Abstract
Herein, expanded Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) are considered as potential deepfake generation and detection tools. The most specific model is the HMM, while the most general is the pairwise Markov chain (PMC). In between, the Markov observation model (MOM) is proposed, where the observations form a Markov chain conditionally on the hidden state. An expectation-maximization (EM) analog to the Baum–Welch algorithm is developed to estimate the transition probabilities as well as the initial hidden-state-observation joint distribution for all the models considered. This new EM algorithm also includes a recursive log-likelihood equation so that model selection can be performed (after parameter convergence). Once models have been learnt through the EM algorithm, deepfakes are generated through simulation, while they are detected using the log-likelihood. Our three models were compared empirically in terms of their generative and detective ability. PMC and MOM consistently produced the best deepfake generator and detector, respectively.
Keywords:
Markov observation models; hidden Markov model; Baum–Welch algorithm; expectation-maximization; pairwise Markov chain; deepfake MSC:
62M05; 60J22; 68T10
1. Introduction
Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) were introduced in papers by Baum and Petrie [1] and Baum and Eagon [2]. Traditional HMMs have enjoyed tremendous modelling success in applications like computational finance (see e.g., Petropoulos et al. [3]), single-molecule kinetic analysis (see Nicolai [4]), animal tracking (see Sidrow et al. [5]), forecasting commodity futures (see Date et al. [6]) and protein folding (see Stigler et al. [7]). The unobservable hidden HMM states are a discrete-time Markov chain, and the observations process is some distorted, corrupted partial information or measurement of the current state of , satisfying the following condition:
These emission probabilities, , have a conditional probability mass function .
Perhaps the most common challenges in HMMs are calibrating the model, decoding the hidden sequence from the observation sequence and real-time belief propagation, i.e., filtering. The first problem is solved recursively in the HMM setting by the Baum–Welch re-estimation algorithm, which is an application of the Expectation-Maximization (EM) algorithm, predating the EM algorithm. The second, decoding problem is solved by the Viterbi algorithm (see Viterbi [8], Rabiner [9], Shinghal and Toussaint [10]), which is a dynamic programming algorithm. The filtering problem is also solved effectively after calibration using a recursive algorithm that is similar to part of the Baum–Welch algorithm. In practice, there can be numeric problems, like a multitude of local maxima to trap the Baum-Welch algorithm, or inefficient matrix operations when the state size is large but the hidden state resides in a small subset most of the time. In these cases, it can be advisable to use particle filters or other alternative methods, which are not the subject of this paper (see instead Cappé et al. [11] for more information). The forward and backward propagation probabilities of the Baum–Welch algorithm also tend to become very small over time, a phenomenon known as the small-number problem. While satisfactory results can sometimes be obtained by (often logarithmic) rescaling, this small-number problem is still a severe limitation of the Baum–Welch algorithm. However, the independent emission form of the observation modelling undertaken in HMMs can be even more fundamentally limiting.
The autoregressive HMM (AR-HMM) and, more generally, the pairwise Markov chain (PMC) were introduced to allow more extensive and practical observation models. For the AR-HMM, the observations take the following structure:
where is a (usually zero-mean Gaussian) i.i.d. sequence of random variables, and the autoregressive coefficients are functions of the current hidden state . The AR-HMM has experienced strong success in applications like speech recognition (see Bryan and Levinson [12]), the diagnosis of blood infections (see Stanculescu et al. [13]) and the study of climate patterns (see Xuan [14]). One advantage of the AR-HMM is that the Baum–Welch algorithm can still be used (see Bryan and Levinson [12]).
The general PMC model from Pieczynski [15] only assumes that is jointly Markov. Derrode and Pieczynski [16], Derrode and Pieczynski [17] and Kuljus and Lember [18] explain the generality of the PMC and give some interesting subclasses of this model. It is now well understood how to filter and decode PMCs. In fact, Kuljus and Lember [18] solve the decoding problem in great generality, while Derrode and Pieczynski [17] use Baum–Welch-like recursions to produce the filter. Both Derrode and Pieczynski [16] and Derrode and Pieczynski [17] assume reversibility of the PMC and have the observations living in a continuous space. To our knowledge, the Baum–Welch rate re-estimation algorithm has not been validated in general for PMCs. Our first goal is to develop and validate this Baum–Welch algorithm for PMCs, while at the same time estimating hidden initial states and overcoming the small-number problem mentioned above by using alternative variables in our forward and backward recursions. Our resulting EM algorithm will apply to many big data problems.
Our second goal is to show the applicability of HMMs and PMCs, as well as a model called the Markov Observation Model (MOM), which falls part way between HMMs and PMCs in deepfake detection and generation. The key to producing and detecting deepfakes is to bring in an element that is easily calculated, yet often overlooked in HMMs and PMCs: likelihood. During training, as well as during detection, likelihood can be used in the place of the discriminator in a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN), while simulation plays the part of the generator. Naturally, the expectation-maximization algorithm also plays a key role in this deepfake application, as explained below.
Our third goal is subtler. Just because the PMC model is more general than the HMM, and the Baum–Welch algorithm can be extended to learn either model, does not mean one should pronounce the death of the HMM. The problem is that the additional generality leads, in general, to a more complicated likelihood with a multitude of maxima for the EM algorithm to become trapped in or choose from. It can become a virtually impossible task to learn a global, or even a useful, maximum. Hence, the performance of the PMC model as a hidden Markov structure can be sub-optimal compared to the performance of the HMM or MOM, as we shall show empirically. Alternatively, the global maximum of the PMC may not be what is wanted. For these reasons, we promote the MOM and, in fact, show that it performs the best in simple deepfake detection, while the PMC generates the best deepfakes.
The HMM and nonlinear filtering theory (NFT) can each be thought of as nonlinear generalization of the Kalman filter (see Kalman [19], Kalman and Bucy [20]). The recent analogues (see [21]) of the celebrated Fujisaki–Kallianpur–Kunita and the Duncan–Mortensen–Zakai equations (see [22,23,24,25,26] for some original and general results) of NFT to continuous-time Markov chain observations provide further evidence of the closeness of the HMM and NFT. The hidden state, called the signal in NFT, can be a general Markov process model and live in a general state space, but there is no universal EM algorithm for identifying the model, like the Baum–Welch algorithm, nor a dynamic programming algorithm for identifying a most likely hidden-state path, like the Viterbi algorithm. Rather, the goals in NFT are usually to compute filters, predictors and smoothers, for which there are no exact closed-form solutions, except in isolated cases (see [27]), and approximations have to be used. Like HMMs, nonlinear filtering has enjoyed widespread application. For instance, the subfield of nonlinear particle filtering, also known as sequential Monte Carlo, has a number of powerful algorithms (see Elfring [28], Pitt and Shephard [29], Del Moral et al. [30], Kouritzin [31], Chopin and Papaspiliopoulos [32]) and has been applied to numerous problems in areas like Bayesian inference (Chopin [33], Kloek and van Dijk [34], van Dijk and Kloek [35]), bioinformatics (Hajiramezanali et al. [36]), economics and mathematical finance (Creal [37]), intracellular movement (Maroulas and Nebenführ [38]), fault detection (D’Amato et al. [39]), pharmacokinetics (Bonate [40]), geosciences (Van Leeuwen et al. [41]), and many other fields. Still, like in HMMs, the observations in nonlinear filter models are largely limited to distorted, corrupted, partial observations of the signal. NFT is used successfully in deepfake generation and detection herein. However, the simplicity of the EM and likelihood algorithms for HMMs, MOMs and PMCs are compelling advantages here in the deepfake application but likely also in some of these other applications of NFT.
The layout of this paper is as follows: In the next section, we explain the models, in particular the Markov observation models, and how they can be simulated. In Section 3 the filter and likelihood calculations are derived. In Section 4, EM techniques are used to derive an analog to the Baum–Welch algorithm for identifying the system (probability) parameters. In particular, joint recursive formulas for the hidden-state and observation transition probabilities, as well as the initial hidden-state-observation joint distribution, are derived. Section 5 contains our deepfake application and results. Section 6 is devoted to connecting the limit points of the EM-type algorithm to the maxima of the conditional likelihood, given the observations. Finally, Section 7 clarifies our contributions, makes our most basic conclusions and suggests some future work the author hopes will be undertaken.
2. Models and Simulation
Let be some final time. We first clarify the HMM assumption of independent emission probabilities.
Under the HMM,
where is a probability mass function for each x. Otherwise, the HMM and PMC are explained elsewhere.
Next, we explain how the MOM generalizes the HMM and fits into the PMC. Suppose is some discrete observation space. In the MOM, like in the HMM, the hidden state is a homogeneous Markov chain on some discrete (finite or countable) state space with one-step transition probabilities for . Contrary to the HMM, the MOM allows self-dependence in the observations (this is illustrated by rightward arrows between the Ys in Figure 1). In particular, MOM observations Y are a (conditional) Markov chain, given the hidden state with the following transition probabilities:
These do not affect the hidden-state transitions, in the sense that
Still, (3) implies that
i.e., that the new observation only depends upon the new hidden state (as well as the past observation). Equations (3) and (4) imply that the hidden-state observation pair is jointly Markov with joint one-step transition probabilities:
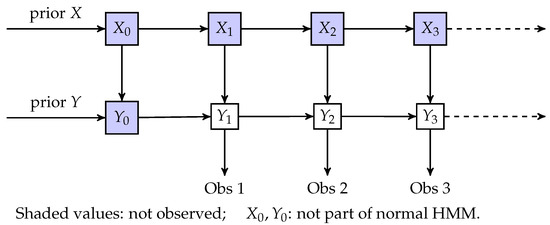
Figure 1.
Markov observation model structure.
The joint Markov property then implies that
Notice that this generalizes the emisson probability to
so the MOM generalizes the HMM by just taking , a state-dependent probability mass function. To see how the MOM is related to the AR-HMM, we rewrite (1) as
which, given the hidden state , gives an explicit formula for in terms of only and some independent noise . Hence, is obviously conditionally Markov, and is an MOM. We have not claimed that this subsumes the AR-HMM yet, because is usually Gaussian in the AR-HMM, and we handle the case of discrete noise herein. This will be further discussed in Section 7.
A subtly that arises with the MOM over the HMM is that we need an enlarged initial distribution, since we have a that is not observed (see Figure 1). Rather, we think of starting up the observation process at time 1, even though there were observations to be made prior to this time. Further, since we generally do not know the model parameters, we need a means to estimate this initial distribution
It is worth noting that the MOM resembles the stationary PMC under Condition (H) in Pieczynski [15], which forces the hidden state to be Markov by Proposition 2.2 of Pieczynski [15].
Simulation
Any PMC is characterized by an initial distribution on and a joint transition probability for its hidden state and observations. In particular,
for the MOM and
for the HMM. In any case, the marginal transitions are denoted as
, p characterize a -PMC. The initial distribution gives the distribution of for the MOM and PMC, while the initial distribution gives the distribution of for the HMM by convention. This convention makes sense since the MOM and PMC have observation history to model in some unknown . In the case of the HMM, an initial can then be drawn from .
The simulation of the HMM, MOM and PMC observations is performed in the same way: Begin by drawing ( for the HMM) from , continue the simulation using and then finally throw out the hidden state X (as well as for MOM and PMC) to leave the observation process Y.
3. Likelihood, Filter and Predictor
A PMC is parameterized by its initial distribution and joint transition probability p for its hidden state and observations. Its ability to fit a given sequence of observations up to time n is naturally judged by its likelihood:
Here, is a probability measure, where is a -PMC. Therefore, given several PMC models, perhaps found by different runs of an expectation-maximization algorithm, as well as an observation data sequence, one can use the likelihoods to judge which model best fits the data. Each run of the EM algorithm would converge to a local maximum of the likelihood function, and then the likelihood function could be used to determine which of these produces a higher maximum. Since the MOM and HMM are PMCs (with specific p given in (8) and (9)), this test extends to judging the best MOM and best HMM.
In applications like filtering, the hidden state has significance, and estimating (the distribution of) it is important. The (optimal) filter is the (conditional) hidden-state probability mass function
We first work with the PMC, and then extract the MOM and HMM from these calculations. The likelihood and filter can computed together in real time using the forward probability
which is motivated from the Baum–Welch algorithm. Then, it follows from (11)–(13) that
Moreover, we obtain, based on the multiplication rule, the joint Markov property and (13), the following:
which can be solved recursively for , starting (according to (13)) at
Recall that is assigned differently. On a computer, we do not recurse , due to risk of underflow (the small-number problem), but rather we revert back to the filter . Using (14) and (15), one finds that the forward recursion for is
which can be solved forward for , starting at
This immediately implies that , and then, by using (14), (17) and induction, that
Thus, the filter and likelihood can be computed in real time (after initialization) via the recursions in (17) and (19).
Once the filter has been computed, predictors can also be computed using Chapman–Kolmogorov-type equations. For example, it follows from the multiplication rule and the Markov property that the one-step predictor is
which reduces to
and
respectively in the cases of the MOM and HMM.
In non-real-time applications, we strengthen our hidden-state estimates to include future observations via the joint path filter
which is a joint pmf for . To compute the joint path filter, we first let
where the last equality follows from the definition of conditional probability, and the normalized versions of :
Notice that we include an extra variable y in . This is because we do not see the first observation , so we have to consider all possibilities and treat it like another hidden state. Then, based on (11), (13), the Markov property, (19) and (14), the following is obtained:
so based on (24)–(26),
for . This means that there are two ways to compute the (marginal) path filter directly from (27):
for , and
for . These all become computationally effective by a backward recursion for . It also follows from (24), the definition of conditional probability, the Markov property, partitioning and our transition probabilities that
so normalizing by (25), the following can be obtained:
which can be solved backward for , starting from
The value for and becomes
to account for the fact that we do not see as the data turns on at time 1. With in hand, we can estimate the joint distribution of , which are the remaining hidden variables. It follows from Bayes’ rule, (11), (19), the multiplication rule, (24) and (25) that
for all , .
The pathspace filter and likelihood algorithm is given in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1: Path filter and likelihood for PMC |
 |
The first part of Algorithm 1, up to the first set of outputs, runs in real time, as the observations arrive, and provides the real-time filter and likelihood. For real-time applications, one would stop there, or else add predictors not included in Algorithm 1 but given as an example in (20). Otherwise, one can refine the estimates of the hidden states based on future observations, which then provides the pathspace filters and is the key to learning a model. This is the second part of Algorithm 1, and is explained below. But first, we note that the recursions developed so far are easily tuned to an MOM or HMM.
3.1. MOM Adjustments
For the MOM, we use (8). We leave (13), (14) and (19) unchanged, so (17) and (18) become
for all , which can be solved forward for , starting at
The backward recursions change a little more, starting with (24) and (25), which change to
and the normalized versions
since
by Lemma 1 (to follow). Then, (27) becomes
for . This then implies the obvious simplifications of (28) and (29) to
for and , respectively. Then, (31) becomes
by (5), which is solved backwards starting from . The values at become
and
for all , .
3.2. HMM Adjustments
For the HMM, we use (9). We have a MOM with the specific
that also starts at with , instead of . This creates modest changes or simplifications for the filter startup:
But otherwise, (36) holds with just the substitution .
To handle the backward recursion, we first reduce the general definition of in (24), using (2), to
and the normalized versions
There are no , , or variables for the HMM. The HMM’s backward-recursion simplifications are based on the following result.
Lemma 1.
For the MOM and the HMM,
Proof.
For the MOM, we have
In the case of the HMM, this becomes. However, it follows from the multiplication rule, the tower property and (2) that
which establishes the desired dependence. □
4. Probability Estimation via EM Algorithm
In this section, we develop a recursive expectation-maximization algorithm that can be used to create convergent estimates for the transition and initial probabilities of our models. We leave the theoretical justification of convergence to Section 6.
The main goal of developing an EM algorithm is to find for all , and for all , . Noting that every time step is considered to be a transition in a discrete-time Markov chain, we would ideally set the following:
which means that we must compute , and, using (23) and (28), for all , and for all , to get this transition probability estimate. Now, by Bayes’ rule, ((11), (19)), ((24), (25)) and ((13), (14)), we obtain the following:
so
and so
and are computed recursively in (17) and (31) using the prior estimates of and .
Expectation-maximization algorithms use these types of formulas and prior estimates to produce better estimates. We take estimates for , and and obtain new estimates for these quantities iteratively using (53), (54), (27), (35) and (28):
and using (35),
Remark 1.
(1) Different iterations of will be used on the left- and right-hand sides of (57) and (58). The new estimates on the left are denoted as .
(2) Setting the marginal or probability will result in it staying zero for all updates. This effectively removes this parameter from the EM optimization update, and should be avoided unless it is known that one of these should be 0.
(3) If there are no successive observations with and in the actual observation sequence, then all new estimates will either be set to 0 or close to it. They might not be exactly zero, due to the first term in the numerator of (57), where we could have an estimate of and an observed .
We now have everything required for our EM algorithms, which are given for the PMC, MOM and HMM cases in Algorithms 2, 3 and 4 respectively.
These algorithms start with the initial estimates , of , , and refine them successively to new estimates , ; , ; etc. It is important to know that our estimates improve as .
Lemma 3 (below) will be used to ensure that an initially positive estimate stays positive as k increases, which is important in our proofs in Section 6. The following lemma follows easily from (31)–(33), (17), (18), (34), induction and the fact that . A sensible initialization of our EM algorithm would ensure that the condition holds.
Lemma 2.
Suppose for all and . Then,
- 1.
- for all and .
- 2.
- for any , such that .
- 3.
- for all and if, in addition, for all .
- 4.
- if .
The following result is the key to ensuring that our non-zero parameters stay non-zero. It follows from the prior lemma, as well as (57), (58) and (31).
Lemma 3.
Suppose , for all and . Then,
- 1.
- if ; occurs; and for all .
- 2.
- if and there exists such that .
| Algorithm 2: EM algorithm for PMC |
 |
| Algorithm 3: EM algorithm for MOM |
 |
| Algorithm 4: EM algorithm for HMM |
 |
5. Deepfake Application
Motivated by [42], we considered our three hidden models in deepfake generation and detection. In particular, we used the models’ EM, simulation and Bayes’ factor capabilities to generate and detect deepfake real coin-flip sequences, and then compared them to determine which of the three is the best at both generation and detection.
We first created 137 real sequences of 400 coin flips by generating independent fair Bernoulli trials. Another 137 hand fake sequences of 200 coin flips were created by students with knowledge of undergraduate probability. They were told to make them look real to try to fool both humans and machines. Note that we worked with coin flip sequences with a length of 200, except for the training with real sequences, where a length of 400 was used so that length was not a defining factor of these real sequences. This added length to the real sequences did not bias either of the HMM, MOM or PMC over the others, as it was consistent for all.
We used HMM, MOM and PMC simulation with a single hidden-state variable taking s possible values (henceforth referred to as s states) to generate deepfake sequences of 200 coin flips based on the 137 real sequences. To do this, we first learnt each of the 137 real sequences using the EM algorithms with hidden states for each model, creating three collections of 137 parameter sets for each s. Then, we simulated a sequence from each set of parameters, throwing the hidden states away, creating three collections of 137 observation coin-flip sequences for each s. These were the HMM-, MOM- and PMC-type deepfake sequences. Note that learning was conducted based on the 400 long real sequences (to remove noise from the parameters), but we created 200 long deepfake sequences.
Once all five sets of (real, fake and deepfake) data had been collected, we ran 100 training and testing trials at each selected s and averaged over these trials. For each trial, we randomly and independently split each of the 137 (hand) fake sequences into 110 training and 27 testing sequences, i.e., an 80-to-20 split. Conversely, we regenerated the 137 independent sets of real sequences and 3 deepfake sequences using, respectively, independent random number and Markov chain simulation with their models, but still divided these sets into 110 training and 27 testing sequences. We then trained the HMM, MOM and PMC with s hidden states on each of these sets of 110 training sequences. Note that since the deepfake sequences were generated with hidden states, the actual model generating these sequences could not be identified. At this point, we had 110 sets of HMM parameters (i.e., HMM models) for each of the real, hand fake, HMM, MOM and PMC different training sequences in that trial. Similarly, we had 550 sets of MOM and PMC parameters.
Detection for each testing sequence was carried out using all the models. In a trial, each of the five sets of 27 sequences was run against the 550 HMM, 550 MOM and 550 PMC models. A sequence was then predicted by the HMM to be real, hand fake, HMM-generated, MOM-generated or PMC-generated based on HMM likelihood with s hidden states. In particular, a sequence was predicted to be real if the sum of the log-likelihood over the 110 real HMM models was higher than that over the 110 hand fake, 110 HMM, 110 MOM and 110 PMC HMM models. In the same way, it was predicted to be hand fake, HMM, MOM or PMC by the HMM. This same procedure was repeated for the MOM and for the PMC, and then for the remaining 99 trials, using the regeneration method mentioned above. The results were averaged and put into Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 in the cases and 7, respectively.

Table 1.
Generative and detection ability with . Blue highlight indicates this detection method is the best detector, while orange indicates the generation method is the most difficult to detect bythis detection method.

Table 2.
Generative and detection ability with .

Table 3.
Generative and detection ability with .
6. Convergence of Probabilities
In this section, we establish the convergence properties of the transition probabilities and the initial distribution that we derived in Section 4. Our method adapts the ideas of Baum et al. [43], Liporace [44] and Wu [45] to our setting.
We think of the transition probabilities and initial distribution as parameters, and let denote all of the non-zero transition and initial distribution probabilities in . Let and be the cardinalities of the hidden and observation spaces, and set . Then, has a domain space of cardinality , and has a domain space of cardinality . Combined, this leads to parameters. However, we are removing the values that will be set to zero and adding sum to one constraints to consider a constrained optimization problem on for some . Removing these zero possibilities gives us the necessary regularity for our re-estimation procedure. However, it is not enough to just remove them at the beginning. We have to ensure that zero parameters will not creep in during our interations, or else we will be doing such things as taking logarithms of 0. Lemma 3 suggests that estimates not initially set to zeros will not occur as zero in later iterations. In general, we will assume the following:
Definition 1.
A sequence of estimates is zero-separating if
- 1.
- iff for all ,
- 2.
- iff for all .
Here, iff stands for if and only if.
This means that we can potentially optimize over the that we initially do not set to zero. Henceforth, we factor the zero out of , consider with and define the parameterized mass functions
in terms of the non-zero values only. The observable likelihood
is not changed by removing the zero values of , and this removal allows us to define the re-estimation function
Note: Here, and in the sequel, the summation in above is only over the non-zero combinations. We would not include an pair where , nor an pair where . Hence, our parameter space is
Later, we will consider the extended parameter space
as limit points. Note that in both and K, is only over the and that are not just set to 0 (before limits).
Then, equating with to ease notation, one obtains the following:
The re-estimation function is used to interpret the EM algorithm we derived earlier. We impose the following condition to ensure everything is well defined.
- (Zero) The EM estimates are zero-separating.
The following result is motivated by Theorem 3 of Liporace [44].
We consider it as an optimization problem over the open set , but with the constraint that we have mass functions, so the values have to be in the set .
Proof.
One obtains based on (62), as well as the constraint , that the maximum must satisfy
where is a Lagrange multiplier and means when . Multiplying by , summing over and then using (11), (35) and (28) and then (19), (14) and (25), one determines that
Substituting (64) into (63) and repeating the argument in (64), but with (27) instead of (28), one determines that
To explain the first term in the numerator in the last equality, we use the multiplication rule and (24) to find
from which it will follow easily.
Finally, for a maximum, one also requires
where is a Lagrange multiplier. Multiplying by and summing over , one obtains that
Substituting (67) into (66), one obtains by (35) that
Now, we have established that the EM algorithm of Section 4 corresponds to the unique critical point of . Moreover, all mixed partial derivatives of Q in the components of are 0, while
and
Hence, the Hessian matrix is diagonal with negative values along its axis, and the critical point is a maximum. □
The upshot of this result is that if the EM algorithm produces parameters , then .
Now, we have the following result, based on Theorem 2.1 of Baum et al. [43], that establishes that the observable likelihood is also increasing i.e., .
Lemma 4.
Suppose (Zero) holds. implies . Moreover, implies .
Proof.
for has convex inverse . Hence, by Jensen’s inequality,
and the result follows. □
The stationary points of P and Q are also related.
Lemma 5.
Suppose (Zero) holds. A point is a critical point of if, and only if, it is a fixed point of the re-estimation function, i.e., , since Q is differentiable on in .
Proof.
The following derivatives are equal:
which are defined since . Similarly,
□
We can rewrite (65), (68) in recursive form, with the values of and substituted in, to find that
where M is a continuous function. Moreover, is continuous and satisfies from above. Now, we have established everything we need for the following result, which follows from the proof of Theorem 1 of Wu [45].
Theorem 2.
Suppose (Zero) holds. Then, is relatively compact, all its limit points (in K) are stationary points of P, producing the same likelihood , say, and converges monotonically to .
Wu [45] provides several interesting results in the context of general EM algorithms to guarantee convergence to local or global maxima under certain conditions. However, the point of this paper is to introduce a new model and algorithms with just enough theory to justify the algorithms. Hence, we do not consider theory under any special cases here, but rather refer the reader to Wu [45].
7. Discussion and Conclusions
We have established a new expectation-maximization (EM) algorithm to converge to the parameters of general pairwise Markov chains and Markov observation models that generalizes the Baum–Welch algorithm for hidden Markov models. Our extension not only expands the model itself, but also identifies the initial distribution and solves the small-number problem. We have shown that the likelihood, filter, and (observation) predictor are all easily computable in real time using a recursion like the forward equation in the EM algorithm (after the parameters have converged). We have shown that the pathspace filter for conditional distribution of the hidden state, given all the observations, is also computable using the results of both the forward and backward equations. We invented a GAN-like setup using the likelihoods of known models (with a voting scheme) for detection and simulation (throwing away the hidden component) for the generation part. Finally, we have shown how all our new technology might be combined to solve interesting problems like deepfake generation and detection. Work that is currently underway appears shows great promise for the application of these methods in areas like fraud detection, statistical process control and deepfake detection. It seems like the quality of the results obtained in these domains will not be satisfactory with any existing approaches in the literature, which will surely validate this present work as more than just theory.
I was asked a couple of intriguing questions by the anonymous reviewers, which I will begin to discuss within this paragraph on potential future work. All our development focused on the discrete-space case. However, the classical Baum–Welch algorithm for HMMs also holds in the continuous (nearly) Gaussian case. A similar generalization to the one we made here should establish an EM algorithm for (nearly) Gauss–Markov coupled hidden-state observation pairs. Then, one would be in a position to properly establish our method for establishing the EM algorithm in the usual AR-HMM with Gaussian noise using the representation (7). Continuing in this direction, one could wonder whether there are EM-based forward–backward equations to estimate the parameters in an ARMA-HMM or ARIMA-HMM, both of which would satisfy an equation like the following:
where and are parameters that depend upon the state of a hidden Markov chain, and is an i.i.d. noise sequence. (Here, the parameters would take different values or the equation might be rearranged if we had an ARIMA model instead of an ARMA model). These observation equations are not naturally Markov. Indeed, they are close to the ARFIMA models that are used to simulate long-range-dependent sequences. However, the ARMA-HMM and ARIMA-HMM still have linear observation equations with a finite number of parameters and dependence upon a hidden Markov chain. It would be intriguing to investigate whether the EM method can be extended to handle these cases, and whether there are analogs to the forward and backward equations that can be can be combined to estimate all the parameters in these models.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Baum, L.E.; Petrie, T. Statistical Inference for Probabilistic Functions of Finite State Markov Chains. Ann. Math. Stat. 1966, 37, 1554–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, L.E.; Eagon, J.A. An inequality with applications to statistical estimation for probabilistic functions of Markov processes and to a model for ecology. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 1967, 73, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, A.; Chatzis, S.P.; Xanthopoulos, S. A novel corporate credit rating system based on Student’s-t hidden Markov models. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 53, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolai, C. Solving ion channel kinetics with the QuB software. Biophys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 8, 191–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidrow, E.; Heckman, N.; Fortune, S.M.; Trites, A.W.; Murphy, I.; Auger-Méthé, M. Modelling multi-scale, state-switching functional data with hidden Markov models. Can. J. Stat. 2022, 50, 327–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Date, P.; Mamon, R.; Tenyakov, A. Filtering and forecasting commodity futures prices under an HMM framework. Energy Econ. 2013, 40, 1001–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stigler, J.; Ziegler, F.; Gieseke, A.; Gebhardt, J.C.M.; Rief, M. The Complex Folding Network of Single Calmodulin Molecules. Science 2011, 334, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viterbi, A.J. Error bounds for convolutional codes and an asymptotically optimum decoding algorithm. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1967, 13, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiner, L.R. A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proc. IEEE 1989, 77, 257–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinghal, R.; Toussaint, G.T. Experiments in text recognition with the modified Viterbi algorithm. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1979, PAMI-l, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappé, O.; Moulines, E.; Rydén, T. Inference in Hidden Markov Models; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Bryan, J.D.; Levinson, S.E. Autoregressive Hidden Markov Model and the Speech Signal. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2015, 61, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanculescu, I.; Williams, C.K.I.; Freer, Y. Autoregressive Hidden Markov Models for the Early Detection of Neonatal Sepsis. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2014, 18, 1560–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, T. Autoregressive Hidden Markov Model with Application in an El Nino Study. Master’s Thesis, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pieczynski, W. Pairwise Markov chains. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2003, 25, 634–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrode, S.; Pieczynski, W. Unsupervised data classification using pairwise Markov chains with automatic copula selection. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2013, 63, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrode, S.; Pieczynski, W. Unsupervised classification using hidden Markov chain with unknown noise copulas and margins. Signal Process. 2016, 128, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuljus, K.; Lember, J. Pairwise Markov Models and Hybrid Segmentation Approach. Methodol. Comput. Appl. Probab. 2023, 25, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E. A New Approach to Linear Filtering and Prediction Problems. J. Basic Eng. 1960, 82, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalman, R.E.; Bucy, R.S. New Results in Linear Filtering and Prediction Theory. ASME. J. Basic Eng. 1961, 83, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouritzin, M.A. Sampling and filtering with Markov chains. Signal Process. 2024, 225, 109613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakai, M. On the optimal filtering of diffusion processes. Z. Wahrsch. Verw. Geb. 1969, 11, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisaki, M.; Kallianpur, G.; Kunita, H. Stochastic differential equations for the nonlinear filtering problem. Osaka J. Math. 1972, 9, 19–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz, T.G.; Ocone, D.L. Unique characterization of conditional distributions in nonlinear filtering. Ann. Probab. 1988, 16, 80–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouritzin, M.A.; Long, H. On extending classical filtering equations. Stat. Probab. Lett. 2008, 78, 3195–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, T.G.; Nappo, G. The Filtered Martingale Problem. In The Oxford Handbook of Nonlinear Filtering; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kouritzin, M.A. On exact filters for continuous signals with discrete observations. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1998, 43, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfring, J.; Torta, E.; van de Molengraft, R. Particle Filters: A Hands-On Tutorial. Sensors 2021, 21, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, M.K.; Shephard, N. Filtering Via Simulation: Auxiliary Particle Filters. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1999, 94, 590–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Moral, P.; Kouritzin, M.A.; Miclo, L. On a class of discrete generation interacting particle systems. Electron. J. Probab. 2001, 6, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouritzin, M.A. Residual and Stratified Branching Particle Filters. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2017, 111, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopin, N.; Papaspiliopoulos, O. An Introduction to Sequential Monte Carlo; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopin, N. Central Limit Theorem for Sequential Monte Carlo Methods and its Application to Bayesian Inference. Ann. Stat. 2004, 32, 2385–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloek, T.; van Dijk, H.K. Bayesian Estimates of Equation System Parameters: An Application of Integration by Monte Carlo. Econometrica 1978, 46, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, H.K.; Kloek, T. Experiments with some alternatives for simple importance sampling in Monte Carlo integration. In Bayesian Statistics, Vol. II; Bernardo, J.M., DeGroot, M.H., Lindley, D.V., Smith, A.F.M., Eds.; North-Holland and Valencia University Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; ISBN 0-444-87746-0. [Google Scholar]
- Hajiramezanali, E.; Imani, M.; Braga-Neto, U.; Qian, X.; Dougherty, E.R. Scalable optimal Bayesian classification of single-cell trajectories under regulatory model uncertainty. BMC Genom. 2019, 20 (Suppl. S6), 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creal, D. A Survey of Sequential Monte Carlo Methods for Economics and Finance. Econom. Rev. 2012, 31, 245–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroulas, V.; Nebenführ, A. Tracking Rapid Intracellular Movements: A Bayesian Random Set Approach. Ann. Appl. Stat. 2015, 9, 926–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, E.; Notaro, I.; Nardi, V.A.; Scordamaglia, V. A Particle Filtering Approach for Fault Detection and Isolation of UAV IMU Sensors: Design, Implementation and Sensitivity Analysis. Sensors 2021, 21, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonate, P. Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Modeling and Simulation; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Van Leeuwen, P.J.; Künsch, H.R.; Nerger, L.; Potthast, R.; Reich, S. Particle filters for high-dimensional geoscience applications: A review. Q. J. R. Meteorol Soc. 2019, 145, 2335–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouritzin, M.A.; Newton, F.; Orsten, S.; Wilson, D.C. On Detecting Fake Coin Flip Sequences. IMS Collect. 2008, 4, 107–122. [Google Scholar]
- Baum, L.E.; Petrie, T.; Soules, G.; Weiss, N. A Maximization Technique Occurring in Statistical Analysis of Probabilistic Functions in Markov Chains. Ann. Math. Stat. 1970, 41, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liporace, L.A. Maximum likelihood estimation for multivariate observations of Markov sources. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1982, 28, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.F.J. On the Convergence Properties of the EM Algorithm. Ann. Statist. 1983, 11, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).