Combined Optimization of Both Sensitivity Matrix and Residual Error for Improving EIT Imaging Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
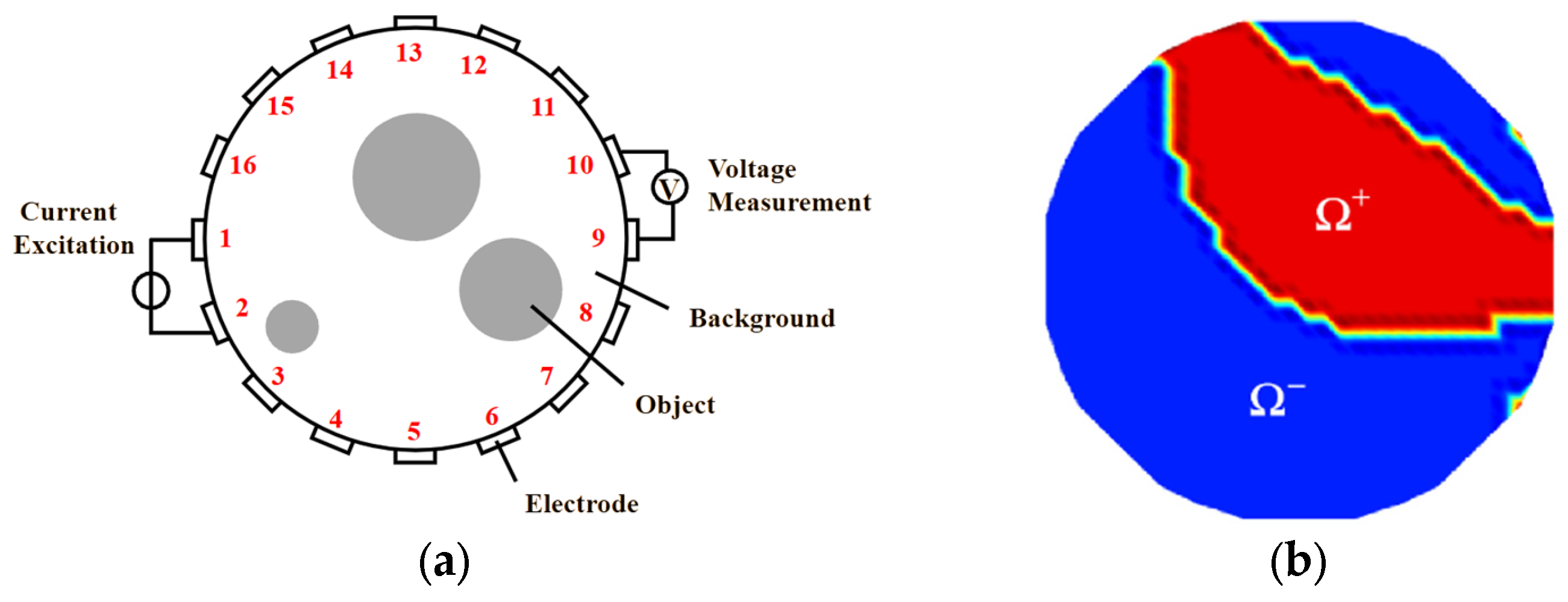
ERT Principle
3. Various Objective Functions for Improving the EIT Reconstruction Quality
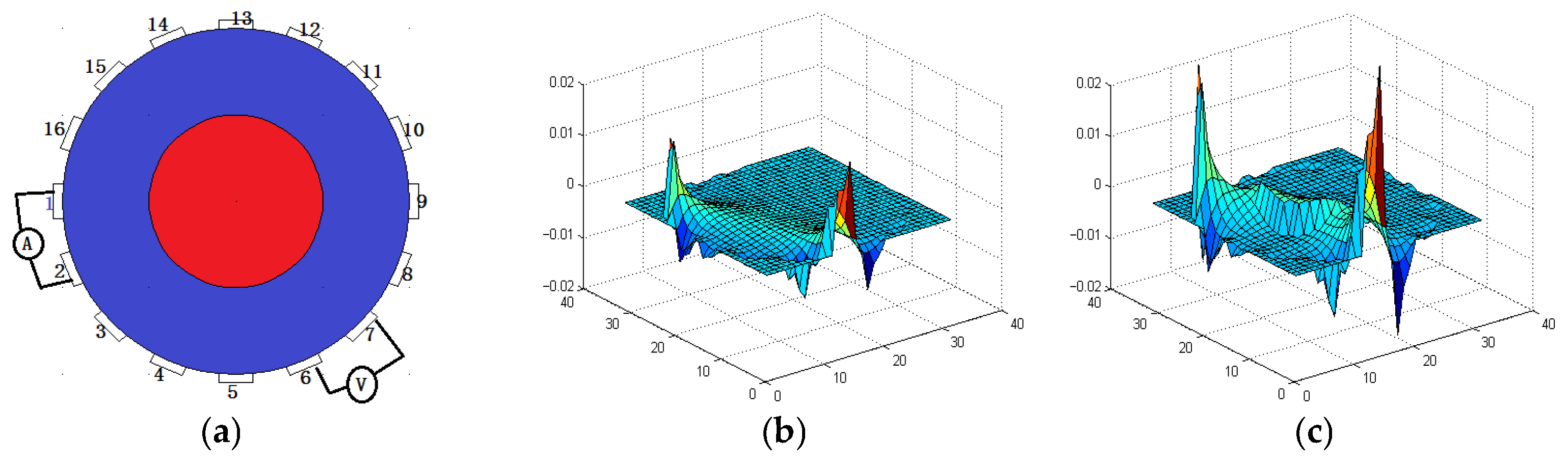
3.1. Sensitivity Matrix Analysis
3.2. NLP-DM Optimization and Solution
- (1)
- Solving the vector St+1 from F(St, gt) to F(St+1, gt) after fixing gt;
- (2)
- Solving the vector gt+1 from F(St+1, gt) to F(St+1, gt+1) after fixing St+1.
3.3. NLP-TCS Optimization and Solution
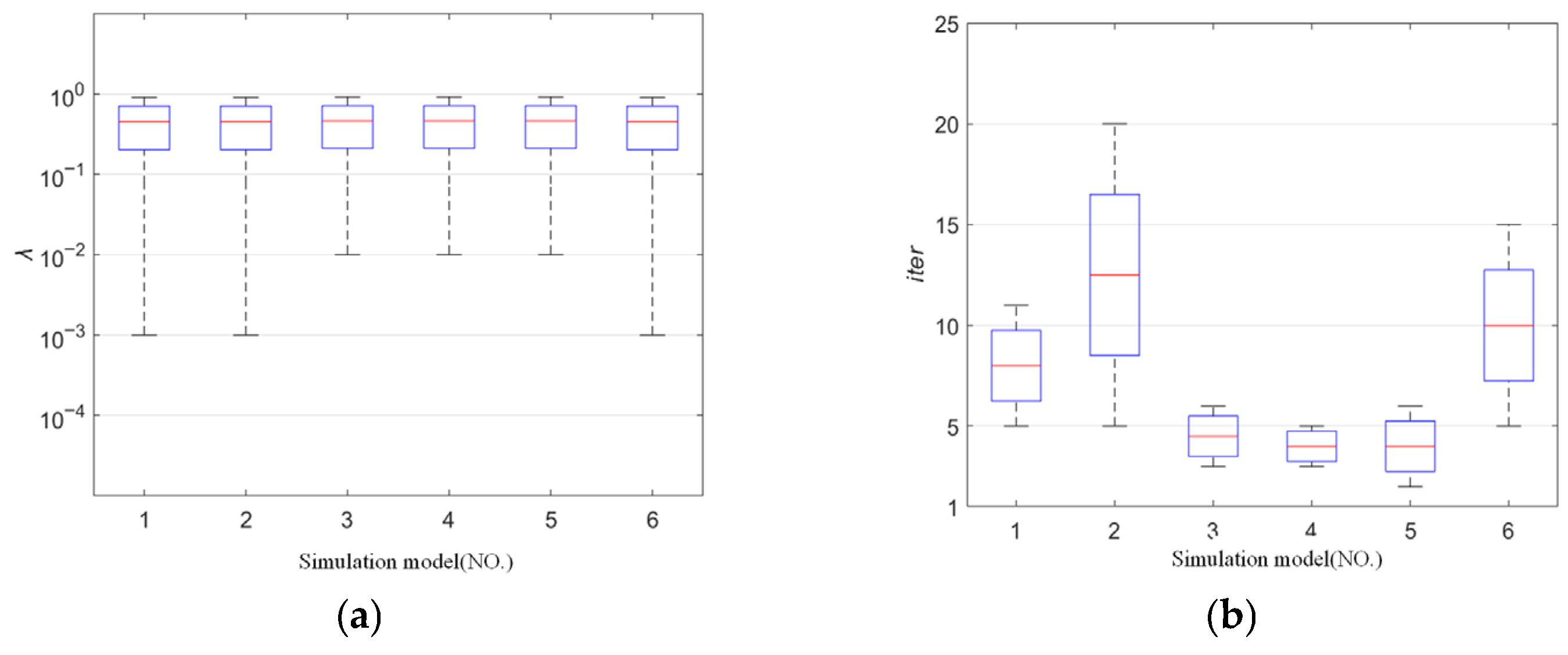
3.4. Simulation Results
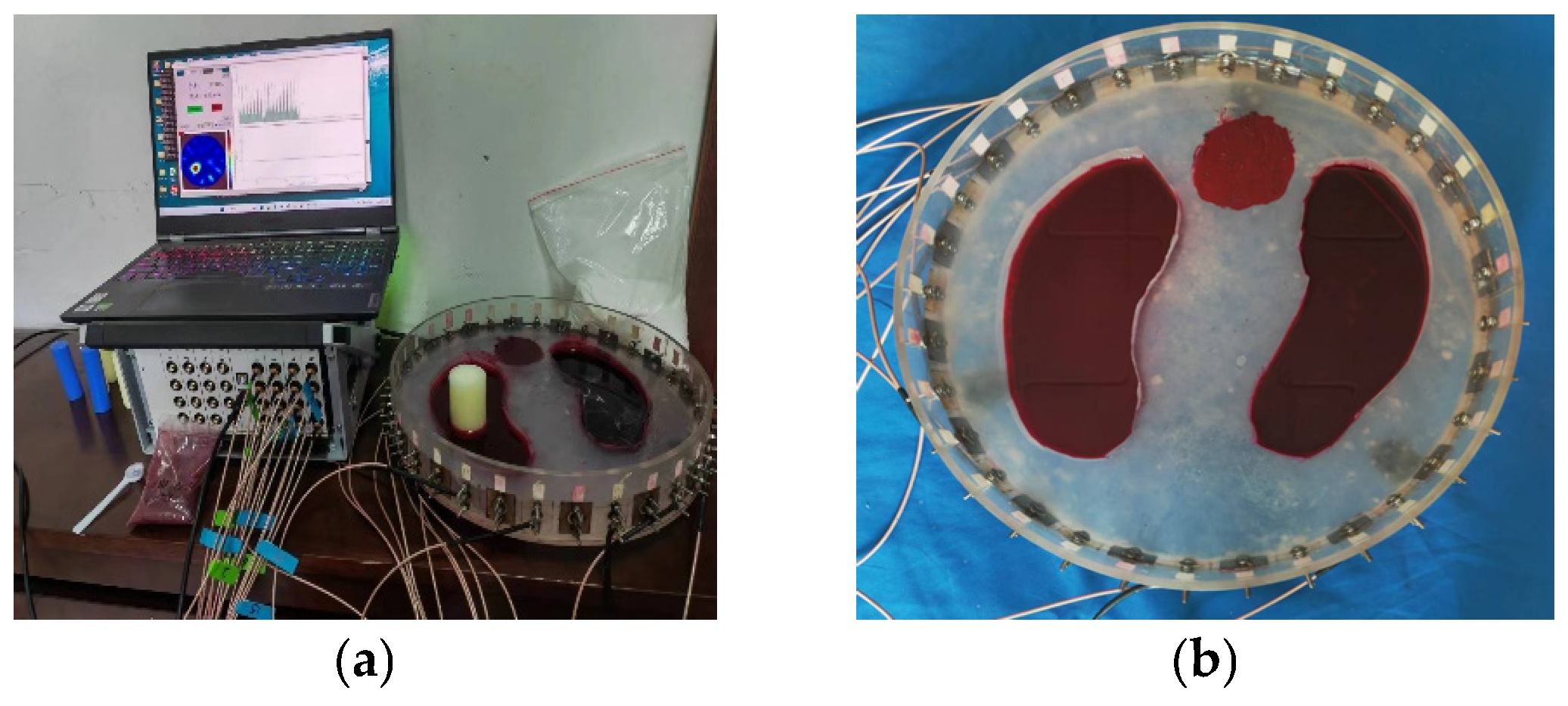
3.5. Real Experiments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.; Mo, H.; Li, R.; Liang, C.; Luo, J.; Bespal’Ko, A.A. Image reconstruction method based on wavelet fusion in electrical capacitance tomography with rotatable electrode sensor. Measurement 2024, 238, 115354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Yue, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, H. Determination of hyperparameter and similarity norm for electrical tomography algorithm using clustering validity index. Measurement 2023, 216, 112976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, X. A regularization structure based on novel iterative penalty term for electrical impedance tomography. Measurement 2023, 209, 112472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yan, Y. An integrated ECT/ERT dual modality sensor. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference, Singapore, 5–7 May 2009; pp. 1434–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, W. A dual-modality electrical tomography sensor for measurement of gas–oil–water stratified flows. Measurement 2015, 66, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Li, M.; Yang, F.; Xu, S.; Abubakar, A. Three-dimensional electrical impedance tomography with multiplicative regularization. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 66, 2470–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, M.T.; Ferree, T.C. Weighted regularization in electrical impedance tomography with applications to acute cerebral stroke. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2002, 21, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S.J.; Hauptmann, A. Deep D-bar: Real-time electrical impedance tomography imaging with deep neural networks. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyakowski, T.L.; Jeanmeure, F.; Jaworski, A.J. Applications of electrical tomography for gas–solids and liquid–solids flows—A review. Powder Technol. 2000, 112, 174–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, E.K.; Mahara, A.; Halter, R.J. A novel regularization technique for microendoscopic electrical impedance tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 1593–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, F.; Wang, X.; Huang, H. Multiclass capped p-norm SVM for robust classifications. In Proceedings of the AAAI, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; pp. 2415–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, S.; Guo, H. Hybrid iterative reconstruction method for imaging problems in ECT. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 8238–8249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, J.; Han, B.; Li, Q. Split Bregman iterative algorithm for sparse reconstruction of electrical impedance tomography. Signal Process. 2012, 92, 2952–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Deng, J.S.; Liu, D. Deep prior embedding method for Electrical Impedance Tomography. Neural Netw. 2025, 188, 1872–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Rao, Z.; Wang, M.; Soleimani, M. Reduction of staircase effect with total generalized variation regularization for electrical impedance tomography. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 9850–9858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Han, B.; Dong, F. A new regularization algorithm based on the neighborhood method for electrical impedance tomography. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2018, 29, 085401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.F.; Chen, D. Image reconstruction of ECT based on second-order hybrid sensitivity matrix and fuzzy nonlinear programming. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 35, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, G. Image reconstruction for ECT based on high-order approximate sensitivity matrix. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2023, 34, 095402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cao, R.; Huang, Y.; Ouypornkochagorn, T.; Jia, J. Time sequence learning for electrical impedance tomography using Bayesian spatiotemporal priors. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 6045–6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Xu, Y.; Dong, F. A hybrid regularization method combining Tikhonov with total variation for electrical resistance tomography. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2015, 46, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.Y.; Yue, S.H.; Hao, Z.; Cui, Z.; Wang, H. An improved Tikhonov regularization method for lung cancer monitoring using electrical impedance tomography. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 3049–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moura, H.L.; Pipa, D.R.; do Nascimento Wrasse, A.; da Silva, M.J. Image reconstruction for electrical capacitance tomography through redundant sensitivity matrix. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 8157–8165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimas, C.; Uzunoglu, N.; Sotiriadis, P.P. An efficient point-matching method-of-moments for 2D and 3D electrical impedance tomography using radial basis functions. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 69, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yue, S.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; McEwan, A. An unsupervised evaluation and optimization for electrical impedance tomography. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.Y.; Yue, S.H.; Cui, Z.Q.; Wang, H.X. A new linear back projection algorithm to electrical tomography based on measuring data decomposition. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 125402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, L. Sparse reconstruction of EMT based on compressed sensing and Lp regularization with the split Bregman method. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2023, 94, 102473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geselowitz, D.B. An application of electrocardiographic lead theory to impedance plethysmography. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1971, 1, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, M.; Neubauer, A.; Scherzer, O. A convergence analysis of the Landweber iteration for nonlinear ill-posed problems. Numer. Math. 1995, 72, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.Z.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Wu, T.L.; Cheung, J.; Chan, W. Tensor Convolution-like Low-Rank Dictionary for High-Dimensional Image Representation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2024, 34, 13257–13270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.H.; Huang, Y.M.; Wu, H.C.; Tan, C. Efficient Multitask Structure-Aware Sparse Bayesian Learning for Frequency-Difference Electrical Impedance Tomography. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
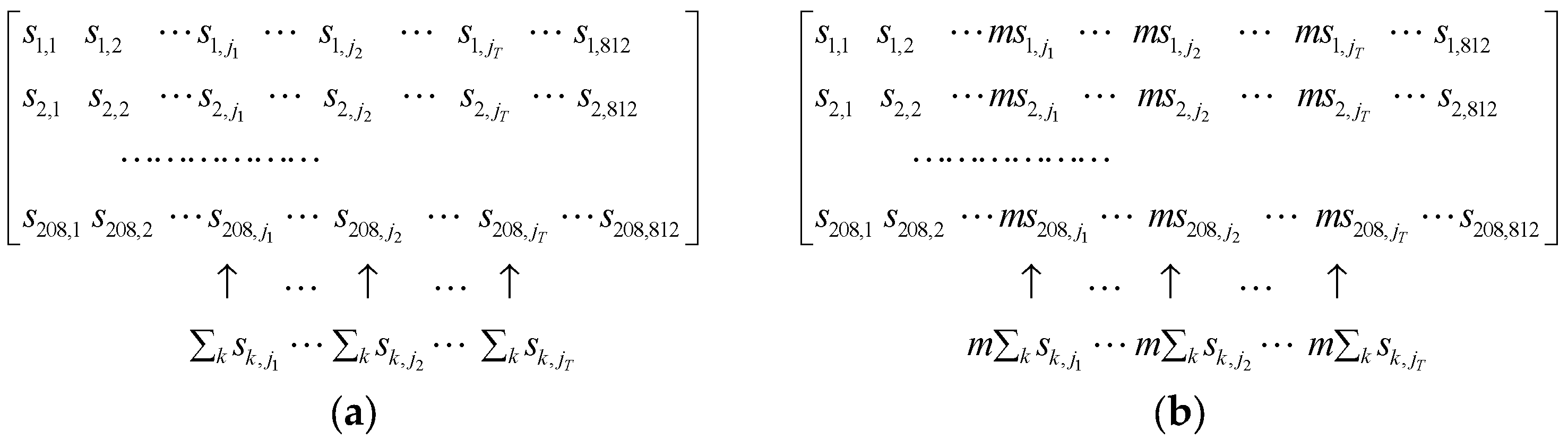
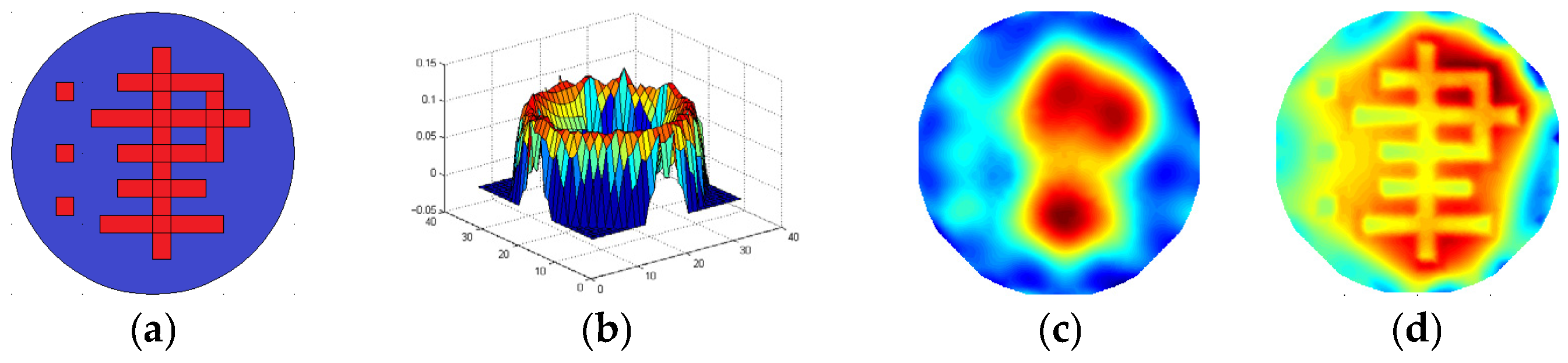

| Model |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
| LBP Imaging | 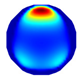 |  | 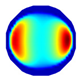 | 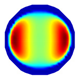 | 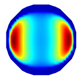 | 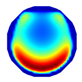 |  |
| NLP-DM Imaging |  |  |  |  | 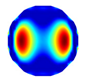 | 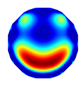 |  |
| NLP-TCS Imaging | 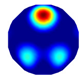 | 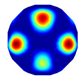 | 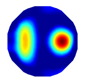 | 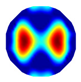 | 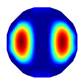 | 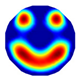 |  |
| Algorithm | Evaluation Metrics | Model I | Model II | Model III | Model IV | Model V | Model VI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LBP | RE | 0.171 | 0.288 | 0.274 | 0.283 | 0.234 | 0.257 |
| CC | 0.477 | 0.417 | 0.421 | 0.502 | 0.550 | 0.555 | |
| NLP-DM | RE | 0.120 | 0.174 | 0.167 | 0.159 | 0.135 | 0.171 |
| CC | 0.736 | 0.671 | 0.693 | 0.793 | 0.816 | 0.721 | |
| NLP-TCS | RE | 0.091 | 0.121 | 0.107 | 0.144 | 0.118 | 0.176 |
| CC | 0.740 | 0.745 | 0.787 | 0.801 | 0.834 | 0.745 |
| Model | 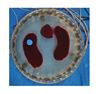 | 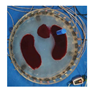 | 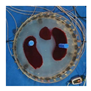 |  | |
| LBP reconstruction | 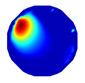 | 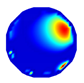 | 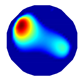 | 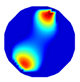 |  |
| NLP-DM reconstruction | 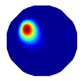 | 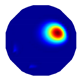 |  | 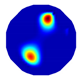 |  |
| NLP-TCS reconstruction | 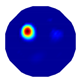 | 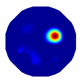 | 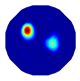 | 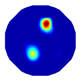 |  |
| Algorithm | Evaluation Index | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LBP | RE | 0.424 | 0.421 | 0.506 | 0.508 |
| CC | 0.271 | 0.261 | 0.280 | 0.264 | |
| NLP-DM | RE | 0.163 | 0.167 | 0.256 | 0.212 |
| CC | 0.599 | 0.630 | 0.488 | 0.516 | |
| NLP-TCS | RE | 0.054 | 0.061 | 0.083 | 0.069 |
| CC | 0.831 | 0.866 | 0.776 | 0.846 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, J.; Xin, Q.; Yue, S. Combined Optimization of Both Sensitivity Matrix and Residual Error for Improving EIT Imaging Quality. Mathematics 2025, 13, 2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162663
Guo J, Xin Q, Yue S. Combined Optimization of Both Sensitivity Matrix and Residual Error for Improving EIT Imaging Quality. Mathematics. 2025; 13(16):2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162663
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Jidong, Qiao Xin, and Shihong Yue. 2025. "Combined Optimization of Both Sensitivity Matrix and Residual Error for Improving EIT Imaging Quality" Mathematics 13, no. 16: 2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162663
APA StyleGuo, J., Xin, Q., & Yue, S. (2025). Combined Optimization of Both Sensitivity Matrix and Residual Error for Improving EIT Imaging Quality. Mathematics, 13(16), 2663. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162663






