Abstract
Zeroing Neural Networks (ZNNs), an ODE-based neural dynamics framework, has become a pivotal approach for solving time-varying problems in dynamic systems. This paper systematically reviews recent advances in improving the convergence of ZNN models, focusing on the optimization of fixed parameters, dynamic parameters, and activation functions. Additionally, structural adaptations and fuzzy control strategies have significantly enhanced the robustness and disturbance rejection capabilities of these systems. ZNNs have been successfully applied in robotic control, demonstrating superior accuracy and robustness compared to traditional methods. Future research directions include exploring nonlinear activation functions, multimodal adaptation strategies, and scalability in real-world environments.
Keywords:
Zeroing Neural Networks; convergence; activation function; structural adaptations; robustness; robotic control MSC:
68T05; 92B20
1. Introduction
In recent years, the field of computer science has developed rapidly [1], and this year’s Nobel laureate in Physics, Hopfield, has drawn attention for his proposal of associative neural networks. Neural networks have gradually entered the public eye and are now applied in various fields such as healthcare [2], environmental and biological resources [3].
Neural networks are the foundation of artificial intelligence [4,5], mimicking the working mechanism of the human brain. They consist of an input layer, hidden layers, and an output layer. Neural networks process input data via forward propagation, extracting features using weights, biases, and activation functions and ultimately generating predictions. During the training process, neural networks calculate errors using a loss function and continuously adjust parameters through optimization algorithms such as backpropagation and gradient descent, minimizing the error. By iterating this process, neural networks can learn complex nonlinear relationships, and once trained, they can quickly predict new data. Neural networks are widely used in areas like sequence prediction, reinforcement learning [6,7], anomaly detection [8,9], image processing, natural language processing, and energy conservation [10,11]. Among these, sequence prediction is one of the most common and complex problems. While recurrent neural networks [12] were proposed for their excellent performance in handling time series data and dynamic systems [13], the ZNN model has demonstrated superior characteristics in more specific problems such as dynamic matrix inversion, dynamic equation solving [14], and dynamic multi-objective optimization [15].
The ZNN model not only possesses outstanding dynamic properties but also exhibits high computational efficiency. Therefore, it can perform efficient calculations even in the hardware-constrained environments, such as in unmanned aerial vehicle trajectory planning [16]. It is precisely because the ZNN model uses specific models for specific problems that it achieves high robustness and finite-time convergence. This characteristic is especially prominent in areas like redundant robotics [17], automotive engineering [18,19], and network services [20]. The control of redundant manipulators, especially in cases where the model is unknown, has become a challenging issue. To address this, many innovative methods have been proposed. For example, data-driven neural- and dynamics-based model predictive control algorithms have been introduced and applied to trajectory tracking tasks of redundant manipulators [21]. This method combines model predictive control schemes, neural dynamics solvers, and discrete-time Jacobian matrix update laws to predict the future outputs of redundant manipulators without precise models, driving the manipulators to achieve accurate trajectory tracking tasks [22]. Cross-disciplinary research informs trajectory tracking in redundant manipulators. Swarm optimized multi-support vector methods and dynamic neural networks excel in real-time computation for dynamic control and path planning. Applications like high-frequency trading leverage model simplification [23] and fuzzy control [6] to enhance efficiency. While ZNN models are task-specific, recent advances, such as neural dynamics for nonlinear programming and novel learning algorithms [24,25], improve their stability and convergence in uncertain environments.
Although ZNNs have been widely applied to time-varying problems due to their superior dynamic performance and computational efficiency, existing review papers have primarily focused on fundamental models and algorithms, lacking a systematic and in-depth summary of the latest advances in convergence optimization and robustness enhancement. Moreover, current studies rarely explore how fixed parameters, variable parameters, nonlinear activation functions, and fuzzy control mechanisms can be integrated to further improve the performance of ZNNs. To address this research gap, this paper presents a comprehensive review of recent advances in the convergence and robustness analysis of ZNNs and systematically summarizes their latest applications in complex dynamic systems such as robotic control, chaotic systems, and multi-vehicle coordination. It is hoped that this survey will provide a solid theoretical foundation and valuable technical reference for future studies, thereby promoting the practical deployment of ZNNs in complex dynamic environments, including online optimization problems, multimodal multi-objective optimization problems, and time-varying convex quadratic programming problems [26].
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. The convergence characteristics of the ZNN model are discussed in Section 2. The anti-noise performance of the ZNN model is discussed in Section 3. Typical applications of ZNN models are presented in Section 4. Finally, the paper is concluded with an outlook in Section 5.
2. The Development of Convergence
It has been proven that although these problems are complex, they can be formulated as a set of equations, where the key lies in finding the zeros of these equations. This constitutes the fundamental principle of the ZNN model, as expressed in the following equation:
where . Convergence refers to the property of a system’s solutions gradually approaching the true or desired solution. Its applications are extensive, such as achieving high convergence accuracy under low cost conditions in loss landscapes [27], improving the precision of localization results in underwater positioning [28], and minimizing convergence time while meeting accuracy constraints in cooperative energy detection [29]. In research on ZNN, the optimization directions for convergence primarily include three aspects: global asymptotic convergence, ensuring that the model gradually converges to the theoretical solution from any initial state; prescribed time convergence, where the upper bound of convergence time depends solely on the activation function and model parameters, enabling the controllability of the convergence process; and strong robustness, which ensures that the model can still converge to the target solution under various noisy environments, enhancing the system’s anti-interference ability and stability [30]. To achieve the optimization objectives of global asymptotic convergence, prescribed time convergence, and strong robustness in ZNN, researchers have mainly explored fixed parameters, variable parameters, and activation functions: optimizing fixed gain coefficients to enhance the model’s stability and convergence performance, introducing time dependent or state dependent dynamic parameters (variable parameters) to improve the model’s adaptability to complex environments, and designing novel activation functions to accelerate convergence speed, ensure time predictability, and enhance robustness in noisy environments.
2.1. Fixed Parameters
Fixed parameters are constants in a model that do not change with time or input. These parameters are typically preset based on empirical data, theoretical analysis, or experimental results, with the aim of optimizing the performance of the ZNN model.
In the study [31], ZNN achieved superior convergence and accuracy over a gradient neural network (GNN). With , ZNN reached a precision better than m. While GNN required to approach the desired path. ZNN’s fixed parameters enhanced both speed and accuracy. The study [32] analyzed five ZNN variants, showing that increasing (e.g., from to ) or decreasing reduced convergence time. All models (ZNN-1 to ZNN-5) confirmed the critical role of parameter tuning. The finite time convergent neural dynamics model [33] demonstrated finite-time convergence: increasing from 20 to reduced convergence time from 0.15 s to s, proving ’s direct proportionality to speed. ZNN’s design excels in time sensitive, high accuracy tasks.
2.2. Variable Parameters
Variable parameters refer to parameters that can be dynamically adjusted based on system states, environmental changes, or the training process. Unlike fixed parameters, which often have a relatively large and static , variable parameters are iteratively adjusted according to the current state of the neural network or task requirements. This approach enables neural network models with variable parameters to achieve better adaptability and flexibility, higher convergence and efficiency, and more precise control compared to those with fixed parameters.
The ZNN model has advanced significantly through variable parameter innovations. Xiao et al. [34] proposed the finite-time ZNN (FTZNN), addressing infinite-time convergence limitations in traditional ZNNs by ensuring finite-time convergence via adjustable parameters (, , ), enhancing real-time task efficiency. Theoretically proven to be superior to original ZNN, FTZNN was applied to robotic control [35]. However, such models were confined to real number domains. To resolve this, Xiao et al. [36] developed the complex-valued nonlinear recurrent neural network (CVNRNN), merging variable parameter ZNN with complex number theory. CVNRNN achieves finite-time convergence for time-varying complex matrix problems, expanding ZNN’s applicability to complex domains.
However, the applicability of the CVNRNN is relatively limited to specific complex number ranges. To overcome this limitation, Xiao et al. proposed the segmented variable-parameter ZNN in [37]. By introducing a segmented variable-parameter design, this model not only enhances adaptability in dynamic environments but also effectively addresses more complex control problems. The segmented variable-parameter settings allow the model to flexibly adjust parameters based on different time segments and task requirements, optimizing the convergence process and ensuring that the system reaches the desired state within a short time. Drawing from the findings of [37], we can express the design equation of segmented variable-parameter ZNN as
where adhere to conditions
thereinto, , , and are parameters used to control segmentation. It not only maintains the stability of time-varying parameters but also enhances the system’s immunity to external disturbances. These performance metrics surpass those of the variable-parameter noise-tolerant ZNN model proposed in [38]. However, despite significant theoretical and practical advancements, these models have not fully aligned with hardware requirements. In recent years, as hardware computational capabilities and application scenarios have continued to evolve, researchers have begun exploring ZNN models more tailored to actual hardware demands. To address this, Xiao et al. proposed the predefined time and anti-noise varying parameter ZNN in [39]. This model not only leverages variable parameters to improve convergence speed but also specifically considers the characteristics of actual hardware parameters, making the model more efficient and stable in hardware implementation.
Under predefined time settings, the predefined time and anti-noise varying parameter ZNN achieves precise convergence within a specified timeframe while avoiding computational delays and uncertainties. However, when addressing constrained problems, its limitation stems from the relatively singular choice of activation functions, which restricts flexible adjustments for diverse task requirements and narrows its applicability. To resolve these issues, Deng et al. [40] proposed the variable-parameter variable-activation-function finite-time neural network. By dynamically optimizing activation paths based on task complexity, this model significantly improves convergence efficiency and precision.
By following the methodology proposed in [40], we arrive at the following design equation for the variable-parameter variable-activation-function finite-time neural network.
the parameters and are both greater than zero, with the time-varying parameters and . The parameter is an odd fractional number greater than 0 and less than 1. The function represents an activation function that processes arrays, where each scalar processing unit must be a monotonically increasing odd activation function. This means that for all real numbers x, the condition is satisfied, and the output increases as the input increases.
Existing models achieve convergence without specialized activation functions but lack theoretical advantages in dynamic control. To address this, He et al. [41] proposed ZNN-based sliding mode control, excelling in rapid target-state convergence and sustained high precision while offering a theoretical practical framework for complex systems. Subsequently, Luo et al. [42] developed a new varying-parameter ZNN model, enabling prescribed time convergence with tunable dynamic convergence parameters to minimize computational waste. Finally, Li et al. [43] introduced a varying-parameter complementary neural network integrated with model predictive control, resolving multi-robot tracking and formation via leader–follower strategies, demonstrating robustness in cooperative robotics.
For the reader’s convenience, we have listed the typical forms of in Table 1.

Table 1.
The typical forms of .
2.3. Activation Function
Activation functions play a critical role in the structure of neural networks. They transform the input of a neuron into an output that can be passed to the next layer. Without an activation function, a neural network can only represent linear mappings. The introduction of nonlinear activation functions significantly enhances the capability of ZNNs in addressing nonlinear problems. These functions reinforce error correction dynamics, mitigate gradient vanishing, and enable the system to achieve finite-time or even fixed-time convergence, thereby improving both convergence efficiency and system controllability. The specific form of the activation function directly influences error evolution and Lyapunov-based stability analysis; appropriately chosen functions help ensure global convergence and overall system stability. Therefore, activation functions play a crucial role in improving the convergence performance, predictability, and theoretical robustness of ZNNs.
The study [46] emphasizes how activation functions critically shape convergence speed in neural networks, including physics informed models. Their role in balancing model expressiveness, convergence, and efficiency makes exploring activation functions essential for optimizing ZNN models. This section chronologically reviews ZNN variants with distinct activation functions and their performance.
Initially, the original Zhang dynamics model addressed nonlinear problems but suffered from slow convergence. However, as task complexity grew, the zeroing dynamics model [47] outperformed improved variants in equality-constrained quadratic optimization due to its finite-time convergence, especially for nonstationary coefficients. While enhanced activation functions boost performance in specific cases, simpler ones may better suit constrained optimization. Nevertheless, these models struggled with uncertainties in control system stability.
To tackle this challenge, Xiao et al. proposed the convergence-accelerated ZNN in [48]. The convergence-accelerated ZNN employed a sign-bi-power activation function, offering optimal convergence performance and significantly enhancing the dynamic behavior of the network through nonlinearity adjustments. It achieved finite-time convergence to the theoretical solution of the Lyapunov equation, as opposed to the exponential convergence over time. Despite improvements in convergence speed, the asymptotic convergence characteristic still necessitated extended durations to approach theoretical solutions for complex problems. Therefore, in 2018, an improved finite-time Zhang dynamics model was proposed in [49]. By utilizing a weighted sign-bi-power function array, the finite-time Zhang dynamics model significantly shortened actual convergence times. Furthermore, its actual convergence time was less than and very close to the theoretical upper bound, offering stricter time predictability and enhanced efficiency. Xiao et al. later argued in [50] that while the existing improvements had made strides in enhancing convergence speed, there was still room to further reduce the theoretical upper bound on convergence time. To this end, they proposed two nonlinear recurrent neural networks based on distinct nonlinear activation functions to achieve higher computational efficiency.
In 2019, Xiao et al. introduced the fast convergent gradient neural network in [51], which utilized a nonlinear activation function design to significantly accelerate convergence. While the fast convergent gradient neural network model excelled in solving systems of linear equations, it often exhibited oscillations near equilibrium points, impacting the precision of the solutions and the stability of the model. To resolve these issues, Xiao et al. proposed the improved ZNN in [52]. It adopted a sign-bi-power function array as its activation function, further optimizing the dynamic behavior of the network and enabling the solutions generated by the network to converge to the theoretical solution within an upper time limit of finite time.
From the literature mentioned above, we know that most of the upper bound of the convergence time for this model is
here, is the critical time, is a constant, and p is a parameter between 0 and 1. The expressions and , respectively, represent the minimum and maximum elements of the initial error matrix . The improved ZNN model achieves smoother convergence to the theoretical solution and alleviates oscillation phenomena near equilibrium points. However, these models still exhibit limitations when applied to practical hardware, particularly in scenarios with constrained computational resources or mismatched hardware characteristics, leading to insufficient convergence speed.
To address these issues, two improved gradient neural network models were proposed in [53]. These models leverage nonlinear activation functions to enhance global convergence performance while being more compatible with hardware requirements, offering greater flexibility for practical engineering applications. Building on this foundation, two finite-time ZNN models (referred to as ZNN-A and ZNN-B) were introduced in [54]. These models incorporate sign-bi-power activation functions and employ innovative error function designs to achieve outstanding stability and finite-time convergence. However, these models still lack deep integration with modern intelligent optimization algorithms. Algorithms with strong optimization capabilities, such as harmony search [55], an improved harmony search algorithm [56], and the greedy energy efficiency algorithm [57], have not been effectively incorporated. As a result, there remains room for improvement in the overall convergence speed and problem solving capability of ZNN models.
In these challenges, Tang et al. proposed the continuous gradient Zhang neural network model [58] and integrated it with three discretized gradient Zhang neural network algorithms. These improvements significantly enhanced both the computational efficiency and practical applications of the model, offering a new direction for solving complex optimization problems. However, the aforementioned research on activation functions primarily focuses on the real number domain, with limited consideration of the complex number domain. To address this gap, Xiao et al. introduced the nonlinear complex ZNN in their 2019 study [59]. This model employs nonlinear sign-bi-power activation functions to effectively address problems in the complex number domain. Its innovation lies in separately activating the real and imaginary components of a complex number or directly activating the modulus of the complex number, enabling finite-time convergence in the complex domain. The nonlinear complex ZNN demonstrates superior stability and efficiency in solving dynamic complex linear equation systems. From reference [59], we obtain the following expression for the upper bound of the convergence time of this model:
where and and are the real and imaginary parts of the k-th element of the initial error matrix , respectively. Additionally, and m lies between 0 and 1 to ensure that the nonlinear activation function of the network model can exert its inherent nonlinear advantages, thereby accelerating the convergence of the network and ultimately achieving the theoretical solution within a finite time. Building on the improvements by Liao et al., the complex zeroing neural dynamic (CAND) model was proposed in 2024 [60]. It has proven to be especially effective for real time measurements and for implementing optimization strategies that focus on reducing distances between robots.
As shown in Figure 1, the typical error–time convergence curves of ZNN and its various variants clearly illustrate their respective dynamic behavior characteristics. The standard ZNN model (black curve) exhibits a typical exponential convergence trend, which is common in fixed-parameter models. The ZNN with a linear activation function (ZNN+LAF, green curve) also demonstrates asymptotic convergence, albeit at a relatively slower rate. In contrast, the ZNN with a power activation function (ZNN+PAF, blue curve) significantly accelerates the convergence rate due to its enhanced nonlinear properties. Particularly noteworthy is the finite-time ZNN model (FTZNN, light blue curve), which achieves complete error elimination within a preset time range, highlighting the advantage of finite-time convergence. These results intuitively support the systematic analysis and comparison of the convergence performance across various ZNN models.
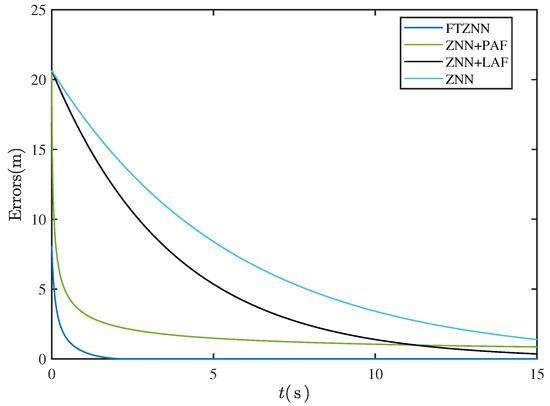
Figure 1.
Convergence curves of ZNN and its variants.
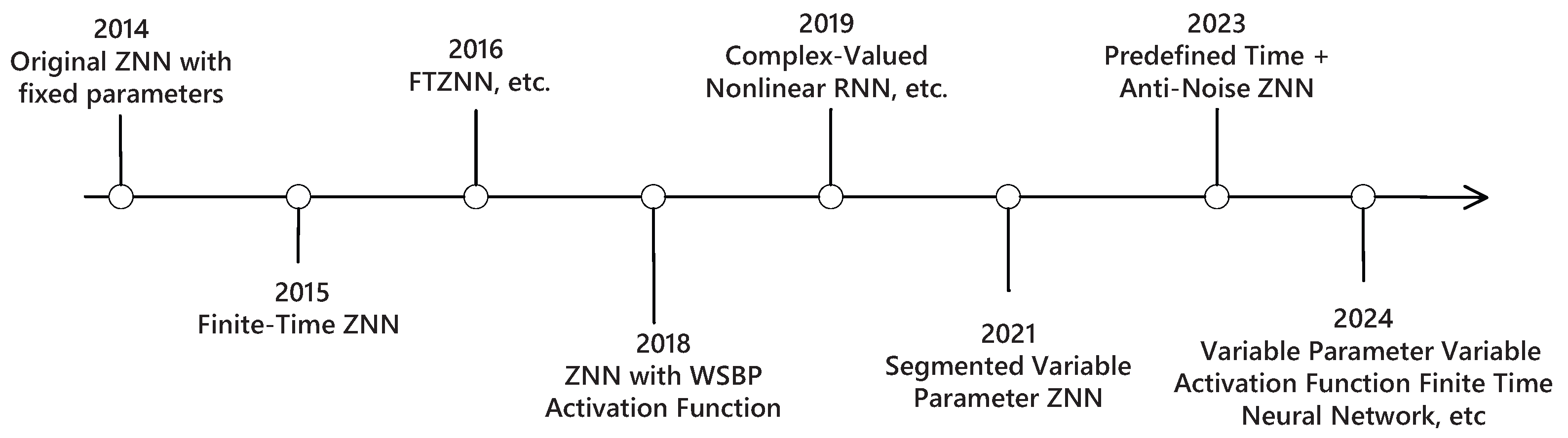
A timeline of the convergence development of ZNN models is presented in Figure 2, summarizing the key milestones in the evolution of ZNN from 2014 to 2024. Beginning with the original fixed-parameter ZNN model in 2014, the field has gradually progressed with the introduction of the finite-time ZNN in 2015 and the FTZNN in 2016. In 2018, the incorporation of advanced activation functions, such as WSBP, enhanced the adaptability of the model. In 2019, complex-valued nonlinear recurrent neural networks inspired by the ZNN framework were introduced. In 2021, segmented variable-parameter ZNNs were proposed to enable more flexible convergence behavior. Recent advancements include predefined time- and noise- resistant ZNNs in 2023, followed by variable parameter, finite time models based on adaptive activation functions in 2024. This timeline highlights the continuous enhancement of ZNN models in terms of convergence speed, robustness, adaptability, and suitability for real time problem solving.
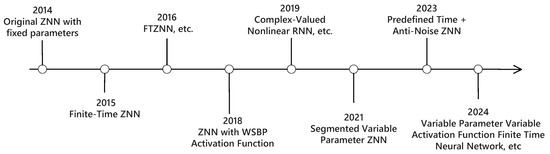
Figure 2.
Time line on development of convergence.
3. The Development of Robustness
The sources of noise in neural networks primarily stem from two aspects: (1) the distributed nature of information storage in neural network models, where local damage may moderately impair model performance but will not lead to catastrophic errors, and (2) the handling of incomplete or noisy data, where neural networks rely on their generalization capability to address these uncertainties. Noise significantly impacts the stability and accuracy of neural network models. Consequently, neural networks must possess dual capabilities to both solve problems and suppress noise, which is referred to as noise tolerance. Noise tolerance has been applied in various domains, including dynamic voltage and frequency scaling technology [61], biclustering algorithms [62], and signal-to-noise ratio estimation [63].
- Structural Adaptations: ZNN incorporates noise factors directly into its structure, enhancing the model’s stability.
- Activation Function Design: By developing specific activation functions within the improved ZNN structure, the model effectively suppresses the interference of noise on output results, thus improving robustness.
- Fuzzy Control Mechanism: ZNN leverages a fuzzy inference mechanism to smooth input data during the processing of noisy information, further improving the model’s adaptability to uncertainty and noise. This ensures that ZNN maintains high accuracy and stability even in complex environments.
3.1. Structural Adaptations for Stochastic Robustness
The architecture or structure of a neural network typically needs to be adjusted according to the requirements of specific application scenarios in order to enhance its flexibility and efficiency in handling different types of problems or noise disturbances, thereby improving the model’s robustness and adaptability. In the context of associative memory networks under stochastic impulses, Reference [64] focuses on the stability analysis of memory networks, aiming to ensure that information can be reliably stored and retrieved even under multiple disturbances. In contrast, ZNN employs the derivative of the error function to solve dynamic problems. This subsection focuses on the constructive algorithm of ZNNs, with the goal of ensuring convergence and robustness in the online solution of dynamic problems.
In response to this challenge, Liao et al. [65] introduced in 2016 Taylor-series-based numerical differentiation and Euler discretization methods. These techniques allowed for the transformation of continuous-time error computations into high-precision discrete-time representations, thereby substantially improving computational accuracy and enhancing model stability. This methodological advancement provided a robust theoretical framework for incorporating increasingly complex and adaptive algorithms into ZNN models in later studies. Moreover, in addressing noise interference, researchers have effectively employed strategies such as the nonlinear optimization of activation functions and integration designs within the model.
For example, ref. [66] introduced a nonlinear activation integration design considering additive noise, described by the following formula:
specifically, the parameters and serve as scaling factors to ensure that . and represent two arrays of odd, monotonically increasing activation functions, which can be either identical or different. denotes an unknown additive noise. Based on Equation (7) above, the versatile recurrent neural network innovatively integrates nonlinear activation functions with considerations for additive noise, thereby ensuring finite-time convergence even under high noise conditions. Building on this foundation, Xiao et al. [67] proposed a novel recurrent neural network. By optimizing the network architecture and incorporating advanced nonlinear activation functions, it significantly enhances global stability, achieves more precise finite-time convergence, and exhibits superior noise resistance.
Despite these advancements, a comprehensive theoretical framework for noise tolerance in ZNN models was not established until 2019, when Xiao et al. [68] proposed the unified gradient Zeroing Neural Network. This model integrates noise-resistance mechanisms with finite-time convergence characteristics, providing a unified mathematical framework to address the challenges faced by ZNN models in noisy environments. Expanding on this work, Liao et al. [69] introduced bounded z-type neurodynamics, which imposes bounded conditions to ensure finite-time convergence and provide preliminary noise tolerance. However, its limitations in handling multiple types of noise restrict its applicability in more complex environments.
To overcome these limitations, Xiang et al. [70] developed the discrete-time noise-tolerant ZNN. This model not only improves tolerance to single noise types but also effectively manages multiple noise types simultaneously, significantly enhancing practical robustness and applicability. Through optimized algorithmic structures and parameter configurations, the discrete-time noise-tolerant ZNN achieves notable improvements in multi-noise environments.
Recognizing that existing noise-tolerance capabilities do not fully exploit digital hardware potential, Li et al. [71] introduced the finite-time-convergent and noise-rejection ZNN (FTNRZNN). Combining rapid convergence with robust noise rejection, it delivers solutions quickly and effectively resists persistent external noise interference. It notably maintains minimal steady state error even in dynamic, bounded, or unbounded linear noise environments, achieving higher precision and stability. According to [71], the design equation of the finite time convergent and noise rejection ZNN can be formulated as follows:
the positive parameters are employed to adjust the convergence speed. The activation monotonically increasing odd function mapping arrays . Advancements in digital hardware implementation spurred the development of a discrete form of the finite-time-convergent and noise-rejection ZNN, utilizing the recently advanced five-step finite difference method. This adaptation significantly enhanced the feasibility and applicability of FTNRZNN in practical digital systems. However, its capability to address long-term dependency problems was limited, restricting its application in complex time series tasks. Recognizing this limitation, Xiao et al. [72] introduced the limited-time robust neural network. Retaining the advantages of finite-time convergence and inherent noise suppression, the limited-time robust neural network incorporated innovative network designs and optimization strategies to effectively tackle long term dependencies. The introduction of the limited-time robust neural network marked a significant advancement in the performance of noise tolerant neural networks in complex dynamic environments.
Despite these advancements, the models had yet to fully demonstrate their potential in processing multimodal data. This challenge was met in 2022, when Zhang et al. [73] proposed a unified GNN model. With its finite-time convergence and streamlined structural design, this model significantly improved the efficiency of multimodal data processing. Noise tolerance in the complex valued domain remained an underexplored area until Long et al. [74] introduced complex-valued inertial neural networks. By integrating an inertial mechanism, complex valued inertial neural networks reduced control costs and expanded the scope of noise tolerance research. However, these models still faced limitations in handling unbounded noise, such as linear noise. Addressing this challenge, Liao et al. [75] proposed the Double Integral Enhanced ZNN model in 2023. Utilizing an innovative integral based design formula, it successfully managed unbounded noise and exhibited inherent linear noise tolerance.
Expanding on the complex valued inertial neural networks model, Dai et al. [76] introduced the norm-based zeroing neural dynamics model in 2024. Moving away from element-wise nonlinear activation functions, it employed a second norm operation. This novel approach ensured finite-time convergence while significantly enhancing robustness in complex, noisy environments. Based on the work presented in [76], the design equation for the norm-based zeroing neural dynamics model is obtained as follows.
where and that . Luo et al., by studying the combination of noise tolerance and swarm intelligence’s distributed exploration capabilities, innovatively integrated continuous time optimization methods in neurodynamics with the global exploration characteristics of swarm intelligence. In the article [77], they proposed a swarm exploring neurodynamic network based on a dual time scale model. By introducing a distributed exploration mechanism of swarm intelligence into the neurodynamic network, the model enables the network to effectively escape from local optima in complex multimodal optimization problems.
3.2. Activation Function Design
Due to the limited noise tolerance of traditional ZNN models, when subjected to dynamic bounded non-vanishing noise disturbances, although the steady-state residual error is theoretically bounded, it can still negatively affect the model performance. In 2019, to address this issue, Li et al. proposed a predefined time-convergent ZNN in their study [78]. They innovatively introduced two new types of activation functions, allowing the model to converge within a predefined time frame while possessing enhanced noise tolerance. With this design, the convergence time of predefined time-convergent ZNNs was explicitly defined as a prior constant parameter, theoretically capable of fully tolerating both vanishing and non-vanishing bounded dynamic noise. This provided a significant breakthrough for the application of ZNN in complex noisy environments. Specifically, the model has not yet achieved optimal performance in mitigating the impact of input noise on system stability and performance, especially when facing various types of noise disturbances.
To further optimize noise resistance, a new noise-tolerant and predefined-time ZNN (NNTZNN) model was introduced in the study [79], which significantly improved the model’s tolerance to multiple types of noise by incorporating multifunctional activation functions. These multifunctional activation functions have dynamic adjustment capabilities, enabling them to adaptively adjust the model’s convergence behavior based on the characteristics of the noise, thus demonstrating excellent robustness across different noisy environments.
The following design equation for the NNTZNN is constructed using the principles outlined in [79].
where . Furthermore, the predefined upper limit of convergence time for the NNTZNN model has been further optimized. However, these ZNN models still have certain limitations when dealing with harmonic noise. To address this issue, researchers proposed two harmonic noise-tolerant ZNN models in 2022 [80]. These models significantly enhance tolerance to harmonic noise by innovatively introducing Li activation functions. The core advantage of the Li activation function lies in its ability to introduce an adaptive compensation term within the model, which is used to dynamically adjust the response of the model to input noise. Additionally, through the optimized design of the error function, the two harmonic noise-tolerant ZNN models exhibit superior convergence performance in complex dynamic environments, achieving faster convergence rates and lower steady-state errors.
3.3. Fuzzy Control Mechanism
Fuzzy control is a control method based on fuzzy logic that addresses the control issues of complex, uncertain, or nonlinear systems by emulating human reasoning and decision-making processes. The core idea of fuzzy control is to use fuzzy sets and fuzzy inference to fuzzify inputs and outputs, thereby achieving effective control of the system, even when the mathematical model is imprecise or difficult to establish. Fuzzy control has been applied in various domains, including e-commerce information security [81], previewing repetitive control problems for Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy systems with state delay, and addressing the “state explosion problem” using fuzzy Petri net models [82].
Although fixed fuzzy rules can partially adapt ZNN models to certain scenarios, they lack flexibility in complex dynamic environments, failing to adjust parameters like network gain and weights across varying conditions. To address this, Zhang et al. proposed the variable-parameter convergent differential neural network [83], integrating fuzzy control dynamics with parameter optimization to enhance noise resilience and adaptability. Its key innovation is a real-time dynamic adjustment mechanism that optimizes network parameters (e.g., gain and weights) based on input noise levels and task complexity. This fuzzy-based strategy overcomes the rigidity of fixed rules, enabling efficient adaptation to dynamic environments while improving model robustness and control precision.
In line with the derivation shown in [83], the design equation is given by
and the parameter is defined as , where . The varying-parameter convergent differential neural network (VP-CDNN) can exhibit strong adaptability in varying tasks and environments by dynamically adjusting network parameters, Despite advancements, practical challenges persist: uncertain constraints and imprecise fuzzy conditions in nonlinear optimization hinder traditional methods, degrading convergence and steady-state performance. To enhance adaptability, Zhang et al. extended VP-CDNN by proposing the finite-time-varying parameter-convergent differential neural network. It integrates fuzzy logic to dynamically tune rules and parameters, addressing uncertain constraints. It employs an adaptive fuzzy inference system, coupling fuzzy logic with real-time noise analysis to precisely adjust network gain and weights, thereby improving robustness in the context of complex scenarios, constraint changes, and optimization objectives. The formula for solving nonlinear optimization problems is
using the finite time-varying parameter-convergent differential neural network found in
where is a varying parameter function. Here, is related to y generated by the Karush–Kuhn–Tucker conditions and the original condition x. To enhance noise tolerance, Wang et al. [84] proposed the fuzzy adaptive tolerant noise Zeroing Neural Network, which uses a Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy controller to adaptively tune convergence parameters based on steady-state residuals, achieving flexible tuning across tasks. Subsequently, Zhang et al. [44] developed the event-triggered control fuzzy adaptive Zeroing Neural Network, integrating event triggered control to reduce computational load while maintaining real time responsiveness, though it struggles with strong nonlinear noise. Addressing this, Liu et al. [85] introduced the intensive noise-tolerant ZNN, suppressing noise inherently via a simplified fuzzy structure without integral formulas, enabling fixed time convergence. Further, Chen et al. [45] designed a double-integral noise-tolerant fuzzy ZNN, combining double integrals and fuzzy logic to handle quadratic noise while dynamically adjusting convergence speed based on real-time noise levels.
Through the integration of fuzzy controllers, the ZNN model exhibits significant improvements in robustness, adaptability, and noise resistance comparable to those achieved by the denoising complex valued neural dynamic model and the adaptive-noise learning-differential neural solver model [86]. These advantages are particularly evident in practical applications. For instance, in multi-robot cooperative systems, the fuzzy enhanced ZNN can dynamically adjust control strategies to accommodate differences among individual robots and adapt to environmental uncertainties, thereby achieving coordinated and synchronized group behavior even under complex tasks and external disturbances. Similarly, in chaotic system synchronization under mixed noise interference, the time-varying fuzzy parameter ZNN successfully maintains stable synchronization in noisy conditions where other models fail to preserve control performance. Moreover, under noise-free conditions, the system controlled by the time-varying fuzzy parameter ZNN achieves the fastest convergence rate and the smallest steady state error, further confirming the superiority of the fuzzy control strategy in enhancing overall system performance.
Table 2 summarizes the primary noise tolerance approaches adopted in ZNN models, categorized by their underlying mechanisms. These approaches include structure-based modifications, activation function innovations, and fuzzy control strategies. By associating each method with the representative literature, the table provides a comprehensive overview of how different designs enhance robustness against noise in dynamic computational environments.

Table 2.
The noise-tolerance approaches in ZNNs: methods, principles, and references.
Table 3 summarizes the common types of activation functions in this review and their convergence and noise tolerance capabilities. To complement the fixed parameters listed for each activation function in Table 3, it is important to emphasize that the selection of these parameters significantly influences the convergence rate of the neural dynamic model. For the PAF, the exponential parameter l is typically chosen such that , with ensuring finite-time convergence. In contrast, for the SBPAF, the exponent l can take any real value. Both the BPAF and HSAF include a steepness control parameter that adjusts the nonlinearity of the function. In the NSBPAF and NEAF, a set of weighting coefficients are defined as positive constants to balance nonlinear and linear components. The power parameters , , and are selected from the positive domain, typically or and , to enhance the diversity of convergence behavior. For the WSBPAF, the shape control parameters p and q are also constrained to be positive. Finally, in the second-order LAF2, the parameters and are employed to regulate the saturation rate and the smoothness of the activation function.

Table 3.
Activation functions for neural dynamic models.
Based on the structural properties of the activation functions listed in Table 3, the system can be comprehensively evaluated in terms of initial value sensitivity, noise tolerance, and convergence speed. In LAF and BPAF, the system exhibits high sensitivity to initial values due to the absence of nonlinear modulation of initial perturbations. In contrast, activation functions such as SBPAF and NSBPAF can attenuate the influence of initial states on the error evolution trajectory to some extent, thereby enhancing the robustness of the system to variations in initial conditions. In terms of noise tolerance, NSBPAF, HSAF, and LAF2 maintain stable convergence trajectories under noise disturbances. This is attributed to features such as multi-parameter tuning, nonlinear control terms, and symmetric structural properties, which outperform traditional structures like PAF and BPAF. Regarding convergence speed, NSBPAF and NEAF achieve predefined time stability through parameter-driven mechanisms to meet the demands of high dynamic response. SBPAF and WSBPAF also exhibit finite-time convergence properties. In contrast, LAF and BPAF generally follow an asymptotic convergence pattern due to their relatively mild convergence mechanisms, making them less suitable for real-time control tasks. Therefore, in practical applications, the selection of activation functions should carefully balance initial value dependence, robustness, and convergence performance according to specific task requirements.
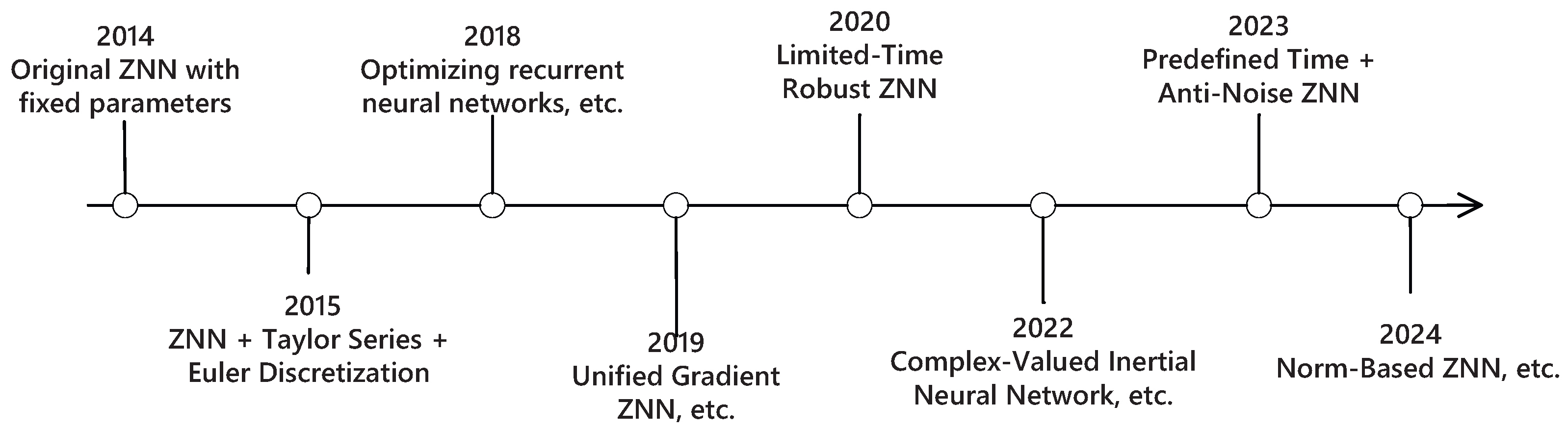
Figure 3 presents a timeline illustrating the evolution of the ZNN model’s noise tolerance capabilities from 2014 to 2024, with an emphasis on algorithmic enhancements and structural improvements. Beginning with the original fixed-parameter ZNN in 2014, the timeline highlights several key milestones. In 2015, Taylor series expansions and Eulerian discretization methods were introduced to improve computational accuracy. In 2018, further optimizations were proposed to enhance the performance of recurrent neural networks based on the ZNN framework. In 2019, a uniform gradient ZNN model was developed, followed in 2020 by a time limited robust ZNN designed to improve robustness within predefined time intervals. Subsequent advances include the development of complex valued inertial neural networks in 2022 and the integration of predefined time and noise resistant mechanisms in 2023. The most recent milestone, introduced in 2024, features a paradigm based ZNN model. Each development stage is clearly annotated along horizontal arrows in the figure, visually emphasizing the chronological progression of ZNN models in terms of robustness and noise tolerance.
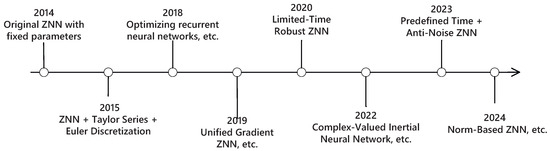
Figure 3.
Time line on development of robustness.
4. Application
ZNNs are a class of neural networks specifically designed for solving the zeros of equations. In recent years, they have played an indispensable role in online solutions to time-varying problems and have reported numerous significant research outcomes in the literature. These applications include machine operations, bio disease studies such as [94,95,96], artistic contributions like [97,98,99], and finance studies [100].
4.1. Robotic Arm
In the field of robotic arm research, the application of the ZNN model primarily focuses on addressing various time-varying problems. Robotic manipulators come in diverse and complex types, including dual-arm robots and robotic arms with redundant degrees of freedom. Among these, robotic arms with redundant degrees of freedom, designed to mimic human arm structures [101], have become a central focus of research and play an indispensable role in robotics studies [16].
The time-varying issues in robotic arms primarily focus on path tracking, which involves enabling the robotic arm to accurately follow and execute predefined paths or movements. While forward kinematics problems can be easily solved using direct analytical methods, inverse kinematics problems are far more complex. Consequently, researchers typically address inverse kinematics problems indirectly through forward kinematics equations. The forward kinematics equation can be expressed as
where and represent the joint angle vector and its derivative over time. The mapping function outputs the position of the end effector within the global coordinate frame, while , defined as , corresponds to a smooth nonlinear Jacobian transformation. In order to address the inverse kinematics (IK) task effectively, a ZNN-based framework is introduced. The error formulation specific to the mobile manipulator setup is given by
where is the target trajectory and denotes the current trajectory of the system. By combining the structure of the ZNN system (1) with the expressions (14) and (15), one can derive a time-dependent model for solving the IK of wheeled mobile manipulators:
Building on the formulation in (16), a set of thorough experimental evaluations was conducted. The findings reveal that, in comparison to classical GNN-based schemes, the ZNN model achieves notably improved precision in addressing IK problems in wheeled robotic platforms. This enhancement is largely due to the ZNN’s predictive capability, as opposed to the reactive nature of the GNN approach, which relies on trajectory tracking. As a result, under dynamically changing and disturbance-prone conditions, the ZNN model exhibits a more robust performance in maintaining accurate motion control and trajectory following. These results confirm the ZNN method’s applicability and robustness in robotic inverse kinematics scenarios.
4.2. Chaotic System
Chaotic systems are a class of nonlinear dynamical systems governed by deterministic rules, even though their behavior appears random and unpredictable. The long-term evolution of such systems is highly sensitive to initial conditions, a phenomenon known as the “butterfly effect”, where minute differences in initial states can lead to significant deviations in system trajectories. The study of chaotic systems is crucial for understanding complex dynamical processes in both nature and social sciences [102,103,104].
As shown in [105], from a mathematical perspective, chaotic systems can be described by the following equations:
where , , and . denotes the output of system (17). The objective is to construct a controller such that can track the desired time-varying trajectory , and the tracking error asymptotically converges to zero. Based on this, the ZNN model is employed for inference:
combining the above formulas, we can obtain
and define to finally conclude
where , The control law contains a singularity on the plane . To overcome this issue, inspired by the ZNN-related approach, the idea is to eliminate the division operation by transforming the direct control law (20) into an optimization problem. By defining and applying the gradient method, a tracking controller of the form can be designed, which eventually yields
In this way, the zeroing dynamics method and the gradient dynamics method are combined for the first time, and the tracking control problem for a class of chaotic systems is rigorously analyzed. This approach achieves satisfactory tracking performance and successfully overcomes the singularity issue encountered during the tracking control process.
4.3. Multi-Vehicle Cooperation
The scenario of multiple robots working together to complete a task can be understood as a problem of interaction and coordination between robots. In order to ensure the reliability and efficiency of task execution, various methods have been adopted to solve potential problems, such as the triple-modular redundancy fault-tolerant mechanism [106] and the ZNN approach [107,108]. Among these methods, the ZNN model stands out for its efficiency in multi-robot formation control. According to Liao et al. [60], the application of ZNN models primarily focuses on addressing time-varying problems in formation control, including nonconvex issues [6]. By integrating the leader–follower framework with sophisticated inter-robot-management representation strategies, the formation control problem can be formalized as an optimization problem and further transformed into an instance of a complex time-varying matrix equation, thereby achieving efficient and stable formation control. This method not only enhances the accuracy of formation control but also improves the adaptability and robustness of the system, allowing multi-robot systems to maintain optimal performance in dynamic environments. Based on the complex zeroing neural dynamic model proposed in [60], the definition can be
By integrating the CZND model, researchers validated its advantages in multi-robot management through three aspects: initial positioning, follower robot handling, and parameter optimization. The CZND model employs dynamic error functions and matrix time derivatives to better address system dynamics, reducing residual errors significantly. Specifically, CZND achieves a steady state error of , demonstrating superior precision and stability in complex systems. This advancement enhances dynatic system control and multi-robot cooperation efficiency, offering a high precision solution for dynamic scenarios like formation control.
4.4. Other Aspects of ZNNs
In addition to its typical application in robotic manipulator trajectory planning, the ZNN model has been widely applied to multi-dimensional spectral estimation tasks in recent years [109]. Multi-dimensional spectral estimation is a critical method in multi-dimensional signal processing for analyzing frequency characteristics. It extends the concept of one-dimensional spectral estimation to multi-dimensional spaces and leverages joint processing across spatial, temporal, and frequency domains to enhance overall communication system performance and frame transmission capacity. For instance, the combination of spherical detectors and Hadamard ratio detectors has demonstrated excellent performance in spectrum sensing [110], and further improvements in sensing efficiency have been achieved in [111]. Moreover, the ZNN model has been successfully applied to downlink multi-user precoding in massive multiple-input–multiple-output systems and to adaptive spectrum sensing methods based on Markov models, making it a key technology for spectrum resource optimization and management in multi-dimensional spectrum communications.
When integrated with multi-dimensional spectrum communication, the ZNN model is also capable of addressing output tracking control problems in single-input–single-output nonlinear systems. A ZNN-based controller design proposed in [112] effectively avoids the risk of division by zero, thereby improving system stability and real-time performance. Additionally, in [113], a discrete-time ZNN model was employed to estimate motion in two-dimensional optical flow fields, further extending ZNN’s applicability to image processing and computer vision tasks.
In addition, recent research [114] has introduced fractional-order stability theorems and synchronization control mechanisms into fractional-order, memory-delayed, bidirectional, associative-memory neural networks, with particular emphasis on memory preservation. This work offers valuable insights into extending ZNN models to fractional-order dynamical systems and synchronization tasks. It also provides a solid theoretical foundation and methodological guidance for applying ZNNs to broader domains such as complex system modeling, dynamic optimization, and intelligent control.
The advances achieved by ZNN in convergence optimization and robustness enhancement have been effectively applied across various practical domains. Specifically, improved ZNN models enable real-time inverse-kinematics control of redundant manipulators in dynamic environments, achieving higher convergence speed and precision while overcoming singularities and maintaining stable tracking performance. They also support robust tracking control in chaotic systems and enhance multi-robot cooperative formation by reducing steady-state errors and improving robustness under time-varying conditions. These applications demonstrate the effectiveness of ZNN-based solutions for optimal motion planning and control of redundant manipulators. Overall, the results validate the practical value and engineering significance of the proposed methods, highlighting their strong potential for deployment in robotics, automation, and complex dynamic systems.
Table 4 summarizes the applications of ZNN models in different domains and their specific mechanisms.

Table 4.
The neural dynamic methods categorized by application scenarios.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Discussion
To clearly demonstrate the performance advantages of ZNN, we compare it with several representative neural network models across four key performance dimensions: accuracy, convergence, noise tolerance, and sensitivity to initial conditions. As shown in Table 5, the comparison includes Gradient Neural Networks (GNNs), Traditional Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), and Model Predictive Control (MPC). This analysis highlights ZNN’s superior capabilities in handling dynamic systems and online control tasks, particularly in terms of accuracy, fast convergence, and robustness to noise and initialization.

Table 5.
Comparison of ZNNs and traditional models.
In addition, we present a systematic comparison between artificial neural networks (ANNs) and ZNNs in terms of their design principles and functional objectives, aiming to highlight the structural innovations embodied in ZNNs. Specifically, ANNs typically consist of multiple layers of neurons with weighted interconnections. Their architecture is determined by network depth and connectivity, and the weights are optimized through data-driven training processes. As such, ANNs are well suited for static tasks such as classification and regression. In contrast, ZNNs are shallow dynamic systems whose parameters are analytically designed rather than learned from data. They evolve in either continuous or discrete time to solve mathematical equations in real time. From a dynamic behavior perspective, an ANN performs static input–output mapping after training, whereas a ZNN exhibits an explicit dynamic evolution process in which the solution converges progressively toward the desired result. This fundamental distinction gives ZNNs a notable advantage in tasks that demand high accuracy, robustness, and real-time performance, particularly in dynamic modeling and control applications.
Although ZNNs and their variants offer numerous advantages, several limitations remain. For example, the finite-time ZNN can theoretically achieve convergence within a finite time, significantly accelerating the solution process. However, it does not inherently possess enhanced robustness against noise and lacks adaptability to multivariate problem settings.
The complex-valued nonlinear recurrent neural network extends the applicability of ZNNs to the complex domain and exhibits favorable convergence speed. Nevertheless, its advantage is typically limited to task-specific scenarios, and it lacks intrinsic anti-jamming capabilities. Similarly, the Predefined Temporal-Noise-Robust ZNN achieves efficient convergence and strong robustness by integrating multifunctional activation functions with a predefined time convergence mechanism. However, this comes at the cost of significantly increased model complexity and more stringent design constraints on the activation functions.
The segmented variable-parameter ZNN improves adaptability in non-stationary environments by dynamically adjusting parameters over different time intervals. Yet, this flexibility also introduces additional structural complexity and increases the difficulty of parameter tuning.
From the perspective of hardware deployment, all the above ZNN variants face practical challenges. Whether in robotics or on unmanned aerial vehicle platforms, hardware resources are often constrained in terms of processing power, energy availability, and real-time performance. The high-frequency computations and complex operations required to achieve finite-time or predefined-time convergence can place a substantial burden on onboard computational units.
In practical implementations, a trade off must often be made between achieving high accuracy or robustness and maintaining low energy consumption and latency. Therefore, to enable the real-world deployment of these theoretically advanced ZNN models, it is crucial to streamline algorithmic structures or apply engineering optimizations. Only through such adaptations can ZNNs provide reliable convergence and control performance under resource constraints, ensuring their feasibility in robotic control and autonomous system tasks.
5.2. Methodological Summary
In this review, we conducted a comprehensive literature search across multiple academic databases using the keywords “Zeroing Neural Network”, “finite time convergence”, “robustness”, and “tensor neural network”. The search was restricted to ZNN-related publications from the past decade to provide a clear understanding of their recent development. We focused on peer-reviewed articles published in high-quality journals and top tier conference proceedings in the fields of neural networks, control systems, and applied mathematics.
Relevant studies were selected based on their contributions to ZNN theory such as convergence analysis and robustness enhancement or their significance in practical applications. Priority was given to highly cited works and publications from reputable academic sources to ensure the reliability and authority of the survey. This selection strategy was designed to capture the most important advancements in the field while maintaining a rigorous standard of source quality.
5.3. Concluding Remarks
ZNNs demonstrate exceptional potential for solving time-varying problems due to their strong convergence properties and robustness in dynamic systems. This review has synthesized recent methodological advances in parameter design, activation function engineering, and structural robustness. These developments not only deepen the theoretical understanding of ZNN dynamics but also facilitate their practical deployment in complex, real time environments.
Looking ahead, several promising research directions merit further investigation. First, enabling ZNNs to handle multimodal data fusion (e.g., vision and kinematics) remains a critical challenge for the development of intelligent systems. Second, enhancing hardware adaptability such as designing low complexity architectures or employing quantized discrete-time variables is essential for deploying ZNNs in edge computing environments. Third, integrating sliding-mode control techniques can improve disturbance rejection and ensure finite-time convergence, while the incorporation of fuzzy logic offers potential for real-time parameter adaptation and increased noise resilience.
Finally, extending ZNNs to emerging application domains including smart transportation, mixed model data driven systems, and distributed edge networks will require addressing these technical challenges, but holds great promise for enabling robust, low latency control in intelligent cyber–physical systems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.L.; validation, X.Z.; investigation, X.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, X.Z.; visualization, X.Z; supervision, B.L.; project administration, X.Z.; funding acquisition, B.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 62466019.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liu, Z.; Wu, X. Structural analysis of the evolution mechanism of online public opinion and its development stages based on machine learning and social network analysis. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2023, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ding, C.; Zhang, M.; Luo, Y.; Mai, J. DCDLN: A densely connected convolutional dynamic learning network for malaria disease diagnosis. Neural Netw. 2024, 176, 106339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, L.; Guo, F.; Wang, J. RGCNPPIS: A Residual Graph Convolutional Network for Protein-Protein Interaction Site Prediction. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2024, 21, 1676–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Ma, M.; Wang, M.; He, S. What is the impact of discrete memristor on the performance of neural network: A research on discrete memristor-based BP neural network. Neural Netw. 2025, 185, 107213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Mai, W. VPT: Video portraits transformer for realistic talking face generation. Neural Netw. 2025, 184, 107122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Jin, L. Collaborative Neural Solution for Time-Varying Nonconvex Optimization with Noise Rejection. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2024, 8, 2935–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Li, W.; Lu, J.; Jin, S. ContexLog: Non-Parsing Log Anomaly Detection with All Information Preservation and Enhanced Contextual Representation. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2024, 21, 4750–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Wang, K.; Cai, Z.; Liu, A.; Li, Y.; Cheang, C.F. Using Imbalanced Triangle Synthetic Data for Machine Learning Anomaly Detection. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2019, 58, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, C.; Li, J.; Peng, H. Asynchronous introspection theory: The underpinnings of phenomenal consciousness in temporal illusion. Minds Mach. 2017, 27, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J. Resonant amplifier-based sub-harmonic mixer for zero-IF transceiver applications. Integration 2017, 57, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Tang, Y.; Tang, F.; Xiao, J.; Huang, C.; Xu, H. Efficient XML query and update processing using a novel prime-based middle fraction labeling scheme. China Commun. 2017, 14, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, Y.; Mai, W.; Luo, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, X.; Lin, R. Convolutional Dynamically Convergent Differential Neural Network for Brain Signal Classification. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 36, 8166–8177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Q.; Gong, H.; Hua, C. A new discrete-time denoising complex neurodynamics applied to dynamic complex generalized inverse matrices. J. Supercomput. 2025, 81, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Ren, X. Double center swarm exploring varying parameter neurodynamic network for non-convex nonlinear programming. Neurocomputing 2025, 619, 129156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Ren, X.; Luo, Y. A swarm exploring neural dynamics method for solving convex multi-objective optimization problem. Neurocomputing 2024, 601, 128203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Jin, L.; Hu, B. Data-driven model predictive control for redundant manipulators with unknown model. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 5901–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Refined self-motion scheme with zero initial velocities and time-varying physical limits via Zhang neurodynamics equivalency. Front. Neurorobot. 2022, 16, 945346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Tian, Y.; Jin, T. A label based ant colony algorithm for heterogeneous vehicle routing with mixed backhaul. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 47, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Peng, S.; Li, G.; Yin, P. Joint computation offloading and resource allocation for end-edge collaboration in internet of vehicles via multi-agent reinforcement learning. Neural Netw. 2024, 179, 106621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Xiang, C.; Li, T.; Guo, Y. A self-adapting hierarchical actions and structures joint optimization framework for automatic design of robotic and animation skeletons. Soft Comput. 2021, 25, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Qi, Y.; Jin, L. A Distributed Competitive and Collaborative Coordination for Multirobot Systems. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 23, 11436–11448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Feng, H.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qu, C.; Zeng, X.; Peng, X. A novel hybrid algorithm based on Harris Hawks for tumor feature gene selection. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2023, 9, e1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Y.; Zheng, L. Equivalent-input-disturbance-based preview repetitive control for Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy systems. Eur. J. Control 2023, 71, 100781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Jiang, Q.; Li, H.; Cao, X.; Lv, X. Finite-time-convergent support vector neural dynamics for classification. Neurocomputing 2025, 617, 128810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Mai, W.; Zhang, Z. A novel swarm budorcas taxicolor optimization-based multi-support vector method for transformer fault diagnosis. Neural Netw. 2025, 184, 107120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. An adaptive variable-parameter dynamic learning network for solving constrained time-varying QP problem. Neural Netw. 2025, 184, 106968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Jin, L.; Shang, M. Efficient Loss Landscape Reshaping for Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Du, X.; Jin, L. A Localization Algorithm for Underwater Acoustic Sensor Networks with Improved Newton Iteration and Simplified Kalman Filter. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 23, 14459–14470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Zheng, W.; Gao, R.; Lei, K. Fast cooperative energy detection under accuracy constraints in cognitive radio networks. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2017, 2017, 3984529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.; Zhang, K.; Tan, M.; Wang, J. Prescribed time convergence and robust Zeroing Neural Network for solving time-varying linear matrix equation. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2023, 100, 1094–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, Y. Solving time-varying inverse kinematics problem of wheeled mobile manipulators using Zhang neural network with exponential convergence. Nonlinear Dyn. 2014, 76, 1543–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Zhang, Y. From different ZFs to different ZNN models accelerated via Li activation functions to finite-time convergence for time-varying matrix pseudoinversion. Neurocomputing 2014, 133, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L. A finite-time convergent neural dynamics for online solution of time-varying linear complex matrix equation. Neurocomputing 2015, 167, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L. A new design formula exploited for accelerating Zhang neural network and its application to time-varying matrix inversion. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2016, 647, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Xiao, L.; Liao, B.; Lu, R.; Peng, H. An improved recurrent neural network for complex-valued systems of linear equation and its application to robotic motion tracking. Front. Neurorobot. 2017, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Liao, B.; Tan, Z. A novel recurrent neural network and its finite-time solution to time-varying complex matrix inversion. Neurocomputing 2019, 331, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dai, J.; Wang, R.; Tang, W. A segmented variable-parameter ZNN for dynamic quadratic minimization with improved convergence and robustness. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2021, 34, 2413–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; He, Y.; Dai, J.; Liu, X.; Liao, B.; Tan, H. A variable-parameter noise-tolerant Zeroing Neural Network for time-variant matrix inversion with guaranteed robustness. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 33, 1535–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, L.; Tao, J.; Li, W. A predefined-time and anti-noise varying-parameter ZNN model for solving time-varying complex Stein equations. Neurocomputing 2023, 526, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Li, C.; Chen, R.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Liu, P.X. A Novel Variable-Parameter Variable-Activation-Function Finite-Time Neural Network for Solving Joint-Angle Drift Issues of Redundant-Robot Manipulators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2024, 30, 1578–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xiao, L.; Li, L.; Zuo, Q.; Wang, Y. Two ZNN-Based Unified SMC Schemes for Finite/Fixed/Preassigned-Time Synchronization of Chaotic Systems. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 2024, 9, 2108–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Gu, Z. Novel Varying-Parameter ZNN Schemes for Solving TVLEIE Under Prescribed Time With UR5 Manipulator Control Application. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ren, X.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, J.; Luo, Y.; Mai, J.; Liao, B. A varying-parameter complementary neural network for multi-robot tracking and formation via model predictive control. Neurocomputing 2024, 609, 128384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Tan, P.; Xiao, L.; Jia, L.; He, Y.; Luo, J. A Fuzzy Adaptive Zeroing Neural Network Model With Event-Triggered Control for Time-Varying Matrix Inversion. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 31, 3974–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Wang, D.; Luo, L.; Dai, J.; Yan, X.; Li, J. A Double Integral Noise-Tolerant Fuzzy ZNN Model for TVSME Applied to the Synchronization of Chua’s Circuit Chaotic System. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 32, 6214–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, A.D.; Kawaguchi, K.; Karniadakis, G.E. Adaptive activation functions accelerate convergence in deep and physics-informed neural networks. J. Comput. Phys. 2020, 404, 109136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L. A nonlinearly-activated neurodynamic model and its finite-time solution to equality-constrained quadratic optimization with nonstationary coefficients. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 40, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Liao, B. A convergence-accelerated Zhang neural network and its solution application to Lyapunov equation. Neurocomputing 2016, 193, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Xiao, L.; Tan, Z.; Yang, Z. Wsbp function activated Zhang dynamic with finite-time convergence applied to Lyapunov equation. Neurocomputing 2018, 314, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Liao, B.; Li, S.; Chen, K. Nonlinear recurrent neural networks for finite-time solution of general time-varying linear matrix equations. Neural Netw. 2018, 98, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, K.; Tan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, B.; Chen, K.; Jin, L.; Li, S. Nonlinear gradient neural network for solving system of linear equations. Inf. Process. Lett. 2019, 142, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Xiao, L.; Tan, Z. Improved Zhang neural network with finite-time convergence for time-varying linear system of equations solving. Inf. Process. Lett. 2019, 147, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Xiao, L.; Tan, Z.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, J. Improved gradient neural networks for solving Moore–Penrose inverse of full-rank matrix. Neural Process. Lett. 2019, 50, 1993–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Tan, H.; Jia, L.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Y. New error function designs for finite-time ZNN models with application to dynamic matrix inversion. Neurocomputing 2020, 402, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Zhou, K.; Zain, A.M.; Wang, F.; Yusoff, Y. A modified harmony search algorithm and its applications in weighted fuzzy production rule extraction. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2023, 24, 1574–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.; Zain, A.M.; Zhou, K.Q. Harmony search algorithm and related variants: A systematic review. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2022, 74, 101126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, X.; Gong, R. Probability model-based early merge mode decision for dependent views coding in 3D-HEVC. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOMM) 2018, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Continuous and discrete gradient-Zhang neuronet (GZN) with analyses for time-variant overdetermined linear equation system solving as well as mobile localization applications. Neurocomputing 2023, 561, 126883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Yi, Q.; Dai, J.; Li, K.; Hu, Z. Design and analysis of new complex Zeroing Neural Network for a set of dynamic complex linear equations. Neurocomputing 2019, 363, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Hua, C.; Xu, Q.; Cao, X.; Li, S. Inter-robot management via neighboring robot sensing and measurement using a zeroing neural dynamics approach. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 244, 122938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, B.; Pan, C.; Li, K. Energy-efficient triple modular redundancy scheduling on heterogeneous multi-core real-time systems. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2024, 191, 104915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.M.; Kong, X.Z.; Liu, J.X.; Zheng, C.H.; Zhang, H. A New Binary Biclustering Algorithm Based on Weight Adjacency Difference Matrix for Analyzing Gene Expression Data. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2023, 20, 2802–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Peng, S.; Yang, X. Deep Learning-Based Signal-To-Noise Ratio Estimation Using Constellation Diagrams. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2020, 2020, 8840340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharajan, C.; Sowmiya, C.; Xu, C. Delay dependent complex-valued bidirectional associative memory neural networks with stochastic and impulsive effects: An exponential stability approach. Kybernetika 2024, 60, 317–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L. Taylor O(h3) discretization of ZNN models for dynamic equality-constrained quadratic programming with application to manipulators. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 27, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z. A new recurrent neural network with noise-tolerance and finite-time convergence for dynamic quadratic minimization. Neurocomputing 2018, 285, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Li, S. Design, verification and robotic application of a novel recurrent neural network for computing dynamic Sylvester equation. Neural Netw. 2018, 105, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, K.; Duan, M. Computing time-varying quadratic optimization with finite-time convergence and noise tolerance: A unified framework for zeroing neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 3360–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Xiang, Q.; Li, S. Bounded Z-type neurodynamics with limited-time convergence and noise tolerance for calculating time-dependent Lyapunov equation. Neurocomputing 2019, 325, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Liao, B.; Xiao, L.; Lin, L.; Li, S. Discrete-time noise-tolerant Zhang neural network for dynamic matrix pseudoinversion. Soft Comput. 2019, 23, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xiao, L.; Liao, B. A finite-time convergent and noise-rejection recurrent neural network and its discretization for dynamic nonlinear equations solving. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2019, 50, 3195–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Dai, J.; Lu, R.; Li, S.; Li, J.; Wang, S. Design and comprehensive analysis of a noise-tolerant ZNN model with limited-time convergence for time-dependent nonlinear minimization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2020, 31, 5339–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Weng, J.; Liao, B. GNN model for time-varying matrix inversion with robust finite-time convergence. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 35, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Zhang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Hu, J. Finite-time stabilization of complex-valued neural networks with proportional delays and inertial terms: A non-separation approach. Neural Netw. 2022, 148, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, B.; Han, L.; Cao, X.; Li, S.; Li, J. Double integral-enhanced Zeroing Neural Network with linear noise rejection for time-varying matrix inverse. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2024, 9, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, B. Norm-based zeroing neural dynamics for time-variant non-linear equations. CAAI Trans. Intell. Technol. 2024, 9, 1561–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X. A Novel Swarm-Exploring Neurodynamic Network for Obtaining Global Optimal Solutions to Nonconvex Nonlinear Programming Problems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 5866–5876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liao, B.; Xiao, L.; Lu, R. A recurrent neural network with predefined-time convergence and improved noise tolerance for dynamic matrix square root finding. Neurocomputing 2019, 337, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, J.; Chen, K.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Liao, B.; Ding, L.; Li, J. A new noise-tolerant and predefined-time ZNN model for time-dependent matrix inversion. Neural Netw. 2019, 117, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, D.; He, Y. Harmonic Noise-Tolerant ZNN for Dynamic Matrix Pseudoinversion and Its Application to Robot Manipulator. Front. Neurorobot. 2022, 16, 928636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Guo, X. Investigation of E-Commerce Security and Data Platform Based on the Era of Big Data of the Internet of Things. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 3023298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhou, K.Q.; Sarkheyli-Hägele, A.; Zain, A.M. Modeling, reasoning, and application of fuzzy Petri net model: A survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2022, 55, 6567–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Weng, J.; Mao, Y.; Lu, W.; Xiao, L. A new varying-parameter recurrent neural-network for online solution of time-varying Sylvester equation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 48, 3135–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Xiao, L. A Fuzzy Adaptive Zeroing Neural Network with Noise Tolerance for Time-varying Stein Matrix Equation Solving. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Annual Conference on Complex Systems and Intelligent Science (CSIS-IAC), Shenzhen, China, 20–22 October 2023; pp. 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Xiao, L.; Dai, J.; Wang, Y. Intensive Noise-Tolerant Zeroing Neural Network Based on a Novel Fuzzy Control Approach. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 31, 4350–4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liufu, Y.; Jin, L.; Li, S. Adaptive Noise-Learning Differential Neural Solution for Time-Dependent Equality-Constrained Quadratic Optimization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Zeng, H.B.; Wang, W.; Yu, F. Improved Stability Criteria of Static Recurrent Neural Networks with a Time-Varying Delay. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 391282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Lu, R. Finite-time solution to nonlinear equation using recurrent neural dynamics with a specially-constructed activation function. Neurocomputing 2015, 151, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Z.; Xiao, L.; Li, K.; Zuo, Q.; Zhang, Y. Adaptive coefficient designs for nonlinear activation function and its application to Zeroing Neural Network for solving time-varying Sylvester equation. J. Frankl. Inst. 2020, 357, 9909–9929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.Q.; Gui, W.H.; Mo, L.P.; Zain, A.M. A bidirectional diagnosis algorithm of fuzzy Petri net using inner-reasoning-path. Symmetry 2018, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L. Accelerating a recurrent neural network to finite-time convergence using a new design formula and its application to time-varying matrix square root. J. Frankl. Inst. 2017, 354, 5667–5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, L.; Huang, W.; Li, X.; Jia, L. A new predefined time Zeroing Neural Network with drop conservatism for matrix flows inversion and its application. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 54, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Xiao, L.; Dai, J.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Design and application of an adaptive fuzzy control strategy to Zeroing Neural Network for solving time-variant QP problem. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2020, 29, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Qu, C.; Zhang, L.; Tang, Y.; Li, J.; Feng, H.; Zeng, X.; Peng, X. A new hybrid algorithm for three-stage gene selection based on whale optimization. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Deng, F.; Tang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Peng, X. Improving feature selection performance for classification of gene expression data using Harris Hawks optimizer with variable neighborhood learning. Briefings Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Mo, Z.; Yan, F.; Xia, L.; Shan, F.; Ding, Z.; Song, B.; Gao, W.; Shao, W.; Shi, F.; et al. Adaptive feature selection guided deep forest for covid-19 classification with chest ct. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 2798–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wu, X. A deep learning-based approach for emotional analysis of sports dance. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2023, 9, e1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, D.; Faisal, M.; Jabeen, F.; Johar, S. Decision support system for evaluating the role of music in network-based game for sustaining effectiveness. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 10775–10788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Guo, Y. Controlling melody structures in automatic game soundtrack compositions with adversarial learning guided gaussian mixture models. IEEE Trans. Games 2020, 13, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Peng, C.; Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Ha, T.T.; Shutyaev, V.; Katsikis, V.; Stanimirovic, P. Neural networks for portfolio analysis in high-frequency trading. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 35, 18052–18061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Huang, R.; Liu, M.; Ma, X. Cerebellum-Inspired Learning and Control Scheme for Redundant Manipulators at Joint Velocity Level. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 6297–6306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, G.; Ma, L.; Yi, X. Recent advances on cooperative control of heterogeneous multi-agent systems subject to constraints: A survey. Syst. Sci. Control Eng. 2022, 10, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaddoum, G. Wireless chaos-based communication systems: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 2621–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, W.; Fu, Y.; Cheng, M.; Deng, L.; Liu, D. Chaos synchronization based on hybrid entropy sources and applications to secure communication. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2021, 33, 1038–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Guo, D.; Mao, M.; Yin, Y. Singularity-conquering tracking control of a class of chaotic systems using Zhang-gradient dynamics. IET Control Theory Appl. 2015, 9, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, B.; Pan, C.; Li, K. Energy-efficient scheduling for parallel applications with reliability and time constraints on heterogeneous distributed systems. J. Syst. Archit. 2024, 152, 103173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L. A nonlinearly activated neural dynamics and its finite-time solution to time-varying nonlinear equation. Neurocomputing 2016, 173, 1983–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, R.; Pan, C.; Li, K. Minimizing energy consumption with reliability goal on heterogeneous embedded systems. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2019, 127, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J. Multi-function current differencing cascaded transconductance amplifier (MCDCTA) and its application to current-mode multiphase sinusoidal oscillator. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2016, 86, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lei, K.; Peng, S.; Hu, L.; Li, S.; Cao, X. Threshold setting for multiple primary user spectrum sensing via spherical detector. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2018, 8, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lei, K.; Peng, S.; Cao, X.; Gao, X. Analytical expressions for the probability of false-alarm and decision threshold of Hadamard ratio detector in non-asymptotic scenarios. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2018, 22, 1018–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Mao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, D.; Yin, Y. ZD, ZG and IOL controllers and comparisons for nonlinear system output tracking with DBZ problem conquered in different relative-degree cases. Asian J. Control 2017, 19, 1482–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charif, F.; Benchabane, A.; Djedi, N.; Taleb-Ahmed, A. Horn & Schunck Meets a Discrete Zhang Neural Networks for Computing 2D Optical Flow. 2013. Available online: https://dspace.univ-ouargla.dz/jspui/handle/123456789/2644 (accessed on 27 May 2025).
- Chen, J.; Sun, W.; Zheng, S. New predefined-time stability theorem and synchronization of fractional-order memristive delayed BAM neural networks. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2025, 148, 108850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, B.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, L.; Jin, L. A velocity-level bi-criteria optimization scheme for coordinated path tracking of dual robot manipulators using recurrent neural network. Front. Neurorobot. 2017, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Dai, W.; Chen, J.; Yi, C. Zeroing Neural Networks combined with gradient for solving time-varying linear matrix equations in finite time with noise resistance. Mathematics 2022, 10, 4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Zhang, Y. Different complex ZFs leading to different complex ZNN models for time-varying complex generalized inverse matrices. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2013, 25, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Tan, H.Z. Performance analysis of gradient neural network exploited for online time-varying matrix inversion. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2009, 54, 1940–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayne, D.Q. Model predictive control: Recent developments and future promise. Automatica 2014, 50, 2967–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).