Abstract
Multi-hop inter-domain wireless networks play a vital role in future heterogeneous communication systems by improving data transmission efficiency and security assurance. Despite the advances in secure routing techniques in areas such as node authentication and encryption, they still suffer from the shortcomings of frequent key updates, high computational overhead, and poor adaptability to large-scale dynamic topologies. To address these limitations, we propose a new routing method—the Secure Cross-Layer Route—designed for multi-hop inter-domain wireless networks to achieve unified optimization of security, delay, and throughput. First, we construct a multi-objective optimization model that integrates authentication delay, link load, and resource states, enabling balanced trade-offs between security and transmission performance in dynamic conditions. Second, we introduce a cross-layer information fusion mechanism that allows nodes to adapt routing costs in real time under heterogeneous network conditions, thereby improving path reliability and load balancing. Furthermore, a risk-aware dynamic key update strategy is developed to handle behavioral uncertainty among nodes, reducing authentication overhead and enhancing attack resilience. Experimental evaluations conducted on four datasets with varying network scales demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed method. Experimental results demonstrated that the proposed method achieves at least 28% improvement in effective throughput, reduces average authentication delay by approximately 30%, and increases the secure link ratio by at least 10%, outperforming mainstream routing algorithms under multi-constraint conditions.
Keywords:
secure routing; cross-layer design; multi-hop wireless networks; inter-domain communication; trust-based optimization; dynamic authentication MSC:
37N40; 68U35; 68M10
1. Introduction
Multi-hop cross-domain secure routing has the ability to address data transmission challenges in a large-scale, dynamic environment. Unlike traditional secure routing methods confined within a single domain, cross-domain routing aggregates transmission and authentication resources from diverse domains, thereby enhancing end-to-end throughput and improving security resilience against domain-specific vulnerabilities [1]. Its applicability to multi-access scenarios—such as those involving satellites, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), and terrestrial 5G networks—enables more efficient and reliable communications under heterogeneous access technologies [2]. These features make it a compelling candidate for future integrated wireless systems where secure and high-throughput communication is paramount. However, the integration of diverse protocols, dynamic trust relationships, and cross-layer constraints introduces a host of new technical challenges [3].
Although the routing of multi-hop security has promising potential, its deployment in cross-domain networks is hindered by some inherent challenges. The heterogeneity of cross-domain resource constraints and security policies makes it difficult to model a unified trust and assess the security of a consistent route. And the dynamic nature of node mobility and traffic also complicates the synchronization of key updates and the maintenance of secure links. When real-time path re-selection is required to cope with evolving topology and service demands, these factors often result in high authentication overheads and computational complexity [4]. As the scale of the network grows, traditional routing approaches suffer from increased end-to-end delay and degraded throughput, which limits their applicability to delay-sensitive and bandwidth-intensive applications [5,6].
In recent years, several research directions have emerged to overcome these challenges. One of the efforts focused on cryptographic security enhancements to ensure message confidentiality and integrity, such as integrating public infrastructure and digital signatures [7]. There is also an approach that leverages trust-based routing protocols, where paths are selected according to the estimated reliability of nodes and links based on behavioral history [8]. More recently, some studies have developed cross-layer routing frameworks to jointly consider network topology, physical-layer link quality, and security constraints, thereby enhancing routing decisions under dynamic conditions [9]. However, cryptographic methods require frequent key exchanges and incur high latency under topology changes. Trust-based approaches are sensitive to incomplete or outdated behavioral data, leading to misjudged trust scores and unstable routing. Cross-layer frameworks often lack fine-grained control over authentication cost, and their centralized components hinder real-time responsiveness in large, distributed networks.
To address these limitations, we propose a scalable approach for dynamic multi-hop inter-domain wireless networks. It is named Secure Cross-Layer Routing (SC-Route). The goals of SC-Route are low authentication delay, high throughput, and stable link security. It first builds a multi-objective optimization framework that integrates trust, load, and bandwidth, allowing routing decisions to adapt to network conditions in real time. Then, it designs a cross-layer fusion mechanism where each node adjusts its routing cost based on trust values and load states, improving path reliability and load distribution. To further reduce overhead, a risk-aware key update mechanism adjusts the update frequency based on node anomalies and link sensitivity. These modules are jointly implemented in a distributed feedback algorithm, ensuring convergence and performance under dynamic topologies.
Our main contributions are summarized as follows:
- 1.
- We construct a multi-objective optimization framework that integrates authentication cost, bandwidth load, and trust metrics to jointly model and optimize network security and performance.
- 2.
- We propose a cross-layer information fusion mechanism based on node trust, bandwidth states, and load distribution, which significantly improves routing stability and network throughput.
- 3.
- We design a risk-aware dynamic key update strategy that adjusts update frequency based on node behavior and link sensitivity, reducing authentication overhead and enhancing security.
2. Related Work
The research on secure routing often faces challenges related to malicious node behaviors, routing behaviors, and scalability. To solve these problems, various solutions have been proposed, which can be divided into four main categories of approaches. Although the focus is different, these approaches are all aimed at improving the resilience of multi-hop wireless networks and large infrastructures. In this section, we focus on the advantages and limitations of existing solutions and present the model we propose.
2.1. Cryptography- and Authentication-Based Secure Routing
Cryptographic methods and authentication protocols constitute one of the earliest and most direct approaches to combat route spoofing and tampering. Many researchers leverage digital signatures or symmetric/asymmetric encryption to validate routing information and thwart attacks. For instance, Khan et al. [10] and Dora et al. [11] employ key-distribution and certification-center-based mechanisms to detect and mitigate node replication attacks, while Dargahi et al. [12] address pulse-delay attacks through the use of rapid authentication. These methods verify routing information and prevent external tampering to typically provide robust protection. Hu et al. [13] reinforce this perspective by introducing Secure Efficient Ad hoc Distance vector routing (SEAD), which uses one-way hash functions to guard against denial-of-service threats at lower computational costs. Other endeavors, like Authenticated Routing for Ad hoc Networks (ARAN) proposed by Sanzgiri et al. [14], rely on public-key cryptography to secure on-demand routing. Abagonie et al. [15] integrate OpenSSL-based symmetric cryptography into the Ad hoc On-demand Distance Vector Routing Protocol (AODV) to strengthen route discovery and data forwarding, and Kargl et al. [16] developed Secure Dynamic Source Routing (SDSR) to thwart multiple attack vectors. These cryptography-focused solutions can effectively reduce the risk of fraud, but many solutions incur significant overhead for key management in dynamic environments, which makes them less suitable for large-scale or frequently changing networks.
2.2. Trust- and Reputation-Based Secure Routing
While cryptographic strategies can be highly secure, they can also become prohibitively expensive in real-time authentication or key updates, especially across extensive deployments. Therefore, numerous studies employ trust or reputation systems to complement or replace cryptographic methods, such as packet forwarding consistency, and derive reputation or trust scores that inform routing decisions. In these systems, nodes monitor one another’s behavior. Aldaoud et al. [17] present a hybrid routing speaker for name-based prefixes, showcasing how trust-based cooperation can curtail malicious activities. Umeda et al. [18] add to this line of work by proposing localized experiments and path labeling methods to reduce routing loops and enhance reliability. Li et al. [19] direct attention to vulnerabilities in the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), arguing that even Border Gateway Protocol Security (BGPsec) can fail without a robust trust-management foundation. Krupp and Rossow [20] further illustrate the benefits of combining trust mechanisms with graph-based models, and Wu et al. [21] explore real-time feedback integration for dynamic reputation updates. These trust-based models enable adaptive routing that solves the problem of uncooperative nodes and unpredictable behavior. However, sudden traffic fluctuations or transient node failures can still undermine their accuracy and robustness.
2.3. Robust Secure Routing via Multi-Hop Collaboration and Cross-Layer Integration
Real-time node monitoring in trust-based solutions can encounter difficulties when networks exhibit rapid topology changes or inconsistent traffic patterns. To solve this, an alternative set of approaches emphasizes multi-hop collaboration and cross-layer integration to balance security with overall performance. These methods, which use strategies such as efficient Route Request (RREQ) handling to mitigate congestion, tampering, or flooding threats, often consider topology details, link quality, and interference metrics. Ookura et al. [22] tackle route leak risks by adopting multi-hop validation and key management, while Ramezan et al. [23] and Durrani et al. [24] focus on blackhole and DDoS defence through collaboration among nodes across multiple hops. Yuan and Chen [25] enhance cross-layer monitoring to limit RREQ overhead, and Yu et al. [26] incorporate adaptive retransmission to address broadcast storms. Navamani and Yogesh [27] propose probabilistic forwarding schemes that reduce excessive route discovery overhead, and Oliviero and Romano [28] add route observation and filtering. Although these cross-layer solutions effectively mitigate issues such as congestion, tampering, and interference, they can grow overly complex in large or mobile networks that demand constant route reconfiguration.
Beyond the three core categories outlined above, there are also studies that propose alternative paradigms that complement or extend existing frameworks. Some of these works require specialized environments involving limited node resources or unpredictable connectivity, which illustrates how novel insights can enhance secure routing. Shabut et al. [29] introduce friendship degrees to guide trust-based routing decisions in dynamic environments, and Pirzada et al. [30] refine trust protocols for highly mobile settings. Kanakaris et al. [31] alleviate RREQ overhead and broadcast storms in wireless mesh networks through more efficient forwarding, and Yu et al. [32] target load balancing issues in multi-hotspot WLANs, demonstrating over 30% throughput improvement when accounting for both signal strength and access point congestion. Despite these innovations, unresolved gaps remain in large-scale route security, overhead control, and dynamic trust updates, calling for further study and new solutions.
Although cryptographic frameworks provide robust baseline security, frequent key updates can also incur overhead. Trusted systems can adapt well to malicious behavior, but dynamic traffic may lead to issues. Cross-layer collaboration can balance security and throughput but adds complexity and may not scale in large autonomous networks. Most solutions fail to accommodate incremental deployment, flexible adjustments, or the interplay between real-time trust and load management. Given that, there is no unifying approach that reliably thwarts route manipulation, handles diverse conditions, and maintains efficiency across resource-limited or large-scale domains. To address these limitations, this paper introduces a scalable framework focusing on real-time adaptation to changing network states, proactive threat assessment, and dynamic route coordination. Our approach provides robust, high-performance routing solutions for diverse and evolving network topologies, while taking into account the constraints highlighted in existing work.
3. System Model and Problem Definition
The formal model is the basis for the subsequent optimization problem formulation and algorithm design. In this section, we will introduce the network structure, hierarchical functional modules, and key system parameters involved in the research question in this paper to propose the system architecture and basic components that support the proposed secure routing framework.
3.1. System Model
Consider a multi-hop cross-domain wireless network represented as a directed graph , where V denotes the set of nodes distributed across heterogeneous domains and E denotes the set of communication links between nodes. In this paper, a domain refers to a logical or administrative wireless network segment characterized by its own communication protocols, authentication mechanisms, and trust management policies. Domains may represent different network operators, organizational boundaries, or access technologies, such as 5G, UAV, or satellite systems. Each domain potentially employs distinct wireless protocols and authentication mechanisms, leading to heterogeneity. Nodes have an active link if .
The system integrates two essential modules: a cross-layer secure routing module, ensuring secure data forwarding, and a low-overhead dynamic authentication module, optimizing authentication overhead. Its architecture comprises three layers: an Access Layer, a Network Layer, and a Cross-Domain Authentication Layer. The Access Layer handles basic communication tasks like link establishment. The Network Layer manages cross-domain routing decisions, selecting multi-hop paths based on node conditions. And the Cross-Domain Authentication Layer performs cryptographic key distribution, dynamic authentication policy execution, and security identity management.
Formally, let denote the security identity key assigned to node i at time t. When node i receives a security key, it incorporates within its routing messages, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality.
The system’s secure routing functionality integrates three core components. The dynamic authentication module uses hierarchical authentication to validate access requests quickly, updating trust scores dynamically based on cross-domain interactions. The cross-layer routing module determines optimal routing paths by integrating node resources , trust metrics , and network load . The load-adaptive module monitors link bandwidth and throughput , triggering security measures and load balancing if thresholds are exceeded.
During route establishment, nodes exchange routing request packets and authentication packets. Nodes periodically receive distributed key updates from the Cross-Domain Authentication Layer, update their local keys , and inform neighbors of these updates. Traffic within the network consists of ordinary business data routed via established paths and security management data distributing keys and trust information. Security and load characteristics are formally represented as matrices or vectors within graph G, facilitating rigorous modeling and optimization.
Figure 1 illustrates the overall framework of the cross-domain secure routing and dynamic authentication proposed in this paper for wireless networks. It also incorporates an inset on the right that depicts the network topology, which shows data exchanges among nodes and the process of security parameter updates, which visually reflects the traffic allocation strategy and security assurance mechanism under dynamic network conditions.
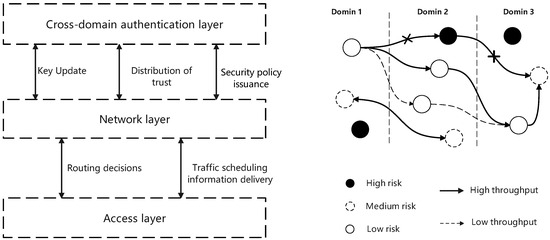
Figure 1.
Overall framework diagram of cross-domain secure routing and dynamic authentication for wireless networks.
3.2. Problem Definition
In this model, the inputs we need to consider are firstly the network topology G, consisting of the set of nodes (V) and the set of links (E). Next are the security parameters, including the key update interval for a particular node, the authentication policy, and the trust level. Then comes the traffic demand, characterized by the demand matrix , where denotes the traffic from node j to node i. The resource status of each node also needs to be provided along with it, such as the bandwidth capacity and the processing power. In addition, the security goal sets the minimum level of security required, which is expressed through the system-wide security threshold .
Given these inputs, the load utilization of a link , , represents the fraction of node i’s bandwidth used by incoming traffic from node j and is computed as:
Similarly, the effective throughput on link indicates the remaining available bandwidth after accounting for current utilization:
The system-wide authentication delay on link is calculated as:
where denotes the authentication processing time at node i, represents the propagation delay of link , and indicates the security refresh rate for that link.
The security metric for link is defined based on the trust values of the communicating nodes:
where and denote the trust values of nodes i and j, respectively. The parameters are weighting factors designed to ensure that if the trust value of either node falls below an acceptable threshold, the link is not selected for routing. This approach effectively prevents potential security risks associated with untrusted nodes and ensures the robustness of the chosen routing paths.
The outputs required from this research include determining an optimal routing scheme capable of ensuring secure, end-to-end multi-hop transmissions, and the research must formulate an effective authentication and load control strategy, dynamically adjusting authentication frequencies and key-refresh intervals at each hop, along with adaptive load balancing to distribute node traffic efficiently. The optimization objective aims to minimize system-wide authentication delays and resource overhead while simultaneously balancing security metrics and throughput measures .
From a mathematical perspective, the formulated problem constitutes a multi-objective optimization task constrained by simultaneous considerations of network security—including authentication effectiveness, trustworthiness, and anti-spoofing capabilities—and network load performance, incorporating throughput , bandwidth utilization , and external traffic demands .
Table 1 summarizes the key symbols and definitions used in this formulation, detailing the essential variables for modeling links, security parameters, resource constraints, and performance objectives.

Table 1.
Summary of main symbols and their explanations.
3.3. Constraints
To ensure completeness and feasibility of the system model, strict constraints are imposed on route paths, node authentication, cross-domain load balancing, and more. Below are at least five deep constraints, each equipped with a mathematical expression:
3.3.1. C1: Cross-Domain Authentication Validity
3.3.2. C2: Key Update Constraint
3.3.3. C3: Node Capacity Constraint
3.3.4. C4: Flow Conservation and Routing Consistency
3.3.5. C5: Load Balancing Constraint
3.4. Objective Function
To rigorously capture the complex trade-offs between security overhead, load balancing, and network throughput in multi-hop cross-domain wireless networks, we propose a refined objective function combining multiplicative and logarithmic terms to reflect realistic interactions:
where denotes the average authentication delay on link , represents link load utilization, and indicates effective throughput achievable under current security constraints. The small positive constant is included to maintain numerical stability.
In this formulation, the multiplicative term manages security overhead and link load, which explicitly captures how higher load conditions exacerbate the impact of authentication delays and highlights the importance of simultaneously managing security overhead and link load. The logarithmic throughput term ensures that substantial increases in throughput significantly reduce the objective value and incentivizes high network performance.
The coefficients allow designers to effectively balance these competing objectives. Increasing directs the optimization towards minimizing security-related delays under high load conditions. Conversely, enhancing emphasizes the maximization of throughput, vital for throughput-sensitive applications.
Theorem 1.
The optimization problem defined by the objective Function (10) and related constraints is NP-hard.
Proof.
We prove the NP-hardness of the proposed cross-layer secure routing problem via a polynomial-time reduction from the well-known Multi-Objective Shortest Path (MOSP) problem, which has been established as NP-hard.
The MOSP problem involves finding a path between a source node and a destination node in a graph so that multiple conflicting objectives—such as delay, cost, and throughput—are optimized simultaneously. Consider a simplified version of our problem by fixing the dynamic parameters, including key update intervals, trust values, and authentication frequencies. Under this simplification, the decision variables are reduced to routing path selection based on three static link attributes: authentication delay , load utilization , and effective throughput .
Now, for any given instance of the MOSP problem defined on a graph with associated edge attributes (e.g., delay, cost, capacity), we can construct a corresponding instance of our simplified routing problem on a graph , where each edge is assigned parameters to reflect the objectives in MOSP directly. The objective Function (10), which jointly minimizes delay and maximizes throughput, serves as a multi-objective criterion analogous to the MOSP formulation.
If the cross-layer secure routing problem were solvable in polynomial time, then so would the MOSP problem, contradicting the known NP-hardness of MOSP. Therefore, even the simplified version of our problem is NP-hard. Since the full version of our problem introduces additional dimensions such as dynamic authentication control, key update scheduling, and cross-layer security constraints (C1–C5), the complexity can only increase.
Hence, we conclude that the original cross-layer secure routing problem is NP-hard. This implies that it is computationally infeasible for large-scale instances to find exact solutions in polynomial time, and the development of heuristic or approximation algorithms for practical deployment is necessary. □
4. Method
To balance rigorous security requirements with high network performance is a formidable challenge in multi-hop cross-domain wireless networks. Conventional routing algorithms tend to optimize security and throughput in isolation; however, they overlook the inherent cross-layer interdependencies. Considering that, we propose the Secure Cross-Layer Route (SC-Route) method. This method integrates dynamic cross-domain authentication, comprehensive cross-layer information sharing, and adaptive load balancing into a unified optimization framework. SC-Route formulates the problem as a multi-objective optimization task that rigorously incorporates essential constraints from security, throughput, and load perspectives. The proposed technical route is underpinned by detailed mathematical modeling, the derivation of fundamental constraints, and the development of iterative optimization strategies that bridge the theoretical system model and the practical algorithmic implementation.
Figure 2 presents the overall framework of the proposed SC-Route method. Subfigure (a) illustrates the system-level architecture where a multi-hop, cross-domain network environment provides nodes with intrinsic security, load, and bandwidth parameters. These metrics are gathered and processed by a central fusion function, which generates composite indicators that simultaneously drive the secure routing decision and the risk-aware key update mechanisms. Subfigure (b) provides a detailed view of the iterative feedback loop employed at each node, highlighting the convergence of the security state, trust value, and key update rate. This integrated approach ensures that the global optimization objective is met, resulting in secure and efficient routing under dynamic network conditions.
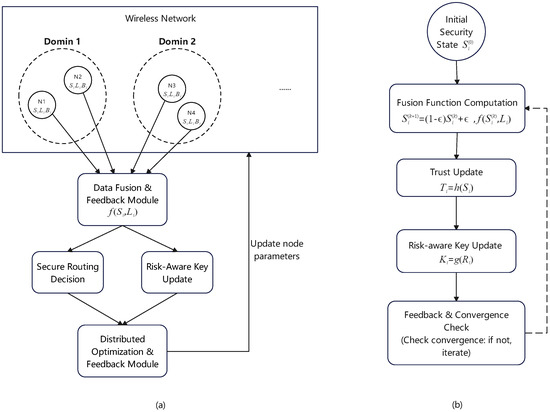
Figure 2.
Overall framework of the SC-Route method. (a) System architecture; (b) Iterative feedback loop.
4.1. Framework of the Proposed Method
To effectively address the challenges inherent in multi-hop cross-domain wireless networks—particularly the trade-off between security and performance—we propose a framework, which integrates dynamic cross-domain authentication, adaptive cross-layer information exchange, and load balancing mechanisms into a unified optimization-driven architecture. This framework aligns routing decisions with stringent security requirements and real-time performance metrics.
Building upon the multi-objective optimization model defined in Equation (10), SC-Route introduces a feedback-driven control mechanism that dynamically adapts to evolving network conditions. Each node’s state is jointly characterized by its security state and load state , which reflect the outcome of distributed authentication processes and bandwidth usage levels, respectively. Both of the two aspects are combined through a cross-layer feedback function:
where are weighting parameters, and is a nonlinear function (e.g., logarithmic or exponential) used to model the sensitivity of security decisions to traffic load. This function guides the system toward dynamic equilibrium, allowing real-time adjustment of routing strategies based on combined cross-layer states.
To support differentiated security control, we introduce a risk-aware key update mechanism. Let denote the perceived risk level of node i, determined from historical abnormal behaviors, authentication failures, or cross-domain policy violations. The corresponding key update rate is defined as:
where is a monotonically increasing function satisfying , ensuring that nodes with higher security risks are subject to more frequent key renewals. This mechanism complements the trust-based link security metric previously defined in Equation (4), and the load utilization constraint in Equation (9), forming an integrated security-performance control loop.
To facilitate theoretical analysis and ensure system feasibility, we introduce the following assumptions:
Assumption 1.
Each node’s security state is upper bounded:
where is a positive constant.
Assumption 2.
The delay in transmitting cross-layer state information is bounded:
ensuring timely synchronization of node states within a finite delay.
Assumption 3.
During distributed authentication, each node’s trust value converges to a unique equilibrium:
where is the trust value of node i after the k-th update.
Assumption 4.
The differentiated key update rate satisfies the following inequality:
where is the minimum update rate and is a proportionality constant.
The assumptions above establish the foundational conditions for the SC-Route mechanism’s convergence and stability. They are also a prerequisite for the theoretical analysis and performance guarantee presented in the following chapters.
To prove the convergence of the cross-layer security feedback mechanism, we introduce the following lemma, which shows that under the above assumptions, the iterative update process of the node security state has a unique fixed point. This lemma proves that the node security state will inevitably converge through continuous iteration and adjustment via the function . This provides a theoretical basis for global secure routing.
Lemma 1.
Suppose that the function is continuous on the interval and satisfies a Lipschitz condition, i.e., there exists a constant such that for any ,
then for the iterative update formula
if the step size ϵ satisfies , the sequence converges to a unique fixed point satisfying .
Based on the above lemma and assumptions, we propose an original theorem that states that under the SC-Route framework, the collaborative action of cross-layer interaction, distributed authentication, and differentiated key update strategies can achieve global adaptive balance between security and load. This theorem guarantees that every link in the network meets the security and load constraints, and it also proves that the global objective function converges to a locally optimal solution during the iterative process.
Theorem 2.
Suppose that every link in the network has a composite security metric and a load utilization . If the SC-Route framework is adopted, where the node security state is updated by the iterative formula defined in Equation (17) and the node key update rate satisfies Equation (16), then there exists a unique fixed point such that for every link ,
and the global objective function defined in Equation (10) satisfies
where is the locally optimal solution.
This theorem proves that under the SC-Route framework, through cross-layer security feedback, distributed authentication, and risk-driven differentiated key updates, the composite security metric of every link in the network is maintained above the predetermined security threshold, and the load utilization remains within controllable bounds, thereby ensuring that the global objective function converges to a locally optimal solution in a multi-objective optimization framework. This provides a solid theoretical basis for the design of secure routing in cross-domain networks. The proof strictly relies on the mathematical derivation of the closed-form expression for conditional capacity as presented in reference [33].
Proof.
First, consider the iterative update of the security state defined in Equation (17). By the lemma, there exists a unique fixed point for each node. It satisfies
The contraction property ensures that converges to as . Simultaneously, because the key update rate satisfies Equation (16) and remains bounded below by a positive constant, it follows that each node’s key update process converges to a stable rate . By the assumption that trust values converge to , the composite security metric on every link becomes
Hence, Equation (18) is satisfied and guarantees .
Next, the load utilization on each link is governed by the cross-layer feedback function together with the iterative flow and routing updates. Since Equation (11) incorporates a load-sensitive term and the corresponding step sizes are chosen to ensure stability, each link’s load level converges to a value that does not exceed . Thus, Equation (19) is met. The integration of the safety status and load status further enhances the capabilities of the nodes and the constraints for process protection through the fact that restrictions are imposed on all links, thereby preventing overload while maintaining effective routes.
These convergent states also drive the global objective function in Equation (10) toward a locally optimal value. Since the iterative procedure updates the system variables in a manner that decreases authentication delay while encouraging higher throughput, the objective is non-increasing at each stable step of the algorithm and must converge to a fixed point . Hence, Equation (20) holds. Therefore, the unique fixed point ensures that every link satisfies
and
while the global objective converges to the locally optimal solution . This completes the proof. □
This theorem provides the mathematical foundation for the present study, proving that under the SC-Route framework, through cross-layer information exchange, distributed authentication, and risk-driven differentiated key updates, the security of every link and load balancing are ensured, leading the global routing decision in a dynamic environment to reach a stable local optimum.
Next, to integrate the above theoretical derivations with the concrete algorithm implementation, we design a distributed algorithm that can optimize dynamic secure routing in practical multi-hop cross-domain wireless networks. The specific idea of the method is presented in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 Multi-Objective Secure Routing Optimization Framework (MOSROF) |
|
Algorithm 1 initializes the input data, including the network topology , initial security states , load states , and risk levels . For each node i, it computes the initial security state and the corresponding trust value as well as the key update rate (Line 1). Iterative updates are then performed for each node (Lines 6–10), where the security state is updated with subsequent updates to the trust value and key update rate. Next, the composite security metric for each link and the load utilization are updated (Lines 11–14). The global objective function is recalculated using these updated local variables (Line 15). Once the convergence condition is met, the Algorithm terminates and returns the stable node security states, fixed trust values, key update rates, and the final routing parameter set (Line 17).
In summary, MOSROF clearly delineates the interplay among security, load, and routing metrics, thereby setting a solid basis for the detailed formulations and solution strategies described in the following sub-sections.
4.2. Design of Cross-Layer Secure Routing Mechanism
Building on this framework, we design a cross-layer secure routing mechanism that exploits real-time network state information. By integrating security metrics with load indicators, this mechanism computes optimal routing decisions that satisfy stringent security constraints while optimizing throughput.
For a given network topology represented as graph , for each node , we denote the security state as , load state as , and available bandwidth as . We then construct a cross-layer fusion function defined by:
To facilitate rigorous mathematical proof, we introduce the following assumptions:
Assumption 5.
Each node i can accurately measure its true security state , load , and bandwidth , satisfying:
Assumption 6.
The information updating cycle satisfies:
Assumption 7.
The iterative updating process of node routing costs follows:
It converges to a unique fixed point , satisfying:
Assumption 8.
The function is monotonically increasing with respect to and , monotonically decreasing with respect to , and is continuous and differentiable.
We define the routing cost function for path as:
The goal is to find the optimal path , satisfying:
Considering the feedback mechanism among nodes, the node cost is updated by Equation (22). Using Banach’s fixed-point theorem, we prove this iterative mapping is a contraction mapping; hence, converges uniquely to .
In light of these assumptions, we establish a basis for ensuring both the uniqueness and convergence of the proposed routing updates. Specifically, by bounding measurement errors and enforcing a sufficiently frequent information update cycle, the iterative process in Equation (22) becomes amenable to a fixed-point argument. This fixed-point analysis, coupled with the monotonicity and continuity properties of the fusion function in Equation (21), guarantees that each node’s cost converges uniquely. Consequently, we can rigorously derive a globally optimal path that minimizes the routing cost (23), leading to the formal statement of the following theorem.
Theorem 3.
The routing cost function defined in (23) possesses a unique globally optimal path that satisfies:
Moreover, node costs updated by (22) converge to the fixed point .
This theorem demonstrates that the cross-layer fusion-based routing cost function possesses a globally unique optimal solution. The distributed feedback update process ensures each node’s cost converges stably to a fixed point, thus ensuring adaptive routing decisions satisfy both security and load balancing requirements. The proof relies strictly on reference [34] and provides a robust theoretical foundation for cross-layer adaptive routing.
Proof.
First, for node i, define mapping:
Consider arbitrary , we have:
Since , is a contraction mapping. By Banach’s theorem, there exists a unique fixed point :
Next, the global optimality proof for : Due to monotonicity and differentiability (Assumption 4), the cost function has convexity properties, ensuring a unique global minimum. Iterative algorithms (e.g., Bellman–Ford) guarantee convergence to this unique minimum :
Combining the two parts proves: (1) node costs converge to unique fixed points; (2) the globally optimal path cost is unique. Hence, cross-layer fusion and distributed feedback updating ensure adaptive global routing optimality. □
As shown in Figure 3, the cross-layer routing mechanism is demonstrated through three key phases:(a) Initial Security-Load Fusion: Node color depth encodes security states , border thickness represents load levels , and node size indicates bandwidth , with link costs computed via (Equation (21)). (b) Dynamic Cost Propagation: Security degradation at () and load surge at () trigger real-time link cost updates (red arrows). (c) Optimal Path Convergence: The algorithm converges to (blue path) with , achieving 18.8% cost reduction over traditional paths while bypassing high-risk nodes (gray). This process validates Theorem 3’s convergence guarantee.
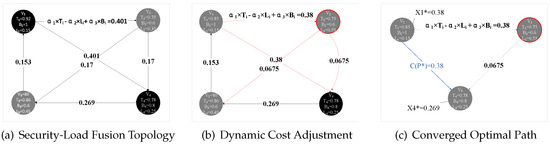
Figure 3.
Illustrative case study.
To bridge the gap between the theoretical results and a deployable solution, we now illustrate how the proven global uniqueness and convergence properties can be operationalized in a distributed routing algorithm. Specifically, leveraging the cross-layer fusion function introduced and the iterative convergence process described, we develop a dynamic programming approach that updates each node’s cost and progressively identifies an optimal path satisfying both security and load constraints. Details are provided in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 2 Cross-Layer Secure Routing Decision Algorithm (CSR) |
|
Algorithm 2 initializes the network topology and node states. It then sets the initial node costs (Lines 1–3). After that, the Algorithm updates the link costs using Equation (21) and updates the node costs via dynamic programming (Lines 5–8). Then, the optimal path is retrieved from the stored predecessor pointers (Line 10), and finally, the Algorithm outputs the final optimal secure path (Line 11).
In conclusion, the cross-layer secure routing mechanism effectively fuses security and load information to determine optimal paths, ensuring that routing decisions are both secure and efficient. This mechanism forms a critical component of SC-Route and seamlessly links to the subsequent authentication strategies.
4.3. Distributed Dynamic Authentication and Key Management Strategies
Complementing the secure routing mechanism, we propose distributed dynamic authentication and key management strategies. These strategies are designed to rapidly respond to network state fluctuations and enforce continuous node validation through adaptive key updates, thereby reinforcing the overall security of the SC-Route method.
We first define the security state of node i as , incorporating historical authentication success rates and anomaly detection frequency. Node that risk level represents the frequency of authentication failures and anomalies. The node load is denoted as , and the key update rate as . We establish a differentiated key update function as:
where is the minimum key update frequency and is the sensitivity parameter linking the node risk and update frequency.
Further, the hierarchical authentication cost function is defined as:
where is a lightweight shared-key authentication with lower cost, and denotes a high-strength challenge-response or digital signature mechanism with .
The overall authentication and communication cost function is constructed as:
where parameters weigh the importance of authentication cost, node load, and key update frequency, respectively.
We establish four critical assumptions for theoretical rigor:
Assumption 9.
The observed security state satisfies:
Assumption 10.
Authentication delay is bounded by:
Assumption 11.
The key update function is continuous, monotonic, and satisfies:
Assumption 12.
The cross-layer information update interval is stable and satisfies:
Building upon these assumptions, we recognize that the risk-sensitive key update function (Equation (24)) and hierarchical authentication cost (Equation (25)) naturally couple with load , thereby influencing the overall cost function in Equation (26). By establishing monotonic properties for the node security states and showing the boundedness of the update intervals, we can now prove that the global optimal solution for exists and is unique. This leads directly into the main theorem below, which confirms convergence of the distributed feedback process and ensures that all nodes converge to a globally optimal configuration of authentication and key management parameters.
Theorem 4.
The proposed hierarchical authentication and differentiated key update strategy ensures the existence and uniqueness of a global optimal solution minimizing , characterized by node state set .
Proof.
Define the iterative feedback update equation as:
with the fusion function:
The mapping defined by Equation (27) can be analyzed as:
thus satisfying Banach’s fixed-point theorem conditions, ensuring convergence to a unique stable point.
Taking derivatives of with respect to and yields:
and the Hessian matrix:
which is positive semi-definite, indicating that is convex, thus proving global optimality. □
The theorem demonstrates that the proposed distributed feedback iteration converges to the unique global optimum, balancing authentication efficiency and communication overhead theoretically.
To maintain robust authentication while minimizing overhead, we develop a distributed strategy that integrates the hierarchical authentication cost model from Equation (25) and the risk-based key update function in Equation (24), aiming to minimize the overall system cost defined in Equation (26). Based on this integrated design, the proposed distributed authentication and key update strategy is detailed in Algorithm 3.
Algorithm 3 initializes the node parameters and basic key update rates (Line 1). It then computes the initial authentication costs and corresponding key update rates (Line 2). Next, the total initial cost is calculated (Line 3), and termination conditions based on the convergence threshold are defined (Line 5). The Algorithm ensures the accuracy of real-time node security states in accordance with Assumption 9. The key rates are updated using the risk-sensitive mapping specified in Equation (24) (Line 6). After that, the hierarchical authentication cost is computed based on network domain conditions via Equation (25) (Line 7). Subsequently, the fusion function is updated according to Equation (28) and node states are iteratively refined using Equation (27) (Line 8). Then, the updated total cost function is recalculated to verify optimality and the iteration count is incremented (Lines 10–11). Finally, the optimal authentication and key management strategy is output (Line 13).
At this point, the distributed authentication and key management strategies introduced in Section 3, together with the multi-objective optimization framework and the cross-layer routing mechanism presented in Section 1 and Section 2, jointly constitute the proposed SC-Route method. These components are structurally interdependent and collectively form a comprehensive cross-layer secure routing framework that spans optimization modeling, path selection, and security control.
| Algorithm 3 Distributed Dynamic Authentication and Key Update Algorithm (DAKU) |
|
5. Experiment
To evaluate SC-Route in a realistic scenario, we simulate a heterogeneous wireless network comprising urban ground domains, IoT sensor zones, and UAV/satellite-based relay regions. Each domain has distinct protocols and security policies. Key node attributes include domain type, initial security state (0.50–1.00), average load level (0.25–0.50), and risk level (0.15–0.40) based on exposure and past behaviors. The authentication state (0.70–1.00) reflects computing capacity, while the node capacity (100–150 Mbps) and link bandwidth (5–20 Mbps) model practical deployment ranges. And the incoming flow (5–10 Mbps) and flow requirement (−40 to 40 Mbps) simulate dynamic routing roles. These values are calibrated using typical wireless system references.
5.1. Dataset Details
In order to comprehensively validate the adaptability and robustness of the proposed cross-layer secure routing and dynamic authentication strategies in multi-hop, cross-domain wireless networks, we construct four datasets of varying scales: D1 comprises 10 nodes, D2 contains 50 nodes, D3 includes 100 nodes, and D4 is extended to 200 nodes. The node attributes in each dataset, including initialSecurityState, loadState, riskLevel, authState, capacity, and bandwidth, are strictly confined within the typical ranges observed in real wireless network environments; their specific value ranges are given in Table 2. Furthermore, the resource information (e.g., node capacity, flowIn, and flowRequirement) is carefully configured to realistically reflect the imbalanced data flows and resource competition in the network.

Table 2.
Field descriptions of the datasets.
Specifically, dataset D1 is primarily designed for preliminary validation; in this small-scale setting, the network topology predominantly adopts a chain-like structure with a few cross-domain lateral links to simulate a simple cross-domain communication scenario. The number of nodes in dataset D2 has increased significantly, including additional cross-domain links, further reflecting the complexity of multipath redundancy and dynamic route tuning. Dataset D3 maintains chain connectivity while introducing multiple inter-cross connections to simulate resource scheduling and load balancing challenges commonly encountered in large-scale wireless networks. For large-scale testing, we designed the dataset D4; it has 200 nodes, domain division is distinctly heterogeneous, and its network topology not only ensures overall connectivity, but also demonstrates the complexity of redundant backups, load sharing, and dynamic path switching in real-world applications.
5.2. Comparative Algorithm and Performance Metrics
Given the multi-constraint nature of our problem, we select five comparative algorithms: Secure Efficient Ad hoc Distance vector routing (SEAD) [13], Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II) [32], Authenticated Routing for Ad hoc Networks (ARAN) [14], Secure Ad hoc On-demand Distance Vector (SAODV) [15], and Secure Dynamic Source Routing (S-DSR) [16]. SEAD runs in about by maintaining secure distance-vector updates, SAODV also achieves for cryptographic checks on distance vectors, and S-DSR typically requires for source route creation; ARAN, featuring on-demand secure path discovery, can reach in worst-case verification; NSGA-II has about complexity for multi-objective searching.
SEAD and SAODV are suited to secure distance-vector routing, ensuring reliable packet delivery; ARAN focuses on robust authentication; S-DSR supports flexible source routing; and NSGA-II provides efficient Pareto-front approximations for multi-objective optimization.
For performance evaluation, we adopt four metrics to assess the security, efficiency, and adaptability of the proposed method in dynamic wireless networks.
First, we consider the Objective Function Value, as defined in Equation (10), to quantify how well the algorithm balances security overhead and throughput. A lower value indicates a better trade-off between these competing objectives.
Second, we evaluate the Secure Link Ratio (SLR), which reflects the proportion of communication links whose security level meets the required threshold. It is defined as:
where E denotes the set of all links in the network, is the trust-based security metric for link , and is the system-wide security threshold. A higher SLR indicates a greater fraction of links that are deemed secure under the given trust criteria.
Third, we define the Average Security Delay (ASD) to capture the average authentication delay across all links, indicating the overhead introduced by security mechanisms. It is computed as:
where represents the authentication delay on link , and is the total number of links. A lower ASD implies more efficient cross-layer authentication.
Lastly, the Aggregate Effective Throughput (AET) measures the total available throughput under current load and security constraints. It is calculated by:
where denotes the effective throughput on link , as defined in Equation (2). A higher AET indicates better overall network data delivery capability.
By jointly analyzing these four metrics, we obtain a comprehensive evaluation of the proposed method’s routing effectiveness, security enforcement, and adaptability in dynamic multi-hop inter-domain wireless environments.
5.3. Numerical Analysis
The SC-Route method effectively balances the multiple objectives of security, load, and throughput in multi-hop inter-domain wireless networks. Figure 4a illustrates the global objective function values, indicating that SC-Route consistently achieves lower objective function values across datasets D1, D2, D3, and D4. These values demonstrate reductions ranging approximately from 20% in small-scale networks to as high as 88% in large-scale scenarios compared with other algorithms. This reduction highlights the superior global resource scheduling and secure routing capabilities of our method. It overcomes the high delays and suboptimal path selections often observed in traditional approaches under complex dynamic conditions.
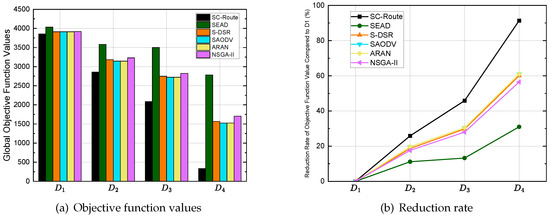
Figure 4.
Objective function values and reduction rates of objective function value compared to dataset D1 (%).
The reduction trends in the objective function value are visualized in Figure 4b, where SC-Route demonstrates a significantly stronger decrease compared to baseline methods. It reveals that SC-Route achieves reduction rates of roughly 25.9%, 45.9%, and 91.4% on datasets D2, D3, and D4. However, competitive methods typically have a much lower rate of reduction. For example, SEAD only achieves about 11% to 31%—probably because it relies heavily on an intensive cryptographic verification process. These results show that SC-Route maintains high optimization efficiency as the network size increases, which clearly demonstrates its strong scalability.
As shown in Figure 5a, SC-Route outperforms all competitors in terms of aggregate effective throughput across all datasets. In D1, for example, SC-Route’s throughput is nearly three times that of SEAD, while the improvements in other datasets range from approximately 100% to 130%. It is evident that the efficient cross-layer information fusion and load balancing strategy of SC-Route successfully reduced network congestion and maximized link utilization.
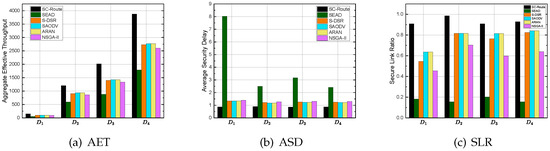
Figure 5.
Performance metrics.
To further quantify the throughput improvement, Table 3 provides detailed comparisons with baseline approaches across different network sizes. These results indicate that SC-Route consistently provides a substantial increase in throughput, with gains ranging from roughly 28% to 185% compared to other algorithms. Such improvements highlight the efficiency of SC-Route in managing network resources and mitigating congestion, thereby achieving higher data delivery rates across different network scales.

Table 3.
Improvement rate of SC-Route’s AET relative to other algorithms.
When evaluating authentication efficiency, the average security delay results in Figure 5b indicate that SC-Route consistently achieves lower delay of around 0.87. In contrast, other methods typically range from 1.2 to 1.4. SEAD performs the worst, with delays reaching up to 8 on certain datasets. Compared to SEAD, SC-Route reduces the average delay by nearly 90% in small-scale networks and by about 20–30% in larger networks. These results confirm that SC-Route meets strict security requirements. More importantly, it significantly improves authentication efficiency by avoiding the high latency caused by frequent key updates and complex verification procedures in traditional schemes.
Complementary to the previous figure, Table 4 highlights the percentage reductions in delay, reinforcing SC-Route’s advantage in minimizing authentication overhead. The most notable improvements emerge in D1 against SEAD, where SC-Route lowers the delay by nearly 90%. Even at larger scales like D4, SC-Route still achieves notable delay reductions, ranging from about 29% to over 63%. This indicates that its security mechanisms remain effective in reducing latency overhead. At the same time, robust authentication and verification are well preserved.

Table 4.
Reduction rate of average security delay achieved by SC-Route relative to other algorithms.
Figure 5c illustrates the secure link ratio, highlighting that SC-Route consistently achieves values above 0.90, whereas competing methods often fall below 0.85 and, in some cases, reach as low as 0.15–0.20. This outcome shows that SC-Route’s dynamic authentication and key update strategies enable more links to meet required security thresholds. As a result, the overall network security is significantly improved. In summary, the experiments confirm that SC-Route performs better than existing algorithms. It achieves stronger global optimization, lower delay, higher throughput, and more stable secure link maintenance. These advantages help overcome the key limitations of traditional methods in dynamic and constraint-heavy environments.
For a clearer view of SC-Route’s improvements in link security, Table 5 presents the relative gains in the secure link ratio against baseline methods. The results indicate that SC-Route achieves substantially higher security across all datasets, with improvement rates exceeding 500% over SEAD in datasets D2 and D4. Even in less extreme cases, the gains consistently demonstrate SC-Route’s robustness in maintaining secure links under varied network scales.

Table 5.
Improvement rate of SC-Route’s secure link ratio relative to other algorithms.
5.4. Summary
In the experimental evaluation, the proposed SC-Route method outperforms baseline algorithms across multiple key performance indicators. SC-Route consistently achieves lower global objective function values across datasets D1, D2, D3, and D4, with reductions ranging from 20% in small-scale networks to 88% in large-scale scenarios compared to other algorithms. This highlights SC-Route’s superior global resource scheduling and secure routing capabilities, overcoming high delays and suboptimal path selections in traditional methods under complex conditions. Regarding the objective function reduction, SC-Route achieves reductions of approximately 25.9%, 45.9%, and 91.4% on datasets D2, D3, and D4, respectively, while competing methods, such as SEAD, show much lower reductions (at least 11%). These results demonstrate SC-Route’s high optimization efficiency and scalability as network size increases. In terms of security delay, SC-Route maintains a low average delay of 0.87, compared to 1.2–1.4 for other methods, with SEAD reaching up to 8 in some datasets, indicating at least 34% reduction in smaller networks and 20–30% in larger ones. SC-Route also achieves the highest throughput across all datasets, with throughput in D1 nearly three times that of SEAD, and improvements at least 40% in other datasets, due to efficient cross-layer fusion and load balancing strategies. Additionally, SC-Route maintains a secure link ratio above 0.90 across all datasets, outperforming other methods (typically below 0.85). This shows that SC-Route adopts more effective strategies for dynamic authentication and key updates. These mechanisms help strengthen overall network security. In conclusion, experiments show that SC-Route outperforms existing methods. It achieves better global optimization, lower delay, higher throughput, and more stable secure link performance. These results highlight its advantages in dynamic and multi-constrained network environments.
6. Conclusions
This paper addresses the challenge of achieving secure and efficient multi-hop routing in dynamic, large-scale cross-domain wireless networks with heterogeneous protocols and constrained resources. The key innovation lies in the SC-Route method, which integrates dynamic authentication, cross-layer information fusion, and risk-aware load balancing into a unified optimization framework. Extensive experiments conducted on four datasets demonstrate that SC-Route substantially outperforms existing approaches in terms of security, delay reduction, and throughput enhancement, validating its scalability and effectiveness. Theoretically, the SC-Route design supports a distributed iterative feedback mechanism, allowing it to maintain robust performance even as the network scales. Our evaluations across datasets ranging from 10 to 200 nodes show stable convergence and consistent improvements across key performance metrics, underscoring its potential for application in larger networks. Nonetheless, we recognize that as the network size further increases, computational and communication overheads may escalate. To address these challenges, future work will explore hierarchical and localized optimization strategies. Furthermore, the proposed risk-aware dynamic key update strategy effectively balances security requirements and operational overhead by adapting update frequencies in response to node risk levels. However, in highly dynamic scenarios where node behavior fluctuates rapidly, this strategy may induce increased update oscillations and transient vulnerabilities. Future research will focus on developing enhanced risk assessment models and predictive mechanisms to improve the stability and responsiveness of key management under such conditions. Additionally, efforts will be directed towards incorporating real-time link prediction and adversarial defense techniques to further bolster routing robustness and adaptability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L.; methodology, Y.Z. and Y.L.; software, Y.Z.; validation, Y.Z. and S.W.; formal analysis, Y.L.; investigation, Y.Z.; resources, Y.L. and S.W.; data curation Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.L. and Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, Y.L. and S.W.; visualization, Y.Z. and S.W.; supervision, S.W.; project administration, Y.L.; funding acquisition, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of Chinaunder Grant U1911401 and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant U1435215.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Meng, L.; Li, J.; Lu, K. Cross-Domain Communications Between Agents Via Adversarial-Based Domain Adaptation in Reinforcement Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communications, ICC 2022, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 16–20 May 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarin, S.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Goyal, S.; Gupta, B.B.; Arya, V.; Attar, R.W.; Bansal, S.; Alhomoud, A. Enhancing smart grid reliability through cross-domain optimization of IoT sensor placement and communication links. Telecommun. Syst. 2025, 88, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yin, M.; Deng, R.; Long, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Yang, H.; Huo, Y. Cross-Species Data Integration for Enhanced Layer Segmentation in Kidney Pathology. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.09278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.S.; Park, Y.M.; Tun, Y.K.; Saad, W.; Han, Z.; Hong, C.S. 3TO: THz-Enabled Throughput and Trajectory Optimization of UAVs in 6G Networks by Proximal Policy Optimization Deep Reinforcement Learning. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.02924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Ge, J.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wen, J. Graph Anomaly Detection via Cross-Layer Integration. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing with Applications, ISPA 2024, Kaifeng, China, 30 October–2 November 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenati, D.; Maimon, T.; Cohen, K. RRO: A Regularized Routing Optimization Algorithm for Enhanced Throughput and Low Latency With Efficient Complexity. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2025, 43, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.A.; Nogueira, L.; Coelho, A.; Silveira, J.A.N.; Marcon, C.A.M. Securet3d: An Adaptive, Secure, and Fault-Tolerant Aware Routing Algorithm for Vertically-Partially Connected 3D-NoC. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2025, 33, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Jha, V.K. Secure and Energy-Aware Data Transmission for IoT-WSNs with the Help of Cluster-Based Secure Optimal Routing. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2024, 134, 1665–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, G.; Han, W.; Jiang, B.; Zhou, T.; Cong, R.; Wang, T. Boundary Constraint Network with Cross Layer Feature Integration for Polyp Segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 4090–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.Z.; Aalsalem, M.Y.; Saad, M.N.B.M.; Xiang, Y. Detection and Mitigation of Node Replication Attacks in Wireless Sensor Networks: A Survey. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2013, 9, 149023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dora, J.R.; Nemoga, K. Clone Node Detection Attacks and Mitigation Mechanisms in Static Wireless Sensor Networks. J. Cybersecur. Priv. 2021, 1, 553–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargahi, T.; Javadi, H.H.S.; Shafiei, H.; Mousavi, P. Detection and mitigation of pulse-delay attacks in pairwise-secured wireless sensor networks. Int. J. High Perform. Comput. Netw. 2018, 11, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.C.; Johnson, D.B.; Perrig, A. SEAD: Secure efficient distance vector routing for mobile wireless ad hoc networks. Ad Hoc Netw. 2003, 1, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanzgiri, K.; LaFlamme, D.; Dahill, B.; Levine, B.; Shields, C.; Belding-Royer, E. Authenticated routing for ad hoc networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2005, 23, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abagonie, K.T.; Genta, A.; Kassahun, E.; Azmeraw, E.; Berara, A. Secure Ad hoc On-demand Distance Vector Routing Protocol for WirelessSensor Networks Data Transmission. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology for Development for Africa (ICT4DA), Bahir Dar, Ethiopia, 18–20 November 2024; pp. 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargl, F.; Geis, A.; Schlott, S.; Weber, M. Secure Dynamic Source Routing. In Proceedings of the 38th Annual Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Big Island, HI, USA, 3–6 January 2005; p. 320c. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldaoud, M.; Al-Abri, D.; Awadalla, M.; Kausar, F. N-BGP: An efficient BGP routing protocol adaptation for named data networking. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2022, 35, e5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeda, N.; Yanai, N.; Takemura, T.; Okada, M.; Cruz, J.P.; Okamura, S. SQUAB: A Virtualized Infrastructure for BGP-related Experiments and Its Applications to Evaluation on BGPsec. J. Inf. Process. 2022, 30, 829–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Hu, Y.; Xu, M.; Wu, J. BGP with BGPsec: Attacks and Countermeasures. IEEE Netw. 2019, 33, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupp, J.; Rossow, C. BGPeek-a-Boo: Active BGP-based Traceback for Amplification DDoS Attacks. In Proceedings of the IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy, EuroS&P 2021, Vienna, Austria, 6–10 September 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, R.; Xu, X. A Certificate Pin BGP Protocol: CP-BGP. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems, ICCCS 2020, Shanghai, China, 15–18 May 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ookura, S.; Kojima, H.; Yanai, N. Performance Evaluation of ID-Based Aggregate Signature Scheme Based on Lattice for Wireless Multi-hop Secure Routing Protocols. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Information and Computer Technologies, ICICT 2024, Honolulu, HI, USA, 15–17 March 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezan, G.; Leung, C.; Wang, Z.J. A Survey of Secure Routing Protocols in Multi-Hop Cellular Networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018, 20, 3510–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrani, N.M.; Khan, N.K.; Shamsi, J.; Haider, W.; Abbsi, A.M. Secure multi-hop routing protocols in Wireless Sensor Networks: Requirements, challenges and solutions. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Digital Information Management (ICDIM 2013), Islamabad, Pakistan, 10–12 September 2013; Bajwa, I.S., Naeem, M.A., Pichappan, P., Eds.; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Chen, Y. Secure routing protocol based on dynamic reputation and load balancing in wireless mesh networks. J. Cloud Comput. 2022, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ning, Z.; Guo, L. A secure routing scheme based on social network analysis in wireless mesh networks. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 2016, 59, 122310:1–122310:12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navamani, T.M.; Yogesh, P. Secure Efficient Routing against Packet Dropping Attacks in Wireless Mesh Networks. In Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Frontiers of Intelligent Computing: Theory and Applications (FICTA) 2014—Volume 2, Bhubaneswar, Odisa, India, 14–15 November 2014; Satapathy, S.C., Biswal, B.N., Udgata, S.K., Mandal, J.K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 328, pp. 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliviero, F.; Romano, S.P. A Reputation-Based Metric for Secure Routing in Wireless Mesh Networks. In Proceedings of the Global Communications Conference, 2008—GLOBECOM 2008, New Orleans, LA, USA, 30 November–4 December 2008; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1935–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabut, A.M.; Dahal, K.P.; Awan, I. Friendship Based Trust Model to Secure Routing Protocols in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud, FiCloud 2014, Barcelona, Spain, 27–29 August 2014; Younas, M., Awan, I., Pescapè, A., Eds.; IEEE Computer Society: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirzada, A.A.; McDonald, C.; Datta, A. Performance Comparison of Trust-Based Reactive Routing Protocols. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2006, 5, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakaris, V.; Ndzi, D.; Ovaliadis, K.; Yang, Y. A new RREQ message forwarding technique based on Bayesian probability theory. EURASIP J. Wirel. Commun. Netw. 2012, 2012, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhan, J.; Libin, J.; Han, J.M. Load balancing strategy for wireless multi-hotspot networks based on improved NSGA-II algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Networking and Network Applications (NaNA), Urumqi, China, 3–5 December 2022; pp. 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Feng, S.; Ding, Y.; Huang, X. Cross-layer resource allocation in wireless multi-hop networks with outdated channel state information. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. C 2014, 15, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velusamy, D.; GaneshKumar, P.; Ramasamy, K. A Cross-Layer Trust Evaluation Protocol for Secured Routing in Communication Network of Smart Grid. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2020, 38, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).