A Learnheuristic Algorithm Based on Thompson Sampling for the Heterogeneous and Dynamic Team Orienteering Problem
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Describing the DTOP
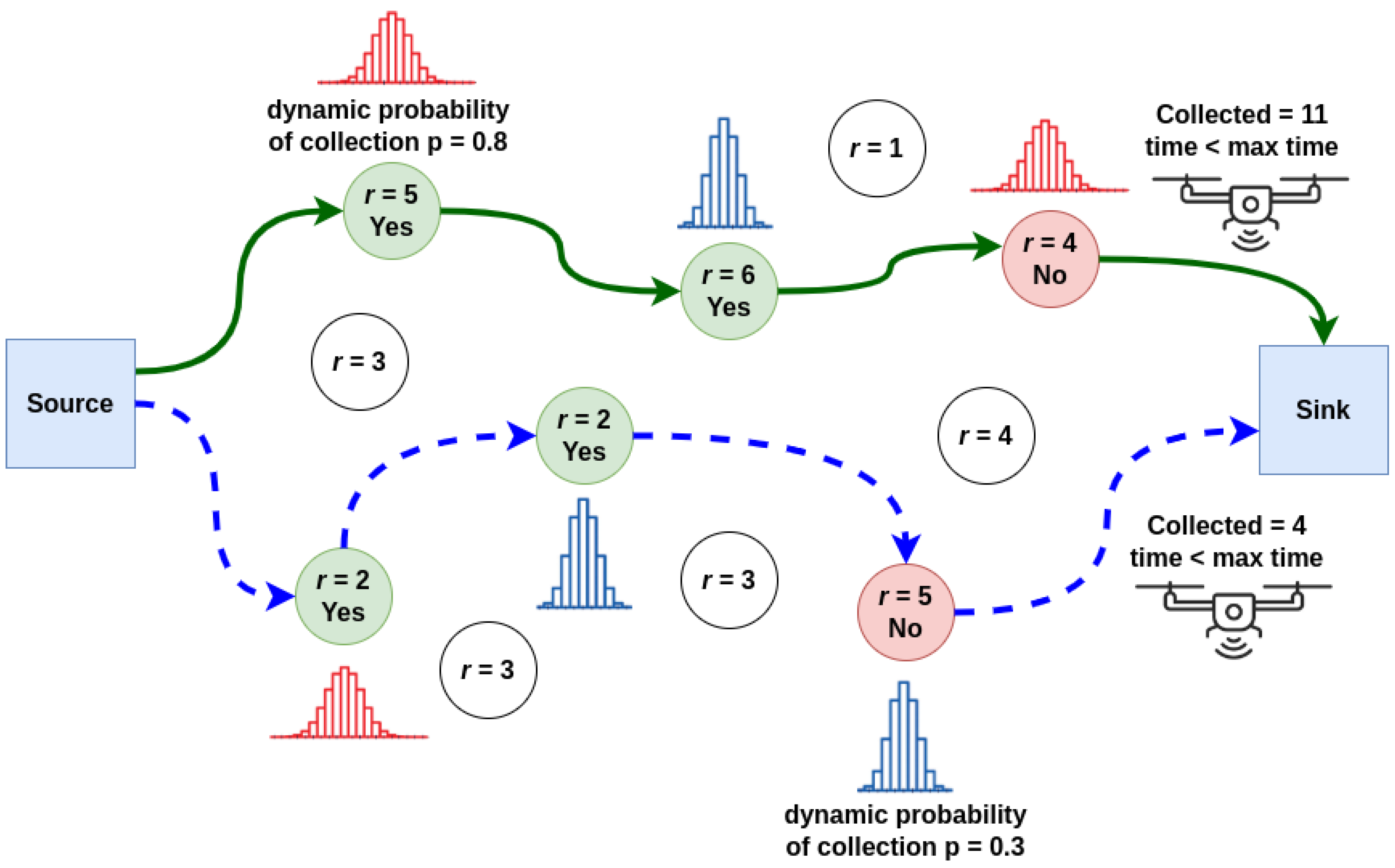
3.1. An Illustrative Example of the DTOP
3.2. A Mathematical Model for the DTOP
4. Modeling Probabilities of Reward for Different Types of Nodes
- Parameter implies the meteorological conditions: a value 0 denotes good meteorological conditions, whereas a value 1 expresses bad ones.
- Parameter represents the congestion level in the urban network: a value 1 denotes severe congestion on the node, whereas a value 0 expresses the lack of it.
- Parameter indicates the remaining battery percentage of an electric vehicle: a value 1 denotes that the battery is full of energy, whereas a value 0 express that the battery is empty.
- Coefficient acts as a baseline intercept term, representing the default scenario when all variables are at their baseline levels.
- Coefficient modulates the influence of meteorological conditions (w).
- Coefficient reflects the impact of congestion (c) at the specific node being visited.
- Coefficient adjusts the outcome based on the remaining battery percentage (b).
5. Solution Approaches for the Heterogeneous DTOP
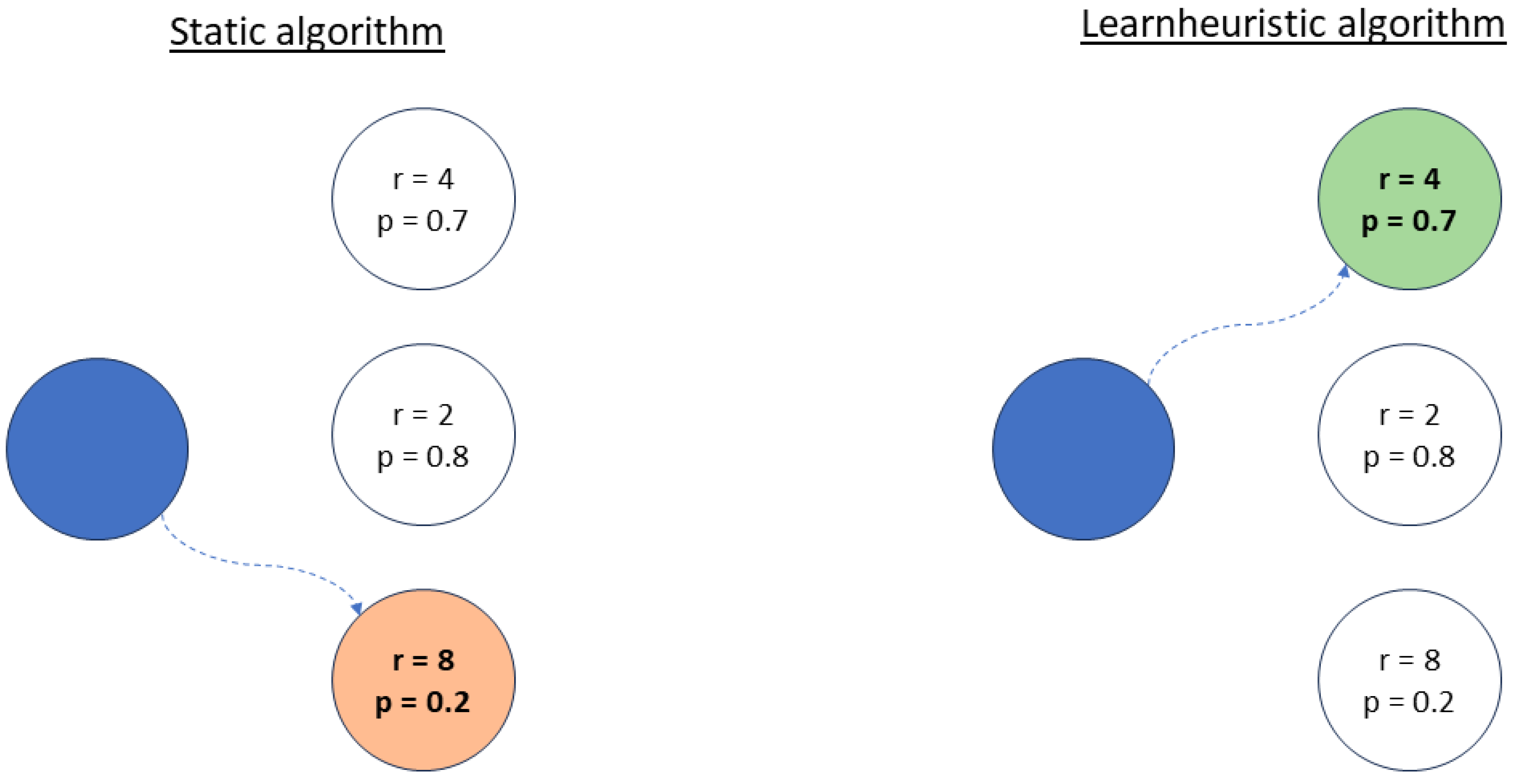
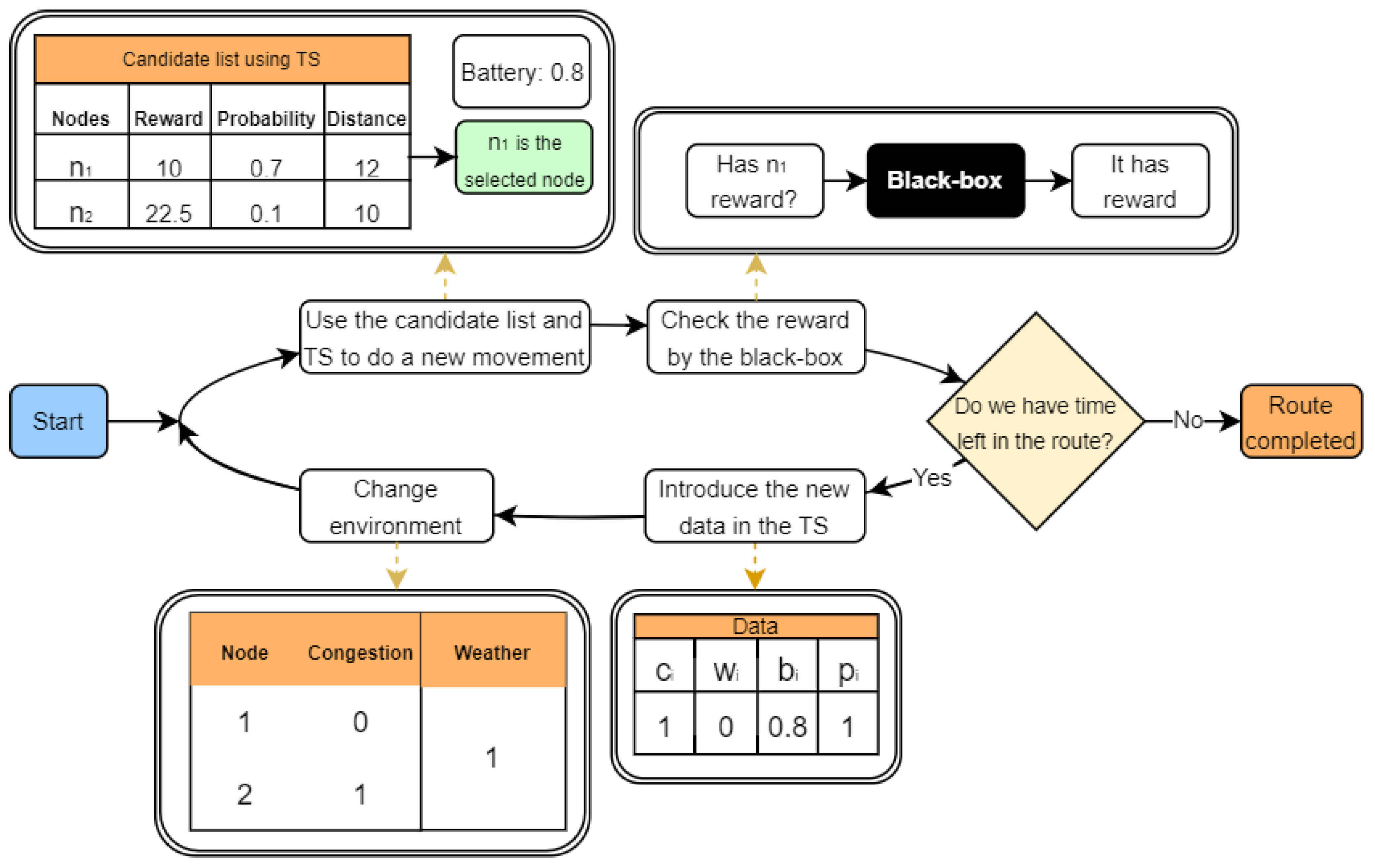
5.1. Online Contextual Thompson Sampling
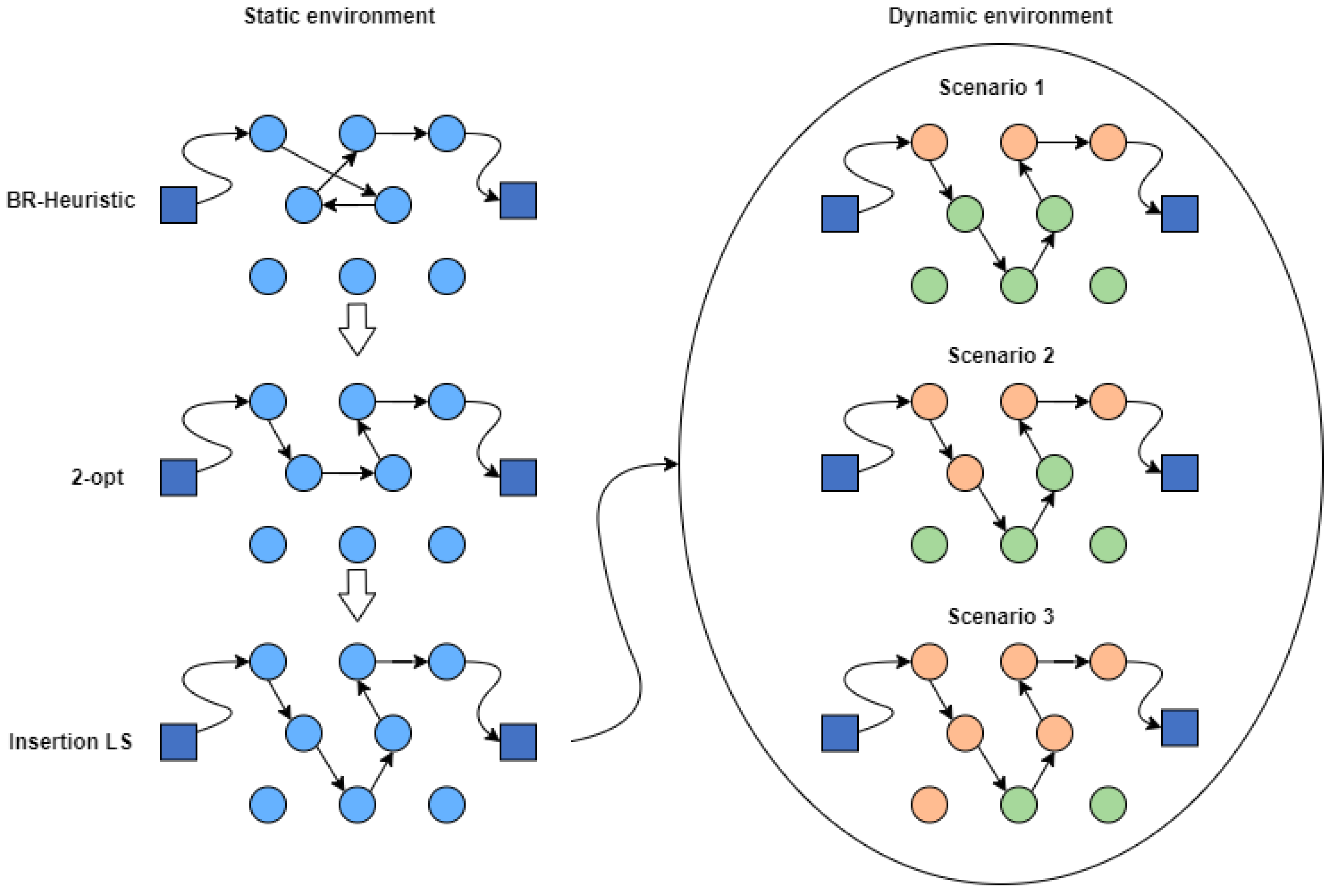
5.2. A Static Constructive Heuristic
| Algorithm 1 Constructive Static Solution (, ) |
|
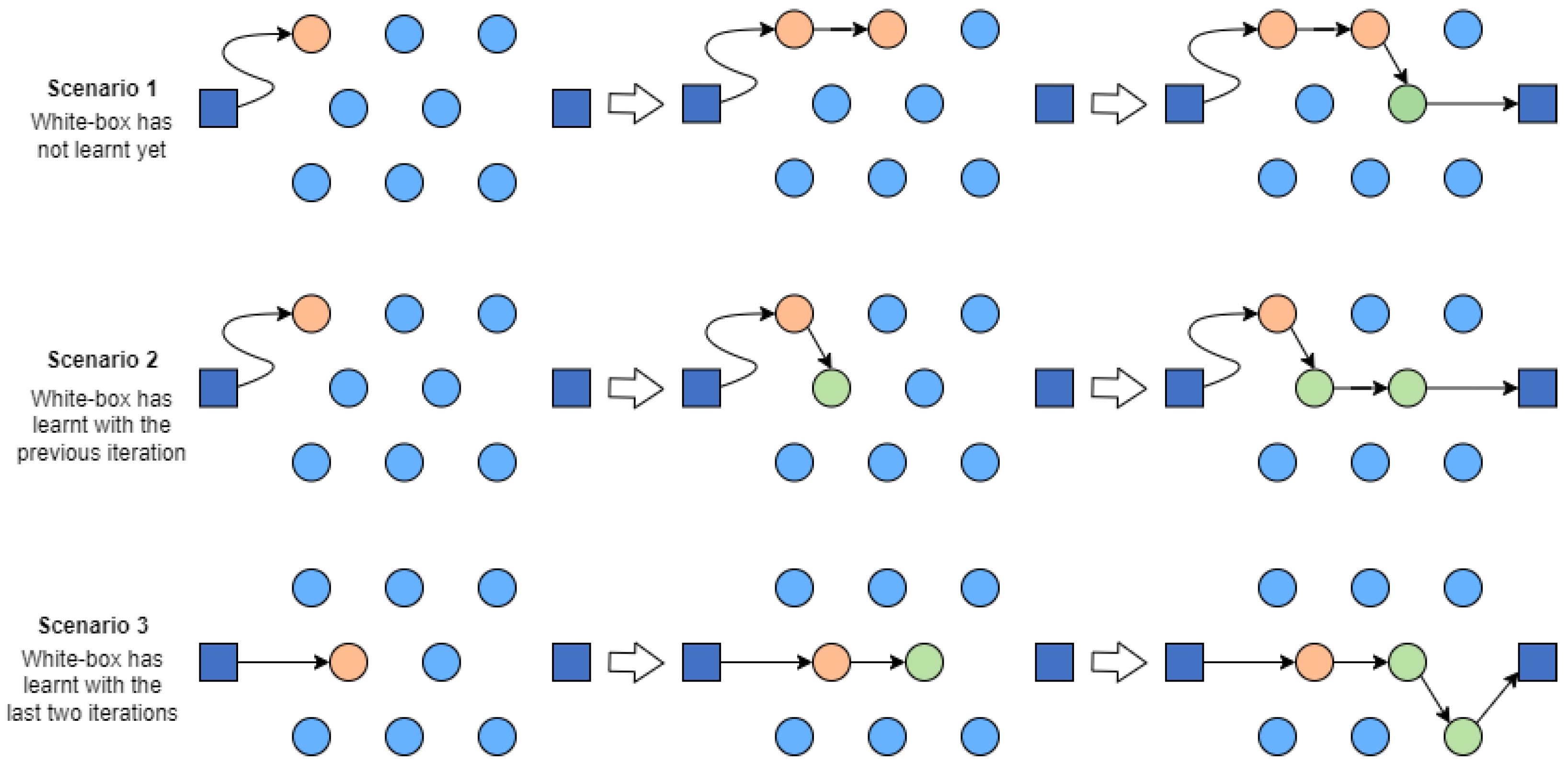
5.3. A Learnheuristic Constructive Heuristic
| Algorithm 2 Constructive Dynamic Solution (, ) |
|
6. Numerical Experiments
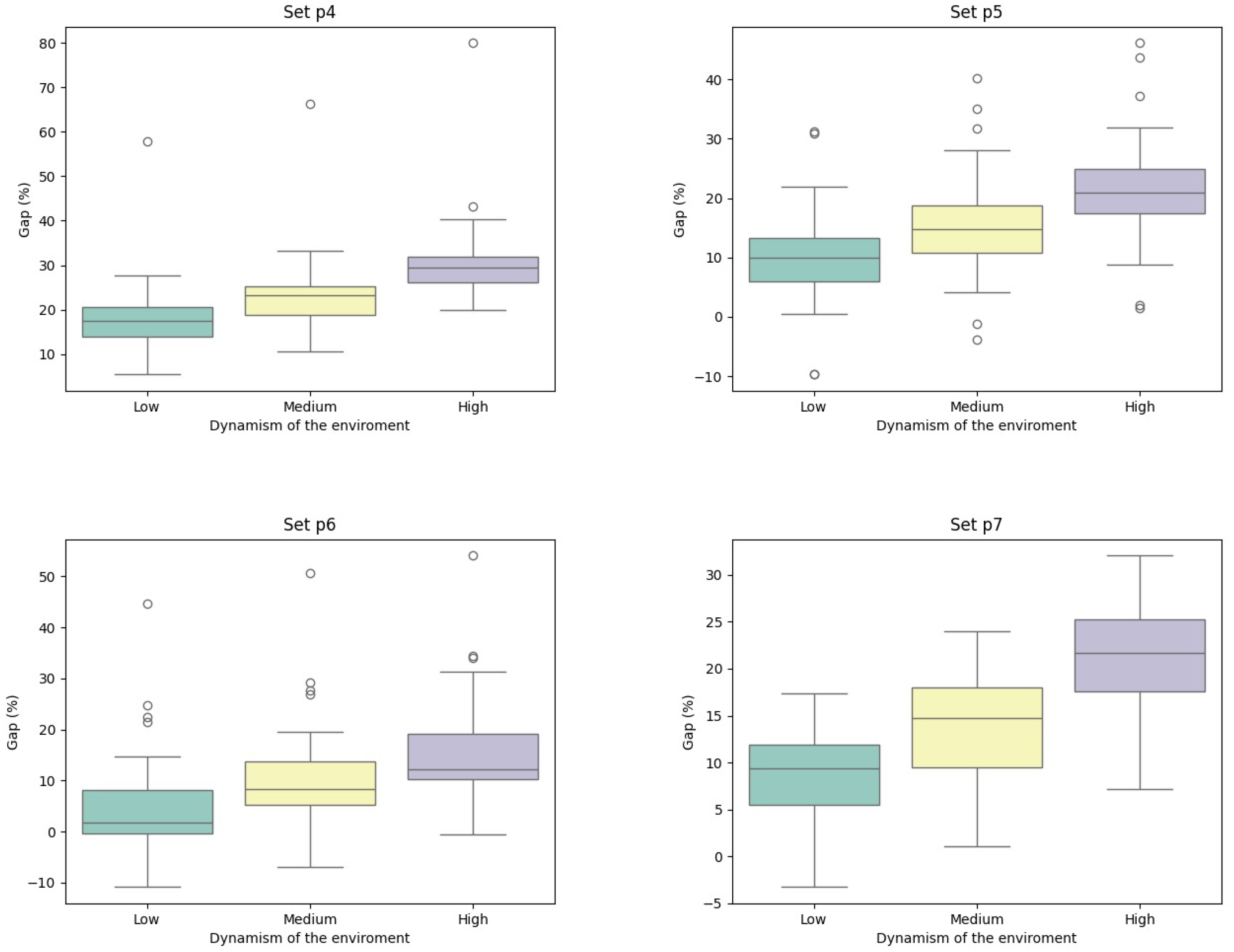
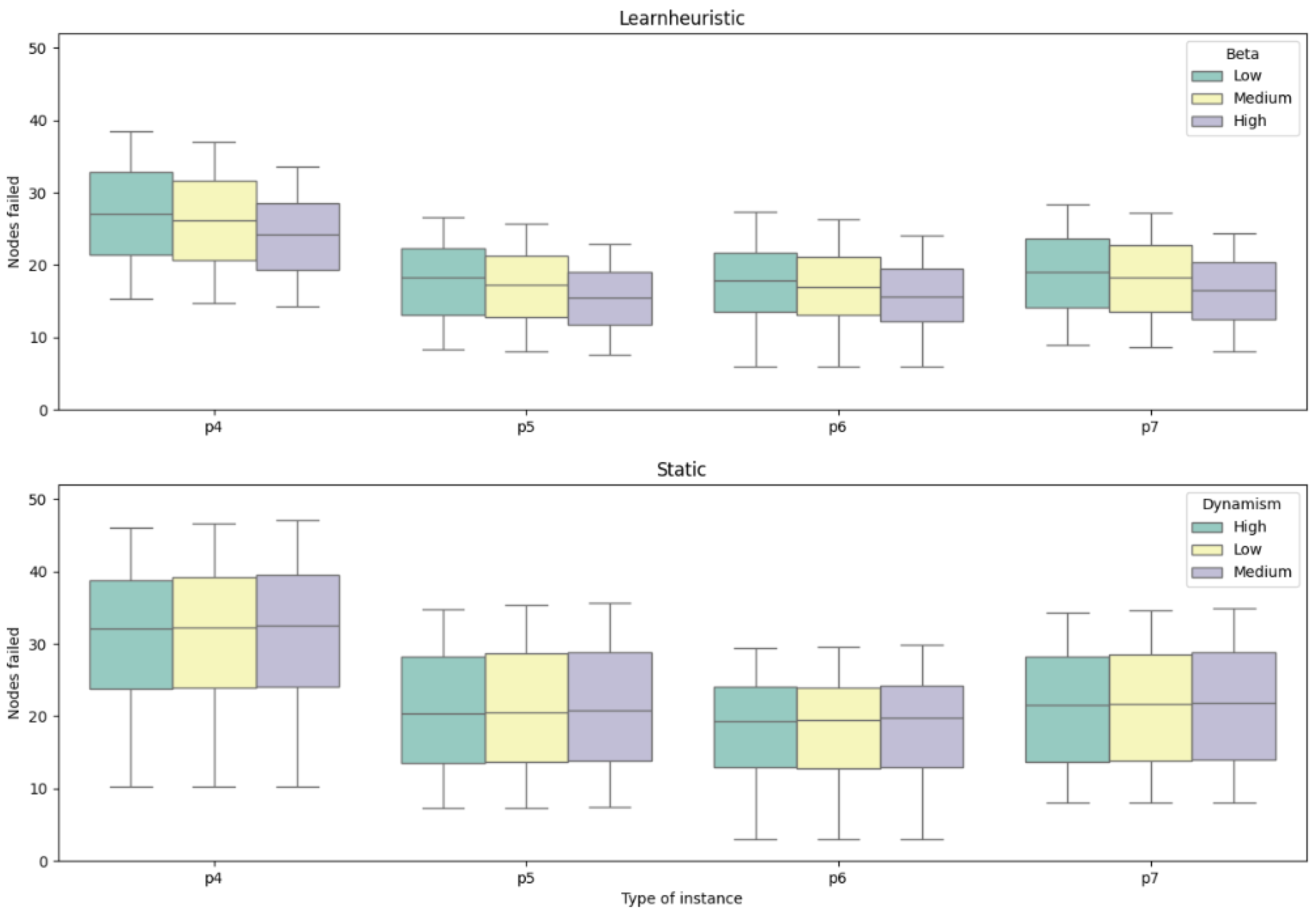
7. Analysis of Results
8. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Archetti, C.; Speranza, M.G.; Vigo, D. Chapter 10: Vehicle routing problems with profits. In Vehicle Routing: Problems, Methods, and Applications, 2nd ed.; SIAM: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 273–297. [Google Scholar]
- Butt, S.E.; Cavalier, T.M. A heuristic for the multiple tour maximum collection problem. Comput. Oper. Res. 1994, 21, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, I.M.; Golden, B.L.; Wasil, E.A. The team orienteering problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1996, 88, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansteenwegen, P.; Souffriau, W.; Van Oudheusden, D. The orienteering problem: A survey. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 209, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, A.; Lau, H.C.; Vansteenwegen, P. Orienteering problem: A survey of recent variants, solution approaches and applications. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 255, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vansteenwegen, P.; Souffriau, W.; Berghe, G.V.; Van Oudheusden, D. Iterated local search for the team orienteering problem with time windows. Comput. Oper. Res. 2009, 36, 3281–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.W.; Vincent, F.Y. A simulated annealing heuristic for the team orienteering problem with time windows. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2012, 217, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeeck, C.; Sörensen, K.; Aghezzaf, E.H.; Vansteenwegen, P. A fast solution method for the time-dependent orienteering problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 236, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, T.; Iravani, S.M.; Daskin, M.S. The orienteering problem with stochastic profits. Iie Trans. 2008, 40, 406–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panadero, J.; Juan, A.A.; Bayliss, C.; Currie, C. Maximising reward from a team of surveillance drones: A simheuristic approach to the stochastic team orienteering problem. Eur. J. Ind. Eng. 2020, 14, 485–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panadero, J.; Barrena, E.; Juan, A.A.; Canca, D. The stochastic team orienteering problem with position-dependent rewards. Mathematics 2022, 10, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Adulyasak, Y.; Rousseau, L.M.; Zhu, N.; Ma, S. Team orienteering with time-varying profit. Informs J. Comput. 2022, 34, 262–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejaz, W.; Anpalagan, A.; Ejaz, W.; Anpalagan, A. Internet of Things enabled electric vehicles in smart cities. In Internet of Things for Smart Cities: Technologies, Big Data and Security; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, L.d.C.; Tordecilla, R.D.; Castaneda, J.; Juan, A.A.; Faulin, J. Electric vehicle routing, arc routing, and team orienteering problems in sustainable transportation. Energies 2021, 14, 5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnau, Q.; Juan, A.A.; Serra, I. On the use of learnheuristics in vehicle routing optimization problems with dynamic inputs. Algorithms 2018, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayliss, C.; Juan, A.A.; Currie, C.S.; Panadero, J. A learnheuristic approach for the team orienteering problem with aerial drone motion constraints. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 92, 106280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrina, G.; Pugliese, L.D.P.; Guerriero, F.; Laporte, G. Drone-aided routing: A literature review. Transp. Res. Part Emerg. Technol. 2020, 120, 102762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, A.; Agatz, N.; Campbell, J.; Golden, B.; Pesch, E. Optimization approaches for civil applications of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or aerial drones: A survey. Networks 2018, 72, 411–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas Viloria, D.; Solano-Charris, E.L.; Muñoz-Villamizar, A.; Montoya-Torres, J.R. Unmanned aerial vehicles/drones in vehicle routing problems: A literature review. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2021, 28, 1626–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyman, M.; Martin, X.A.; Panadero, J.; Juan, A.A. A Sim-Learnheuristic for the Team Orienteering Problem: Applications to Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. Algorithms 2024, 17, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mufalli, F.; Batta, R.; Nagi, R. Simultaneous sensor selection and routing of unmanned aerial vehicles for complex mission plans. Comput. Oper. Res. 2012, 39, 2787–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Ahn, J. Multi-start team orienteering problem for UAS mission re-planning with data-efficient deep reinforcement learning. Appl. Intell. 2024, 54, 4467–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, K.; Sanjeevi, S.; Montez, C. A branch-and-price algorithm for a team orienteering problem with fixed-wing drones. Euro J. Transp. Logist. 2022, 11, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggi, M.; Viana, H.; Uchoa, E. The team orienteering problem: Formulations and branch-cut and price. In Proceedings of the 10th Workshop on Algorithmic Approaches for Transportation Modelling, Optimization, and Systems (ATMOS’10). Schloss Dagstuhl-Leibniz-Zentrum fuer Informatik, Liverpool, UK, 9 September 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, D.C.; El-Hajj, R.; Moukrim, A. A branch-and-cut algorithm for solving the team orienteering problem. In Proceedings of the Integration of AI and OR Techniques in Constraint Programming for Combinatorial Optimization Problems: 10th International Conference, CPAIOR 2013, Yorktown Heights, NY, USA, 18–22 May 2013; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 332–339. [Google Scholar]
- Keshtkaran, M.; Ziarati, K.; Bettinelli, A.; Vigo, D. Enhanced exact solution methods for the team orienteering problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2016, 54, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, D.C.; Guibadj, R.N.; Moukrim, A. A PSO-based memetic algorithm for the team orienteering problem. In Proceedings of the Applications of Evolutionary Computation: EvoApplications 2011: EvoCOMNET, EvoFIN, EvoHOT, EvoMUSART, EvoSTIM, and EvoTRANSLOG, Torino, Italy, 27–29 April 2011; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 471–480. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, D.C.; Guibadj, R.N.; Moukrim, A. An effective PSO-inspired algorithm for the team orienteering problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2013, 229, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuswamy, S.; Lam, S.S. Discrete particle swarm optimization for the team orienteering problem. Memetic Comput. 2011, 3, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.; Quintas, A.; Oliveira, J.A.; Pereira, G.A.; Dias, L. Solving the team orienteering problem: Developing a solution tool using a genetic algorithm approach. In Proceedings of the Soft Computing in Industrial Applications: Proceedings of the 17th Online World Conference on Soft Computing in Industrial Applications, Online, 3–14 December 2012; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 365–375. [Google Scholar]
- Bouly, H.; Dang, D.C.; Moukrim, A. A memetic algorithm for the team orienteering problem. 4OR 2010, 8, 49–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archetti, C.; Hertz, A.; Speranza, M.G. Metaheuristics for the team orienteering problem. J. Heuristics 2007, 13, 49–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, V.; Martí, R.; Sánchez-Oro, J.; Duarte, A. GRASP with path relinking for the orienteering problem. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2014, 65, 1800–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, M.; Marti, R. GRASP and path relinking for 2-layer straight line crossing minimization. Informs J. Comput. 1999, 11, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Rubiano, L.; Juan, A.; Bayliss, C.; Panadero, J.; Faulin, J.; Copado, P. A biased-randomized learnheuristic for solving the team orienteering problem with dynamic rewards. Transp. Res. Procedia 2020, 47, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Peyman, M.; Panadero, J.; Juan, A.A.; Xhafa, F. IoT analytics and agile optimization for solving dynamic team orienteering problems with mandatory visits. Mathematics 2022, 10, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.F.; Uguina, A.R.; Panadero, J.; Juan, A.A. A learnheuristic algorithm for the capacitated dispersion problem under dynamic conditions. Algorithms 2023, 16, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, L.; Glorie, K.; Van Der Ster, S.; Barros, A.I.; Monsuur, H. A two-stage approach to the orienteering problem with stochastic weights. Comput. Oper. Res. 2014, 43, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osisanwo, F.; Akinsola, J.; Awodele, O.; Hinmikaiye, J.; Olakanmi, O.; Akinjobi, J. Supervised machine learning algorithms: Classification and comparison. Int. J. Comput. Trends Technol. 2017, 48, 128–138. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, D.J.; Van Roy, B.; Kazerouni, A.; Osband, I.; Wen, Z. A tutorial on Thompson sampling. Found. Trends Mach. Learn. 2018, 11, 1–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, W.R. On the likelihood that one unknown probability exceeds another in view of the evidence of two samples. Biometrika 1933, 25, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q. Multi-Armed Bandits: Theory and Applications to Online Learning in Networks; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.K.; Nadarajah, S. Handbook of Beta Distribution and Its Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chapelle, O.; Li, L. An empirical evaluation of thompson sampling. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2011, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Askhedkar, A.R.; Chaudhari, B.S. Multi-Armed Bandit Algorithm Policy for LoRa Network Performance Enhancement. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2023, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S.T.; Moothedath, S. Thompson sampling for stochastic bandits with noisy contexts: An information-theoretic regret analysis. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.11565. [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez, O.; Juan, A.A.; Faulin, J. A biased-randomized algorithm for the two-dimensional vehicle routing problem with and without item rotations. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2014, 21, 375–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, T.M. Introduction to Deep Learning for Engineers: Using Python and Google Cloud Platform; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
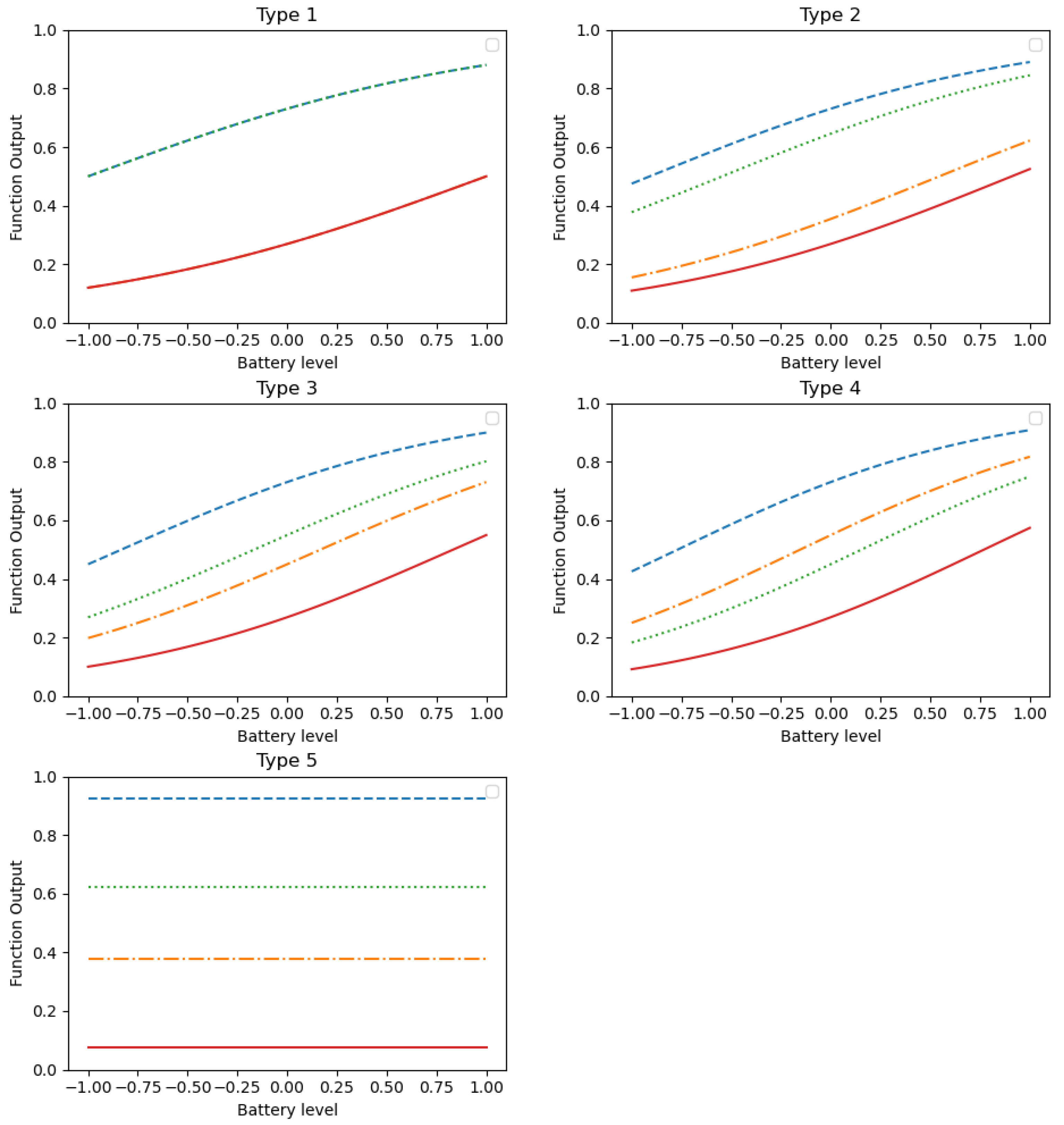
| Node Type | Low | Medium | High | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 0 | −1 | 1 | 0 | −1.2 | 1.2 | 0 | −2 | 1 |
| N2 | −0.2 | −0.8 | 1.1 | −0.4 | 1 | 1.4 | −0.6 | −1.5 | 2 |
| N3 | −0.4 | −0.6 | 1.2 | −0.6 | −0.8 | 1.6 | −1.2 | −1 | 3 |
| N4 | −0.6 | −0.4 | 1.3 | −0.8 | −0.6 | 1.8 | −1.8 | −0.8 | 4 |
| N5 | −1 | −1.5 | 0 | −1.5 | −2 | 0 | −2 | −3 | 0 |
| Instance | Static | Learnheuristic | Gap (%) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Low (1) | Medium (2) | High (3) | Low (4) | Medium (5) | High (6) | ||||||||||||||||
| Time | OF | Dyn. OF | Time | OF | Dyn. OF | Time | OF | Dyn. OF | Time | OF | Dyn. OF | Time | OF | Dyn. OF | Time | OF | Dyn. OF | (1)–(4) | (2)–(5) | (3)–(6) | |
| p4.2 | 12.07 | 901.90 | 431.54 | 12.02 | 876.17 | 428.36 | 12.03 | 901.90 | 437.75 | 23.06 | 804.40 | 492.11 | 23.00 | 800.48 | 512.88 | 22.77 | 796.39 | 551.54 | 14.04% | 19.73% | 25.99% |
| p4.3 | 10.71 | 804.40 | 384.37 | 10.64 | 804.40 | 381.14 | 10.66 | 804.40 | 388.59 | 19.71 | 728.19 | 449.91 | 19.68 | 726.84 | 464.95 | 19.57 | 724.11 | 503.12 | 17.05% | 21.99% | 29.47% |
| p4.4 | 9.30 | 677.13 | 323.75 | 9.31 | 652.40 | 321.59 | 9.24 | 652.40 | 329.19 | 16.15 | 632.55 | 389.08 | 16.12 | 632.55 | 404.64 | 16.07 | 630.45 | 436.25 | 20.18% | 25.83% | 32.52% |
| p5.2 | 4.98 | 995.00 | 460.21 | 4.99 | 995.00 | 456.15 | 4.98 | 995.00 | 470.05 | 9.59 | 808.99 | 491.18 | 9.58 | 805.59 | 509.95 | 9.59 | 804.18 | 554.34 | 6.73% | 11.79% | 17.93% |
| p5.3 | 4.53 | 843.56 | 391.34 | 4.51 | 843.56 | 387.32 | 4.49 | 843.56 | 398.28 | 8.50 | 703.94 | 430.44 | 8.48 | 700.71 | 445.13 | 8.47 | 698.28 | 480.76 | 9.99% | 14.93% | 20.71% |
| p5.4 | 4.17 | 718.94 | 331.94 | 4.16 | 718.94 | 328.33 | 4.17 | 718.94 | 337.54 | 7.49 | 607.85 | 372.75 | 7.49 | 607.20 | 386.45 | 7.49 | 602.68 | 416.14 | 12.29% | 17.70% | 23.28% |
| p6.2 | 4.84 | 868.60 | 411.58 | 4.83 | 868.60 | 406.55 | 4.84 | 868.60 | 411.90 | 9.54 | 703.31 | 424.62 | 9.53 | 704.34 | 441.83 | 9.53 | 702.32 | 476.01 | 3.17% | 8.68% | 15.56% |
| p6.3 | 4.74 | 766.58 | 363.46 | 4.71 | 766.58 | 358.49 | 4.69 | 766.58 | 364.34 | 9.08 | 670.13 | 391.32 | 9.06 | 667.54 | 403.94 | 9.06 | 662.22 | 426.72 | 7.67% | 12.68% | 17.12% |
| p6.4 | 4.37 | 664.00 | 315.66 | 4.44 | 664.00 | 310.76 | 4.42 | 664.00 | 317.22 | 8.51 | 633.14 | 354.50 | 8.52 | 631.78 | 365.79 | 8.45 | 622.72 | 384.12 | 12.31% | 17.71% | 21.09% |
| p7.2 | 82.17 | 700.16 | 332.47 | 84.15 | 700.16 | 329.20 | 84.10 | 700.16 | 335.54 | 157.27 | 581.28 | 360.32 | 157.12 | 579.53 | 373.86 | 155.19 | 570.09 | 401.66 | 8.37% | 13.57% | 19.70% |
| p7.3 | 77.82 | 650.45 | 307.38 | 77.33 | 650.45 | 304.01 | 77.41 | 650.45 | 310.06 | 136.70 | 544.72 | 335.94 | 136.43 | 543.56 | 349.74 | 135.88 | 316.64 | 469.32 | 9.29% | 15.04% | 51.37% |
| p7.4 | 67.27 | 547.23 | 259.14 | 67.15 | 547.21 | 256.89 | 67.05 | 547.21 | 262.05 | 108.88 | 472.65 | 293.58 | 109.25 | 472.42 | 306.31 | 107.99 | 467.08 | 332.55 | 13.29% | 19.24% | 26.90% |
| Average | 23.92 | 761.49 | 359.40 | 24.02 | 757.29 | 355.73 | 24.01 | 759.43 | 363.54 | 42.87 | 657.60 | 398.81 | 42.86 | 656.04 | 413.79 | 42.50 | 633.10 | 452.71 | 11.20% | 16.57% | 25.14% |
| Instance | Static | Learnheuristic | Gap (%) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Low (1) | Medium (2) | High (3) | Low (4) | Medium (5) | High (6) | (1)–(4) | (2)–(5) | (3)–(6) | |||||||||||||
| Nodes | Fails | Nodes | Fails | Nodes | Fails | Nodes | Fails | Nodes | Fails | Nodes | Fails | ||||||||||
| p4.2 | 60.62 | 33.23 | 60.62 | 33.52 | 60.62 | 32.93 | 59.62 | 27.59 | 59.19 | 26.36 | 58.71 | 23.93 | −16.97% | −21.37% | −27.33% | ||||||
| p4.3 | 56.77 | 31.65 | 56.77 | 31.94 | 56.77 | 31.47 | 56.68 | 27.19 | 56.49 | 26.36 | 56.14 | 24.11 | −14.10% | −17.48% | −23.39% | ||||||
| p4.4 | 51.33 | 29.31 | 51.33 | 29.52 | 51.33 | 29.00 | 52.76 | 26.77 | 52.71 | 25.94 | 52.46 | 24.07 | −8.66% | −12.12% | −16.99% | ||||||
| p5.2 | 38.50 | 21.61 | 38.50 | 21.78 | 38.50 | 21.29 | 36.60 | 17.05 | 36.51 | 16.23 | 36.47 | 14.50 | −21.10% | −25.46% | −31.93% | ||||||
| p5.3 | 36.48 | 20.91 | 36.48 | 21.07 | 36.48 | 20.67 | 36.07 | 17.70 | 35.99 | 16.96 | 35.92 | 15.41 | −15.34% | −19.49% | −25.45% | ||||||
| p5.4 | 34.65 | 20.39 | 34.65 | 20.53 | 34.65 | 20.17 | 35.57 | 18.52 | 35.57 | 17.87 | 35.47 | 16.38 | −9.20% | −12.98% | −18.79% | ||||||
| p6.2 | 38.50 | 21.18 | 38.50 | 21.40 | 38.50 | 21.20 | 37.89 | 17.63 | 37.85 | 16.88 | 37.78 | 15.25 | −16.75% | −21.14% | −28.05% | ||||||
| p6.3 | 39.17 | 22.00 | 39.17 | 22.26 | 39.17 | 22.03 | 40.49 | 20.63 | 40.38 | 19.92 | 40.25 | 18.67 | −6.24% | −10.53% | −15.23% | ||||||
| p6.4 | 38.13 | 21.81 | 38.13 | 22.06 | 38.13 | 21.80 | 42.89 | 23.51 | 42.87 | 22.82 | 42.59 | 21.52 | 7.83% | 3.43% | −1.28% | ||||||
| p7.2 | 41.50 | 22.95 | 41.50 | 23.13 | 41.50 | 22.72 | 39.77 | 18.43 | 39.60 | 17.67 | 39.12 | 15.78 | −19.70% | −23.60% | −30.55% | ||||||
| p7.3 | 38.54 | 21.81 | 38.54 | 21.97 | 38.54 | 21.61 | 38.64 | 19.19 | 38.52 | 18.45 | 38.23 | 16.65 | −12.03% | −16.03% | −22.93% | ||||||
| p7.4 | 35.63 | 20.70 | 35.63 | 20.84 | 35.63 | 20.49 | 37.65 | 19.87 | 37.60 | 19.21 | 37.19 | 17.52 | −3.99% | −7.83% | −14.46% | ||||||
| Average | 42.49 | 23.96 | 42.49 | 24.17 | 42.49 | 23.78 | 42.89 | 21.17 | 42.77 | 20.39 | 42.53 | 18.65 | −11.35% | −15.38% | −21.36% | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uguina, A.R.; Gomez, J.F.; Panadero, J.; Martínez-Gavara, A.; Juan, A.A. A Learnheuristic Algorithm Based on Thompson Sampling for the Heterogeneous and Dynamic Team Orienteering Problem. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12111758
Uguina AR, Gomez JF, Panadero J, Martínez-Gavara A, Juan AA. A Learnheuristic Algorithm Based on Thompson Sampling for the Heterogeneous and Dynamic Team Orienteering Problem. Mathematics. 2024; 12(11):1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12111758
Chicago/Turabian StyleUguina, Antonio R., Juan F. Gomez, Javier Panadero, Anna Martínez-Gavara, and Angel A. Juan. 2024. "A Learnheuristic Algorithm Based on Thompson Sampling for the Heterogeneous and Dynamic Team Orienteering Problem" Mathematics 12, no. 11: 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12111758
APA StyleUguina, A. R., Gomez, J. F., Panadero, J., Martínez-Gavara, A., & Juan, A. A. (2024). A Learnheuristic Algorithm Based on Thompson Sampling for the Heterogeneous and Dynamic Team Orienteering Problem. Mathematics, 12(11), 1758. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12111758








