Sliding Mode Control Method Based on a Fuzzy Logic System for ROVs with Predefined-Time Convergence and Stability
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel approach is introduced in predefined-time control design, making it more practical and efficient. This method ensures precise tunability of the system states’ convergence time, effectively addressing the challenges associated with fixed-time designs.
- The proposed predefined-time control method is based on an advanced terminal sliding mode control (TSMC) framework, ensuring nonsingular and fast convergence. The controller dynamically adjusts the dominant convergence term based on configurable parameters. Consequently, the actual convergence time closely aligns with the predefined target, significantly improving the accuracy and reliability of convergence time adjustments.
- This study also introduces an AFLS that enhances system performance by improving robustness, reducing chattering, and eliminating singularities. The AFLS effectively estimates unstructured model uncertainties and compounded disturbances, seamlessly integrating these factors into the control framework.
- A rigorous stability analysis of the proposed strategy is conducted, demonstrating its tunability in achieving predefined convergence times. Extensive comparative simulation experiments validate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed control scheme, showcasing its ability to provide fast, stable, and precise trajectory tracking for ROVs.
2. Preliminaries and Problem Formulation
Definitions and Lemmas
3. Modeling of ROV
ROV Dynamic Model
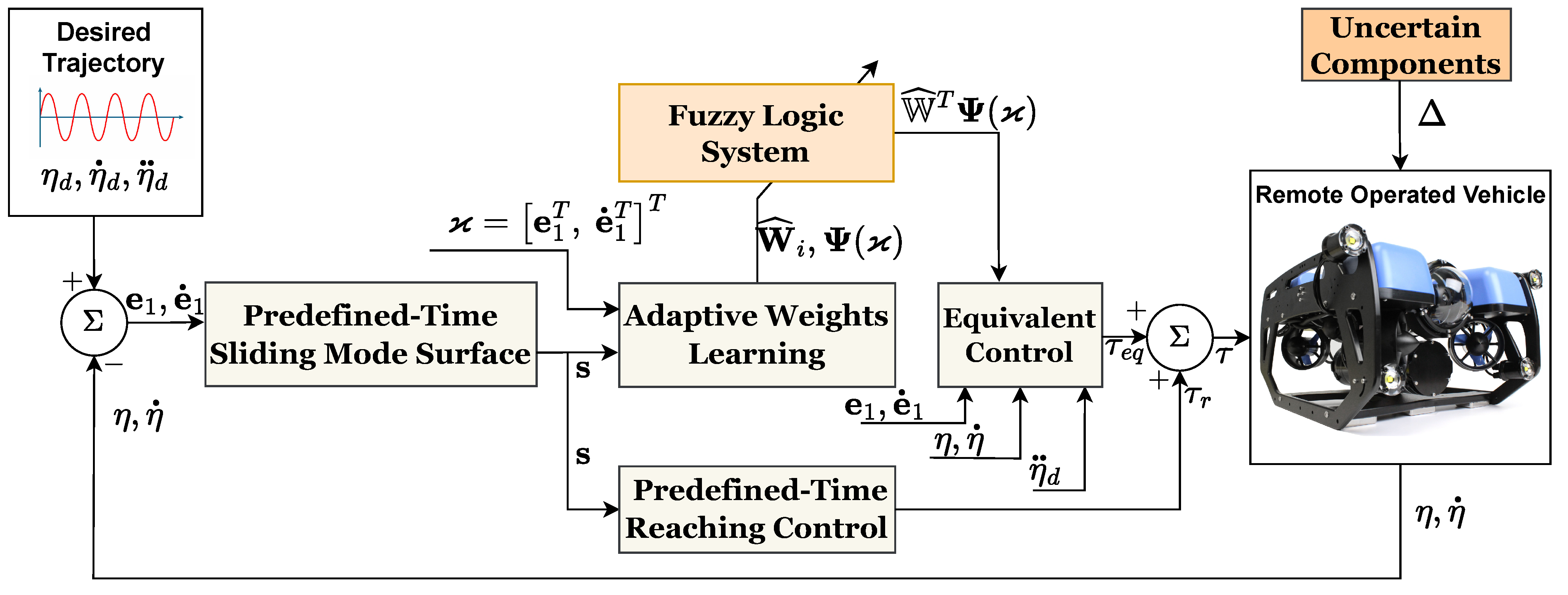
4. Synthesis of Control Design
4.1. Formulation of Sliding Mode Surface
4.2. FLS Approximation
- where , , …, and represent fuzzy sets. The fuzzy output, when utilizing a singleton fuzzifier, is determined as follows:
4.3. Formulation of Controller and Its Stability Proof
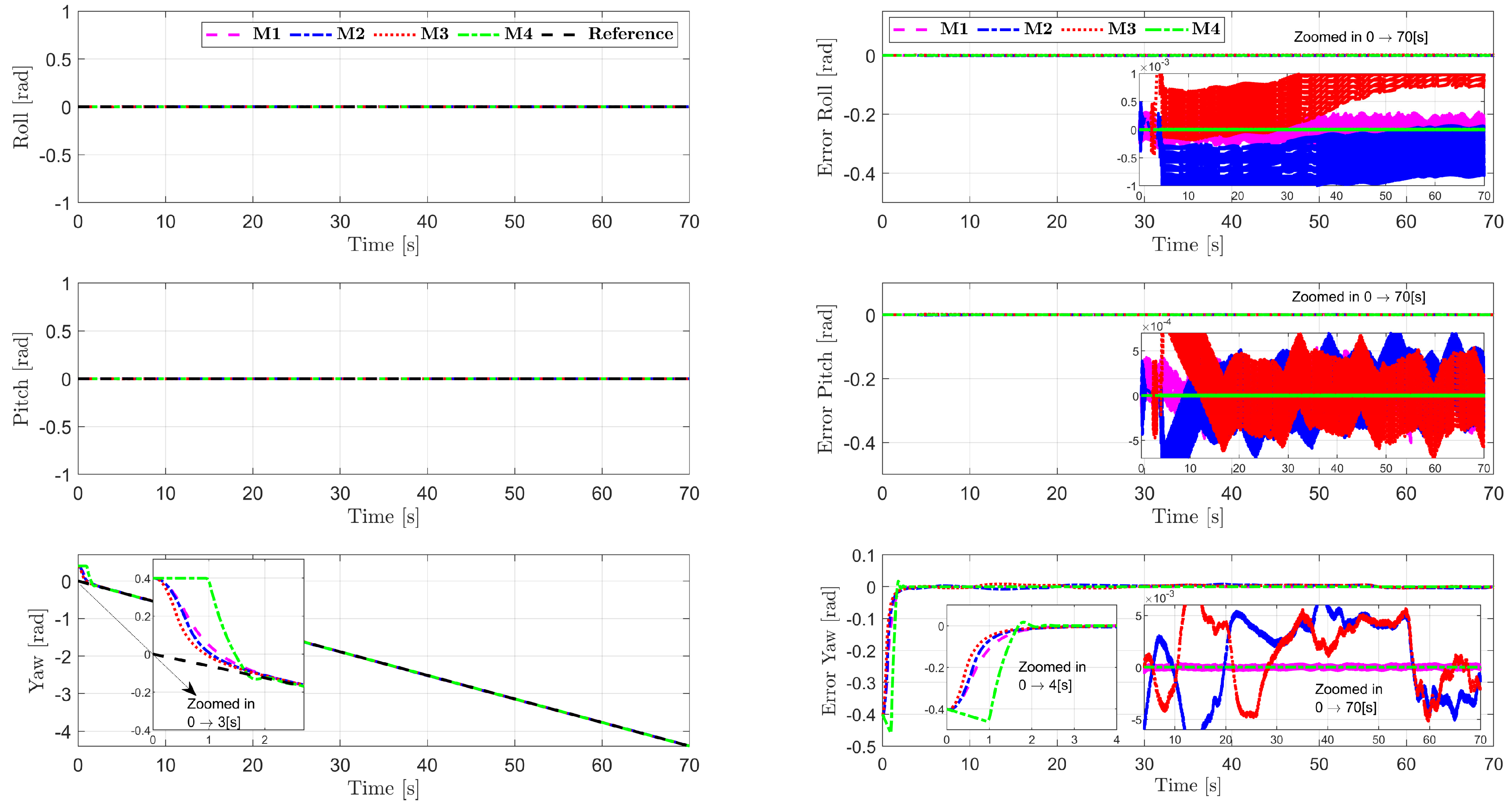
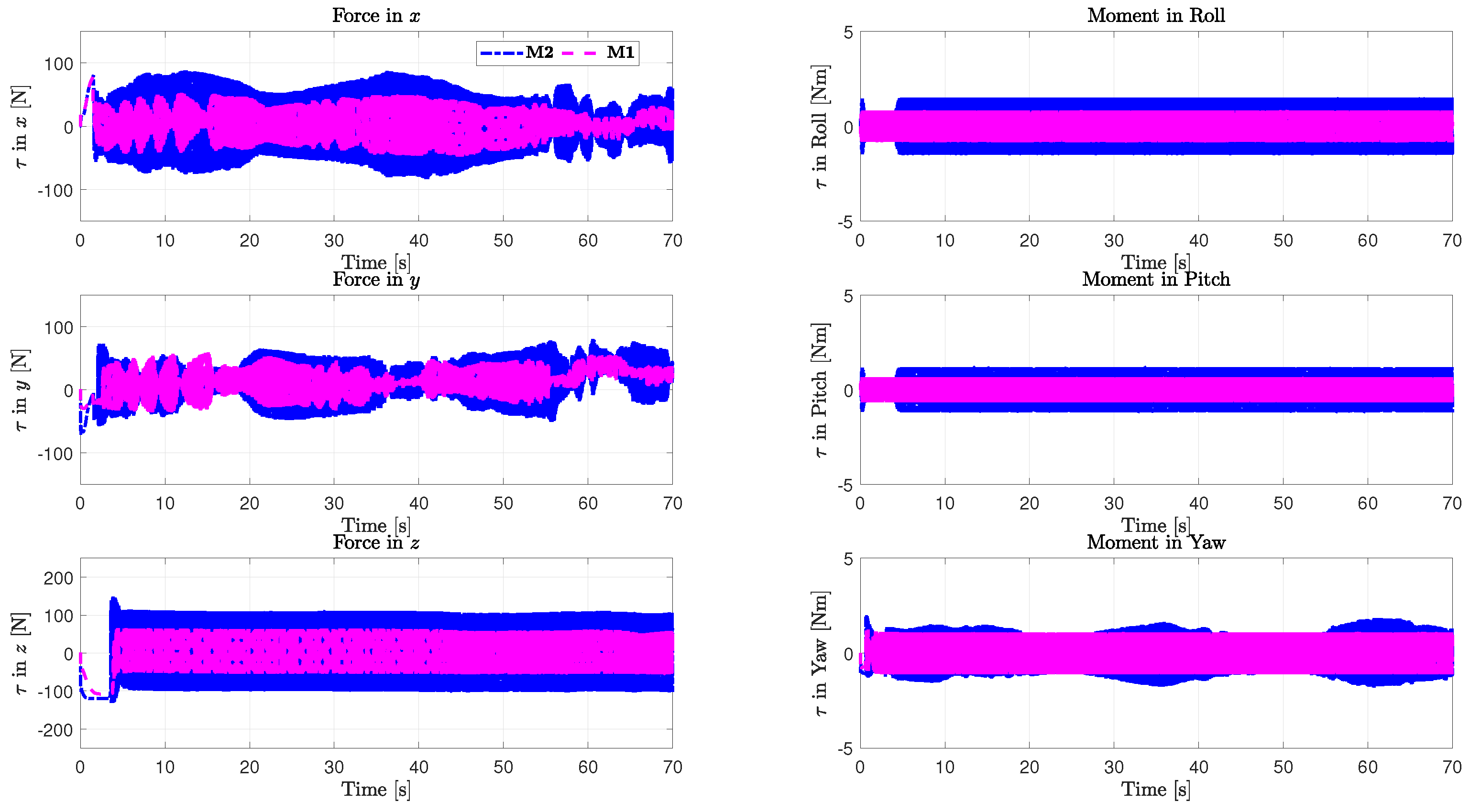
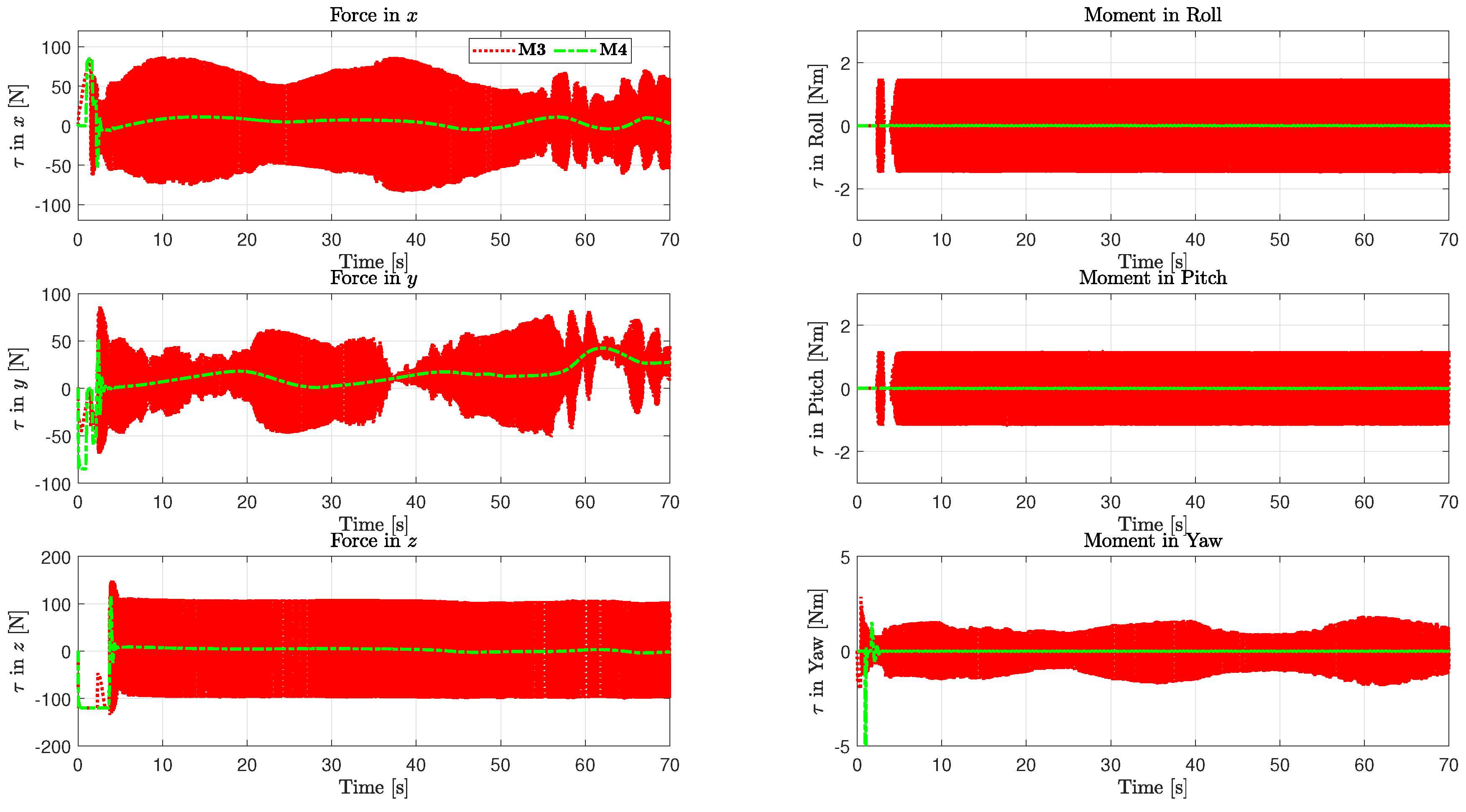
5. Simulations
5.1. Configuration of the Testing System
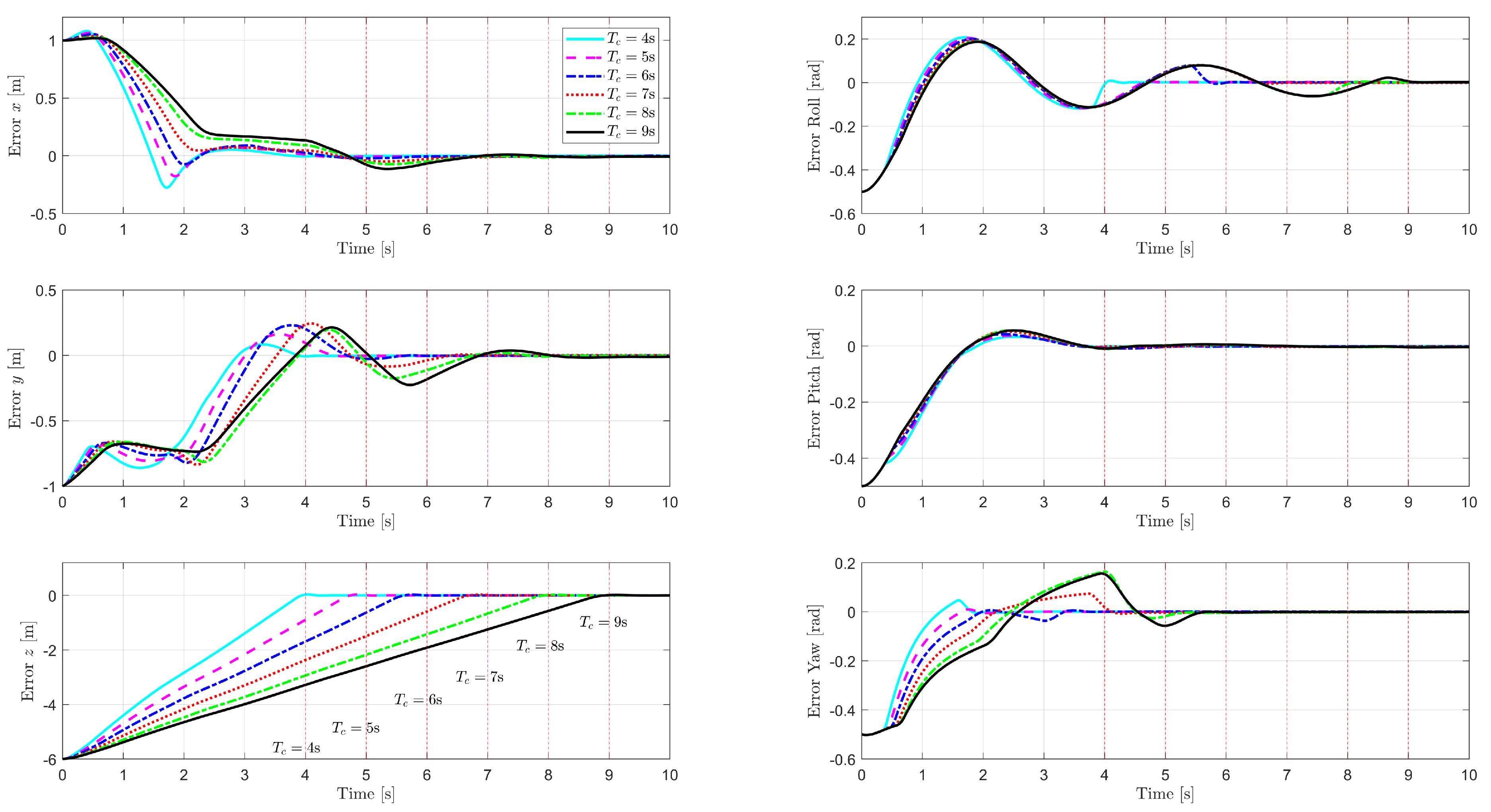
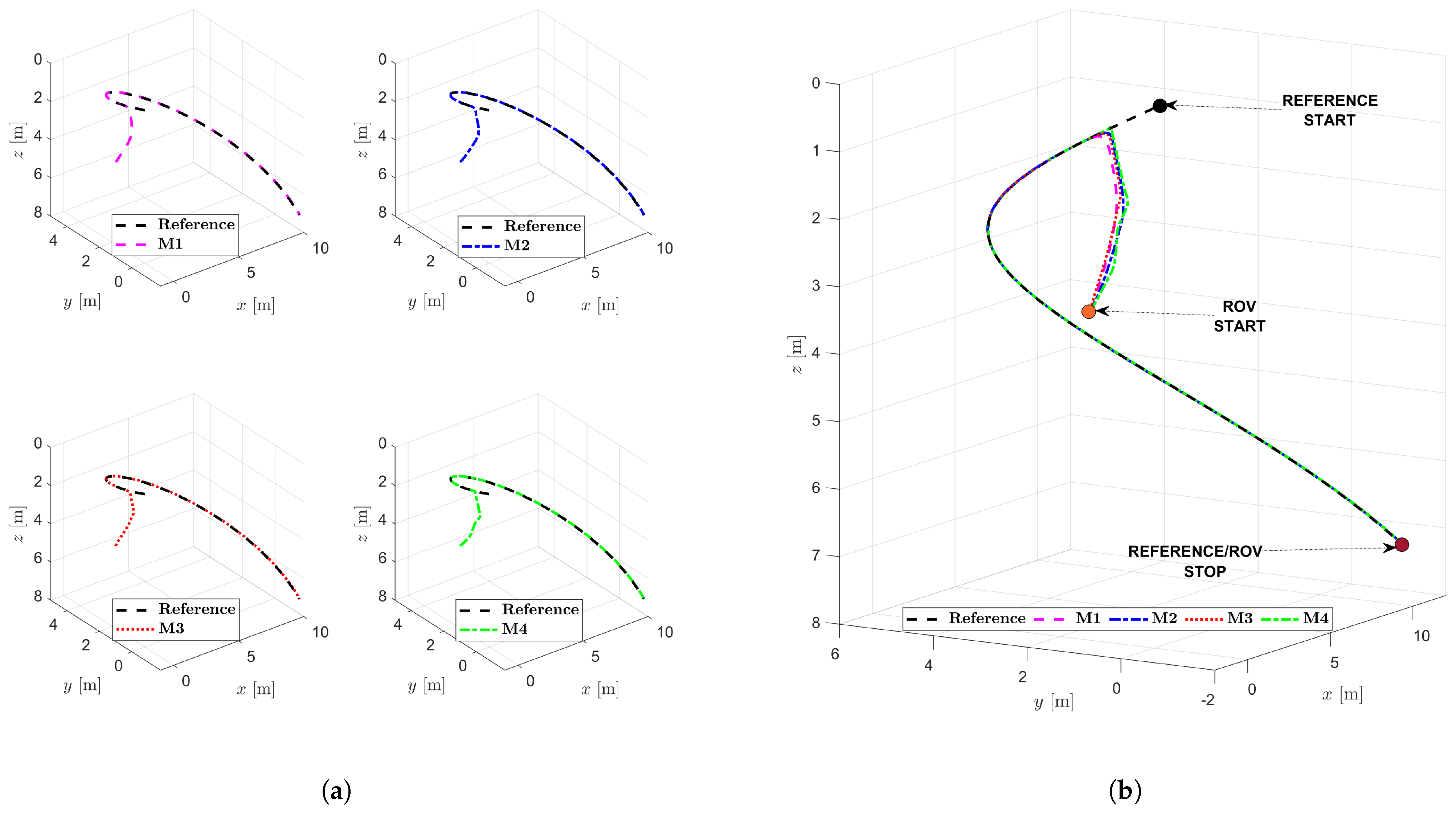
5.2. Analysis of Example 1
5.3. Analysis of Example 2
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chin, C.S.; Lin, W.P. Robust genetic algorithm and fuzzy inference mechanism embedded in a sliding-mode controller for an uncertain underwater robot. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 2018, 23, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossen, T.I. Mathematical models of ships and underwater vehicles. In Encyclopedia of Systems and Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 1185–1191. [Google Scholar]
- Fossen, T.I. Marine Control Systems: Guidance, Navigation and Control of Ships, Rigs and Underwater Vehicles; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; ISBN 82 92356 00 2. Available online: www.marinecybernetics.com (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Soylu, S.; Proctor, A.A.; Podhorodeski, R.P.; Bradley, C.; Buckham, B.J. Precise trajectory control for an inspection class ROV. Ocean. Eng. 2016, 111, 508–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Hu, M.; Qin, X.; Bian, Y. Hierarchical trajectory tracking control for ROVs subject to disturbances and parametric uncertainties. Ocean. Eng. 2022, 266, 112733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Yang, Q. Double-loop sliding mode controller with a novel switching term for the trajectory tracking of work-class ROVs. Ocean. Eng. 2019, 178, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Guan, Z.; Zhang, Y. An adaptive sliding mode motion control method of remote operated vehicle. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 22447–22454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.N.; Vo, A.T.; Kang, H.J.; Van, M. A Novel Active Fault-Tolerant Tracking Control for Robot Manipulators with Finite-Time Stability. Sensors 2021, 21, 8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.N.; Vo, A.T.; Kang, H.J. An Adaptive Terminal Sliding Mode Control Scheme via Neural Network Approach for Path-following Control of Uncertain Nonlinear Systems. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2022, 20, 2081–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.X.; Tong, S. Event-based finite-time control for nonlinear multiagent systems with asymptotic tracking. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2022, 68, 3790–3797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Xue, G.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Pan, Y.; Cao, J. Finite-time sliding mode fault-tolerant neural network control for nonstrict-feedback nonlinear systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 17205–17227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Guo, Z.; Yang, X.; Luo, X.; Guan, X. Finite-time tracking control of autonomous underwater vehicle without velocity measurements. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2021, 52, 6759–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Q.; Zhang, W.; Su, Y.; Yang, H. Guidance and Control of Underwater Hexapod Robot Based on Adaptive Sliding Mode Strategy. J. Bionic Eng. 2024, 22, 118–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Zhang, W.; Du, X. Finite-time extended state observer based collision-free leaderless formation control of multiple AUVs via event-triggered control. Ocean. Eng. 2023, 268, 113605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, A.T.; Truong, T.N.; Kang, H.J.; Van, M. A Robust Observer-Based Control Strategy for n-DOF Uncertain Robot Manipulators with Fixed-Time Stability. Sensors 2021, 21, 7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, A.T.; Truong, T.N.; Kang, H.J.; Le, T.D. A fixed-time sliding mode control for uncertain magnetic levitation systems with prescribed performance and anti-saturation input. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 133, 108373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.N.; Vo, A.T.; Kang, H.J. A Novel Time Delay Nonsingular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Robot Manipulators with Input Saturation. Mathematics 2024, 13, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Close, J.; Van, M.; McIlvanna, S. PID-Fixed Time Sliding Mode Control for Trajectory Tracking of AUVs under Disturbance. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2024, 58, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, M.; Sun, Y.; Mcllvanna, S.; Nguyen, M.N.; Zocco, F.; Liu, Z. Control of Multiple AUV Systems with Input Saturations using Distributed Fixed-Time Consensus Fuzzy Control. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 32, 3142–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, K.; Li, X.; Li, K.; Zou, Y. Distributed predefined-time control for cooperative tracking of multiple quadrotor UAVs. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2024, 11, 2179–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. Predefined-Time Control for Multi-Agent Systems With Input Saturation: An Improved Dynamic Surface Control Scheme. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2024, 22, 3661–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.; Chadli, M.; Xiang, Z. Fuzzy fault-tolerant predefined-time control for switched systems: A singularity-free method. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 32, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhu, Q. Predefined time nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode control for trajectory tracking of ROVs. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 107864–107876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Zheng, J.; Zhu, P.; Yang, D. Predefined-time stability control method based on Lyapunov function. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, M.; Song, Y. Terminal Sliding-Mode Control of Uncertain Robotic Manipulator System with Predefined Convergence Time. Complexity 2021, 2021, 9991989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garraffa, G.; Sferlazza, A.; D’Ippolito, F.; Alonge, F. Localization based on parallel robots kinematics as an alternative to trilateration. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 69, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keymasi Khalaji, A.; Bahrami, S. Finite-time sliding mode control of underwater vehicles in 3D space. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2022, 44, 3215–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtare, Z.; Vu, M.T.; Mobayen, S.; Fekih, A. Design of an LMI-based fuzzy fast terminal sliding mode control approach for uncertain MIMO systems. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robot, S.P. Optimized Fuzzy Enhanced Robust Control Design for Stewart Parallel Robot. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.A.; Kim, S.H. Non-PDC-based local stabilization conditions of discrete-time nonhomogeneous fuzzy Markov jump systems with dynamic event-triggered mechanism. ISA Trans. 2025, 161, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.A.; Kim, S.H. Admissibility and event-triggered dissipative observer-based stabilization of discrete-time TS fuzzy singular systems via fuzzy Lyapunov functions. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 112, 17257–17272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, T.N.; Vo, A.T.; Kang, H.J. Neural network-based sliding mode controllers applied to robot manipulators: A review. Neurocomputing 2023, 562, 126896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Huang, C.; Cao, J.; Liu, H. Adaptive fuzzy finite-time PID backstepping control for chaotic systems with full states constraints and unmodeled dynamics. Inf. Sci. 2024, 661, 120148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Karimi, T.; Amanifard, N. Tracking performance control of a cable communicated underwater vehicle using adaptive neural network controllers. Appl. Soft Comput. 2010, 10, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Liu, X.; Xu, J. Predefined-Time Nonsingular Sliding Mode Control and Its Application to Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 20, 5829–5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Benzon, M.; Sørensen, F.F.; Uth, E.; Jouffroy, J.; Liniger, J.; Pedersen, S. An open-source benchmark simulator: Control of a bluerov2 underwater robot. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossen, T.I.; Johansen, T.A. A survey of control allocation methods for ships and underwater vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2006 14th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, Ancona, Italy, 28–30 June 2006; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fossen, T. Handbook of Marine Craft Hydrodynamics and Motion Control; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, W.; Ma, H.; Zhou, L.; Li, H. Adaptive Fuzzy Fixed-Time Formation-Containment Control for Euler-Lagrange Systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 31, 3700–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labiod, S.; Boucherit, M.S.; Guerra, T.M. Adaptive fuzzy control of a class of MIMO nonlinear systems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2005, 151, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Tawiah, I.; Zhang, W. Finite-time extended state observer based nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode control of autonomous underwater vehicles. Ocean. Eng. 2020, 218, 108179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
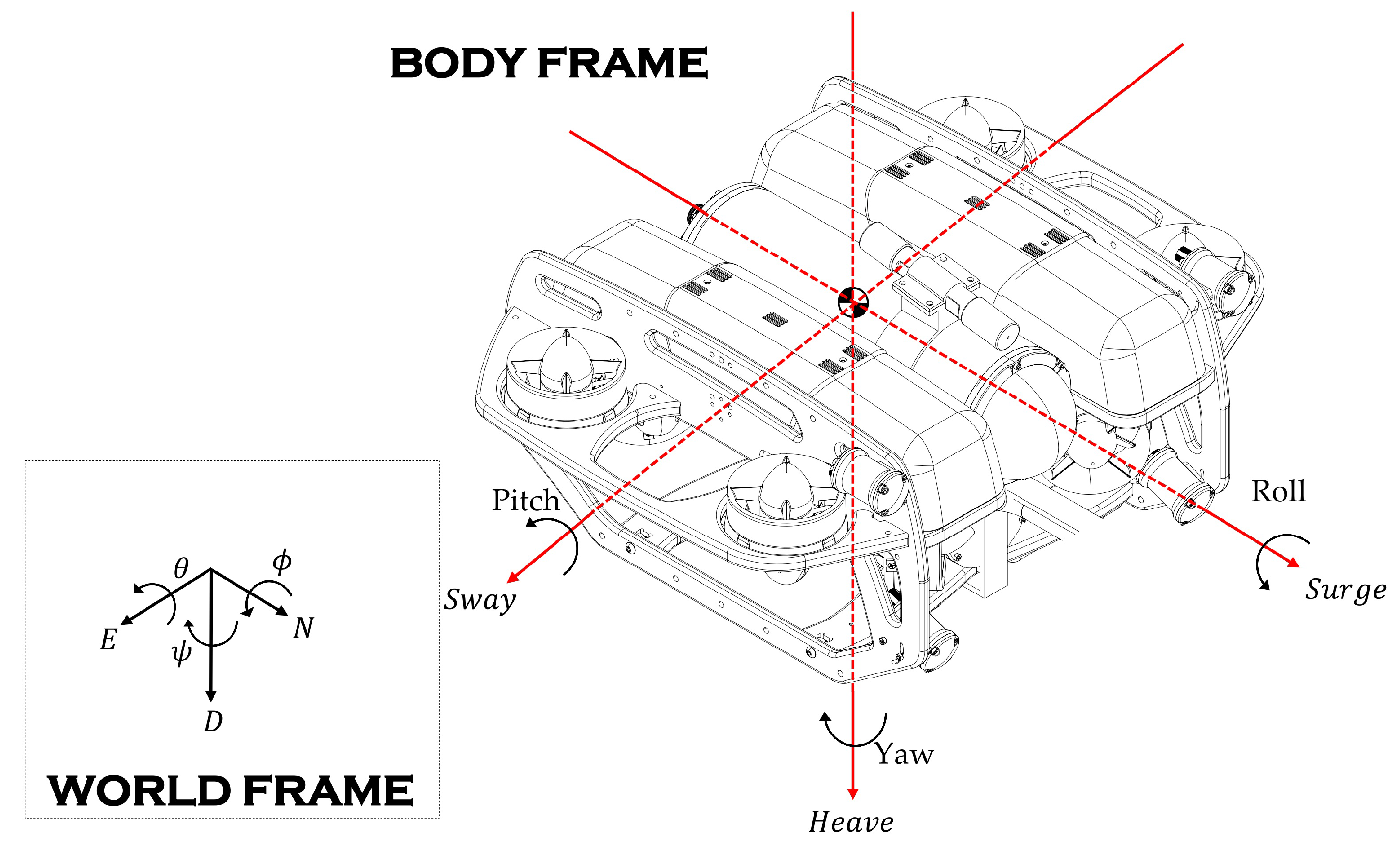



| Motion Parameters | Force Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Motion | Parameter | Velocity | Parameter | Force Type | Parameter |
| Surge | x | Surge Velocity | u | Surge Force | X |
| Sway | y | Sway Velocity | v | Sway Force | Y |
| Heave | z | Heave Velocity | w | Heave Force | Z |
| Roll | Roll Velocity | p | Roll Moment | K | |
| Pitch | Pitch Velocity | q | Pitch Moment | M | |
| Yaw | Yaw Velocity | r | Yaw Moment | N | |
| Parameter | Value (Units) | Parameter | Value (Units) | Parameter | Value (Units) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| m | kg | W | N | B | N |
| kg·m2 | kg·m2 | kg·m2 | |||
| Ns/rad | Ns/rad | Ns/rad | |||
| kg·m2/rad | kg·m2/rad | kg·m2/rad | |||
| Ns2/rad2 | Ns2/rad2 | Ns2/rad2 | |||
| Ns/m | Ns/m | Ns/m | |||
| kg | kg | kg | |||
| Ns2/m2 | Ns2/m2 | Ns2/m2 |
| Control Method | Category | Notation | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | Parameters | ||
| M2 | Parameters | ||
| M3 | Parameters | ||
| M4 | Parameters | ||
| Membership Functions | |||
| – | Desired Trajectory |
| Method | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | ||||||
| M2 | ||||||
| M3 | ||||||
| M4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vo, A.T.; Truong, T.N.; Hong, I.-P.; Kang, H.-J. Sliding Mode Control Method Based on a Fuzzy Logic System for ROVs with Predefined-Time Convergence and Stability. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101573
Vo AT, Truong TN, Hong I-P, Kang H-J. Sliding Mode Control Method Based on a Fuzzy Logic System for ROVs with Predefined-Time Convergence and Stability. Mathematics. 2025; 13(10):1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101573
Chicago/Turabian StyleVo, Anh Tuan, Thanh Nguyen Truong, Ic-Pyo Hong, and Hee-Jun Kang. 2025. "Sliding Mode Control Method Based on a Fuzzy Logic System for ROVs with Predefined-Time Convergence and Stability" Mathematics 13, no. 10: 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101573
APA StyleVo, A. T., Truong, T. N., Hong, I.-P., & Kang, H.-J. (2025). Sliding Mode Control Method Based on a Fuzzy Logic System for ROVs with Predefined-Time Convergence and Stability. Mathematics, 13(10), 1573. https://doi.org/10.3390/math13101573








