An Unfitted Method with Elastic Bed Boundary Conditions for the Analysis of Heterogeneous Arterial Sections
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
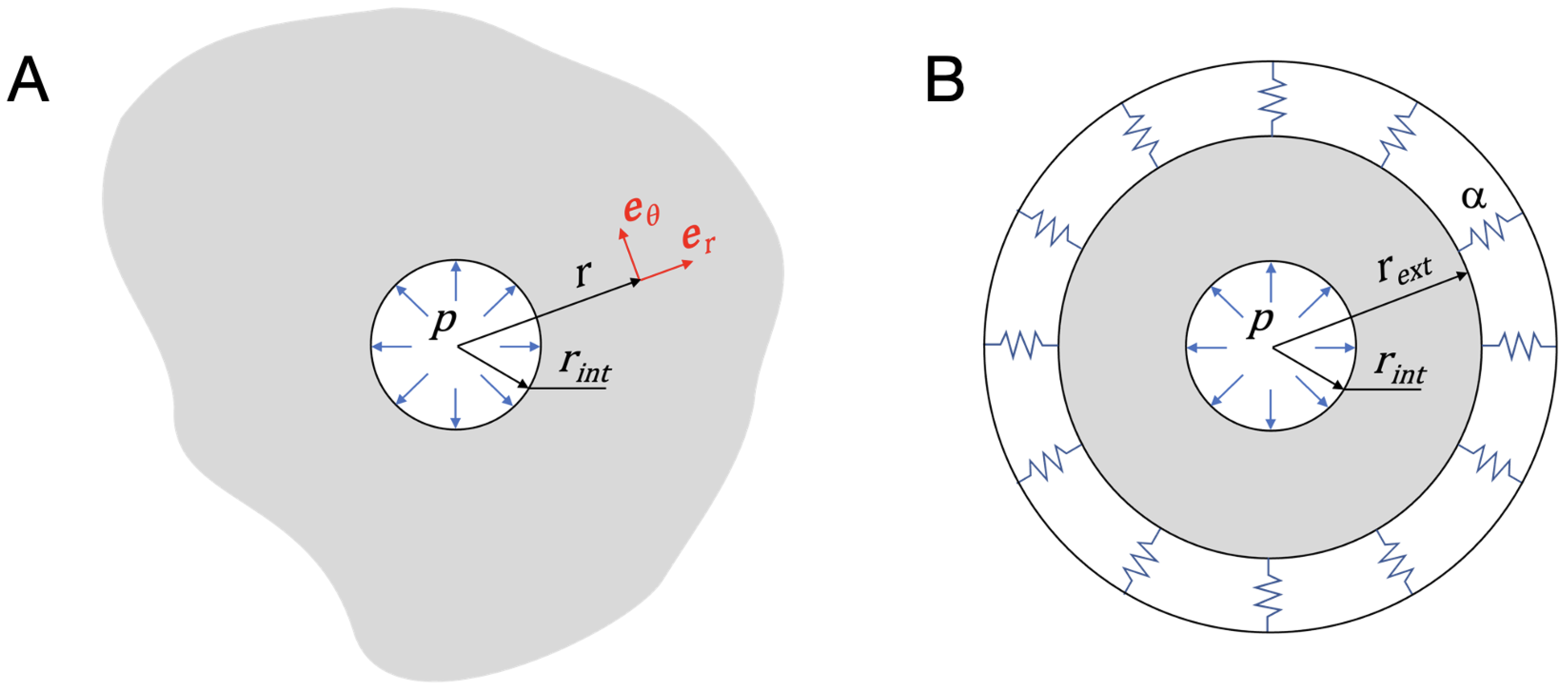
2.1. Problem Statement
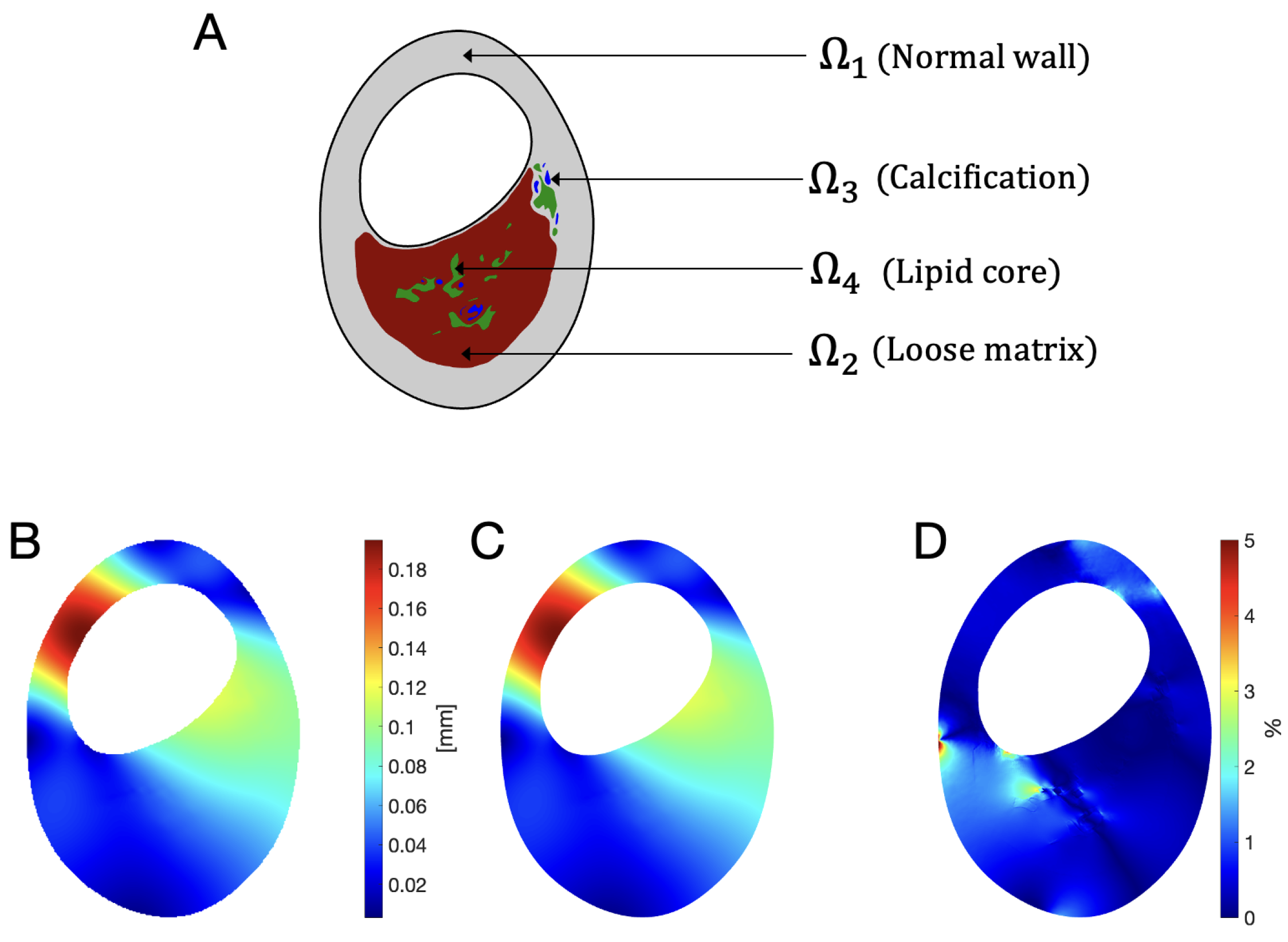
2.2. Level Set Description of the Domain and Subdomains
2.3. Discretization of the Level Set Functions in a Background Mesh
2.4. Unfitted Approach: Solving the Problem in the Background Mesh
2.5. Validating the Methodolgy
3. Results
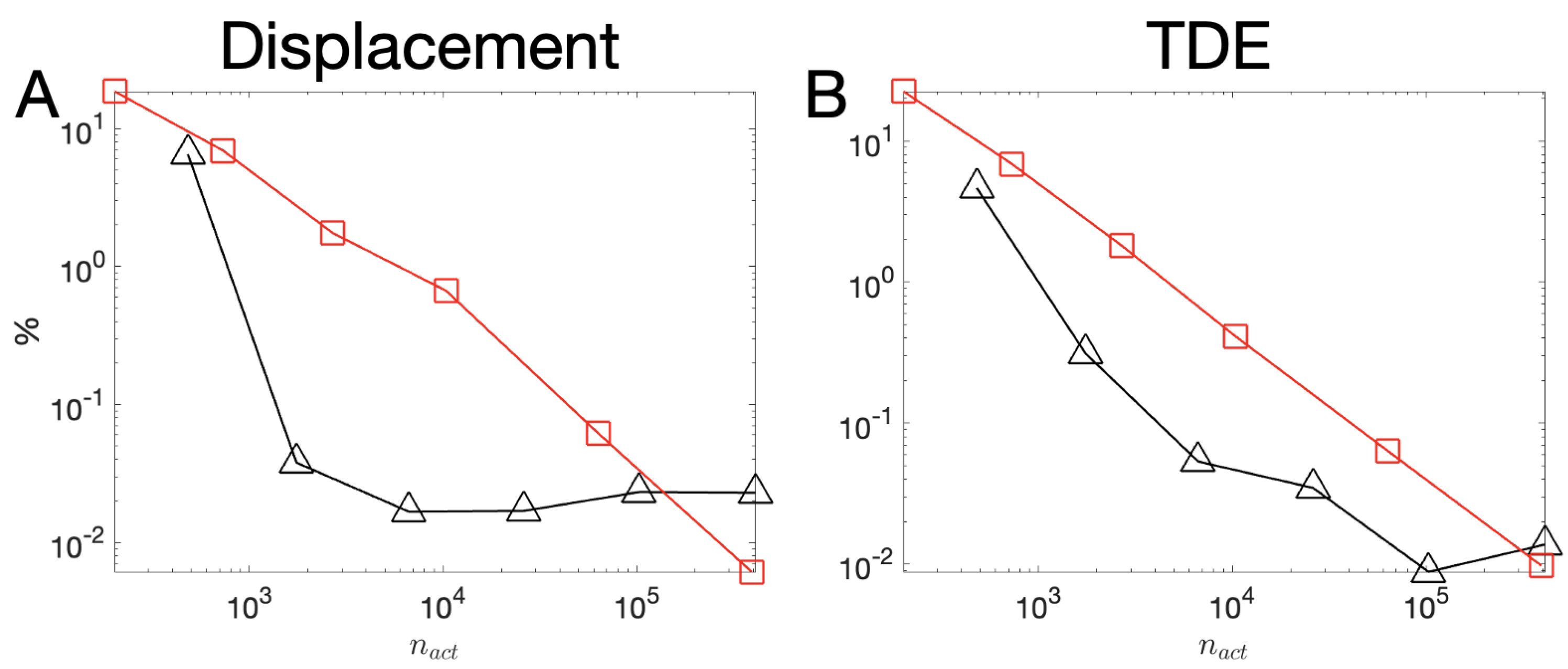
3.1. Covergence Analysis
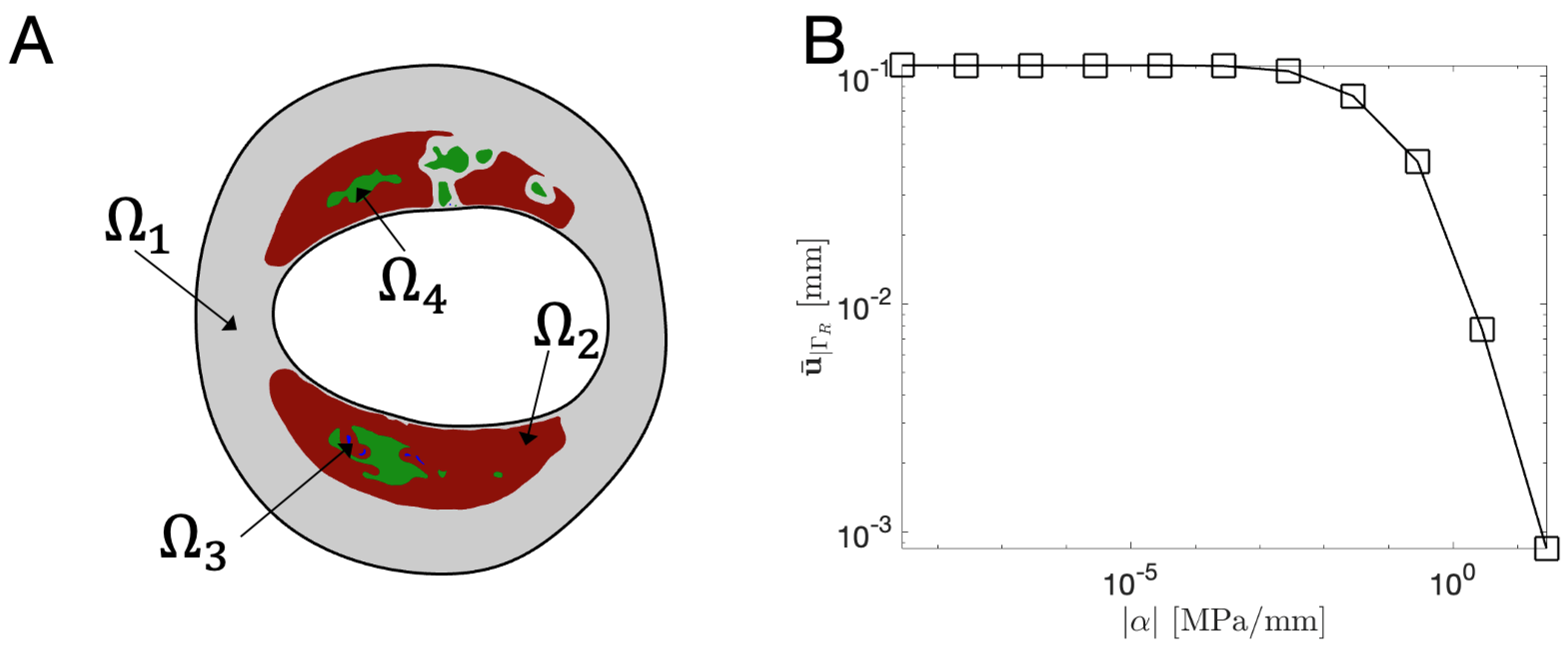
3.2. Elastic Bed Coeficient : Sensitivity Analysis
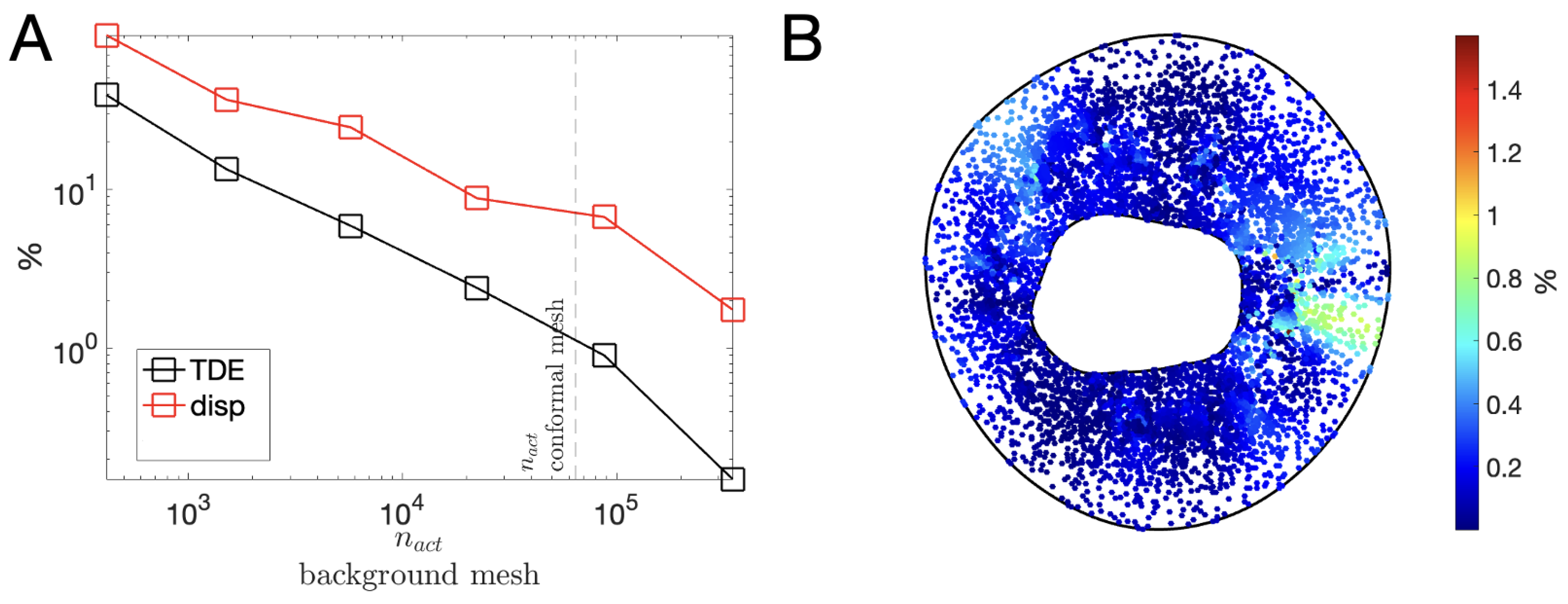
3.3. Characteristic Length h of the Background Mesh : Sensitivity Analysis
3.4. Realistic Immersed Boundary Robin-Based approach
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BC | Boundary conditions |
| FE | Finite element |
| IB | Immersed Boundary |
| TDE | Total Deformation Energy |
References
- World Health Statistics 2020: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240005105 (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- The Top 10 Causes of Death. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death (accessed on 20 September 2022).
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; White, H.D. Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2007, 116, 2634–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, A.; Zeltser, R. Unstable Angina. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK442000/ (accessed on 27 September 2022).
- Holzapfel, G.A.; Mulvihill, J.J.; Cunnane, E.M.; Walsh, M.T. Computational approaches for analyzing the mechanics of atherosclerotic plaques: A review. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiner, T.; Gerretsen, S.; Botnar, R.; Lutgens, E.; Cappendijk, V.; Kooi, E.; van Engelshoven, J. Magnetic resonance imaging of atherosclerosis. Eur. Radiol. 2005, 15, 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corti, R.; Fuster, V. Imaging of atherosclerosis: Magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, M.P.; Gopal, A.; Ahmadi, N.; Nasir, K.; Yang, E.; Kakadiaris, I.; Flores, F.; Mao, S.S.; Budoff, M.J. Mortality Incidence and the Severity of Coronary Atherosclerosis Assessed by Computed Tomography Angiography. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achenbach, S.; Raggi, P. Imaging of coronary atherosclerosis by computed tomography. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 1442–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabushita, H.; Bouma, B.E.; Houser, S.L.; Aretz, H.T.; Jang, I.K.; Schlendorf, K.H.; Kauffman, C.R.; Shishkov, M.; Kang, D.H.; Halpern, E.F.; et al. Characterization of Human Atherosclerosis by Optical Coherence Tomography. Circulation 2002, 106, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, M.; Park, S.J.; Dauerman, H.L.; Uemura, S.; Kim, J.S.; Mario, C.D.; Johnson, T.W.; Guagliumi, G.; Kastrati, A.; Joner, M.; et al. Optical coherence tomography in coronary atherosclerosis assessment and intervention. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 684–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böse, D.; von Birgelen, C.; Erbel, R. Intravascular Ultrasound for the Evaluation of Therapies Targeting Coronary Atherosclerosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garcia, H.M.; Costa, M.A.; Serruys, P.W. Imaging of coronary atherosclerosis: Intravascular ultrasound. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 2456–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyildiz, A.C.; Speelman, L.; Nieuwstadt, H.A.; van Brummelen, H.; Virmani, R.; van der Lugt, A.; van der Steen, A.F.; Wentzel, J.J.; Gijsen, F.J. The effects of plaque morphology and material properties on peak cap stress in human coronary arteries. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 19, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, A.M.; van der Lugt, A.; Verhagen, H.J.; van der Steen, A.F.; Wentzel, J.J.; Gijsen, F.J. Model-based cap thickness and peak cap stress prediction for carotid MRI. J. Biomech. 2017, 60, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.Y.; Howarth, S.; Trivedi, R.A.; U-King-Im, J.M.; Graves, M.J.; Brown, A.; Wang, L.; Gillard, J.H. Stress analysis of carotid plaque rupture based on in vivo high resolution MRI. J. Biomech. 2006, 39, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat, U.; Teng, Z.; Young, V.; Graves, M.; Gaunt, M.; Gillard, J. High-resolution Magnetic Resonance Imaging-based Biomechanical Stress Analysis of Carotid Atheroma: A Comparison of Single Transient Ischaemic Attack, Recurrent Transient Ischaemic Attacks, Non-disabling Stroke and Asymptomatic Patient Groups. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2011, 41, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gijsen, F.J.; Nieuwstadt, H.A.; Wentzel, J.J.; Verhagen, H.J.; van der Lugt, A.; van der Steen, A.F. Carotid Plaque Morphological Classification Compared With Biomechanical Cap Stress. Stroke 2015, 46, 2124–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwstadt, H.A.; Kassar, Z.A.M.; van der Lugt, A.; Breeuwer, M.; van der Steen, A.F.W.; Wentzel, J.J.; Gijsen, F.J.H. A Computer-Simulation Study on the Effects of MRI Voxel Dimensions on Carotid Plaque Lipid-Core and Fibrous Cap Segmentation and Stress Modeling. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyildiz, A.C.; Speelman, L.; van Brummelen, H.; Gutiérrez, M.A.; Virmani, R.; van der Lugt, A.; van der Steen, A.F.; Wentzel, J.J.; Gijsen, F.J. Effects of intima stiffness and plaque morphology on peak cap stress. BioMed. Eng. Online 2011, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat, U.; Teng, Z.; Gillard, J.H. Biomechanical structural stresses of atherosclerotic plaques. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2010, 8, 1469–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Feng, J.; Yuan, J.; Lu, Q.; Sutcliffe, M.P.; Brown, A.J.; Jing, Z.; Gillard, J.H. Material properties of components in human carotid atherosclerotic plaques: A uniaxial extension study. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 5055–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebenstein, D.M.; Coughlin, D.; Chapman, J.; Li, C.; Pruitt, L.A. Nanomechanical properties of calcification, fibrous tissue, and hematoma from atherosclerotic plaques. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2009, 91A, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milzi, A.; Lemma, E.D.; Dettori, R.; Burgmaier, K.; Marx, N.; Reith, S.; Burgmaier, M. Coronary plaque composition influences biomechanical stress and predicts plaque rupture in a morpho-mechanic OCT analysis. eLife 2021, 10, e64020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, E.E.; Young, M.; Erdemir, A. A pragmatic approach to understand peripheral artery lumen surface stiffness due to plaque heterogeneity. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 22, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, C.; Carlson, K.D.; Neumann, E.; Lewis, B.; Dragomir-Daescu, D.; Lerman, A.; Erdemir, A.; Young, M.D. Finite element analysis in clinical patients with atherosclerosis. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 125, 104927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costopoulos, C.; Huang, Y.; Brown, A.J.; Calvert, P.A.; Hoole, S.P.; West, N.E.; Gillard, J.H.; Teng, Z.; Bennett, M.R. Plaque Rupture in Coronary Atherosclerosis Is Associated With Increased Plaque Structural Stress. JACC 2017, 10, 1472–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Brown, A.J.; Calvert, P.A.; Parker, R.A.; Obaid, D.R.; Huang, Y.; Hoole, S.P.; West, N.E.; Gillard, J.H.; Bennett, M.R. Coronary Plaque Structural Stress Is Associated with Plaque Composition and Subtype and Higher in Acute Coronary Syndrome. Circulation 2014, 7, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, A.; Bakhaty, A.; Kim, J.; Mubarak, Y.; Mofrad, M.R.K. Bridging Finite Element and Machine Learning Modeling: Stress Prediction of Arterial Walls in Atherosclerosis. J. Biomech. Eng. 2019, 141, 84502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyildiz, A.C.; Hansen, H.H.G.; Nieuwstadt, H.A.; Speelman, L.; Korte, C.L.D.; van der Steen, A.F.W.; Gijsen, F.J.H. A Framework for Local Mechanical Characterization of Atherosclerotic Plaques: Combination of Ultrasound Displacement Imaging and Inverse Finite Element Analysis. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 44, 968–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyildiz, A.C.; Speelman, L.; Velzen, B.V.; Stevens, R.R.; Steen, A.F.V.D.; Huberts, W.; Gijsen, F.J. Intima heterogeneity in stress assessment of atherosclerotic plaques. Interface Focus 2018, 8, 20170008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohayon, J.; Gharib, A.M.; Garcia, A.; Heroux, J.; Yazdani, S.K.; Malvè, M.; Tracqui, P.; Martinez, M.A.; Doblare, M.; Finet, G.; et al. Is arterial wall-strain stiffening an additional process responsible for atherosclerosis in coronary bifurcations: An in vivo study based on dynamic CT and MRI. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 301, H1097–H1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morlacchi, S.; Pennati, G.; Petrini, L.; Dubini, G.; Migliavacca, F. Influence of plaque calcifications on coronary stent fracture: A numerical fatigue life analysis including cardiac wall movement. J. Biomech. 2014, 47, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peskin, C.S. The immersed boundary method. Acta Numer. 2002, 11, 479–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandrov, M.; Zlatanova, S.; Heslop, D.J. Voxelisation Algorithms and Data Structures: A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 8241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, A.; Yezzi, A.; Wells, W.; Tempany, C.; Tucker, D.; Fan, A.; Grimson, W.; Willsky, A. A shape-based approach to the segmentation of medical imagery using level sets. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2003, 22, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, K.; Kumar, G.; Swapna, K.; Datta, D.; Rajest, S. A Review of Medical Image Segmentation Algorithms. EAI Endorsed Trans. Pervasive Health Technol. 2018, 7, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. A Review of Deep-Learning-Based Medical Image Segmentation Methods. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghanaki, S.A.; Abhishek, K.; Cohen, J.P.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Hamarneh, G. Deep semantic segmentation of natural and medical images: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 137–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarteroni, A. Numerical Models for Differential Problems; Springer: Milan, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.; Faugeras, O. Reconciling Distance Functions and Level Sets. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2000, 11, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osher, S.; Fedkiw, R. Signed Distance Functions; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotnik, S.; Díez, P. Hierarchical X-FEM for n-phase flow. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2009, 198, 2329–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayareh, M.; Mortazavi, S. Equilibrium Position of a Buoyant Drop in Couette and Poiseuille Flows at Finite Reynolds Numbers. J. Mech. 2012, 29, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvester, P. Symmetric Quadrature Formulae for Simplexes. Math. Comput. 1970, 24, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mal, A.K.; Singh, S.J. Deformation of Elastic Solids; Prentice-Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]

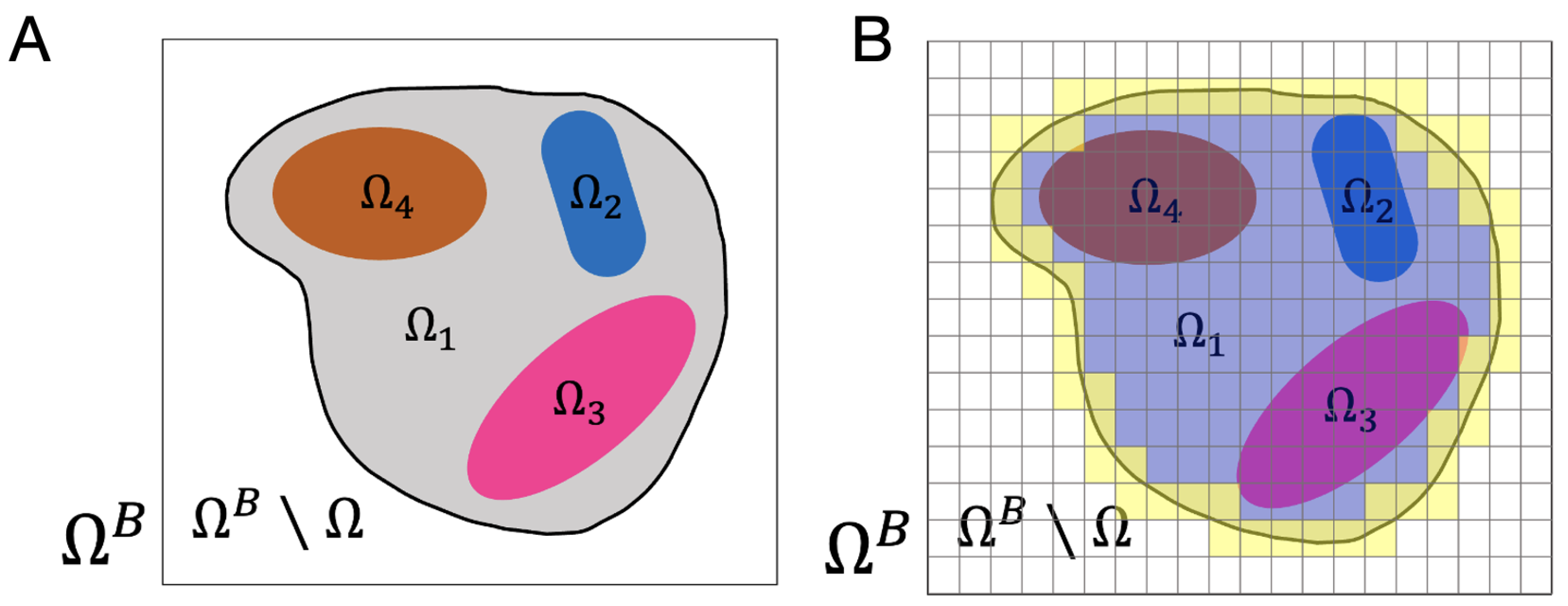
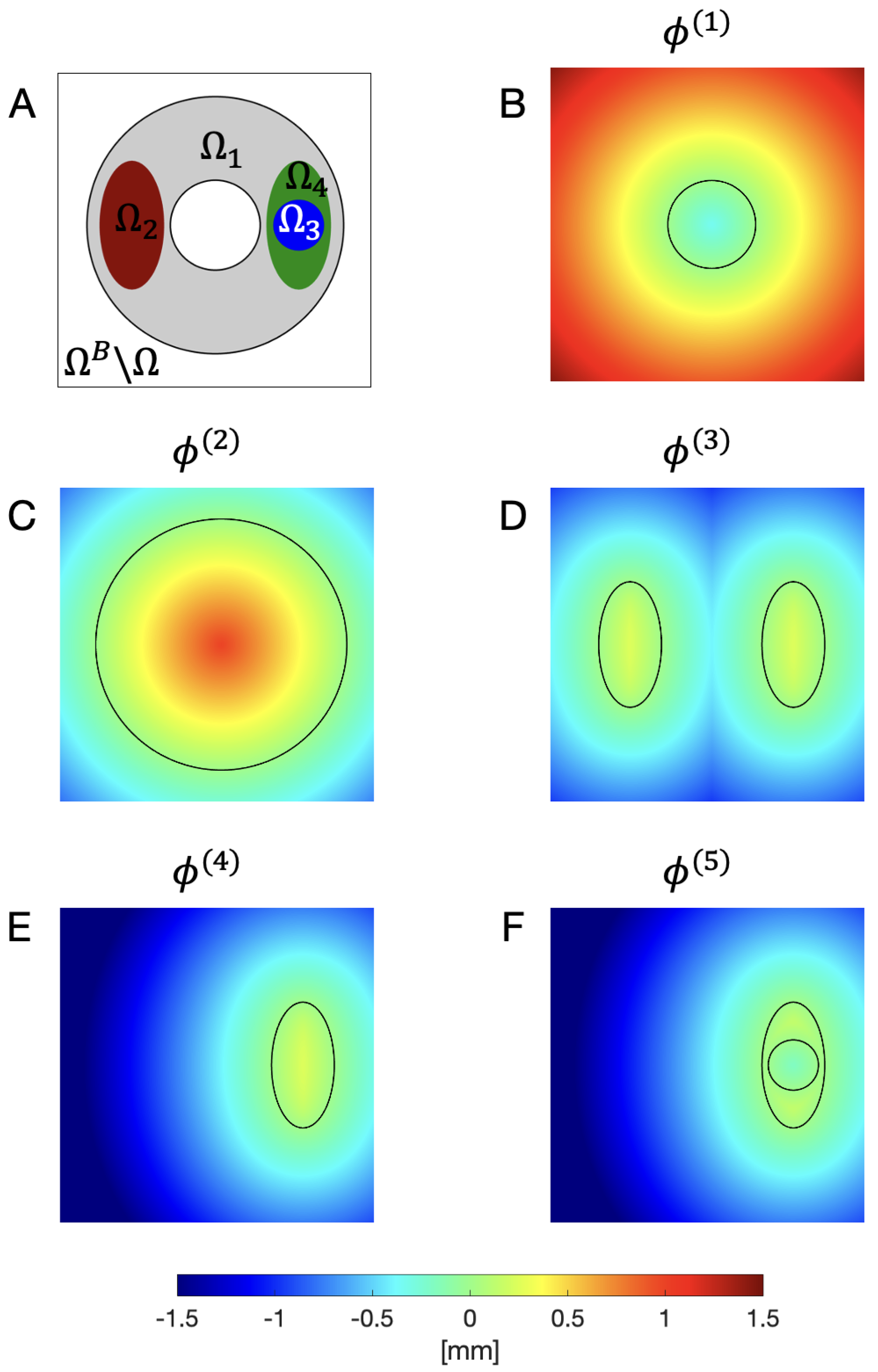
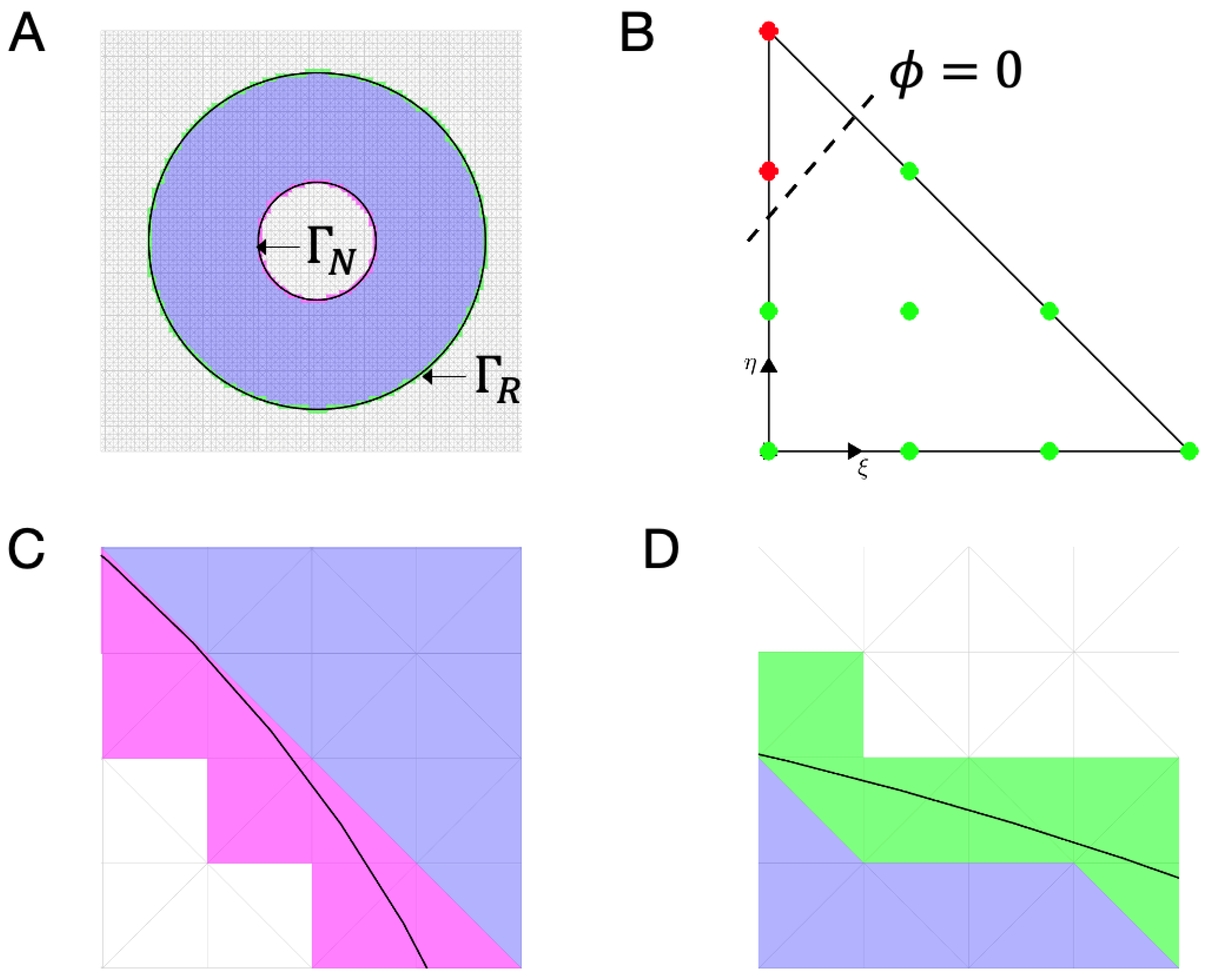
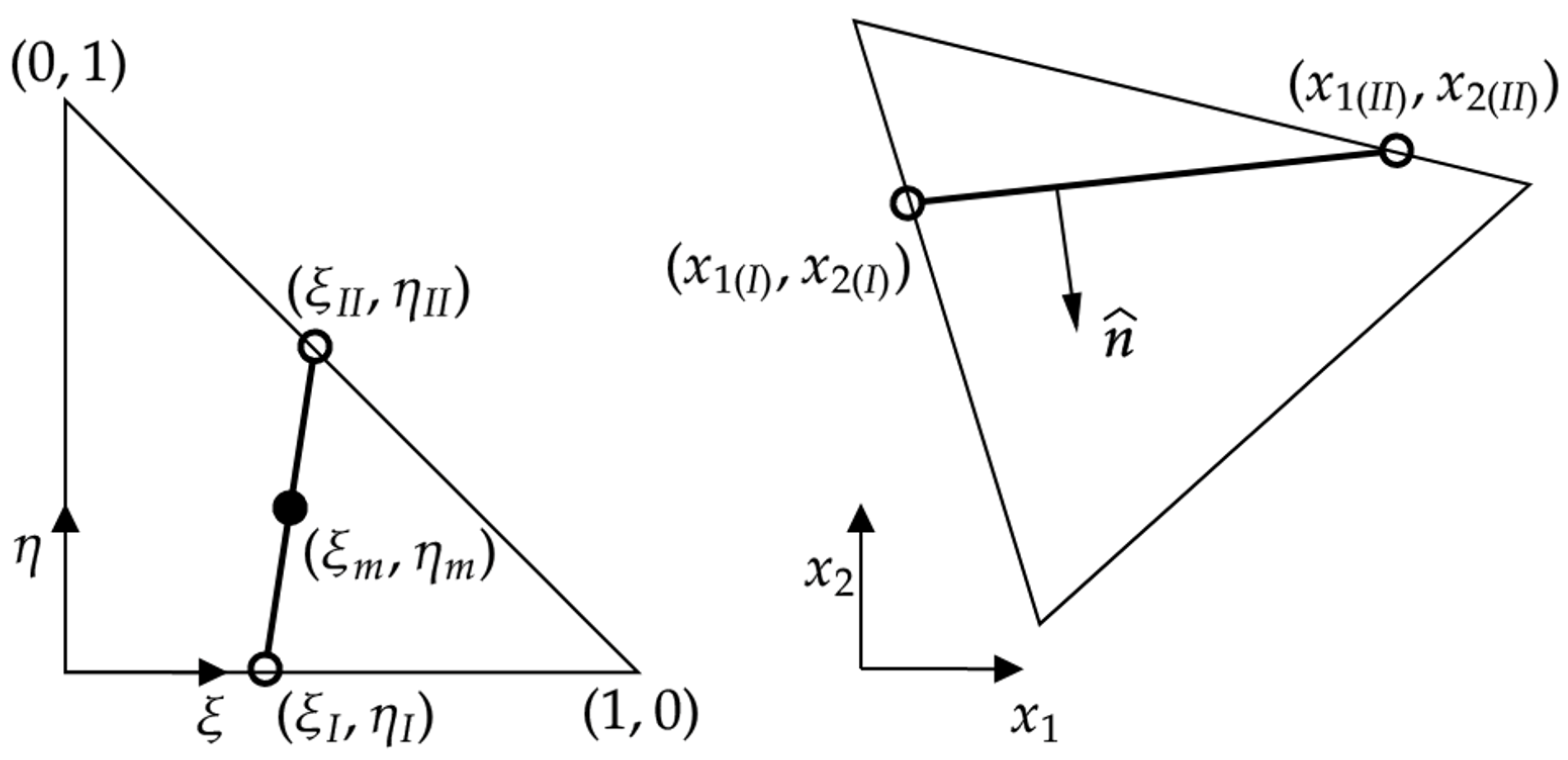

| Condition | Classification |
|---|---|
| and | |
| and and | |
| and and and | |
| and and and and | |
| and and |
| E (MPa) | (MPa/mm) | (mm) | (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 |
| Subdomain | Material | E [MPa] | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal vessel-wall | [22] | |||
| Loose matrix | [22] | |||
| Calcification | [23] | |||
| Lipid core | [22] |
| Mesh # | Diff. for TDE | max Diff. for Displacement Magnitude | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 414 | % | % |
| 2 | 1507 | % | % |
| 3 | 5734 | % | % |
| 4 | % | % | |
| 5 | % | % | |
| 6 | % | % |
| Active Elements | (MPa/mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 42,397 | 83,378 | ||
| 47,505 | 94,210 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gahima, S.; Díez, P.; Stefanati, M.; Rodríguez Matas, J.F.; García-González, A. An Unfitted Method with Elastic Bed Boundary Conditions for the Analysis of Heterogeneous Arterial Sections. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11071748
Gahima S, Díez P, Stefanati M, Rodríguez Matas JF, García-González A. An Unfitted Method with Elastic Bed Boundary Conditions for the Analysis of Heterogeneous Arterial Sections. Mathematics. 2023; 11(7):1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11071748
Chicago/Turabian StyleGahima, Stephan, Pedro Díez, Marco Stefanati, José Félix Rodríguez Matas, and Alberto García-González. 2023. "An Unfitted Method with Elastic Bed Boundary Conditions for the Analysis of Heterogeneous Arterial Sections" Mathematics 11, no. 7: 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11071748
APA StyleGahima, S., Díez, P., Stefanati, M., Rodríguez Matas, J. F., & García-González, A. (2023). An Unfitted Method with Elastic Bed Boundary Conditions for the Analysis of Heterogeneous Arterial Sections. Mathematics, 11(7), 1748. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11071748







