Evolutionary Approach for DISCO Profit Maximization by Optimal Planning of Distributed Generators and Energy Storage Systems in Active Distribution Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Literature Review
1.2. Research Motivations and Contributions
- Existing research on maximizing DISCO profit in deregulated electricity markets separately performs the planning of DGs or ESSs, while planning both technologies simultaneously has been rarely addressed. Therefore, this paper simultaneously investigates the optimal planning of DGs and ESSs in ADNs to maximize the DISCO profit;
- Unlike most previous studies, the model presented in this paper includes both active and reactive power of DGs and ESSs. This can greatly increase the reactive power support and enhance their role as effective ancillary services;
- In deregulated electricity markets, not only active power but also reactive power is traded between the upstream grid and customers. Therefore, the revenues from trading both active and reactive power are included in the model, which has not been properly studied in previous relevant papers;
- The optimization techniques used so far for the DISCO profit maximization are either traditional, software-based, or outdated EAs, which may not provide superior solutions. Therefore, developing hybrid methods to be specifically compatible with the studied model is necessary and worth investigation;
- Moreover, although SEO has been applied to solve various optimization problems, it has not yet been applied to solve the optimal planning of DGs and ESSs in ADNs for DISCO profit maximization;
- However, despite the remarkable results obtained by the SEO in solving the above problems, it may require further improvements to specifically solve the optimal planning of DGs and ESSs in ADNs;
- Hence, this paper proposes a new hybrid approach that combines the optimization mechanisms of SEO, differential evolution (DE), Lévy flights (LFs), and quasi-oppositional-based learning (QOBL). With this developed combination, the global best of SEO is improved by distinctively applying the search mechanisms of DE and LFs. In addition, the QOBL technique is applied to improve the initial population of the proposed algorithm;
- The new algorithm called the oppositional social engineering differential evolution with Lévy flights (OSEDE/LFs) is benchmarked and compared to several state-of-the-art EAs;
- Furthermore, the developed OSEDE/LFs is applied to solve the optimal planning problem of DGs and ESSs in ADNs for DISCO profit maximization. The standard 30-Bus and IEEE 69-Bus distribution networks are used as test systems. The results are obtained for two case studies and compared to various algorithms, including the original SEO.
2. Integrating DGs and ESSs into Distribution Networks
3. Mathematical Model of the DISCO Profit Maximization Problem
3.1. Objective Function
3.2. Constraints
4. The Proposed Algorithm for DISCO Profit Maximization
4.1. Mechanisms of the Proposed Algorithm
4.1.1. Oppositional and Quasi-Oppositional-Based Learning
4.1.2. Social Engineering Optimizer (SEO)
- The first technique is known as “obtaining”, in which the attacker directly mistreats the defender to effectively obtain its desired traits. Based on that, the defender’s new position is updated using the following equation:
- 2.
- The second technique, known as “phishing”, involves the attacker faking an attack against the defender. The defender then reacts by moving to a safe place. As a result, two new positions of the defender are generated based on the movement of both the attacker and defender, as described in the following equations:
- 3.
- The next technique is called “diversion theft”, in which the attacker deceives the defender by leading the defender to a desired position (set by the attacker). This is achieved using the average distance between the defender and a scaled amount of the attacker. The defender’s new position is then updated by:
- 4.
- The final technique is defined as “pretext”, in which the attacker uses some of the defender’s favorite traits as bait to completely guide and defeat the defender. By the end of this process, the defender’s new position is re-updated using a scaled amount of the defender’s current position and the average distance between the weighted attacker and defender as follows:
4.1.3. Differential Evolution (DE)
4.1.4. Lévy Flights (LFs)
4.1.5. The Proposed OSEDE/LFs Algorithm
4.2. Benchmarking of the OSEDE/LFs Algorithm
4.3. Applying OSEDE/LFs Algorithm to Maximize DISCO Profit
| Algorithm 1: OSEDE/LFs for DISCO profit maximization |
| I—Input the distribution network’s data, define the algorithm’s parameters, and decision variables (number and type). II—Run the power flow and calculate the base-case value of the objective function (before adding DGs or ESSs). III—The algorithm’s initialization: 1. Generate a random population of initial solutions () containing locations and sizes of DGs and ESSs. Active and reactive powers of DGs and ESSs are considered, and charging and discharging schedules of ESSs are defined. 2. Initialize random values for the attacker and defender. 3. Run the power flow and evaluate by the objective function (OF) using Equation (1) subject to all constraints using Equations (11)–(21). 4. Regenerate an initial population by QOBL technique () using Equation (22) and run the power flow to evaluate it by the OF subject to all constraints. 5. Compare and , save the best population, and assign it as the input population to the main loop. IV—Main loop: 6. While stopping criteria are not satisfied: 7. Perform SEO on the current population: ● Train-retrain process. ● Set the 1st social attack. ● While number of attacks < max. number of attacks: ➢ Spot a social attack by the “obtaining,” Equation (25), “phishing,” Equations (26) and (27), “diversion theft,” Equation (28), and “pretext,” Equation (29). ➢ Respond to the social attack. ➢ Number of attacks is increased by 1. End while ● Evaluate the population by the OF subject to all constraints. ● Select a new defender. 8. Update the Global Best based on the new attacker. 9. Apply DE to the current population: ● Mutation using Equation (30) and evaluation of the population using the OF subject to all constraints. ● Crossover using Equation (32) and evaluate the population using the OF subject to all constraints. ● Greedy selection to compare the populations and save the best. 10. Execute LF perturbation on the best population using Equation (33) and evaluate it using the OF subject to all constraints. 11. Crossover using Equation (32) and evaluate the population using the OF subject to all constraints. 12. Greedy selection to compare the populations and save the best. 13. Update the Global Best and set its value as the new attacker. 14. End while. V—Save the global best solutions and display the final results. |
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. The 30-Bus Network
5.1.1. Case 1: The Optimal Planning of DGs
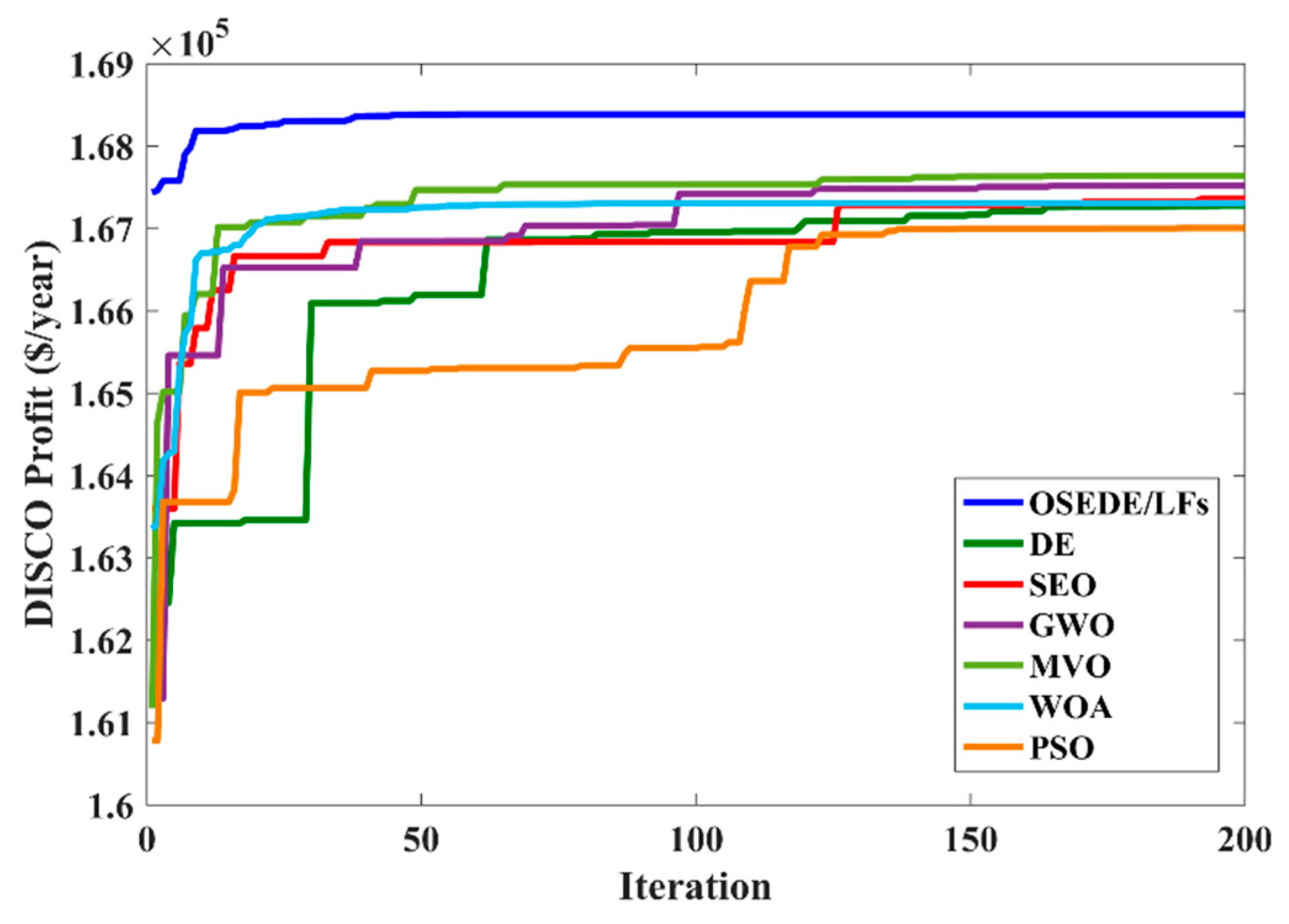
5.1.2. Case 2: The Optimal Planning of DGs and ESSs Simultaneously
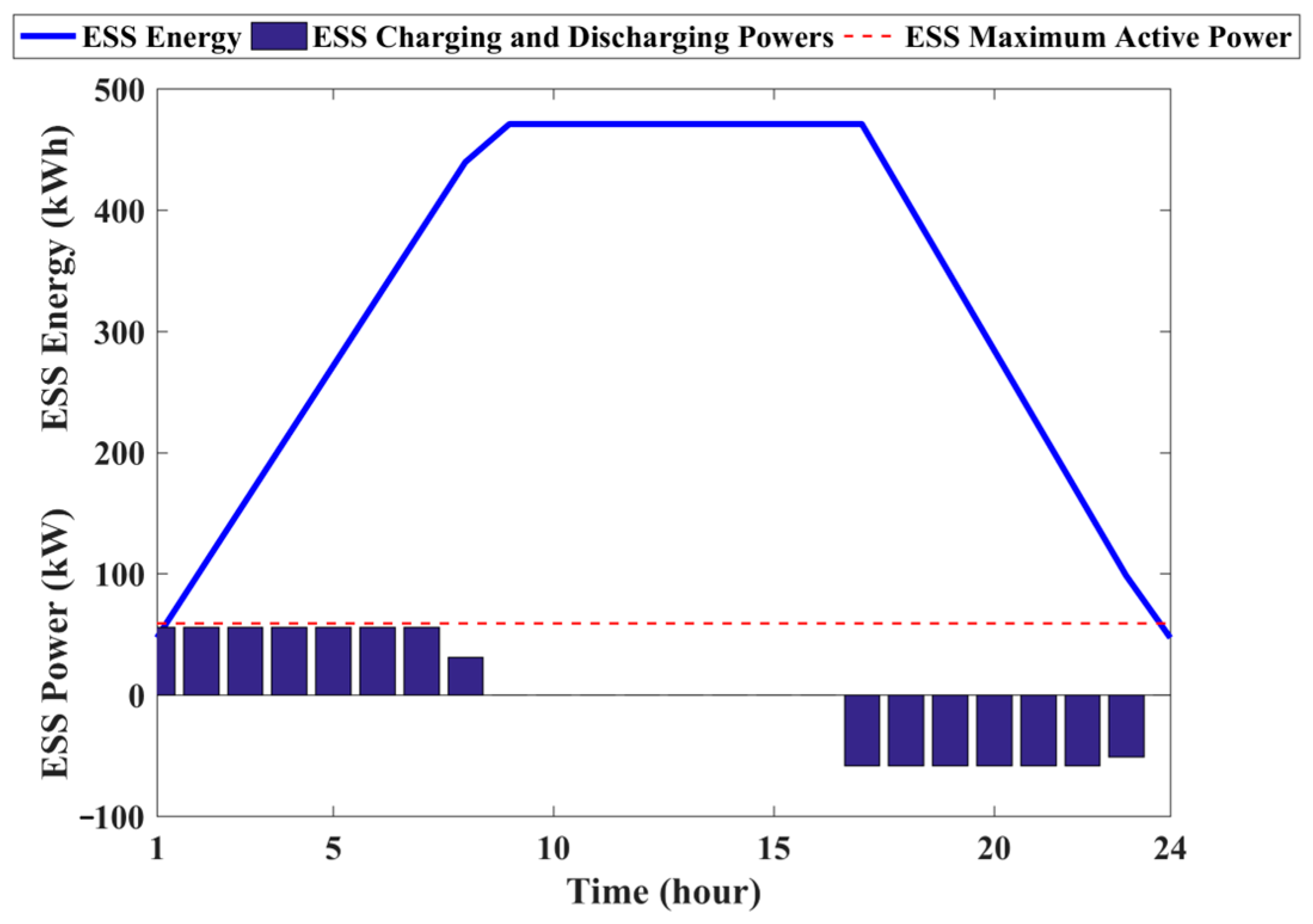
5.1.3. Technical Impacts of DGs and ESSs
5.2. The 69-Bus Network
5.2.1. Case 1: The Optimal Planning of DGs
5.2.2. Case 2: The Optimal Planning of DGs and ESSs Simultaneously
5.2.3. Technical Impacts of DGs and ESSs
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, D.; Shafiullah, G.M.; Das, C.K.; Wong, K.W. A systematic review of optimal planning and deployment of distributed generation and energy storage systems in power networks. J. Energy Storage 2022, 56, 105937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, P.; Meena, D.C.; Malik, H.; Alotaibi, M.A.; Khan, I.A. A Novel Hybrid Approach for Optimal Placement of Non-Dispatchable Distributed Generations in Radial Distribution System. Mathematics 2021, 9, 3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elseify, M.A.; Kamel, S.; Abdel-Mawgoud, H.; Elattar, E.E. A Novel Approach Based on Honey Badger Algorithm for Optimal Allocation of Multiple DG and Capacitor in Radial Distribution Networks Considering Power Loss Sensitivity. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Huang, H.; Song, X.; Peña-Mora, F.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J. Optimal sizing and operations of shared energy storage systems in distribution networks: A bi-level programming approach. Appl. Energy 2022, 307, 118170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrjerdi, H. Simultaneous load leveling and voltage profile improvement in distribution networks by optimal battery storage planning. Energy 2019, 181, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, B.; Wang, B.; Sun, S. Joint planning of distributed generations and energy storage in active distribution networks: A Bi-Level programming approach. Energy 2022, 245, 123226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, J. Deep reinforcement learning based topology-aware voltage regulation of distribution networks with distributed energy storage. Appl. Energy 2023, 332, 120510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zang, W.; Zheng, J.; Cappietti, L.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, E. The influence of waves propagating with the current on the wake of a tidal stream turbine. Appl. Energy 2021, 290, 116729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, C.K.; Bass, O.; Mahmoud, T.S.; Kothapalli, G.; Masoum, M.A.S.; Mousavi, N. An optimal allocation and sizing strategy of distributed energy storage systems to improve performance of distribution networks. J. Energy Storage 2019, 26, 100847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, S.A.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z. Minimization of Active Power Loss Using Enhanced Particle Swarm Optimization. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuradha, K.B.J.; Jayatunga, U.; Perera, H.Y.R. Loss-Voltage Sensitivity Analysis Based Battery Energy Storage Systems Allocation and Distributed Generation Capacity Upgrade. J. Energy Storage 2021, 36, 102357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboori, H.; Hemmati, R.; Abbasi, V. Multistage distribution network expansion planning considering the emerging energy storage systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 105, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Jiang, T.; Li, F.; Chen, H.; Li, X. Distributed energy storage planning in soft open point based active distribution networks incorporating network reconfiguration and DG reactive power capability. Appl. Energy 2018, 210, 1082–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ela, A.A.A.; El-Seheimy, R.A.; Shaheen, A.M.; Wahbi, W.A.; Mouwafi, M.T. PV and battery energy storage integration in distribution networks using equilibrium algorithm. J. Energy Storage 2021, 42, 103041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qiu, J.; Tao, Y. Robust energy systems scheduling considering uncertainties and demand side emission impacts. Energy 2022, 239, 122317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarenia, O.; Shabani, M.J.; Salehpour, M.J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. A new two-stage game-based approach for energy storage pricing in radial distribution system considering uncertainty. J. Energy Storage 2021, 38, 102510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saboori, H.; Hemmati, R. Maximizing DISCO profit in active distribution networks by optimal planning of energy storage systems and distributed generators. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 71, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadati, S.M.B.; Moshtagh, J.; Shafie-khah, M.; Rastgou, A.; Catalão, J.P.S. Bi-level model for operational scheduling of a distribution company that supplies electric vehicle parking lots. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2019, 174, 105875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeddi, B.; Vahidinasab, V.; Ramezanpour, P.; Aghaei, J.; Shafie-khah, M.; Catalão, J.P.S. Robust optimization framework for dynamic distributed energy resources planning in distribution networks. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2019, 110, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weckesser, T.; Dominković, D.F.; Blomgren, E.M.V.; Schledorn, A.; Madsen, H. Renewable Energy Communities: Optimal sizing and distribution grid impact of photovoltaics and battery storage. Appl. Energy 2021, 301, 117408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabzadeh, M.; Kalantar, M. Improving the resilience of distribution network in coming across seismic damage using mobile battery energy storage system. J. Energy Storage 2022, 52, 104891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaki, B. Joint sizing and placement of battery energy storage systems and wind turbines considering reactive power support of the system. J. Energy Storage 2021, 35, 102264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh Nguyen, T.; Trung Nguyen, T.; Le, B. Artificial ecosystem optimization for optimizing of position and operational power of battery energy storage system on the distribution network considering distributed generations. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 208, 118127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Mawgoud, H.; Fathy, A.; Kamel, S. An effective hybrid approach based on arithmetic optimization algorithm and sine cosine algorithm for integrating battery energy storage system into distribution networks. J. Energy Storage 2022, 49, 104154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.A.; Kamel, S.; Hassan, M.H.; Mosaad, M.I.; Aljohani, M. Optimal Power Flow Analysis Based on Hybrid Gradient-Based Optimizer with Moth–Flame Optimization Algorithm Considering Optimal Placement and Sizing of FACTS/Wind Power. Mathematics 2022, 10, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R. The Social Engineering Optimizer (SEO). Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 72, 267–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, V.F.; Pombo, A.V.; Lourenço, J.M. Multi-objective optimization with post-pareto optimality analysis for the integration of storage systems with reactive-power compensation in distribution networks. J. Energy Storage 2019, 24, 100769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, P.; Gidwani, L. An investigation for battery energy storage system installation with renewable energy resources in distribution system by considering residential, commercial and industrial load models. J. Energy Storage 2022, 45, 103493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tizhoosh, H.R. Opposition-Based Learning: A New Scheme for Machine Intelligence. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Intelligence for Modelling, Control and Automation and International Conference on Intelligent Agents, Web Technologies and Internet Commerce (CIMCA-IAWTIC’06), Vienna, Austria, 28–30 November 2005; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Mahfoud, R.J.; Alkayem, N.F.; Sun, Y.; Haes Alhelou, H.; Siano, P.; Parente, M. Improved Hybridization of Evolutionary Algorithms with a Sensitivity-Based Decision-Making Technique for the Optimal Planning of Shunt Capacitors in Radial Distribution Systems. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkayem, N.F.; Shen, L.; Al-hababi, T.; Qian, X.; Cao, M. Inverse Analysis of Structural Damage Based on the Modal Kinetic and Strain Energies with the Novel Oppositional Unified Particle Swarm Gradient-Based Optimizer. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 11689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storn, R.; Price, K. Differential Evolution—A Simple and Efficient Heuristic for Global Optimization over Continuous Spaces. J. Glob. Optim. 1997, 11, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.S.; Deb, S. Cuckoo search via Lévy flights. In Proceedings of the 2009 World Congress on Nature & Biologically Inspired Computing (NaBIC), Coimbatore, India, 9–11 December 2009; pp. 210–214. [Google Scholar]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Hatamlou, A. Multi-Verse Optimizer: A nature-inspired algorithm for global optimization. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 27, 495–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S. SCA: A Sine Cosine Algorithm for solving optimization problems. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2016, 96, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S. The Ant Lion Optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2015, 83, 80–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S. Dragonfly algorithm: A new meta-heuristic optimization technique for solving single-objective, discrete, and multi-objective problems. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 27, 1053–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saremi, S.; Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. Grasshopper Optimisation Algorithm: Theory and application. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 105, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey Wolf Optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S. Moth-flame optimization algorithm: A novel nature-inspired heuristic paradigm. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2015, 89, 228–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Gandomi, A.H.; Mirjalili, S.Z.; Saremi, S.; Faris, H.; Mirjalili, S.M. Salp Swarm Algorithm: A bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 114, 163–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The Whale Optimization Algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




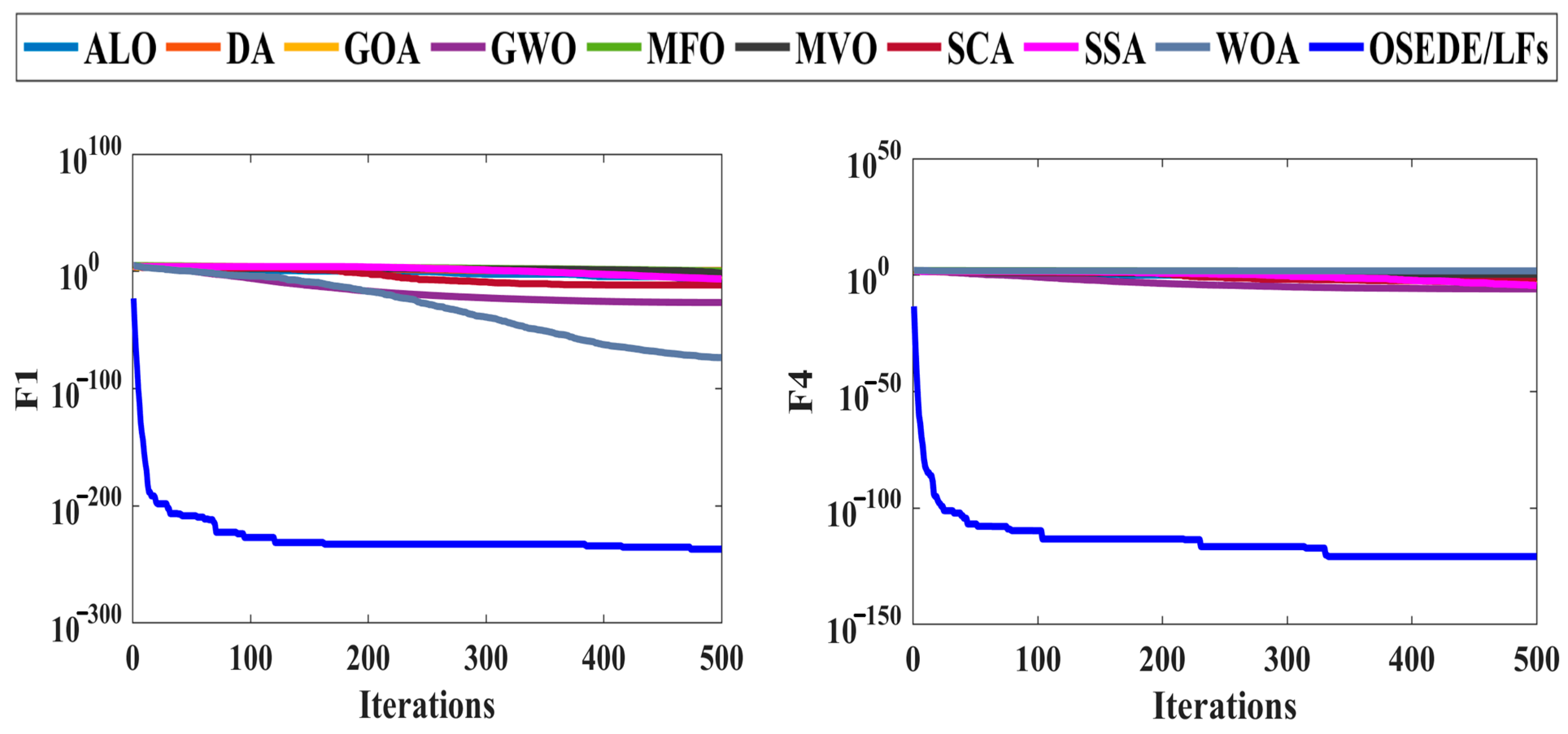
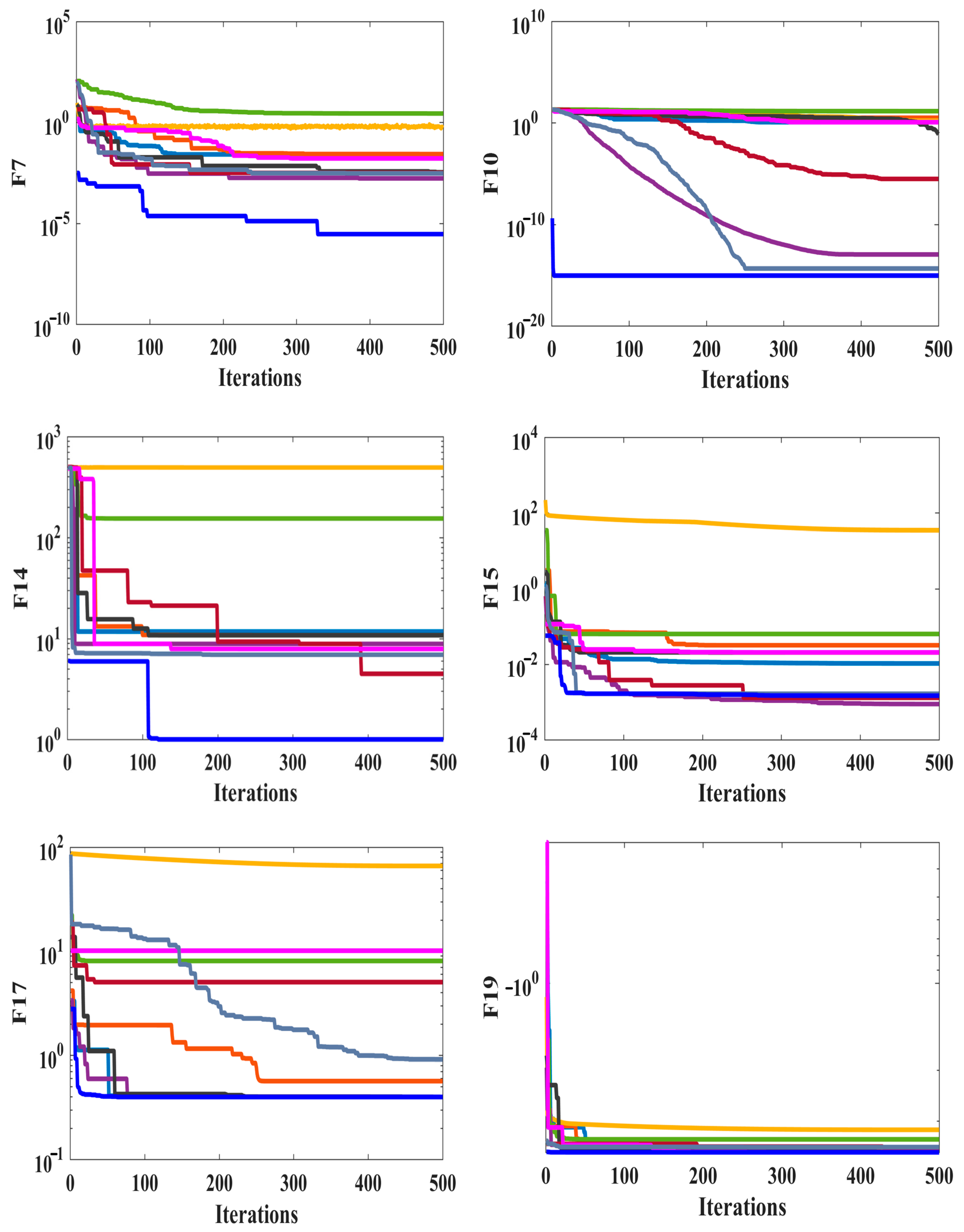







| Function | ALO | DA | GOA | GWO | MFO | MVO | SCA | SSA | WOA | OSEDE/LFs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg | 1.03 × 10−8 | 3.949819 | 1.42 × 10−8 | 1.67 × 10−27 | 1.241253 | 0.014665 | 1.58 × 10−12 | 2.69 × 10−7 | 1.64 × 10−74 | 1.94 × 10−229 | |
| STD | 8.12 × 10−9 | 9.015141 | 9.60 × 10−9 | 3.28 × 10−27 | 0.837278 | 0.005057 | 3.00 × 10−12 | 4.86 × 10−7 | 5.58 × 10−74 | 0 | |
| Rank | 5 | 10 | 6 | 3 | 9 | 8 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 1 | |
| Avg | 0.468302 | 1.599196 | 1.405281 | 7.46 × 10−17 | 23.15880 | 0.037429 | 5.18 × 10−10 | 0.000147 | 6.99 × 10−51 | 6.33 × 10−116 | |
| STD | 1.135663 | 1.284330 | 2.105733 | 5.56 × 10−17 | 20.41869 | 0.010797 | 8.11 × 10−10 | 0.000341 | 2.26 × 10−50 | 2.32 × 10−115 | |
| Rank | 7 | 9 | 8 | 3 | 10 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 1 | |
| Avg | 0.057536 | 413.5663 | 1.15 × 10−5 | 2.48 × 10−5 | 17309.75 | 0.107485 | 0.002350 | 3.86 × 10−6 | 42423.25 | 2.93 × 10−228 | |
| STD | 0.114693 | 1254.954 | 3.48 × 10−5 | 7.41 × 10−5 | 9753.122 | 0.082220 | 0.005775 | 1.63 × 10−5 | 15003.66 | 0 | |
| Rank | 6 | 8 | 3 | 4 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 10 | 1 | |
| Avg | 0.002035 | 3.347957 | 0.000246 | 7.15 × 10−7 | 40.44441 | 0.095011 | 0.001631 | 2.34 × 10−5 | 52.05566 | 9.89 × 10−116 | |
| STD | 0.002150 | 2.075659 | 0.000441 | 8.15 × 10−7 | 10.34281 | 0.031363 | 0.005651 | 1.03 × 10−5 | 29.41085 | 2.27 × 10−115 | |
| Rank | 6 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 10 | 1 | |
| Avg | 84.75871 | 1453.581 | 245.0097 | 26.88655 | 23671.32 | 260.3831 | 7.531969 | 268.6981 | 27.85087 | 28.689685 | |
| STD | 154.9974 | 1966.364 | 598.7379 | 0.731425 | 39396.17 | 471.3051 | 0.561004 | 641.2532 | 0.413844 | 0.0212941 | |
| Rank | 5 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 10 | 7 | 1 | 8 | 3 | 4 | |
| Avg | 6.90 × 10−9 | 20.02457 | 2.76 × 10−8 | 0.713936 | 1.120453 | 0.013753 | 0.374948 | 0.547076 | 0.494683 | 9.06 × 10−10 | |
| STD | 2.36 × 10−9 | 31.59926 | 5.67 × 10−8 | 0.354781 | 0.896267 | 0.006095 | 0.133507 | 0.141783 | 0.321910 | 3.99 × 10−10 | |
| Rank | 2 | 10 | 3 | 8 | 9 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 1 | |
| Avg | 0.027927 | 0.026891 | 0.026351 | 0.001713 | 2.231993 | 0.003225 | 0.003166 | 0.016537 | 0.003342 | 2.17 × 10−5 | |
| STD | 0.014574 | 0.015940 | 0.038760 | 0.001462 | 6.655355 | 0.001524 | 0.003221 | 0.011196 | 0.002799 | 1.87 × 10−5 | |
| Rank | 9 | 8 | 7 | 2 | 10 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 1 | |
| Avg | −2294.46 | −2611.78 | −1502.40 | −6216.58 | −8779.65 | −2981.60 | −5987.54 | −2862.42 | −9428.42 | −2207.91 | |
| STD | 422.8099 | 312.7750 | 175.4154 | 619.3926 | 919.0249 | 374.4465 | 860.8516 | 318.0720 | 1492.768 | 252.9189 | |
| Rank | 2 | 3 | 4 | 8 | 9 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 10 | 1 | |
| Avg | 26.76432 | 27.10466 | 9.728792 | 3.484453 | 127.0368 | 18.16475 | 1.325983 | 20.34688 | 1.14 × 10−14 | 0 | |
| STD | 13.63410 | 13.54998 | 8.528671 | 4.477779 | 46.11280 | 7.303766 | 4.098378 | 8.942808 | 3.50 × 10−14 | 0 | |
| Rank | 8 | 9 | 5 | 4 | 10 | 6 | 3 | 7 | 2 | 1 | |
| Avg | 0.356285 | 2.999678 | 1.789284 | 1.03 × 10−13 | 12.71217 | 0.109276 | 2.67 × 10−6 | 0.937622 | 4.26 × 10−15 | 8.88 × 10−16 | |
| STD | 0.658060 | 1.104676 | 3.609173 | 2.05 × 10−14 | 8.279653 | 0.248928 | 9.34 × 10−6 | 1.026054 | 3.15 × 10−15 | 0 | |
| Rank | 6 | 9 | 8 | 3 | 10 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 1 | |
| Avg | 0.194509 | 0.665993 | 0.139938 | 0.005206 | 14.26329 | 0.341601 | 0.100953 | 0.235602 | 0 | 0 | |
| STD | 0.104195 | 0.365076 | 0.059471 | 0.008578 | 32.85796 | 0.106914 | 0.151824 | 0.140456 | 0 | 0 | |
| Rank | 6 | 9 | 5 | 3 | 10 | 8 | 4 | 7 | 1 | 1 | |
| Avg | 1.846053 | 2.098039 | 0.033959 | 0.042583 | 3.188568 | 0.052179 | 0.109533 | 0.354158 | 0.031228 | 0.095399 | |
| STD | 2.207358 | 1.551511 | 0.142477 | 0.016548 | 3.829839 | 0.170313 | 0.038326 | 0.538863 | 0.042258 | 0.031320 | |
| Rank | 8 | 9 | 2 | 3 | 10 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 1 | 5 | |
| Avg | 0.004241 | 0.840557 | 2.869110 | 0.547333 | 4.282131 | 0.005557 | 0.342977 | 0.002747 | 0.431719 | 0.001131 | |
| STD | 0.008568 | 1.215182 | 0.329120 | 0.208381 | 3.569888 | 0.007426 | 0.085893 | 0.004881 | 0.247168 | 0.003385 | |
| Rank | 3 | 8 | 9 | 7 | 10 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 6 | 1 | |
| Avg | 11.87036 | 11.51923 | 289.5171 | 9.702993 | 203.7239 | 9.958775 | 6.62373 | 6.336665 | 7.455311 | 0.998004 | |
| STD | 6.678188 | 7.662714 | 227.8556 | 5.229677 | 217.4068 | 6.613166 | 4.770185 | 4.018664 | 4.929486 | 9.30 × 10−12 | |
| Rank | 8 | 7 | 10 | 5 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 | |
| Avg | 0.011380 | 0.039980 | 2.064983 | 0.001570 | 0.327337 | 0.018534 | 0.001430 | 0.005387 | 0.001545 | 0.001493 | |
| STD | 0.017426 | 0.050395 | 7.749271 | 0.004541 | 1.386298 | 0.027542 | 0.000476 | 0.007532 | 0.002281 | 0.004136 | |
| Rank | 6 | 8 | 10 | 4 | 9 | 7 | 1 | 5 | 3 | 2 | |
| Avg | −0.95001 | −0.70088 | 178.4440 | −1.01906 | 77.97936 | −1.03159 | −1.03038 | −1.03163 | −1.00860 | −1.03163 | |
| STD | 0.251210 | 0.408504 | 368.3589 | 0.015822 | 215.1951 | 3.51 × 10−5 | 0.001595 | 2.36 × 10−13 | 0.033520 | 4.73 × 10−9 | |
| Rank | 7 | 8 | 10 | 5 | 9 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 6 | 2 | |
| Avg | 0.397887 | 0.518911 | 13.61041 | 0.397961 | 7.499672 | 0.397959 | 1.817831 | 10.88912 | 0.724203 | 0.397887 | |
| STD | 1.83 × 10−10 | 0.344932 | 17.48689 | 0.000156 | 13.10111 | 0.000120 | 2.164800 | 10.22242 | 1.046828 | 2.96 × 10−8 | |
| Rank | 1 | 5 | 10 | 4 | 8 | 3 | 7 | 9 | 6 | 2 | |
| Avg | 11.1 | 85.69132 | 757.7885 | 11.11088 | 6094.757 | 38.10078 | 7.088386 | 3 | 33.92338 | 3.000001 | |
| STD | 19.78277 | 182.3800 | 986.2936 | 19.78185 | 21684.51 | 36.22453 | 18.11531 | 2.87 × 10−12 | 51.15743 | 1.14 × 10−6 | |
| Rank | 4 | 8 | 9 | 5 | 10 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 2 | |
| Avg | −3.84879 | −3.61741 | −2.61897 | −3.57359 | −3.47050 | −3.86112 | −3.66962 | −3.86071 | −3.70897 | −3.86239 | |
| STD | 0.01954 | 0.347895 | 0.968000 | 0.879876 | 0.669847 | 0.002963 | 0.727990 | 0.004423 | 0.190813 | 0.000588 | |
| Rank | 4 | 7 | 10 | 8 | 9 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 5 | 3 | |
| Avg | −3.26794 | −2.93263 | −2.45848 | −3.26838 | −3.15473 | −3.25628 | −2.44660 | −3.21957 | −2.93217 | −3.24402 | |
| STD | 0.077511 | 0.686012 | 0.672128 | 0.123730 | 0.179302 | 0.067931 | 0.719194 | 0.070374 | 0.403542 | 0.062463 | |
| Rank | 2 | 7 | 9 | 1 | 6 | 3 | 10 | 5 | 8 | 4 | |
| Avg | −4.47386 | −3.77144 | −1.65018 | −5.64516 | −3.95988 | −5.73927 | −0.79106 | −5.51181 | −3.86936 | −5.05515 | |
| STD | 1.771646 | 1.899046 | 1.761302 | 3.554868 | 3.106963 | 2.797988 | 0.968610 | 3.268046 | 2.583665 | 8.35 × 10−5 | |
| Rank | 5 | 8 | 9 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 10 | 3 | 7 | 4 | |
| Avg | −5.45753 | −4.56419 | −1.03874 | −8.58711 | −3.88754 | −5.97999 | −1.38504 | −5.71782 | −4.41368 | −5.61545 | |
| STD | 3.449533 | 3.064162 | 0.714230 | 2.95061 | 1.981279 | 3.746717 | 1.161892 | 3.25645 | 2.421325 | 1.62468 | |
| Rank | 5 | 6 | 10 | 1 | 8 | 2 | 9 | 3 | 7 | 4 | |
| Avg | −6.75264 | −4.66103 | −0.91397 | −8.45723 | −4.15571 | −6.53090 | −2.16716 | −6.25604 | −3.87789 | −5.12839 | |
| STD | 3.598021 | 2.814268 | 0.324818 | 3.336493 | 3.298330 | 4.116066 | 1.672882 | 3.715353 | 2.273931 | 0.000214 | |
| Rank | 2 | 6 | 10 | 1 | 7 | 3 | 9 | 4 | 8 | 5 | |
| Total rank | 117 | 179 | 167 | 88 | 206 | 113 | 118 | 107 | 120 | 49 | |
| Average rank | 5.09 | 7.78 | 7.26 | 3.83 | 8.96 | 4.91 | 5.13 | 4.65 | 5.22 | 2.13 | |
| Function | p-Value | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALO | DA | GOA | GWO | MFO | MVO | SCA | SSA | WOA | |
| 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | |
| 8.86 × 10−5 | 1.03 × 10−4 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | |
| 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | |
| 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | |
| 0.601200 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.550300 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.145400 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.601200 | 1.03 × 10−4 | |
| 8.86 × 10−5 | 3.90 × 10−4 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.052200 | 0.001700 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.002200 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.350700 | |
| 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | |
| 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.295900 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | |
| 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.75 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 1.32 × 10−4 | 8.77 × 10−5 | 0.500000 | |
| 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 7.69 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.82 × 10−5 | 0.000488 | |
| 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.031250 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 1.00000 | |
| 0.009996 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.001507 | 0.000120 | 0.000103 | 0.013741 | 0.390530 | 0.295880 | 0.000254 | |
| 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.000254 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.191330 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | |
| 0.000130 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.000130 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.73 × 10−5 | 0.000282 | 8.43 × 10−5 | |
| 0.000892 | 0.000681 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.217960 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.002204 | 0.001507 | 0.033340 | |
| 0.226560 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.000488 | 0.000103 | |
| 8.83 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.000103 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.000103 | |
| 0.247140 | 0.000103 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | |
| 0.004550 | 0.000120 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.001713 | 0.000120 | 0.040044 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.278960 | 8.86 × 10−5 | |
| 0.108430 | 0.005111 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.125860 | 0.191330 | 0.501590 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.262720 | 0.000120 | |
| 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.525650 | 0.116890 | 0.601210 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.708910 | 0.015240 | |
| 0.550290 | 0.156000 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.005111 | 0.006425 | 0.708910 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.851920 | 0.012374 | |
| 0.092963 | 0.370260 | 8.86 × 10−5 | 0.001507 | 0.232230 | 0.061953 | 0.000140 | 0.217960 | 0.003592 | |
| Hours | 1–5 | 6–8 | 9–10 | 11–14 | 15–16 | 17–20 | 21–22 | 23–24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Load (%) | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 90 | 70 |
| Energy prices in autumn and winter | ||||||||
| (USD/kWh) | 0.14 | 0.14 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.22 |
| (USD/kVArh) | 0.028 | 0.028 | 0.044 | 0.044 | 0.060 | 0.060 | 0.060 | 0.044 |
| Energy prices in spring and summer | ||||||||
| (USD/kWh) | 0.18 | 0.20 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.26 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 0.24 |
| (USD/kVArh) | 0.036 | 0.04 | 0.048 | 0.048 | 0.05 | 0.066 | 0.066 | 0.048 |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | 15 | (USD/kWh) | 81 |
| (%) | 20 | (%) | 95 |
| (years) | 5 | (USD/kVAh) | 0.02 |
| (p.u.) | 0.9 | (USD/kWh), autumn and winter | 0.189 |
| (p.u.) | 1.05 | (USD/kVArh), autumn and winter | 0.021 |
| (USD/kVA) | 1150 | (USD/kWh), spring and summer | 0.2268 |
| (USD/kVA) | 805 | (USD/kVArh), spring and summer | 0.0252 |
| Algorithm | Optimal Locations | Optimal Sizes | (USD/Year) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P (kW) | Q (kVAr) | Max | Min | Avg | STD | ||
| Base case | - | - | - | 109,960.54 | |||
| DE | 11 | 102.64 | 68.71 | 167,276.76 | 167,209.48 | 167,270.00 | 21.28 |
| 22 | 170.92 | 111.74 | |||||
| 27 | 77.48 | 51.46 | |||||
| SEO | 11 | 78.27 | 52.80 | 167,354.22 | 167,278.66 | 167,346.70 | 23.89 |
| 21 | 137.95 | 94.86 | |||||
| 25 | 136.29 | 93.01 | |||||
| GWO | 10 | 112.75 | 75.18 | 167,518.23 | 167,480.62 | 167,510.70 | 15.86 |
| 22 | 154.58 | 102.27 | |||||
| 26 | 89.25 | 60.44 | |||||
| MVO | 10 | 112.45 | 75.86 | 167,639.37 | 167,592.21 | 167,634.70 | 14.91 |
| 22 | 155.04 | 103.79 | |||||
| 26 | 88.51 | 60.17 | |||||
| WOA | 11 | 99.07 | 66.57 | 167,308.25 | 167,214.94 | 167,298.90 | 29.51 |
| 21 | 124.11 | 81.46 | |||||
| 25 | 130.36 | 86.92 | |||||
| PSO | 11 | 102.76 | 65.84 | 167,003.63 | 166,923.33 | 166,995.60 | 25.39 |
| 22 | 164.25 | 107.38 | |||||
| 26 | 87.06 | 55.33 | |||||
| OSEDE/LFs | 10 | 110.58 | 79.48 | 168,383.40 | 168,359.84 | 168,381.00 | 7.43 |
| 22 | 154.02 | 111.91 | |||||
| 26 | 86.33 | 61.60 | |||||
| Algorithm | DG Units | ESS Units | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimal Locations | Optimal Sizes | Optimal Locations | Optimal Sizes | |||
| P (kW) | Q (kVAr) | P (kW) | Q (kVAr) | |||
| DE | 12 | 39.83 | 24.99 | 6 | 56 | 112 |
| 23 | 161.02 | 100.21 | 9 | 43 | 79 | |
| 28 | 27.32 | 17.22 | 27 | 42 | 87 | |
| SEO | 12 | 20.03 | 12.47 | 6 | 101 | 200 |
| 21 | 102.79 | 63.98 | 10 | 29 | 55 | |
| 24 | 99.75 | 61.82 | 27 | 34 | 67 | |
| GWO | 11 | 70.75 | 45.70 | 3 | 41 | 85 |
| 21 | 97.16 | 61.74 | 8 | 53 | 101 | |
| 26 | 84.41 | 53.20 | 23 | 61 | 114 | |
| MVO | 10 | 57.74 | 38.35 | 5 | 48 | 96 |
| 12 | 35.63 | 23.57 | 18 | 54 | 103 | |
| 23 | 157.50 | 104.61 | 27 | 39 | 74 | |
| WOA | 11 | 75.67 | 51.05 | 3 | 51 | 103 |
| 20 | 78.64 | 52.23 | 8 | 45 | 86 | |
| 23 | 113.16 | 75.75 | 27 | 50 | 96 | |
| PSO | 21 | 114.09 | 71.30 | 6 | 59 | 116 |
| 24 | 93.72 | 60.05 | 10 | 47 | 88 | |
| 30 | 21.04 | 13.26 | 27 | 39 | 76 | |
| OSEDE/LFs | 11 | 65.52 | 40.78 | 9 | 40 | 74 |
| 22 | 124.63 | 77.24 | 18 | 59 | 113 | |
| 25 | 54.60 | 33.98 | 27 | 35 | 68 | |
| Algorithm | (USD/Year) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Avg | STD | |
| Base case | 109,960.54 | |||
| DE | 176,975.90 | 176,907.66 | 176,969.10 | 21.58 |
| SEO | 177,100.48 | 177,023.97 | 177,092.80 | 24.20 |
| GWO | 177,282.74 | 177,223.70 | 177,276.80 | 18.67 |
| MVO | 177,359.65 | 177,322.13 | 177,352.15 | 15.82 |
| WOA | 177,097.47 | 177,010.40 | 177,088.77 | 27.53 |
| PSO | 176,734.33 | 176,655.29 | 176,726.40 | 24.99 |
| OSEDE/LFs | 178,314.58 | 178,295.48 | 178,308.80 | 9.23 |
| Algorithm | Optimal Locations | Optimal Sizes | (USD/Year) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P (kW) | Q (kVAr) | Max | Min | Avg | STD | ||
| Base case | - | - | - | 729,008.14 | |||
| DE | 22 | 86.58 | 54.79 | 872,448.63 | 872,360.19 | 872,439.80 | 27.97 |
| 61 | 1003.17 | 655.84 | |||||
| 65 | 20.00 | 12.76 | |||||
| SEO | 20 | 168.26 | 111.76 | 871,500.15 | 871,445.35 | 871,483.70 | 26.47 |
| 61 | 146.47 | 94.99 | |||||
| 62 | 853.11 | 575.52 | |||||
| GWO | 24 | 72.46 | 48.88 | 873,201.55 | 873,145.33 | 873,195.90 | 17.78 |
| 61 | 976.67 | 646.15 | |||||
| 65 | 43.91 | 28.82 | |||||
| MVO | 21 | 90.52 | 60.60 | 873,765.87 | 873,715.50 | 873,760.80 | 15.93 |
| 61 | 786.28 | 518.14 | |||||
| 64 | 231.27 | 151.20 | |||||
| WOA | 17 | 68.23 | 44.78 | 871,831.28 | 871,751.03 | 871,817.00 | 30.44 |
| 21 | 21.56 | 13.93 | |||||
| 61 | 1020.37 | 661.76 | |||||
| PSO | 61 | 147.01 | 99.18 | 871,266.96 | 871,110.72 | 871,267.00 | 49.41 |
| 62 | 244.06 | 161.47 | |||||
| 63 | 640.21 | 440.21 | |||||
| OSEDE/LFs | 24 | 88.03 | 60.53 | 875,457.79 | 875,438.81 | 875,450.20 | 9.80 |
| 61 | 765.34 | 530.23 | |||||
| 64 | 240.87 | 169.38 | |||||
| Algorithm | DG Units | ESS Units | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimal Locations | Optimal Sizes | Optimal Locations | Optimal Sizes | |||
| P (kW) | Q (kVAr) | P (kW) | Q (kVAr) | |||
| DE | 17 | 81.14 | 54.52 | 19 | 136 | 295 |
| 61 | 398.98 | 270.19 | 40 | 42 | 141 | |
| 64 | 347.69 | 230.93 | 61 | 181 | 433 | |
| SEO | 10 | 30.78 | 20.53 | 8 | 174 | 390 |
| 22 | 180.25 | 122.07 | 49 | 278 | 747 | |
| 61 | 620.86 | 410.75 | 61 | 289 | 528 | |
| GWO | 18 | 58.618 | 36.48 | 61 | 199 | 366 |
| 25 | 41.51 | 26.27 | 64 | 118 | 221 | |
| 61 | 670.89 | 429.85 | 67 | 212 | 446 | |
| MVO | 17 | 20.27 | 12.93 | 42 | 17 | 38 |
| 26 | 20.00 | 12.61 | 61 | 316 | 584 | |
| 61 | 690.55 | 449.66 | 69 | 159 | 322 | |
| WOA | 22 | 42.90 | 28.27 | 62 | 243 | 491 |
| 23 | 62.03 | 41.84 | 63 | 13 | 24 | |
| 62 | 689.98 | 460.08 | 66 | 114 | 302 | |
| PSO | 27 | 181.65 | 122.07 | 56 | 204 | 393 |
| 60 | 155.16 | 100.23 | 60 | 115 | 262 | |
| 62 | 436.43 | 289.87 | 62 | 176 | 274 | |
| OSEDE/LFs | 61 | 478.16 | 320.08 | 12 | 111 | 232 |
| 64 | 178.24 | 122.09 | 21 | 88 | 178 | |
| 65 | 55.11 | 36.61 | 61 | 281 | 526 | |
| Algorithm | (USD/Year) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | Min | Avg | STD | |
| Base case | 729,008.14 | |||
| DE | 898,119.76 | 898,054.43 | 898,100.20 | 31.56 |
| SEO | 891,756.92 | 891,629.72 | 891,744.20 | 40.23 |
| GWO | 900,334.02 | 900,253.20 | 900,325.90 | 25.56 |
| MVO | 900,813.13 | 900,767.78 | 900,799.50 | 21.91 |
| WOA | 897,791.51 | 897,721.00 | 897,770.40 | 34.06 |
| PSO | 889,726.09 | 889,551.00 | 889,708.60 | 55.37 |
| OSEDE/LFs | 904,013.05 | 903,979.67 | 904,006.40 | 14.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahfoud, R.J.; Alkayem, N.F.; Fernandez-Rodriguez, E.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y. Evolutionary Approach for DISCO Profit Maximization by Optimal Planning of Distributed Generators and Energy Storage Systems in Active Distribution Networks. Mathematics 2024, 12, 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020300
Mahfoud RJ, Alkayem NF, Fernandez-Rodriguez E, Zheng Y, Sun Y, Zhang S, Zhang Y. Evolutionary Approach for DISCO Profit Maximization by Optimal Planning of Distributed Generators and Energy Storage Systems in Active Distribution Networks. Mathematics. 2024; 12(2):300. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020300
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahfoud, Rabea Jamil, Nizar Faisal Alkayem, Emmanuel Fernandez-Rodriguez, Yuan Zheng, Yonghui Sun, Shida Zhang, and Yuquan Zhang. 2024. "Evolutionary Approach for DISCO Profit Maximization by Optimal Planning of Distributed Generators and Energy Storage Systems in Active Distribution Networks" Mathematics 12, no. 2: 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020300
APA StyleMahfoud, R. J., Alkayem, N. F., Fernandez-Rodriguez, E., Zheng, Y., Sun, Y., Zhang, S., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Evolutionary Approach for DISCO Profit Maximization by Optimal Planning of Distributed Generators and Energy Storage Systems in Active Distribution Networks. Mathematics, 12(2), 300. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020300











