A Statistical Analysis of the Effect of Fin Design Factors on the Cooling Performance and System Mass of PCM–Fin Structured BTMS for LIB Cell
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Thermal Fluid Analysis Method of PCM–Fin Structured BTMS
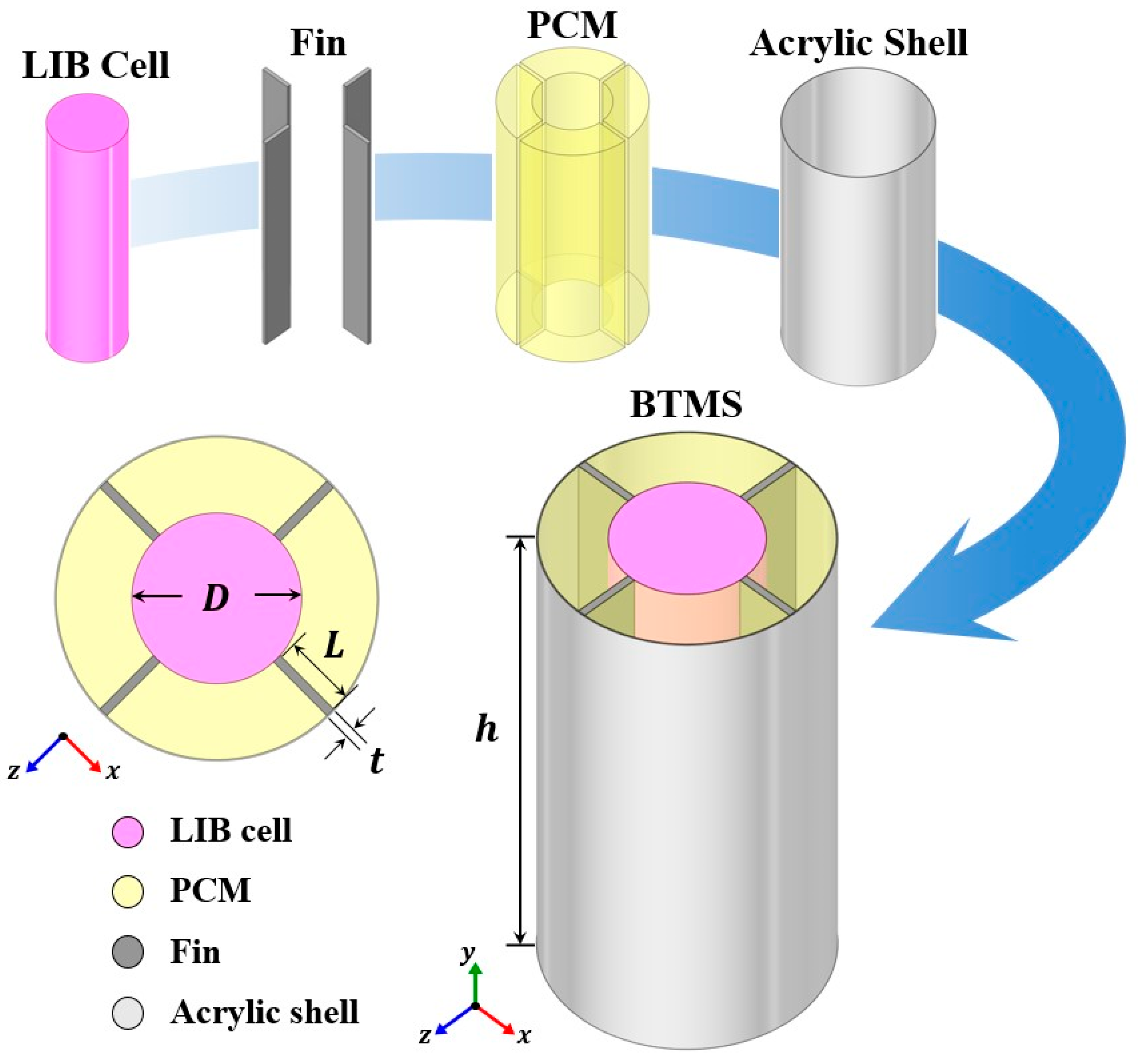
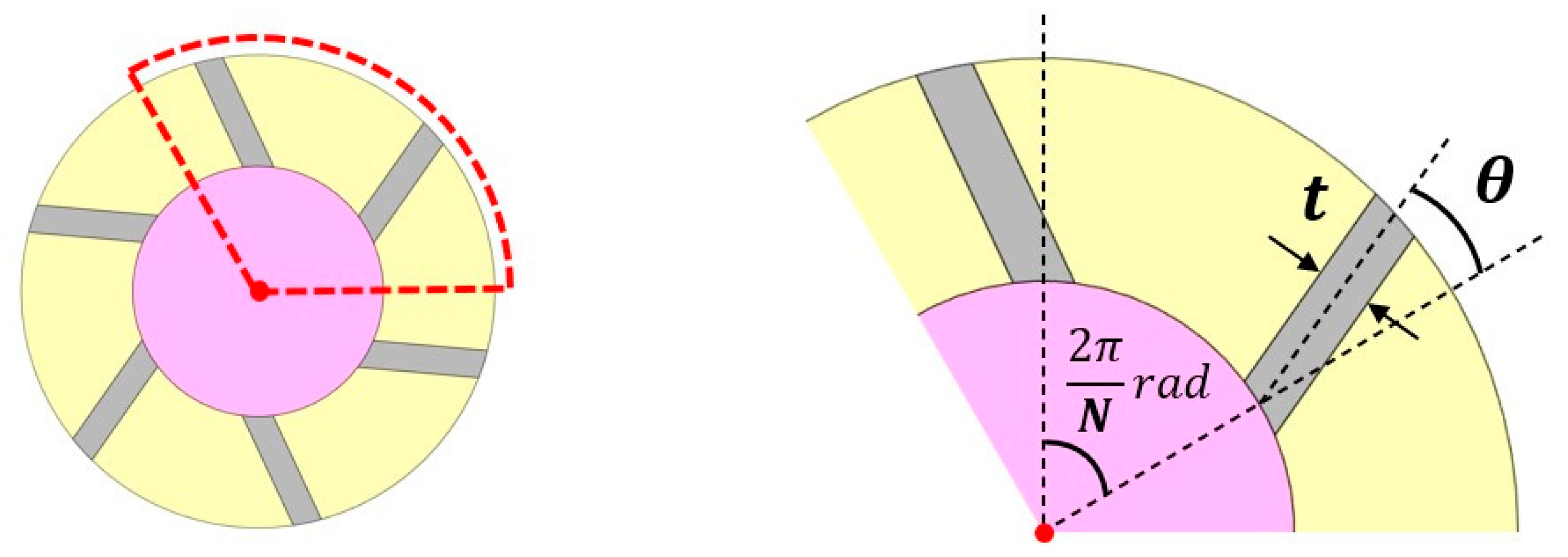
2.1. 18650 Cylindrical LIB Cell with PCM-Fin Structured BTMS
2.2. Numerical Analysis
2.2.1. Governing Equations
- The phase state of PCM is homogeneous and isotropic [30].
- The flow of liquid PCM is unsteady, laminar, and incompressible.
- The effect of radiation heat transfer is neglected.
- The BTMS interior is assumed to be fully filled with PCM without voids, and additional structural elements (e.g., encapsulation layers, other protective casings beyond the acrylic shell, and adhesives) are not considered.
- The thermal contact resistance between the cell and the fins is neglected, assuming ideal thermal contact [31].
2.2.2. Initial and Boundary Conditions
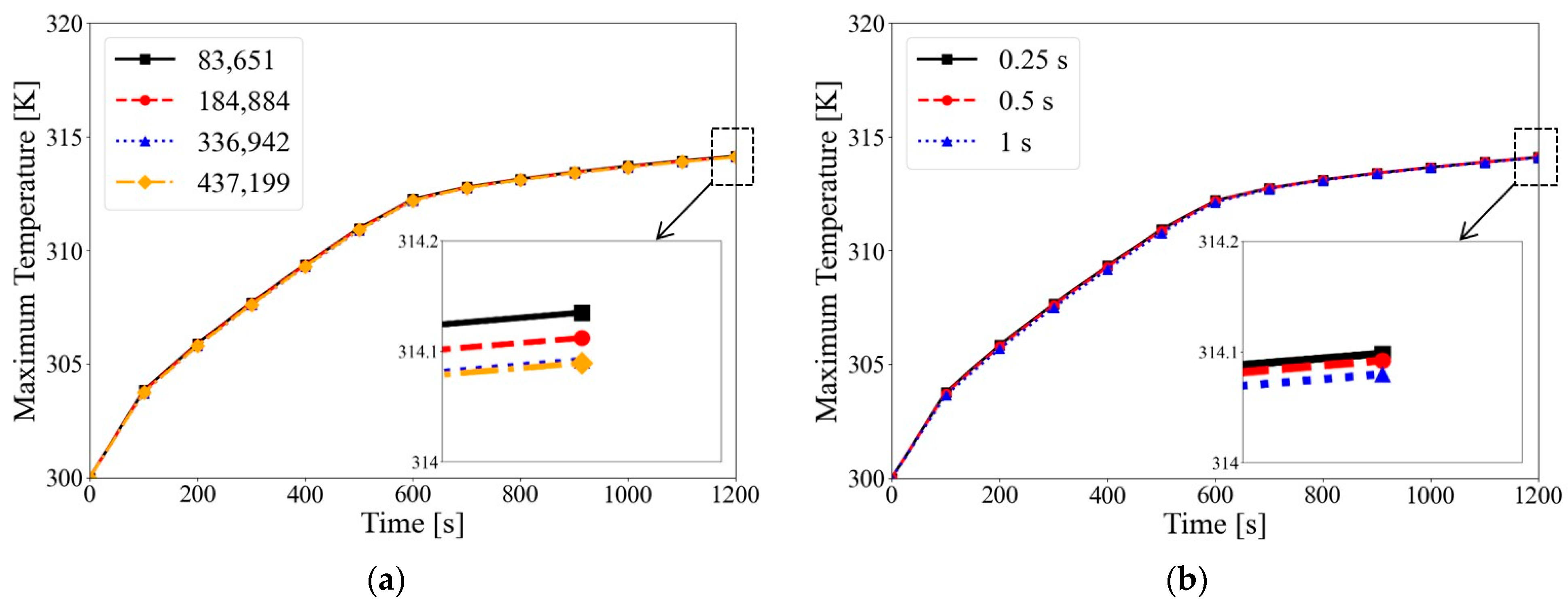
2.2.3. Grid and Time Step Independence
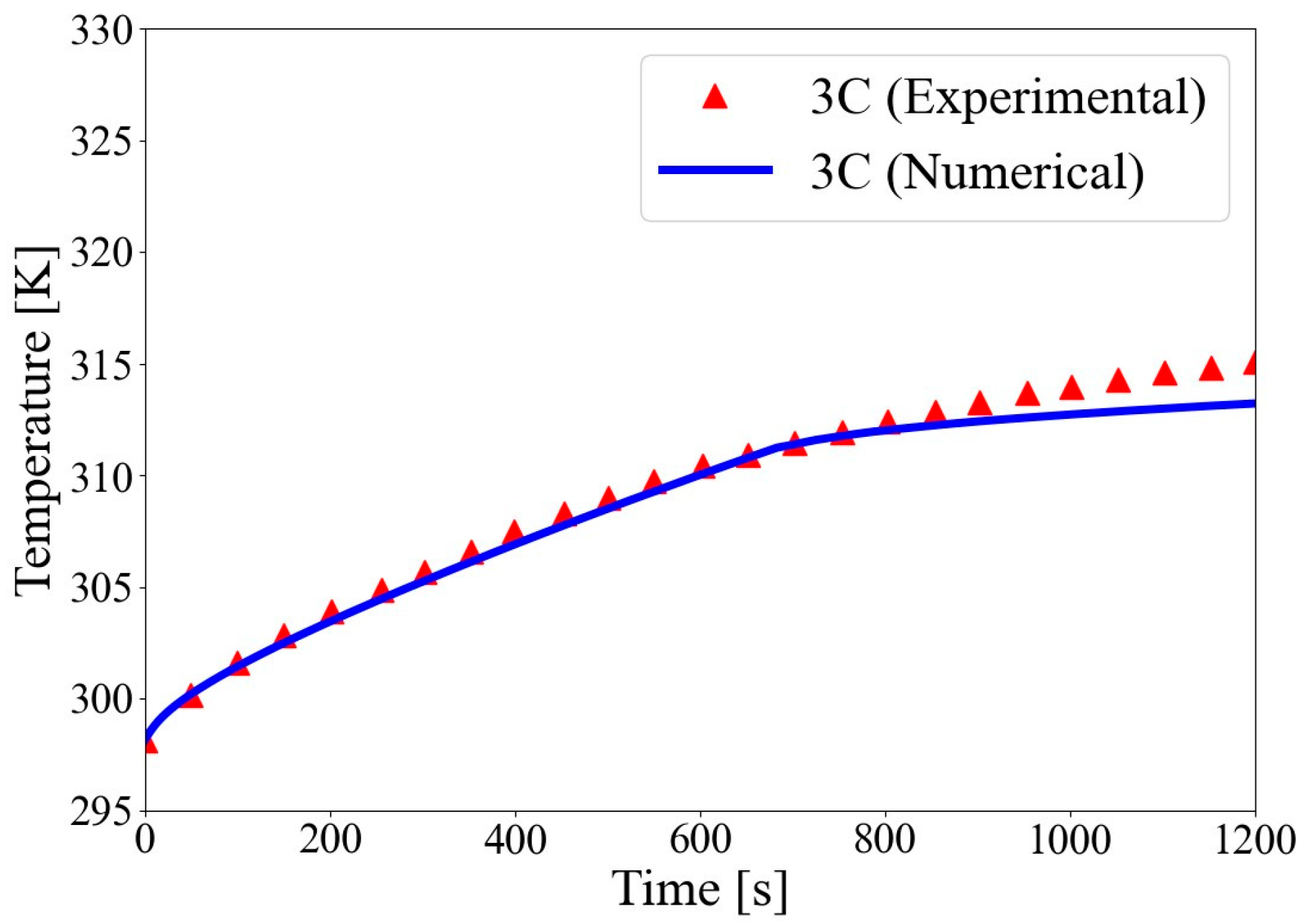
2.2.4. Validation of Numerical Analysis Method
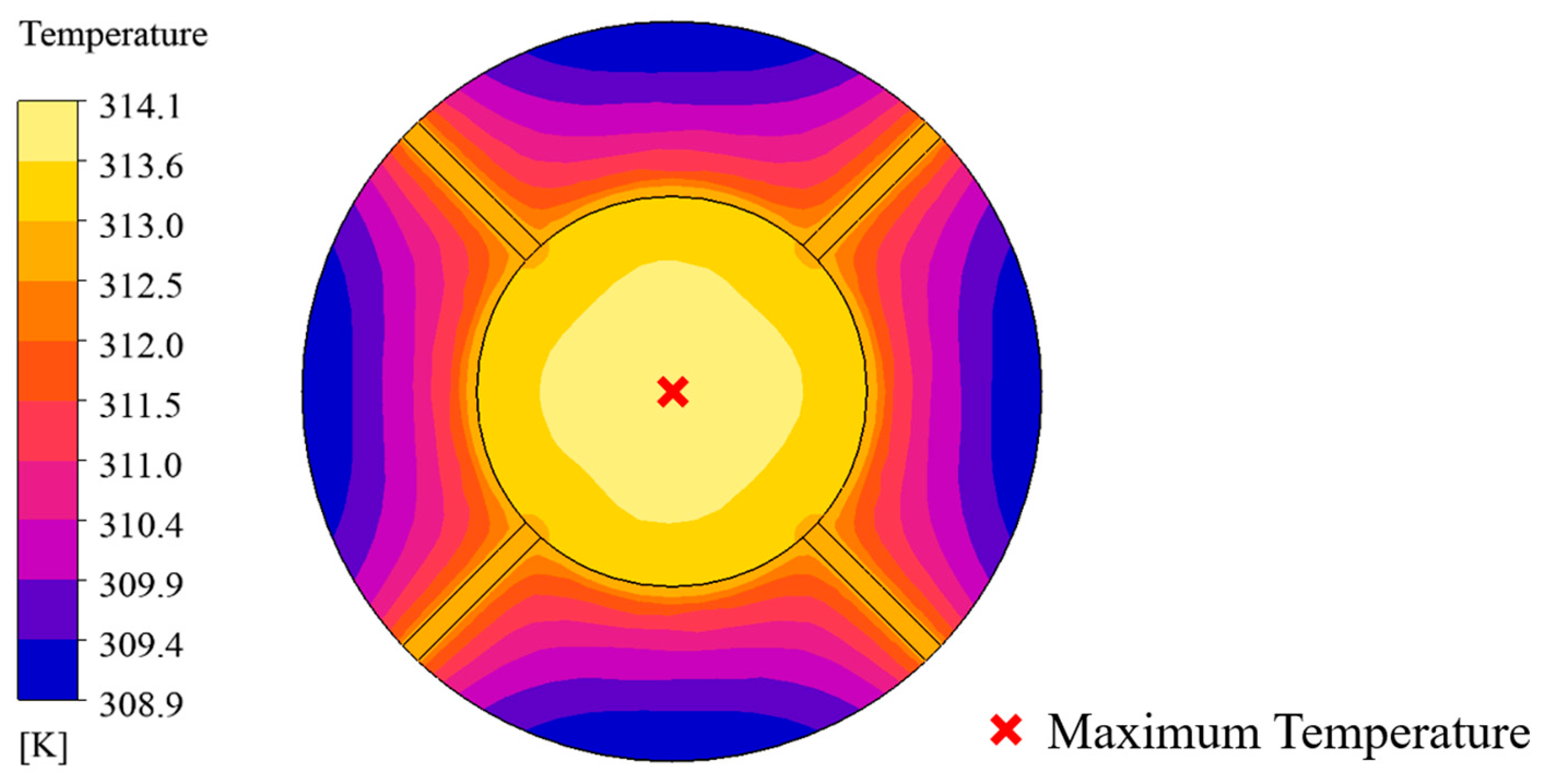
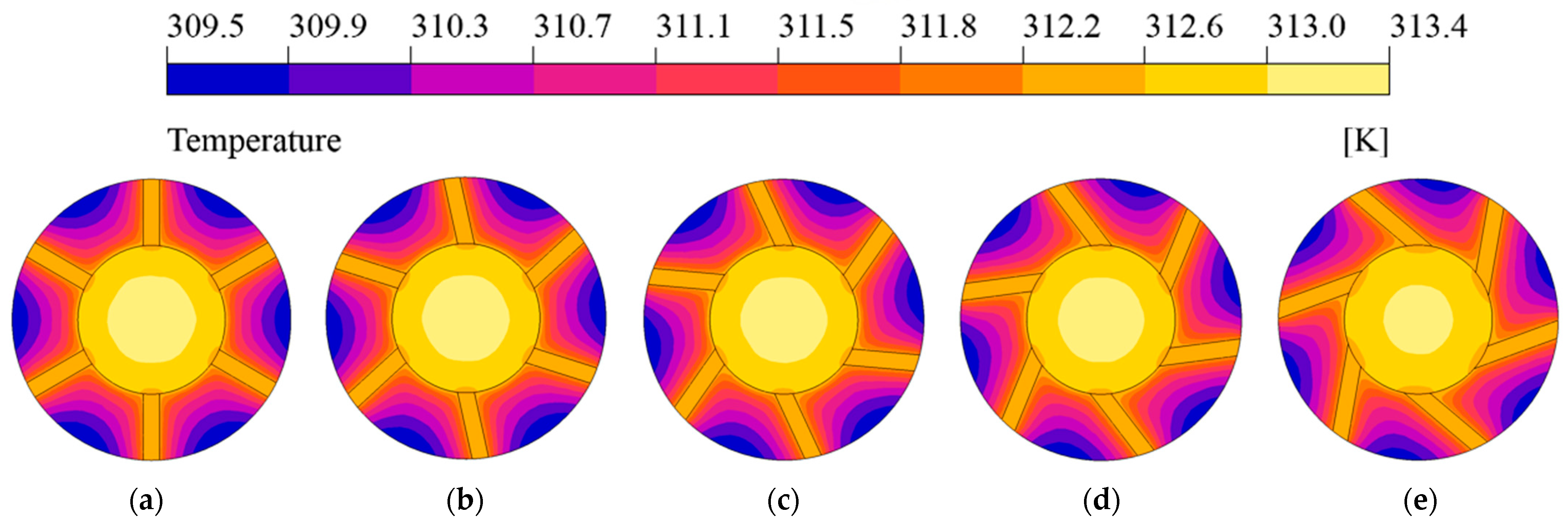
2.3. Numerical Analysis Result
3. Statistical Analysis for Thermal Characteristics of a LIB Cell
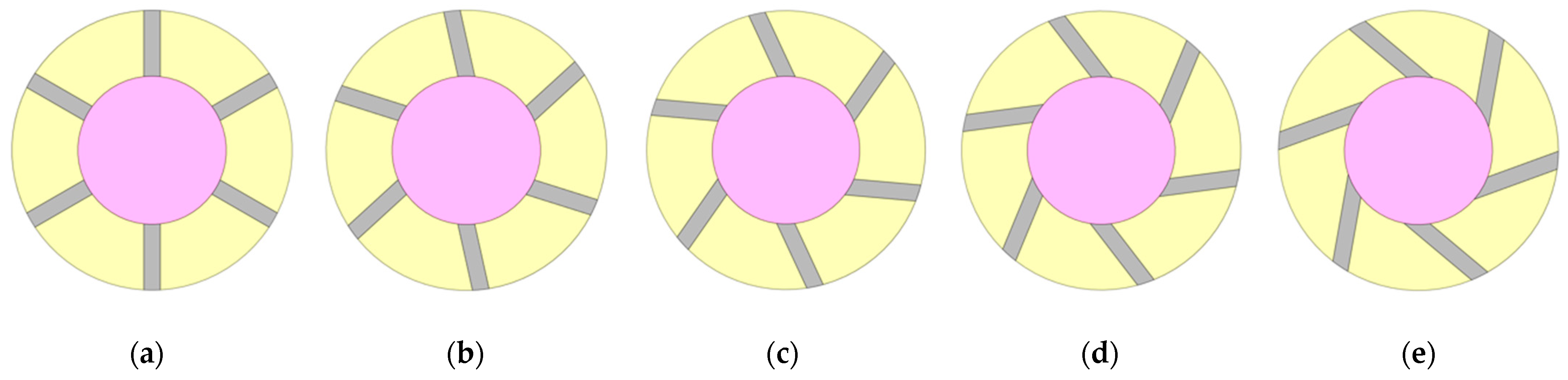
3.1. Design Factors and Responses of DoE
3.2. Analysis of Variance (ANOVA)
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Effect of Fin Design Factors of BTMS
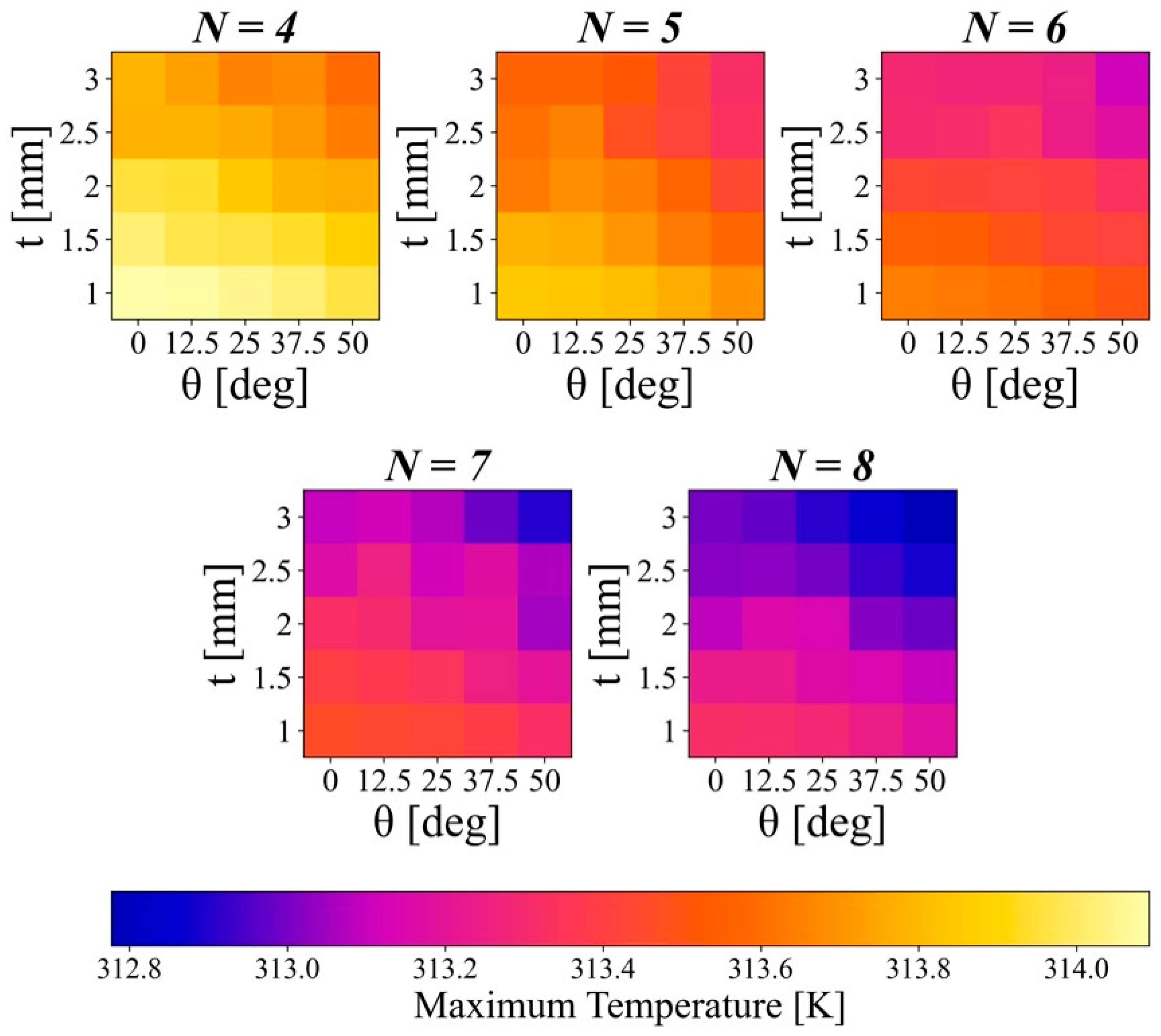
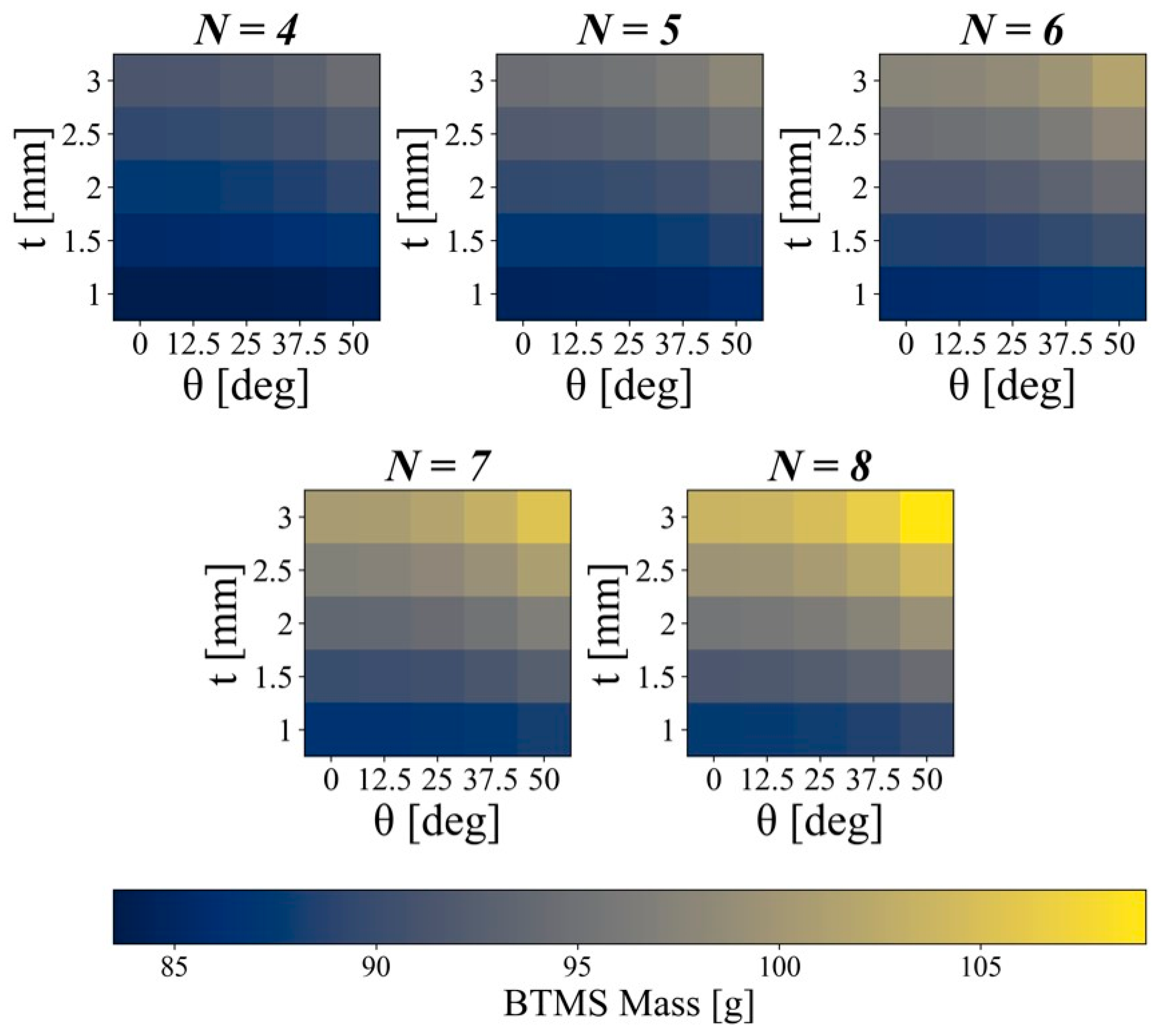
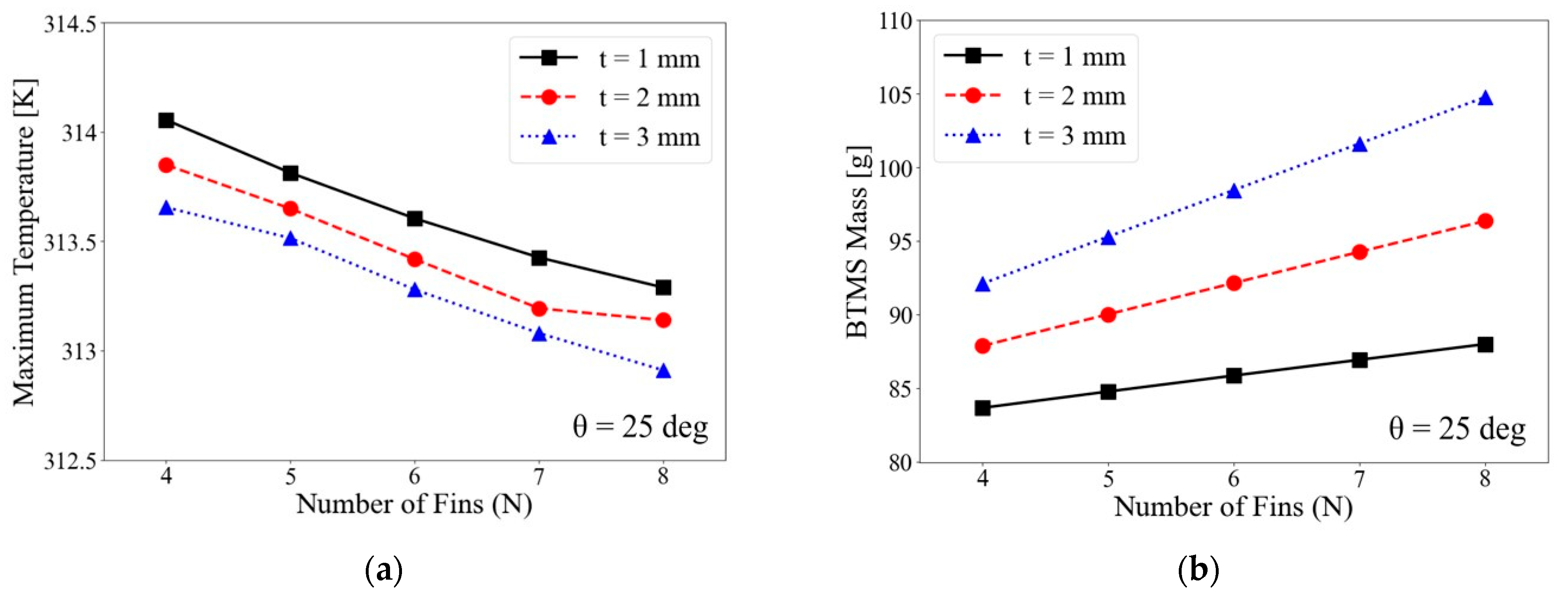
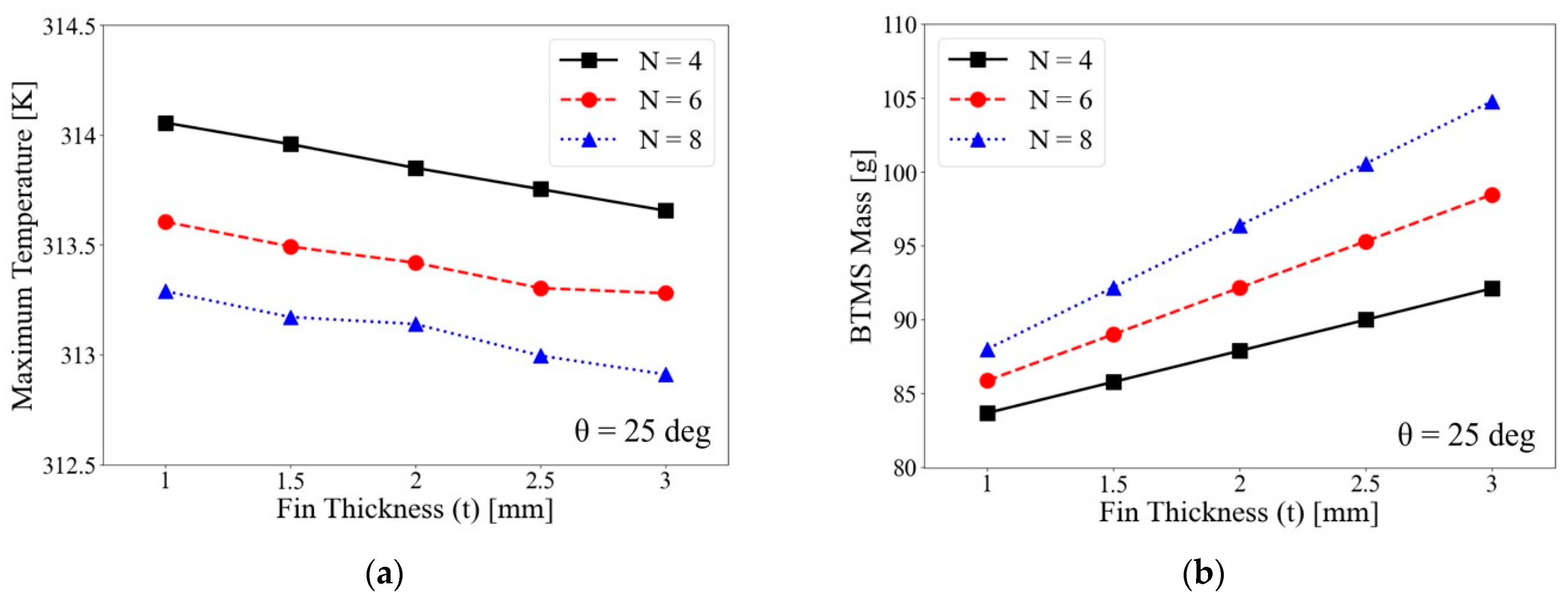
4.1.1. Number of Fins
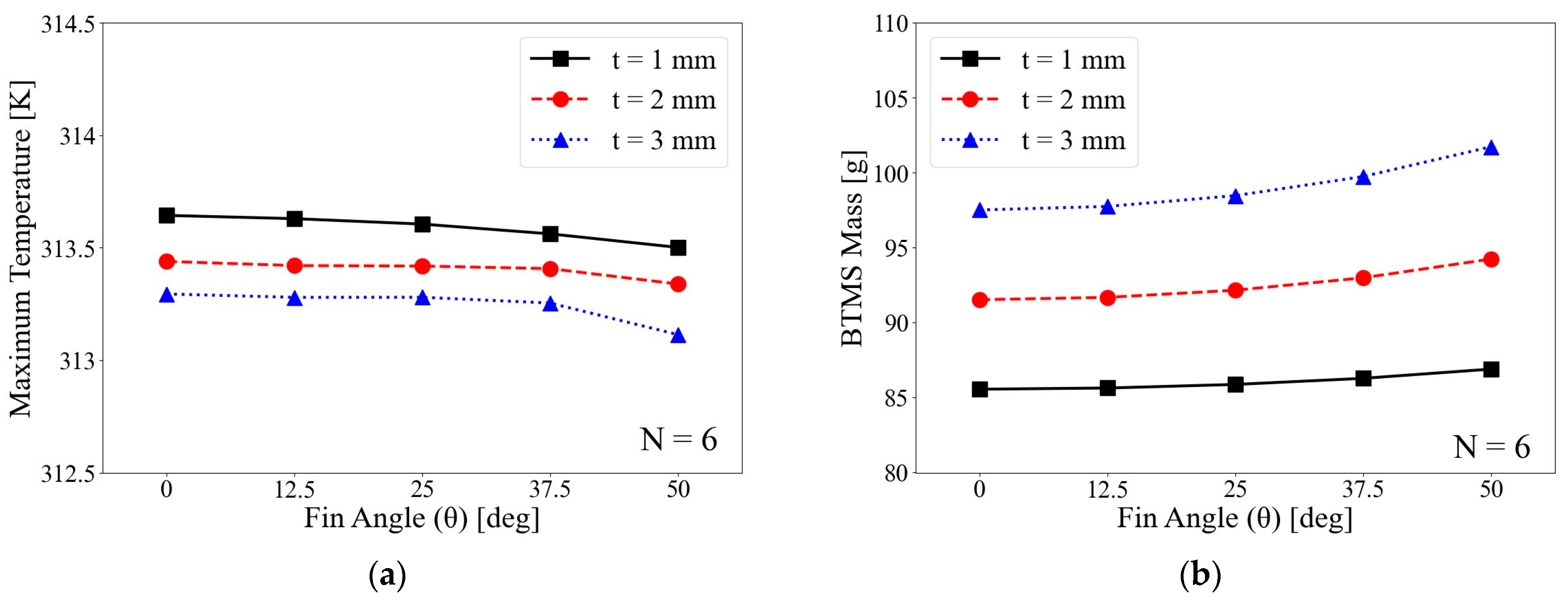
4.1.2. Fin Thickness
4.1.3. Fin Angle
4.2. ANOVA Results for Responses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCM | Phase Change Material |
| LIB | Lithium-ion Battery |
| BTMS | Battery Thermal Management System |
| DoE | Design of Experiments |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| PDE | Partial Differential Equation |
| FFD | Full Factorial Design |
| CFD | Computational Fluid Dynamics |
| SS | Sum of Squares |
| MS | Mean Square |
| DoF | Degrees of Freedom |
References
- Jaguemont, J.; Omar, N.; Van den Bossche, P.; Mierlo, J. Phase-Change Materials (PCM) for Automotive Applications: A Review. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2018, 132, 308–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Chang, H.K.; Kim, C.W. Enhancing Thermal Stability in Prismatic Lithium-Ion Battery Pack in Electric Vehicle through Optimization for an Indirect Liquid-Cooling System. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2025, 12, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Ouyang, D.; Chen, M.; Yuen, A.C.Y.; Li, A.; Lee, E.W.M.; Yang, W.; et al. Safety Issue on PCM-Based Battery Thermal Management: Material Thermal Stability and System Hazard Mitigation. Energy Storage Mater. 2022, 53, 580–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, C.W. A Statistical Analysis of Thermal Characteristics of 55-Ah Large-Format LIB Pouch Cell with Different Tab-Type, Tab Size, and Tab Position. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 30, 101777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zou, B.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, Z.; Ding, J.; Ding, Y. A Comprehensive Review of Composite Phase Change Material Based Thermal Management System for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, B.; Cai, S. A Review of Battery Thermal Management Systems Using Liquid Cooling and PCM. J. Energy Storage 2024, 76, 109836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, H.; Park, C.; An, J.; Kim, C.W. Optimization Using Kriging Metamodel and CMA-ES to Improve Temperature Uniformity of Electric Vehicle Liquid-Cooled Cylindrical Li-Ion Battery BTMS. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2024, 12, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouhara, H.; Khordehgah, N.; Serey, N.; Almahmoud, S.; Lester, S.P.; Machen, D.; Wrobel, L. Applications and Thermal Management of Rechargeable Batteries for Industrial Applications. Energy 2019, 170, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Sun, X.D.; Hu, D.H.; Li, R.Z.; Tang, W. Research on Heat Dissipation Performance and Flow Characteristics of Air-Cooled Battery Pack. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 42, 3658–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.; Agelin-Chaab, M. Experimental and Numerical Studies on Air Cooling and Temperature Uniformity in a Battery Pack. Int. J. Energy Res. 2018, 42, 2246–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Qi, H.; Liu, X.; Ouyang, C.; Wang, Y. Structural Optimization of Lithium-Ion Battery for Improving Thermal Performance Based on a Liquid Cooling System. Int. J. Heat Mass. Transf. 2019, 130, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, C.; Li, W.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Qi, D. Heat Dissipation Optimization for a Serpentine Liquid Cooling Battery Thermal Management System: An Application of Surrogate Assisted Approach. J. Energy Storage 2021, 40, 102771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, J.; Kumar Hotta, T. A Comprehensive Review of Heat Pipe: Its Types, Incorporation Techniques, Methods of Analysis and Applications. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2023, 42, 101860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Singh, R.; Hinterberger, M.; Mochizuki, M. Battery Thermal Management System for Electric Vehicle Using Heat Pipes. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2018, 134, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Cheng, W.L.; Zhao, R. Thermal Management of Li-Ion Battery Pack with the Application of Flexible Form-Stable Composite Phase Change Materials. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 182, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Gao, R.; Liu, S. A Novel Battery Thermal Management System Based on P Type Triply Periodic Minimal Surface. Int. J. Heat Mass. Transf. 2022, 194, 123090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zou, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, L. Battery Thermal Management Systems (BTMs) Based on Phase Change Material (PCM): A Comprehensive Review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 132741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Su, S.; Xin, Q.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, H.; Zeng, X.; Xiao, J. Thermal Management of Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on Honeycomb-Structured Liquid Cooling and Phase Change Materials. Batteries 2023, 9, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Cao, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, X.; Gao, X. Compact Liquid Cooling Strategy with Phase Change Materials for Li-Ion Batteries Optimized Using Response Surface Methodology. Appl. Energy 2018, 228, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Dang, C.; Yin, L.; Ren, H. Optimal Distribution of the Fin Structures in a Phase Change Material Module for Battery Thermal Management. J. Energy Storage 2024, 99, 113194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darkwa, J.; Zhou, T. Enhanced Laminated Composite Phase Change Material for Energy Storage. Energy Convers. Manag. 2011, 52, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, K.A.; Verma, S.; Bhattacharyya, S. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of Nanoparticle Assisted PCM-Based Battery Thermal Management System. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2024, 149, 11223–11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samimi, F.; Babapoor, A.; Azizi, M.; Karimi, G. Thermal Management Analysis of a Li-Ion Battery Cell Using Phase Change Material Loaded with Carbon Fibers. Energy 2016, 96, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Li, Z.; Hong, W.; Wu, Q.; Yu, X. Experimental and Numerical Study of PCM Thermophysical Parameters on Lithium-Ion Battery Thermal Management. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhai, L.; Zhang, L.; Yi, M.; Du, B.; Li, S. A Novel Hybrid Battery Thermal Management System with Fins Added on and between Liquid Cooling Channels in Composite Phase Change Materials. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2022, 207, 118198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Zheng, N.; Sun, Z. Evaluation of Fin Intensified Phase Change Material Systems for Thermal Management of Li-Ion Battery Modules. Int. J. Heat Mass. Transf. 2021, 166, 120753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Gao, R.; Liu, S. Thermal Conductivity Enhancement and Thermal Saturation Elimination Designs of Battery Thermal Management System for Phase Change Materials Based on Triply Periodic Minimal Surface. Energy 2022, 259, 125091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Fan, R.; Yan, F.; Zhou, T.; Zheng, N. Thermal Management of the Lithium-Ion Battery by the Composite PCM-Fin Structures. Int. J. Heat Mass. Transf. 2019, 145, 118739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhari, V.G.; Dhoble, A.S.; Panchal, S. Numerical Analysis of Different Fin Structures in Phase Change Material Module for Battery Thermal Management System and Its Optimization. Int. J. Heat Mass. Transf. 2020, 163, 120434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, J. Thermal Management Optimization Strategy for Lithium-Ion Battery Based on Phase Change Material and Fractal Fin. J. Energy Storage 2024, 102, 114159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Fan, R.; Zheng, N. Thermal Management of a Simulated Battery with the Compound Use of Phase Change Material and Fins: Experimental and Numerical Investigations. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2021, 165, 106945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutheesh, P.M.; Jose, J.; Hotta, T.K.; Rohinikumar, B. Numerical Investigations on Thermal Performance of PCM-Based Lithium-Ion Battery Thermal Management System Equipped with Advanced Honeycomb Structures. Int. Commun. Heat Mass. Transf. 2024, 158, 107937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagdevir, T.; Ding, Y. Numerical Investigation of Battery Thermal Management by Using Helical Fin and Composite Phase Change Material. J. Energy Storage 2024, 75, 109674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Ouyang, N.; Yuan, J.; Xie, Y.; Wu, W. Optimization Design of a Hybrid Thermal Runaway Propagation Mitigation System for Power Battery Module Using High-Dimensional Surrogate Models. Renew. Energy 2024, 225, 120288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Peng, R.; Ping, P.; Du, J.; Chen, G.; Wen, J. A Novel Battery Thermal Management System Coupling with PCM and Optimized Controllable Liquid Cooling for Different Ambient Temperatures. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 204, 112280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lu, F.; Liang, B.; Zhu, Y.; Gou, H.; Xiao, K.; He, Y. Thermal Performance Analysis of a New Type of Branch-Fin Enhanced Battery Thermal Management PCM Module. Renew. Energy 2023, 206, 1049–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, H.; Park, C.; Kim, C.W. A Statistical Analysis of the Effect of Design Factors of the Cylindrical Battery Module on the Thermal Behavior by C-Rate. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Park, S.; Kim, C.W. Electrochemical–Thermal Fluid Coupled Analysis and Statistical Analysis of Cooling System for Large Pouch Cells. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


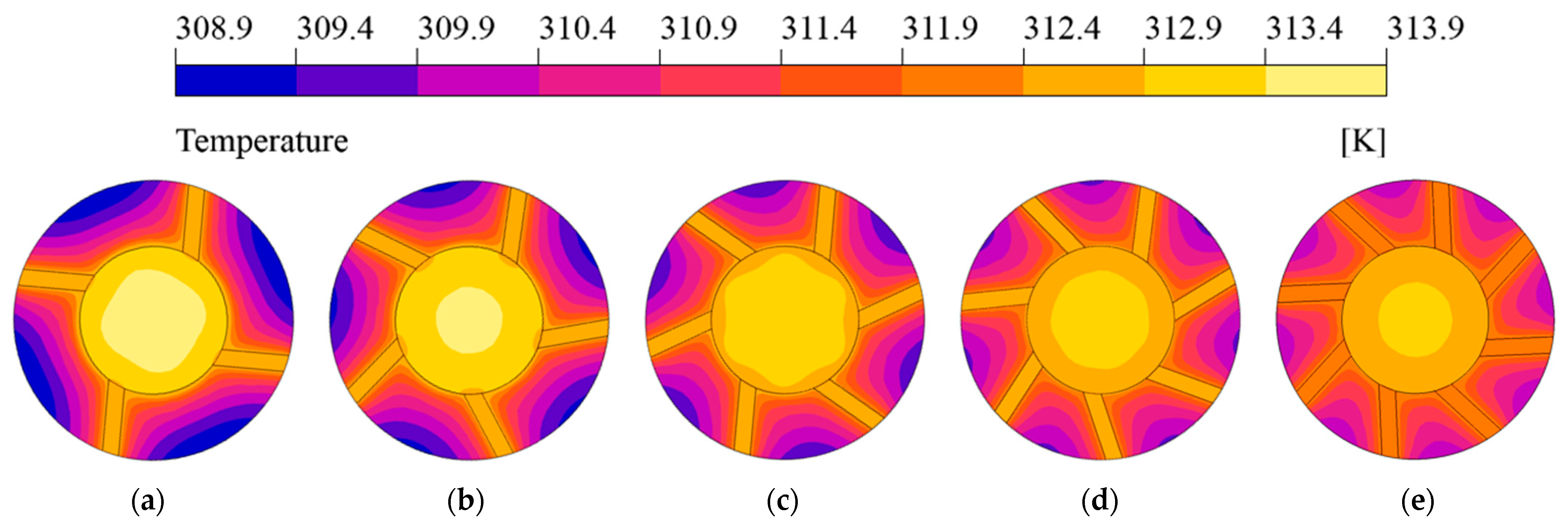
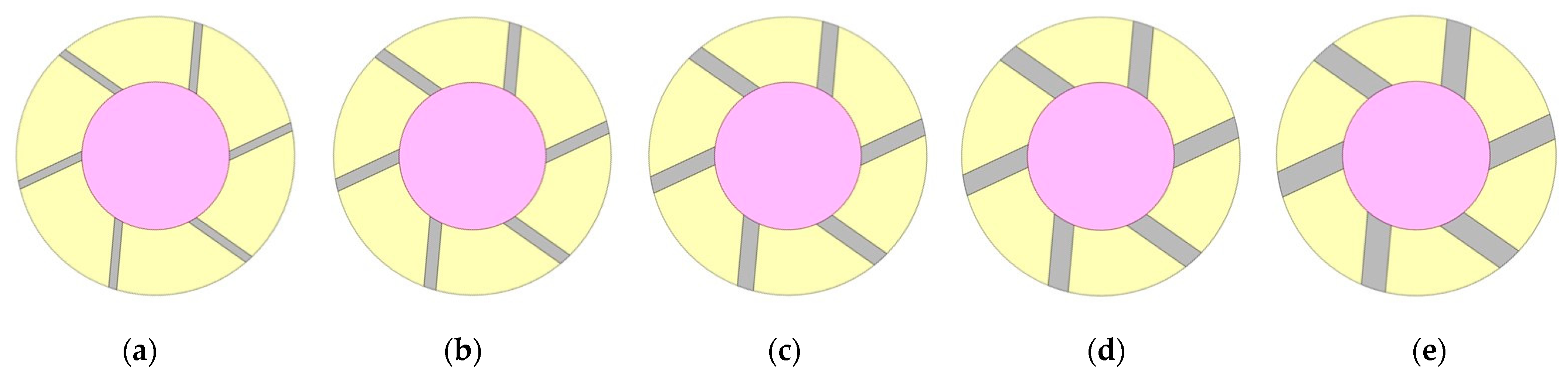
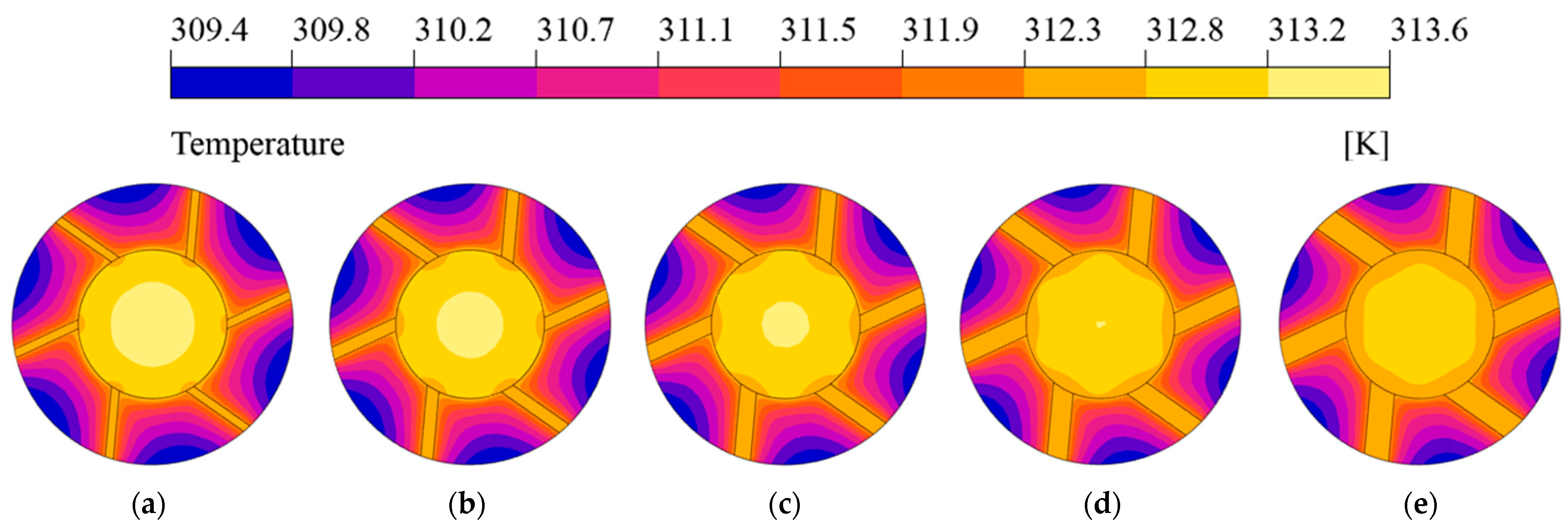
| Items | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Type | 18,650 | |
| Diameter | 18 | |
| Height | 65 | |
| Mass | 44.5 | |
| Nominal voltage | 3.6 | |
| Nominal capacity | 2.4 | |
| Internal resistance | 30 |
| Properties | Unit | LIB Cell | PCM | Aluminum | Acryl |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 2720 | 820 | 2719 | 1215 | |
| Specific heat capacity | 300 | 2000 | 871 | 1300 | |
| Thermal conductivity | 3 | 0.2 | 202.4 | 0.17 | |
| Dynamic viscosity | 0.02 | ||||
| Latent heat | 165,000 | ||||
| Solidus temperature | 311.15 | ||||
| Liquidus temperature | 316.15 |
| Design Factors | 1st Level | 2nd Level | 3rd Level | 4th Level | 5th Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | |
| [mm] | 1 | 1.5 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 |
| [deg] | 0 | 12.5 | 25 | 37.5 | 50 |
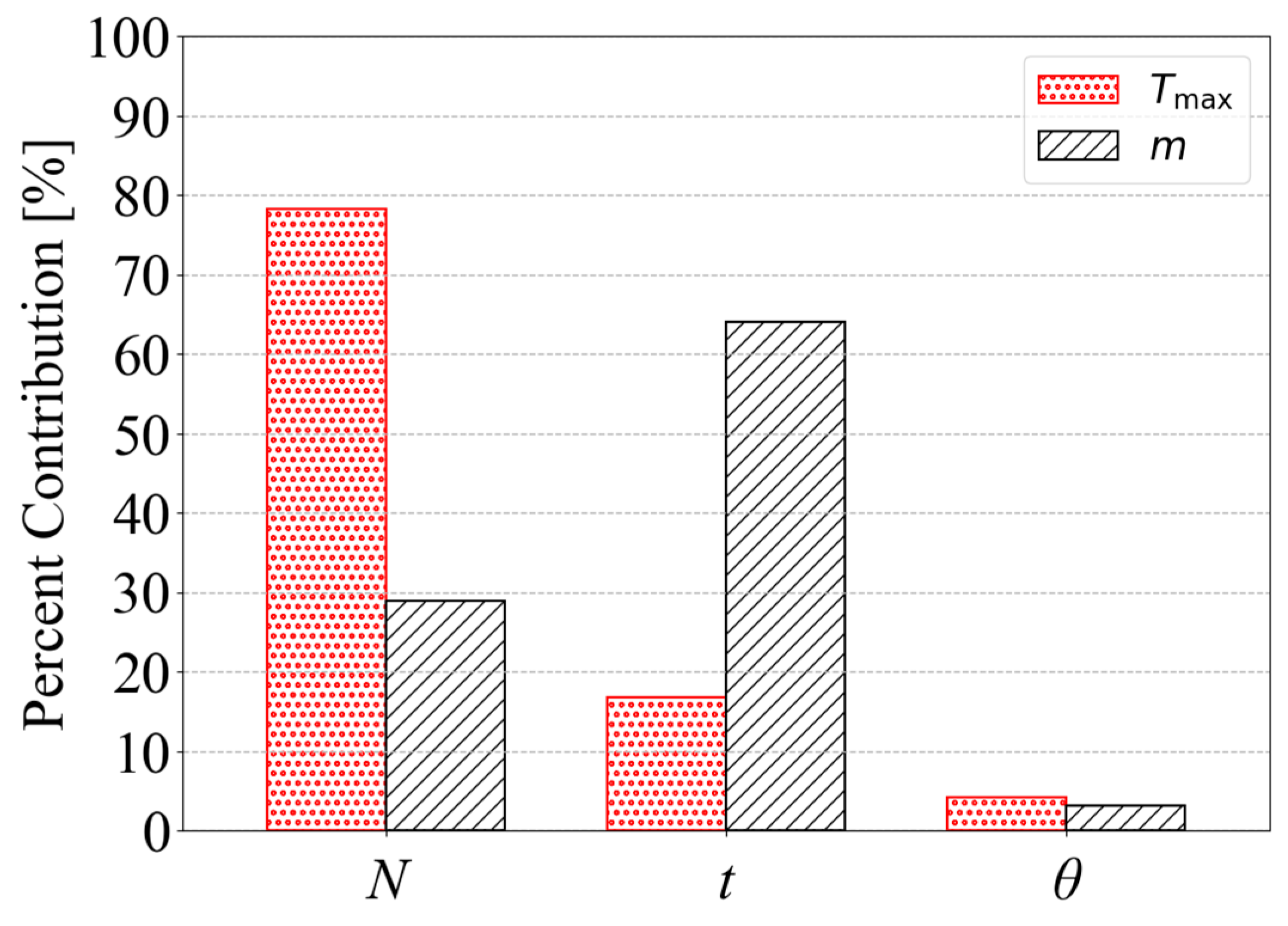
| Design Factors | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Square | -Value | Percent Contribution | -Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.460649 | 4 | 2.365162 | 3001.024 | 78.27% | <0.05 | |
| 2.019834 | 4 | 0.504958 | 640.7139 | 16.71% | <0.05 | |
| 0.495804 | 4 | 0.123951 | 157.2744 | 4.10% | <0.05 | |
| 0.022388 | 16 | 0.001399 | 1.775435 | 0.19% | 0.0548 | |
| 0.022116 | 16 | 0.001382 | 1.753866 | 0.18% | 0.0587 | |
| 0.015983 | 16 | 0.000999 | 1.267474 | 0.13% | 0.2456 | |
| Error | 0.050440 | 64 | 0.000788 | 0.42% |
| Design Factors | Sum of Squares | Degrees of Freedom | Mean Square | -Value | Percent Contribution | -Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1188.581 | 4 | 297.1452 | 196.4693 | 28.85% | <0.05 | |
| 2633.993 | 4 | 658.4983 | 435.3922 | 63.93% | <0.05 | |
| 127.8065 | 4 | 31.95162 | 21.12608 | 3.10% | <0.05 | |
| Error | 169.3917 | 112 | 1.512426 | 4.11% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Go, J.; Park, C.; Lee, H.; Kang, W.; Kim, C.-W. A Statistical Analysis of the Effect of Fin Design Factors on the Cooling Performance and System Mass of PCM–Fin Structured BTMS for LIB Cell. Mathematics 2025, 13, 2800. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13172800
Go J, Park C, Lee H, Kang W, Kim C-W. A Statistical Analysis of the Effect of Fin Design Factors on the Cooling Performance and System Mass of PCM–Fin Structured BTMS for LIB Cell. Mathematics. 2025; 13(17):2800. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13172800
Chicago/Turabian StyleGo, Jaekyung, Cheonha Park, Hamin Lee, Wonmo Kang, and Chang-Wan Kim. 2025. "A Statistical Analysis of the Effect of Fin Design Factors on the Cooling Performance and System Mass of PCM–Fin Structured BTMS for LIB Cell" Mathematics 13, no. 17: 2800. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13172800
APA StyleGo, J., Park, C., Lee, H., Kang, W., & Kim, C.-W. (2025). A Statistical Analysis of the Effect of Fin Design Factors on the Cooling Performance and System Mass of PCM–Fin Structured BTMS for LIB Cell. Mathematics, 13(17), 2800. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13172800






