Thermal Investigation of the Magnetised Porous Triangular Fins and Comparative Analysis of Magnetised and Non-Magnetised Triangular Fins
Abstract
1. Introduction
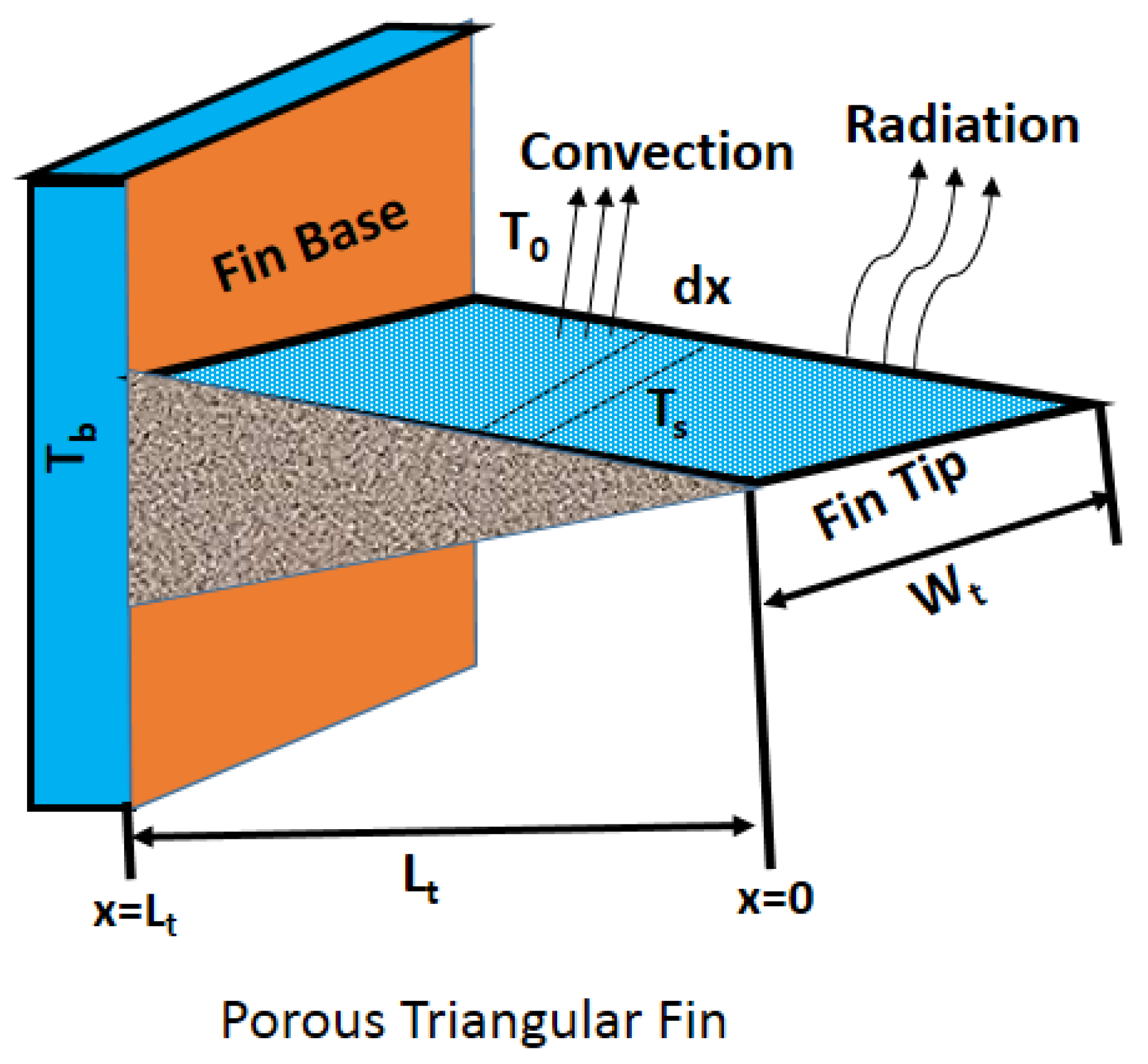
2. Mathematical Formulation
- The thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity of the fin material, as well as the convective heat transfer coefficient, are assumed constant.
- The porous medium is homogeneous, isotropic, and fully saturated with a single-phase fluid.
- The temperature variation within the fin is considered to be one-dimensional and varies along the length of the fin.
- The Darcy model is used to simulate fluid flow through porous media.
3. The Shooting Method
4. Application of Shooting Method
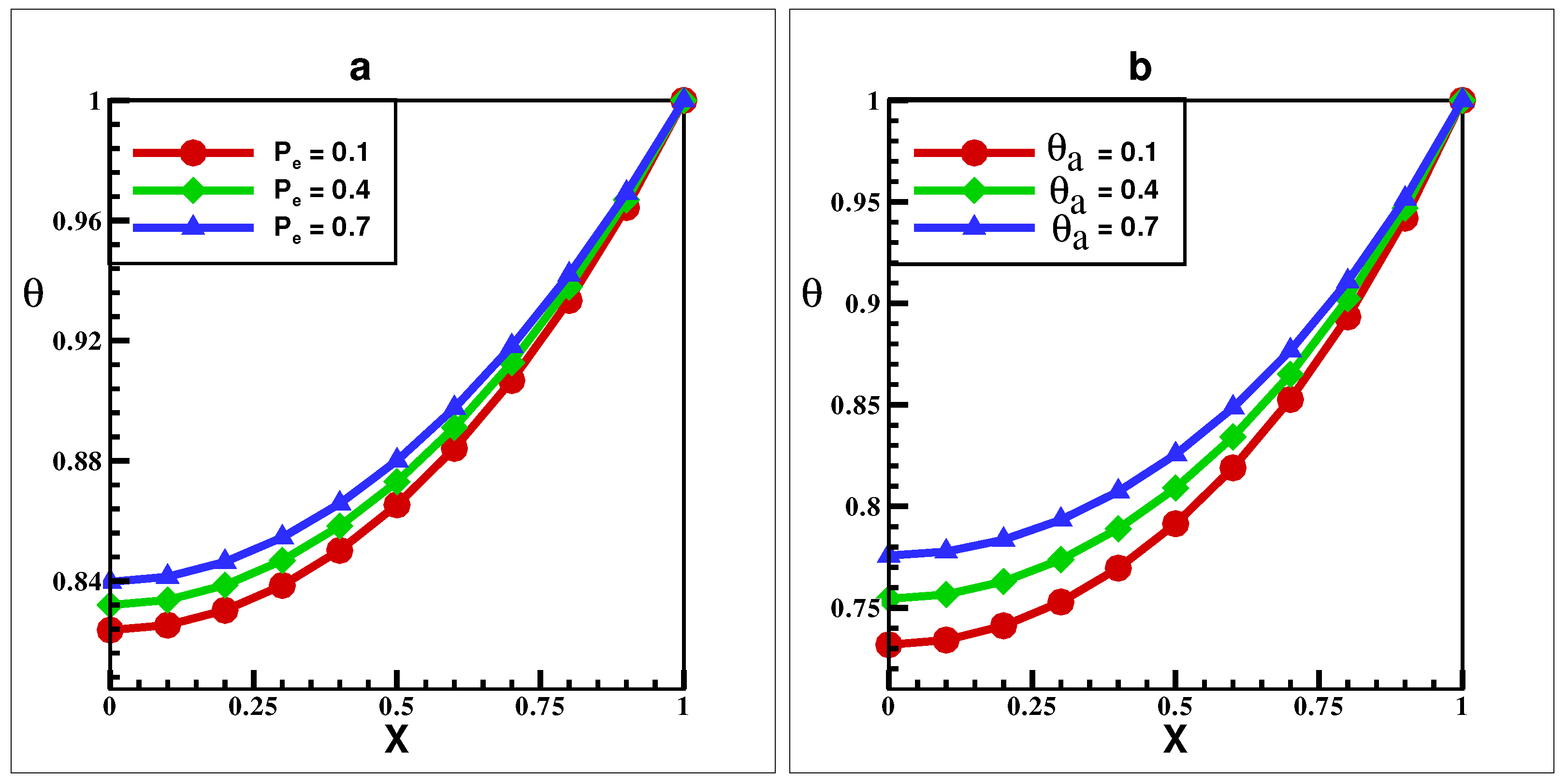
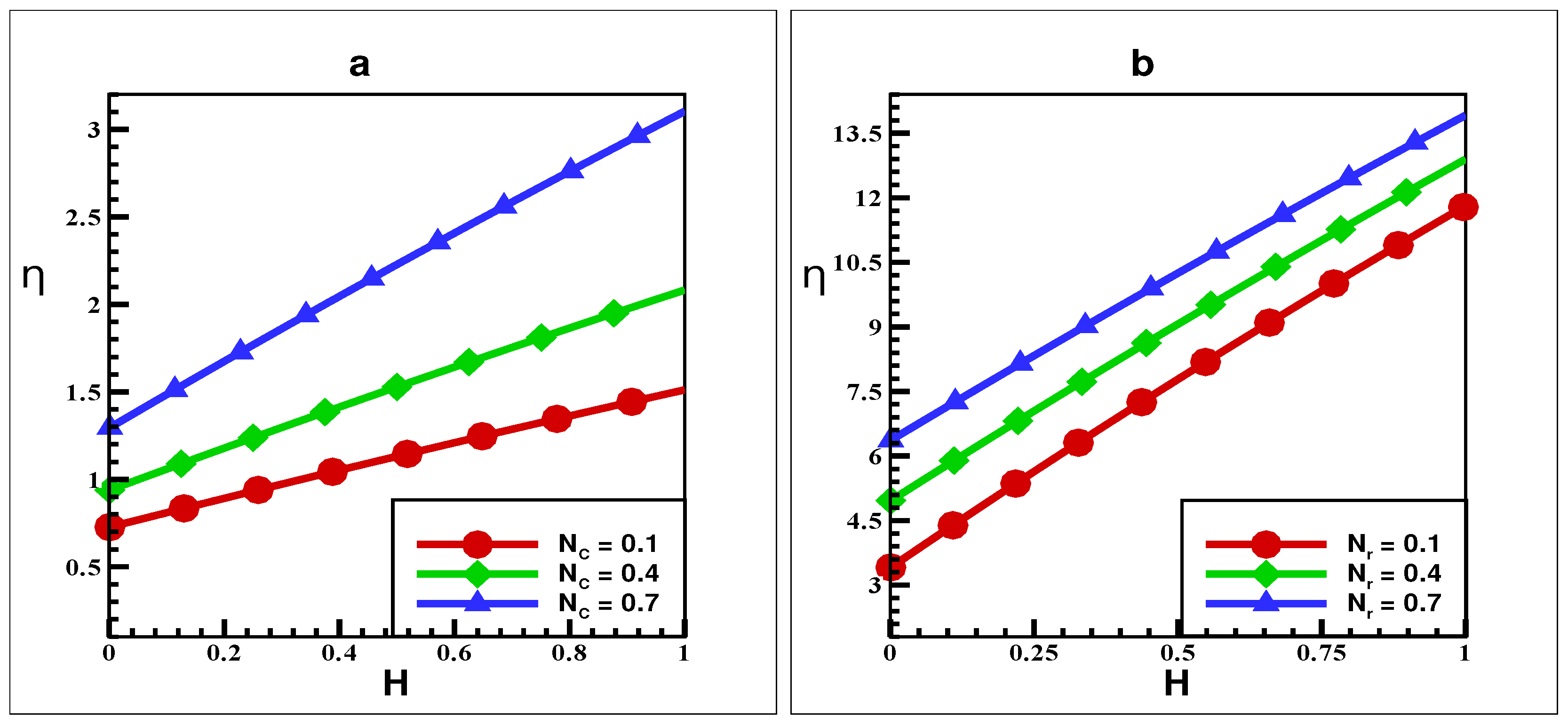
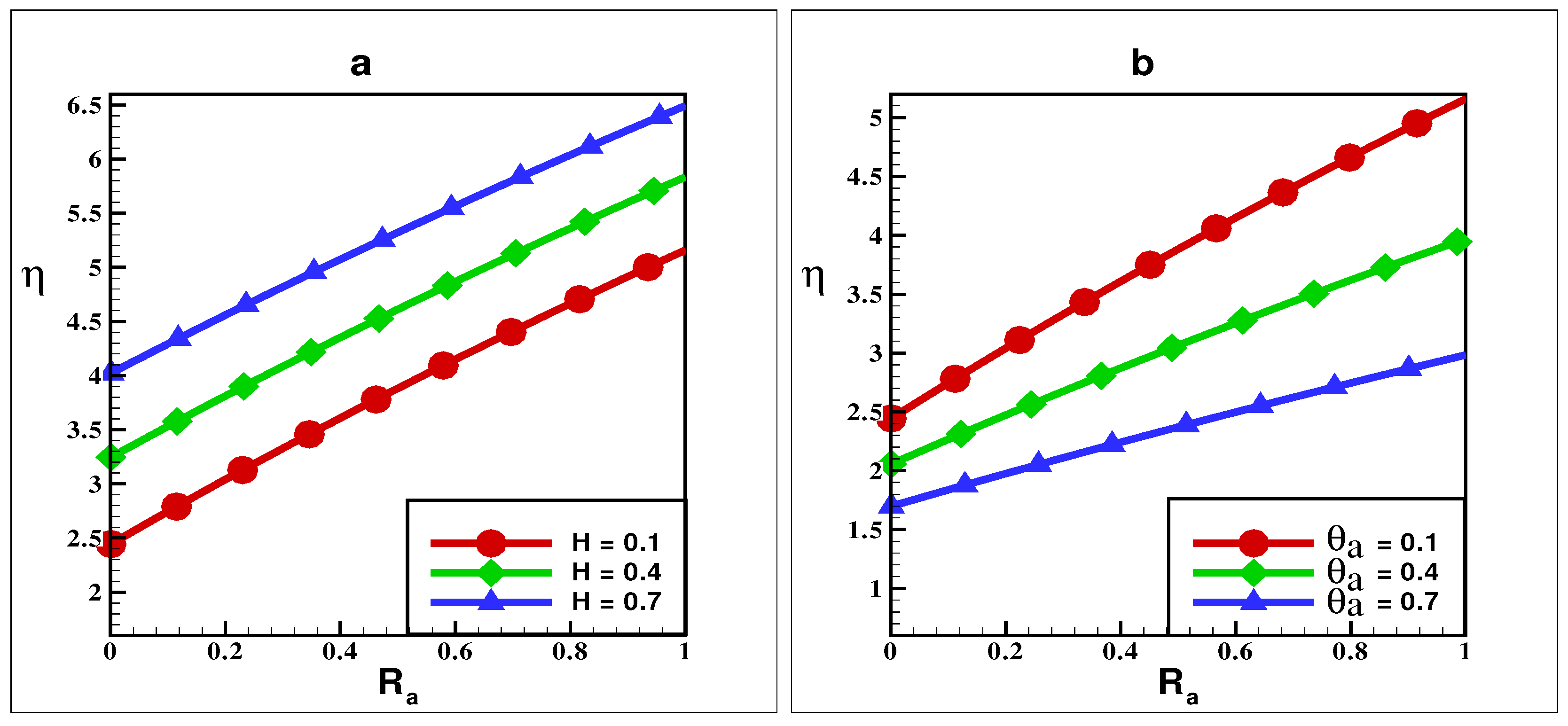
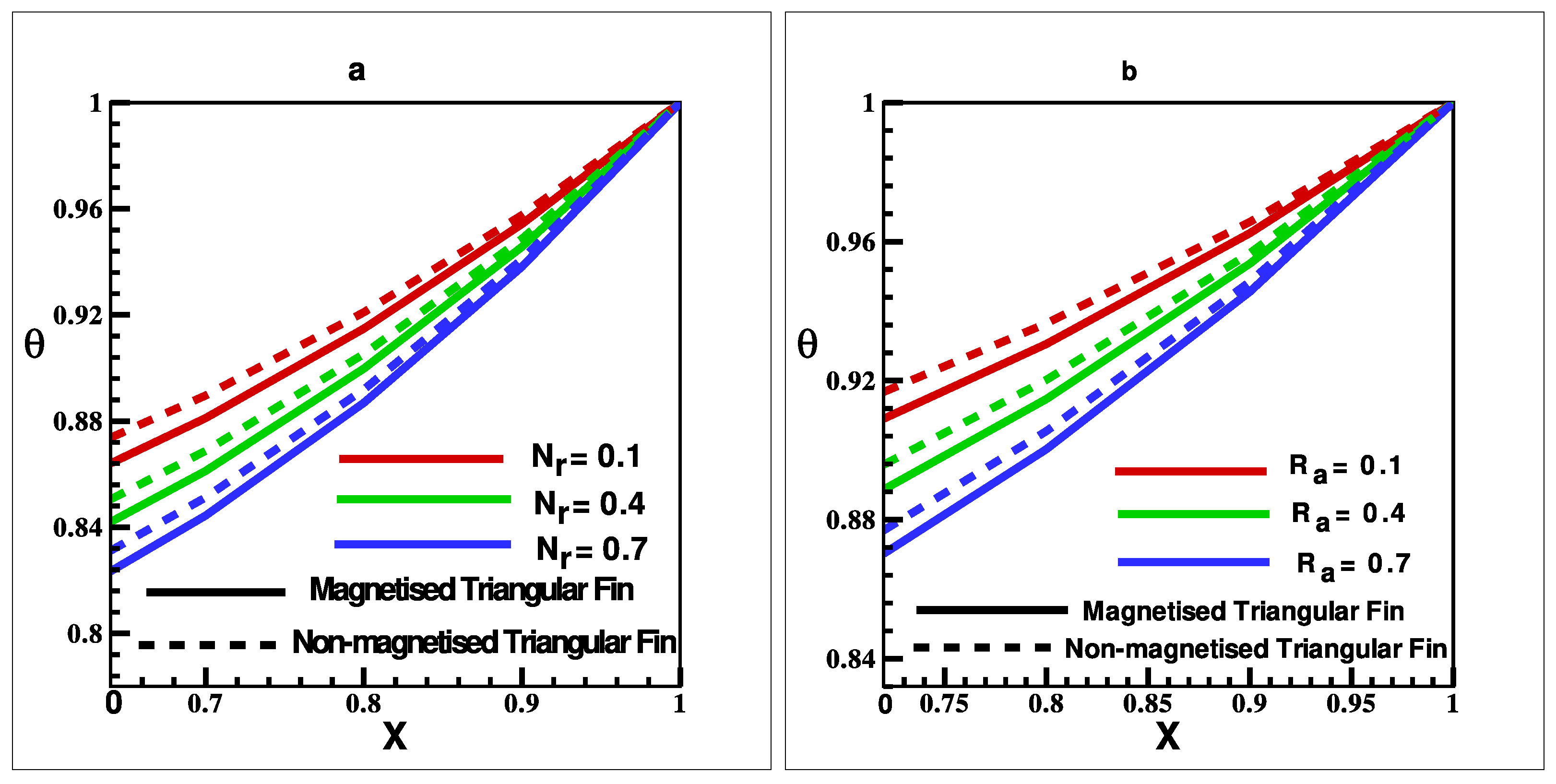
5. Results and Discussion
6. Comparative Numerical Analysis
7. Comparison with Experimental Results
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Peclet number | Fins length | ||
| Radiation parameter | Kinematics viscosity | ||
| Heat transfer rate | T | Fin temperature | |
| Volumetric thermal expansion coefficient | fluid velocity | ||
| Fin’s porosity | H | Hartmann number | |
| V | Voltage | Fin efficiency | |
| Density of material (kg/m3) | X | Dimensionless distance | |
| Magnetic field intensity | Dimensional distance | ||
| Convection parameter | Specific heat coefficient | ||
| Area of fin’s surface (m2) | Initial value problem | ||
| Dimensional surface temperature | x | Dimensional distance | |
| B | Magnetic Induction | Dimensionless temperature | |
| Darcy number | Mass flow rate | ||
| Peclet number | h | Convective heat coefficient | |
| Emissivity | Fin’s thickness | ||
| Rayleigh number | Specific heat coefficient | ||
| Total current density | dimensional ambient temperature |
| k | Thermal conductivity number | Fin’s moving speed | |
| Boundary conditions | Stefan–Boltzmann constant (W/m2 K4) | ||
| Diffusivity | Conduction current density | ||
| Fin base temperature | Axial velocity | ||
| Fin’s width | g | Gravity constant (ms−2) | |
| E | Electric field | K | Fin permeability |
| Dimensionless surface temperature | Non-dimensional ambient temperature |
References
- Kraus, A.D.; Aziz, A.; Welty, J. Extended Surface Heat Transfer; John Wiley, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kalpakjian, S. Manufacturing Engineering and Technology; Pearson Education: Bengaluru, India, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, A. Optimum dimensions of extended surfaces operating in a convective environment. Appl. Mech. Rev. 1992, 45, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffin, R. A variational problem relating to cooling fins. J. Math. Mech. 1959, 8, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, B.; Das, P.K. Optimum profile of thin fins with volumetric heat generation—A unified approach. ASME J. Heat Trans. 2005, 127, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, A.D. Sixty-five years of extended surface technology (1922–1987). Appl. Mech. Rev. 1988, 41, 321–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirapalli, S.; Kishore, P.S. Heat Transfer Analysis on a Triangular Fin. Int. J. Eng. Trends. Tech. 2015, 19, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogonchi, A.S.; Ganji, D.D. Convection—radiation heat transfer study of moving fin with temperature-dependent thermal conductivity, heat transfer coefficient and heat generation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 103, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobamowo, M.G. Thermal analysis of longitudinal fin with temperature-dependent properties and internal heat generation using Galerkin’s method of weighted residual. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 99, 1316–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shateri, A.R.; Salahshour, B. Comprehensive thermal performance of convection—radiation longitudinal porous fins with various profiles and multiple nonlinearities. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 136, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logesh, K.; Arunraj, R.; Govindan, S.; Thangaraj, M.; Yuvashree, G.K. Numerical investigation on the possibility of heat transfer enhancement using reduced weight fin configuration. Int. J. Ambient Energy 2018, 41, 142–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Ma, T.; Zhou, N.; Feng, J.; Huayan, P.; Luo, J.; Pennacchi, P.; Chu, F.; Han, Q. Extremely compact and lightweight triboelectric nanogenerator for spacecraft flywheel system health monitoring. Nano Energy 2024, 122, 109330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, Z.U.; Ali, A.; Khan, Z.A.; Zaman, G. Heat transfer analysis: Convective-radiative moving exponential porous fins with internal heat generation. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2022, 19, 11491–11511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boussandel, A.; Laouar-Meftah, S.; Retiel, N. Numerical analysis of gray gas radiation effects on heat and mass transfer in an annular cavity. Therm. Sci. 2024, 28, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ouyang, X. Numerical simulation of heat transfer and flow characteristics for plate fin-and-tube heat exchanger with ring-bridge slit fins. Therm. Sci. 2023, 28, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekzadeh, P.; Rahideh, H. IDQ two-dimensional nonlinear transient heat transfer analysis of variable section annular fins. Energy Convers. Manag. 2007, 48, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, J.D.; Abu-Mulaweh, H.I. Prediction of the temperature in a fin cooled by natural convection and radiation. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2006, 26, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.A.; Chaddock, J.B. An experimental investigation of the radiation and free convection heat transfer from a cylindrical disk extended surface. Trans. Am. Soc. Heat Refrig. Air-Conditioning Eng. 1963, 69, 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Arslanturk, C. Optimum design of space radiators with temperature-dependent thermal conductivity. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2006, 26, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.B.; Chandan, K.; Karthik, K.; Devanathan, S.; Kumar, R.V.; Nagaraja, K.V.; Prasannakumara, B.C. Investigation of the thermal analysis of a wavy fin with radiation impact: An application of extreme learning machine. Phys. Scr. 2023, 99, 015225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaddock, J.B. Free convection heat transfer from vertical fin arrays. J. Am. Soc. Heat Refrig. Air-Cond. Eng. 1970, 12, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshyar, H.A.; Ganji, D.D.; Majidian, A.R. Least square method for porous fin in the presence of uniform magnetic field. J. Appl. Fluid Mech. 2016, 9, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, P.; Niu, X.; Yamaguchi, H.; Li, D. Non-contact manipulation of nonmagnetic materials by using a uniform magnetic field: Experiment and simulation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 497, 165957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.Q.; Li, X.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yu, P. Magnetic field effect on the sedimentation process of two non-magnetic particles inside a ferrofluid. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2024, 589, 171501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, T.; Meher, R. Thermal Analysis of the porous fin with uniform magnetic field using Adomian decomposition Sumudu transform method. Nonlinear Eng. 2017, 6, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguntala, G.; Abd-Alhameed, R.; Ngala, M. Transient thermal analysis and optimization of convective-radiative porous fin under the influence of magnetic field for efficient microprocessor cooling. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 2019, 145, 106019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguntala, G.; Sobamowo, G.; Abd-Alhameed, R.; Jones, S. Efficient iterative method for investigation of the convective—radiative porous fin with internal heat generation under a uniform magnetic field. Int. J. Appl. Comp. Math. 2019, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedevi, P.; Reddy, P.S. Effect of SWCNTs and MWCNTs Maxwell MHD nanofluid flow between two stretchable rotating disks under convective boundary conditions. Heat Transf.—Asian Res. 2019, 48, 4105–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, K.L.; Hsu, C.H. Conjugate heat transfer of mixed convection for visco-elastic fluid past a triangular fin. Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl. 2009, 10, 130–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, B.; Barman, D.; Debnath, S. An analytical approach for predicting fin performance of triangular fins subject to simultaneous heat and mass transfer. J. Mol. Liq. 2008, 31, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.W.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Souayeh, B.; Dey, K.; Hammami, F.; Rahimi-Gorji, M.; Biswas, R. CPU heat sink cooling by triangular shape micro-pin-fin: Numerical study. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 112, 104455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Ullah, S.; Ali, A.; Shah, S.I.; Weera, W.; Alam, M.M. Heat transfer analysis from moving convection-radiative triangular porous fin exposed to heat generation. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 38, 102177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afaynou, I.; Faraji, H.; Choukairy, K.; Khallaki, K.; Akrour, D. Effectiveness of a PCM-based heat sink with partially filled metal foam for thermal management of electronics. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 235, 126196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Ooi, K.T. Predicting multiple combinations of parameters for designing a porous fin subjected to a given temperature requirement. Energy Convers. Manag. 2013, 66, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, W.; Sulaiman, M.; Islam, S.; Kumam, P.; Nawaz, R.; Raja, M.A.Z.; Farooq, M.; Shoaib, M. A study of changes in temperature profile of porous fin model using cuckoo search algorithm. Alex. Eng. J. 2020, 59, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turkyilmazoglu, M. Efficiency of heat and mass transfer in fully wet porous fins: Exponential fins versus straight fins. Int. J. Refrig. 2014, 46, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, L.; Kumar, A.; Tewari, S. An experimental study of heat transfer enhancement in the perforated rectangular fin. J. Integr. Sci. Technol. 2016, 4, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kiwan, S.; Alwan, H.; Abdelal, N. An experimental investigation of the natural convection heat transfer from a vertical cylinder using porous fins. App. Therm. Eng. 2020, 179, 115673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, S.; Jain, K.; Kumar, P.; Wang, X.; Pant, R.P. Improved thermal performance of annular fin-shell tube storage system using magnetic fluid. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 1524–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ullah, S.; Jeelani, M.B.; Alhamzi, G. Thermal Investigation of the Magnetised Porous Triangular Fins and Comparative Analysis of Magnetised and Non-Magnetised Triangular Fins. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1990. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13121990
Ullah S, Jeelani MB, Alhamzi G. Thermal Investigation of the Magnetised Porous Triangular Fins and Comparative Analysis of Magnetised and Non-Magnetised Triangular Fins. Mathematics. 2025; 13(12):1990. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13121990
Chicago/Turabian StyleUllah, Sharif, Mdi Begum Jeelani, and Ghaliah Alhamzi. 2025. "Thermal Investigation of the Magnetised Porous Triangular Fins and Comparative Analysis of Magnetised and Non-Magnetised Triangular Fins" Mathematics 13, no. 12: 1990. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13121990
APA StyleUllah, S., Jeelani, M. B., & Alhamzi, G. (2025). Thermal Investigation of the Magnetised Porous Triangular Fins and Comparative Analysis of Magnetised and Non-Magnetised Triangular Fins. Mathematics, 13(12), 1990. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13121990





