Abstract
In this paper, we propose a weighted link-specific (WLS) approach that establishes a unified statistical inference framework for high-dimensional Poisson and Gamma regression. We regress the parameter deviations as well as the initial estimation errors and utilize the resulting regression coefficients as correction weights to reduce the total mean square error (MSE). We also develop the asymptotic normality of the correction estimates under sparse and non-sparse conditions and construct associated confidence intervals (CIs) to verify the robustness of the new method. Finally, numerical simulations and empirical analysis show that the WLS method is extensive and effective.
MSC:
62F12
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of modern computer technology, data collection and processing capabilities are also rapidly increasing. In such a high-dimensional environment, our focuses will become different—for example, what is the relationship between productivity and age in the context of big data [1], how air pollution affects the mortality rate of urban residents [1], and how does the spectrum of raindrops affect mobile dual-polarization radar [2]. Under such conditions, most traditional inference procedures, such as the maximum likelihood method, are no longer valid and yield significantly different results in sparse and non-sparse states. Our attention is thus turned to high-dimensional generalized linear models, such as Poisson regression, Gamma regression, etc., in the expectation that they can solve these problems.
In the face of count data, the Poisson regression model is one of the most commonly used tools, which is a regression model specifically designed to analyze the dependent variable as a count variable based on a Poisson distribution. In contrast, among generalized linear models, the Gamma regression model can usually only be used to model continuous data with response data greater than or equal to zero. This paper establishes a unified inference framework for Poisson regression and Gamma regression through different linkage functions, aiming to build a suitable model for either continuous or discrete data.
High-dimensional Generalized Linear Model (GLM) inferences have been studied by many scholars [3,4,5,6]. Deshpande [7] proposed a debiasing method for constructing CIs. Cai, Athey and Zhu [8,9,10] proposed a more general linear comparison method under the condition of special load vectors. For high-dimensional logistic regression models, Sur and Candès [11] have studied the likelihood ratio test procedure when setting the sparsity . Among them, p is the parameter dimension, and n is the number of samples. Ma, Cai, and Li [12] put forward the testing procedure of the global null hypothesis and large-scale simultaneous hypothesis at the time of setting . Recently, Shi, C et al. [13] imposed certain strict constraints such as bounded individual probability conditions based on the logical link function to perform hypothesis testing. Under the high-dimensional sparse space, Lasso [14] usually leads to a large bias, and the current correction estimation is mainly performed under linear regression [15,16] and logistic regression models. In the work of Ma, R [12], a weighted low-dimensional projection method was proposed, which achieves the effect of debiasing and constructs its CIs by constructing specific weights and a dimensionality reduction process. In the work of Shi [13], a low-dimensional regression coefficient was proposed to reduce the dimensionality from high to medium dimensionality by recursively performing model selection for de-weighting. Cai and Guo [17] developed a weighted link function method that also constructs specific de-weighting and applies it to logistic regression. Generally speaking, the current research is mainly focused on logistic regression [18,19,20], but there are no other GLMs, such as Poisson and Gamma regression.
Motivated by literature such as [12,13,17], different link functions set their corresponding weights. In this paper, we propose a weighted link-specific (WLS) method to correct the bias of the penalty likelihood estimate of the Poisson and Gamma models. Now, we write as the parameter to be estimated in the one-parameter exponential model and as the corresponding penalized likelihood estimate. However, in high-dimensional space, there is a large estimation error between the estimates obtained using the great likelihood method and the true values, so we propose a new bias correction method. Specifically, to optimize the overall mean squared error, we regress the , and the obtained regression coefficients are identified as correction weights. Finally, we establish the asymptotic normality of the WLS estimates and construct CIs, and this weight construction method has independent implications for studying other inference problems under high-dimensional GLMs.
Overall, we find that the WLS method proposed in this paper is superior to other methods in terms of interval coverage and power, and the method in this paper performs robustly and has good generalizability in both sparse and non-sparse scenarios.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. In the second section, under the condition that the design distribution is unknown, we perform bias correction on individual regression coefficients under high-dimensional GLMs. In the third section, for our proposed confidence interval, its related theoretical properties are given, and asymptotic normality is proved. In Section 4, the superiority of our method is demonstrated by comparing the numerical performance of the proposed method with other methods through numerical simulations. In the fifth section, through the analysis of a real data set, the False Discovery Rate (FDR) and its power line chart of the four methods are drawn to indirectly illustrate the powerful performance of the method. The final section discusses the overall superiority of our approach as well as some areas for improvement.
Notation and terminology. Throughout, for a vector , we define the norm: , the norm: , and the norm: , and let stand for the subvector of a without the j-th component. For a matrix , stands for the i-th largest singular value of A and . For a smooth function defined on R, we denote and . For any positive integer n, we denote the set as . For any , we denote , as the regularized incomplete beta function, where is the incomplete beta function. We define and as the density function and the cumulative distribution function(CDF) of the standard Gaussian random variable, respectively. We denote as convergence in distribution. For positive sequences and , we write , or if , and write or if there exists a constant such that for all n, we write if and .
2. Weighted Link-Specific Method of Generalized Linear Model
In GLM, the standard form of the exponential distribution family is as follows,
where is the known dispersion function, and denote the natural and dispersion parameters, respectively, while is only related to the expected u, i.e., . In addition, for the simplicity of subsequent sample split, we collect samples . In this paper, we mainly focus on Poisson and Gamma distributions and aim to establish a unified statistical inference framework for them in high-dimensional spaces.
2.1. Poisson Regression
For the Poisson distribution, we assume that its observations are independently generated by Formula (1),
where is the link function given in advance, is a highly sparse regression vector, and its sparsity is denoted by k and is some probability distribution. In the subsection, we denote the link function as and define as the likelihood function,
and -penalized negative log-likelihood estimator under GLM is as follows,
where . Although achieves the best convergence rate [21,22], there is a large error between the penalty likelihood estimator and the real value which could be reduced. Specifically, to optimize the overall MSE, we regress the deviation of parameters on the original estimation error and determine the obtained regression coefficients as the correction weights.
Since the correction method involves a penalized likelihood estimation step and weighting step, we divide the samples into two independent data sets and perform penalized likelihood estimation on . The splitting process of samples can better promote the relevant theoretical analysis [17], and the numerical performance obtained is also good enough compared with the non-splitting sample. Perhaps this is not a practical limitation, and so we weighted it on .
For a given , we consider the general form of the bias correction estimate as follows [17,23]:
where we note that , and is the penalty likelihood estimate defined in (2). and denote the link-specific weight vector and projection direction to be constructed, respectively, such that is an accurate estimate of the deviation . Then, we decompose the error of Formula (3), which can help us to construct the weight vector and projection direction. The model (1) can be re-expressed as
and we carry out Taylor expansion near as follows
where . Combining (3) and (5), we can get the estimated error expression of
where is the standard basis of the Euclidean space . In the above Formula (6), the bias can be divided into the sum of three errors. The first part is the random error due to the model error , the second part is the residual bias due to the penalized likelihood estimator , and the last part is the approximation error due to the nonlinearity of the link function f.
We give two optimization criteria to determine the weight vector and the projection vector. First, the random error in (6) must satisfy asymptotic normality, and its standard error must reach a minimum value. Second, the residual bias and approximation error of the latter two items are negligible compared to the random error.
To satisfy these two conditions, we first construct the weight vector and then the projection direction. The variance of the random error in Formula (6) is
and according to Hölder’s inequality, the upper bound of the residual deviation in (6) can be obtained:
According to [8,17], in order to achieve the constraint that the first random error in Formula (6) dominates and the next two terms are relatively negligible, it is sufficient to make the right-hand part in (7) approximately equal to the right-hand part in (8),
also known as,
then, the construction of the weighted vector is obtained as with
the above weight vector constructed from Formula (10) above ensures that the first random error dominates in Formula (6). Next, we record and use the optimization method to estimate the projection direction as
subject to
where . The constraints in Formula (11) above are used to control the errors in the second and third terms of Formula (6), so this projection could ensure that the deviation is very small [23,24]. Then, the bias correction estimator is
2.2. Gamma Regression
For the Gamma distribution, we assume that its observations are independently generated by Formula (13),
where is a known parameter. The correction estimates under Gamma regression are essentially the same as the Poisson regression correction method. First, we determine the link function, assuming that the samples come from (13); then, there is
It is easy to know that the expectation is ; now, record , then as well as . Then, (14) can be simplified to a standard exponential family of distributions as follows,
The link function is , but to satisfy the regularity assumption in this paper, the link function is constructed as . Next, we compute its negative log-likelihood function as follows,
3. Theoretical Properties
3.1. Asymptotic Normality
In the subsection, we prove the asymptotic normality of the parameters and construct the associated CIs. First, we give a set of mildness conditions [12,13,25] that the link function needs to satisfy. For link function , we have the following:
- The connection function f is a monotone, second-order differentiable concave function on ;
- There is a normal constant such that for all , is a standard Gaussian distribution, and ;
- There exists a constant , such that ;
- For defined by Formula (2), there is a constant C, which can make the Hessian matrix expressed as , with andNone of the above four conditions is very strict, and a large number of link functions can satisfy them, where 1∼3 are relatively easy to verify, while condition 4 is from Huang [26]. Second, for the random design variables and their distributions, we assume that
- is an independent and identically distributed sub-Gaussian random vector, that is, there is a constant that satisfies .
It can be found that if , is its intercept as well as k is its sparsity level, then there exists a parameter space associated with k as follows.
where .
In a high-dimensional space, the size of sparsity k can easily affect the theoretical distribution of the bias corrector , so we build a parameter space associated with k. Under this parameter space, we present Theorem 1, which establishes the asymptotic properties of a bias-corrected estimator .
Theorem 1.
Assuming that the conditions 1∼5 are established, , then for any , if
- (1)
- , then we have , and ,
- (2)
- , then .
Proof of Theorem 1.
By the definition of , we have
where we denote
and
In what follows, on the one hand, we show that, in Formula (15), under the conditions of Theorem 1, with probability at least ,
furthermore, we have with probability at least ,
which along with (16) leads to the upper bound of . On the other hand, the asymptotic normality of the stochastic term in (16) can be derived from the following formulation.
Under the conditions of and , it can be assumed that:
The major contribution of Theorem 1 is that it removes many of the strict conditions in high-dimensional GLM inference, such as the bounded individual probability condition and the bounded design condition, greatly relaxing the preconditions for a wider range of situations. □
3.2. Confidence Interval
Under the mild regularity conditions in Section 3.1, in (12) has the following asymptotic variance:
At this point, the variance of the error can be estimated as
then, the variance of is estimated as follows,
Based on this, we construct CIs for the regression coefficient at the confidence level as
where . Note that it is necessary for sparsity in the confidence interval given in Formula (18): . In this ultra-sparse state, Formula (18) holds, while for the non-ultra-sparse state, the above formula will not hold with high probability.
4. Simulations
In this section, we evaluate the numerical performance of the proposed method and compare it with other inference methods under high-dimensional GLMs. For the evaluation of CIs, we mainly consider the coverage of regression coefficients and the length of CIs.
CIs for High-Dimensional Poisson and Gamma Regression
We build CIs from Poisson regression and Gamma regression. We set n = 100; let p vary between 400 and 1300, and let the sparsity level k vary between 25 and 35. For the real regression coefficient, given a support set , we set , and the ratio of to is equal. For the design covariates , generated by a multivariate Gaussian distribution, its covariance matrix is a block diagonal matrix consisting of 10 identical unit diagonal Toeplitz matrices, with off-diagonal entries falling from 0.6 to 0.
In the subsection, we construct the confidence interval of the non-zero regression coefficient and the zero regression coefficient and set the desired confidence level to . We compare three methods separately to evaluate their numerical performance: (i) the WLS method proposed in this paper; (ii) based on the weighted low-dimensional projection method (WLP) proposed by [12]; (iii) finally, the original Lasso estimate is used for comparison. The comparison regression results of zero coefficients and non-zero coefficients of Poisson regression are summarized in Table 1 and Table 2, and the comparison regression results of zero coefficients and non-zero coefficients of Gamma regression are summarized in Table 3 and Table 4, where each entry represents the average simulation results for 100 rounds.

Table 1.
Empirical performances of CIs for under in Poisson.

Table 2.
Empirical performances of CIs for under in Poisson.

Table 3.
Empirical performances of CIs for under in Gamma.

Table 4.
Empirical performances of CIs for under in Gamma.
In the non-sparse space setting, the results in Table 1 and Table 3 show that the coverage obtained by using the WLS method for bias correction is much better than that of the WLP and Lasso methods in both Poisson and Gamma regressions. Although the coverage obtained by the WLP method is longer, it is worthwhile to ensure its accuracy while sacrificing some precision. Moreover, it can be seen that the interval coverage obtained by the WLP and Lasso methods is so small that it fails almost completely, and perhaps there are other limitations in applying them in sparse scenarios.
In the sparse space setting, the results in Table 2 and Table 4 show that both the WLS method and the WLP method can achieve the interval coverage we expect. It can be seen that the interval lengths obtained by the WLP method are generally shorter than those of the WLS method, and their accuracy is higher. However, in our setting, the WLP method produces significantly higher Type II errors than the WLS method, and its precision decreases, while the Lasso method still performs poorly and does not meet our expectations.
In summary, our method is highly adaptable and robust. Under sparse conditions, our method is quite similar to existing comparison methods, but our method is more applicable to some cases where low Type II error rates are retained.
5. Real Data Analysis
We analyze a single-cell RNA-seq dataset in [27], which contains the expression estimates (transcripts per million) for all the 27,723 UCSC-annotated mouse genes of a total of 1861 primary mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells spanning over several experimental conditions. The complete dataset was downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus with the accession code GSE48968.
5.1. False Discovery Rate and Power Comparison
We apply the WLS method and the four comparison methods to the fit high-dimensional Poisson regression model (1) and Gamma regression model (13), respectively, to obtain FDR plots and power plots for the five methods. Specifically, taking model (1) as an example. WLS regression is the method proposed in this paper. Weighted low-dimensional projection regression (WLP) was proposed in [12], while the remaining “Lasso” regression, “rproj” regression, and “lproj” regression can be found in the relevant software packages of R language software. By comparing Figure 1 and Figure 2, we can see the advantages of our proposed method.
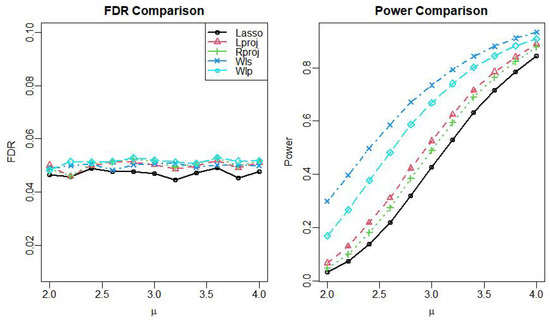
Figure 1.
The FDR versus power comparison under the Poisson mode.
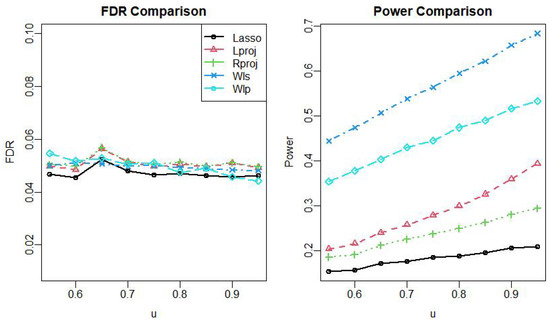
Figure 2.
The FDR versus Power comparison under the Gamma mode.
In Figure 1 and Figure 2, we can see that all the methods can control the FDR, but the original Lasso method is conservative and has the weakest efficacy, while methods such as “lproj” and “rproj” have improved but have not increased much, and the power obtained by WLS based on WLP is much higher than other methods. In addition, our proposed WLS results are the most outstanding, showing the great superiority of our approach, which is closely related to the fact that our proposed method has no strict limitation on the data, and this trend becomes increasingly obvious in the Gamma distribution.
5.2. CIs for the Different Stimuli
In the subsection, we use the above data set as a basis to derive the CI produced by different stimuli. This experiment is mainly used to analyre the effect of different stimuli on gene expression. Specifically, we focus on three pathogenic components, namely LPS (a component of Gram-negative bacteria), PIC (virulent double-stranded RNA), and PAM (a synthetic mimic of bacterial lipopeptides), and a set of unstimulated control cells. Sample screening is an important step, and we plot the gene expression profiles of stimulated cells at 0, 1, 2, 4, and 6. For better experimentation, we only consider data at 6 because the variance in this state is the most pronounced. We also remove gene samples with zero counts over and those with significant variance changes, etc. Finally, we fit a high-dimensional Poisson regression model (1) and apply the proposed method to obtain the CIs of each regression coefficient.
Specifically, there are three stimuli in the experiments in this paper: LPS, PIC, and PAM stimuli. Different stimuli are assigned to different sub-datasets: Sdata, Cdata, and Mdata. As an example, consider the PAM stimulus: n = 160, p = 768. The experiments of model (1) are performed on the Mdata data set, and parameter represents the PAM stimulus. We use the WLS method and other comparison methods (WLP, “rproj,” “lproj”) to calculate the confidence interval for each gene under that stimulus, allowing us to compare the performance of different genes under different conditions, as shown in the figure below.
As can be seen in Figure 3, the PAM stimuli obtained by the WLS, WLP, and “lproj” methods all have CI values for one or more genes whose regression coefficients do not cover 0 (i.e., the red part of the interval). This indicates a potential functional response to the stimulus; specifically, for the PAM-stimulated cells, it identifies the specific gene that codes for the protein. However, for the “rproj” method, the regression coefficients for all genes in response to the PAM stimulus cover the value of 0, which is probably related to its specific stimulus.
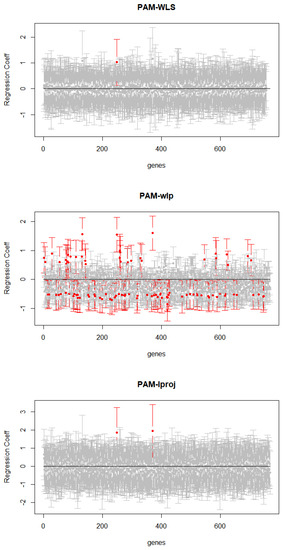
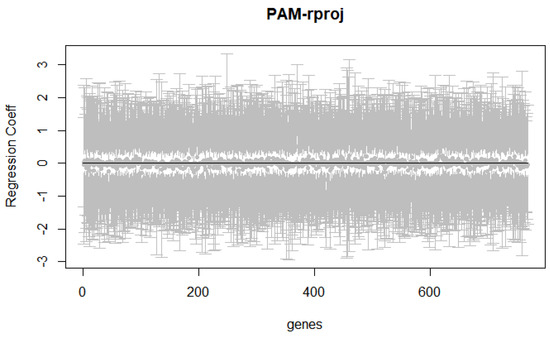
Figure 3.
CIs under different methods.
In the PAM stimulation experiment, we draw the interval length images using four methods. The average interval lengths of all genes produced by WLS, WLP, “lproj”, and “rproj” were calculated to be 1.5, 1.2, 3.5, and 3.5, respectively. The above computational results and images show that the WLP method usually produces shorter CIs and does not cover many genes with a value of 0. On the other hand, the “lproj” method usually highlights similar genes and has a longer CI coverage. Finally, the “rproj” method also tends to produce long CIs and cover zero genes.
6. Discussion
In this paper, we propose a unified framework to perform debiased estimation for distributions with different connectivity functions while constructing confidence intervals under sparse and non-sparse conditions to ensure the validity of interval coverage and coverage length. For technical reasons, we use sample splitting means to establish the relevant theoretical properties. In Van de Geer et al. [28], the random errors (6) are guaranteed to be asymptotically normal if conditions similar to theirs are imposed, and such conditions allow us to establish the relevant theoretical properties without sample partitioning. However, these strict conditions limit the adaptability of the proposed method, so we use sample splitting means to remove other strong assumptions to present our results. Moreover, we cannot guarantee that the proposed method will perform worse without the sample segmentation condition. Therefore, it is of interest to develop a new technical tool to perform inference experiments without sample segmentation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.Z.; Methodology, Q.Z.; Software, S.T.; Validation, Y.S.; Formal analysis, Q.Z.; Data curation, S.T.; Writing—original draft, S.T.; Supervision, Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper is supported by National Social Science Fund project of China (No. 21BTJ045).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fotuhi, H.; Amiri, A.; Maleki, M.R. Phase I monitoring of social networks based on Poisson regression profiles. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2018, 34, 572–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, E.M.; Bolfarine, H.; Paula, G.A. Influence diagnostics in generalized log-gamma regression models. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2003, 42, 165–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, Ø.; Hellton, K.H.; Frigessi, A.; Thoresen, M. Covariate selection in high-dimensional generalized linear models with measurement error. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2018, 27, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piironen, J.; Paasiniemi, M.; Vehtari, A. Projective inference in high-dimensional problems: Prediction and feature selection. Electron. J. Stat. 2020, 14, 2155–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Xue, J.; Jia, B. Markov neighborhood regression for high-dimensional inference. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2022, 117, 1200–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhao, X.; Huang, J. A Random Projection Approach to Hypothesis Tests in High-Dimensional Single-Index Models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2022, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, Y.; Javanmard, A.; Mehrabi, M. Online debiasing for adaptively collected high-dimensional data with applications to time series analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.T.; Guo, Z. Confidence intervals for high-dimensional linear regression: Minimax rates and adaptivity. Ann. Stat. 2017, 45, 615–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athey, S.; Imbens, G.W.; Wager, S. Approximate residual balancing: Debiased inference of average treatment effects in high dimensions. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2018, 80, 597–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Bradic, J. Linear hypothesis testing in dense high-dimensional linear models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2018, 113, 1583–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sur, P.; Chen, Y.; Candès, E.J. The likelihood ratio test in high-dimensional logistic regression is asymptotically a rescaled chi-square. Probab. Theory Relat. Fields 2019, 175, 487–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Tony Cai, T.; Li, H. Global and simultaneous hypothesis testing for high-dimensional logistic regression models. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2021, 116, 984–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Song, R.; Lu, W.; Li, R. Statistical inference for high-dimensional models via recursive online-score estimation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2021, 116, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Lin, L. Robust variable selection with exponential squared loss for the spatial autoregressive model. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2021, 155, 107094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, R.; Mima, Y.; Yanagihara, H.; Fujikoshi, Y. A high-dimensional bias-corrected AIC for selecting response variables in multivariate calibration. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 2021, 50, 3453–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janková, J.; van de Geer, S. De-biased sparse PCA: Inference and testing for eigenstructure of large covariance matrices. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.10567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.T.; Guo, Z.; Ma, R. Statistical inference for high-dimensional generalized linear models with binary outcomes. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloni, A.; Chernozhukov, V.; Wei, Y. Post-selection inference for generalized linear models with many controls. J. Bus. Econ. Stat. 2016, 34, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, F.; Liang, H.; Ruppert, D. Model Checking for Logistic Models When the Number of Parameters Tends to Infinity. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2022, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y.; Liu, H. A general theory of hypothesis tests and confidence regions for sparse high dimensional models. Ann. Stat. 2017, 45, 158–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccini, A.; De la Cruz Cabrera, O.; Donatelli, M.; Martinelli, A.; Reichel, L. Large-scale regression with non-convex loss and penalty. Appl. Numer. Math. 2020, 157, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xie, B.; Liao, J.; Liao, W. Outlier detection and robust variable selection via the penalized weighted LAD-LASSO method. J. Appl. Stat. 2021, 48, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, T.; Tony Cai, T.; Guo, Z. Optimal statistical inference for individualized treatment effects in high-dimensional models. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2021, 83, 669–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanmard, A.; Lee, J.D. A flexible framework for hypothesis testing in high dimensions. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Stat. Methodol.) 2020, 82, 685–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Rakshit, P.; Herman, D.S.; Chen, J. Inference for the case probability in high-dimensional logistic regression. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2021, 22, 11480–11533. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, C.H. Estimation and selection via absolute penalized convex minimization and its multistage adaptive applications. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2012, 13, 1839–1864. [Google Scholar]
- Shalek, A.K.; Satija, R.; Shuga, J.; Trombetta, J.J.; Gennert, D.; Lu, D.; Chen, P.; Gertner, R.S.; Gaublomme, J.T.; Yosef, N.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals dynamic paracrine control of cellular variation. Nature 2014, 510, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Geer, S.; Bühlmann, P.; Ritov, Y.; Dezeure, R. On asymptotically optimal confidence regions and tests for high-dimensional models. Ann. Stat. 2014, 42, 1166–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).