Efficient Quantum Private Comparison with Unitary Operations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Unitary Operations
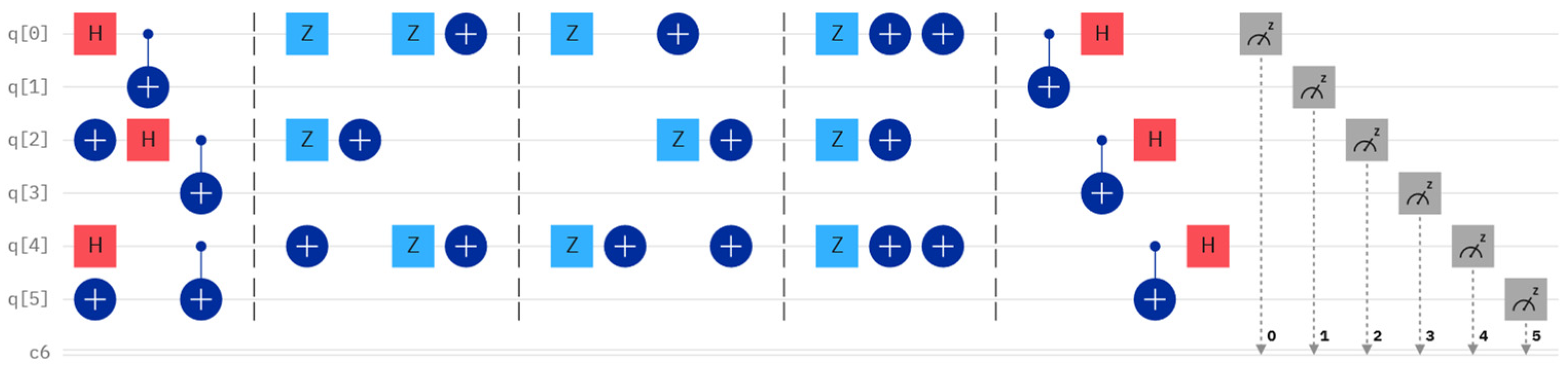
3. The Proposed QPC Protocol
- (1)
- She applies on each j-th qubit in to produce a transformed sequence denoted as .
- (2)
- She generates her own secret key , where for .
- (3)
- She performs on each j-th qubit in to produce a transformed sequence denoted as .
- (4)
- She prepares decoy states chosen from and inserts them into to create a sequence .
- (5)
- She sends to Bob via a quantum channel.
- (1)
- He applies on each j-th qubit in to produce a transformed sequence denoted as .
- (2)
- He generates his own secret key , where for .
- (3)
- He performs on each j-th qubit in to produce a transformed sequence denoted as .
- (4)
- He prepares decoy states chosen from and inserts them into to create a sequence .
- (5)
- He sends to TP through a quantum channel.
- (1)
- TP applies and on each j-th qubit in to produce a transformed sequence denoted as .
- (2)
- TP performs a Bell basis measurement on the qubits in and to obtain the measurement results.
- (3)
- TP compares the measurement results with the prepared Bell states to determine whether . If they are identical, ; otherwise, .
- (4)
- TP conveys the outcomes of the comparison to Alice and Bob.
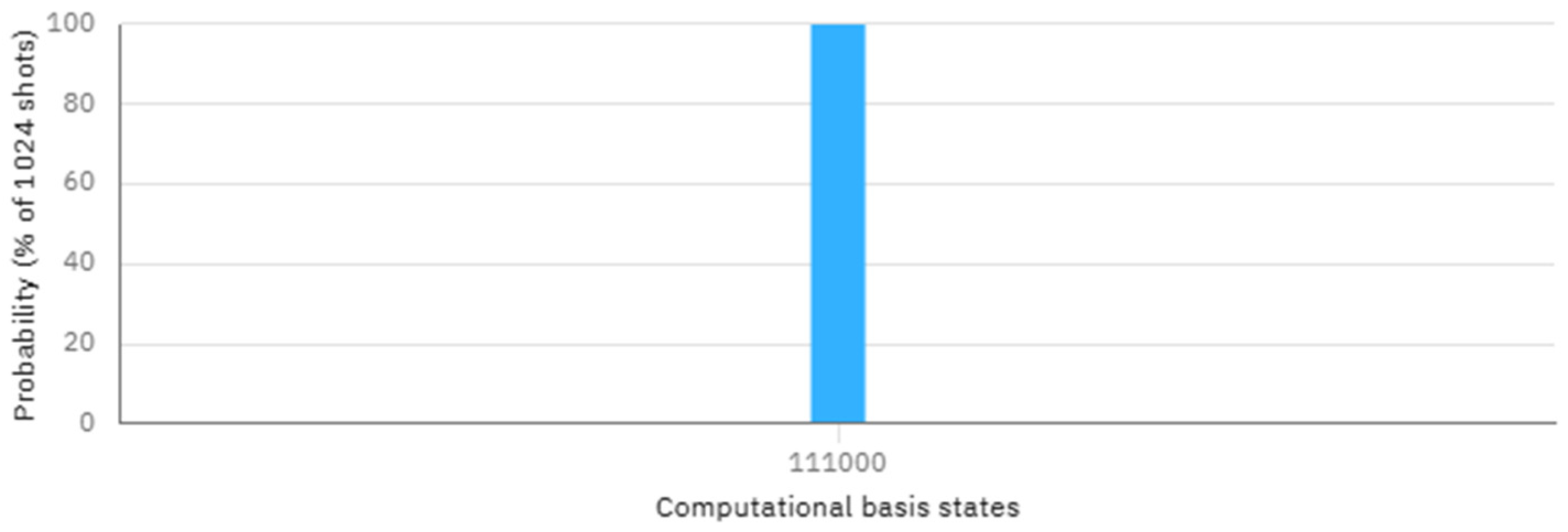
4. Correctness
5. Simulation
6. Security Analysis
6.1. External Attacks
6.1.1. Intercept–Resend Attack
6.1.2. Entangle–Measure Attack
6.1.3. Trojan Horse Attacks
6.2. Participant Attacks
6.2.1. TP’s Attacks
6.2.2. Alice’s Attacks
6.2.3. Bob’s Attack
7. Efficiency Analysis and Comparison
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cramer, R.; Damgård, I.B. Secure Multiparty Computation; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Beimel, A. Secret-sharing schemes: A survey. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Coding and Cryptology, Qingdao, China, 30 May–3 June 2011; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 11–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hillery, M.; Bužek, V.; Berthiaume, A. Quantum secret sharing. Phys. Rev. A 1999, 59, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, D.; Agudo, I.; Lopez, J. Private set intersection: A systematic literature review. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2023, 49, 100567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S. Quantum multi-party private set intersection using single photons. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2024, 649, 129974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannetti, V.; Lloyd, S.; Maccone, L. Quantum private queries. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 230502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Qin, S.; Huang, W.; Wen, Q. Quantum private query: A new kind of practical quantum cryptographic protocol. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2019, 62, 70301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutradhar, K.; Om, H. A Privacy-preserving comparison protocol. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2022, 72, 1815–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chang, Y.; Cheng, W.; Hou, M.; Zhang, S.B. Quantum private comparison of arbitrary single qubit states based on swap test. Chin. Phys. B 2022, 31, 040303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, S.; Xia, J. Efficient Quantum Private Comparison Using Locally Indistinguishable Orthogonal Product States. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Security, Qinghai, China, 15–20 July 2022; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 260–273. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, A.C. Protocols for secure computations. In Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS’ 82), Washington, DC, USA, 3–5 November 1982; p. 160. [Google Scholar]
- Boudot, F.; Schoenmakers, B.; Traoré, J. A fair and efficient solution to the socialist millionaires’ problem. Discret. Appl. Math. 2001, 111, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.-K. Insecurity of quantum secure computations. Phys. Rev. A 1997, 56, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shor, P.W. Polynomial-time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM Rev. 1999, 41, 303–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, L.K. Quantum mechanics helps in searching for a needle in a haystack. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 79, 325–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-G.; Wen, Q.-Y. An efficient two-party quantum private comparison protocol with decoy photons and two-photon entanglement. J. Phys. A Math. Theor. 2009, 42, 055305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-B.; Xu, G.; Niu, X.-X.; Wen, Q.-Y.; Yang, Y.-X. An efficient protocol for the private comparison of equal information based on the triplet entangled state and single-particle measurement. Opt. Commun. 2010, 283, 1561–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, H.-Y.; Lin, J.; Hwang, T. New quantum private comparison protocol using EPR pairs. Quantum Inf. Process. 2011, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Y.-F. Quantum gate-based quantum private comparison. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2020, 59, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Sun, S.-Y.; Zhang, W. Quantum private comparison for the socialist millionaire problem. Front. Phys. 2024, 12, 1408446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, S.-B.; Chang, Y.; Hou, M.; Cheng, W. Efficient Quantum private comparison based on entanglement swapping of bell states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2021, 60, 3783–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Wu, Y. New Quantum Private Comparison Using Bell States. Entropy 2024, 26, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, S.-B.; Cheng, W. Quantum Private Comparison Based on GHZ-type States. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE AFRICON, Arusha, Tanzania, 13–15 September 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Quantum private comparison protocols with a number of multi-particle entangled states. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 44613–44621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; Rahman, A.U.; Ji, Z.; Ji, X.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, H. Two-party quantum private comparison based on eight-qubit entangled state. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2022, 37, 2250026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.X.; Zhang, H.G.; Fan, P.R. Two-party quantum private comparison protocol with maximally entangled seven-qubit state. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2019, 34, 1950229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.-Y.; Ji, Z.-X. Two-party quantum private comparison with five-qubit entangled states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2017, 56, 1517–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, C.; Kues, M.; Roztocki, P.; Wetzel, B.; Grazioso, F.; Little, B.E.; Chu, S.T.; Johnston, T.; Bromberg, Y.; Caspani, L.; et al. Generation of multiphoton entangled quantum states by means of integrated frequency combs. Science 2016, 351, 1176–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S. New Quantum Private Comparison Using Four-Particle Cluster State. Entropy 2024, 26, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Long, D. Quantum private comparison protocol based on cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2013, 52, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, X.-W.; Yu, X.-Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, S.-K. Quantum private comparison protocol with five-particle cluster states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2018, 57, 3874–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Zhang, W.-B.; Zhang, S.-B.; Wang, H.-C.; Yan, L.-L.; Han, G.-H.; Sheng, Z.-W.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Suo, W.; Xiong, J.-X. Quantum private comparison of equality based on five-particle cluster state. Commun. Theor. Phys. 2016, 66, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao-Xu, J.; Tian-Yu, Y. Multi-party quantum private comparison based on the entanglement swapping of d-level cat states and d-level Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 2017, 16, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.-F.; Yao, Z.-Q. Quantum private comparison protocol with d-dimensional Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 2012, 12, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.Z.; Gao, F.; Qin, S.J.; Zhang, J.; Wen, Q.Y. Quantum private comparison protocol based on entanglement swapping of-level Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 2013, 12, 2793–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhao, Y. Quantum private comparison of size using d-level Bell states with a semi-honest third party. Quantum Inf. Process. 2021, 20, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Ma, W.; Lü, L.; He, Y.; Liu, G. Multi-party quantum privacy comparison of size based on d-level GHZ states. Quantum Inf. Process. 2019, 18, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.-R.; Xu, Q.-D.; Du, N.-S.; Gong, L.-H. Semi-quantum private comparison protocol of size relation with d-dimensional Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 2021, 20, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gong, L.-H.; Liu, S.-Q. Multi-party quantum private size comparison protocol with d-dimensional Bell states. Front. Phys. 2022, 10, 981376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.Y.; Lian, J.Y. A novel multi-party semiquantum private comparison protocol of size relationship with d-dimensional single-particle states. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2023, 611, 128424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kues, M.; Reimer, C.; Roztocki, P.; Cortés, L.R.; Sciara, S.; Wetzel, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cino, A.; Chu, S.T.; Little, B.E.; et al. On-chip generation of high-dimensional entangled quantum states and their coherent control. Nature 2017, 546, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, C.; Sciara, S.; Roztocki, P.; Islam, M.; Cortés, L.R.; Zhang, Y.; Fischer, B.; Loranger, S.; Kashyap, R.; Cino, A.; et al. High-dimensional one-way quantum processing implemented on d-level cluster states. Nat. Phys. 2018, 15, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, W.-F.; Zhang, S.-B. Efficient multiparty quantum private comparison protocol based on single photons and rotation encryption. Quantum Inf. Process. 2023, 22, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S. Practical quantum protocols for blind millionaires’ problem based on rotation encryption and swap test. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2024, 637, 129614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhang, S.; Chang, Y.; Yang, F.; Hou, M.; Cheng, W. Quantum secure direct communication based on quantum homomorphic encryption. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2021, 36, 2150263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Anisimova, E.; Khan, I.; Makarov, V.; Marquardt, C.; Leuchs, G. Trojan-horse attacks threaten the security of practical quantum cryptography. New J. Phys. 2014, 16, 123030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mower, J.; Zhang, Z.; Desjardins, P.; Lee, C.; Shapiro, J.H.; Englund, D. High-dimensional quantum key distribution using dispersive optics. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 87, 062322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Zhou, H.; Horansky, R.D.; Lee, C.; Verma, V.B.; Lita, A.E.; Restelli, A.; Bienfang, J.C.; Mirin, R.P.; Gerrits, T.; et al. Photon-efficient quantum key distribution using time–energy entanglement with high-dimensional encoding. New J. Phys. 2015, 17, 022002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Sarihan, M.C.; Chang, K.-C.; Wong, C.W.; Dolecek, L. Efficient information reconciliation for energy-time entanglement quantum key distribution. In Proceedings of the 2019 53rd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 3–6 November 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1364–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Boutros, J.J.; Soljanin, E. Time-entanglement QKD: Secret key rates and information reconciliation Coding. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2023, 71, 7174–7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Bell States | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protocol | Quantum Resource | Unitary Operation | Entanglement Swapping | Quantum Measurement | QKD | Qubit Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref. [16] | EPR pairs | Yes | No | Bell-basis | No | 25% |
| Ref. [17] | GHZ state | Yes | No | Single-particle | No | 33% |
| Ref. [18] | EPR pairs | No | No | Single-particle | No | 50% |
| Ref. [19] | Bell states | Yes | No | basis | No | 50% |
| Ref. [20] | Bell states | Yes | No | Bell-basis | Yes | 50% |
| Ref. [21] | Bell state | No | Yes | GHZ-basis | Yes | 50% |
| Ref. [22] | Bell states | Yes | No | Bell-basis | Yes | 50% |
| Ours | Bell states | Yes | No | Bell-basis | No | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, M.; Wu, Y. Efficient Quantum Private Comparison with Unitary Operations. Mathematics 2024, 12, 3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12223541
Hou M, Wu Y. Efficient Quantum Private Comparison with Unitary Operations. Mathematics. 2024; 12(22):3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12223541
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Min, and Yue Wu. 2024. "Efficient Quantum Private Comparison with Unitary Operations" Mathematics 12, no. 22: 3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12223541
APA StyleHou, M., & Wu, Y. (2024). Efficient Quantum Private Comparison with Unitary Operations. Mathematics, 12(22), 3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12223541





