When Mathematical Methods Meet Artificial Intelligence and Mobile Edge Computing
Abstract
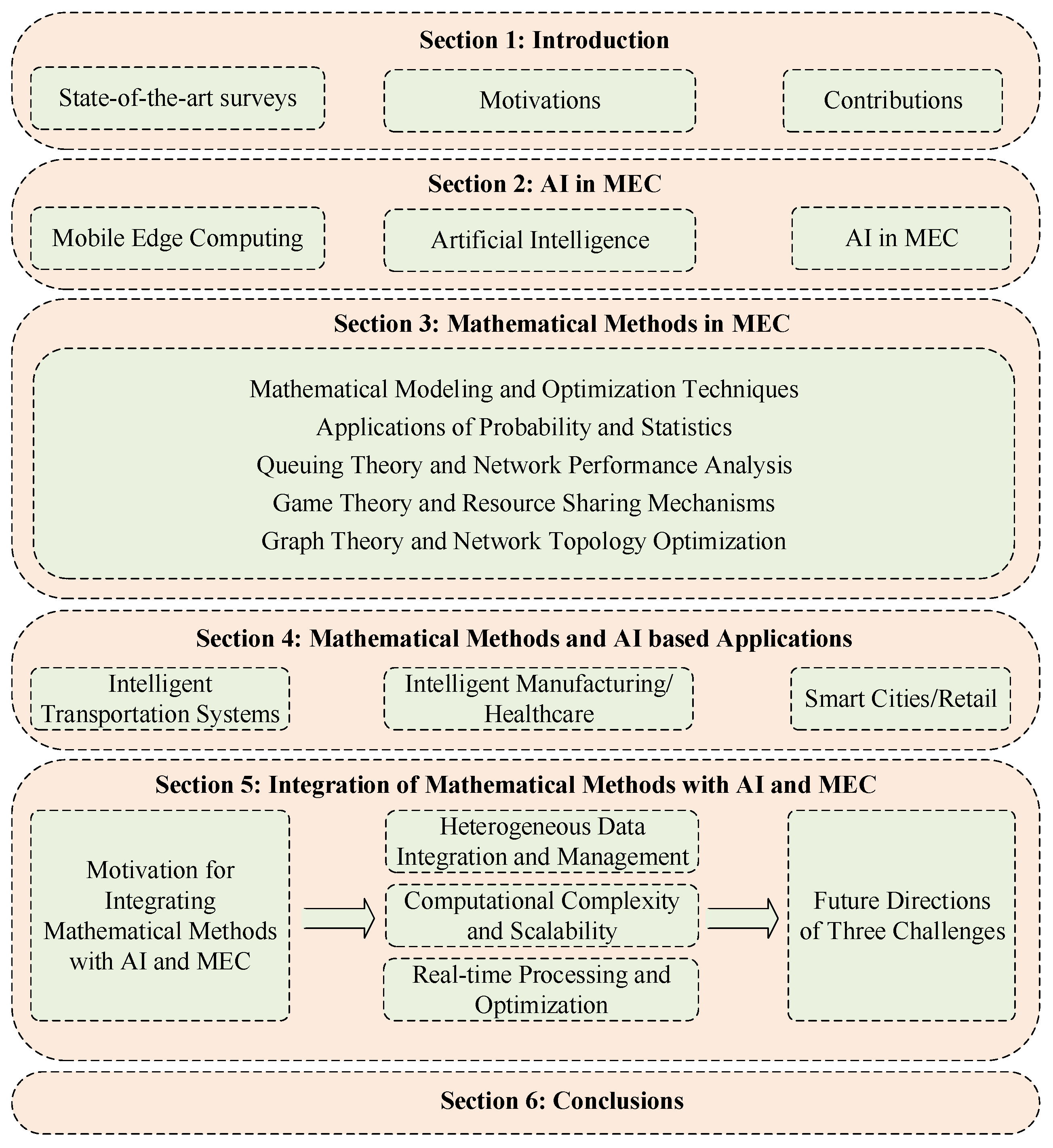
1. Introduction
- We present a comprehensive survey of mathematical methods integrated with AI in MEC, highlighting how mathematical rigor enhances system robustness, interpretability, and efficiency.
- We develop a comprehensive taxonomy linking mathematical methods to core MEC challenges, offering a structured guide for system-level optimization in edge intelligence.
- We survey cross-domain application and retail—and illustrate how the fusion of AI and mathematical modeling enables real-time, resource-constrained decision making.
- We focus on addressing three key challenges: heterogeneous data integration, real-time optimization, and computational scalability. We summarize state-of-the-art schemes to address these challenges and identify several open issues and promising future research directions.
2. Artificial Intelligence Algorithms in Mobile Edge Computing
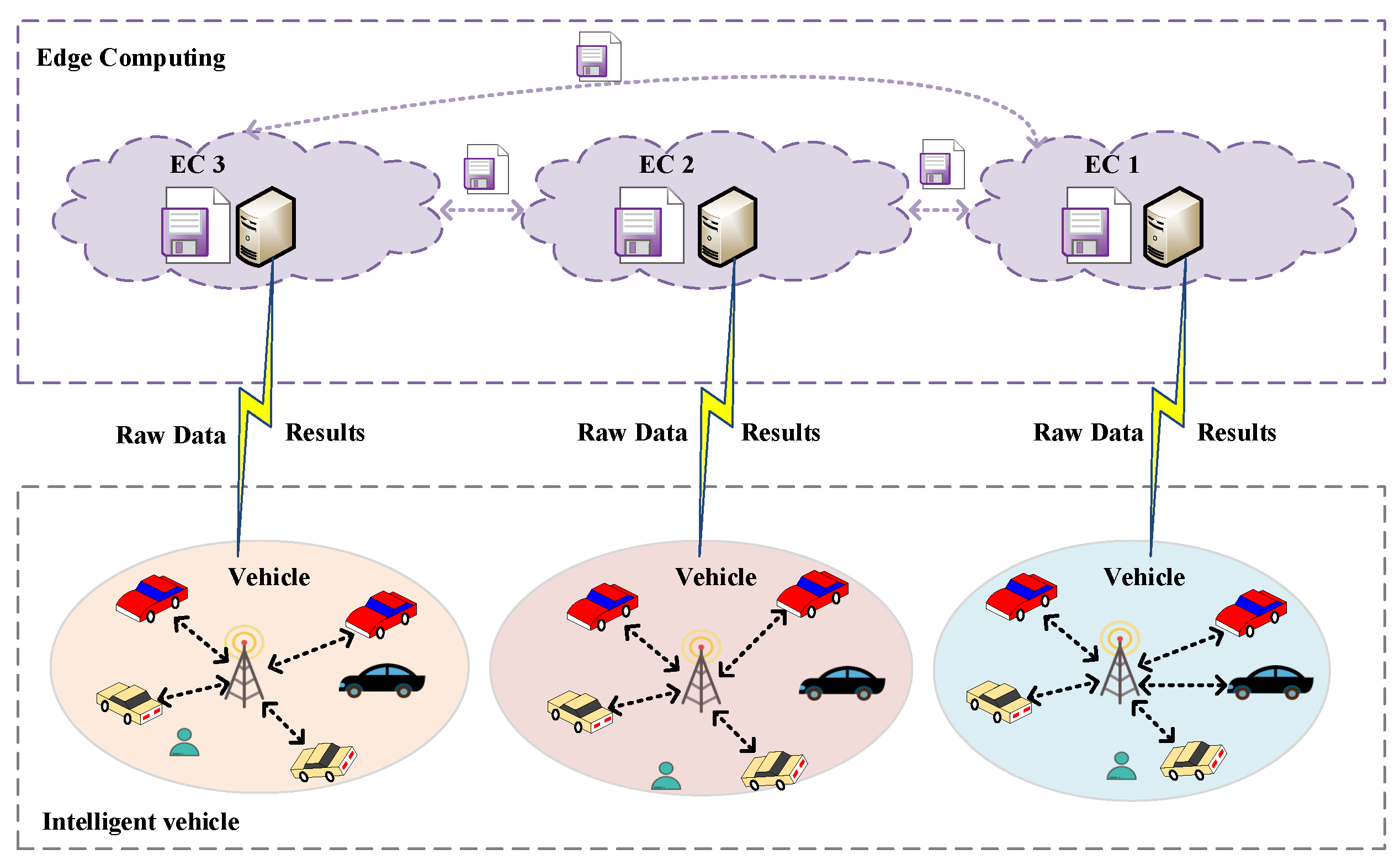
2.1. Mobile Edge Computing
2.2. Artificial Intelligence
2.3. Combination of Mobile Edge Computing and Artificial Intelligence
2.3.1. Motivations
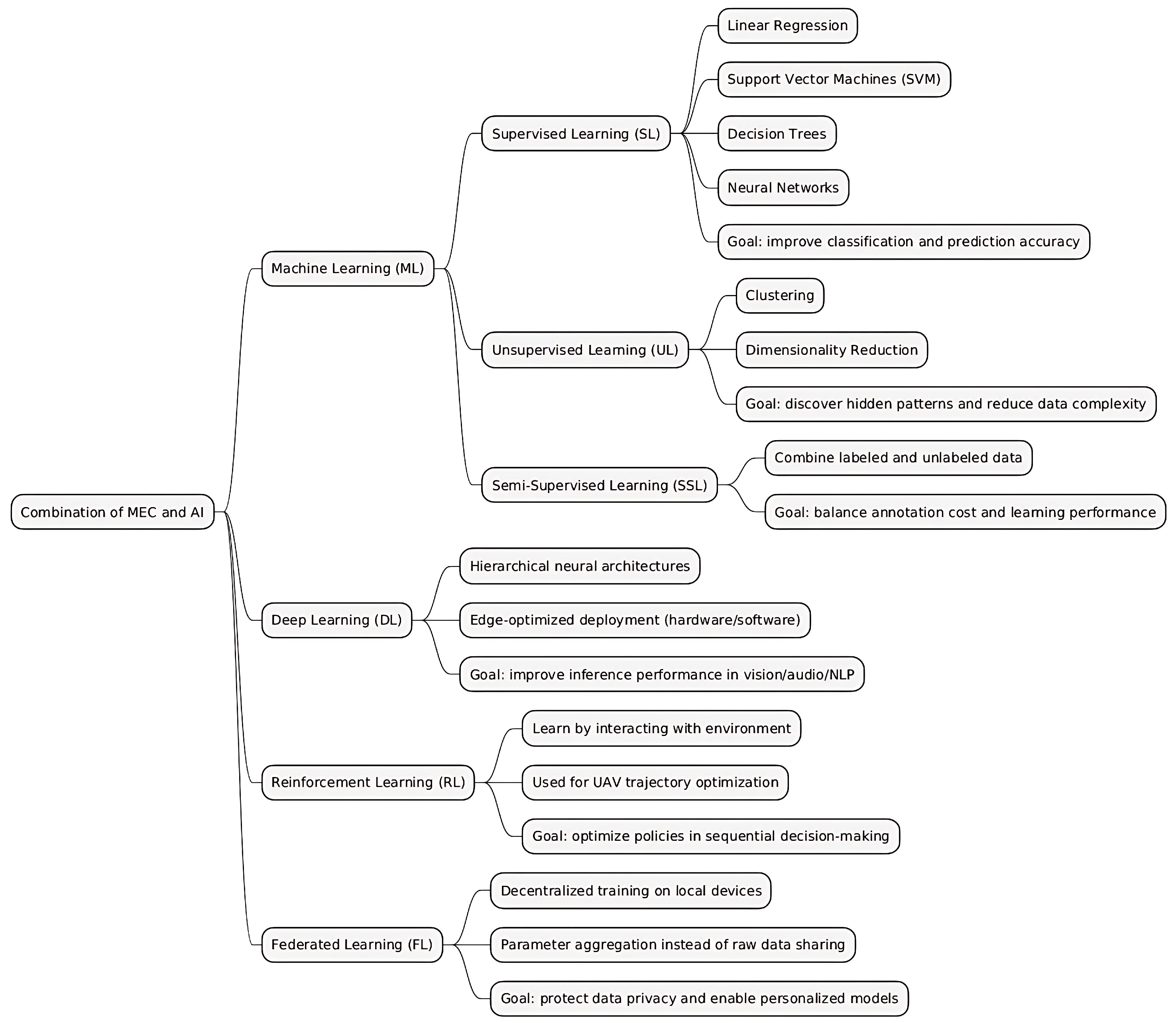
2.3.2. Machine Learning
2.3.3. Deep Learning
2.3.4. Reinforcement Learning
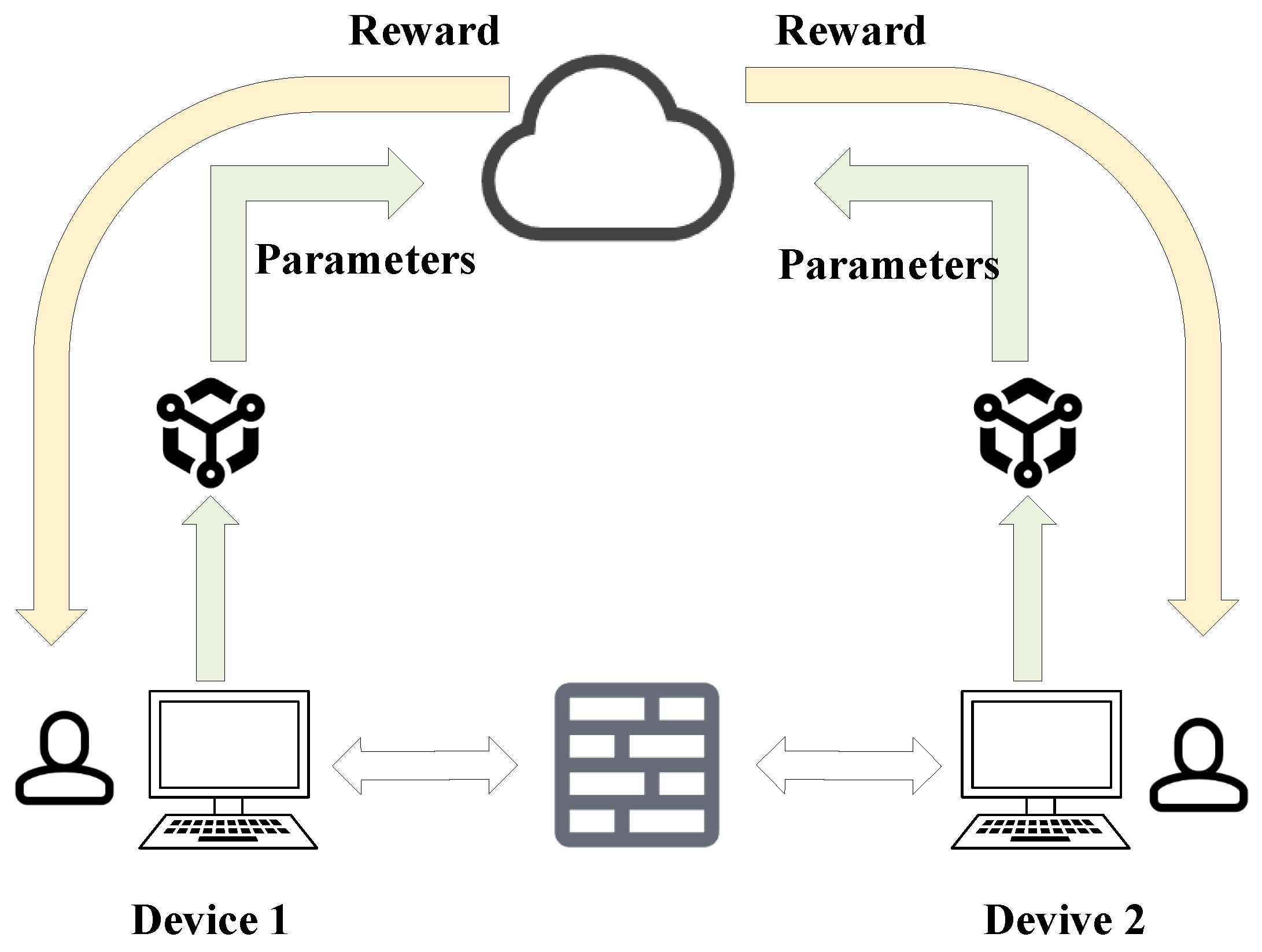
2.3.5. Federated Learning
2.3.6. Role of IoT in Driving Edge Intelligence
2.3.7. Key Challenges in AI-MEC Integration
2.4. Summary
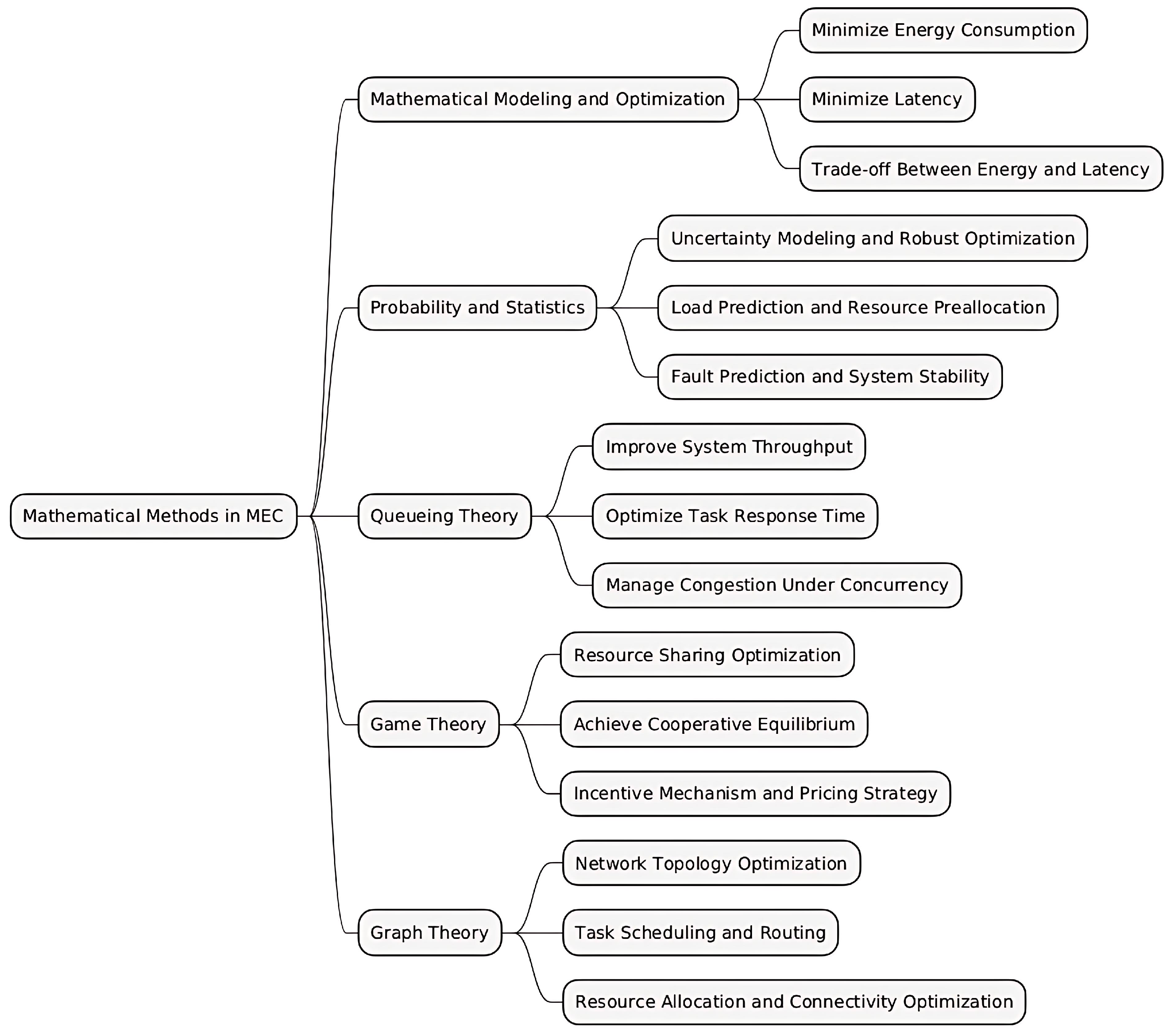
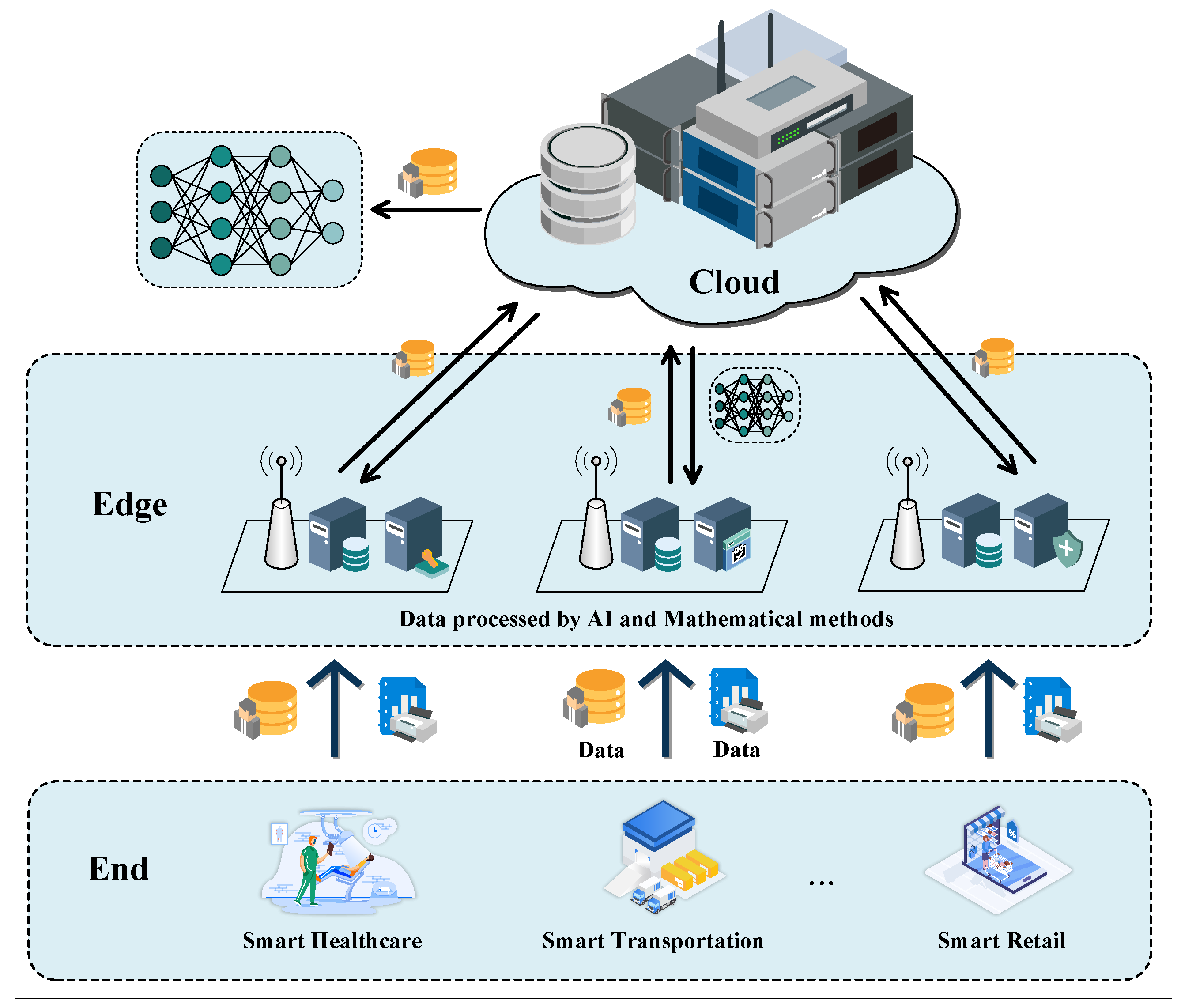
3. Mathematical Methods in Mobile Edge Computing
3.1. Motivations
3.2. Mathematical Modeling and Optimization Techniques
3.3. Applications of Probability and Statistics
3.4. Queuing Theory and Network Performance Analysis
3.5. Game Theory and Resource Sharing Mechanisms
3.6. Graph Theory and Network Topology Optimization
3.7. Summary
4. Mathematical Methods and Artificial Intelligence Based Applications
4.1. Intelligent Transportation Systems
4.2. Smart Cities
4.3. Intelligent Healthcare
4.4. Smart Retail
4.5. Emerging AI-SDN-Fog Convergence and Streaming Applications
4.6. Summary
5. Integration of Mathematical Methods with Artificial Intelligence and Mobile Edge Computing
5.1. Motivations
5.2. Integration Challenges and Opportunities
5.2.1. Heterogeneous Data Integration and Management
5.2.2. Computational Complexity and Scalability
5.2.3. Real-Time Processing and Optimization
5.2.4. Reconciling Trade-Offs Between AI and Mathematical Methods
5.3. Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| MEC | Mobile Edge Computing |
| TLA | Three-Letter Acronym |
| LD | Linear Dichroism |
| ITSs | Intelligent Transportation Systems |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| SL | Supervised Learning |
| UL | Unsupervised Learning |
| SSL | Semi-Supervised Learning |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| RL | Reinforcement Learning |
| FL | Federated Learning |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| EC | Edge Computing |
| URLLC | Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communication |
| PINN | Physics-Informed Neural Network |
| DQN | Deep Q-Network |
| QoE | Quality of Experience |
| QoS | Quality of Service |
| ISCC | Integrated Sensing–Communication–Computation |
| VCP | Vehicular Cooperative Perception |
| SoC | System on Chip |
| CDN | Content Delivery Network |
| AR/VR | Augmented Reality/Virtual Reality |
| DBN | Deep Belief Network |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| AIGC | AI-Generated Content |
| M3FM | Multimodal Multidomain Multilingual Foundation Model |
| GNN | Graph Neural Network |
| RoI | Region of Interest |
| ISCC | Integrated Sensing–Communication–Computation |
| TDA | Topological Data Analysis |
| SDN | Software-Defined Networking |
| SD-IoV | Software-Defined Internet of Vehicles |
| PINN | Physics-Informed Neural Network |
| P2P | Peer to Peer |
References
- Wang, T.; Liang, Y.; Jia, W.; Arif, M.; Liu, A.; Xie, M. Coupling resource management based on fog computing in smart city systems. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2019, 135, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maathuis, C.; Cidota, M.A.; Datcu, D.; Marin, L. Integrating Explainable Artificial Intelligence in Extended Reality Environments: A Systematic Survey. Mathematics 2025, 13, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, G.; Guo, J.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, X.; Wang, T. Efficient Request Scheduling in Cross-Regional Edge Collaboration via Digital Twin Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/ACM 32nd International Symposium on Quality of Service (IWQoS), Guangzhou, China, 19–21 June 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Hua, L. Major Issues in High-Frequency Financial Data Analysis: A Survey of Solutions. Mathematics 2025, 13, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liang, Y.; Shen, X.; Zheng, X.; Mahmood, A.; Sheng, Q.Z. Edge computing and sensor-cloud: Overview, solutions, and directions. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Jiang, K.; He, S.; Min, G.; Wu, J. Distributed deep multi-agent reinforcement learning for cooperative edge caching in internet-of-vehicles. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 22, 9595–9609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surianarayanan, C.; Lawrence, J.J.; Chelliah, P.R.; Prakash, E.; Hewage, C. A survey on optimization techniques for edge artificial intelligence (AI). Sensors 2023, 23, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, X.; Chen, M. In-edge ai: Intelligentizing mobile edge computing, caching and communication by federated learning. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhao, H.; Fang, W.; Yin, J.; Dustdar, S.; Zomaya, A.Y. Edge intelligence: The confluence of edge computing and artificial intelligence. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 7457–7469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Z.; Liu, S.; Xiong, X.; Cai, Z.; Tu, G. A survey of recent advances in edge-computing-powered artificial intelligence of things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 13849–13875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Liu, Y.; Meng, G.; Sun, Q. An overview on edge computing research. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 85714–85728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzesik, P.; Mrozek, D. Combining machine learning and edge computing: Opportunities, challenges, platforms, frameworks, and use cases. Electronics 2024, 13, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.S.; George, A.H.; Baskar, T. Edge computing and the future of cloud computing: A survey of industry perspectives and predictions. Partners Univers. Int. Res. J. 2023, 2, 19–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M.; Tomar, A.; Hazra, A. Edge computing for industry 5.0: Fundamental, applications and research challenges. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 19070–19093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, S.; Srivastava, G.; Jhaveri, R.; Babu, M.R.; Bhattacharya, S.; Maddikunta, P.K.R.; Mastorakis, S.; Piran, M.J.; Gadekallu, T.R. Federated learning for smart cities: A comprehensive survey. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2023, 55, 102987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.; Hashmi, U.S.; Imran, A. Edge computing in smart health care systems: Review, challenges, and research directions. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2022, 33, e3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, Z.; Dong, W. Overview of edge computing in the agricultural internet of things: Key technologies, applications, challenges. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 141748–141761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L. Artificial intelligence in retail: Applications and value creation logics. Int. J. Retail. Distrib. Manag. 2021, 49, 958–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y. Artificial intelligence: A survey on evolution, models, applications and future trends. J. Manag. Anal. 2019, 6, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.J.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach; Pearson: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, C.L.; Suen, C.Y. Towards robust pattern recognition: A review. Proc. IEEE 2020, 108, 894–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Chen, L.; Dan, C.; Rezaeipanah, A. A systematic survey of data mining and big data analysis in internet of things. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 18405–18453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWitt, D.; Gray, J. Parallel database systems: The future of high performance database systems. Commun. ACM 1992, 35, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nti, I.K.; Quarcoo, J.A.; Aning, J.; Fosu, G.K. A mini-review of machine learning in big data analytics: Applications, challenges, and prospects. Big Data Min. Anal. 2022, 5, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, N.J. Principles of Artificial Intelligence; Morgan Kaufmann: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Janiesch, C.; Zschech, P.; Heinrich, K. Machine learning and deep learning. Electron. Mark. 2021, 31, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yves Kodratoff, R.S.M. Machine Learning: An Artificial Intelligence Approach; Morgan Kaufmann: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1990; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Maulud, D.; Abdulazeez, A.M. A review on linear regression comprehensive in machine learning. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. Trends 2020, 1, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, J.; Garcia-Lamont, F.; Rodríguez-Mazahua, L.; Lopez, A. A comprehensive survey on support vector machine classification: Applications, challenges and trends. Neurocomputing 2020, 408, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.G.; Pedreira, C.E. Recent advances in decision trees: An updated survey. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 4765–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samek, W.; Montavon, G.; Lapuschkin, S.; Anders, C.J.; Müller, K.R. Explaining deep neural networks and beyond: A review of methods and applications. Proc. IEEE 2021, 109, 247–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Song, Z.; King, I.; Xu, Z. A survey on deep semi-supervised learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 35, 8934–8954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Leung, V.C.; Niyato, D.; Yan, X.; Chen, X. Convergence of edge computing and deep learning: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 869–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1251–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Z.; Hu, H.; Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Guo, S.; Wang, G.; Gao, X. Mobile edge computing and machine learning in the internet of unmanned aerial vehicles: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 56, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jararweh, Y.; Otoum, S.; Al Ridhawi, I. Trustworthy and sustainable smart city services at the edge. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 62, 102394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, M.; Sun, P.; Guo, B.; Yu, Z. Accelerating federated learning via parameter selection and pre-synchronization in mobile edge-cloud networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 23, 10313–10328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banabilah, S.; Aloqaily, M.; Alsayed, E.; Malik, N.; Jararweh, Y. Federated learning review: Fundamentals, enabling technologies, and future applications. Inf. Process. Manag. 2022, 59, 103061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Guo, J.; Zeng, J.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, T. Fine-Grained Service Lifetime Optimization for Energy-Constrained Edge-Edge Collaboration. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 44th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), Jersey City, NJ, USA, 23–26 July 2024; pp. 565–576. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Zou, H.; Jia, W.; Wang, T. Dynamic parallel multi-server selection and allocation in collaborative edge computing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 23, 10523–10537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhayo, J.; Shah, S.A.; Hameed, S.; Ahmed, A.; Nasir, J.; Draheim, D. Towards a machine learning-based framework for DDOS attack detection in software-defined IoT (SD-IoT) networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 123, 106432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Roh, B.H. A novel scheme for controller selection in software-defined internet-of-things (SD-IoT). Sensors 2022, 22, 3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, G.; Guo, J.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, J.; Wang, T. Latency Reduction in Immersive Systems through Request Scheduling with Digital Twin Networks in Collaborative Edge Computing. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifeng, Z.; Haowei, D.; Yaxing, Y.; Hao, C.; Hai, Z. Improved NSGA-II algorithm-based task offloading decision in the internet of vehicles edge computing scenario. Multimed. Syst. 2025, 31, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, W. CL-ADMM: A cooperative-learning-based optimization framework for resource management in MEC. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 8191–8209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Curtò, J.; de Zarzà, I.; Roig, G.; Cano, J.C.; Manzoni, P.; Calafate, C.T. Llm-informed multi-armed bandit strategies for non-stationary environments. Electronics 2023, 12, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.; Aivodji, U.; Gambs, S.; Huguet, M.J.; Siala, M. Improving fairness generalization through a sample-robust optimization method. Mach. Learn. 2023, 112, 2131–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yin, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Jia, W.; Wang, T. Grouping reduces energy cost in directionally rechargeable wireless vehicular and sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 10840–10851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A.; Maheshwari, S.; Pompili, D. Energy-latency computation offloading and approximate computing in mobile-edge computing networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2024, 21, 3401–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Z. Robust trajectory and offloading for energy-efficient UAV edge computing in industrial Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 20, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, X.; Huang, H.; Cheng, S.; Wu, M. A NSGA-II algorithm for task scheduling in UAV-enabled MEC system. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 9414–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L. Convergence in high probability of distributed stochastic gradient descent algorithms. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2023, 69, 2189–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, G.; Chen, W. Efficient multidimensional dynamic programming-based energy management strategy for global composite operating cost minimization for fuel cell trams. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 8, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Jin, D.; Han, Z. Attentional Markov model for human mobility prediction. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2021, 39, 2213–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X. A hierarchical object oriented Bayesian network-based fault diagnosis method for building energy systems. Appl. Energy 2022, 306, 118088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, L.; Varela, C.A.; Patterson, S. A continuum approach for collaborative task processing in UAV MEC networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 15th International Conference on Cloud Computing (CLOUD), Barcelona, Spain, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 247–256. [Google Scholar]
- Meydani, A.; Shahinzadeh, H.; Ramezani, A.; Moazzami, M.; Nafisi, H.; Askarian-Abyaneh, H. Comprehensive review of artificial intelligence applications in smart grid operations. In Proceedings of the 2024 9th International Conference on Technology and Energy Management (ICTEM), Behshahr, Iran, 14–15 February 2024; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Maina, S.C.; Mwigereri, D.; Weyn, J.; Mackey, L.; Ochieng, M. Evaluation of Dependency Structure for Multivariate Weather Predictors Using Copulas. ACM J. Comput. Sustain. Soc. 2023, 1, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Green, R.C., II. Leveraging survival analysis in cost-aware deepnet for efficient hard drive failure prediction. Neural Comput. Appl. 2025, 37, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, M. Priority-aware task scheduling using M/G/1 queueing model in edge computing. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2021, 32, 1432–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Gui, L.; Sun, Y. Edge-cloud collaboration architecture based on queuing networks for latency reduction. IEEE Trans. Cloud Comput. 2020, 8, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Li, X.; Niyato, D. Stochastic Petri net modeling for resource contention analysis in multi-hop edge networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 10123–10137. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Park, S. G/G/m queue-based load balancing for heterogeneous edge servers. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2019, 12, 742–755. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, J. Fluid flow modeling for large-scale traffic prediction in edge networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 2100–2113. [Google Scholar]
- Niyato, D.; Wang, P.; Kim, D. Queueing game theory for mitigating congestion in selfish edge computing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2020, 19, 643–658. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, S.; Ren, T.; Zhang, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, J. A Stackelberg Game Based Framework for Edge Pricing and Resource Allocation in Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 20514–20530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Ota, K.; Dong, M.; Yuan, H. Stackelberg game-based pricing and offloading in mobile edge computing. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 11, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou El Houda, Z.; Brik, B.; Ksentini, A.; Khoukhi, L.; Guizani, M. When federated learning meets game theory: A cooperative framework to secure IIoT applications on edge computing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 7988–7997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, C.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, T. New method of energy efficient subcarrier allocation based on evolutionary game theory. Mob. Netw. Appl. 2021, 26, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Zhu, K.; Luong, N.C.; Yi, C.; Niyato, D.; Kim, D.I. Applications of auction and mechanism design in edge computing: A survey. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2022, 8, 1034–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, X.; Cai, X.; He, X.; Liu, Y. Contract-theory-based incentive mechanism for federated learning in health crowdsensing. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 10, 4475–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Jat, S.C. A Minimum Spanning Tree-based Energy Efficient Cluster Head Election in WSN. Turk. J. Comput. Math. Educ. 2021, 12, 3065–3073. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Liang, J.; Wang, J. A community detection algorithm based on graph compression for large-scale social networks. Inf. Sci. 2021, 551, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alex, S.A.; Singh, N.; Adhikari, M. Digital Twin-based Dynamic Resource Provisioning Using Deep Q-Network on 6G-enabled Mobile Edge Networks. In Proceedings of the 2025 17th International Conference on COMmunication Systems and NETworks (COMSNETS), Bengaluru, India, 6–10 January 2025; pp. 774–781. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Li, Z.; Shi, H.; Luo, P.; Ma, Y.; Liu, K. Multi-Dimensional Optimization for Collaborative Task Scheduling in Cloud-Edge-End System. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2025, 141, 103099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzaben, N.; Engels, D.W. End-to-end routing in sdn controllers using max-flow min-cut route selection algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 23rd International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), PyeongChang, Republic of Korea, 7–10 February 2021; pp. 461–467. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, T.; Zhu, L.; Yu, F.R.; Tang, T. Edge intelligence in intelligent transportation systems: A survey. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 8919–8944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, W.; Zheng, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, T. Collaborative edge service placement for maximizing qos with distributed data cleaning. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/ACM 31st International Symposium on Quality of Service (IWQoS), Orlando, FL, USA, 19–21 June 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Rajak, S.; Dang, S.; Liu, R.; Li, J.; Chinnadurai, S. Deep learning enabled IRS for 6G intelligent transportation systems: A comprehensive study. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 24, 12973–12990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Lin, Q.; Hu, B. Knowledge distillation-based edge-decision hierarchies for interactive behavior-aware planning in autonomous driving system. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 11040–11057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aziz, M.K.; Perfecto, C.; Samarakoon, S.; Bennis, M.; Saad, W. Vehicular cooperative perception through action branching and federated reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 70, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakr, A.H. Evaluation of Redundancy Mitigation Rules in V2X Networks for Enhanced Collective Perception Services. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 137696–137711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Shu, J.; Jiang, H.; Min, G.; Chen, H.; Han, Z. Perception task offloading with collaborative computation for autonomous driving. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2022, 41, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, A.M.; Elsayed, S.A.; Elgazzar, K.; Hassanein, H.S. Quality-Aware Task Offloading for Cooperative Perception in Vehicular Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 73, 18320–18332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Fu, Y.; Li, C.; Tian, M.; Yu, F.R.; Cheng, N. Task Offloading and Resource Allocation in Vehicular Cooperative Perception with Integrated Sensing, Communication, and Computation. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, C.; Zou, P.; Tian, H.; Kuang, X.; Yang, S.; Zhong, L.; Niyato, D. How to mitigate DDoS intelligently in SD-IoV: A moving target defense approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 19, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Li, Y.; Chu, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, T. Improving Fairness in Coexisting 5G and Wi-Fi Network on Unlicensed Band with URLLC. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/ACM 31st International Symposium on Quality of Service (IWQoS), Orlando, FL, USA, 19–21 June 2023; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Al Sharif, R.; Pokharel, S. Smart city dimensions and associated risks: Review of literature. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 77, 103542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mour, N.; Smith, L. Machine learning based on reinforcement learning for smart grids: Predictive analytics in renewable energy management. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 109, 105510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Qin, Y.; Hao, C.; Cao, J. Optimal energy management strategies for energy Internet via deep reinforcement learning approach. Appl. Energy 2019, 239, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tang, Z.; Guo, J.; Meng, T.; Wang, C.; Wang, T.; Jia, W. Empowering Edge Intelligence: A Comprehensive Survey on On-Device AI Models. ACM Comput. Surv. 2025, 57, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Hu, X. Efficient crowd density estimation with edge intelligence via structural reparameterization and knowledge transfer. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 154, 111366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicioğlu, M.; Çalhan, A. A multiprotocol controller deployment in SDN-based IoMT architecture. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 20833–20840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Meng, T.; Guo, J.; Wei, X.; Jia, W. SecEG: A secure and efficient strategy against DDoS attacks in mobile edge computing. ACM Trans. Sens. Netw. 2024, 20, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.A.; Vu Khanh, Q.; Nguyen, V.H.; Nguyen, T.; Nguyen, D.C. Intelligent healthcare: Integration of emerging technologies and Internet of Things for humanity. Sensors 2023, 23, 4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabireen, H.; Neelanarayanan, V. A review on fog computing: Architecture, fog with IoT, algorithms and research challenges. ICT Express 2021, 7, 162–176. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Shareeda, M.; Hergast, D.; Manickam, S. Review of Intelligent Healthcare for the Internet of Things: Challenges, Techniques and Future Directions. J. Sens. Netw. Data Commun. 2024, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, A.; Debnath, T.; Kundu, D.; Khan, M.S.I.; Aishi, A.A.; Sazzad, S.; Sayduzzaman, M.; Band, S.S. Machine learning and deep learning-based approach in smart healthcare: Recent advances, applications, challenges and opportunities. AIMS Public Health 2024, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, Z.; Yin, Q.; Huang, J.; Luo, J.; Thakur, A.; Branson, K.; Schwab, P.; Yin, B.; Wu, X.; et al. A multimodal multidomain multilingual medical foundation model for zero shot clinical diagnosis. npj Digit. Med. 2025, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob Akbar, M.I. Leveraging Edge AI and IoT for Remote Healthcare: A Novel Framework for Real-Time Diagnosis and Disease Prediction. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/388641638_Leveraging_Edge_AI_and_IoT_for_Remote_Healthcare_A_Novel_Framework_for_Real-Time_Diagnosis_and_Disease_Prediction (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Mohsin, S.S.; Salman, O.H.; Jasim, A.A.; Alwindawi, H.; Abdalkareem, Z.A.; Salman, O.S.; Kairaldeen, A.R. AI-Powered IoMT Framework for Remote Triage and Diagnosis in Telemedicine Applications. Al-Iraqia J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2025, 4, 61–76. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.R.; Kabir, M.M.; Mridha, M.F.; Alfarhood, S.; Safran, M.; Che, D. Deep learning-based IoT system for remote monitoring and early detection of health issues in real-time. Sensors 2023, 23, 5204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolawole, O.O. IoT and AI-Based Remote Patient Monitoring for Chronic Disease Management. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/389504944_IoT_and_AI-Based_Remote_Patient_Monitoring_for_Chronic_Disease_Management/ (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Leuzy, A.; Heeman, F.; Bosch, I.; Lenér, F.; Dottori, M.; Quitz, K.; Moscoso, A.; Kern, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; et al. REAL AD—Validation of a realistic screening approach for early Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dementia 2024, 20, 8172–8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berron, D.; Olsson, E.; Andersson, F.; Janelidze, S.; Tideman, P.; Düzel, E.; Palmqvist, S.; Stomrud, E.; Hansson, O. Remote and unsupervised digital memory assessments can reliably detect cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dementia 2024, 20, 4775–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umer, M.; Aljrees, T.; Karamti, H.; Ishaq, A.; Alsubai, S.; Omar, M.; Bashir, A.K.; Ashraf, I. Heart failure patients monitoring using IoT-based remote monitoring system. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; An, Q.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, L.; Xue, C. A novel wearable device integrating ECG and PCG for cardiac health monitoring. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2025, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Morshed, B.I. A Smart Wearable for Real-Time Cardiac Disease Detection Using Beat-by-Beat ECG Signal Analysis with an Edge Computing AI Classifier. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 20th International Conference on Body Sensor Networks (BSN), Chicago, IL, USA, 15–17 October 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Moody, G.B.; Mark, R.G. The impact of the MIT-BIH arrhythmia database. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2001, 20, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahan, B.; Moore, E.; Ramage, D.; Hampson, S.; y Arcas, B.A. Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data. In Proceedings of the Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Lauderdale, FL, USA, 20–22 April 2017; pp. 1273–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, E.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, L.; Xie, M. A federated recommendation algorithm based on user clustering and meta-learning. Appl. Soft Comput. 2024, 158, 111483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronis, C.; Varlamis, I.; Himeur, Y.; Sayed, A.N.; Al-Hasan, T.M.; Nhlabatsi, A.; Bensaali, F.; Dimitrakopoulos, G. A survey on the use of federated learning in privacy-preserving recommender systems. IEEE Open J. Comput. Soc. 2024, 5, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Qu, L.; Chen, T.; Yuan, W.; Zheng, R.; Long, J.; Xia, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, C. On-Device Recommender Systems: A Comprehensive Survey. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.11441. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Wei, L.; Chen, F.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; Wang, H. Fedai: Federated recommendation system with anonymized interactions. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 271, 126564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, F.; Zhu, C.; He, S.; Zhang, S.; Su, Y. BP-YOLO: A Real-Time Product Detection and Shopping Behaviors Recognition Model for Intelligent Unmanned Vending Machine. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 21038–21051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, W.; Huang, M.; Gao, Z.; Wang, X. Distributed dynamic pricing of multiple perishable products using multi-agent reinforcement learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganga, B.; Lata, B.; Venugopal, K. Object detection and crowd analysis using deep learning techniques: Comprehensive review and future directions. Neurocomputing 2024, 597, 127932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duja, K.U.; Khan, I.A.; Alsuhaibani, M. Video Surveillance Anomaly Detection: A Review on Deep Learning Benchmarks. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 164811–164842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, V.; Karunanayake, I.; Ahmed, N. Intelligence at the extreme edge: A survey on reformable TinyML. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z. From simple digital twin to complex digital twin part II: Multi-scenario applications of digital twin shop floor. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2023, 56, 101915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Dong, N.; Li, W.; Cao, J. Edge computing with artificial intelligence: A machine learning perspective. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Lu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Shu, L.; Zheng, X.; Liu, A.; Xie, M. When sensor-cloud meets mobile edge computing. Sensors 2019, 19, 5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Guo, J.; Zeng, J.; Li, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, T. Incorporating Startup Delay into Collaborative Edge Computing for Superior Task Efficiency. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/ACM 32nd International Symposium on Quality of Service (IWQoS), Guangzhou, China, 19–21 June 2024; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, H.; Yu, Z.; Bin, G.; Xiao, M.; Wu, J. Federated distributed deep reinforcement learning for recommendation-enabled edge caching. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2024, 17, 3640–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeik, F.; Avgeris, M.; Spatharakis, D.; Santi, N.; Dechouniotis, D.; Violos, J.; Leivadeas, A.; Athanasopoulos, N.; Mitton, N.; Papavassiliou, S. Task offloading in Edge and Cloud Computing: A survey on mathematical, artificial intelligence and control theory solutions. Comput. Netw. 2021, 195, 108177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wu, T.; Chen, X.; He, S.; Guo, D.; Wu, J. Reverse auction-based computation offloading and resource allocation in mobile cloud-edge computing. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2022, 22, 6144–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Arif, M.; Wang, J.; Jin, Q. An intelligent dynamic offloading from cloud to edge for smart iot systems with big data. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2020, 7, 2598–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trilles, S.; Hammad, S.S.; Iskandaryan, D. Anomaly detection based on artificial intelligence of things: A systematic literature mapping. Internet Things 2024, 25, 101063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.C.; Ding, M.; Pathirana, P.N.; Seneviratne, A.; Li, J.; Poor, H.V. Federated learning for internet of things: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1622–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, C.; Wang, W. A survey on model compression for large language models. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2024, 12, 1556–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xiao, A.; Wu, S.; Jiang, C.; Kuang, L.; Shi, Y. Adaptive partitioning and placement for two-layer collaborative caching in mobile edge computing networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2024, 23, 8215–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Qin, Z.; Tao, X. Meta federated reinforcement learning for distributed resource allocation. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 23, 7865–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, I.; Tofigh, F.; Piccardi, M.; Abolhasan, M.; Franklin, D.; Lipman, J. Secure multi-party computation for machine learning: A survey. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 53881–53899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demelius, L.; Kern, R.; Trügler, A. Recent advances of differential privacy in centralized deep learning: A systematic survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2025, 57, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Jin, R.; Quek, T.Q.; Wong, K.K. An edge-cloud collaboration framework for generative AI service provision with synergetic big cloud model and small edge models. IEEE Netw. 2024, 38, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Han, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J. Lyapunov-Assisted Decentralized Dynamic Offloading Strategy based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 12, 8368–8380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhang, R.; He, Z.; Li, K. Joint Optimization of Trajectory, Offloading, Caching, and Migration for UAV-Assisted MEC. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2024, 24, 1981–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.; Zhao, L.; Fernando, X. Task offloading and resource allocation in vehicular networks: A Lyapunov-based deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 13360–13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantas, P.V.; Sabino da Silva, W., Jr.; Cordeiro, L.C.; Carvalho, C.B. A comprehensive review of model compression techniques in machine learning. Appl. Intell. 2024, 54, 11804–11844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Hao, Y.; Cao, X.; Fang, Y.; Lin, X.; Mao, H.; Xu, Z. Dynamic Graph Embedding via Meta-Learning. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2023, 36, 2967–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ding, J.; Feng, L.; Tan, K.C.; Li, K. Solving Expensive Optimization Problems in Dynamic Environments with Meta-learning. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2024, 54, 7430–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Yin, M.; Wang, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Zheng, X.; Wang, T. Collaborative Edge Server Placement for Maximizing QoS with Distributed Data Cleaning. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchinato, D.; Erseghe, T.; Rossi, M. Elastic and predictive allocation of computing tasks in energy harvesting IoT edge networks. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2021, 8, 1772–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, X. Edge AI: On-demand accelerating deep neural network inference via edge computing. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2019, 19, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsgaard, H.J.; Grenier, A.; Katare, D.; Taufique, Z.; Shakibhamedan, S.; Troccoli, T.; Chatzitsompanis, G.; Kanduri, A.; Ometov, A.; Ding, A.Y.; et al. Adaptive approximate computing in edge AI and IoT applications: A review. J. Syst. Archit. 2024, 150, 103114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.I.; Galindo, M.; Xie, H.; Wong, L.K.; Shuai, H.H.; Li, Y.H.; Cheng, W.H. Lightweight deep learning for resource-constrained environments: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 56, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Gill, S.S. Edge AI: A survey. Internet Things-Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2023, 3, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Gu, Q.; Sun, P.; Zhou, X.; Leung, V.C.; Fan, X. Incentive-Driven and Energy Efficient Federated Learning in Mobile Edge Networks. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2025, 11, 832–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, X.; Li, E.; Zeng, L.; Luo, K.; Zhang, J. Edge intelligence: Paving the last mile of artificial intelligence with edge computing. Proc. IEEE 2019, 107, 1738–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Duan, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, F. Stochastic long-term energy optimization in digital twin-assisted heterogeneous edge networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2024, 42, 3157–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Shao, J.; Zhang, X.; Lin, Z.; Pan, H.; Li, D.; Zhang, J.; Letaief, K.B. Large language models empowered autonomous edge AI for connected intelligence. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2024, 62, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Han, Z. Hybrid quantum-classical computing for future network optimization. IEEE Netw. 2022, 36, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Lin, Y.; Gao, Z.; Yu, X.; Xie, Z. Diffusion Model Empowered Efficient Data Distillation Method for Cloud-Edge Collaboration. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2025, 11, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, M.; Sood, S. Quantum-Computing-Inspired Optimal Power Allocation Mechanism in Edge Computing Environment. IEEE Internet Things J. 2024, 11, 17878–17885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.; Ambainis, A.; Augustino, B.; Bärtschi, A.; Buhrman, H.; Coffrin, C.; Cortiana, G.; Dunjko, V.; Egger, D.J.; Elmegreen, B.G.; et al. Challenges and opportunities in quantum optimization. Nat. Rev. Phys. 2024, 6, 718–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeini, H.K.; Shomali, R.; Pishahang, A.; Hasanzadeh, H.; Mohammadi, M.; Asadi, S.; Lonbar, A.G. PINN-DT: Optimizing Energy Consumption in Smart Building Using Hybrid Physics-Informed Neural Networks and Digital Twin Framework with Blockchain Security. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.00331. [Google Scholar]
| AI Method | Problem | Goal | Contribution | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supervised learning (SL) | Data labeledness requirement | Classification and prediction | Learns from labeled data for tasks like classification/regression | [28] |
| Linear regression | Modeling linear relationships | Reduce prediction error | Applies to continuous output prediction tasks | [29] |
| Support vector machines (SVMs) | Nonlinear classification | Improve classification accuracy | Learns complex boundaries via kernel tricks | [30] |
| Decision trees | Decision interpretability | Simplify decisions | Hierarchical rule-based decisions for interpretability | [31] |
| Neural networks | Complexity in DL | Improve transparency | Layered learning + interpretability of internal representations | [32] |
| Unsupervised learning (UL) | Unstructured data without labels | Discover hidden patterns | Enables clustering/correlation/dimensionality reduction | [27] |
| Semi-supervised learning (SSL) | Label scarcity | Boost learning performance | Combines labeled and unlabeled data to balance efficiency and accuracy | [33] |
| DL offloading mechanism | Offloading DL workloads | Runtime efficiency | Optimizes edge DL execution with adaptive offloading and resource allocation | [34] |
| Reinforcement learning (RL) | Exploration vs. exploitation in RL | Learn optimal action policy | Balances reward seeking and state–space exploration | [35] |
| RL for UAVs | UAV trajectory planning | Real-time decision optimization | Learns adaptive policies via interaction with environment | [36] |
| Federated learning (FL) | Privacy in distributed training | Protect user data | Trains global model while keeping data local | [37] |
| Personalized FL | Poor personalization in FL | Personalize global model | Aggregates local models for better personalized prediction | [39] |
| Mathematical Methods | Problem | Goal | Contribution | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear/nonlinear programming | Resource allocation and task scheduling | Balance energy and latency | Mathematical modeling for optimized offloading and resource coordination | [46,50,51] |
| Multi-objective optimization | Trade-offs in UAV edge computing | Improve scheduling efficiency | Pareto-based optimization balancing performance and resource use | [52] |
| SGD | Large-scale distributed training | Reduce delay and communication | Distributed SGD with high-probability convergence guarantees | [53] |
| Dynamic programming | Energy strategy for vehicles | Minimize operating costs | Multi-dimensional optimization for smart transport systems | [54] |
| Probability models | Uncertainty and faults | Enhance prediction and robustness | Demand fluctuation prediction and fault inference | [55,56] |
| Statistical learning | Load balancing and risk assessment | Improve generalization and fault tolerance | Data resampling and failure probability modeling | [58,60] |
| Copula theory | Dependency modeling | Optimize cooperation | Multivariate dependency modeling for collaborative computing | [59] |
| Queuing models | Task latency and congestion | Reduce queuing delay | Priority-aware and scalable queuing systems for edge/cloud | [61,64,77] |
| Petri net, fluid model, Queuing Game | Bottleneck detection and fairness | Optimize performance and fairness | Stochastic modeling for congestion control and fairness enhancement | [63,65,66] |
| Game theory | Task/resource allocation under competition | Improve system efficiency | Incentive and pricing models for fair and efficient resource sharing | [67,68,69,70] |
| Auction theory and contract theory | Market-based resource trading | Reduce waste and ensure cooperation | Economic models for edge market and federated learning incentives | [71,72] |
| Graph theory | Network topology and scheduling | Optimize structure and communication | Topology-aware scheduling and resource clustering models | [73,74,75,76] |
| Field | Goal | AI | Mathematical Method | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intelligent transportation systems | Autonomous driving | ✓ | Decision trees, Kalman filters | [81] |
| Task offloading and resource allocation | ✓ | Multi-objective optimization | [86] | |
| Smart Cities | Urban energy management | ✓ | Markov decision | [90,91] |
| Public safety and emergency response | ✓ | Regression, statistical modeling | [92,93] | |
| Intelligent healthcare | Remote disease diagnosis | ✓ | Optimization | [100,102,103,104] |
| Epidemic surveillance | ✓ | Statistical forecasting | [109] | |
| Smart Retail | Personalized recommendation | ✓ | Collaborative filtering, matrix factorization | [112,113,115] |
| Unmanned retail | ✓ | Queuing models | [116,117,120] |
| Key Issues | Handoff | Edge Collaboration | Provided APIs | Client Modification | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heterogeneous data integration | Number of abnormal nodes | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | [130,131,132] |
| Compatibility across devices | ✓ | × | ✓ | [131] | |
| Communication cycles and latency | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | [133,134,135,136] | |
| Computational complexity and scalability | Computational delay | ✓ | ✓ | × | [137,138,139] |
| Model overhead | ✓ | × | × | [140] | |
| Communication costs and scalability | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | [141,142] | |
| Real-time processing | Latency | ✓ | ✓ | × | [144,145] |
| Processing delay | ✓ | ✓ | × | [146,147] | |
| Adaptive update cycles | ✓ | × | × | [146] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, Y.; Bi, X.; Shen, R.; He, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, X. When Mathematical Methods Meet Artificial Intelligence and Mobile Edge Computing. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111779
Liang Y, Bi X, Shen R, He Z, Wang Y, Xu J, Zhang Y, Fan X. When Mathematical Methods Meet Artificial Intelligence and Mobile Edge Computing. Mathematics. 2025; 13(11):1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111779
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Yuzhu, Xiaotong Bi, Ruihan Shen, Zhengyang He, Yuqi Wang, Juntao Xu, Yao Zhang, and Xinggang Fan. 2025. "When Mathematical Methods Meet Artificial Intelligence and Mobile Edge Computing" Mathematics 13, no. 11: 1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111779
APA StyleLiang, Y., Bi, X., Shen, R., He, Z., Wang, Y., Xu, J., Zhang, Y., & Fan, X. (2025). When Mathematical Methods Meet Artificial Intelligence and Mobile Edge Computing. Mathematics, 13(11), 1779. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13111779








