Abstract
Credit-linked notes (CLNs) are vital for transferring and diversifying credit risks in asset securitization, yet their application in China remains limited despite policy support. This paper optimizes China’s CLN pricing mechanism by developing the structured model incorporating the dynamic default boundary and the probability of government implicit guarantees. The model transforms the pricing problem into a semi-unbounded problem via partial differential methods, yielding an explicit pricing solution through Poisson’s formula. Empirical analysis reveals that government implicit guarantees are observed in systemically important institutions in the domestic CLN market and significantly reduce credit risk premiums, with Monte Carlo simulations indicating an approximately positive linear correlation between guarantee probability and CLN prices. Our results demonstrate the dual impact of implicit guarantees—lowering risk premiums while potentially hindering market discipline. This research advances China’s credit derivative pricing theory, offering institutions a pricing tool and further providing policy and practical suggestions for regulatory authorities.
Keywords:
credit-linked notes; structured model; dynamic default boundary; government implicit guarantee MSC:
91G20; 91G40
1. Introduction
Credit risk is the core risk in the financial system, and its management efficiency directly affects the market stability. Traditional credit risk management tools struggle to cope with diversified risk demands, which makes credit derivatives become a key risk-transferring means. Among them, CLNs combine fixed-income securities and Credit Default Swaps (CDSs) achieve the function of dispersing credit risk without transferring the underlying assets. Particularly under the “second arrow” policy, CLNs have become a vital tool for bond financing among private enterprises.
China’s credit derivatives market started late compared to developed markets (e.g., the US market initiated in the 1990s). In 2010, the National Association of Financial Market Institutional Investors (NAFMII) issued guidelines, and the first batch of CRMAs and CRMWs were launched [1]. In recent years, the market has operated smoothly, but the scope of CLN trading is small, and the secondary trading is illiquid with low market activity. This situation is closely related to the government implicit guarantees in China’s financial market. But its effect is two-sided: on the one hand, it reduces the risk of default and maintains market stability; on the other hand, it triggers moral hazard and distorts the pricing mechanism.
The existing pricing models for credit risk include structured models and reduced models. The reduced model is not based on a firm’s financial position, and default events are described as a function of a set of state variables. The structured model relies entirely on the rules for distributing the value of enterprise assets between shareholders and creditors, that is, the actual capital structure of the enterprise is used to characterize the default time. The structured model was first introduced by Merton [2], assuming that the company’s default is only related to the debt that needs to be repaid on the maturity date. Black and Cox [3] developed the structured model further, believing that at any moment, if the value of a company’s assets falls below a certain level, default occurs. The Black–Cox model is also known as a first-passage-time model. This paper adopts the structured model for CLN pricing based on two critical considerations. First, the extant literature on credit risk derivatives predominantly employs reduced models and is limited to giving basic pricing formulas, rarely considering the impact of the actual market situation. They characterized default events via exogenous jump processes that abstract from issuers’ financial fundamentals. For example, Jiang, Qian, and Yuan [4,5] investigated the pricing of CLN contracts with counterparty credit risk under the framework of the reduced method, and analyzed whether there was an impact of default contagion between credit entities when the CLN has multiple reference assets; Zhi, Qian, and Wang [6] developed a Markov chain model incorporating contagion risk and a stochastic CIR interest rate process to value counterparty risk and compute credit valuation adjustments (CVAs) for kth-to-default credit-linked notes. Second, structured models intrinsically link default to the evolution of a company’s assets and liabilities, enabling direct incorporation of the dynamic default boundaries. This mechanism can capture how implicit guarantees respond to deteriorating asset values, aligning with China’s regulatory interventions.
As for government implicit guarantees, domestic research mainly focuses on their impact on the bond market and local government debt. They mostly focus on the complexity of implicit guarantees and its impact on financial market, which provides important theoretical and empirical support for understanding how the Chinese government maintains market stability through implicit guarantee mechanisms in the financing process. Han and Hu [7] analyzed the different manifestations of government implicit guarantees in state-owned enterprise bonds and local financing platform bonds, as well as their relationship with credit ratings. Luo and Liu [8] argued that the market believes that unsecured urban investment bonds have government implicit guarantees.
This paper uses the first-passage-time approach [3] of the structured model. In the Merton model [2], default is only related to the debt on the maturity date; that is, when the company’s asset value is less than the debt, default occurs. This is not consistent with the real situation. The first-passage-time approach overcomes the drawbacks, assuming that the company’s asset value obeys geometric Brownian motion, and default occurs once the asset value is less than a predetermined threshold. Then we transform the problem into a semi-unbounded problem and solve it to obtain an explicit expression of pricing.
The main contribution of this paper is that we optimize dynamic default boundaries and consider government implicit guarantees, aiming to improve the CLN pricing model and make it more applicable to the actual situation of China’s financial market. The result demonstrates the dual impact of implicit guarantees—lowering risk premiums while potentially hindering market discipline. It can also provide an effective decision-making basis for policy makers and market participants, and promote the healthy development of the market.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: In Section 2, we provide necessary mathematical preliminaries to simplify the final pricing formula. In Section 3, we construct the pricing model of a CLN and return the pricing formula. In Section 4, we process the parameters in the model, calculate the probability of government implicit guarantees, and validate the feasibility by the Monte Carlo method. Finally we conclude the article in Section 5.
2. Preliminaries
Lemma 1
([9]). Let satisfy and . Then for every
Proof.
See Appendix A. □
Remark.
For every , we have
After simplifying Expression (2) by integration by parts, we can obtain
3. Pricing of CLNs
3.1. Model Assumptions
This paper adopts the first-passage-time model, improving the definition of dynamic default boundaries while allowing for default to occur on or before the maturity date, and introducing the influencing factor of government implicit guarantees. We make the following assumptions about the model:
- (1)
- The market meets the requirement of no arbitrage opportunities;
- (2)
- The market is frictionless, with no transaction costs or bankruptcy costs, and all asset losses are involved in financial transactions.
3.2. Model Establishment and Solution
We introduce a complete probability space with flow , where Ω is the sample space, P is the risk neutral probability, and is a domain flow in this probability space—the market information flow, composed of all known information in the market at time t.
Let the face value of the CLN be M, the contract maturity date be T, and the coupon be paid at a constant interest rate k.
Based on a structured model, we assume that the asset value of a company follows geometric Brownian motion, that is
where the constant is the risk-free rate, the constant is the volatility of the company assets, and is the standard Brownian motion.
We establish a default boundary value
where K, a constant greater than zero, is the critical value of the company assets value at time t. Let to ensure that the payment to the CLN buyer at the default time does not exceed the face value M of the CLN. The constant γ is the decay rate, reflecting the rate at which the default boundary decays over time before the maturity date.
At any time on or before the maturity date, when the value of the company assets falls below or equal to the boundary value, that is to say , it is considered that default occurs and the CLN buyer will receive the remaining assets value at a constant recovery rate after liquidation; that is to say, the buyer will receive . The default time satisfies
Taking the existence of government implicit guarantee into account and assuming the probability of government implicit guarantee is p, therefore, in the presence of guarantee, assuming a company defaults, the CLN buyer still has a probability of p to obtain the current face value of the CLN, that is , and the remaining probability of to obtain the recovered assets value, that is .
So the cash flow of this CLN with implicit guarantee is as follows:
- Receive interest at a continuous coupon rate k before the default time and maturity date of the contract.
- When the underlying asset defaults before the maturity date, the CLN buyer has a probability of p to obtain the current face value and of to obtain the value of the recovered assets value at the recovery rate .
- When the underlying asset does not default before the maturity date, at time T, if the value of the underlying asset is greater than or equal to the face value M, the buyer can obtain face value. If the value of the underlying asset is less than the face value M, the buyer has a probability of p to obtain all of the face value, and to obtain the current value of the underlying asset.
Therefore, in the sense of probability, the price of the CLN at time t can be expressed as
where s represents time, and denotes the minimum maturity date and default time.
Utilizing the partial differential equation method and the Feynman-Kac formula, we derive that the price of the CLN satisfies the following partial differential equation:
To solve the above partial differential equation, first let and , then Equation (4) is transformed into
Let to eliminate the right term in the boundary condition, then Equation (5) is transformed into
Further, let , so we can obtain and , and substitute Equation (6) into
Let the constant term of and be zero, then
By further calculation, the expressions for α and β can be solved as
Ultimately, the partial differential Equation (6) can be transformed into the following semi-unbounded problem:
where
To solve the above heat equation, we first use the odd prolongation method to transform the problem into a Cauchy problem [10]. Then the solution can be obtained according to the Poisson formula. Finally, after a series of transformations and simplifications and the application of Equation (3) in the Remark, we can obtain the pricing formula. See Appendix B for details.
Ultimately, the pricing formula of the CLN is as follows:
Theorem 1.
The price of the CLN issued by a company with asset value V at time t is
4. Numerical Analysis
4.1. Parameter Setting Standards
The parameters in the model can be divided into three categories, namely the relevant variables of the issuing entity company, the characteristic variables of the CLN, and other model variables. Relevant variables of the issuing entity company include the company assets value V, the critical company assets value K at time t, and the volatility of the company assets value. The characteristic variables of the CLN include the face value M, the maturity date T of the contract, and the coupon rate k. Other model variables include the risk-free rate r, the recovery rate , the decay rate γ, and the probability of government implicit guarantees p.
Firstly, regarding the relevant variables of the issuing entity company, for the company assets value V, it can be directly observed from the relevant data in the company’s financial statements. This paper selects the sum of the company’s total liabilities D and stock market value S to represent it. For the critical company assets value K at time t, K is a constant less than or equal to M to ensure that the payment made to the CLN buyer at the default time does not exceed the face value of the CLN. This paper sets K = M. For the volatility of the company assets value, the corresponding volatility can be calculated based on the stock prices of the 150 trading days prior to the observation time t.
Secondly, regarding the characteristic variables of the CLN, the face value M, the maturity date T of the contract, and the coupon rate k can all be directly obtained from the CLN creation information.
Finally, regarding other model variables, for the risk-free rate r, this paper selects the one-year Shibor as the reference basis to ensure fairness and transparency of transactions and to match the actual market situation in China. For the recovery rate , it is usually determined based on the historical default recovery scale of the issuing entity. This paper uses the credit rating of the issuer as the measurement standard. For the decay rate γ, this paper sets , which reflects the boundary discounted with the risk-free rate for the convenience of calculation. We can simplify it because the decay rate has a relatively small impact on the price and is only used to adjust the speed of change in the default boundary. The probability of government implicit guarantees p, which is unobservable, will be the object of subsequent analysis.
4.2. Data Selection and Calculation
Due to the lack of market information for the public issuance of CLNs, this paper selects the first CLN issued by Agricultural Bank of China Limited (hereinafter referred to as “Agricultural Bank”) in 2020 and the fourth CLN issued by CITIC Securities Co., Limited. (hereinafter referred to as “CITIC Securities”) in 2022 as the analysis subjects. The basic information for these two CLNs is shown in Table 1. Using the pricing Formula (8), we can calculate the probability of government implicit guarantees and analyze it.

Table 1.
Relevant information of the two CLNs.
We process the basic information and market information as follows:
- The average value of the one-year Shibor rate in 2024 is 2.0771%. This paper sets the risk-free rate r to 2%, and therefore the decay rate γ is also set to 2%.
- The company assets value V is represented by the sum of the company’s total liabilities D and stock market value S. However, in the actual market, the company’s capital structure includes various debts, so it is necessary to adjust the V value in the pricing Formula (8). To reflect the fact that not all liabilities contribute equally to default risk, Moody’s KMV [11] adjusts the default point using short-term debt and a fraction of long-term debt. Building on this idea, we follow an empirical method widely used in Chinese credit risk studies, which allocates the assets value V proportionally to interest-bearing debt as a proxy for the relevant assets value, using the following expression:
This adjustment ensures consistency between the structure of the company’s liabilities and the estimation of asset value relevant to default probability.
- 3.
- The recovery rate is usually determined based on the historical default recovery scale of the issuing entity. But due to the relatively short history of the Chinese market’s development and the lack of available data, it is not possible to directly calculate the value of the recovery rate. The asset recovery rate is usually related to the issuing entity itself. This paper uses the credit rating of the issuing entity as a measurement standard, and refers to Liu’s [12] estimation of default loss rates for different credit rating entities. The sum of the recovery rate and default loss rate is 1, and the specific values are shown in Table 2.
 Table 2. Default loss rate and recovery rate of different credit rating entities.
Table 2. Default loss rate and recovery rate of different credit rating entities. - 4.
- For the convenience of calculation, we uniformly select the data at time t = 0 to substitute into the pricing Formula (8).
We calculate the probability of government implicit guarantees below. Taking the first CLN issued by Agricultural Bank in 2020 as an example, the term T is one year, the face value M is CNY 100, the issue price is also CNY 100, and the annual coupon rate is 4.5%.
For the item in the pricing formula, the yield needs to be calculated based on the face value, coupon rate, and term, that is
We obtain that . Using the coupon rate, we can calculate the theoretical value of the CLN
For the item V in the pricing formula, selecting the data at time t = 0, the company’s total liabilities D are CNY 249,943.01 hundred million, and the stock market value S is CNY 10,989.47 hundred million. Therefore, the adjusted company assets value is CNY 104.40, which is the item V.
For the item in the pricing formula, select the stock prices of the 150 trading days prior to the observation time t = 0, calculate the volatility of stock return, and annualize it. The volatility of company assets value is substituted by the annual volatility of stock return. We can calculate and obtain that .
For the item , as the credit rating of Agricultural Bank is AAA, the recovery rate is set to according to the data in Table 2.
By substituting all data values into the pricing formula and using Matlab, the probability of government implicit guarantees can be calculated to be 88.31%. Similarly, the probability of government implicit guarantees for CITIC Securities can be calculated to be 98.96%.
4.3. Monte Carlo Simulation and Verification
To verify the robustness of the structured CLN pricing model, this subsection uses the Monte Carlo numerical simulation method to randomly generate company assets’ value paths, dynamically capture default events, and calculate the expected price of the CLN. The Monte Carlo method can not only verify the accuracy of analytical solutions, but also further analyze the sensitivity of parameters and the impact of policy scenarios.
According to the model in Section 3, the Monte Carlo method is used to simulate the asset paths, dynamic default boundary, cash flow, etc. Assuming that the company assets value follows geometric Brownian motion and there is a dynamic default boundary, this process randomly generates N (we set N = 1,000,000) paths and checks at each time point of each path whether the first-passage-time condition is met. If the default occurs, the payment amount is . If not, the payment amount is M. Then we discount the cash flow at a risk-free rate to time t = 0 and take the average of the present values of the N simulated paths to obtain the Monte Carlo estimate. By substituting the basic information parameters of the model and the probability of government implicit guarantees calculated in Section 4.2, the expected price of the first CLN issued by Agricultural Bank in 2020 is CNY 97.57, and the expected price of the fourth CLN issued by CITIC Securities in 2022 is CNY 99.78. The expected price is roughly in line with the actual market situation, and the pricing model is feasible. In addition, the prices obtained by discounting based on the yield in Section 4.2 are, respectively, CNY 95.70 and CNY 99.24. The discounted prices are slightly lower, while the prices obtained by Monte Carlo simulation are slightly higher, indicating that market investors’ expectations of government implicit guarantees will increase the price of the CLN.
In addition, we quantify the impact on the CLN prices by adjusting the probability of government implicit guarantees (shown in Figure 1) and conduct linear regression analysis of the probability. The results are as follows:
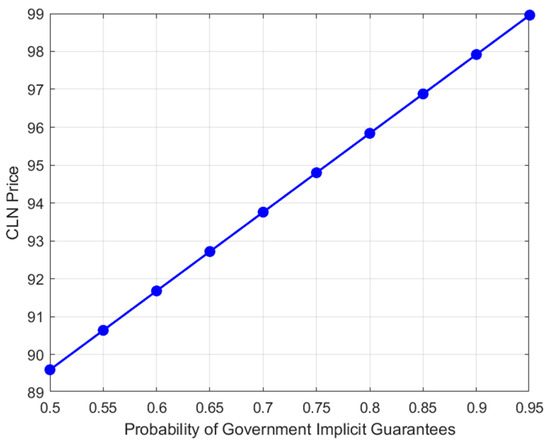
Figure 1.
The impact of the decrease in the probability of government implicit guarantees on CLN prices.
With the fixed volatility, the CLN price and probability are approximately linearly positively correlated, which verifies the direct effect of government implicit guarantees on credit risk mitigation. For every 0.1 increase in the probability between 0.5 and 0.95, the price increases by about 2%. The goodness-of-fit exceeds 0.95, indicating that the government implicit guarantee probability can effectively explain the price changes.
When the probability of government implicit guarantees decreases, investors in the market believe that the possibility of receiving government compensation after default decreases, and therefore demand a higher credit risk premium to compensate for potential losses. At the same time, investors may become conservative in their risk preference, and a decrease in demand for CLNs will further lower prices.
Moreover, a short analysis is conducted varying γ from 0.5r to 1.5r. The change in the probability (shown in Figure 2) can be almost negligible, confirming that this parameter does not materially affect the computed guarantee probability.
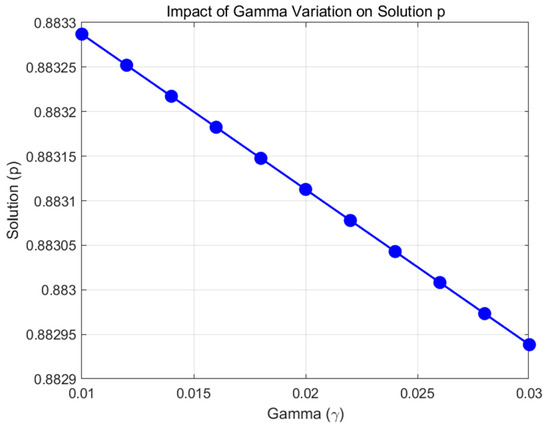
Figure 2.
The impact of γ variation on the probability of government implicit guarantees.
4.4. Result Analysis
According to the calculation results, investors in the market expect the government to provide implicit guarantees for CLNs, and the probability of such guarantees is extremely high. NAFMII has repeatedly advocated for increasing the support for private enterprises through the “second arrow” service, actively providing credit enhancement support for private enterprises to issue green and transformational products through various means, and continuously improving the requirements for the asset size and management capabilities of the issuing entity. Therefore, the government has strong attention, support, and strict requirements for CLNs. The probability of default events is extremely low, while the market expectations for government implicit guarantees are extremely high.
At the same time, the calculation results also show that the probability of government implicit guarantees for CITIC Securities is higher than that for Agricultural Bank, reflecting the different levels of government support for different entities’ CLNs. As a large state-owned commercial bank, Agricultural Bank mainly relies on traditional credit assets, and its credit risk management capabilities have strong market recognition. However, as a non-bank financial institution, CITIC Securities’ business involves more complex financial products, and the market’s expectation of its risk management capabilities relies more on government support. In addition, compared to Agricultural Bank’s CLN, the term of CITIC Securities’ CLN is shorter, and the liquidity and flexibility are stronger. Therefore, the market has higher expectations for the probability of government implicit guarantees.
The Monte Carlo method predicts that the price of CITIC Securities’ CLN will be higher than that of Agricultural Bank’s CLN. Although the volatility of CITIC Securities’ assets price is higher, its higher probability of government implicit guarantees significantly offsets the default risk, highlighting the core role of government implicit guarantees in credit risk pricing.
5. Conclusions
Since NAFMII released the guidelines in 2010, China’s credit derivative product system has gradually flourished and the market has gradually improved. In the early stages, due to conservative product design and insufficient demand in the bond market, market activity was low. NAFMII has been supporting private enterprises in issuing bonds through a series of policies, encouraging product innovation and rule optimization, and promoting market expansion. Therefore, the pricing issue of credit risk mitigation tools has always been a concern, and it is necessary to construct a pricing model that is in line with China’s financial market to maintain the stable development of the market.
In this context, this paper constructs a mathematical model based on the structured model and conducts parameter processing analysis to study the pricing issue of CLNs.
When constructing the model, we consider dynamic default boundaries and incorporate factors such as the recovery rate and the probability of government implicit guarantees to optimize the pricing model of CLNs.
In empirical analysis, this paper only selects the two CLNs of Agricultural Bank and CITIC Securities due to the lack of publicly available information in the market. Based on their respective information and relevant data, the pricing formula can be used to solve the corresponding probability of government implicit guarantees. The research results show that the market expects the government to provide implicit guarantees for CLNs, and the probability is extremely high. Also, the probability of government implicit guarantees is related to the size, nature, and business scope of the issuing company. The Monte Carlo method validates the feasibility of the pricing model and shows a positive correlation between CLN prices and the probability of government implicit guarantees. Moreover, changes in the probability of government implicit guarantees can lead to pricing fluctuations. The government needs to carefully manage market expectations of implicit guarantees in order to avoid policy changes that may cause drastic price fluctuations in CLNs, and thereby affect the stability of corporate finance.
This study reveals the “double-edged sword” effect of government implicit guarantees in the CLN market. On the one hand, implicit guarantees help expand the “second arrow” of private enterprise bond financing tools by reducing financing costs and enhancing investors’ confidence; on the other hand, excessive reliance on government credit may lead to moral hazards and weaken the market’s ability to set prices independently. Therefore, when formulating policies, it is necessary to balance risk mitigation and market self-discipline, gradually promoting the improvement of liquidity in the CLN secondary market. Regulators can take measures, such as the following: (i) classifying institutions into different tiers based on systemic importance; (ii) mandating disclosure of guarantee probability assumptions in CLN prospectuses; and (iii) introducing explicit bailout bonds to replace implicit guarantees.
However, our findings are subject to some qualifications. First, the model assumes geometric Brownian motion for asset values and exogenous government implicit guarantees, omitting potential jump risks and other policy responses. Second, empirical analysis relies on only two CLNs issued by important institutions, limiting generalization to private or smaller issuers where government implicit guarantees may be weaker. Given data limitations, our analysis serves as an illustrative case study on CLNs issued by systemically important institutions rather than a comprehensive market analysis. Third, the simplification of parameters, while analytically convenient, may not fully capture the change and impact. Future work should (i) incorporate stochastic recovery rates and correlated defaults across entities; (ii) test the framework on a broader sample, especially non-state-owned enterprises; and (iii) explore regulatory mechanisms to transition from implicit to explicit guarantees so that investors can take measures faster and more efficiently.
The pricing issue of CLNs has always had profound theoretical value and application prospects. As an important tool in the credit risk mitigation tool market, the reasonable pricing of CLNs is the core issue of balancing risk management efficiency and market stability, especially in the Chinese market where government implicit guarantees are obviously observed in systemically important institutions. It is necessary to continuously improve their accuracy and effectiveness to provide the market with more efficient and powerful credit risk mitigation tools.
Author Contributions
Methodology, X.Q.; Software, X.W.; Writing—original draft preparation, X.W.; Writing—review and editing, X.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 12371474) and Hui-Chun Chin and Tsung-Dao Lee Chinese Undergraduate Research Endowment (2024).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
Proof of Lemma 1.
Let
where is the probability density function of the standard normal distribution. On the other hand,
and
Consequently,
and
Thus, can be represented as follows:
Since , we can conclude that for every , we have
□
Appendix B
To solve the heat equation, we use the odd prolongation method to transform the problem into a Cauchy problem for the solution. So let
then are both odd functions of . The original problem is transformed into a solution of the Cauchy problem as follows:
where is also an odd function, so that the function must satisfy the boundary condition when .
According to the Poisson formula, its solution can be described as
where is the fundamental solution of the heat equation.
Let , where
Therefore, for E
We write , where
Letting , we have
where is the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution and
Similarly, we can obtain
where
For F,
We write , where
Similarly, let , so we can determine that
Let , then
By using Equation (3), we can further calculate and obtain
where . After substitution, we obtain
where . After substitution, we obtain
In Equations (A3) and (A4),
Due to , we can derive the pricing Formula (8).
References
- National Association of Financial Market Institutional Investors. Guidelines for Pilot Business of Credit Risk Mitigation Instruments in the Interbank Market; NAFMII Announcement No. 13; National Association of Financial Market Institutional Investors: Beijing, China, 2010; Available online: https://www.nafmii.org.cn/ggtz/gg/201204/t20120406_197914.html (accessed on 22 July 2025).
- Merton, R.C. On the Pricing of Corporate Debt: The Risk Structure of Interest Rates. J. Financ. 1974, 29, 449–470. [Google Scholar]
- Black, F.; Cox, J.C. Valuing Corporate Securities: Some Effects of Bond Indenture. J. Financ. 1976, 31, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Qian, X.; Yuan, G.X. Partial differential equation pricing method for double-name credit-linked notes with counterparty risk in a reduced-form model with common shocks. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2017, 451, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Qian, X.; Yuan, G.X. Counterparty risk valuation on credit-linked notes under a Markov Chain framework. Appl. Math.-A J. Chin. Univ. 2021, 36, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, K.; Qian, X.; Wang, P. Counterparty risk valuation of kth-to-default credit-linked notes with contagion risk. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 2025, 54, 3584–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Hu, Y. Does the Bond with Government Implicit Guarantee Usually Have the Lower Capital Cost? An Empirical Study on the Bonds of the State-owned Enterprises and the Local Financing Platforms. J. Financ. Res. 2015, 417, 116–130. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, R.; Liu, J. Is Government’s Invisible Guarantee Effective? An Empirical Test Based on Quasi-municipal Bonds’ Issuing Price. J. Financ. Res. 2016, 430, 83–98. [Google Scholar]
- Bielecki, T.R.; Rutkowski, M. Credit Risk: Modeling, Valuation and Hedging; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 74–75. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X. Lectures on Partial Differential Equations, 3rd ed.; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2007; pp. 135–136. [Google Scholar]
- Crosbie, P.; Bohn, J. Modeling Default Risk; Moody’s KMV Company: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Default Bond Pricing and Government Recessive Guarantee Research Based on Dynamic Default Boundaries. Master’s Dissertation, Shanghai University of Financial and Economics, Shanghai, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).