VL-Meta: Vision-Language Models for Multimodal Meta-Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
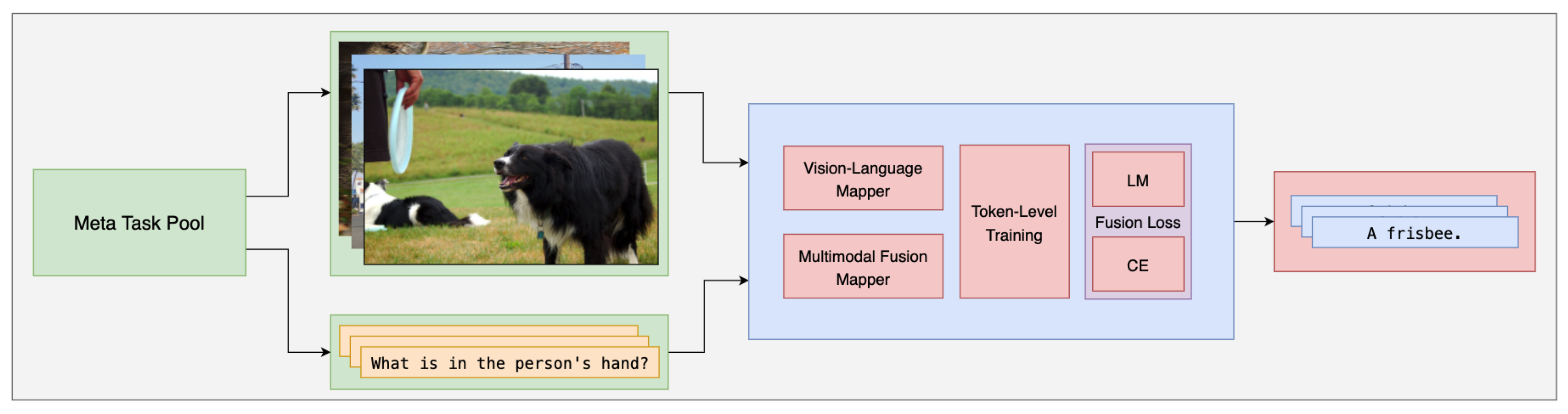
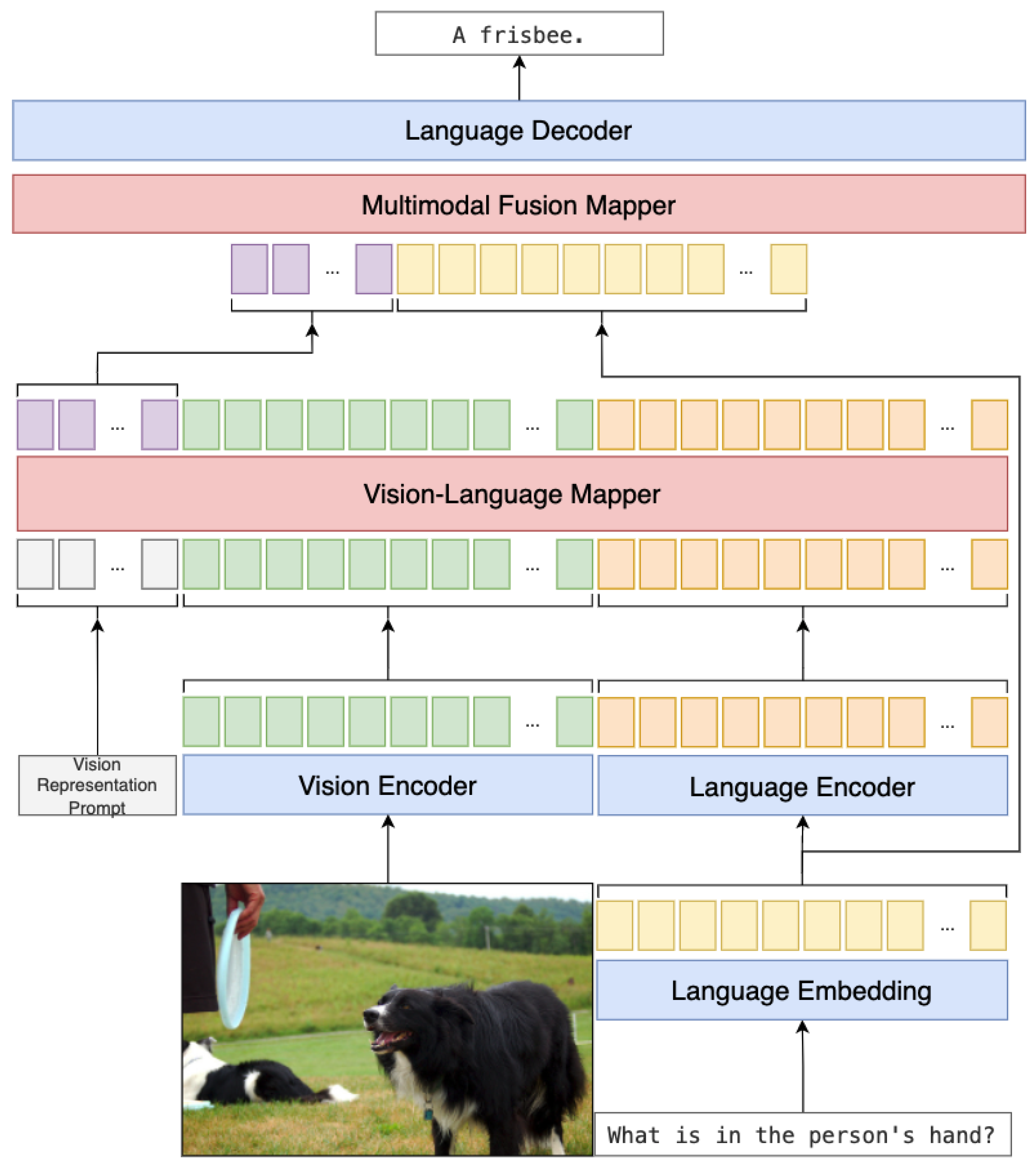
- We present the VL-Meta model structure, including the vision-language mapper and multimodal fusion mapper, simple and light networks that make the large language models understand the visual features by mapping the vision features into language feature space and fusing the final feature, as shown in Section 3.4.
- We propose the meta-task pool that constructs the support set and query set by meta-learning for training and validating the model, as shown in Section 3.2.
- We present the token-level training that makes the training phase align with the generation phase that can import the performance of the model, as shown in Section 3.3.
- We adopt the multi-task fusion loss to help the model learn from different perspectives of data and tasks, as shown in Section 3.5.
2. Related Work
2.1. Multimodal Learning
2.2. Multimodal Meta-Learning
3. VL-Meta
3.1. Problem Definition
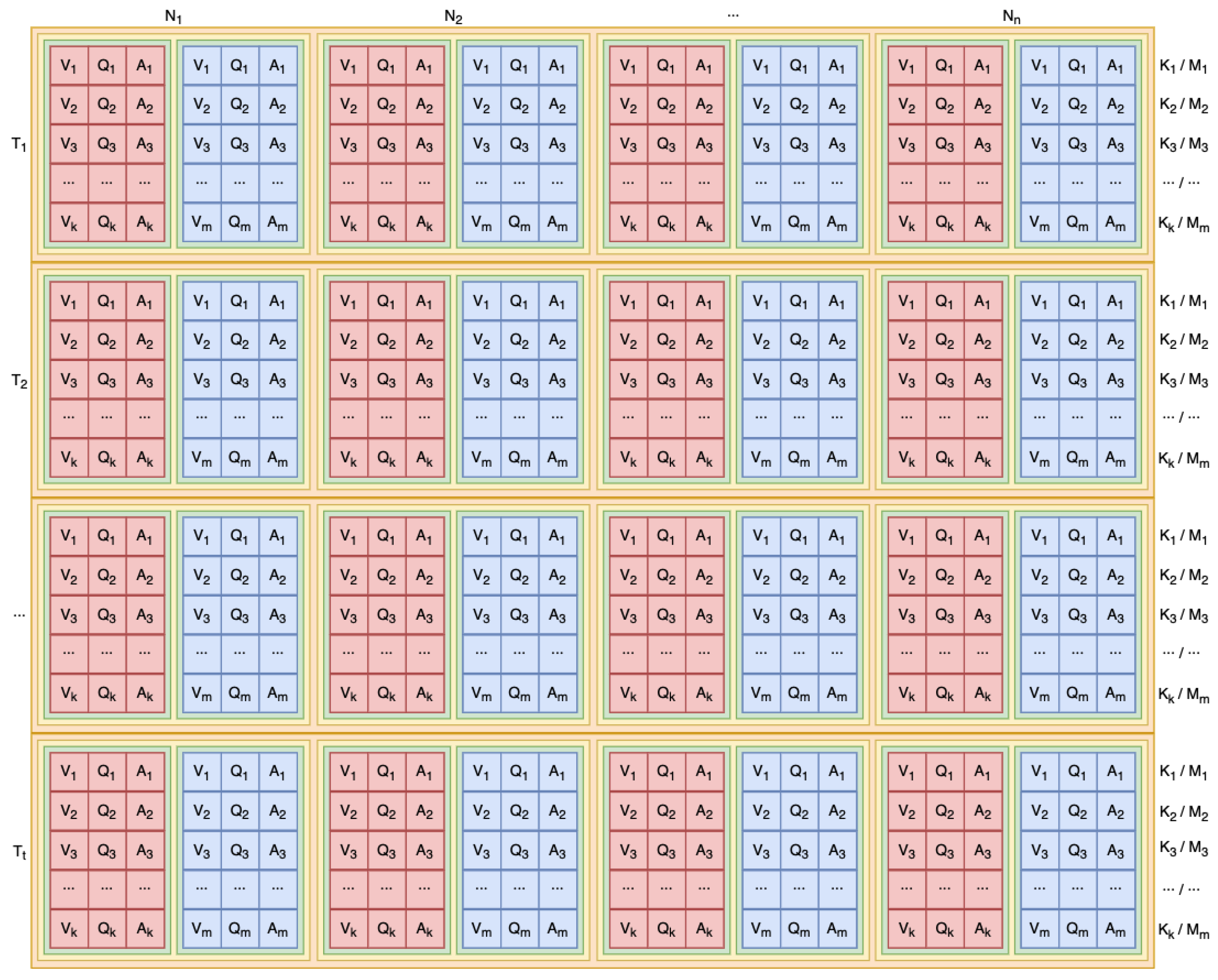
3.2. Meta-Task Pool
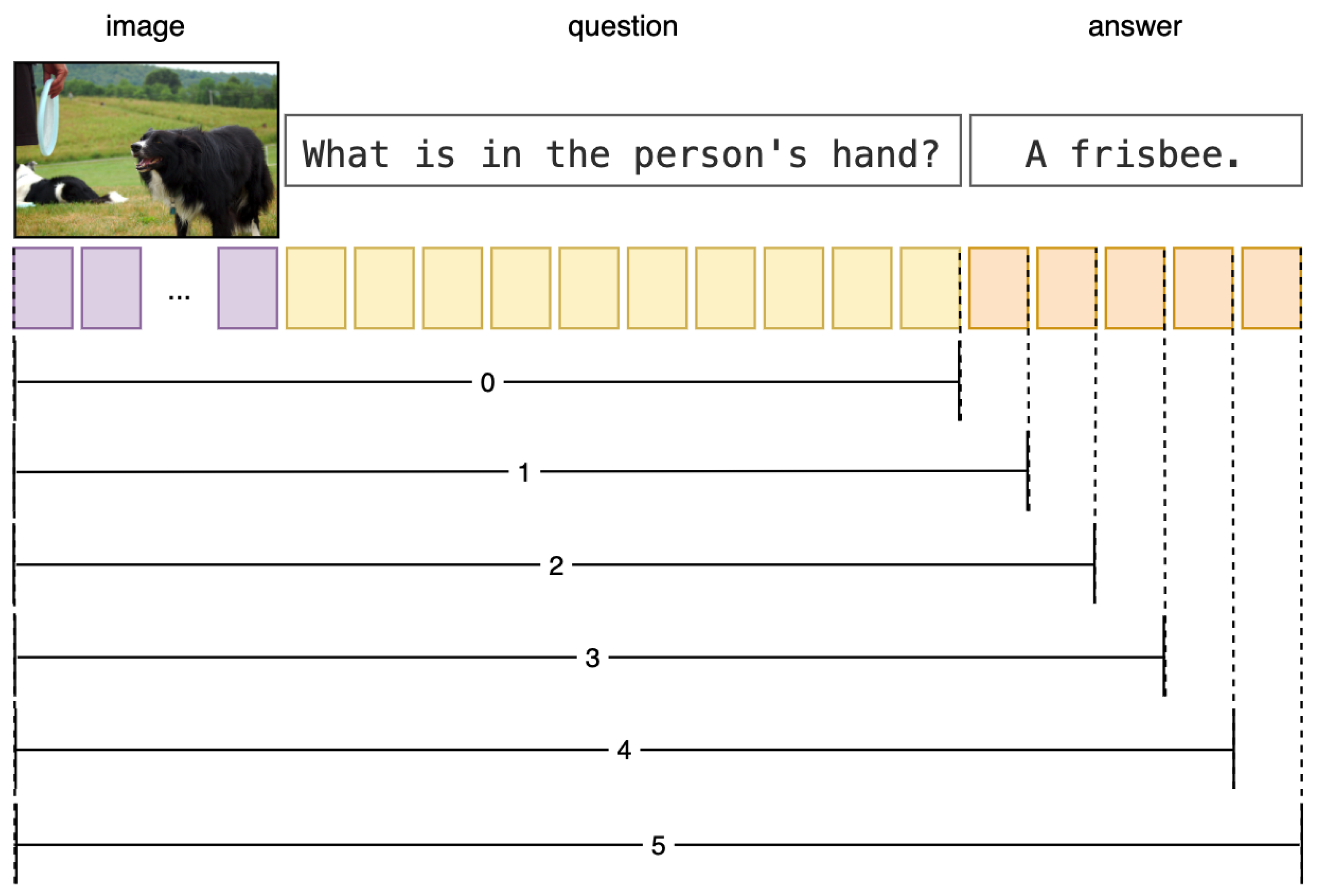
3.3. Token-Level Training
3.4. Model Structure
3.5. Multi-Task Fusion Loss
3.6. Pseudocode
| Algorithm 1 VL -Meta Pseudocode. |
|
4. Experiment
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Implementation Details
4.3. Evaluation Metric
4.4. Results and Discussion
4.5. Ablation Study
4.6. Qualitative Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, M.; Kiros, R.; Zemel, R. Exploring models and data for image question answering. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Antol, S.; Agrawal, A.; Lu, J.; Mitchell, M.; Batra, D.; Zitnick, C.L.; Parikh, D. VQA: Visual Question Answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2425–2433. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Park, E.; Berg, A.C.; Berg, T.L. Visual Madlibs: Fill in the blank Image Generation and Question Answering. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.00278. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2014: 13th European Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; Proceedings, Part V 13. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, J.; Hariharan, B.; Van Der Maaten, L.; Fei-Fei, L.; Lawrence Zitnick, C.; Girshick, R. Clevr: A diagnostic dataset for compositional language and elementary visual reasoning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2901–2910. [Google Scholar]
- Acharya, M.; Kafle, K.; Kanan, C. TallyQA: Answering complex counting questions. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2019, 33, 8076–8084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Mishra, A.; Yadati, N.; Talukdar, P.P. KVQA: Knowledge-Aware Visual Question Answering. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2019, 33, 8876–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreas, J.; Rohrbach, M.; Darrell, T.; Klein, D. Neural module networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Krishna, R.; Zhu, Y.; Groth, O.; Johnson, J.; Hata, K.; Kravitz, J.; Chen, S.; Kalantidis, Y.; Li, L.J.; Shamma, D.A.; et al. Visual genome: Connecting language and vision using crowdsourced dense image annotations. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2017, 123, 32–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Misra, I.; Rohrbach, M.; Learned-Miller, E.; Chen, X. In defense of grid features for visual question answering. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 10267–10276. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Li, R. Differential Networks for Visual Question Answering. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2019, 33, 8997–9004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, A.; Park, D.H.; Yang, D.; Rohrbach, A.; Darrell, T.; Rohrbach, M. Multimodal compact bilinear pooling for visual question answering and visual grounding. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1606.01847. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Yin, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, P.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Hu, H.; Dong, L.; Wei, F.; et al. Oscar: Object-semantics aligned pre-training for vision-language tasks. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Proceedings, Part XXX 16. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 121–137. [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.; Zhu, X.; Cao, Y.; Li, B.; Lu, L.; Wei, F.; Dai, J. VL-BERT: Pre-training of Generic Visual-Linguistic Representations. arXiv 2020, arXiv:1908.08530. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.; Son, B.; Kim, I. Vilt: Vision-and-language transformer without convolution or region supervision. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 5583–5594. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Selvaraju, R.; Gotmare, A.; Joty, S.; Xiong, C.; Hoi, S.C.H. Align before fuse: Vision and language representation learning with momentum distillation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 9694–9705. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yu, J.; Yu, A.W.; Dai, Z.; Tsvetkov, Y.; Cao, Y. SimVLM: Simple Visual Language Model Pretraining with Weak Supervision. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2108.10904. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Changpinyo, S.; Piergiovanni, A.; Padlewski, P.; Salz, D.; Goodman, S.; Grycner, A.; Mustafa, B.; Beyer, L.; et al. PaLI: A Jointly-Scaled Multilingual Language-Image Model. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2209.06794. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Wang, S.; Lin, J.; Bai, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, C. ONE-PEACE: Exploring One General Representation Model Toward Unlimited Modalities. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.11172. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Savarese, S.; Hoi, S. BLIP-2: Bootstrapping Language-Image Pre-training with Frozen Image Encoders and Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.12597. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, M.; Xu, H.; Li, C.; Tian, J.; Bi, B.; Wang, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, S.; Huang, F.; et al. Achieving Human Parity on Visual Question Answering. ACM Trans. Inf. Syst. 2023, 41, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xu, H.; Tian, J.; Wang, W.; Yan, M.; Bi, B.; Ye, J.; Chen, H.; Xu, G.; Cao, Z.; et al. mPLUG: Effective and Efficient Vision-Language Learning by Cross-modal Skip-connections. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.12005. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Wang, Z.; Vasudevan, V.; Yeung, L.; Seyedhosseini, M.; Wu, Y. CoCa: Contrastive Captioners are Image-Text Foundation Models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.01917. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Bao, H.; Dong, L.; Bjorck, J.; Peng, Z.; Liu, Q.; Aggarwal, K.; Mohammed, O.K.; Singhal, S.; Som, S.; et al. Image as a Foreign Language: BEiT Pretraining for All Vision and Vision-Language Tasks. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.10442. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, H.; Wang, W.; Dong, L.; Liu, Q.; Mohammed, O.K.; Aggarwal, K.; Som, S.; Piao, S.; Wei, F. Vlmo: Unified vision-language pre-training with mixture-of-modality-experts. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 32897–32912. [Google Scholar]
- Thrun, S.; Pratt, L. Learning to learn: Introduction and overview. In Learning to Learn; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Vanschoren, J. Meta-Learning: A Survey. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.03548. [Google Scholar]
- Hospedales, T.; Antoniou, A.; Micaelli, P.; Storkey, A. Meta-learning in neural networks: A survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 5149–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Faria, A.C.A.M.; de Castro Bastos, F.; da Silva, J.V.N.A.; Fabris, V.L.; de Sousa Uchoa, V.; de Aguiar Neto, D.G.; dos Santos, C.F.G. Visual Question Answering: A Survey on Techniques and Common Trends in Recent Literature. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.11033. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.X. Meta-learning in natural and artificial intelligence. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2021, 38, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, A.; Moore, R.; Jahromi, S.; Hajati, F.; Kamaleswaran, R. Meta-learning in healthcare: A survey. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2308.02877. [Google Scholar]
- Gharoun, H.; Momenifar, F.; Chen, F.; Gandomi, A.H. Meta-learning approaches for few-shot learning: A survey of recent advances. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.07502. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zang, T.; Yu, J.; Tang, F. Deep Meta-learning in Recommendation Systems: A Survey. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.04415. [Google Scholar]
- yi Lee, H.; Li, S.W.; Vu, N.T. Meta Learning for Natural Language Processing: A Survey. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.01500. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, D.; Medya, S.; Uzzi, B.; Aggarwal, C. Metalearning with graph neural networks: Methods and applications. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2022, 23, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, M.; Van Rijn, J.N.; Plaat, A. A survey of deep meta-learning. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 4483–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H. A Comprehensive Overview and Survey of Recent Advances in Meta-Learning. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.11149. [Google Scholar]
- Tsimpoukelli, M.; Menick, J.L.; Cabi, S.; Eslami, S.; Vinyals, O.; Hill, F. Multimodal few-shot learning with frozen language models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2021, 34, 200–212. [Google Scholar]
- Najdenkoska, I.; Zhen, X.; Worring, M. Meta Learning to Bridge Vision and Language Models for Multimodal Few-Shot Learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.14794. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Liu, S.; An, R.; Zhuo, Y.; Tao, J. An End-to-End Framework Based on Vision-Language Fusion for Remote Sensing Cross-Modal Text-Image Retrieval. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omri, M.; Abdel-Khalek, S.; Khalil, E.M.; Bouslimi, J.; Joshi, G.P. Modeling of Hyperparameter Tuned Deep Learning Model for Automated Image Captioning. Mathematics 2022, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Chen, X.; Song, Z.; Xue, Y.; Cai, Q. Multimodal Interaction and Fused Graph Convolution Network for Sentiment Classification of Online Reviews. Mathematics 2023, 11, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokady, R.; Hertz, A.; Bermano, A.H. ClipCap: CLIP Prefix for Image Captioning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.09734. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Keller, F. Meta-Learning For Vision-and-Language Cross-lingual Transfer. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.14843. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, M.E.; Neumann, M.; Iyyer, M.; Gardner, M.; Clark, C.; Lee, K.; Zettlemoyer, L. Deep Contextualized Word Representations. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Volume 1 (Long Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: New Orleans, Louisiana, 2018; pp. 2227–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K.; Salimans, T.; Sutskever, I. Improving Language Understanding by Generative pre-Training; OpenAI: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Bourdev, L.; Girshick, R.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Zitnick, C.L.; Dollár, P. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in Context. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1405.0312. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtual, 3–7 May 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05101. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Ding, N.; Goodman, S.; Soricut, R. Conceptual Captions: A Cleaned, Hypernymed, Image Alt-text Dataset For Automatic Image Captioning. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers); Gurevych, I., Miyao, Y., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: Melbourne, Australia, 2018; pp. 2556–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kenton, J.D.M.W.C.; Toutanova, L.K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the NAACL-HLT, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; Volume 1, p. 2. [Google Scholar]
| Accuracy (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Methods | Meta | 1-Shot | 5-Shots |
| Frozen [39] | × | 7.8 | 10.5 |
| MML [40] | × | 6.9 | 10.7 |
| ✓ | 8.5 | 13 | |
| VL-Meta (Ours) | × | 7.952 | 10.864 |
| ✓ | 10.936 | 14.456 | |
| Accuracy (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Method | Meta | Cross-Domain | 1-Shot | 5-Shots |
| VL-Meta | × | × | 5.750 | 6.700 |
| × | ✓ | 7.952 | 10.864 | |
| ✓ | × | 7.100 | 8.600 | |
| ✓ | ✓ | 10.936 | 14.456 | |
| No. | Methods | Accuracy (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-Shot | 5-Shots | ||
| 1 | Meta-task pool (w/o) | 7.952 | 10.864 |
| 2 | Cross-domain (w/o) | 7.100 | 8.600 |
| 3 | Vision-language mapper (linear) | 7.280 | 9.096 |
| 4 | Token-level training (w/o) | 8.304 | 9.496 |
| 5 | Multi-task fusion loss (LM) | 7.864 | 8.464 |
| 6 | VL-Meta | 10.936 | 14.456 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, H.; Fan, B.; Ng, B.K.; Lam, C.-T. VL-Meta: Vision-Language Models for Multimodal Meta-Learning. Mathematics 2024, 12, 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020286
Ma H, Fan B, Ng BK, Lam C-T. VL-Meta: Vision-Language Models for Multimodal Meta-Learning. Mathematics. 2024; 12(2):286. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020286
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Han, Baoyu Fan, Benjamin K. Ng, and Chan-Tong Lam. 2024. "VL-Meta: Vision-Language Models for Multimodal Meta-Learning" Mathematics 12, no. 2: 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020286
APA StyleMa, H., Fan, B., Ng, B. K., & Lam, C.-T. (2024). VL-Meta: Vision-Language Models for Multimodal Meta-Learning. Mathematics, 12(2), 286. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12020286






