and runtime. These findings underscore the robustness of the IBP-HL algorithm and highlight the effectiveness of the proposed acceleration strategies in solving moderately large and structurally diverse instances.
The comparative results in Figure 4 clearly illustrate that the incorporation of heuristic labeling and adaptive pricing strategies significantly accelerates convergence. In almost all instances, the IBP-HL algorithm achieved superior or comparable performance with substantially reduced computation time, particularly for instances with dispersed BSC layouts. Notably, the solution time variability remains substantial even among instances of the same size. This variability can be attributed to differences in customer spatial distribution (clustered, random, mixed) and BSC layouts, which affect the difficulty of generating and improving columns and the branching process. This indicates that the computational performance is influenced not only by problem size but also by structural instance characteristics, such as customer spatial distribution, time window tightness, and the geographic configuration of BSCs. Overall, the comparison confirms that IBP-HL provides a clear computational advantage over the baseline B&P on medium-scale cases, validating the effectiveness of the proposed enhancements in improving scalability.
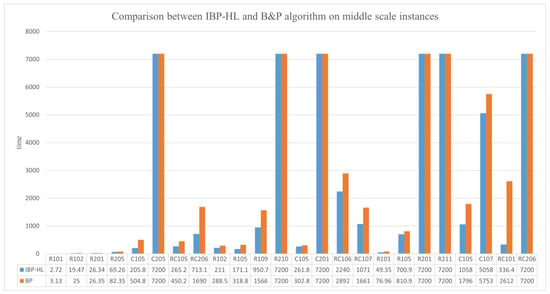
Figure 4.
The comparison between IBP-HL and the B&P algorithm on middle-scale instances.
5.4. Performance on Large-Scale Instances
To further assess the scalability and robustness of the proposed IBP-HL algorithm, we conducted computational experiments on large-scale instances involving 40 and 50 customers. These instances pose significant computational challenges due to the combinatorial explosion of feasible paths and labels. Table 4 reports the detailed results for five benchmark instances from each size category. The performance metrics are consistent with those in previous sections, including the best lower bound (), best upper bound (), root node time , number of explored nodes, best objective value, total computation time , and the number of columns generated. For the 40-customer instances, the IBP-HL algorithm successfully solved all five instances to proven optimality within the time limit, with an average runtime of 3385.82 s. This confirms the algorithm’s capability to handle moderately large problems effectively. Notably, the algorithm achieved convergence within 600 s for instances such as R101 and RC105, which highlights the effectiveness of the tailored labeling and intelligent branching strategies in significantly reducing the size of the B&B tree under favorable structural configurations. In contrast, the 50-customer instances presented significantly greater computational burden. Among the five tested instances, only one (R101) was solved to proven optimality, with a runtime of 2529.57 s and 2735 columns generated. The remaining instances reached the time limit without closing the optimality gap, underscoring the increased complexity associated with larger customer sets. The average runtime across these larger instances was 14,905.91 s. Additionally, the expanded number of depots and BSCs further enlarged the feasible label space, leading to longer solution times and more intensive column generation cycles.

Table 4.
Comparative results for larger-scale instances.
Overall, these results highlight that while the IBP-HL algorithm demonstrates strong performance on small- and medium-scale instances, its computational efficiency diminishes as instance size increases, revealing scalability challenges. Nevertheless, its ability to solve several large-scale instances within reasonable time frames underscores the practical potential of the proposed framework. Future enhancements may benefit from techniques such as stronger dual stabilization, parallelized label generation, and learning-based pricing heuristics to further improve performance on large-scale applications.
6. Conclusions
This paper studies the BSC-LRP for electric delivery bicycles in on-demand services. We propose a mixed-integer formulation and an improved branch-and-price algorithm with hybrid labeling (IBP-HL) that preserves optimality while accelerating pricing. Computational experiments on modified Solomon instances show that IBP-HL consistently outperforms a commercial solver on small cases and a baseline B&P on medium cases. For larger cases, scalability becomes the main bottleneck, although several instances can still be solved to optimality within reasonable limits.
Practically, the results indicate that jointly planning battery-swapping infrastructure and routing can reduce operating costs and improve service reliability under time-window constraints. For city planners and policymakers, the framework quantifies how station availability and capacity influence sustainable last-mile investment decisions; for logistics operators, it informs fleet sizing and depot-station cooperation in dense urban cores and supports real-time decision-making when adapted to streaming operations. Furthermore, we plan to incorporate charging operations and inventory dynamics under rolling or stochastic demand, and to explore heuristic/metaheuristic integrations to enhance scalability for very large-scale or real-time deployments. In addition, for practical industrial implementation, it would be important to conduct more comprehensive parameter investigations, including systematic sensitivity analyses on factors such as battery capacity and time-window tightness.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.C. and S.Z.; Methodology, H.Z.; Software, H.Z.; Formal analysis, Y.C., H.Z. and S.Z.; Writing—original draft, Y.C.; Writing—review & editing, S.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. LY23G020001).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xiao, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, T.; Li, N.; Martinez-Sykora, A. The electric vehicle routing problem with synchronized mobile partial recharging and non-strict waiting strategy. Ann. Oper. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghalari, A.; Salamah, D.; Kabli, M.; Marufuzzaman, M. A two-stage stochastic location–routing problem for electric vehicles fast charging. Comput. Oper. Res. 2023, 158, 106286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.; Piecyk, M.; Cherrett, T.; Juhari, M.N.; McLeod, F.; Piotrowska, M.; Bates, O.; Bektas, T.; Cheliotis, K.; Friday, A. Understanding the transport and CO2 impacts of on-demand meal deliveries: A London case study. Cities 2021, 108, 102973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnieder, M.; Hinde, C.; West, A.; Health, P. Emission Estimation of On-Demand Meal Delivery Services Using a Macroscopic Simulation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 11667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, B.; Jiang, J.; Xia, J.; Li, Q. OCD: Online crowdsourced delivery for on-demand food. IEEE Internet Things J. 2019, 7, 6842–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, M.D.; Winkenbach, M. Crowdsourced on-demand food delivery: An order batching and assignment algorithm. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2023, 149, 104055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yan, P.; Pu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Kaisar, E.I. Hybrid artificial immune algorithm for optimizing a Van-Robot E-grocery delivery system. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2021, 154, 102466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Hu, C.; Zhu, J.; Wu, M.; Malekian, R. Stochastic task scheduling in UAV-based intelligent on-demand meal delivery system. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 13040–13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. An optimization-driven dynamic vehicle routing algorithm for on-demand meal delivery using drones. Comput. Oper. Res. 2019, 111, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Hu, M. Courier Dispatch in On-Demand Delivery. Manage. Sci. 2024, 70, 3789–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Stenger, A.; Goeke, D. The Electric Vehicle-Routing Problem with Time Windows and Recharging Stations. Transp. Sci. 2014, 48, 500–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe, Á.; Ortuño, M.T.; Righini, G.; Tirado, G. A heuristic approach for the green vehicle routing problem with multiple technologies and partial recharges. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2014, 71, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, M.; Çatay, B. Partial recharge strategies for the electric vehicle routing problem with time windows. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2016, 65, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, A.; Guéret, C.; Mendoza, J.E.; Villegas, J.G. The electric vehicle routing problem with nonlinear charging function. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2017, 103, 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, R.; Kulcsár, B.; Egardt, B.; Lindroth, P.; Sanchez-Diaz, I. Energy consumption estimation integrated into the Electric Vehicle Routing Problem. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2019, 69, 141–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, S.; Jabali, O.; Laporte, G. The electric vehicle routing problem with energy consumption uncertainty. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2019, 126, 225–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, M.; Çatay, B.; Laporte, G. A simulation-based heuristic for the electric vehicle routing problem with time windows and stochastic waiting times at recharging stations. Comput. Oper. Res. 2021, 125, 105060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, T.; Fang, C.; Yang, S. A novel collaborative electric vehicle routing problem with multiple prioritized time windows and time-dependent hybrid recharging. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 244, 122990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiermann, G.; Puchinger, J.; Ropke, S.; Hartl, R.F. The Electric Fleet Size and Mix Vehicle Routing Problem with Time Windows and Recharging Stations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 252, 995–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gajpal, Y.; Appadoo, S.S.; Abdulkader, M.M.S. Electric vehicle routing problem with recharging stations for minimizing energy consumption. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 203, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Y.; Fan, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H. Collaborative multidepot electric vehicle routing problem with time windows and shared charging stations. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 219, 119654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.L.S.; Papini, M.; Penna, P.H.V.; Souza, M.J.F. A flexible variable neighbourhood search algorithm for different variants of the Electric Vehicle Routing Problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 2024, 168, 106713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Hu, W.; Gu, W.; Yu, Y.; Xu, M. A multi-mode hybrid electric vehicle routing problem with time windows. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2025, 195, 103976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.H.; Liu, X.M.; Hou, L.W.; Qi, J.H. Quantized Fuzzy Feedback Control for Electric Vehicle Lateral Dynamics. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2024, 54, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picotti, E.; Bruschetta, M.; Mion, E.; Beghi, A. A Nonlinear Model-Predictive Contouring Controller for Shared Control Driving Assistance in High-Performance Scenarios. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2023, 53, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Sun, H. Battery swap station location-routing problem with capacitated electric vehicles. Comput. Oper. Res. 2015, 55, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hof, J.; Schneider, M.; Goeke, D. Solving the battery swap station location-routing problem with capacitated electric vehicles using an AVNS algorithm for vehicle-routing problems with intermediate stops. Transp. Res. Part B Methodol. 2017, 97, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wahab, M.I.M.; Jiang, Y. Solving the battery swap station location-routing problem with a mixed fleet of electric and conventional vehicles using a heuristic branch-and-price algorithm with an adaptive selection scheme. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 186, 115683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z.; Huang, W. Simultaneous charging station location-routing problem for electric vehicles: Effect of nonlinear partial charging and battery degradation. Energy 2022, 250, 12374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, M.; Walther, G. The electric location routing problem with time windows and partial recharging. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 260, 995–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, M.; Zhang, W. A novel location-routing problem in electric vehicle transportation with stochastic demands. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 221, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çalık, H.; Oulamara, A.; Prodhon, C.; Salhi, S. The electric location-routing problem with heterogeneous fleet: Formulation and Benders decomposition approach. Comput. Oper. Res. 2021, 131, 105251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Miao, L.; Zhang, C. A branch-and-price algorithm for a green location routing problem with multi-type charging infrastructure. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2021, 156, 102529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghalari, A.; Salamah, D.E.; Marino, C.; Marufuzzaman, M. Electric vehicles fast charger location-routing problem under ambient temperature. Ann. Oper. Res. 2023, 324, 721–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, E.M.; Franco, J.F.; Echeverri, M.G.; Guimarães, F.G. A multi-objective model for the green capacitated location-routing problem considering environmental impact. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 110, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, S.N.; Souza, M.J.F.; de Souza, S.R.J.C.; Research, O. A variable neighborhood search-based algorithm with adaptive local search for the Vehicle Routing Problem with Time Windows and multi-depots aiming for vehicle fleet reduction. Comput. Oper. Res. 2023, 149, 106016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desrosiers, J.; Soumis, F.; Desrochers, M.J.N. Routing with time windows by column generation. Networks 1984, 14, 545–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, D.M.; Foster, B.A. An integer programming approach to scheduling. In Computer Scheduling of Public Transport: Urban Passenger Vehicle and Crew Scheduling; Brans, W., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1981; pp. 269–280. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).