DSC-CBAM-BiLSTM: A Hybrid Deep Learning Framework for Robust Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Forecasting
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Adaptive Feature Selection: An adaptive feature selection method combining PCA and PSO is used to identify key features for prediction, eliminating redundancy and noise to improve model performance.
- Depthwise Separable Convolution (DSC) for Feature Extraction: The model employs DSC to extract local spatial features from photovoltaic data. These features are then used as initial input to the BiLSTM, improving the model’s ability to capture relevant spatial patterns.
- Channel-Spatial Attention Mechanism (CBAM): The CBAM adjusts feature weights to help the model focus on important information in both the channel and spatial dimensions. This enhances its ability to capture key temporal patterns across different time periods.
- Bidirectional LSTM Network (BiLSTM): The model uses BiLSTM to capture temporal dependencies in photovoltaic data, utilizing both past and future information. This improves long-term dependency understanding, enhancing prediction performance and robustness.
2. Methodology
2.1. Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
2.2. Principal Component Analysis
2.3. Research Model Construction
2.4. Depthwise Separable Convolution
2.5. Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory
2.6. Convolutional Block Attention Module
2.7. The DSC-CBAM-BiLSTM Model
3. Experimental Environment
3.1. Data Selection and Preprocessing
3.2. Network Parameters
3.3. Error Evaluation Index
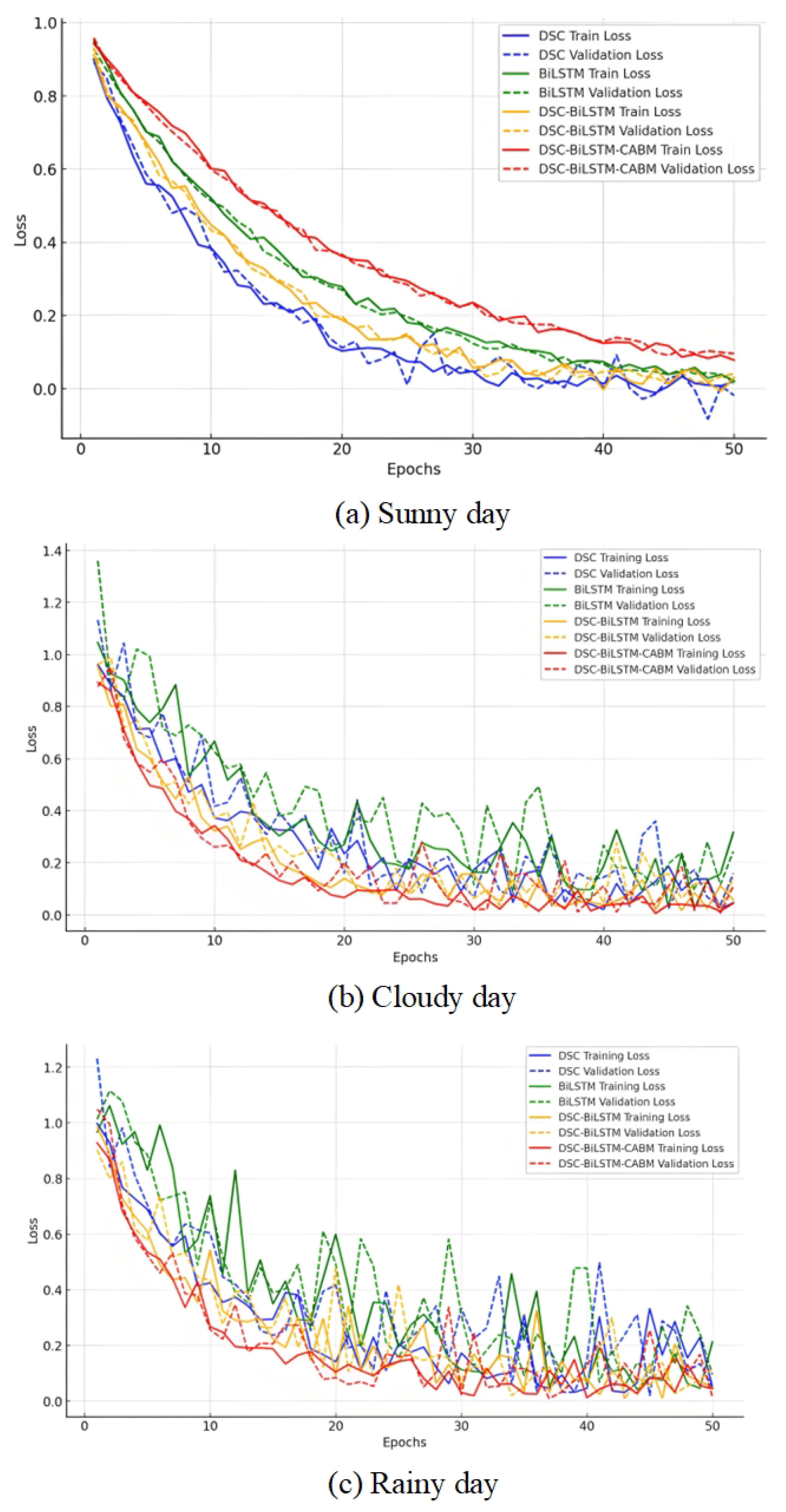
3.4. Prediction Results and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Wan, S. Prediction of Photovoltaic Power Generation Based on Parallel Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Networks. Energy Rep. 2024, 112, 3620–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Zang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liu, M.; Cui, Y.; Dang, D. A Physics-Constrained Deep Learning Framework Enhanced with Signal Decomposition for Accurate Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Generation Forecasting. Energy 2025, 326, 136220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, A.; Gupta, P.; Sharma, R.; Singh, R. Day Ahead Solar Forecast Using Long Short-Term Memory Network Augmented with Fast Fourier Transform-Assisted Decomposition Technique. Renew. Energy 2025, 247, 123021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Q. A PV Power Forecasting Based on Mechanism Model-Driven and Stacking Model Fusion. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2024, 19, 4683–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, R.; Dilshod, M.; Ulmas, Z.; Kumar, A.; Rizwan, M. A novel hybrid GWO-Bi-LSTM-based metaheuristic framework for short-term solar photovoltaic power forecasting. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 2025, 17, 046101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, R.; Qiu, Z.; Wan, H.; Yang, Z.; Li, X. Dung Beetle Optimization Algorithm-Based Hybrid Deep Learning Model for Ultra-Short-Term PV Power Prediction. iScience 2024, 27, 111126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.; Alkhayyat, A. Sentiment analysis using long short term memory and amended dwarf mongoose optimization algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 17206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriadis, C.N.; Passalis, N.; Georgiadis, M.C. A Deep Learning Framework for Photovoltaic Power Forecasting in Multiple Interconnected Countries. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2025, 77, 104330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.; Canhoto, P.; Oozeki, T.; Salgado, R. Comprehensive Approach to Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Using Numerical Weather Prediction Data, Physics-Based Models, and Data-Driven Techniques. Renew. Energy 2025, 251, 123495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Guan, L.; Wang, Z.; Yao, R.; Guan, X. A Double-Layer Forecasting Model for PV Power Forecasting Based on GRU-Informer-SVR and Blending Ensemble Learning Framework. Appl. Soft Comput. 2025, 172, 112768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Geng, H.; Zhang, H. Multi-Step Power Forecasting Method for Distributed Photovoltaic (PV) Stations Based on Multimodal Model. Sol. Energy 2025, 298, 113572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ma, R.; Zeng, L.; Yan, Q.; Johnston, A.J. Improved Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Network-Based Short-Term Forecasting of Photovoltaic Power for Different Seasonal Types and Weather Factors. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2025, 123 Pt C, 110219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souhe, F.G.Y.; Mbey, C.F.; Kakeu, V.J.F.; Meyo, A.E.; Boum, A.T. Optimized forecasting of photovoltaic power generation using hybrid deep learning model based on GRU and SVM. Electr. Eng. 2024, 106, 7879–7898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, H.; Noh, B. SolarNexus: A Deep Learning Framework for Adaptive Photovoltaic Power Generation Forecasting and Scalable Management. Appl. Energy 2025, 391, 125848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Rao, C.; Gao, M.; Xiao, X.; Goh, M. Efficient Calculation of Distributed Photovoltaic Power Generation Power Prediction via Deep Learning. Renew. Energy 2025, 246, 122901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubillo-Leyton, P.I.; Montoya, O.D.; Grisales-Noreña, L.F. Optimized Integration of Photovoltaic Systems and Distribution Static Compensators in Distribution Networks Using a Novel Discrete-Continuous Version of the Adaptive JAYA Algorithm. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 104726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattnaik, S.R.; Bisoi, R.; Dash, P.K. Solar Irradiance Forecasting Using Hybrid Long-Short-Term-Memory Based Recurrent Ensemble Deep Random Vector Functional Link Network. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2025, 123 Pt C, 110174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Wei, W.; Ren, J.; Han, S.; Di, H. An Investigation of Photovoltaic Power Forecasting in Buildings Considering Shadow Effects: Modeling Approach and SHAP Analysis. Renew. Energy 2025, 245, 122821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayed, M.E.; Rehman, S.; Elgendy, I.A.; Al-Shaikhi, A.; Mohandes, M.A.; Irshad, K.; Abdelrazik, A.S.; Alam, M.A. Benchmarking Reinforcement Learning and Prototyping Development of Floating Solar Power System: Experimental Study and LSTM Modeling Combined with Brown-Bear Optimization Algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2025, 332, 119696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zang, H.; Cheng, L.; Ding, T.; Wei, Z.; Sun, G. Robust Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Against Multi-modal Adversarial Attack via Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2025, 213, 16397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şener, İ.F.; Tuğal, İ. Optimized CNN-LSTM with Hybrid Metaheuristic Approaches for Solar Radiation Forecasting. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2025, 72, 106356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardarabadi, A.; Heydarian Ardakani, A.; Matrone, S.; Ogliari, E.; Shirazi, E. Multi-temporal PV Power Prediction Using Long Short-Term Memory and Wavelet Packet Decomposition. Energy AI 2025, 21, 100540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Cai, Y.; Cheng, J. A Deep Learning Model Based on Multi-Attention Mechanism and Gated Recurrent Unit Network for Photovoltaic Power Forecasting. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2025, 123, 110250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharthi, Y.; Chiroma, H.; Gabralla, L. Enhanced framework embedded with data transformation and multi-objective feature selection algorithm for forecasting wind power. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 16119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunqiao, L.; Yan, F. An innovative power prediction method for bifacial PV modules. Electr. Eng. 2023, 105, 2151–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, H.; Lv, Y. Variational Autoencoder-Based Learning Intrinsic Periodic-Trend Representations of Power Load Series for Short-Term Forecasting. Energy Rep. 2025, 13, 6584–6595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ren, X.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. A Novel Deep Learning-Based Method for Theoretical Power Fitting of Photovoltaic Generation. Renew. Energy 2025, 250, 123271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

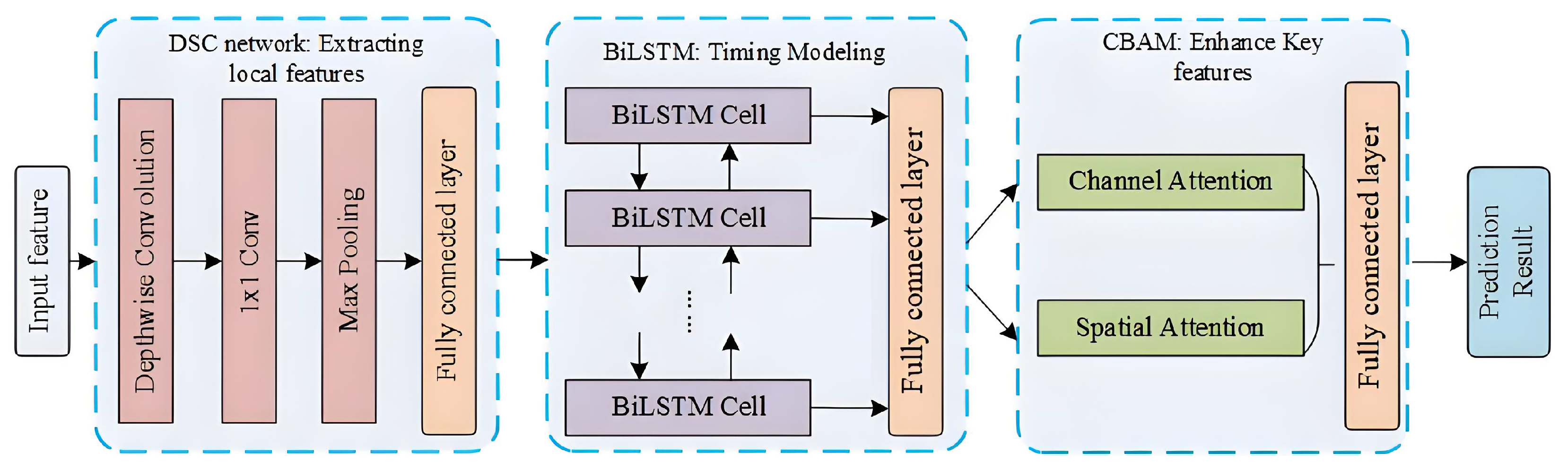
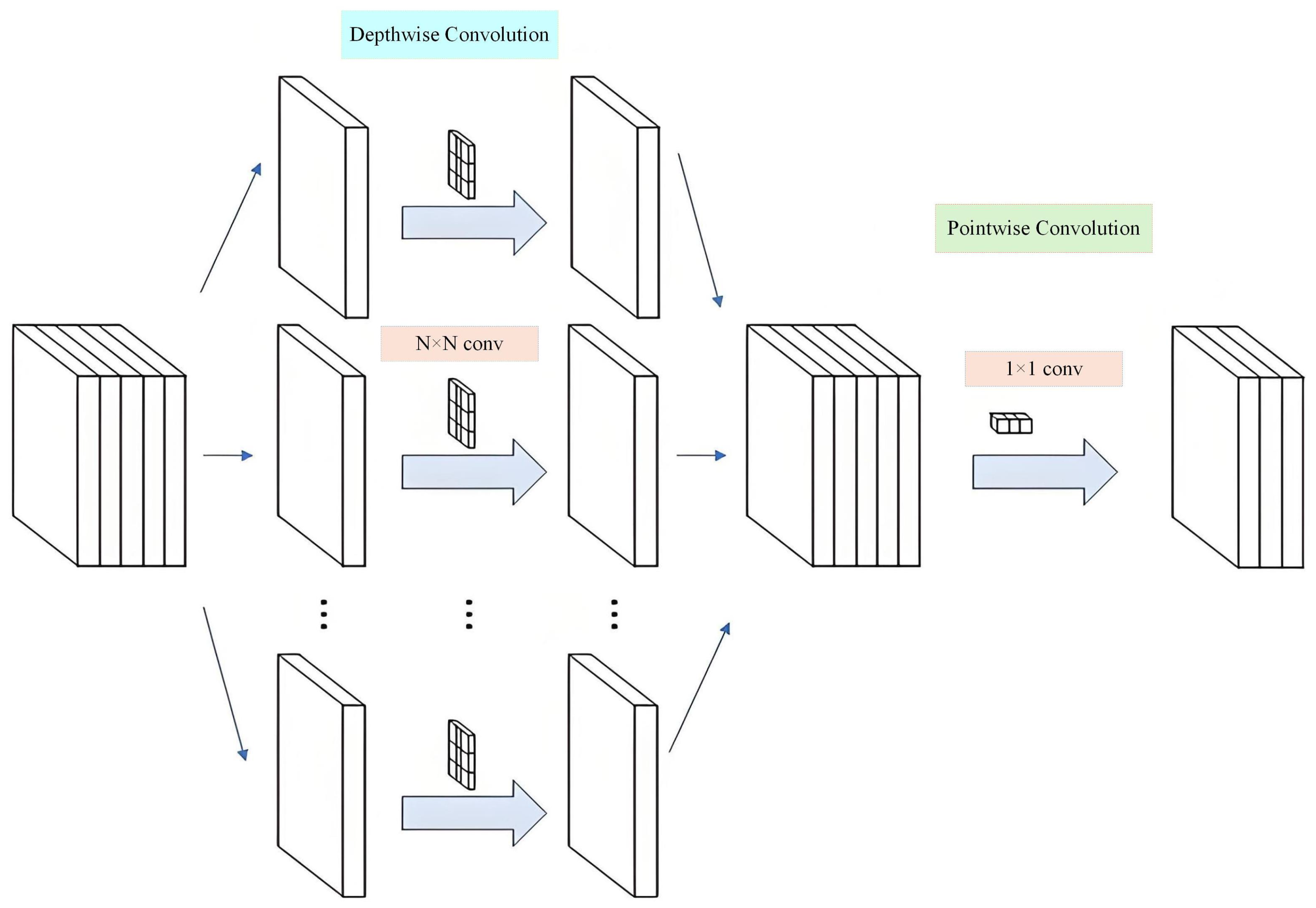

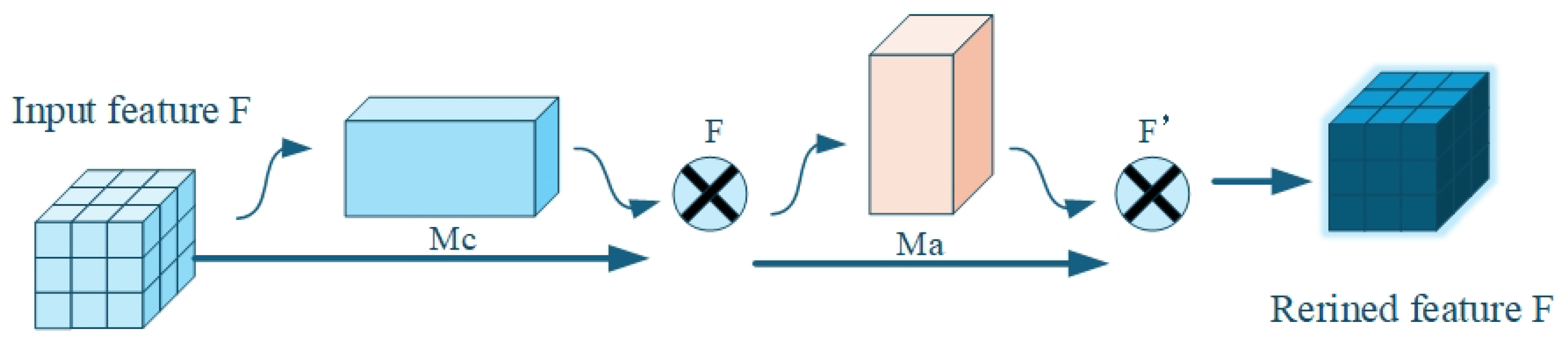
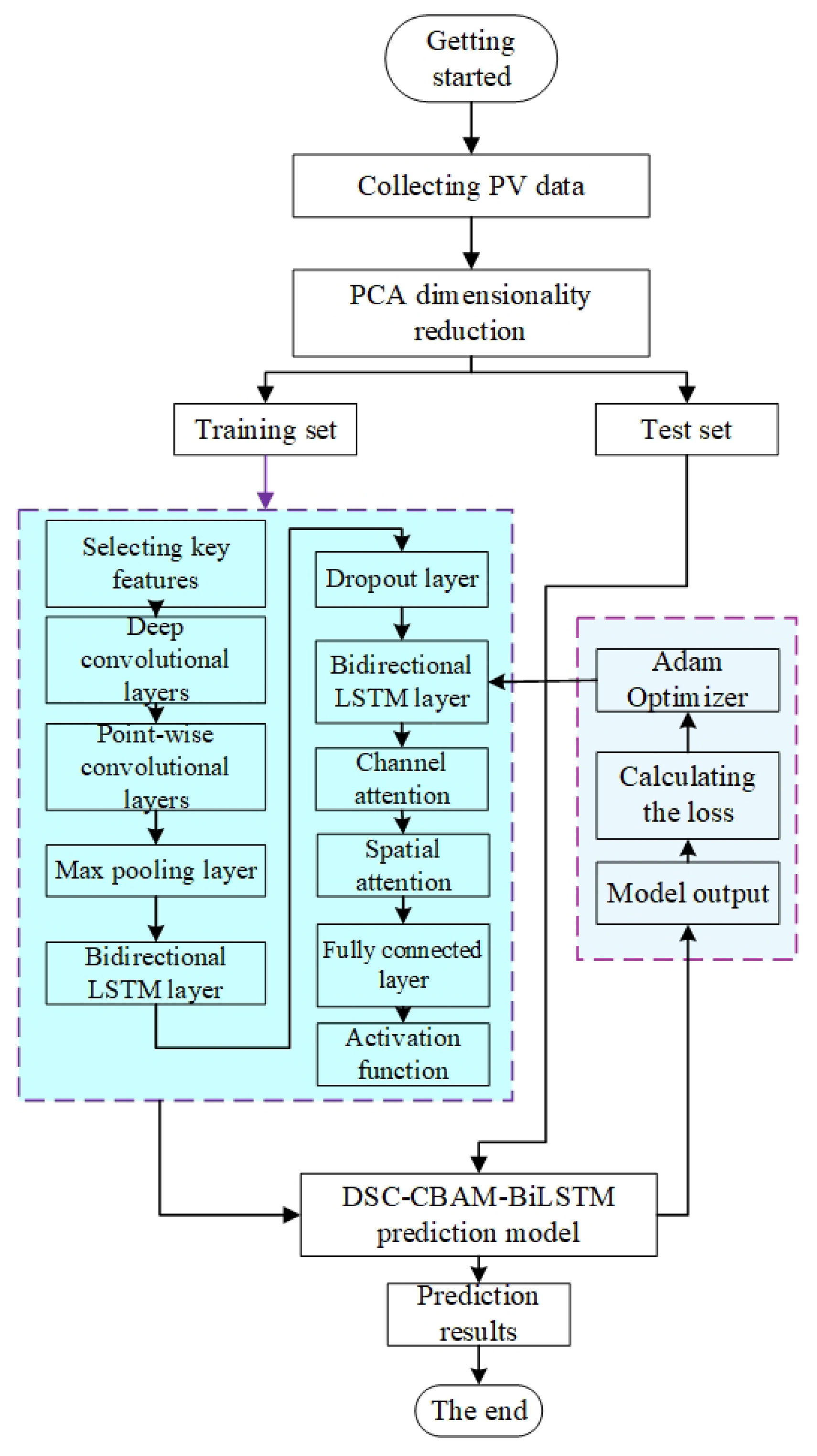
| Component | Eigenvalue | Variance Contribution (%) | Cumulative Contribution (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 45.28 | 45.32 | 45.32 |
| Humidity | 29.75 | 29.80 | 75.12 |
| Radiation intensity | 15.83 | 14.78 | 89.90 |
| Atmospheric pressure | 5.26 | 5.00 | 94.90 |
| Wind speed | 3.50 | 3.00 | 97.90 |
| Precipitation | 1.50 | 1.00 | 98.90 |
| Season | 0.80 | 0.20 | 99.10 |
| Generation power | 0.40 | 0.10 | 99.20 |
| Principal Name | Time Range |
|---|---|
| Sub 1 | 00:00 17 June 2023–24:00 15 July 2023 |
| Sub 2 | 00:00 16 July 2023–24:00 15 August 2023 |
| Sub 3 | 00:00 16 August 2023–24:00 15 September 2023 |
| Sub 4 | 00:00 16 September 2023–24:00 15 October 2023 |
| Sub 5 | 00:00 16 October 2023–24:00 15 November 2023 |
| Fold Number | Training Set | Validation Set | Average Error % | Accuracy % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | sub 1,2,3,4 | sub 5 | 5.23 | 85.4 |
| 2 | sub 1,2,3,5 | sub 4 | 4.76 | 86.3 |
| 3 | sub 1,2,4,5 | sub 3 | 5.14 | 84.9 |
| 4 | sub 1,3,4,5 | sub 2 | 4.95 | 86.1 |
| 5 | sub 2,3,4,5 | sub 1 | 5.08 | 85.7 |
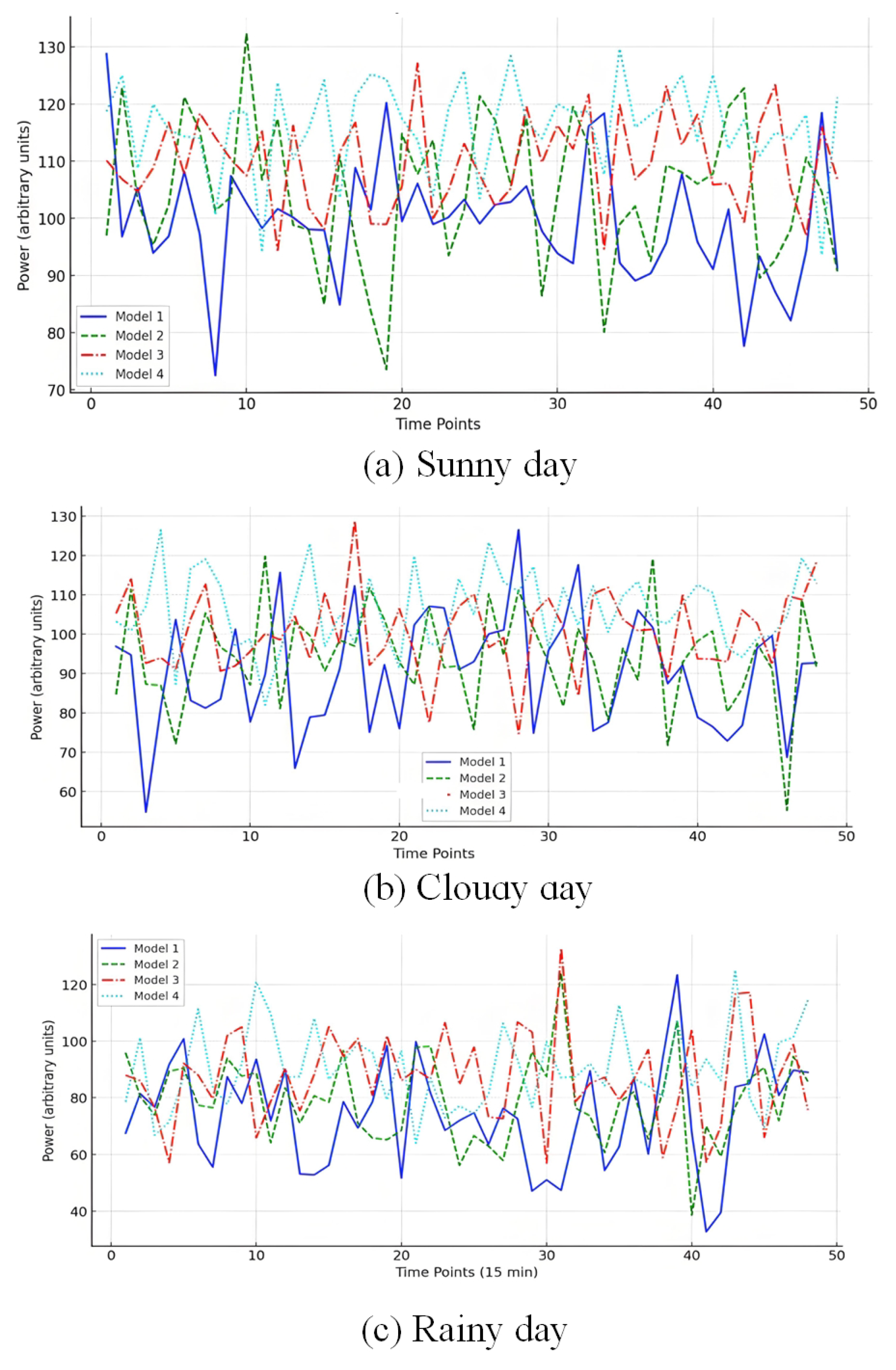
| Weather | Model | RMSE | MAE | CIRMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunny | model 1 | 8.265 | 6.125 | 0.894 | [7.852, 8.678] |
| Sunny | model 2 | 6.674 | 5.836 | 0.918 | [6.320, 7.028] |
| Sunny | model 3 | 2.438 | 1.653 | 0.935 | [2.234, 2.642] |
| Sunny | model 4 | 2.126 | 1.476 | 0.954 | [1.963, 2.289] |
| Cloudy | model 1 | 7.452 | 6.285 | 0.876 | [7.112, 7.792] |
| Cloudy | model 2 | 7.004 | 5.105 | 0.894 | [6.693, 7.315] |
| Cloudy | model 3 | 2.785 | 1.927 | 0.917 | [2.596, 2.974] |
| Cloudy | model 4 | 2.467 | 1.706 | 0.936 | [2.311, 2.623] |
| Rainy | model 1 | 8.053 | 7.727 | 0.854 | [7.654, 8.452] |
| Rainy | model 2 | 7.574 | 6.301 | 0.887 | [7.236, 7.912] |
| Rainy | model 3 | 3.206 | 2.053 | 0.905 | [2.974, 3.438] |
| Rainy | model 4 | 2.853 | 1.832 | 0.927 | [2.671, 3.035] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, A.; Lin, Y.; Peng, Y.; U, K.; Zhao, S. DSC-CBAM-BiLSTM: A Hybrid Deep Learning Framework for Robust Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Forecasting. Mathematics 2025, 13, 2581. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162581
Shen A, Lin Y, Peng Y, U K, Zhao S. DSC-CBAM-BiLSTM: A Hybrid Deep Learning Framework for Robust Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Forecasting. Mathematics. 2025; 13(16):2581. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162581
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Aiwen, Yunqi Lin, Yiran Peng, KinTak U, and Siyuan Zhao. 2025. "DSC-CBAM-BiLSTM: A Hybrid Deep Learning Framework for Robust Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Forecasting" Mathematics 13, no. 16: 2581. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162581
APA StyleShen, A., Lin, Y., Peng, Y., U, K., & Zhao, S. (2025). DSC-CBAM-BiLSTM: A Hybrid Deep Learning Framework for Robust Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Forecasting. Mathematics, 13(16), 2581. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162581






