A Double-Inertial Two-Subgradient Extragradient Algorithm for Solving Variational Inequalities with Minimum-Norm Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
- (1)
- For all ,
- (2)
- For all and ,
- (3)
- For all and ,
- (4)
- Let be a half-space defined by with . Then the projection of onto Q is explicitly given by
- (1)
- is γ-strongly monotone if there exists such that for all ,
- (2)
- is γ-inverse strongly monotone (or γ-cocoercive) if for some ,
- (3)
- is monotone if for all ,
- (4)
- is L-Lipschitz continuous for some if
- 1.
- ;
- 2.
- and there exists a constant such that ,
3. Main Results
- (C1)
- The feasible set is defined aswhere is a continuously differentiable convex function with -Lipschitz continuous gradient . The constant is not assumed to be known in advance.
- (C2)
- The operator satisfies the following conditions:
- (a)
- is monotone and -Lipschitz-continuous (where is also unknown);
- (b)
- For all , the growth condition holds for some constant ;
- (c)
- The solution set is nonempty.
- (C3)
- The parameters satisfy the following conditoins:
- (a)
- ;
- (b)
- The sequence is nonnegative and summable, i.e., .
- (i)
- The half-space construction guarantees that for all , which follows directly from the convexity of and the subgradient inequality.
- (ii)
- Under the assumptions on () and , the inertial terms satisfyConsequently, combining this with and the uniform lower bound , we obtain the uniform boundedness result: For any , there exists such that
| Algorithm 1: Double-Inertial Two-Subgradient Extragradient Method |
|
- Case 1:
- . In this scenario, the desired result follows immediately from (16).
- Case 2:
- . By Lemma 2, we have
- ;
- There exists such that .
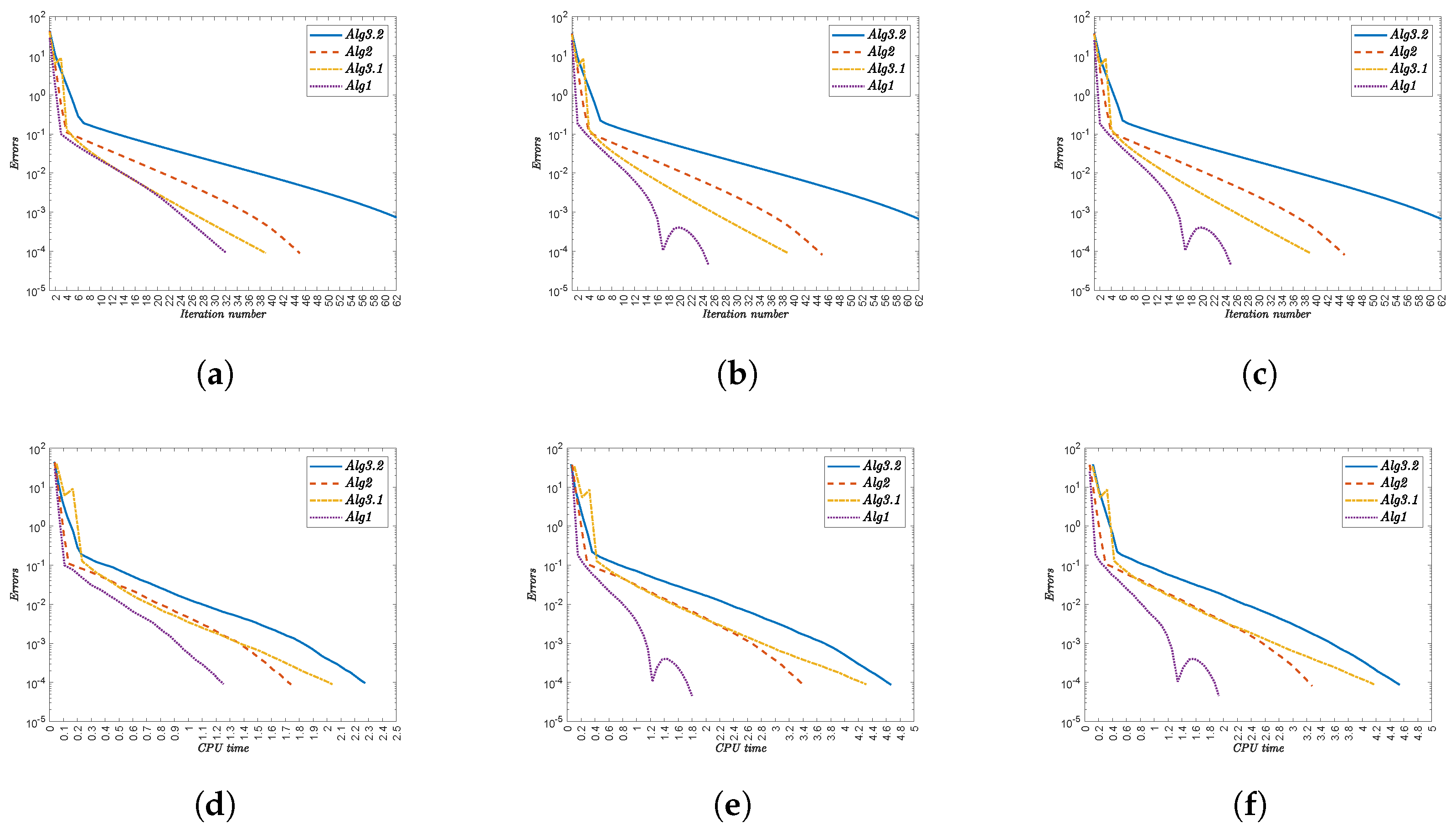
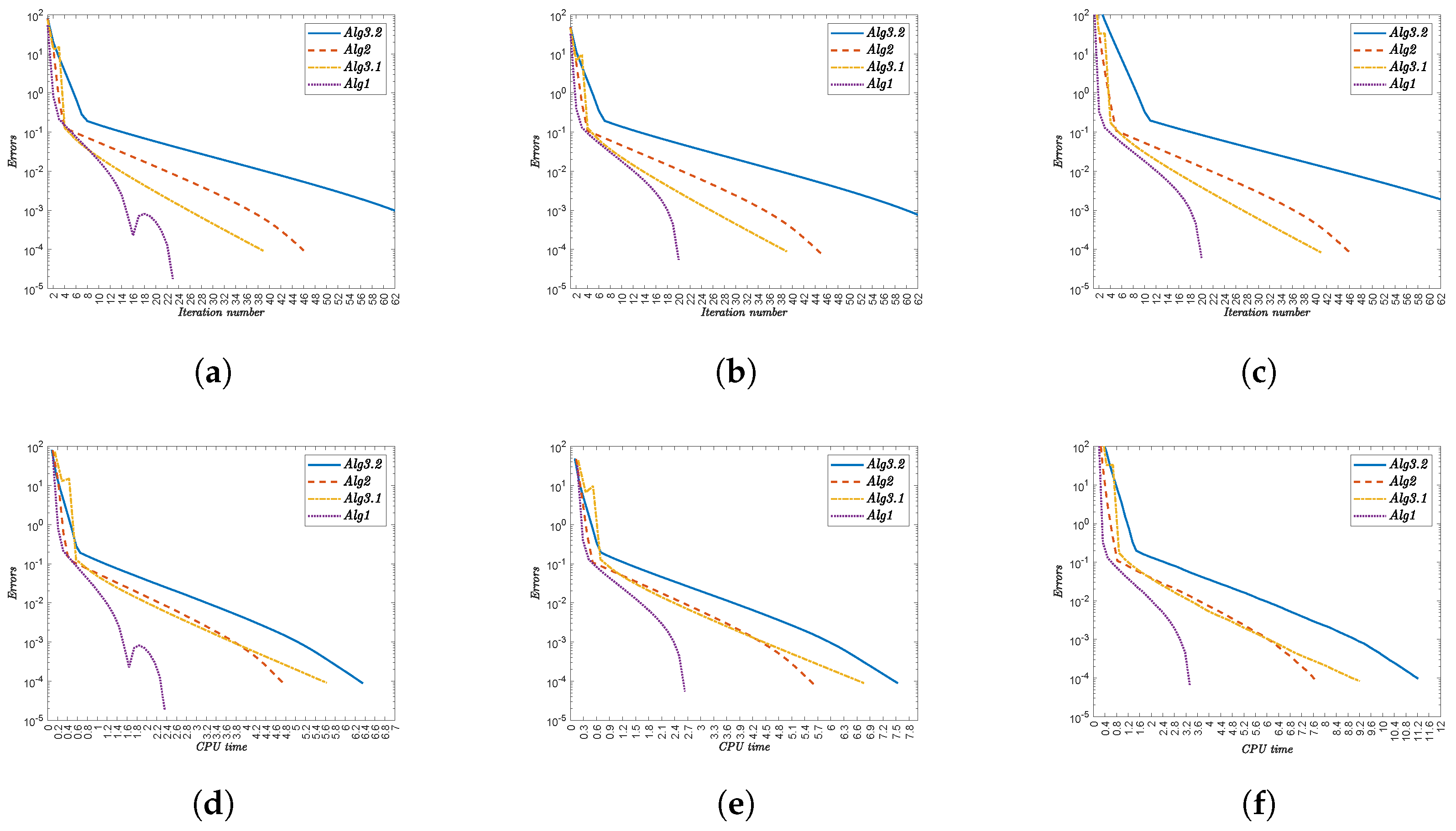
4. Numerical Illustrations
- Monotonicity: for all ;
- Lipschitz continuity with : .
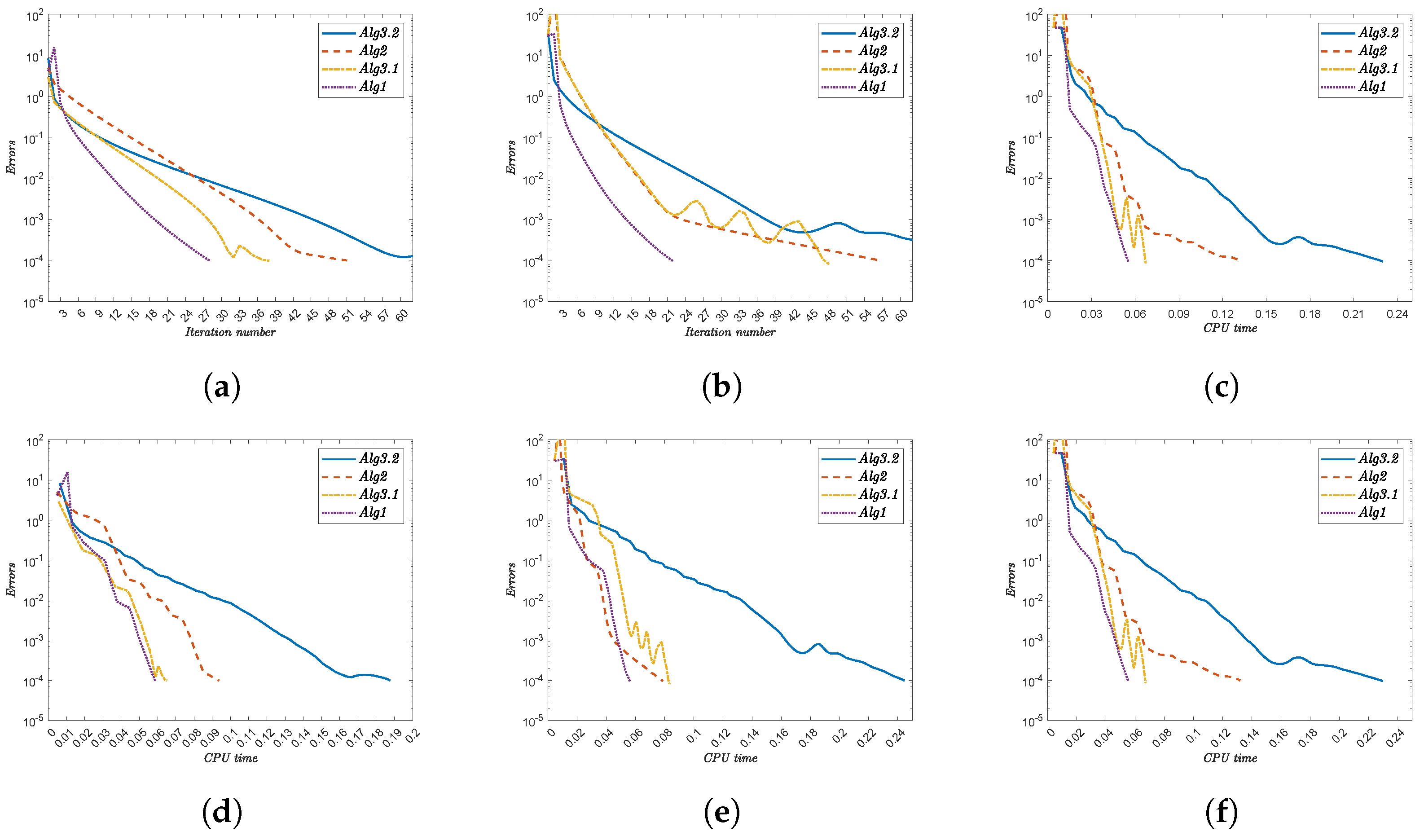
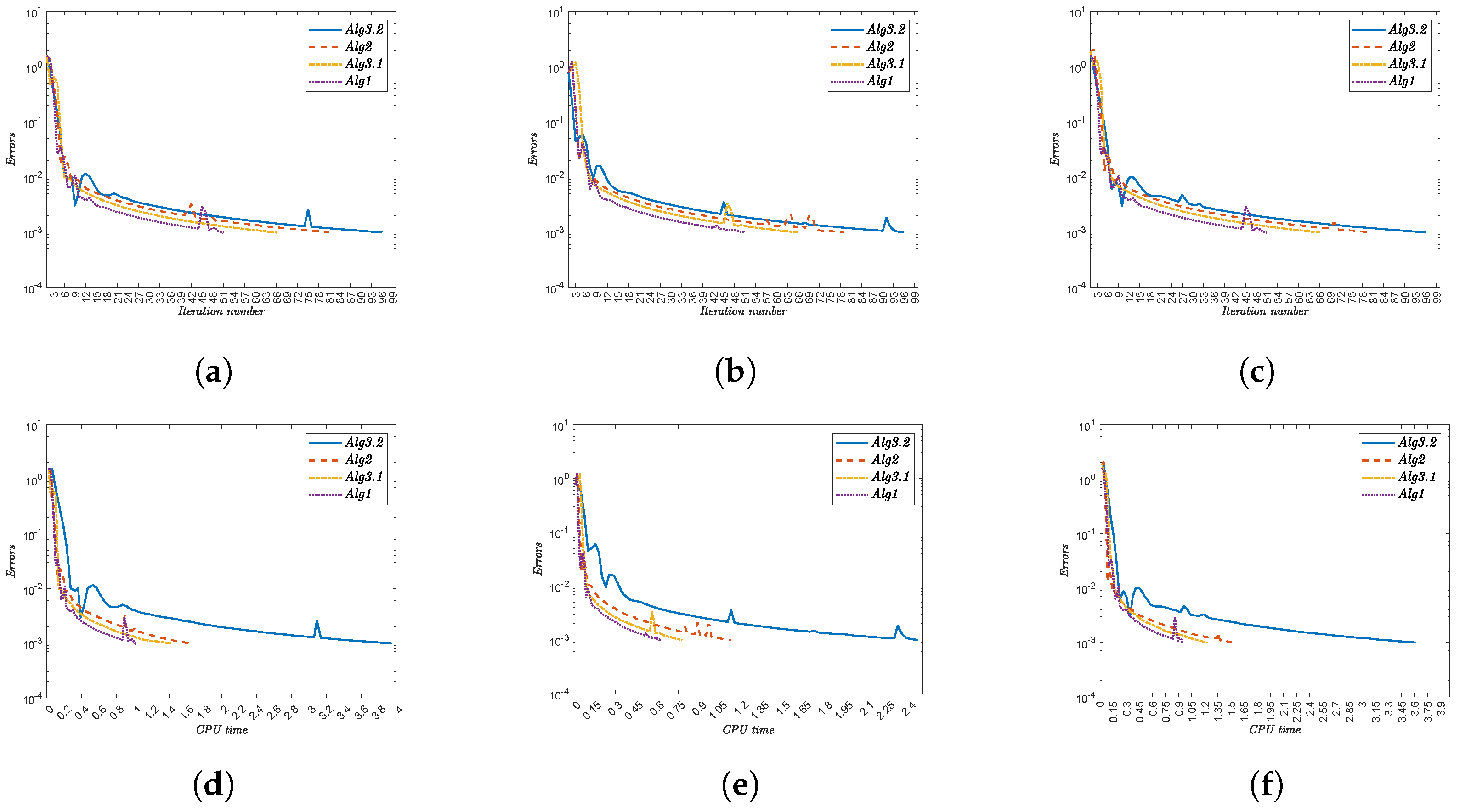
- (i)
- Alg1 demonstrates superior efficiency, consistently achieving the lowest iteration counts and CPU times. For instance,
- For x, Alg1 requires 32 iterations (1.225 s) versus Alg3.2’s 75 iterations (2.274 s).
- For , Alg1 converges in 20 iterations (2.634 s), while Alg3.2 needs 76 iterations (7.542 s).
- (ii)
- The initial point significantly impacts convergence. Complex functions (e.g., ) amplify this effect, with Alg3.2 requiring 84 iterations (11.222 s) compared to Alg1’s 20 iterations (3.336 s).
- (iii)
- Nonlinearities in functions like increase computational demand, yet Alg1 maintains robust performance.
- (iv)
- The performance gap widens with function complexity, reinforcing Alg1’s scalability.
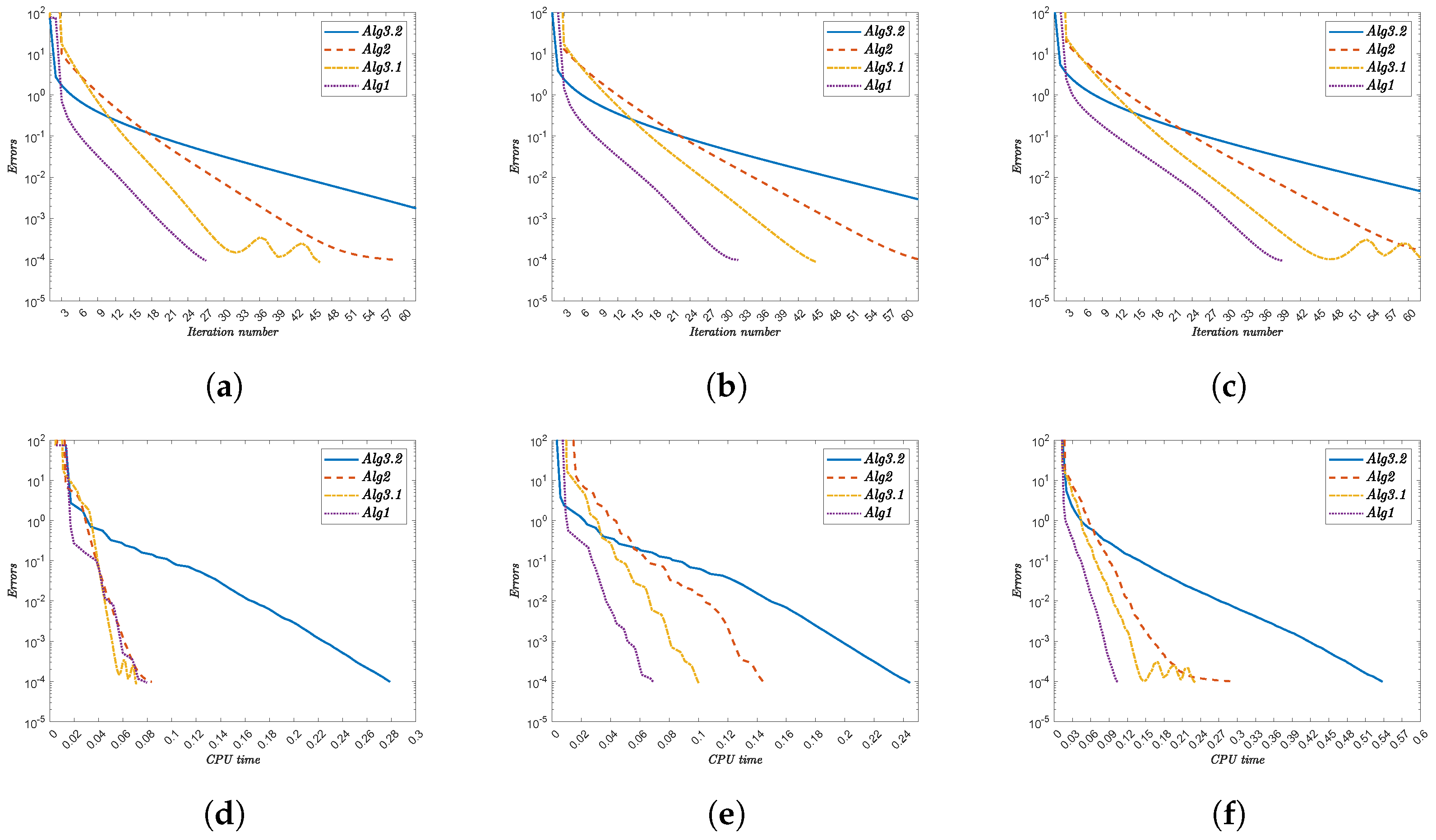
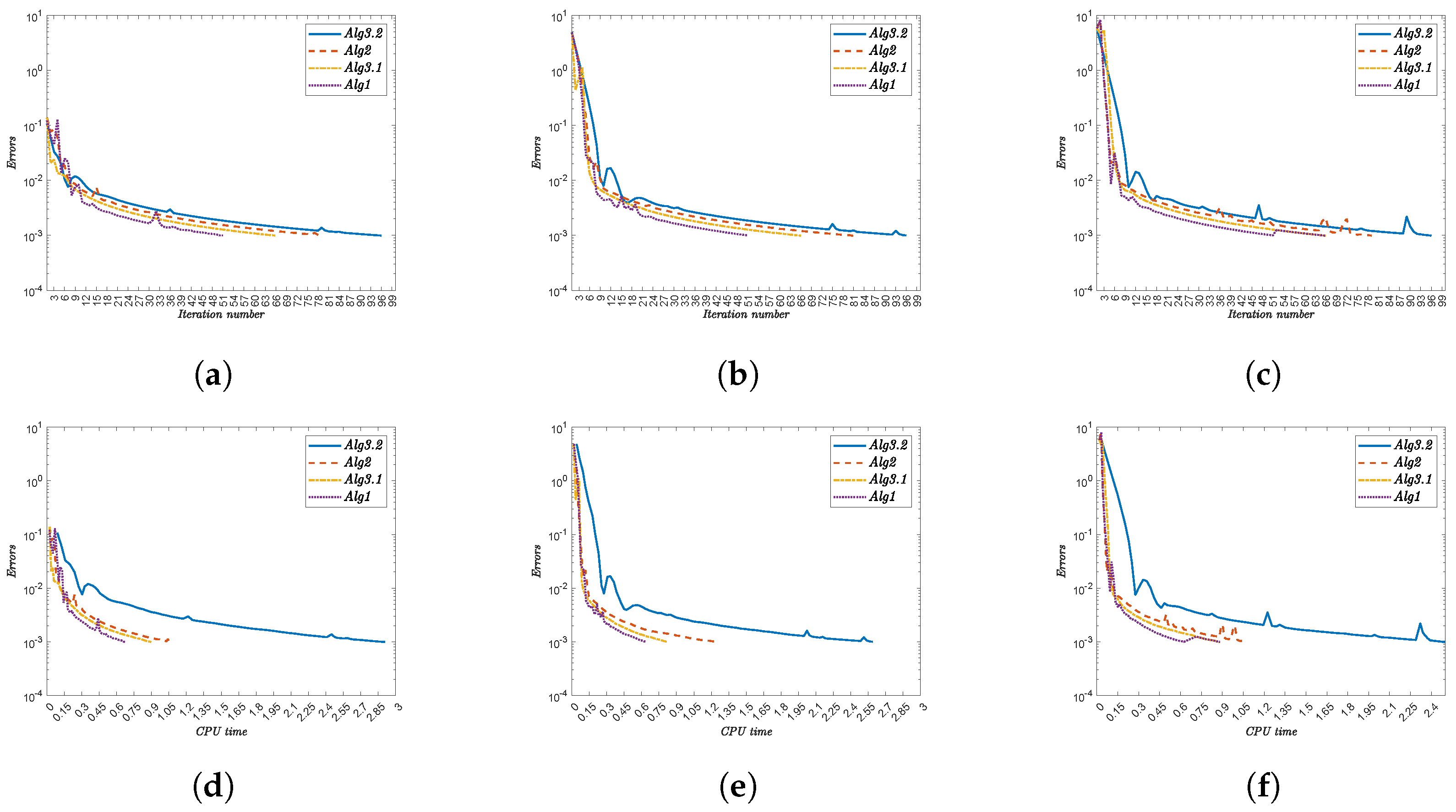
- (i)
- Alg1 outperforms all other algorithms in both metrics. For , it completes in 51 iterations (0.69481 s) versus Alg3.2’s 96 iterations (2.51503 s).
- (ii)
- The performance advantage persists across all test cases. At , Alg1 requires 51 iterations (0.62848 s) compared to Alg3.2’s 96 iterations (2.46246 s).
- (iii)
- Iteration counts remain constant for each algorithm regardless of :
- Alg3.2: 96 iterations.
- Alg2: 79–81 iterations.
- Alg3.1: 66 iterations.
- Alg1: 51 iterations.
- (iv)
- CPU times show minor variations with . For Alg1, they range from 0.62848 s () to 0.96045 s ().
- (v)
- The computational advantage of Alg1 is most pronounced against Alg3.2. At , Alg1 uses 0.67053 s versus Alg3.2’s 2.90826 s.
- (vi)
- Alg1 demonstrates robust efficiency across all test cases, maintaining low CPU times without compromising convergence speed.
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Future Research Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alakoya, T.O.; Mewomo, O.T. Viscosity s-iteration method with inertial technique and self-adaptive step size for split variational inclusion, equilibrium and fixed point problems. Comput. Appl. Math. 2022, 41, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubin, J.-P.; Ekeland, I. Applied Nonlinear Analysis; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Ogwo, G.N.; Izuchukwu, C.; Shehu, Y.; Mewomo, O.T. Convergence of relaxed inertial subgradient extragradient methods for quasimonotone variational inequality problems. J. Sci. Comput. 2022, 90, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiocchi, C.; Capelo, A. Variational and Quasivariational Inequalities: Applications to Free Boundary Problems; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Censor, Y.; Gibali, A.; Reich, S. Algorithms for the split variational inequality problem. Numer. Algorithms 2012, 59, 301–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, E.C.; Mewomo, O.T.; Alakoya, T.O. A strongly convergent algorithm for solving multiple set split equality equilibrium and fixed point problems in Banach spaces. Proc. Edinb. Math. Soc. 2023, 66, 475–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinderlehrer, D.; Stampacchia, G. An Introduction to Variational Inequalities and Their Applications; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Geunes, J.; Pardalos, P.M. Network optimization in supply chain management and financial engineering: An annotated bibliography. Networks 2003, 42, 66–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagurney, A. Network Economics: A Variational Inequality Approach, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Nagurney, A.; Dong, J. Supernetworks: Decision-Making for the Information Age; Edward Elgar Publishing: Northampton, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.J. The existence, uniqueness and stability of traffic equilibria. Transp. Res. B 1979, 13, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafermos, S. Traffic equilibrium and variational inequalities. Transp. Sci. 1980, 14, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawphongpanich, S.; Hearn, D.W. Simplicial decomposition of the asymmetric traffic assignment problem. Transp. Res. B 1984, 18, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panicucci, B.; Pappalardo, M.; Passacantando, M. A path-based double projection method for solving the asymmetric traffic network equilibrium problem. Optim. Lett. 2007, 1, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aussel, D.; Gupta, R.; Mehra, A. Evolutionary variational inequality formulation of the generalized Nash equilibrium problem. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2016, 169, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarciá, C.; Daniele, P. New existence Theorems for quasi-variational inequalities and applications to financial models. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 251, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagurney, A.; Parkes, D.; Daniele, P. The internet, evolutionary variational inequalities, and the time-dependent Braess paradox. Comput. Manag. Sci. 2007, 4, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scrimali, L.; Mirabella, C. Cooperation in pollution control problems via evolutionary variational inequalities. J. Glob. Optim. 2018, 70, 455–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, S. A strongly convergent alternated inertial algorithm for solving equilibrium problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2025, 206, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Adamu, A.; Shehu, Y. Strongly convergent golden ratio algorithms for variational inequalities. Math. Methods Oper. Res. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Qin, X. Two relaxed inertial forward-backward-forward algorithms for solving monotone inclusions and an application to compressed sensing. Can. J. Math. 2025, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyros, I.K. The Theory and Applications of Iteration Methods, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Korpelevich, G.M. The extragradient method for finding saddle points and other problems. Ekonom. Mat. Methods 1976, 12, 747–756. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, P. A modified forward-backward splitting method for maximal monotone mappings. SIAM J. Control Optim. 2000, 38, 431–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, D.V.; Hieu, D.V. Modified subgradient extragradient method for variational inequality problems. Numer. Algorithms 2018, 79, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, S.; Thong, D.V.; Cholamjiak, P.; Long, L.V. Inertial projection-type methods for solving pseudomonotone variational inequality problems in Hilbert space. Numer. Algorithms 2021, 88, 813–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, Y.I.; Kumam, P.; Rehman, H.U.; Kumam, W. A new extragradient algorithm with adaptive step-size for solving split equilibrium problems. J. Inequal. Appl. 2021, 2021, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, H.U.; Tan, B.; Yao, J.C. Relaxed inertial subgradient extragradient methods for equilibrium problems in Hilbert spaces and their applications to image restoration. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2025, 146, 108795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceng, L.C.; Ghosh, D.; Rehman, H.U.; Zhao, X. Composite Tseng-type extragradient algorithms with adaptive inertial correction strategy for solving bilevel split pseudomonotone VIP under split common fixed-point constraint. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2025, 470, 116683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwawuru, F.O.; Ezeora, J.N.; Rehman, H.U.; Yao, J.C. Self-adaptive subgradient extragradient algorithm for solving equilibrium and fixed point problems in Hilbert spaces. Numer. Algorithms 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Cho, Y.; Zhong, L.; Rassias, T.M. Inertial projection and contraction algorithms for variational inequalities. J. Glob. Optim. 2018, 70, 687–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solodov, M.V.; Svaiter, B.F. A new projection method for variational inequality problems. SIAM J. Control Optim. 1999, 37, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censor, Y.; Gibali, A.; Reich, S. The subgradient extragradient method for solving variational inequalities in Hilbert space. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2011, 148, 318–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censor, Y.; Gibali, A.; Reich, S. Extensions of Korpelevich’s extragradient method for the variational inequality problem in Euclidean space. Optimization 2012, 61, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyak, B.T. Some methods of speeding up the convergence of iterative methods. USSR Comput. Math. Math. Phys. 1964, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibali, A.; Jolaoso, L.O.; Mewomo, O.T.; Taiwo, A. Fast and simple Bregman projection methods for solving variational inequalities and related problems in Banach spaces. Results Math. 2020, 75, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godwin, E.C.; Alakoya, T.O.; Mewomo, O.T.; Yao, J.-C. Relaxed inertial Tseng extragradient method for variational inequality and fixed point problems. Appl. Anal. 2023, 102, 4253–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alakoya, T.O.; Mewomo, O.T. Strong convergent inertial two-subgradient extragradient method for finding minimum-norm solutions of variational inequality problems. Netw. Spat. Econ. 2024, 24, 425–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.H.; Iyiola, O.S.; Shehu, Y. Subgradient extragradient method with double inertial steps for variational inequalities. J. Sci. Comput. 2022, 90, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, D.V.; Dung, V.T.; Anh, P.K.; Van Thang, H. A single projection algorithm with double inertial extrapolation steps for solving pseudomonotone variational inequalities in Hilbert space. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2023, 426, 115099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, X. Subgradient extragradient method with double inertial steps for quasi-monotone variational inequalities. Filomat 2023, 37, 9823–9844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakkaranang, N. Double inertial extragradient algorithms for solving variational inequality problems with convergence analysis. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 2024, 47, 11642–11669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Iyiola, O.S.; Shehu, Y. Double inertial projection method for variational inequalities with quasi-monotonicity. Optimization 2024, 73, 707–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauschke, H.H.; Combettes, P.L. Convex Analysis and Monotone Operator Theory in Hilbert Spaces, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, M.; Schaible, G. Generalized monotone bifunctions and equilibrium problems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1996, 90, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauschke, H.H.; Combettes, P.L. A weak-to-strong convergence principle for Fejér-monotone methods in Hilbert spaces. Math. Oper. Res. 2001, 26, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Xu, H.-K. Uniqueness of supporting hyperplanes and an alternative to solutions of variational inequalities. J. Glob. Optim. 2013, 57, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saejung, G.; Yotkaew, P. Approximation of zeros of inverse strongly monotone operators in Banach spaces. Nonlinear Anal. Theory Methods Appl. 2012, 75, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.K.; Xu, H.-K. Approximating fixed points of nonexpansive mappings by the Ishikawa iteration process. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 1993, 178, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muangchoo, K.; Alreshidi, N.A.; Argyros, I.K. Approximation results for variational inequalities involving pseudomonotone bifunction in real Hilbert spaces. Symmetry 2021, 13, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Sunthrayuth, P.; Cholamjiak, P.; Cho, Y.J. Modified inertial extragradient methods for finding minimum-norm solution of the variational inequality problem with applications to optimal control problem. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2023, 100, 525–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harker, P.T.; Pang, J.S. For the linear complementarity problem. Lect. Appl. Math. 1990, 26, 265–284. [Google Scholar]
- Van Hieu, D.; Anh, P.K.; Muu, L.D. Modified hybrid projection methods for finding common solutions to variational inequality problems. Comput. Optim. Appl. 2017, 66, 75–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehu, Y.; Dong, Q.L.; Jiang, D. Single projection method for pseudo-monotone variational inequality in Hilbert spaces. Optimization 2018, 68, 385–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| m | Alg3.2 | Alg2 | Alg3.1 | Alg1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 72 | 0.1876 | 51 | 0.0937 | 38 | 0.0652 | 28 | 0.0587 |
| 10 | 81 | 0.2445 | 57 | 0.0789 | 48 | 0.0833 | 22 | 0.0560 |
| 20 | 86 | 0.2299 | 57 | 0.1320 | 41 | 0.0672 | 27 | 0.0554 |
| 50 | 92 | 0.2788 | 59 | 0.0836 | 46 | 0.0709 | 27 | 0.0796 |
| 100 | 99 | 0.2444 | 63 | 0.1448 | 45 | 0.1004 | 32 | 0.0695 |
| 200 | 104 | 0.5379 | 83 | 0.2917 | 69 | 0.2309 | 39 | 0.1052 |
| Algorithm | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Alg3.2 [38] | , , |
| , | |
| , | |
| Alg2 [50] | , , |
| , | |
| Alg3.1 [51] | , , |
| , | |
| , , | |
| Algorithm 1 (Alg1) | , |
| , | |
| (), | |
| Function | Alg3.2 | Alg2 | Alg3.1 | Alg1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | 75 | 2.274 | 45 | 1.740 | 39 | 2.038 | 32 | 1.225 |
| 75 | 4.669 | 45 | 3.418 | 39 | 4.310 | 25 | 1.799 | |
| 75 | 4.539 | 45 | 3.277 | 39 | 4.170 | 25 | 1.931 | |
| 78 | 6.355 | 46 | 4.734 | 39 | 5.626 | 23 | 2.362 | |
| 76 | 7.542 | 46 | 5.620 | 39 | 6.760 | 20 | 2.635 | |
| 84 | 11.222 | 46 | 7.699 | 41 | 9.201 | 20 | 3.336 | |
| Alg3.2 | Alg2 | Alg3.1 | Alg1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 96 | 2.51503 | 80 | 1.05539 | 66 | 0.83240 | 51 | 0.69481 | |
| 96 | 2.46246 | 79 | 1.12663 | 66 | 0.77810 | 51 | 0.62848 | |
| 96 | 3.61541 | 80 | 1.50510 | 66 | 1.23019 | 51 | 0.96045 | |
| 96 | 2.90826 | 79 | 1.06613 | 66 | 0.89569 | 51 | 0.67053 | |
| 96 | 2.59047 | 81 | 1.25559 | 66 | 0.82584 | 51 | 0.63624 | |
| 96 | 2.49513 | 79 | 1.07621 | 66 | 0.88292 | 51 | 0.63624 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Argyros, I.K.; Amir, F.; Rehman, H.u.; Argyros, C. A Double-Inertial Two-Subgradient Extragradient Algorithm for Solving Variational Inequalities with Minimum-Norm Solutions. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13121962
Argyros IK, Amir F, Rehman Hu, Argyros C. A Double-Inertial Two-Subgradient Extragradient Algorithm for Solving Variational Inequalities with Minimum-Norm Solutions. Mathematics. 2025; 13(12):1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13121962
Chicago/Turabian StyleArgyros, Ioannis K., Fouzia Amir, Habib ur Rehman, and Christopher Argyros. 2025. "A Double-Inertial Two-Subgradient Extragradient Algorithm for Solving Variational Inequalities with Minimum-Norm Solutions" Mathematics 13, no. 12: 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13121962
APA StyleArgyros, I. K., Amir, F., Rehman, H. u., & Argyros, C. (2025). A Double-Inertial Two-Subgradient Extragradient Algorithm for Solving Variational Inequalities with Minimum-Norm Solutions. Mathematics, 13(12), 1962. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13121962






