A New Biorthogonal Spline Wavelet-Based K-Layer Network for Underwater Image Enhancement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Methodology
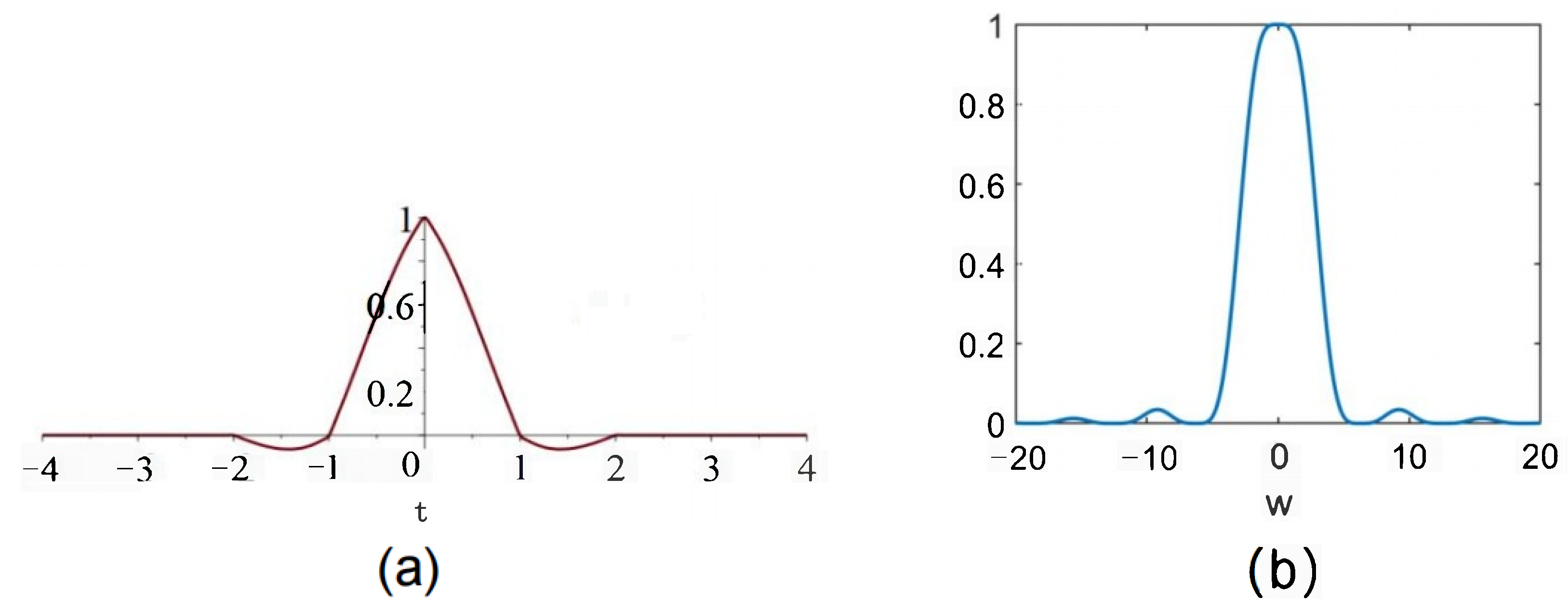
3.1. A New Biorthogonal Cubic Special Spline Wavelet (BCS-SW)
3.1.1. Cubic Special Spline Algorithm
3.1.2. Constructing Biorthogonal Cubic Special Spline Wavelet (BCS-SW)
| Algorithm 1 BCS-SW Filter Algorithm |
| Input: L: sum of the vanishing moment order of and by Equations (8) and (9), and ; : defined by Equation (11); : axis angel; n: integer, the subscript of the low-pass filter coefficient; Output: : the set of corresponding low-pass filter coefficients of ; : the set of corresponding low-pass filter coefficients of ;
|
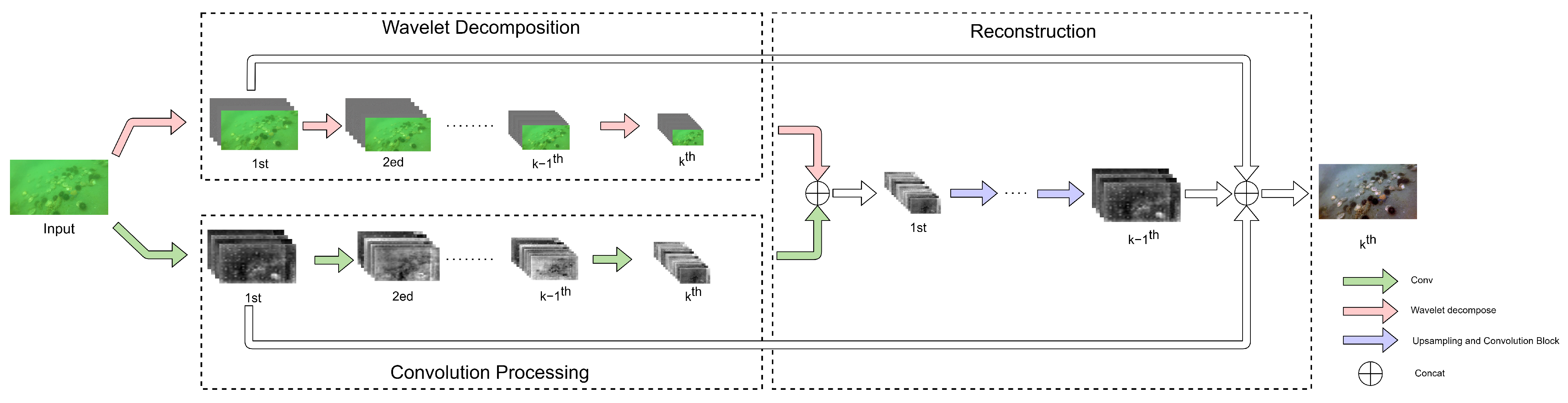
3.2. K-Layer Network
4. Experiments
4.1. Implementation Details
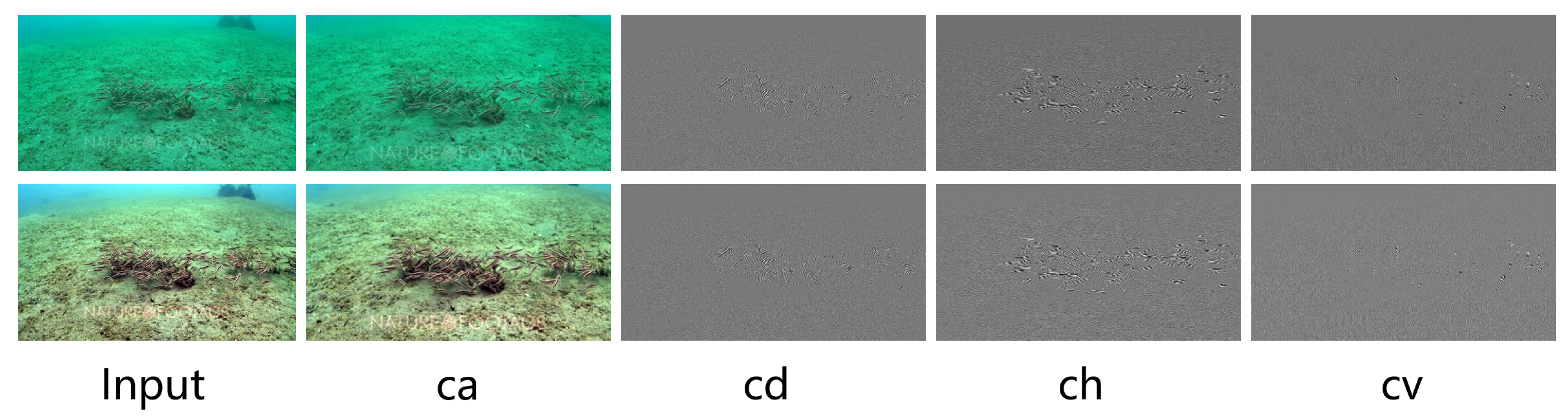
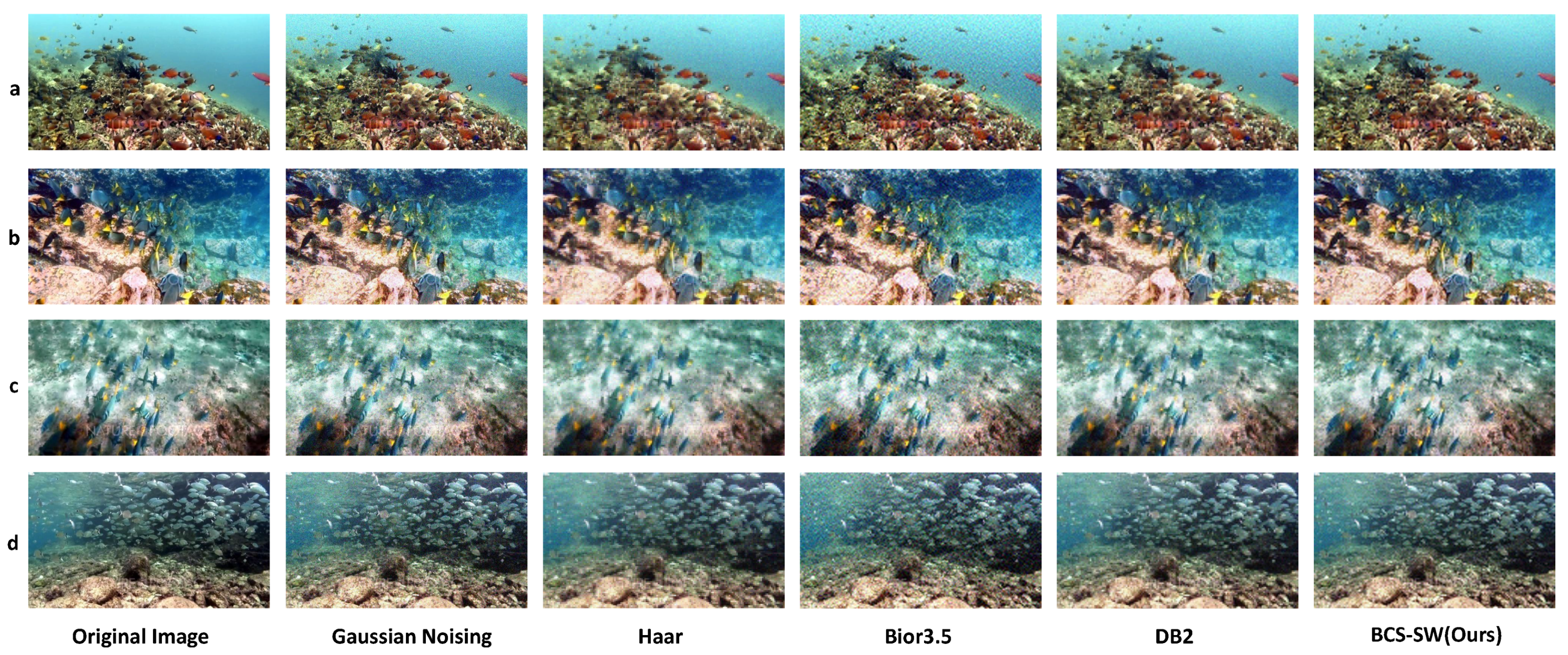
4.2. BCS-SW vs. Other Wavelets in Underwater Image Related Tasks
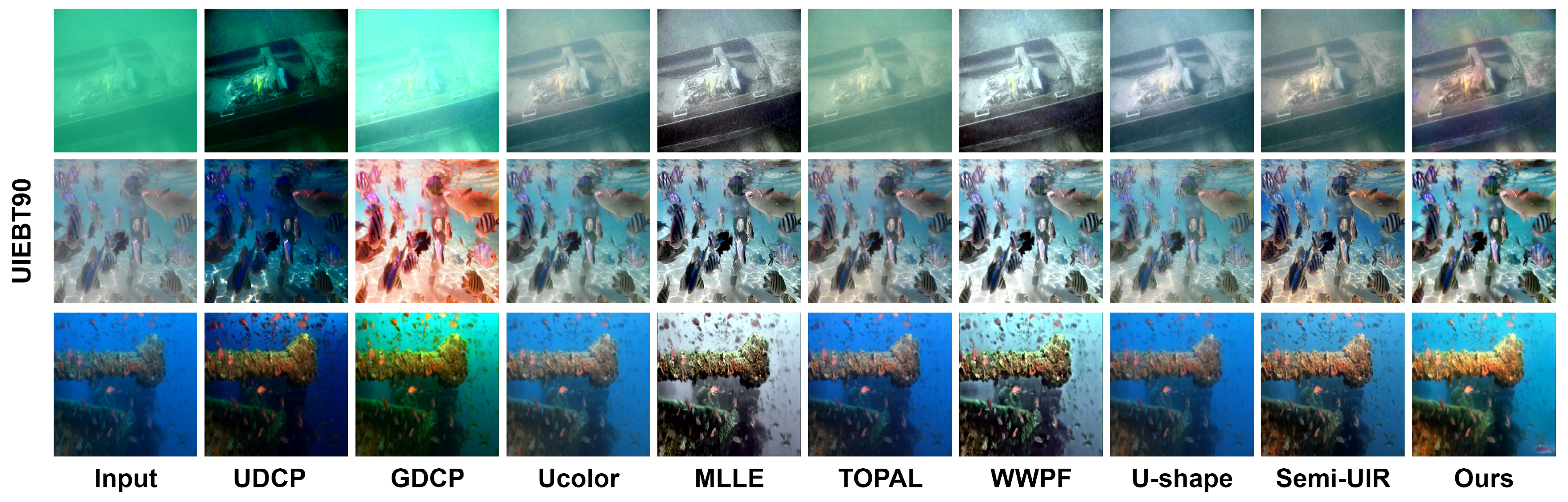
4.3. KLN vs. Other Underwater Image Enhancement Algorithms
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, H.; Wang, R. Underwater Image Enhancement Based on Multi-Scale Fusion and Global Stretching of Dual-Model. Mathematics 2021, 9, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D. Underwater image enhancement based on the improved algorithm of dark channel. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.T.; Cosman, P.C. Underwater Image Restoration Based on Image Blurriness and Light Absorption. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 1579–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z. Voiceprint Recognition under Cross-Scenario Conditions Using Perceptual Wavelet Packet Entropy-Guided Efficient-Channel-Attention–Res2Net–Time-Delay-Neural-Network Model. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garai, S.; Paul, R.K.; Rakshit, D.; Yeasin, M.; Emam, W.; Tashkandy, Y.; Chesneau, C. Wavelets in combination with stochastic and machine learning models to predict agricultural prices. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallat, S.G. Multiresolution approximations and wavelet orthonormal bases of L2(R). Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 1989, 315, 69–87. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Ahmad, M.K. A study on B-spline wavelets and wavelet packets. Appl. Math. 2014, 5, 3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cohen, A.; Daubechies, I.; Feauveau, J.C. Biorthogonal bases of compactly supported wavelets. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 1992, 45, 485–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olkkonen, H.; Olkkonen, J.T. Gamma splines and wavelets. J. Eng. 2013, 2013, 625364. [Google Scholar]
- Tavakoli, A.; Esmaeili, M. Construction of Dual Multiple Knot B-Spline Wavelets on Interval. Bull. Iran. Math. Soc. 2019, 45, 843–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; He, R.; Sun, Z.; Tan, T. Wavelet-srnet: A wavelet-based cnn for multi-scale face super resolution. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1689–1697. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, E.; Chang, W.; Yoo, J.; Ye, J.C. Deep convolutional framelet denosing for low-dose CT via wavelet residual network. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 37, 1358–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banham, M.R.; Katsaggelos, A.K. Spatially adaptive wavelet-based multiscale image restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 1996, 5, 619–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sree Sharmila, T.; Ramar, K.; Sree Renga Raja, T. Impact of applying pre-processing techniques for improving classification accuracy. Signal Image Video Process. 2014, 8, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.R. Enhancement of contrast and resolution of gray scale and color images by wavelet decomposition and histogram shaping and shifting. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Medical Imaging, m-Health and Emerging Communication Systems (MedCom), Greater Noida, India, 7–8 November 2014; pp. 300–305. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Oh, C. A Wavelet-Based Dual-Stream Network for Underwater Image Enhancement. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2022—2022 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Singapore, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 2769–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haar, A. Zur Theorie der Orthogonalen Funktionensysteme; Georg-August-Universitat: Gottingen, Germany, 1909. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, J.; Attanasio, A.C.; Nechyporenko, N.; Sanz, P.J. A deep learning approach for underwater image enhancement. In Proceedings of the Biomedical Applications Based on Natural and Artificial Computing: International Work-Conference on the Interplay between Natural and Artificial Computation, IWINAC 2017, Corunna, Spain, 19–23 June 2017; pp. 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Z. A deep CNN method for underwater image enhancement. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017; pp. 1382–1386. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial nets. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Skinner, K.A.; Eustice, R.M.; Johnson-Roberson, M. WaterGAN: Unsupervised generative network to enable real-time color correction of monocular underwater images. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2017, 3, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, C.; Islam, M.J.; Sattar, J. Enhancing underwater imagery using generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 7159–7165. [Google Scholar]
- Chui, C.K.; Wang, J.Z. On compactly supported spline wavelets and a duality principle. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 1992, 330, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Cai, Z. A New Class of Explicit Interpolatory Splines and Related Measurement Estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2020, 68, 2799–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, C.K. An Introduction to Wavelets; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Graps, A. An introduction to wavelets. IEEE Comput. Sci. Eng. 1995, 2, 50–61. [Google Scholar]
- Lamnii, A.; Nour, M.Y.; Zidna, A. A reverse non-stationary generalized B-splines subdivision scheme. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2628. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Guo, C.; Ren, W.; Cong, R.; Hou, J.; Kwong, S.; Tao, D. An underwater image enhancement benchmark dataset and beyond. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 4376–4389. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, L.; Zhu, C.; Bian, L. U-shape transformer for underwater image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2023, 32, 3066–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Fan, X.; Zhu, M.; Hou, M.; Luo, Z. Real-world underwater enhancement: Challenges, benchmarks, and solutions under natural light. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 30, 4861–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Sowmya, A. An underwater color image quality evaluation metric. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2015, 24, 6062–6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panetta, K.; Gao, C.; Agaian, S. Human-visual-system-inspired underwater image quality measures. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2015, 41, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ma, K.; Yeganeh, H.; Wang, Z.; Lin, W. A patch-structure representation method for quality assessment of contrast changed images. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2015, 22, 2387–2390. [Google Scholar]
- Drews, P.; Nascimento, E.; Moraes, F.; Botelho, S.; Campos, M. Transmission estimation in underwater single images. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 825–830. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.T.; Cao, K.; Cosman, P.C. Generalization of the dark channel prior for single image restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 2856–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Anwar, S.; Hou, J.; Cong, R.; Guo, C.; Ren, W. Underwater image enhancement via medium transmission-guided multi-color space embedding. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 4985–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhuang, P.; Sun, H.H.; Li, G.; Kwong, S.; Li, C. Underwater image enhancement via minimal color loss and locally adaptive contrast enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2022, 31, 3997–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Fan, X.; Liu, R. Target oriented perceptual adversarial fusion network for underwater image enhancement. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2022, 32, 6584–6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, L.; Zhuang, P.; Li, G.; Pan, X.; Zhao, W.; Li, C. Underwater image enhancement via weighted wavelet visual perception fusion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 2469–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, J.; You, J. Peak signal-to-noise ratio revisited: Is simple beautiful? In Proceedings of the 2012 Fourth International Workshop on Quality of Multimedia Experience, Melbourne, Australia, 5–7 July 2012; pp. 37–38. [Google Scholar]
- Hore, A.; Ziou, D. Image quality metrics: PSNR vs. SSIM. In Proceedings of the 2010 20th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, Istanbul, Turkey, 23–26 August 2010; pp. 2366–2369. [Google Scholar]


| N | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1417/1969, 737/1491, 389/2760, 5/907, −1/1415, 1/6154, −1/19,642, 1/51,496… | 2 | 813/731, 63/298, −419/1066, 91/1301, 81/992, −8/273, 3/689, −1/647, 1/1482, −1/3011, 1/5619… |
| 3 | 330/317, 38/141, −157/398, −3/488, 137/972, −13/669, −17/1051, 7/1205, −1/1437, 1/4657, −1/12,080 … | ||
| 4 | 645/643, 96/319, −231/593, −45/733, 143/838, 3/610, −3/83, 7/1030, 5/1491, −1/819, 1/8087… | ||
| 5 | 483/493, 319/994, −589/1535, −65/634, 93/502, 23/749, −25/496, 1/369, 3/308, −1/479, −1/1397… |
| Image | Haar | BCS-SW | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR ↑ | SSIM ↑ | |
| Figure 4a | 31.7752 | 0.9922 | 32.7565 | 0.9938 |
| Figure 4b | 36.6892 | 0.9820 | 40.8069 | 0.9928 |
| Figure 4c | 40.3920 | 0.9979 | 42.1529 | 0.9986 |
| Figure 4d | 27.8036 | 0.9121 | 30.3055 | 0.9477 |
| Image | Haar | Bior3.5 | DB2 | BCS-SW | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR | SSIM | PSNR ↑ | SSIM ↑ | |
| Figure 5a | 22.00 | 0.6166 | 21.80 | 0.5366 | 22.89 | 0.6664 | 23.36 | 0.6911 |
| Figure 5b | 22.11 | 0.5597 | 21.89 | 0.5521 | 23.12 | 0.6232 | 23.76 | 0.6547 |
| Figure 5c | 24.62 | 0.6159 | 23.53 | 0.5824 | 25.92 | 0.7137 | 27.00 | 0.7484 |
| Figure 5d | 22.31 | 0.5626 | 21.83 | 0.5335 | 23.19 | 0.6205 | 23.85 | 0.6528 |
| Original | CLAHE (1994) | UCDP (2013) | GDCP (2018) | Ucolor (2021) | MLLE (2022) | TOPAL (2022) | U-Shape (2023) | WWPF (2023) | Semi-UIR (2023) | OURS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UIQM ↑ | 2.4745 | 2.7409 | 2.0180 | 2.0995 | 3.0305 | 1.9561 | 2.8994 | 3.0141 | 2.3900 | 2.9503 | 2.8546 |
| UCIQE ↑ | 0.5031 | 0.5527 | 0.5860 | 0.6141 | 0.5709 | 0.6216 | 0.5726 | 0.5748 | 0.6341 | 0.6188 | 0.6089 |
| PCQI ↑ | — | 1.2036 | 0.9324 | 1.0161 | 1.1033 | 1.2242 | 1.1377 | 1.0866 | 1.2187 | 1.1704 | 1.2516 |
| PSNR ↑ | — | 23.9048 | 14.0771 | 15.5725 | 21.5026 | 15.3689 | 22.2745 | 21.9905 | 15.8602 | 19.3214 | 25.6162 |
| SSIM ↑ | — | 0.9114 | 0.6379 | 0.7581 | 0.8984 | 0.5848 | 0.9028 | 0.8528 | 0.6345 | 0.8005 | 0.9538 |
| Original | CLAHE (1994) | UCDP (2013) | GDCP (2018) | Ucolor (2021) | MLLE (2022) | TOPAL (2022) | U-Shape (2023) | WWPF (2023) | Semi-UIR (2023) | OURS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UIQM ↑ | 2.4641 | 2.6795 | 2.1315 | 2.4002 | 2.9963 | 2.4112 | 2.8644 | 2.9705 | 2.6591 | 2.9582 | 2.7684 |
| UCIQE ↑ | 0.4321 | 0.4761 | 0.5128 | 0.5467 | 0.5317 | 0.5829 | 0.5004 | 0.5456 | 0.5958 | 0.5667 | 0.5897 |
| PCQI ↑ | — | 1.2268 | 1.1041 | 1.2127 | 1.2121 | 1.3304 | 1.0899 | 1.2035 | 1.3002 | 1.2911 | 1.2616 |
| U-Shape | Semi-UIR | OURS | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flops (G) | 26.11 | 36.44 | 207.8 |
| Total Parameters (M) | 31.6 | 1.68 | 57.24 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, D.; Cai, Z.; He, D. A New Biorthogonal Spline Wavelet-Based K-Layer Network for Underwater Image Enhancement. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12091366
Zhou D, Cai Z, He D. A New Biorthogonal Spline Wavelet-Based K-Layer Network for Underwater Image Enhancement. Mathematics. 2024; 12(9):1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12091366
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Dujuan, Zhanchuan Cai, and Dan He. 2024. "A New Biorthogonal Spline Wavelet-Based K-Layer Network for Underwater Image Enhancement" Mathematics 12, no. 9: 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12091366
APA StyleZhou, D., Cai, Z., & He, D. (2024). A New Biorthogonal Spline Wavelet-Based K-Layer Network for Underwater Image Enhancement. Mathematics, 12(9), 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12091366







