Interference Management for a Wireless Communication Network Using a Recurrent Neural Network Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Wireless Network Interference
3. Method with RNN for Interference Management
3.1. Dataset Generation
| Algorithm 1 Training Data Generation Process |
|
3.2. Details of RNN Models
3.2.1. LSTM
3.2.2. BiLSTM
3.2.3. GRU
4. Experiment Result and Discussion
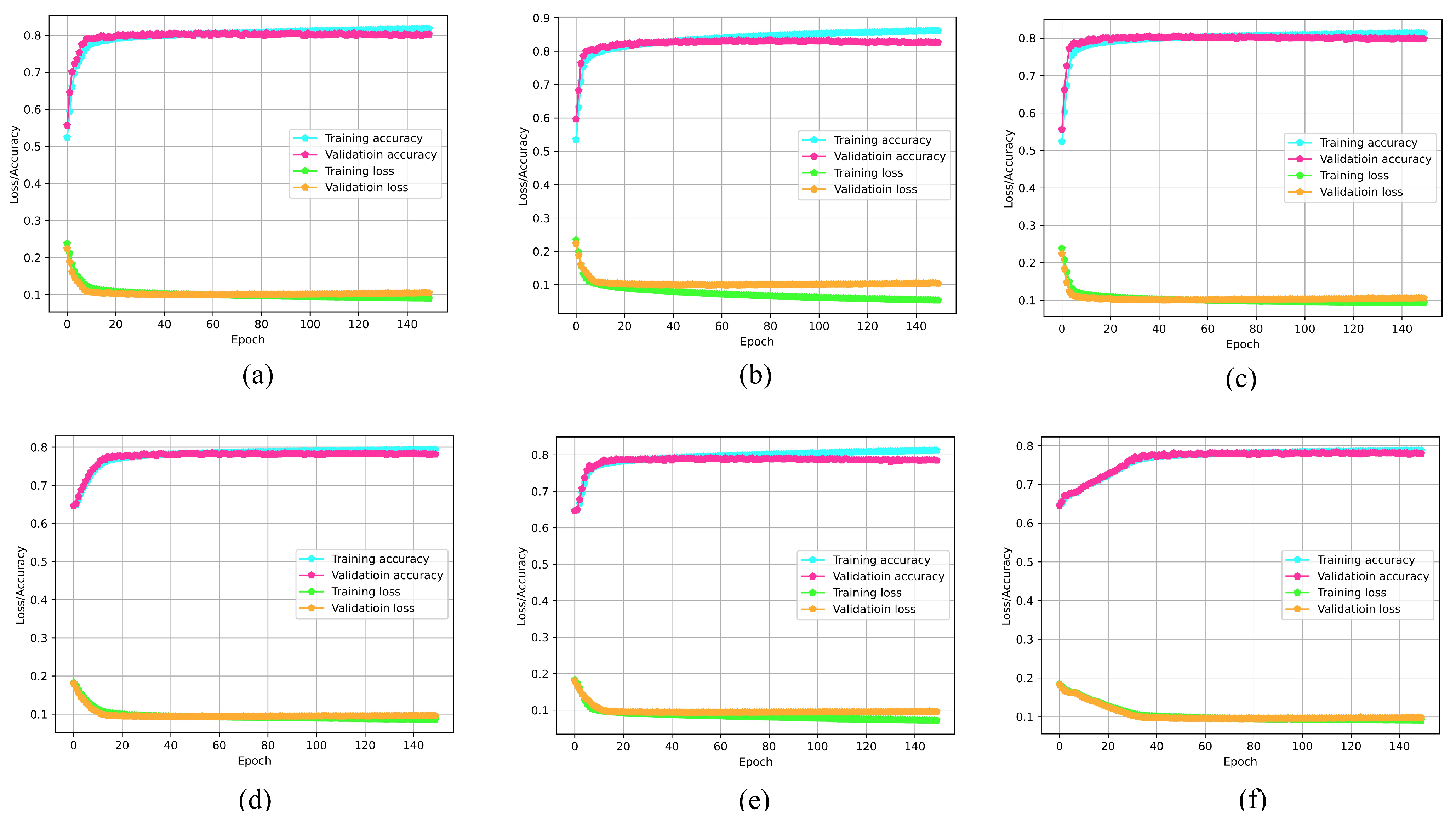
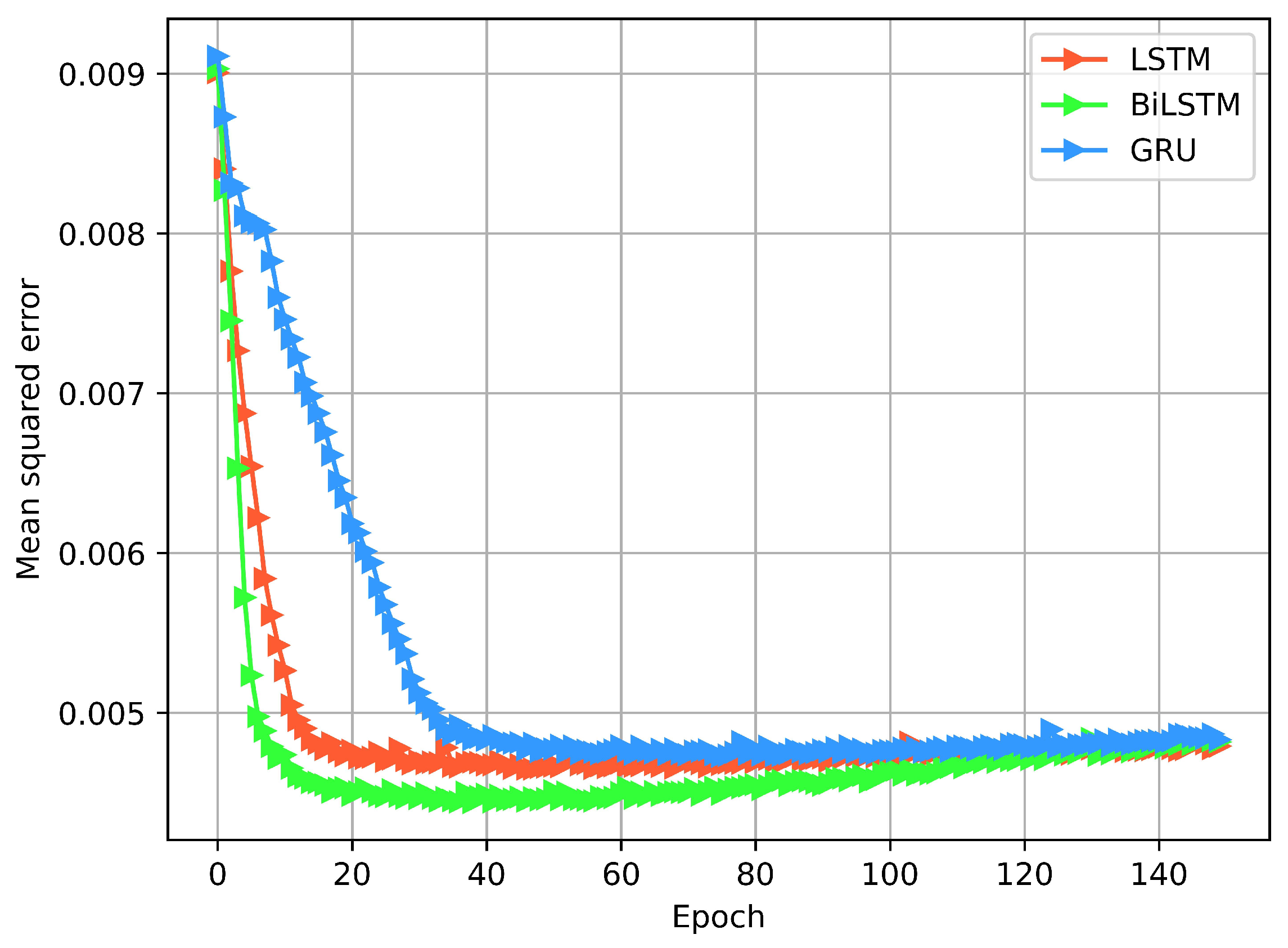
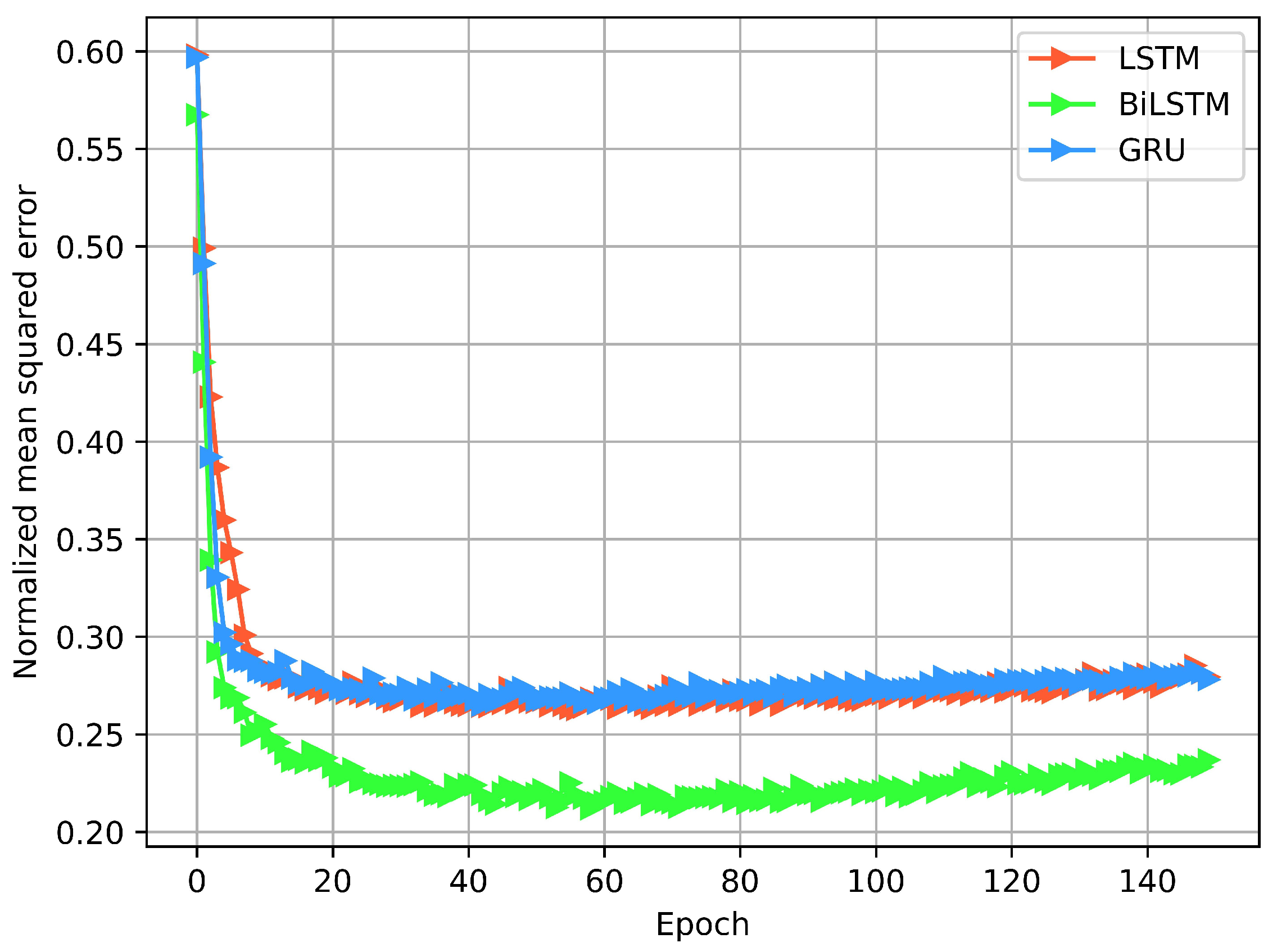
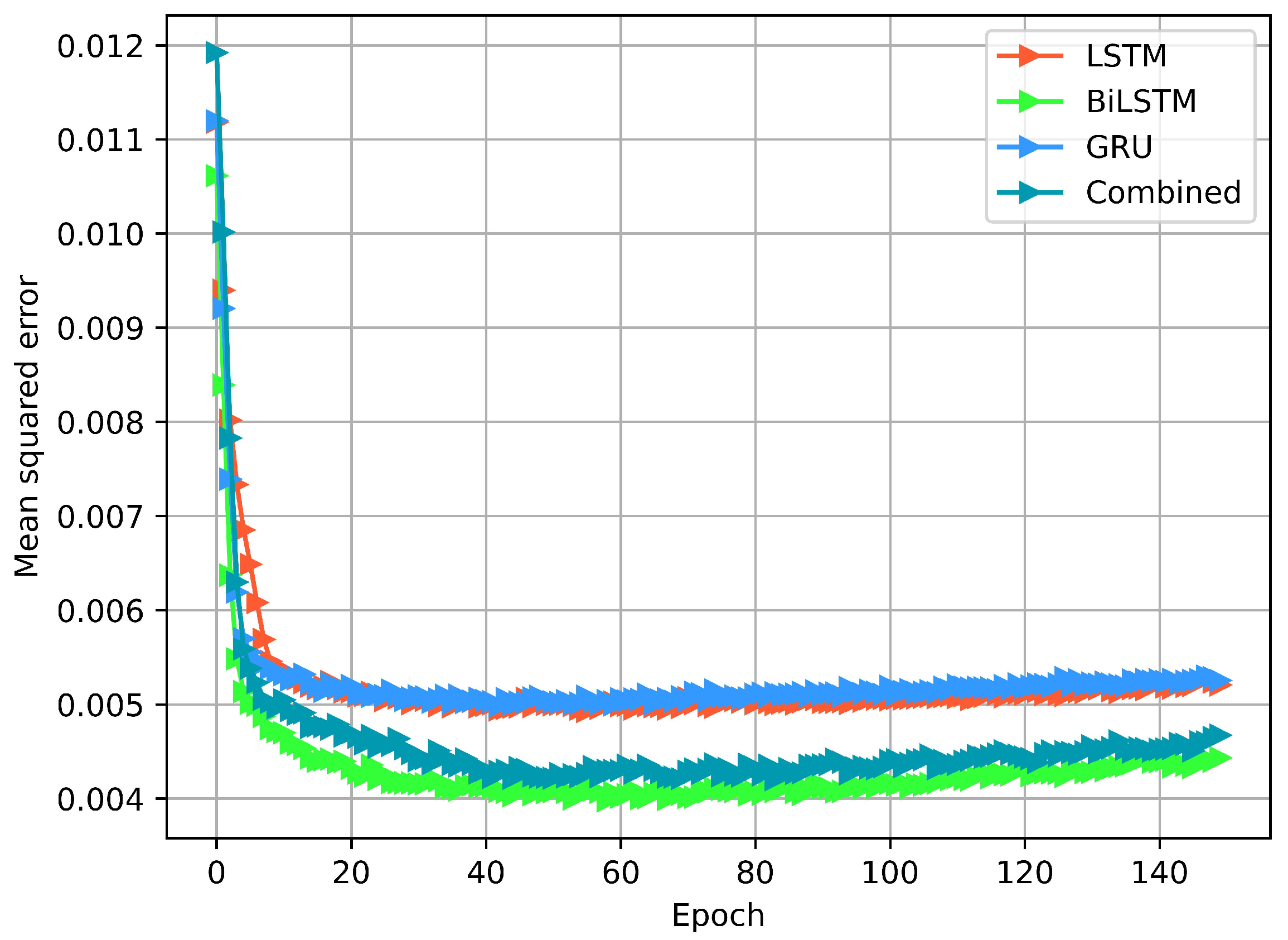
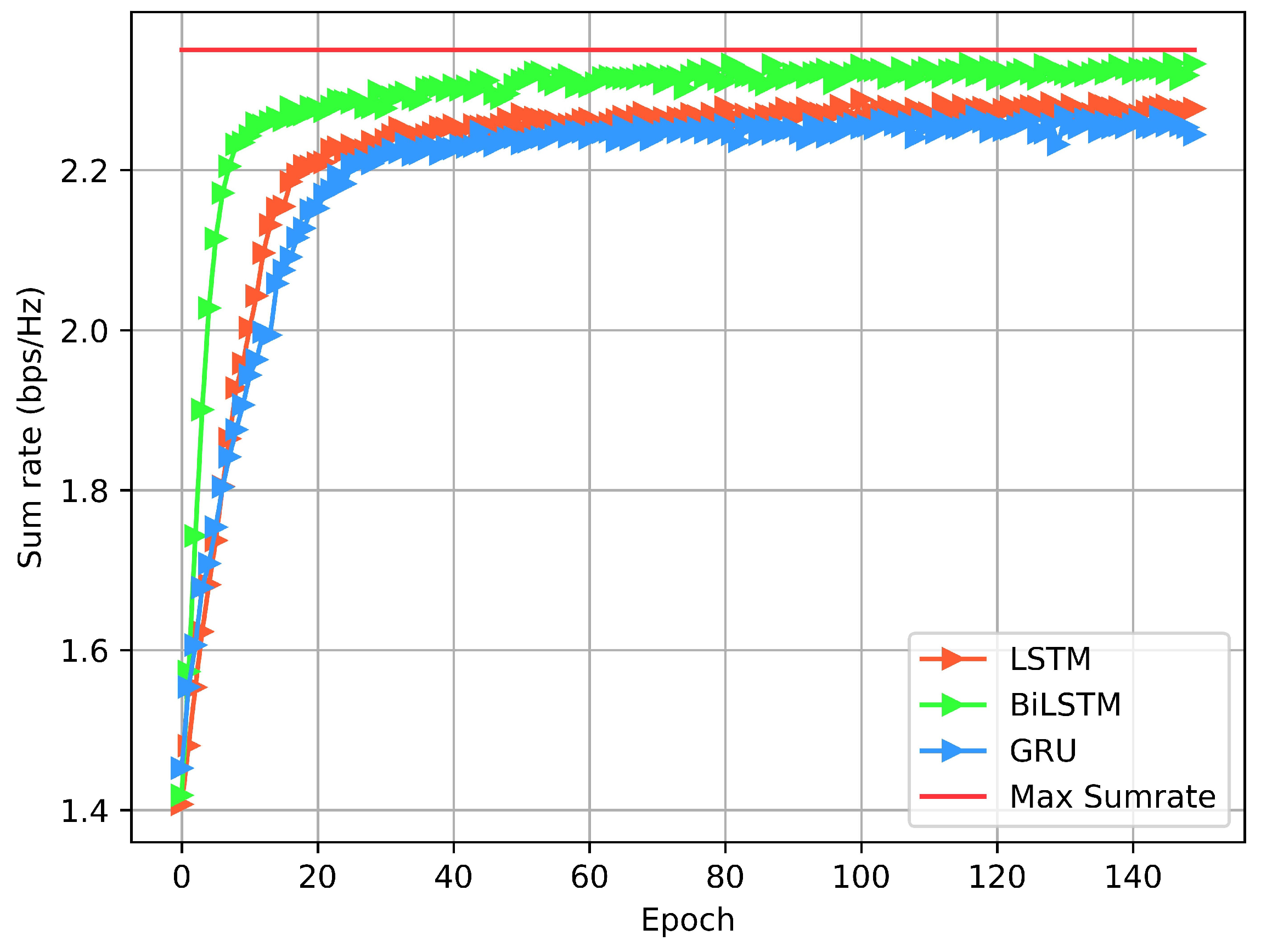
4.1. Training and Testing of the Models
4.2. Model Performance in Wireless Network
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Q.; Li, G.Y.; Chen, W.; Ng, D.W.K.; Schober, R. An overview of sustainable green 5G networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Gu, J.; Wen, M.; Zhang, G.; Ji, Y.; Mumtaz, S. Emerging Technologies for 5G-IoV Networks: Applications, Trends and Opportunities. IEEE Netw. 2020, 34, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, O.T.H.; Hindia, M.N.; Dimyati, K.; Noordin, K.A.; Wahab, A.N.A.; Qamar, F.; Hassan, R. Interference challenges and management in B5G network design: A comprehensive review. Electronics 2022, 11, 2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.U.A.; Qamar, F.; Ahmed, F.; Nguyen, Q.N.; Hassan, R. Interference management in 5G and beyond network: Requirements, challenges and future directions. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 68932–68965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangi, R.; Lalwani, P.; Choudhary, G.; You, I.; Pau, G. Study and investigation on 5G technology: A systematic review. Sensors 2021, 22, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldsmith, A. Wireless Communications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J. CFAR-based interference mitigation for FMCW automotive radar systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 12229–12238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaisar, Z.H.; Irfan, M.; Ali, T.; Ahmad, A.; Ali, G.; Glowacz, A.; Glowacz, W.; Caesarendra, W.; Mashraqi, A.M.; Draz, U.; et al. Effective beamforming technique amid optimal value for wireless communication. Electronics 2020, 9, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Björnson, E.; Ai, B. Local partial zero-forcing combining for cell-free massive MIMO systems. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2021, 69, 8459–8473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambianco, M.; Verticale, G. Interference minimization in 5G physical-layer network slicing. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2020, 68, 4554–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Vucetic, B.; Chikkam, K.; Aliberti, P.; Hardjawana, W. Graph Representation Learning for Contention and Interference Management in Wireless Networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Netw. 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irkicatal, O.N.; Ceran, E.T.; Yuksel, M. Deep Reinforcement Learning Enhanced Rate-Splitting Multiple Access for Interference Mitigation. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.05974. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, X.; Lei, Y.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hanzo, L. Interference Management by Harnessing Multi-Domain Resources in Spectrum-Sharing Aided Satellite-Ground Integrated Networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2024, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, M.; Cui, Q.; Chen, K.C.; Liao, Y. RIS-aided proactive mobile network downlink interference suppression: A deep reinforcement learning approach. Sensors 2023, 23, 6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, O.M.; Kulhandjian, M.; Kantarci, B.; Touazi, A.; Ellement, C.; D’amours, C. Secure industrial iot systems via rf fingerprinting under impaired channels with interference and noise. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 26289–26307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulodimos, A.; Doulamis, N.; Doulamis, A.; Protopapadakis, E. Deep learning for computer vision: A brief review. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2018, 2018, 7068349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Huang, C.; Yune, S.; Tajmir, S.H.; Kim, M.; Do, S. Machine friendly machine learning: Interpretation of computed tomography without image reconstruction. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadhim, A.I. Survey on supervised machine learning techniques for automatic text classification. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 52, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seota, S.B.W.; Klein, R.; Van Zyl, T. Modeling e-behaviour, personality and academic performance with machine learning. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dornadula, V.N.; Geetha, S. Credit card fraud detection using machine learning algorithms. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019, 165, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.S.; Prasad, P.; Alsadoon, A.; Maag, A. A systematic review: Machine learning based recommendation systems for e-learning. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2020, 25, 2635–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, I.; Castro, L.; Rodriguez-Fernandez, N.; Torrente-Patino, A.; Carballal, A. Artificial neural networks and deep learning in the visual arts: A review. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 121–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, R.; Islam, N.; Islam, M.; Ahsan, M.M. A comparative analysis on suicidal ideation detection using NLP, machine, and deep learning. Technologies 2022, 10, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Chen, X.; Ni, W.; Hossain, E.; Wang, X. Distributed Machine Learning for Wireless Communication Networks: Techniques, Architectures, and Applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2021, 23, 1458–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejan, M.A.S.; Rahman, M.H.; Shin, B.S.; Oh, J.H.; You, Y.H.; Song, H.K. Machine learning for intelligent-reflecting-surface-based wireless communication towards 6G: A review. Sensors 2022, 22, 5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.H.; Sejan, M.A.S.; Aziz, M.A.; Tabassum, R.; Baik, J.I.; Song, H.K. A Comprehensive Survey of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Detection and Classification Using Machine Learning Approach: Challenges, Solutions, and Future Directions. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Alam, M.S.B.; Hassan, M.; Rozbu, M.R.; Ishtiak, T.; Rafa, N.; Mofijur, M.; Shawkat Ali, A.; Gandomi, A.H. Deep learning modelling techniques: Current progress, applications, advantages, and challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 13521–13617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Jiang, C.; Wang, J.; Ren, Y.; Debbah, M. Machine learning for 6G wireless networks: Carrying forward enhanced bandwidth, massive access, and ultrareliable/low-latency service. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2020, 15, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.A.; Rahman, M.H.; Sejan, M.A.S.; Baik, J.I.; Kim, D.S.; Song, H.K. Spectral Efficiency Improvement Using Bi-Deep Learning Model for IRS-Assisted MU-MISO Communication System. Sensors 2023, 23, 7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Lin, K.C.; Chen, M.Y.; Hsu, J.H.Y. Wind turbine fault diagnosis and predictive maintenance through statistical process control and machine learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 23427–23439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Heng, F.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Y. A novel machine learning method for multiaxial fatigue life prediction: Improved adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Int. J. Fatigue 2024, 178, 108007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Liu, D.; Du, Y.; You, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K. Toward an intelligent edge: Wireless communication meets machine learning. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2020, 58, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehinejad, H.; Sankar, S.; Barfett, J.; Colak, E.; Valaee, S. Recent advances in recurrent neural networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1801.01078. [Google Scholar]
- Cossu, A.; Carta, A.; Lomonaco, V.; Bacciu, D. Continual learning for recurrent neural networks: An empirical evaluation. Neural Netw. 2021, 143, 607–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliyan, A.; Batra, A.; Singh, S.P. Multilingual sentiment analysis using RNN-LSTM and neural machine translation. In Proceedings of the 2021 8th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), New Delhi, India, 17–19 March 2021; pp. 710–713. [Google Scholar]
- Onan, A. Bidirectional convolutional recurrent neural network architecture with group-wise enhancement mechanism for text sentiment classification. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 2098–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Samiee, A.; Zhou, T.; Jalali, B. Deep learning interference cancellation in wireless networks. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.05533. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatia, A.; Robinson, J.; Carmack, J.; Kuzdeba, S. FPGA implementation of radio frequency neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 12th Annual Computing and Communication Workshop and Conference (CCWC), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26–29 January 2022; pp. 0613–0618. [Google Scholar]
- Grunau, S.; Block, D.; Meier, U. Multi-label wireless interference identification with convolutional neural networks. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.04395. [Google Scholar]
- Rock, J.; Roth, W.; Toth, M.; Meissner, P.; Pernkopf, F. Resource-efficient deep neural networks for automotive radar interference mitigation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2021, 15, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rock, J.; Toth, M.; Messner, E.; Meissner, P.; Pernkopf, F. Complex signal denoising and interference mitigation for automotive radar using convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 22th International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2–5 July 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mun, J.; Kim, H.; Lee, J. A deep learning approach for automotive radar interference mitigation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 88th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC-Fall), Chicago, IL, USA, 27–30 August 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wei-Lung, M. Gps interference mitigation using derivative-free kalman filter-based rnn. Radioengineering 2016, 25, 519. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Chen, X.; Shi, Q.; Hong, M.; Fu, X.; Sidiropoulos, N.D. Learning to optimize: Training deep neural networks for interference management. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2018, 66, 5438–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Sejan, M.A.S.; Aziz, M.A.; You, Y.H.; Song, H.K. HyDNN: A Hybrid Deep Learning Framework Based Multiuser Uplink Channel Estimation and Signal Detection for NOMA-OFDM System. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 66742–66755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Sejan, M.A.S.; Aziz, M.A.; Kim, D.S.; You, Y.H.; Song, H.K. Deep Convolutional and Recurrent Neural-Network-Based Optimal Decoding for RIS-Assisted MIMO Communication. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, P.; Srivallapanondh, S.; Spinnler, B.; Napoli, A.; Costa, N.; Prilepsky, J.E.; Turitsyn, S.K. Computational Complexity Optimization of Neural Network-Based Equalizers in Digital Signal Processing: A Comprehensive Approach. J. Light. Technol. 2024, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, C.J.; Kang, J.M.; Kim, I.M. Deep learning-based joint pilot design and channel estimation for multiuser MIMO channels. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2019, 23, 1999–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of devices | 20, 10 |
| Training samples | 20,000 |
| Noise variance | 1 |
| Feature of each device | 20 |
| Label for each device | 1 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| RNN approach | LSTM, BiLSTM, GNN, Combied |
| Layers | Single layer |
| Hidden units LSTM | 50 |
| Hidden units BiLSTM | 50 |
| Hidden units GRU | 50 |
| Training epochs | 150 |
| Learning rate | 0.001 |
| Number of iterations | 200 |
| Learning rate decay | None |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Loss function | Mean squared error |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sejan, M.A.S.; Rahman, M.H.; Aziz, M.A.; Tabassum, R.; You, Y.-H.; Hwang, D.-D.; Song, H.-K. Interference Management for a Wireless Communication Network Using a Recurrent Neural Network Approach. Mathematics 2024, 12, 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12111755
Sejan MAS, Rahman MH, Aziz MA, Tabassum R, You Y-H, Hwang D-D, Song H-K. Interference Management for a Wireless Communication Network Using a Recurrent Neural Network Approach. Mathematics. 2024; 12(11):1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12111755
Chicago/Turabian StyleSejan, Mohammad Abrar Shakil, Md Habibur Rahman, Md Abdul Aziz, Rana Tabassum, Young-Hwan You, Duck-Dong Hwang, and Hyoung-Kyu Song. 2024. "Interference Management for a Wireless Communication Network Using a Recurrent Neural Network Approach" Mathematics 12, no. 11: 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12111755
APA StyleSejan, M. A. S., Rahman, M. H., Aziz, M. A., Tabassum, R., You, Y.-H., Hwang, D.-D., & Song, H.-K. (2024). Interference Management for a Wireless Communication Network Using a Recurrent Neural Network Approach. Mathematics, 12(11), 1755. https://doi.org/10.3390/math12111755









