A New Fractional-Order Adaptive Sliding-Mode Approach for Fast Finite-Time Control of Human Knee Joint Orthosis with Unknown Dynamic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- It is assumed that KJO dynamic parameters are completely unknown. Then, a new FFOASMC is designed in order to achieve finite-time stability in which the unknown dynamic parameters of the KJO system are estimated via adaptive laws.
- (2)
- Introducing a novel approach for mitigating chattering by utilizing the developed fractional-order sliding mode control (SMC).
- (3)
- Notably, the design methodology presented in this paper can be readily extended to encompass the broader spectrum of high-order non-linear affine systems, encompassing entities like robot manipulators and rigid bodies.
2. Preliminaries
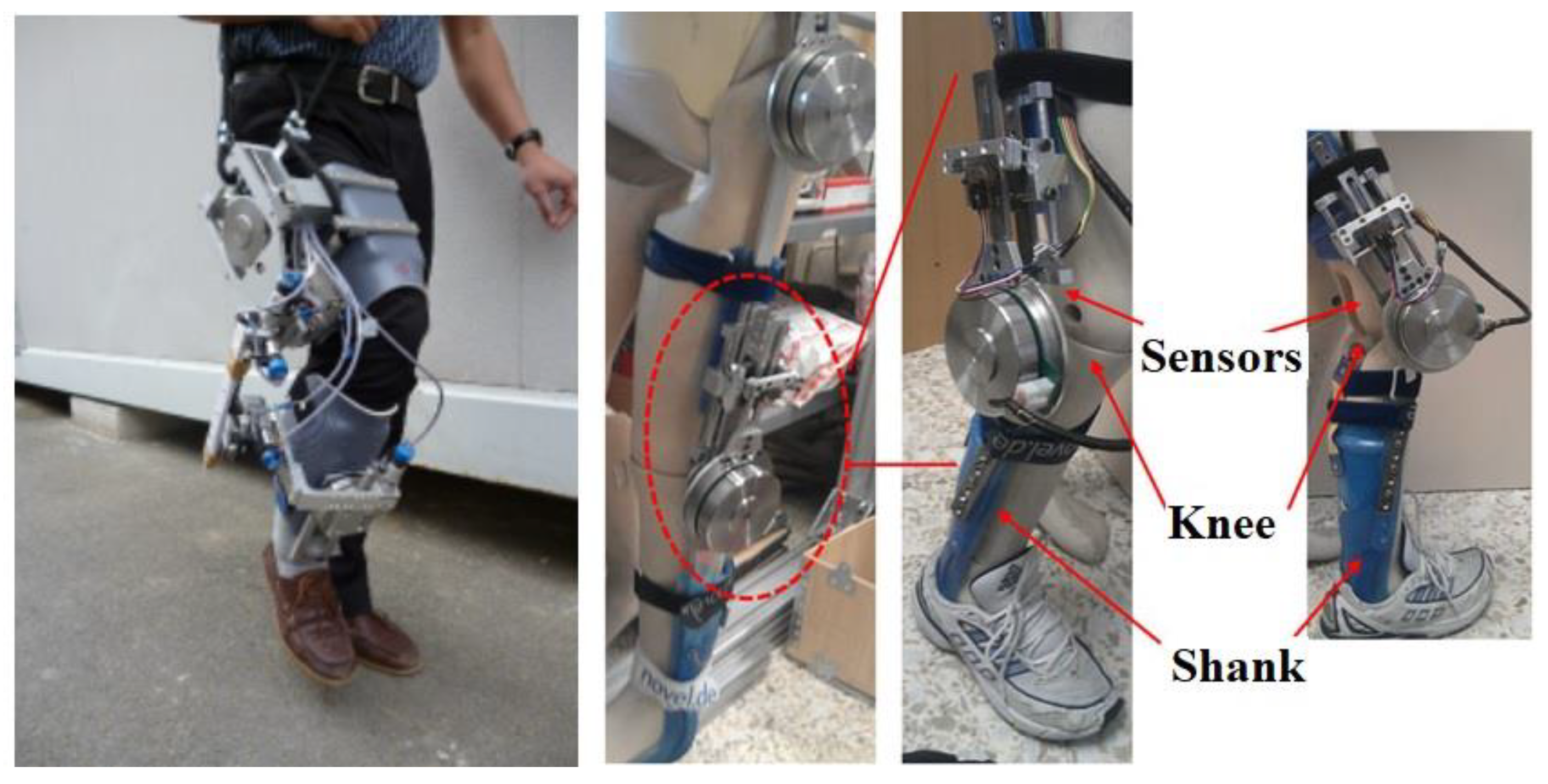
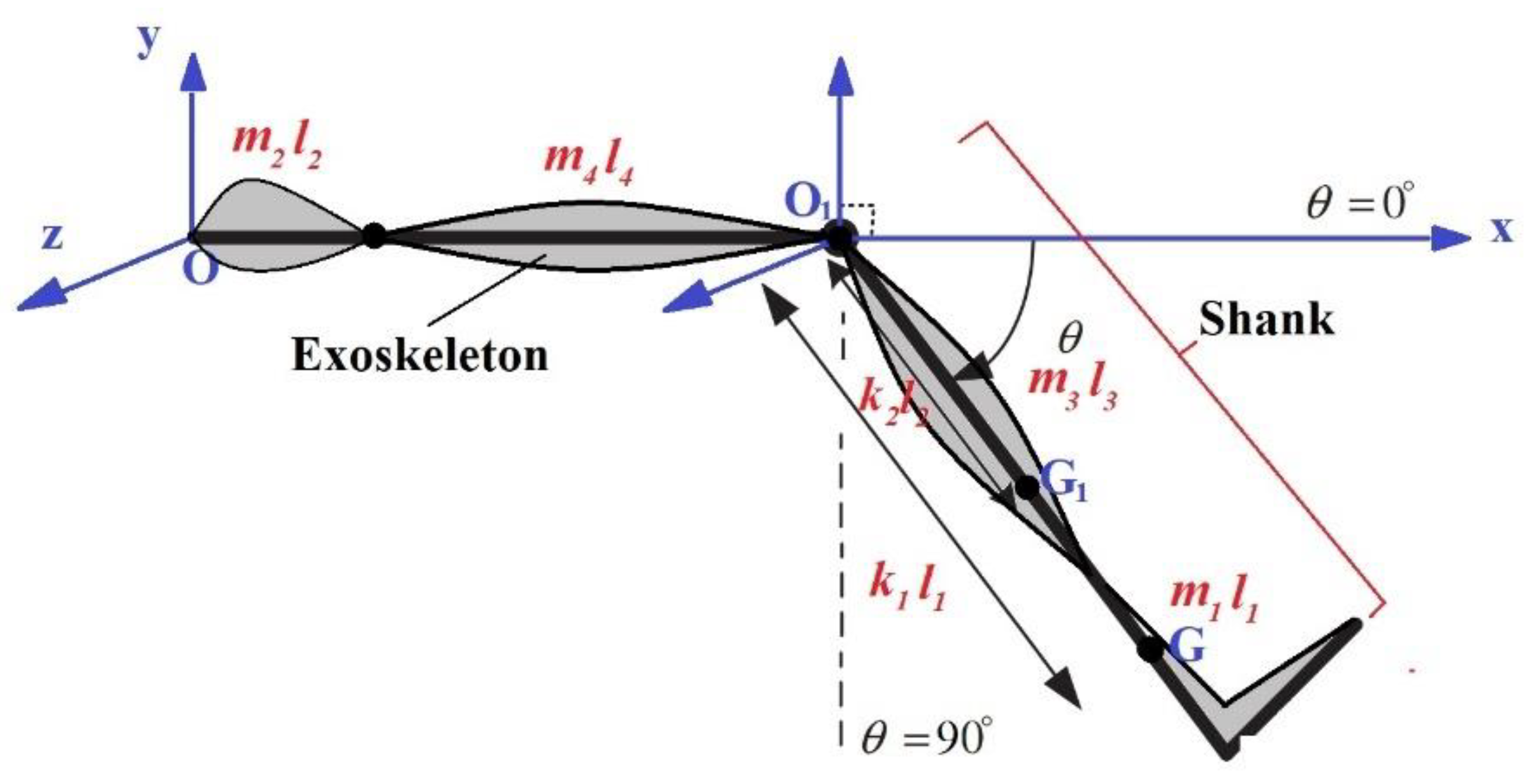
3. Description of Knee-Orthosis System
4. FFOASMC Design Considering Unknown Dynamics
4.1. Rewriting the Dynamic Model of KJO System
4.2. Fractional-Order Sliding Surface and Reaching Law Formulation
4.3. Fractional-Order Adaptive SMC
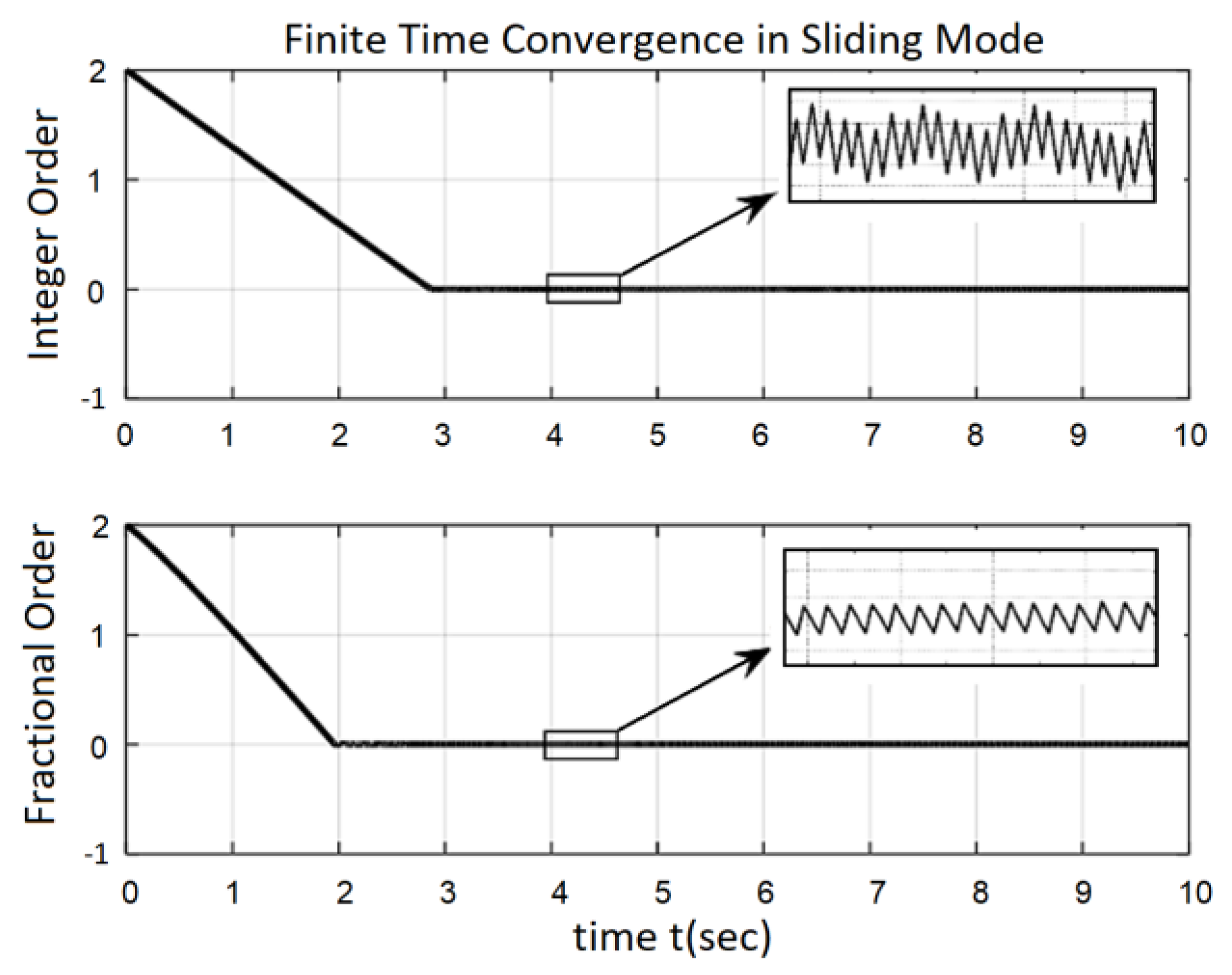
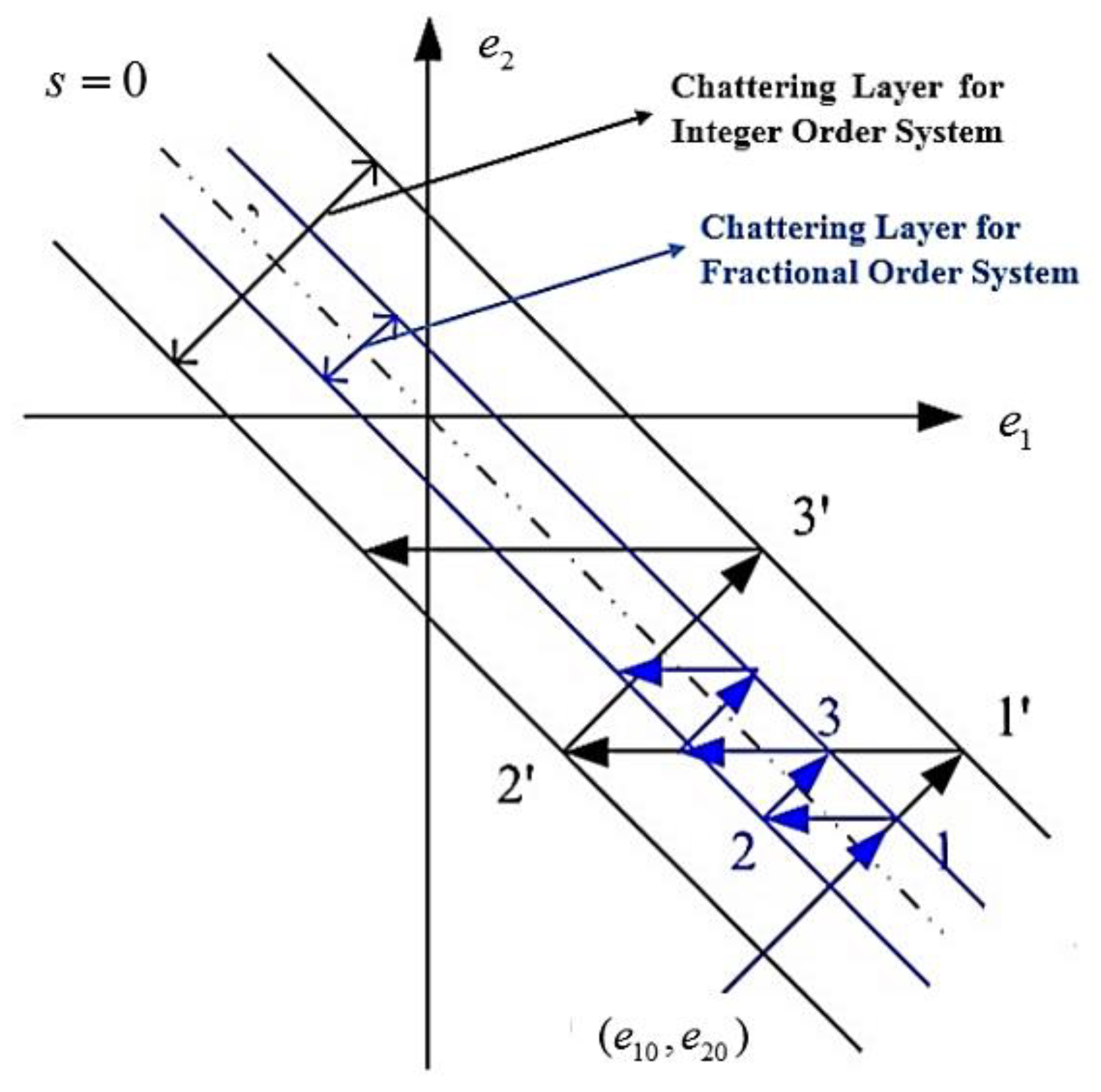
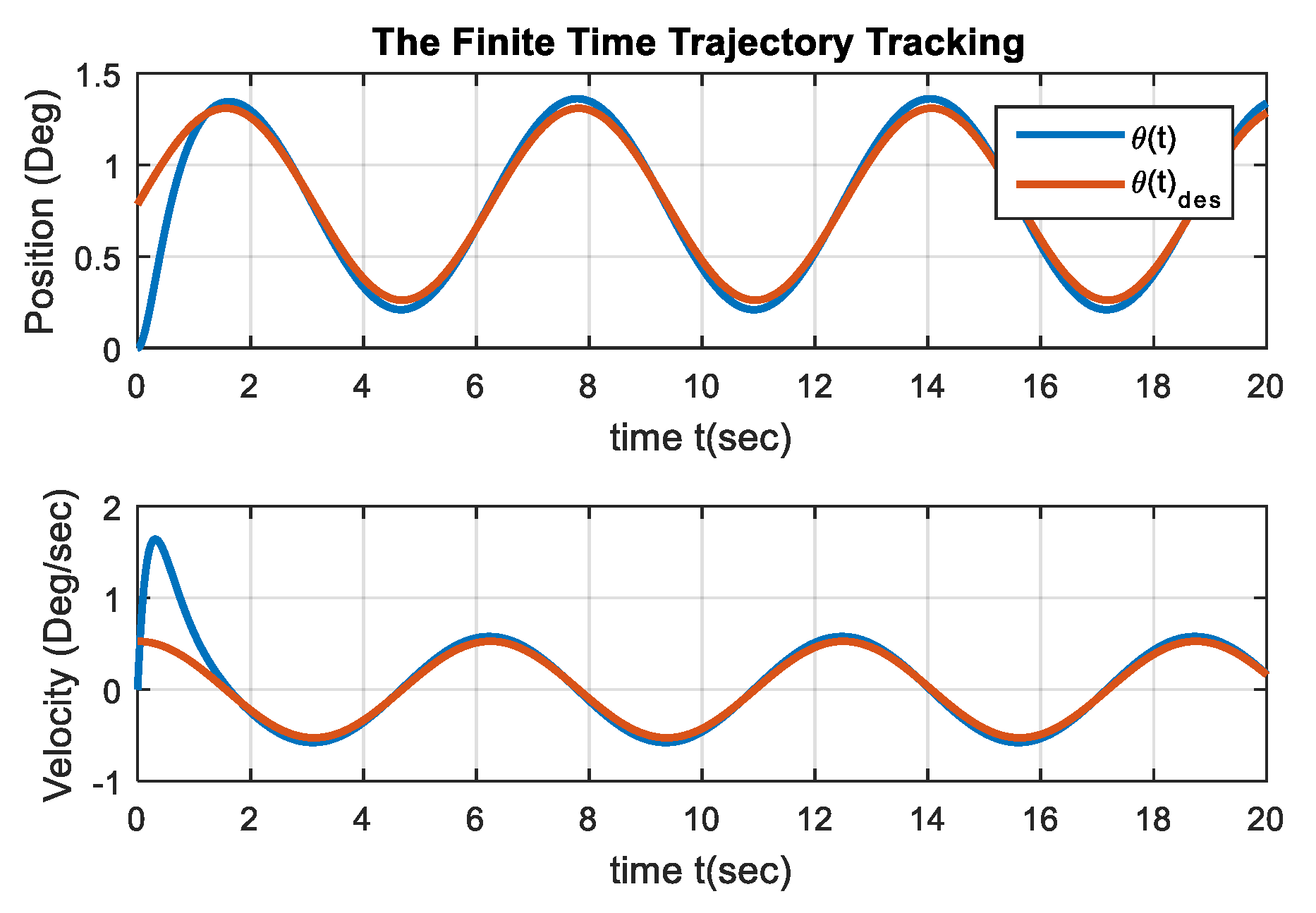
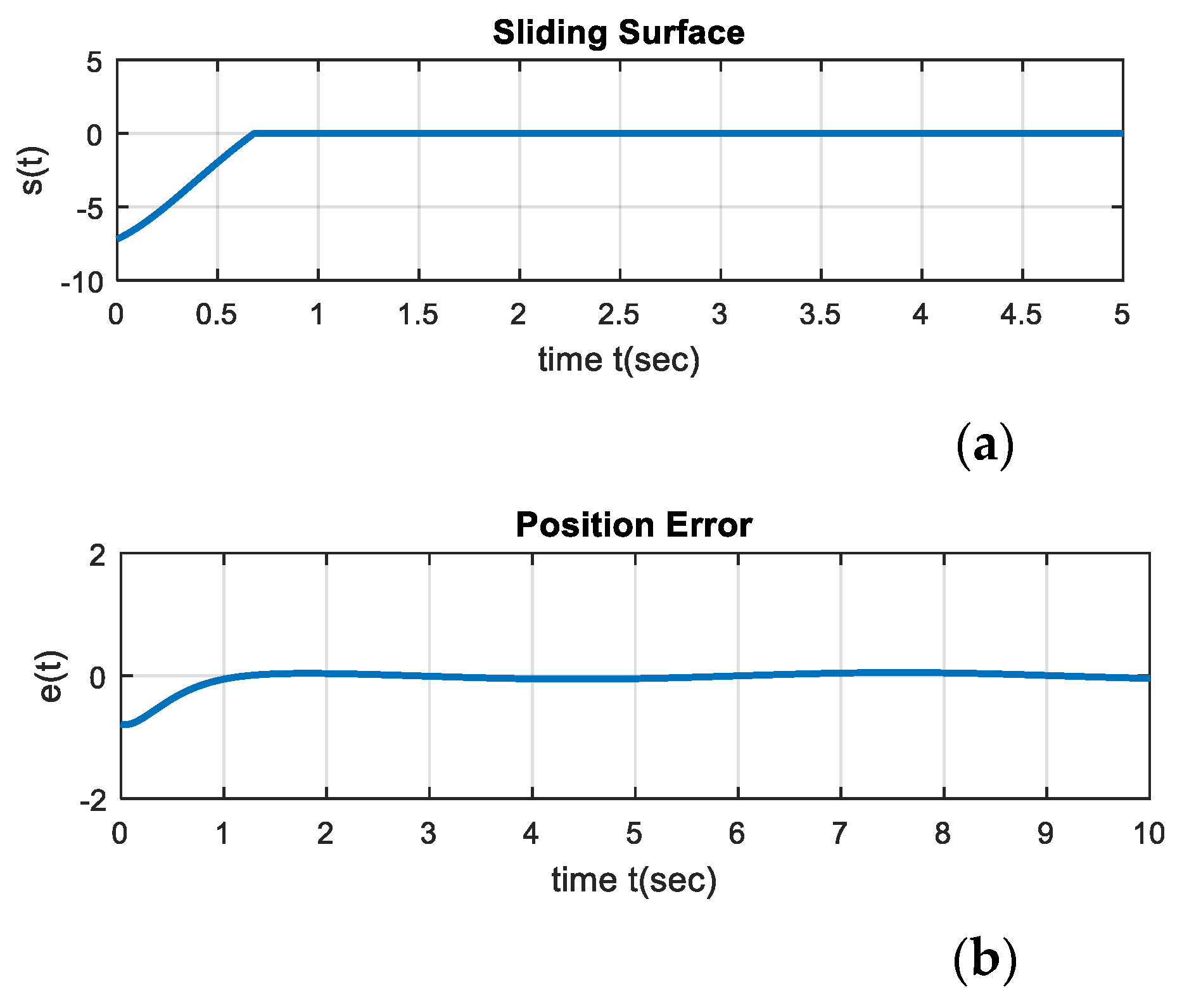
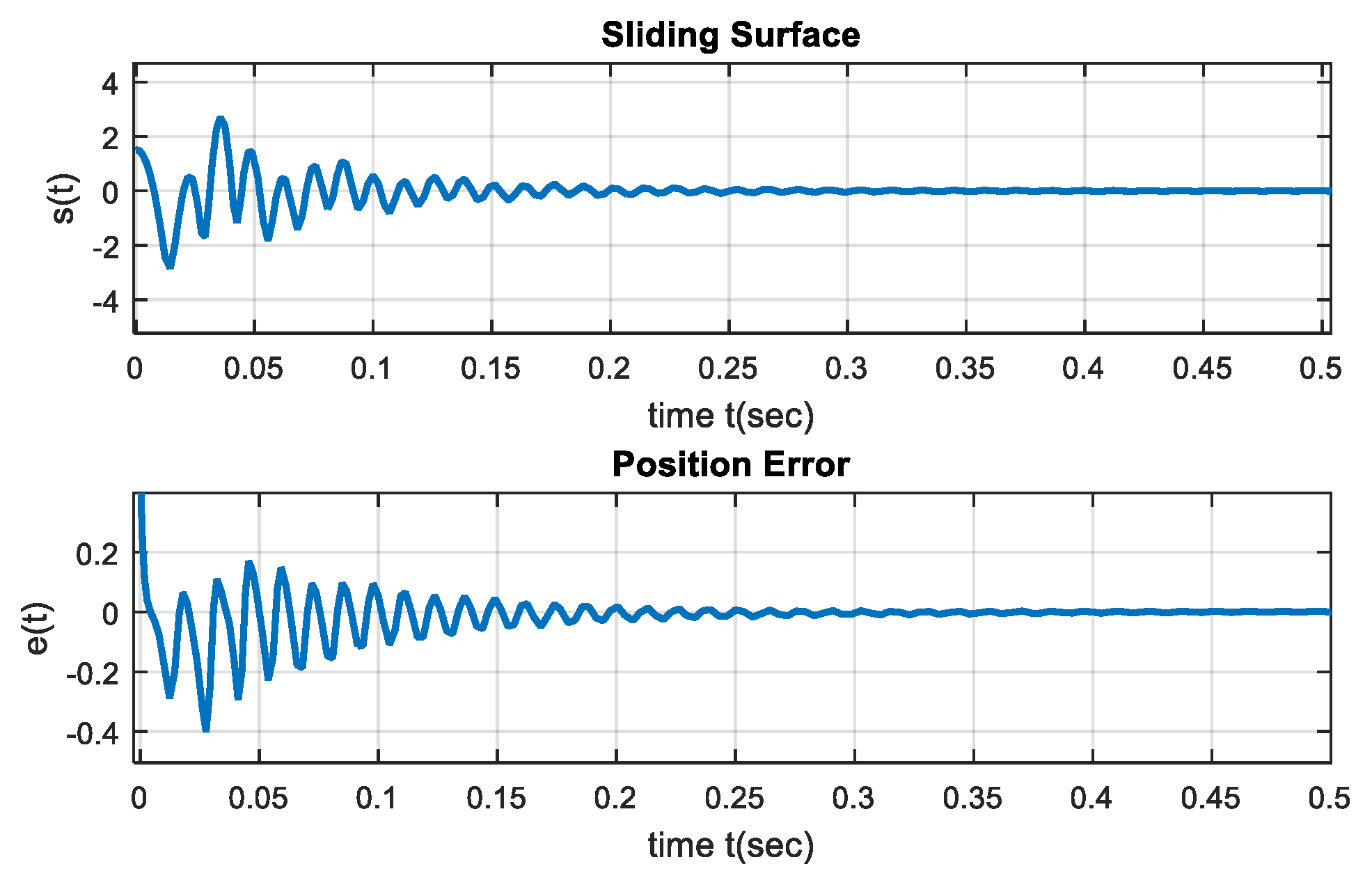
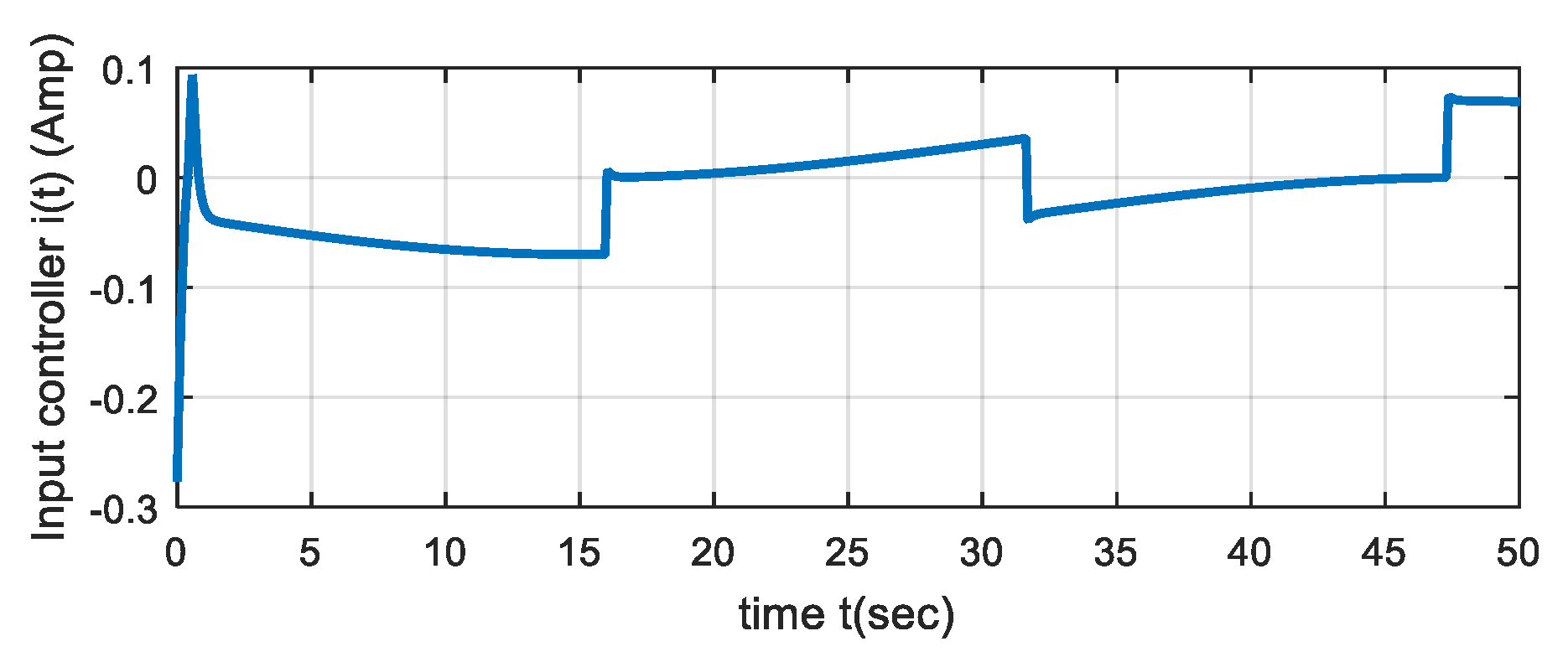
5. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rupal, B.; Rafique, S.; Singla, A.; Singla, E.; Isaksson, M.; Virk, G. Lower-limb exoskeletons: Research trends and regulatory guidelines in medical and non-medical applications. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2017, 14, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.G.; Ren, Z.; Zhao, K.; Deng, C.; Feng, Y. Human-cooperative control design of a walking exoskeleton for body weight support. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 16, 2985–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.X.; Wang, X.S.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Xi, R.; Wu, Q.C. Development and control of a robotic lower-limb exoskeleton for paraplegic patients. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2019, 233, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.C.; Figueiredo, J.; Pons, J.L. Chapter 7—exoskeletons for lower-limb rehabilitation. In Rehabilitation Robotics; Colombo, R., Sanguineti, V., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Chan, C.; Guo, Z.; Yu, H. A review of lower extremity assistive robotic exoskeletons in rehabilitation therapy. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 41, 343–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Huo, W.; Huang, J.; Amirat, Y.; Mohammed, S. Robust and Safe Control of a Knee Joint Orthosis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Intelligence and Safety for Robotics (ISR), Shenyang, China, 24–27 August 2018; pp. 343–348. [Google Scholar]
- Tsukahara, A.; Kawanishi, R.; Hasegawa, Y.; Sankai, Y. Sit-to-Stand and Stand-to-Sit Transfer Support for Complete Paraplegic Patients with Robot Suit HAL. Adv. Robot. 2010, 24, 161–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehbi, F.Z.; Huo, W.; Amirat, Y.; Rafei, M.E.; Khalil, M.; Mohammed, S. Active impedance control of a knee-joint orthosis during swing phase. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), London, UK, 17–20 July 2017; pp. 435–440. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, W.; Mohammed, S.; Amirat, Y. Observer-based active impedance control of a knee-joint assistive orthosis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics (ICORR), Singapore, 11–14 August 2015; pp. 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Daachi, B.; Madani, T.; Daachi, M.E.; Djouani, K. MLPNN adaptive controller based on a reference model to drive an actuated lower limb orthosis. In Proceedings of the 5th IEEE RAS/EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Sao Paulo, Brazil, 12–15 August 2014; pp. 638–643. [Google Scholar]
- Mefoued, S. A robust adaptive neural control scheme to drive an actuated orthosis for assistance of knee movements. Neurocomputing 2014, 140, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mefoued, S. A second-order sliding mode control and a neural network to drive a knee joint actuated orthosis. Neurocomputing 2015, 155, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifaï, H.; Mohammed, S.; Hassani, W.; Amirat, Y. Nested saturation based control of an actuated knee joint orthosis. Mechatronics 2013, 23, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifaï, H.; Mohammed, S.; Djouani, K.; Amirat, Y. Toward lower limbs functional rehabilitation through a knee-joint exoskeleton. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2017, 25, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, T.; Daachi, B.; Djouani, K. Non-singular terminal sliding mode controller: Application to an actuated exoskeleton. Mechatronics 2016, 33, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.; Huo, W.; Huang, J.; Rifaï, H.; Amirat, Y. Non-linear disturbance observer-based sliding mode control of a human-driven knee joint orthosis. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2016, 75, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, T.; Daachi, B.; Djouani, K. Modular-controller-design-based fast terminal sliding mode for articulated exoskeleton systems. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2017, 25, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yao, B.; Zhu, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, S.; Song, Y. Adaptive robust backstepping force control of 1-DOF joint exoskeleton for human performance augmentation. IFAC-Pap. Online 2015, 48, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L. Command Filter Backstepping Sliding Model Control for Lower-Limb Exoskeleton. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 1064535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifai, H.; Mohammed, S.; Daachi, B.; Amirat, Y. Adaptive control of a human-driven knee joint orthosis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Saint Paul, MN, USA, 14–18 May 2012; pp. 2486–2491. [Google Scholar]
- Mushage, B.O.; Chedjou, J.C.; Kyamakya, K. Fuzzy neural network and observer based fault-tolerant adaptive non-linear control of uncertain 5-DOF upper-limb exoskeleton robot for passive rehabilitation. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 87, 2021–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, D.; Dong, X. Enhanced neural network control of lower limb rehabilitation exoskeleton by add-on repetitive learning. Neurocomputing 2020, 323, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Huo, W.; Xu, W.; Mohammed, S.; Amirat, Y. Control of upper-limb power-assist exoskeleton using a human-robot interface based on motion intention recognition. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2015, 12, 1257–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro, R.; Salgado, I.; Chairez, I. Adaptive sliding-mode controller of a lower limb mobile exoskeleton for active rehabilitation. ISA Trans. 2020, 109, 210–228. [Google Scholar]
- Arabtelgerd, Z.; Koochakzadeh, A.; Soorki, M.N.; Yasoubi, S.M. Path Tracking Control of Bioflexible Probes Exposed to Uncertainties and Internal Tissues Disturbances with Unknown Upper Bonds Using Robust-Adaptive Sliding Mode Control. In Control Engineering in Mechatronics; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 103–121. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.; Du, Z.J.; Wang, W.D.; Dong, W. Robust sliding mode control based on GA optimization and CMAC compensation for lower limb exoskeleton. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2016, 2016, 5017381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Xie, S.Q.; Das, R. MIMO sliding mode controller for gait exoskeleton driven by pneumatic muscles. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2018, 26, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrett, C.; McDaid, A.J. Robust Control of a Cable-Driven Soft Exoskeleton Joint for Intrinsic Human-Robot Interaction. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2017, 25, 976–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achili, B.; Madani, T.; Daachi, B. Adaptive observer based on MLPNN and sliding mode for wearable robots: Application to an active joint orthosis. Neurocomputing 2016, 197, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Wang, H.; Tian, Y. Model-free based adaptive non-singular fast terminal sliding mode control with time-delay estimation for a 12 DOF multi-functional lower limb exoskeleton. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2018, 119, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, T.; Daachi, B.; Djouani, K. Finite-time control of an actuated orthosis using the fast terminal sliding mode. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2015, 47, 4607–4612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levant, A. Chattering Analysis. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2010, 55, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiko, I. Analysis of chattering in sliding mode control systems with continuous boundary layer approximation of discontinuous control. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 757–762. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, W. Adaptive sliding mode control for a lower-limb exoskeleton rehabilitation robot. In Proceedings of the 13th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Wuhan, China, 31 May–2 June 2018; pp. 1481–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Bkekri, R.; Benamor, A.; Messaoud, H.; Mohammed, S.; Amirat, Y. Adaptive sliding mode control with application super-twisting algorithm of a Human-Driven Knee Joint Orthosis. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Bio-Engineering for Smart Technologies, Paris, France, 30 August–1 September 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Saif, A.-W.A.; Gaufan, K.B.; El Ferik, S.; Al-Dhaifallah, M. Fractional Order Sliding Mode Control of Quadrotor Based on Fractional Order Model. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 79823–79837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Liu, X. Model-Free Fractional-Order Sliding Mode Control of Electric Drive System Based on Nonlinear Disturbance Observer. Fractal Fract. 2022, 6, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahraoui, Y.; Zaihidee, F.M.; Kermadi, M.; Mekhilef, S.; Mubin, M.; Tang, J.R.; Zaihidee, E.M. Fractional Order Sliding Mode Controller Based on Supervised Machine Learning Techniques for Speed Control of PMSM. Mathematics 2023, 11, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delavari, H.; Jokar, R. Fractional order adaptive fuzzy terminal sliding mode controller design for a knee joint orthosis with non-linear disturbance observer. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Control, Instrumentation, and Automation, Shiraz, Iran, 21–23 November 2017; pp. 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.; Wang, H.; Tian, Y. Robust adaptive fractional-order terminal sliding mode control for the lower-limb exoskeleton. Asian J. Control 2019, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaei, M.H.; Sheikh Ahmadi, S.; Naderi Soorki, M.; Amini, A.S. Comment on S. Ahmed, H. Wang, and Y. Tian, “Robust adaptive fractional-order terminal sliding mode control for lower-limb exoskeleton,” Asian J. Control, vol. 21, no. 1, pp. 1–10 (2019). Asian J. Control 2023, 25, 2433–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlubny, I. Fractional Differential Equations, Mathematics in Science and Engineering; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Soorki, M.N.; Tavazoei, M.S. Adaptive robust control of fractional-order systems in the presence of model uncertainties and external disturbances. IET Control Theory Appl. 2018, 12, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gu, L.; Xu, Y.; Cao, X. Practical Tracking Control of Robot Manipulators with Continuous Fractional-Order Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6194–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera Sánchez, A.; Blanco Ortega, A.; Martínez Rayón, E.; Gómez Becerra, F.A.; Abúndez Pliego, A.; Campos Amezcua, R.; Guzmán Valdivia, C.H. State of the Art Review of Active and Passive Knee Orthoses. Machines 2022, 10, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mefoued, S.; Mohammed, S.; Amirat, Y. Knee joint movement assistance through robust control of an actuated orthosis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011; pp. 1749–1754. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, V.M. Hyperstability of Control System; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Soorki, M.N.; Tavazoei, M.S. Fractional-order linear time-invariant swarm systems: Asymptotic swarm stability and time response analysis. Cent. Eur. J. Phys. 2013, 11, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azizi, A.; Naderi Soorki, M.; Vedadi Moghaddam, T.; Soleimanizadeh, A. A New Fractional-Order Adaptive Sliding-Mode Approach for Fast Finite-Time Control of Human Knee Joint Orthosis with Unknown Dynamic. Mathematics 2023, 11, 4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11214511
Azizi A, Naderi Soorki M, Vedadi Moghaddam T, Soleimanizadeh A. A New Fractional-Order Adaptive Sliding-Mode Approach for Fast Finite-Time Control of Human Knee Joint Orthosis with Unknown Dynamic. Mathematics. 2023; 11(21):4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11214511
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzizi, Aydin, Mojtaba Naderi Soorki, Tahmineh Vedadi Moghaddam, and Ali Soleimanizadeh. 2023. "A New Fractional-Order Adaptive Sliding-Mode Approach for Fast Finite-Time Control of Human Knee Joint Orthosis with Unknown Dynamic" Mathematics 11, no. 21: 4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11214511
APA StyleAzizi, A., Naderi Soorki, M., Vedadi Moghaddam, T., & Soleimanizadeh, A. (2023). A New Fractional-Order Adaptive Sliding-Mode Approach for Fast Finite-Time Control of Human Knee Joint Orthosis with Unknown Dynamic. Mathematics, 11(21), 4511. https://doi.org/10.3390/math11214511






