Accurate Implementation of Rotating Magneto-Hydrodynamics in a Channel Geometry Using an Influence Matrix Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
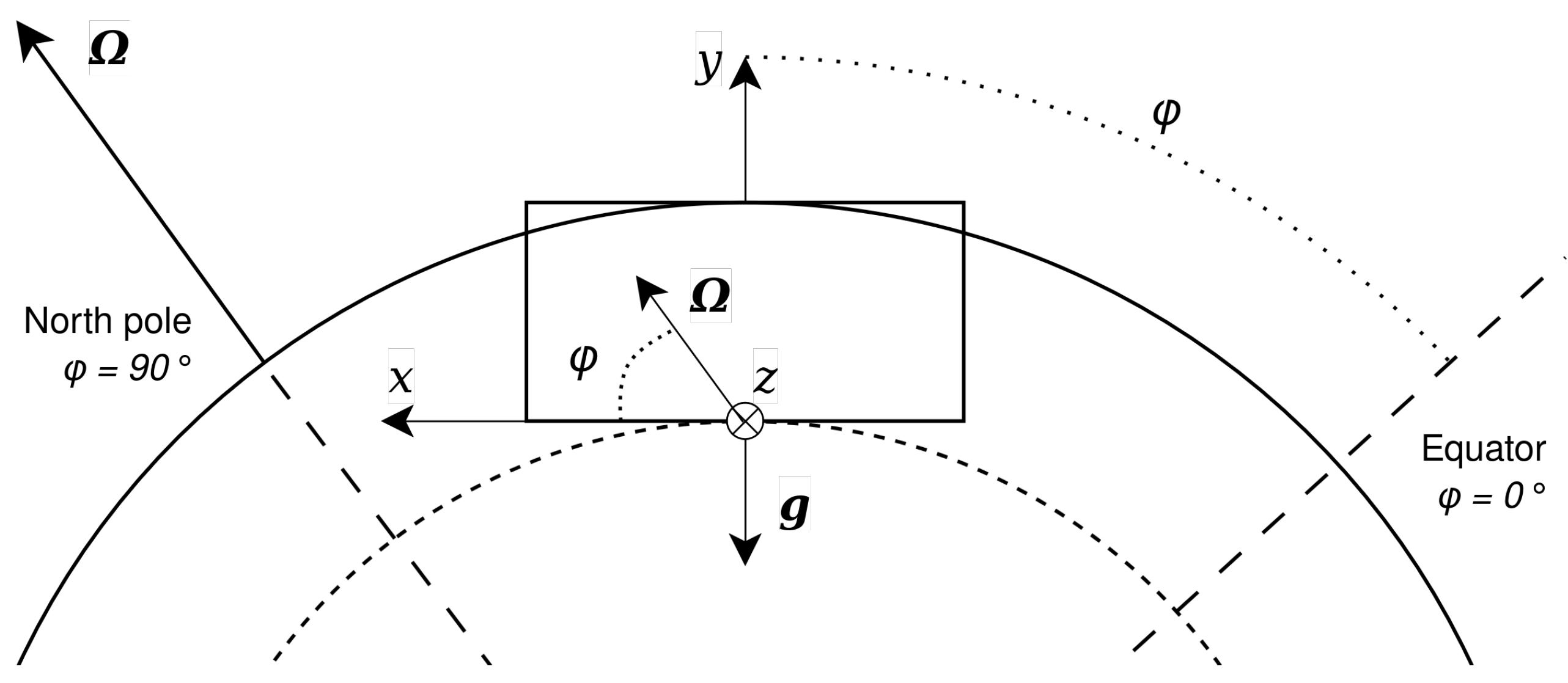
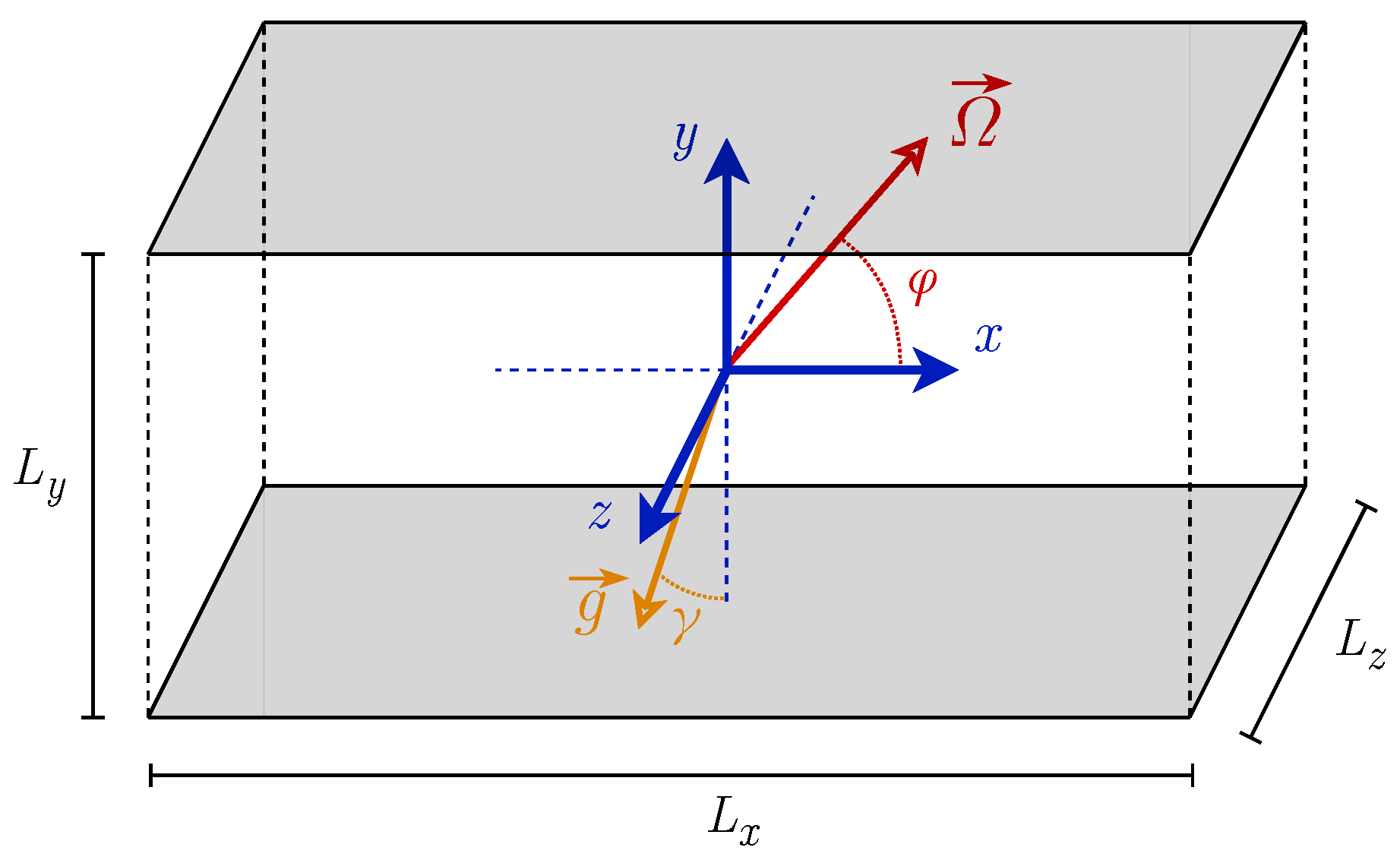
2.1. Equations and Control Parameters
2.2. Perturbative Formulation
2.3. Enforcing Magnetic Solenoidality Through a Fictitious Pressure
2.4. Spatial and Temporal Discretization
2.5. Influence Matrix with Robin Boundary Conditions
2.5.1. Tau Correction Method
2.5.2. Extended Influence Matrix Method
2.6. Implementation of the Methods
3. Validation and Benchmark Results
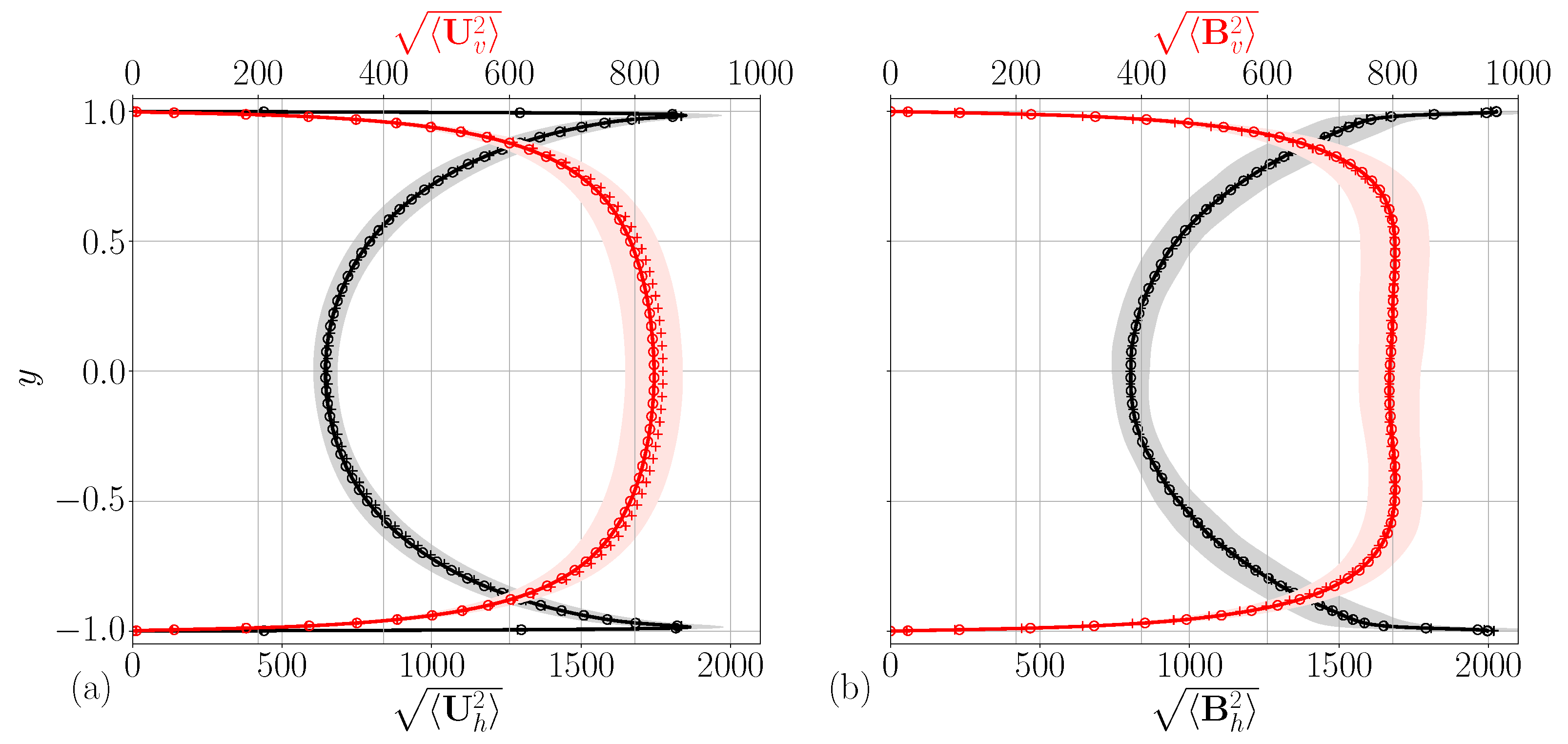
3.1. Linear Stability Analysis
3.2. Direct Numerical Simulation Statistics
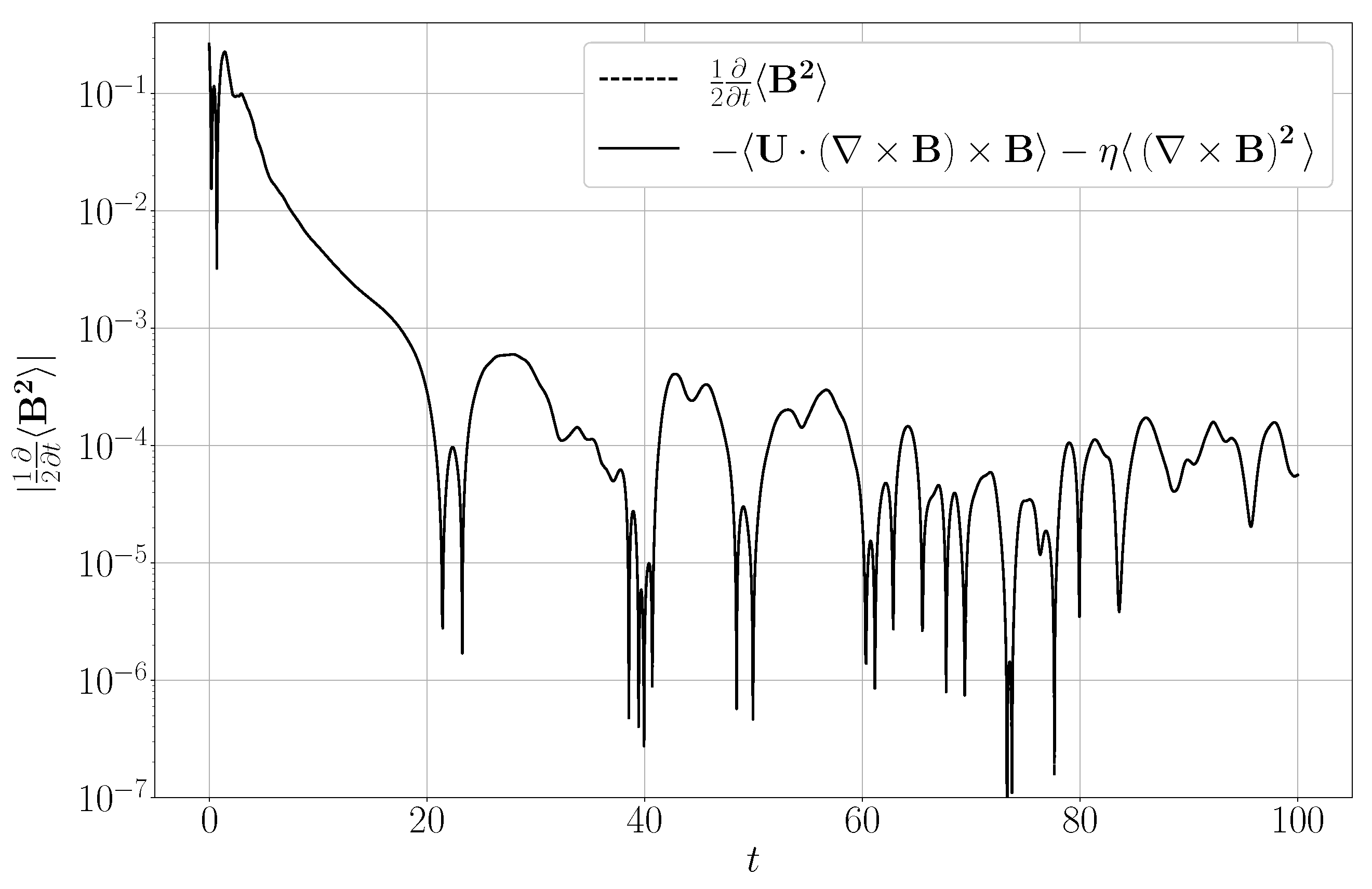
3.3. Energy Equation
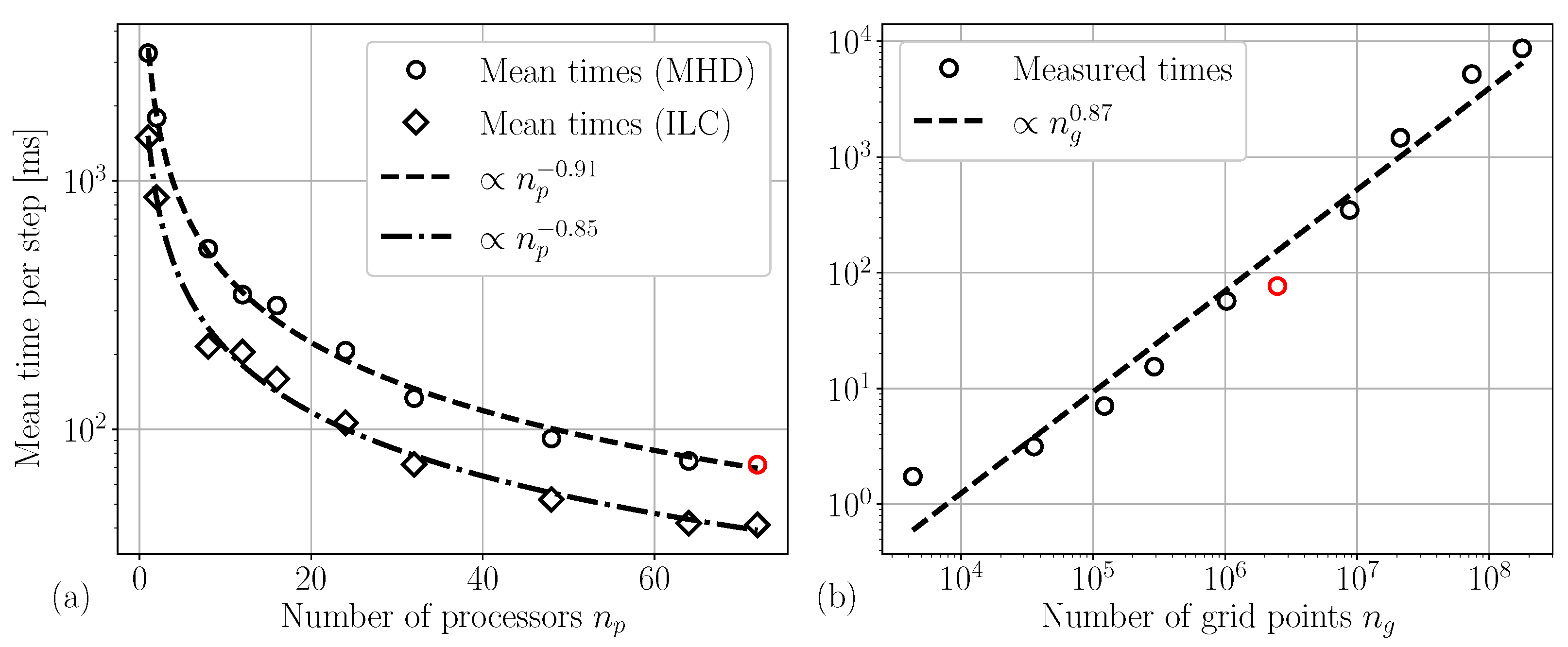
3.4. Code Benchmarks
4. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hathaway, D.H. The Solar Cycle. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2015, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElhinny, M.W.; Senanayake, W.E. Paleomagnetic evidence for the existence of the geomagnetic field 3.5 Ga ago. J. Geophys. Res. 1980, 85, 3523–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivelson, M.G.; Khurana, K.K.; Volwerk, M. The Permanent and Inductive Magnetic Moments of Ganymede. Icarus 2002, 157, 507–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtari, O.; Schneider, T.M. Identifying invariant solutions of wall-bounded three-dimensional shear flows using robust adjoint-based variational techniques. J. Fluid Mech. 2023, 977, A7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, M. Three-dimensional finite-amplitude solutions in plane Couette flow: Bifurcation from infinity. J. Fluid Mech. 1990, 217, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reetz, F.; Schneider, T.M. Invariant states in inclined layer convection. Part 1. Temporal transitions along dynamical connections between invariant states. J. Fluid Mech. 2020, 898, A22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feudel, F.; Tuckerman, L.S.; Zaks, M.; Hollerbach, R. Hysteresis of dynamos in rotating spherical shell convection. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2017, 2, 053902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skene, C.S.; Marcotte, F.; Tobias, S.M. On nonlinear transitions, minimal seeds and exact solutions for the geodynamo. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.05499v2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naskar, S.; Pal, A. Direct numerical simulations of optimal thermal convection in rotating plane layer dynamos. J. Fluid Mech. 2022, 942, A37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellmach, S.; Hansen, U. Cartesian convection driven dynamos at low Ekman number. Phys. Rev. E 2004, 70, 056312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, S. Hydrodynamic and Hydromagnetic Stability; Oxford University Press: London, UK, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, N.O.; Proctor, M.R.E. Magnetoconvection; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, R.G.; Bushby, P.J.; Guervilly, C. Subcritical dynamos in rapidly rotating planar convection. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2020, 5, 113702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.H. Diffusive instabilities in magnetohydrodynamic convection. In Les Instabilitiés Hydrodynamiques en Convection Libre, Forcée et Mixte; Legros, J.C., Platten, J.K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1978; pp. 102–111. [Google Scholar]
- Kleiser, L.; Schumann, U. Treatment of Incompressibility and Boundary Conditions in 3-D Numerical Spectral Simulations of Plane Channel Flows. In Proceedings of the Third GAMM—Conference on Numerical Methods in Fluid Mechanics, Cologne, Germany, 10–12 October 1979; Hirschel, E.H., Ed.; Vieweg+Teubner Verlag: Wiesbaden, Germany, 1980; pp. 165–173. [Google Scholar]
- ChannelFlow 2.0. Available online: https://www.channelflow.ch/ (accessed on 27 March 2025).
- Gibson, J.F.; Reetz, F.; Azimi, S.; Ferraro, A.; Kreilos, T.; Schrobsdorff, H.; Farano, M.; Yesil, A.F.; Schütz, S.S.; Culpo, M.; et al. Channelflow 2.0. 2019; manuscript in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.F. Introduction to Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 3rd ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Arter, W. Nonlinear Convection in an Imposed Horizontal Magnetic Field. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 1983, 25, 259–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, N.O. Convection in an imposed magnetic field. Part 1. The development of nonlinear convection. J. Fluid Mech. 1981, 108, 247–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobias, S.M. The turbulent dynamo. J. Fluid Mech. 2021, 912, P1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, S.H.; Zhu, Z. AFiD-MHD: A finite difference method for magnetohydrodynamic flows. J. Comput. Phys. 2005, 523, 113658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyret, R. Spectral Methods for Incompressible Viscous Flow; Applied Mathematical Sciences; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 148. [Google Scholar]
- Tenam, R. Navier-Stokes Equations: Theory and Numerical Analysis, 3rd ed.; American Mathematical Society: Providence, RI, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, K.; Estep, D.; Hansbo, P.; Johnson, C. Computational Differential Equations; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Min, T.; Kim, J. Effects of hydrophobic surface on skin-friction drag. Phys. Fluids 2004, 16, L55–L58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X. Extension of Kleiser & Schumann’s influence-matrix method for generalized velocity boundary conditions. J. Comput. Phys. 2011, 230, 7911–7916. [Google Scholar]
- Canuto, C.; Hussaini, Y.M.; Quarteroni, A.; Zang, T.A. Spectral Methods in Fluid Dynamics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Tuckerman, L.S. Divergence-free Velocity Fields in Nonperiodic Geometries. J. Comput. Phys. 1989, 80, 403–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Message Passing Interface Forum. MPI: A Message-Passing Interface Standard, Version 3.1; High Performance Computing Center Stuttgart (HLRS): Stuttgart, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Reetz, F.; Kreilos, T.; Schneider, T.M. Exact invariant solution reveals the origin of self-organized oblique turbulent-laminar stripes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, A. Exploiting Marginal Stability in Slow-Fast Quasilinear Dynamical Systems. Ph.D. Thesis, EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Reetz, F. Turbulent Patterns in Wall-Bounded Shear Flows: Invariant Solutions and Their Bifurcations. Ph.D. Thesis, EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Tuckerman, L.S.; Schneider, T.M. Natural convection in a vertical channel. Part 2. Oblique solutions and global bifurcations in a spanwise-extended domain. J. Fluid Mech. 2024, 1000, A29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolhey, P.; Stellmach, S.; Heyner, D. Influence of boundary conditions on rapidly rotating convection and its dynamo action in a plane fluid layer. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2022, 7, 043502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellmach, S.; Hansen, U. An efficient spectral method for the simulation of dynamos in Cartesian geometry and its implementation on massively parallel computers. Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2008, 9, Q05003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, J.F. ChannelFlow User Guide 0.9.18 2009. Available online: http://channelflow.org/dokuwiki/doku.php?id=docs (accessed on 25 November 2024).
- SCITAS JED Documentation, EPFL. Available online: https://scitas-doc.epfl.ch/supercomputers/jed/ (accessed on 14 November 2024).
| Parameter | Theoretical | Obtained | Rel. Error | Grid Size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| − | |||||
| − | |||||
| 16,721 | 16,720 | ||||
| 17,103 | 17,103 | ||||
| 124,508 | 124,509 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ringenbach, J.-C.; Tobias, S.M.; Schneider, T.M. Accurate Implementation of Rotating Magneto-Hydrodynamics in a Channel Geometry Using an Influence Matrix Method. Mathematics 2025, 13, 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162549
Ringenbach J-C, Tobias SM, Schneider TM. Accurate Implementation of Rotating Magneto-Hydrodynamics in a Channel Geometry Using an Influence Matrix Method. Mathematics. 2025; 13(16):2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162549
Chicago/Turabian StyleRingenbach, Jean-Clément, Steven M. Tobias, and Tobias M. Schneider. 2025. "Accurate Implementation of Rotating Magneto-Hydrodynamics in a Channel Geometry Using an Influence Matrix Method" Mathematics 13, no. 16: 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162549
APA StyleRingenbach, J.-C., Tobias, S. M., & Schneider, T. M. (2025). Accurate Implementation of Rotating Magneto-Hydrodynamics in a Channel Geometry Using an Influence Matrix Method. Mathematics, 13(16), 2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13162549






